Inflammatory pseudotumors may be defined as lesions
|
|
|
- Moses Higgins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2008;74(2): CASE REPORT Inflammatory pseudotumors of the paranasal sinuses Guilherme de Toledo Leme Constantino 1, Fernando Sasaki 2, Raquel Aguiar Tavares 3, Richard L. Voegels 4, Ossamu Butugan 5 Keywords: pseudotumor, sinuses, inflammatory, paranasal. Summary Inflammatory pseudotumors may be defined as lesions that clinically and radiologically simulate neoplasms. These tumor are not a single clinical-pathological entity, but rather a generic term applied to any nonspecific, chronic, inflammatory expanding lesion. There are few reports of inflammatory pseudotumors in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Case report: We report three cases of inflammatory pseudotumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses seen at the Division of Otolaryngology of the Medical School University Hospital, Sao Paulo University. Discussion: Inflammatory pseudotumors of the paranasal sinuses present a variety of symptoms according to the site. 1 Otorhinolaryngologist, endonasal endoscopic surgery fellow, HC/FMUSP. 2 Medical resident, Division of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Sao Paulo University Clinical Hospital. 3 Physician, collaborator of the Division of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, HC/FMUSP. 4 Associate professor, Division of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, HC/FMUSP. 5 Associate professor, Division of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, HC/FMUSP. This study was undertaken in the Division of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, São Paulo University Clinical Hospital, Brazil. Address for correspondence: R. Cristiano Viana 647 ap. 103 São Paulo SP Brasil Tel. (0xx11) guilherme@constantino.med.br Paper submitted to the ABORL-CCF SGP (Management Publications System) on March 22th, 2005 and accepted for publication on September 8th, cod
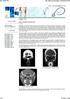
2 INTRODUCTION Inflammatory pseudotumors may be defined as lesions that clinically and radiologically simulate neoplasms. 1 Various terms have been used to describe these lesions, given their histological variety, 1,2 including: inflammatory pseudotumors, plasmocytic cell granulomas, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors, inflammatory myofibrohistiocitary proliferation, myofibroblastomas, xantogranulomas, and tumefactive fibroinflammatory lesions. These multiple terms suggest that inflammatory pseudotumors are not a single clinical and pathological entity, but rather a generic term for any non-specific chronic inflammatory expanding lesion. 2 Some pathologists have classified these tumors, according to their origin, into: idiopathic, regenerative/ post-traumatic, developmental (embryological), functional (endocrine), iatrogenic, and infectious. 3 Idiopathic lesions are the classical presentation of these tumors, synonymous with inflammatory pseudotumors, depending on the classification that is used. Inflammatory pseudotumors are different from neoplasms not only histologically, but also by being self-limited and having the possibility of regressing spontaneously. 3 Various sites in the body may harbor these lesions, but the lungs, the urinary tract and the intestine are the most susceptible areas. 3 In the head and neck, they occur mostly in the orbit and the upper aerodigestive tract. 2 Wold and Weiland first used the term tumefactive fibroinflammatory lesion to describe a fibrosclerosing lesion of the head and neck that had histological findings similar to those encountered in Riedel s thyroiditis, in sclerosing mediastinitis and in retroperitoneal fibrosis. 4 Macroscopically, the lesions are firm, well-defined, white, grey or brownish-yellow, and non-encapsulated. 4,5 Microscopic findings are: dense fibrous tissue associated with chronic inflammatory cells, proliferation of fibroblasts and peripheral connective tissue that matures to yield a densely collagenized and hyalinized stroma with poorly apparent vascularization. 5 There have been few reports of inflammatory pseudotumors in the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses; of these, most were in the maxillary sinus. 6 We present three cases of nasal and paranasal sinus inflammatory pseudotumors, including the methods for diagnosis and therapy; these patients were seen at the Division of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology in the Clinical Hospital of the São Paulo University Medical School (HC/FMUSP). CASE REPORTS Case 1 MFS, female, age 66 years, black, previously healthy, presented with purulent rhinorrhea in the left nasal fossa in the past one and a half years. The patient developed progressive nasal obstruction during the past four months in the left nasal fossa, hyposmia, pain in the left maxillary region and repeated episodes of nasal bleeding. Fever, headaches or other complaints were absent. The patient had no underlying diseases, no previous surgery, and no allergies; she used no medication, was a non-smoker and did not drink alcoholic beverages. The physical examination revealed good general health; the patient had a normal-colored mucosa and was hydrated and eupneic. Anterior rhinoscopy showed a yellowish tumor filling the left nasal fossa, and a small amount of secretion; the right nasal fossa was unaltered. Oroscopy, otoscopy and palpation of the neck were normal. The complete blood count was within normal limits. Rigid nasal endoscopy revealed a solid yellowish tumor originating from the left middle meatus. Computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses (Figures 1 and 2) revealed a contrast-enhanced heterogeneous lesion in the left maxillary sinus, widening of the ethmoidal infundibulum, erosion of the posterior wall and roof of the maxillary sinus, and tumor extension to the infratemporal fossa. Figure 1. CT, axial slice, soft tissue window. A tumor biopsy through the nasal fossa revealed coagulation necrosis with vascular thrombi within a polypoid structure that was partially covered with respiratory epithelium. Following this inconclusive result, a deeper sublabial biopsy was done; the procedure coursed uneventfully. This biopsy revealed necrotic tissue, and a small fragment of respiratory mucosa with fibroplasia of the chorion and a mononuclear inflammatory infiltrate; there 298
3 Symptoms regressed, and the patient developed a small oroantral fistula in the gingivo-labial sulcus. Telescopy revealed wide opening of the medial wall of the maxillary sinus, with no lesions in the posterior area or secretion. A control tomography six months postoperatively (Figures 3 and 4) showed a small lytic lesion with soft tissue components on the floor of the left maxillary sinus; this is being monitored clinically. The patient has no complaints one year and one month after surgery. Figure 2. CT coronal slice, soft tissue window. were no signs of malignancy. Surgical treatment was undertaken, with removal of the tumor sublabially (excisional biopsy) under general anesthesia. There was erosion of the anterior wall of the left maxillary sinus and a friable, well-defined tumor that filled the sinus; the tumor was completely removed. Pathology revealed an inflammatory polyp with extensive necrosis, confirming a diagnosis of inflammatory pseudotumor. Figure 4. CT coronal slice, soft tissue window. Figure 3. CT axial slice, soft tissue window. Case 2 MIHS, female, age 62 years, white, born in the state of Bahia, and living in Sao Paulo. The patient presented bilateral, progressive nasal obstruction, worse to the right, developing over four years. She complained of frontal, pressure-like, moderately intense headaches, hyposmia, clear rhinorrhea, nasal pruritus and bleeding episodes through the right nasal fossa. The patient reported a history of systemic high blood pressure and no other disease. The patient had not been operated previously, had no allergies and did not drink alcoholic beverages. She had stopped smoking five years ago. The physical examination revealed good general health; the patient had normal colored mucosa, and was hydrated and eupneic. The arterial pressure was 130x100mmHg and the heart rate was 80bpm. Anterior rhinoscopy showed left nasal septum deviation, a hypertrophic left lower turbinate and a reddish tumor filling the entire right nasal fossa to the nasal vestibule; there was a small amount of hyaline secretion. Oroscopy, otoscopy and neck palpation were normal. Nasal telescopy brought no further information, 299
4 as the tumor did not allow progression of the endoscope. The complete blood count was within normal limits; there was mild hypergammaglobulinemia (22.3% or 1.87 g/dl; reference values are 12 to 21% or 0.7 to 1.6 g/dl). Computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses revealed a large, heterogeneous expanding solid tumor in the right maxillary sinus, extending to the right nasal fossa; the tumor widened the right nasal fossa and displaced the septum towards the left. The lesion also extended to the choana, the rhinopharynx, the sphenoidal sinus and the ethmoidal cells, bulging the papyraceous lamina. Three biopsies were done of the nasal fossa tumor. The first biopsy demonstrated inflammatory polyps. The second biopsy showed a chronic, non-specific inflammatory process of the respiratory mucosa, with fibrosis of the chorion. The third biopsy revealed a chronic eosinophilic inflammatory process in the nasal mucosa, areas of squamous metaplasia of the respiratory epithelium, and fibrosis of the chorion. A sublabial approach for excisional biopsy was done to remove the entire tumor. Pathology revealed an inflammatory mucosal polyp with non-specific chronic inflammation and ample hemorrhagic, necrotic and hyalinized areas, suggesting an inflammatory pseudotumor. Nasal obstruction and bleeding regressed; there was hypoestesia in the right maxillary area. Telescopy showed an ample cavity with no signs of recurrence to the present (one year and three months postoperatively). Case 3 MSM, male, age 26 years, white, born in the state of Pernambuco, single, an IBGE survey worker. The patient presented a history of nasal bulging to the left since age 12 years, together with bilateral nasal bleeding and obstruction. At that time there was facial asymmetry and left proptosis. A first surgery was done in 1991 at another unit; pathology revealed an inflammatory pseudotumor. A new surgical procedure was done in 1993 due to recurrence of the lesion. A further biopsy was done in 1996; pathology suggested paracoccidioidomycosis. The patient was treated with amphotericin B, with no improvement. In 1998, the patient was seen at the HC/FMUSP. At this time the patient reported that nasal obstruction and bleeding had regressed, but there was still proptosis to the left. There was no diplopia or altered visual acuity. The physical examination showed facial asymmetry and left proptosis. Nasal telescopy revealed an ample nasal cavity with signs of previous surgery and no tumors within. The complete blood count was within normal limits. Computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses revealed an expanding solid lesion in the left anterior and posterior ethmoidal sinuses, extending to the left orbital area. Four biopsies were done of the ethmoidal lesion, revealing a chronic, non-specific inflammatory process with an intense lymphoplasmocytic infiltrate in all samples. On September 1999, an excisional biopsy was done through an external approach, accessing the ethomoidal sinus from the left. Pathology demonstrated a non-specific chronic inflammatory process with no granulomas (Figures 5 and 6). Investigation for alcohol acid-resistant bacilli and fungi was negative. Following this result, the diagnosis was defined as inflammatory pseudotumor of the ethmoidal sinus. The patient is clinically stable, nasal obstruction has regressed and there have been no further episodes of nasal bleeding. Figure 5. Histological sections showing a non-specific chronic inflammatory process. Figure 6. Histological sections showing a non-specific chronic inflammatory process. DISCUSSION Inflammatory pseudotumors are chronic inflammatory lesions of unknown origin. They have no common 300
5 identifiable cause, although some authors have assumed that any inflammatory stimulus may originate these pseudotumors. 7 The name is given because these lesions simulate neoplasms, both clinically and radiologically. 1,8 There are many synonyms, such as histiocytoma, xanthogranuloma, plasmocytic cell granuloma, and inflammatory myofibroblastic proliferation, due to its wide histological presentation spectrum. 2,6,8 Histology is non-specific, 8 showing two typical cell types: myofibroblasts and inflammatory cells. Myofibroblasts express vimentin in 99% of cases and actin in 89 to 92% of cases on immunohistochemistry. They variably express desmin (69%) and cytokeratin (36%). The inflammatory infiltrate consists of lymphocytes, plasmocytes and granulocytes in variable proportions. These cells are found within edematous connective tissue, associated with very thin capillaries. It should be realized that this description of microscopy might vary significantly among different tumors and within the same lesion. 6 Inflammatory pseudotumors occur in various anatomical sites; the lung is the most commonly affected organ. 2 Inflammatory pseudotumors of the head and neck occur mainly in the orbit, and less frequently in the mouth and paranasal sinuses. 1 Often, these areas are secondarily involved by the extension of a primary tumor of the orbit. 6 There appears to be no sex or age preference. In a review of the literature that included 28 cases of mouth and maxillary sinus inflammatory pseudotumors, Vigneswaran found a 1.5:1 male to female ratio and a mean presentation age of 33 years (ranging from 2 to 67 years). 1 Two of the three patients in our series were female. The age ranged from 26 to 66 years; both females were aged over 60 years. Inflammatory pseudotumors of the paranasal sinuses present a variety of symptoms depending on the site of origin. The most frequent clinical picture is a non-specific nasosinusal tumor that grows to a stable state over months or years; it may be painful and may be associated with nasal obstruction, nose bleeding, proptosis, increased lymph nodes, dysphagia or cranial nerve dysfunction. 5,6 Variation in symptoms, edema, erythema and fever may suggest an inflammatory etiology. 7 Systemic symptoms are usually not encountered. 6,8 All patients in our sample presented a typical clinical picture that included progressive nasal obstruction, repeated nasal bleeding episodes and a nasal tumor. Nasal bulging, facial asymmetry and proptosis seen in patient number 3 are also typical. Although these tumors usually follow a benign course, such clinical behavior may not be generalized to all cases. There have been reports of local recurrence in about 37% of cases in some abdominal and mediastinal inflammatory pseudotumor series, and also cases of metastases at a distance. 2 Vigneswaran has reported a case of an inflammatory pseudotumor in the maxillary sinus that relapsed twice within two years; this author concluded that this tumor is locally aggressive, in contrast with the more benign lesions of the orbit. 1 Case 1 of our series presented a small postoperative lesion on the floor of the maxillary sinus, with no clinical repercussion currently (13th month postoperatively). Patient 2 was recurrence-free 15 months after surgery. Case 3 required three surgeries and a number of biopsies between 1991 and 1999 due to recurrences of the lesion; since 1999, however, this patient has remained clinically stable. Computed tomographic findings that indicate inflammatory pseudotumors of the maxilla suggest a more aggressive appearance compared to findings in such tumors located in the orbit. 8 Soft tissue images in maxillary sinus pseudotumors are associated with erosion, remodeling, sclerosis and bone thinning, mimicking malignant tumors. 8 We raised the question of whether patient 3 originally had a tumor of the orbit that invaded the paranasal sinuses; this, however, appears unlikely, as orbitary forms are less aggressive radiographically. Although there are suggestive clinical features, multiple biopsies are frequently required to establish a diagnosis of an inflammatory pseudotumor. It is an exclusion diagnosis, after eliminating the possibility of benign and malignant neoplasias, collagen diseases, vasculitis, infection and other inflammatory diseases. 8 A cytological diagnosis of inflammatory pseudotumors is difficult. 9 Laboratory exams may be altered, such as thrombocytosis, hypochromic microcytic anemia, hypergammaglobulinemia and an increased hemosedimentation rate, which resolve following tumor resection.2 The three patients had normal complete blood counts. Protein electrophoresis was done only in case 2, revealing mild elevation of gammaglobulins. Corticosteroids, surgery and radiotherapy have been used in the treatment of inflammatory pseudotumors. Some authors have preferred corticosteroid therapy, while others have chosen surgery as the treatment of choice. 6,7 High-dose corticosteroid therapy usually yields a favorable response; early lesions that include lymphoid follicles tend to be more responsive to corticosteroids, while mature lesions with a more fibrous content respond less. 7 Our first measure is to biopsy the lesion. The material is sent for histopathology and cultured for fungi. If pathology is inconclusive, we perform an excisional biopsy for a final diagnosis. Surgery was done in all three cases; corticosteroid therapy was not used. Radiotherapy is used in selected cases, as its success rate is low; furthermore, it may induce a malignancy in a previously benign lesion. 7 CONCLUSION The aggressive aspect of paranasal sinus inflammatory pseudotumors is a diagnostic challenge. The first concern should be to exclude neoplasia; multiple biopsies 301
6 may be required. Rhinologists should raise the possibility of an inflammatory pseudotumor in the differential diagnosis of sinusal tumors, given the possibility of treating this condition medically, avoiding unnecessary ample resection. REFERENCES 1.Viegneswaran N, Bailey W, Tilashalski K, et al. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor (Inflammatory Pseudotumor) of the Maxilla: Clinicopathologic Features of a Case and Review of the Current Literature. Oral Surg, Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol and Endodontics 1997;84(2): Batsakis JG, Luna MA, El-Naggar AK, et al. Inflammatory Pseudotumor : What Is It? How Does It Behave? Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1995;104: Wick MR, Ritter JH. Pseudoneoplastic Lesions: An Overview. In: Pathology of Pseudoneoplastic Lesions. Lippincott Raven Publishers; Chapter 1: Wold LE, Weiland LH. Tumefactive Fibro-inflammatory Lesions of the Head and Neck. Am J Surg Pathol 1983;7: El-Mofty SK. Pseudoneoplastic Lesions of the Head and Neck. In: Pathology of Pseudoneoplastic Lesions. Lippincott Raven Publishers; Chapter 3: Ruaux C, Noret P, Godey B. Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Nasal Cavity and Sinuses. J Laryngol Otol 2001;115: Weisman RA, Osguthorpe JD. Pseudotumor of the Head and Neck Masquerading as Neoplasia. Laryngoscope 1998;98: Som PM, Brandwein MS, Maldjian C, et al. Inflamatory Pseudotumor of the Maxillary Sinus: CT and MR Findings in Six Cases. AJR 1994;163: Nishioka K, Masuda Y, Yanagi E, et al. Cytologic Diagnosis of the Maxillary Sinus Reevaluated. Laryngoscope 1989;99:
NASAL SEPTUM ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA: A CASE REPORT
 NASAL SEPTUM ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA: A CASE REPORT Shu-Yu Tai, 1 Chen-Yu Chien, 2 Chih-Feng Tai, 2,4 Wen-Rei Kuo, 2,4 Wan-Ting Huang, 3 and Ling-Feng Wang 2,4 Departments of 1 Family Medicine, 2 Otolaryngology
NASAL SEPTUM ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA: A CASE REPORT Shu-Yu Tai, 1 Chen-Yu Chien, 2 Chih-Feng Tai, 2,4 Wen-Rei Kuo, 2,4 Wan-Ting Huang, 3 and Ling-Feng Wang 2,4 Departments of 1 Family Medicine, 2 Otolaryngology
Endoscopic Management Of A Giant Ethmoid Mucocele
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases
 Original article: Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases 1 Dr. Vijay Kumar Kalra, 2 Dr. Samar Pal Singh Yadav, 3 Dr. Swati 1Assistant Professor, 2 Senior Professor
Original article: Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases 1 Dr. Vijay Kumar Kalra, 2 Dr. Samar Pal Singh Yadav, 3 Dr. Swati 1Assistant Professor, 2 Senior Professor
Four cases of Pleomorphic Adenoma of the nasal cavity: An unusual entity
 J. Acad. Indus. Res. Vol. 1(4) September 2012 203 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN: 2278-5213 Four cases of Pleomorphic Adenoma of the nasal cavity: An unusual entity Kiran Naik Dept. of ENT, Adichunchanagiri Inst.
J. Acad. Indus. Res. Vol. 1(4) September 2012 203 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN: 2278-5213 Four cases of Pleomorphic Adenoma of the nasal cavity: An unusual entity Kiran Naik Dept. of ENT, Adichunchanagiri Inst.
years old female with paratracheal lymph nodes infiltration and mediastinal extension, who presented
 Case Report Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumour of the Trachea with Paratracheal Lymph Nodes and Mediastinal Invasion Salina Husain From Department of Otolaryngology, Univerti Kebengsaan, Malaysia. Received:
Case Report Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumour of the Trachea with Paratracheal Lymph Nodes and Mediastinal Invasion Salina Husain From Department of Otolaryngology, Univerti Kebengsaan, Malaysia. Received:
Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Juvenile Angiofibroma
 Juvenile Angiofibroma Disclaimer The pictures used in this presentation have been obtained from a number of sources. Their use is purely for academic and teaching purposes. The contents of this presentation
Juvenile Angiofibroma Disclaimer The pictures used in this presentation have been obtained from a number of sources. Their use is purely for academic and teaching purposes. The contents of this presentation
Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
Endoscopic surgery in the treatment of crista galli pneumatization evolving with localizated frontal headaches
 Original Article Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;17(3):246-250. DOI: 10.7162/S1809-97772013000300003 Endoscopic surgery in the treatment of crista galli pneumatization evolving with localizated frontal
Original Article Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;17(3):246-250. DOI: 10.7162/S1809-97772013000300003 Endoscopic surgery in the treatment of crista galli pneumatization evolving with localizated frontal
Mucoceles of the paranasal sinus are epithelial lesions
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol. V.70, n.6, 850-4, nov./dec. 2004 ARTIGO DE REVISÃO CASE REPORT Frontoethmoidal mucoceles: a case report and literature review Andy de Oliveira Vicente 1, Adriana Gonzaga Chaves
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol. V.70, n.6, 850-4, nov./dec. 2004 ARTIGO DE REVISÃO CASE REPORT Frontoethmoidal mucoceles: a case report and literature review Andy de Oliveira Vicente 1, Adriana Gonzaga Chaves
A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF TÂRGU MUREȘ ROMANIA A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS PhD THESIS ABSTRACT PhD Student Viorel Emanoil
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF TÂRGU MUREȘ ROMANIA A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS PhD THESIS ABSTRACT PhD Student Viorel Emanoil
Nasal Polyposis. DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore
 Nasal Polyposis DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore Def: INTRODUCTION Chronic inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane in the nose & PNS, presenting as pedunculated smooth
Nasal Polyposis DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore Def: INTRODUCTION Chronic inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane in the nose & PNS, presenting as pedunculated smooth
Leiomyosarcoma of Maxillary Sinus A Rare Clinical Entity
 Open Access Heighpubs Otolaryngology and Rhinology Case Report ISSN 2573-7716 Leiomyosarcoma of Maxillary Sinus A Rare Clinical Entity Sah BP 1 *, Chettri ST 2, Karki S 2, Shah SP 1, Manandhar S 1 and
Open Access Heighpubs Otolaryngology and Rhinology Case Report ISSN 2573-7716 Leiomyosarcoma of Maxillary Sinus A Rare Clinical Entity Sah BP 1 *, Chettri ST 2, Karki S 2, Shah SP 1, Manandhar S 1 and
BJORL Retrospective analysis of 26 cases of inverted nasal papillomas
 Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;78(1):26-30. ORIGINAL ARTICLE BJORL Retrospective analysis of 26 cases of inverted nasal papillomas Ana Maria Almeida de Sousa 1, Alcioni Boldrini Vicenti 2, José Speck Filho
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;78(1):26-30. ORIGINAL ARTICLE BJORL Retrospective analysis of 26 cases of inverted nasal papillomas Ana Maria Almeida de Sousa 1, Alcioni Boldrini Vicenti 2, José Speck Filho
Histopathology of Nasal Masses
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Hemant Chopra, 2 Kapil Dua, 3 Neha Chopra, 4 Vikrant Mittal AIJCR Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Professor and Head, Dayanand Medical College, Ludhiana,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Hemant Chopra, 2 Kapil Dua, 3 Neha Chopra, 4 Vikrant Mittal AIJCR Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Professor and Head, Dayanand Medical College, Ludhiana,
Case Presentation. Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD. Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan
 Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
ISSN: Volume 4 Issue CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS Sunita Singh Sonia Chhabra Pansi Gupta Priya Malik Pt B.D. Sharma PGIMS, Rohtak, Haryana
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS Sunita Singh Sonia Chhabra Pansi Gupta Priya Malik Pt B.D. Sharma PGIMS, Rohtak, Haryana
A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma
 August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
Mucocele of paranasal sinuses
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
Is the Classical Classification of Aspergillosis of the Paranasal Sinuses to non invasive and invasive still valid or not?
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.3, September 2002 Is the Classical Classification of Aspergillosis of the Paranasal Sinuses to non invasive and invasive still valid or not? Abdul Aziz Ashoor (FA-HNO)*
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.3, September 2002 Is the Classical Classification of Aspergillosis of the Paranasal Sinuses to non invasive and invasive still valid or not? Abdul Aziz Ashoor (FA-HNO)*
PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA OF LATERAL WALL OF NOSE A RARE PRESENTATION
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 1 2014 PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA OF LATERAL WALL OF NOSE A RARE PRESENTATION *USHA KUMAR MAHESH *RATNAKAR MADHAVARAO POTEKAR * B.L.D.E UNIVERSITY ABSTRACT: The aim of the article
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 1 2014 PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA OF LATERAL WALL OF NOSE A RARE PRESENTATION *USHA KUMAR MAHESH *RATNAKAR MADHAVARAO POTEKAR * B.L.D.E UNIVERSITY ABSTRACT: The aim of the article
First author: Krishnamurti Sarmento Junior (Sarmento, KJ) Attending doctor at the Otolaryngology department of Bonsucesso General Hospital.
 Title: Endoscopic resection of a sinonasal cavernous hemangioma. First author: Krishnamurti Sarmento Junior (Sarmento, KJ) Attending doctor at the Otolaryngology department of Bonsucesso General Hospital.
Title: Endoscopic resection of a sinonasal cavernous hemangioma. First author: Krishnamurti Sarmento Junior (Sarmento, KJ) Attending doctor at the Otolaryngology department of Bonsucesso General Hospital.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Computed Tomographic Findings in Patients With Invasive Fungal Sinusitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Computed Tomographic Findings in Patients With Invasive Fungal Sinusitis John M. DelGaudio, MD; Ron E. Swain Jr, MD; Todd T. Kingdom, MD; Susan Muller, DMD; Patricia A. Hudgins, MD Objective:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Computed Tomographic Findings in Patients With Invasive Fungal Sinusitis John M. DelGaudio, MD; Ron E. Swain Jr, MD; Todd T. Kingdom, MD; Susan Muller, DMD; Patricia A. Hudgins, MD Objective:
Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Chapter Five. 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM.
 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Case Report
 Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Vahit Mutlu 1, Ozgur Yoruk 1, Ozalkan Ozkan 2 1 Atatürk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ears, Nose and Throat, Erzurum, Turkey 2 Erzincan University
Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Vahit Mutlu 1, Ozgur Yoruk 1, Ozalkan Ozkan 2 1 Atatürk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ears, Nose and Throat, Erzurum, Turkey 2 Erzincan University
Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia
 Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
Rhinosinusitis. John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD
 Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
Spheno-Ethmoidectomy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
Case Report Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Nasal Septum
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 670105, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/670105 Case Report Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Nasal Septum Yuri Okumura, 1 Kazuhiro
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 670105, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/670105 Case Report Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Nasal Septum Yuri Okumura, 1 Kazuhiro
I ntroduction: Bone marrow transplantation (BMT)
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2006;72(3):328-32. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Chronic GVHD: predictive factor for rhinosinusitis in bone marrow transplantation Erica Ortiz 1, Eulalia Sakano 2, Carmino Antonio De Souza
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2006;72(3):328-32. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Chronic GVHD: predictive factor for rhinosinusitis in bone marrow transplantation Erica Ortiz 1, Eulalia Sakano 2, Carmino Antonio De Souza
Orbital facia. Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia
 Anatomy Orbital facia Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia Physiology of symptoms 1) Proptosis ( exophthalmos) Pseudoproptosis Axial Non axial Pulsating Positional Intermittent
Anatomy Orbital facia Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia Physiology of symptoms 1) Proptosis ( exophthalmos) Pseudoproptosis Axial Non axial Pulsating Positional Intermittent
Frontal sinus disease continues to be one of the great
 Unilateral transnasal endoscopic approach to frontal sinuses: Draf IIc Mohammed K. Al Komser, M.D., M.A.S. and Andrew N. Goldberg, M.D., M.S.C.E. ABSTRACT For chronic sinusitis surgery, the Draf III approach
Unilateral transnasal endoscopic approach to frontal sinuses: Draf IIc Mohammed K. Al Komser, M.D., M.A.S. and Andrew N. Goldberg, M.D., M.S.C.E. ABSTRACT For chronic sinusitis surgery, the Draf III approach
Clinical analysis of 29 cases of nasal mucosal malignant melanoma
 1166 Clinical analysis of 29 cases of nasal mucosal malignant melanoma HUANXIN YU and GANG LIU Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Tianjin Huanhu Hospital, Tianjin 300060, P.R. China
1166 Clinical analysis of 29 cases of nasal mucosal malignant melanoma HUANXIN YU and GANG LIU Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Tianjin Huanhu Hospital, Tianjin 300060, P.R. China
Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group. Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer. Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i & 11-1C-106i
 Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations
 White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Despite recent advances in instrumentation
White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Despite recent advances in instrumentation
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 30/July 28, 2014 Page 8403
 BENIGN TUMOR OF NOSE AND PARANASAL SINUS IN A CHILD: A CASE REPORT Mujtaba Khan 1, S. Muneeruddin Ahmed 2, A. Sesha Prasad 3, M. Mahendra Kumar 4, G. Shahul Hameed 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Mujtaba Khan,
BENIGN TUMOR OF NOSE AND PARANASAL SINUS IN A CHILD: A CASE REPORT Mujtaba Khan 1, S. Muneeruddin Ahmed 2, A. Sesha Prasad 3, M. Mahendra Kumar 4, G. Shahul Hameed 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Mujtaba Khan,
Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis Involving Frontal Sinus: A Prospective Study comparing Surgical Modalities
 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1141 H Verma et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis Involving Frontal Sinus: A Prospective Study comparing Surgical Modalities H Verma, Rijuneeta, AK Gupta, A Chakrabarti
10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1141 H Verma et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis Involving Frontal Sinus: A Prospective Study comparing Surgical Modalities H Verma, Rijuneeta, AK Gupta, A Chakrabarti
Contemporary cohort cross-sectional study. Introduction:
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2008;74(2):207-12. original article Histological Aspects of Rhinosinusal Polyps Luciano Gustavo Ferreira Couto 1, Atílio Maximino Fernades 2, Daniel Ferracioli Brandão 3, Dalisio
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2008;74(2):207-12. original article Histological Aspects of Rhinosinusal Polyps Luciano Gustavo Ferreira Couto 1, Atílio Maximino Fernades 2, Daniel Ferracioli Brandão 3, Dalisio
Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p
 Title Radiological conference. Frontal sinus osteoma complicated by pneumocephalus Author(s) Fung, WT; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p. 658-662 Issued Date 1996 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44655
Title Radiological conference. Frontal sinus osteoma complicated by pneumocephalus Author(s) Fung, WT; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p. 658-662 Issued Date 1996 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44655
Frontal Sinus Mucocele After Osteoplastic Flap Surgery: Case Report
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550013 Volume 1, Issue 3 Case Report Frontal Sinus Mucocele After Osteoplastic Flap Surgery: Case Report Peter Catalano, MD * and Michael
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550013 Volume 1, Issue 3 Case Report Frontal Sinus Mucocele After Osteoplastic Flap Surgery: Case Report Peter Catalano, MD * and Michael
The Role of Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Paranasal Sinuses Lesions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Role of Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Paranasal Sinuses Lesions Bhumikaben P. Suthar 1 *, Divya Vaidya 2, Pukhraj P. Suthar 3. 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Third Year Resident,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Role of Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Paranasal Sinuses Lesions Bhumikaben P. Suthar 1 *, Divya Vaidya 2, Pukhraj P. Suthar 3. 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Third Year Resident,
Cavernous haemangioma of the left nasal cavity and maxillary sinus
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 3, No. 10, April - June 2013 CASE REPORT Cavernous haemangioma of the left nasal cavity and maxillary sinus Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Andreea Naca 2, Mioara Mircea 3 1 ENT
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 3, No. 10, April - June 2013 CASE REPORT Cavernous haemangioma of the left nasal cavity and maxillary sinus Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Andreea Naca 2, Mioara Mircea 3 1 ENT
Commen Nose Diseases
 Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
The Role of Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Paranasal Sinuses Lesions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Role of Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Paranasal Sinuses Lesions Bhumikaben P. Suthar 1 *, Divya Vaid 2, Pukhraj P. Suthar 3. 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Third Year Resident,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Role of Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Paranasal Sinuses Lesions Bhumikaben P. Suthar 1 *, Divya Vaid 2, Pukhraj P. Suthar 3. 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Third Year Resident,
Case Report Clinical and pathological features in a case of angiomatous nasal polyp
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):22901-22906 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0038069 Case Report Clinical and pathological features in a case of angiomatous nasal polyp Yangyang Bao 1*, Jiang Bian 2*,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):22901-22906 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0038069 Case Report Clinical and pathological features in a case of angiomatous nasal polyp Yangyang Bao 1*, Jiang Bian 2*,
CASE REPORTS. Inflammatory Polyp of the Bronchus. V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
ISPUB.COM. Primary nasal amyloidosis. D Prasad, G Somayaji, R Aroor, M Abdulla INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 9 Number 2 Primary nasal amyloidosis D Prasad, G Somayaji, R Aroor, M Abdulla Citation D Prasad, G Somayaji, R Aroor, M Abdulla. Primary nasal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 9 Number 2 Primary nasal amyloidosis D Prasad, G Somayaji, R Aroor, M Abdulla Citation D Prasad, G Somayaji, R Aroor, M Abdulla. Primary nasal
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017
 Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
Low-Grade Papillary Schneiderian Carcinoma: A Case Report
 DOI 10.1007/s12105-017-0832-z CASE REPORT Low-Grade Papillary Schneiderian Carcinoma: A Case Report Hui Jeong Jeong 1 Jin Roh 1 Bong Jae Lee 2 Kyung Ja Cho 1 Received: 13 March 2017 / Accepted: 13 June
DOI 10.1007/s12105-017-0832-z CASE REPORT Low-Grade Papillary Schneiderian Carcinoma: A Case Report Hui Jeong Jeong 1 Jin Roh 1 Bong Jae Lee 2 Kyung Ja Cho 1 Received: 13 March 2017 / Accepted: 13 June
Catholic University of Louvain, St - Luc University Hospital Head and Neck Oncology Programme. Anatomopathology. Pathology 1 Sept.
 Anatomopathology Pathology 1 Anatomopathology Biopsies Frozen section Surgical specimen Peculiarities for various tumor site References Pathology 2 Biopsies Minimum data, which should be given by the pathologist
Anatomopathology Pathology 1 Anatomopathology Biopsies Frozen section Surgical specimen Peculiarities for various tumor site References Pathology 2 Biopsies Minimum data, which should be given by the pathologist
Evaluation of the Change in Recent Diagnostic Criteria of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Cross-sectional Study
 Abhishek Ramadhin REVIEW ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1246 Evaluation of the Change in Recent Diagnostic Criteria of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Cross-sectional Study Abhishek Ramadhin ABSTRACT There
Abhishek Ramadhin REVIEW ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1246 Evaluation of the Change in Recent Diagnostic Criteria of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Cross-sectional Study Abhishek Ramadhin ABSTRACT There
SINONASAL RESPIRATORY EPITHELIAL ADENOMATOID HAMARTOMA: A REPORT ON THREE CASES.
 EUROMEDITERRANEAN BIOMEDICAL JOURNAL 2018,13 (12) 060 064 (FORMERLY: CAPSULA EBURNEA) Original article SINONASAL RESPIRATORY EPITHELIAL ADENOMATOID HAMARTOMA: A REPORT ON THREE CASES. Carmelo Saraniti
EUROMEDITERRANEAN BIOMEDICAL JOURNAL 2018,13 (12) 060 064 (FORMERLY: CAPSULA EBURNEA) Original article SINONASAL RESPIRATORY EPITHELIAL ADENOMATOID HAMARTOMA: A REPORT ON THREE CASES. Carmelo Saraniti
Tumefactive Fibroinflammatory Lesion: A Diagnostic Dilemma
 IJMS Vol 42, No 2, March 2017 Tumefactive Fibroinflammatory Lesion: A Diagnostic Dilemma Case Report Promil Jain 1, MD; Rajeev Sen 1, MD; Nisha Sharma 1, MD; Shilpi Bhargava 1, MD; Virender Singh 2, MDS
IJMS Vol 42, No 2, March 2017 Tumefactive Fibroinflammatory Lesion: A Diagnostic Dilemma Case Report Promil Jain 1, MD; Rajeev Sen 1, MD; Nisha Sharma 1, MD; Shilpi Bhargava 1, MD; Virender Singh 2, MDS
Clinical and imagistic correlations in the inflammatory pathology of nasosinusal cavities
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 29, January-March 2018 ORIGINAL STUDY DOI: 10.2478/rjr-2018-0003 Clinical and imagistic correlations in the inflammatory pathology of nasosinusal cavities Emilia
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 29, January-March 2018 ORIGINAL STUDY DOI: 10.2478/rjr-2018-0003 Clinical and imagistic correlations in the inflammatory pathology of nasosinusal cavities Emilia
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma Nasal Type: Detection by Computed Tomography Features
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma Nasal Type: Detection by Computed Tomography Features Yin-Ping
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma Nasal Type: Detection by Computed Tomography Features Yin-Ping
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem
 Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma in the Head and Neck: A Pictorial Essay
 Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal 64 (2013) 363e369 Neuroradiology / Neuroradiologie Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma in the Head and Neck: A Pictorial Essay Michael Chan, BHSc a, Eric Bartlett,
Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal 64 (2013) 363e369 Neuroradiology / Neuroradiologie Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma in the Head and Neck: A Pictorial Essay Michael Chan, BHSc a, Eric Bartlett,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Group Chandler Maloney. First Inflammatory oedema Preseptal cellulitis. Second Orbital Cellulitis Subperiosteal abscess
 ORBITAL MANIFESTATIONS OF SINUS DISEASE T. Jyothirmayi 1, V. Meenakshi 2, M. Deepika 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: T. Jyothirmayi, V. Meenakshi, M. Deepika. Orbital Manifestations of Sinus Disease. Journal
ORBITAL MANIFESTATIONS OF SINUS DISEASE T. Jyothirmayi 1, V. Meenakshi 2, M. Deepika 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: T. Jyothirmayi, V. Meenakshi, M. Deepika. Orbital Manifestations of Sinus Disease. Journal
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
ORIGINAL ARTICLE RELATIONSHIP OF CONCHA BULLOSA WITH OSTEOMEATAL UNIT BLOCKAGE. TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY IN 200 PATIENTS.
 RELATIONSHIP OF CONCHA BULLOSA WITH OSTEOMEATAL UNIT BLOCKAGE. TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY IN 200 PATIENTS. Shrikrishna B H 1, Jyothi A C 2, Sanjay G 3, Sandeep Samson G 4. 1. Associate Professor, Department of
RELATIONSHIP OF CONCHA BULLOSA WITH OSTEOMEATAL UNIT BLOCKAGE. TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY IN 200 PATIENTS. Shrikrishna B H 1, Jyothi A C 2, Sanjay G 3, Sandeep Samson G 4. 1. Associate Professor, Department of
Cystic fibrosis, also known as mucoviscidosis, is a
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2007;73(6): 852-6. CASE REPORT Cystic Fibrosis-Associated Bilateral Pseudomucocele - Case Report Karla Palma Portes 1, Silvio Antonio Monteiro Marone 2, Elder Yoshimitsu Goto
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2007;73(6): 852-6. CASE REPORT Cystic Fibrosis-Associated Bilateral Pseudomucocele - Case Report Karla Palma Portes 1, Silvio Antonio Monteiro Marone 2, Elder Yoshimitsu Goto
Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: detection of fungal DNA in sinus aspirate using polymerase chain reaction
 1- Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: detection of fungal DNA in sinus aspirate using polymerase chain reaction Abstract Objective: This study investigated allergic fungal rhinosinusitis cases, and aimed
1- Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: detection of fungal DNA in sinus aspirate using polymerase chain reaction Abstract Objective: This study investigated allergic fungal rhinosinusitis cases, and aimed
1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING
 RHINOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING Exposure to clinical rhinology is provided in each of the four ORL years over the course of several rotations in a graduated approach. MEE General Otolaryngology
RHINOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING Exposure to clinical rhinology is provided in each of the four ORL years over the course of several rotations in a graduated approach. MEE General Otolaryngology
Ethmoid mucocele and post traumatic nasal deformity
 Ethmoid mucocele and post traumatic nasal deformity Abdullah Musleh, Hefni Montaser Abdelazeem Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Armed Forces Hospital, South Region, Saudi Arabia shahrani99@hotmail.com
Ethmoid mucocele and post traumatic nasal deformity Abdullah Musleh, Hefni Montaser Abdelazeem Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Armed Forces Hospital, South Region, Saudi Arabia shahrani99@hotmail.com
Boundaries Septum Turbinates & Meati Lamellae Drainage Pathways Variants
 The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP SINUS CT Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70486, 70487, 70488, 76380
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP SINUS CT Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70486, 70487, 70488, 76380
AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY-
 TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2
 STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Santhosha Kumar B, Manjunath Rao S. V. Study of Correlation between
STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Santhosha Kumar B, Manjunath Rao S. V. Study of Correlation between
Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
Orbital Tumors - A Clinico Pathological Study
 Orbital Tumors - A Clinico Pathological Study Radha. J. DO, Ani Sreedhar. MS. Little Flower Hospital, Angamaly, Kerala ORIGINAL ARTICLES Abstract: Aim. To study the clinical and histopathological profiles
Orbital Tumors - A Clinico Pathological Study Radha. J. DO, Ani Sreedhar. MS. Little Flower Hospital, Angamaly, Kerala ORIGINAL ARTICLES Abstract: Aim. To study the clinical and histopathological profiles
Case of the Day Chest
 Case of the Day Chest Darin White MDCM FRCPC Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic 76 th Annual Scientific Meeting Canadian Association of Radiologists Montreal, QC April 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Case of the Day Chest Darin White MDCM FRCPC Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic 76 th Annual Scientific Meeting Canadian Association of Radiologists Montreal, QC April 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions. Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology
 Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology Medical College of Georgia of Georgia Regents University Department of Otolaryngology / Head
Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology Medical College of Georgia of Georgia Regents University Department of Otolaryngology / Head
Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery
 Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery Poster No.: C-0509 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Dobra 1, C. A. Badiu 1,
Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery Poster No.: C-0509 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Dobra 1, C. A. Badiu 1,
Original Article Effect of lamina papyracea ingression on orbito-ocular complications after functional endoscopic sinus surgery
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):10317-10321 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0025371 Original Article Effect of lamina papyracea ingression on orbito-ocular complications after functional endoscopic sinus
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):10317-10321 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0025371 Original Article Effect of lamina papyracea ingression on orbito-ocular complications after functional endoscopic sinus
Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes
 CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
9/18/2018. Disclosures. Objectives
 Is It Really Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis? Assessment, Differential Diagnosis and Management of Common Sinonasal Symptoms Kristina Haralambides, MS, RN, FNP-C Disclosures The content of this presentation
Is It Really Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis? Assessment, Differential Diagnosis and Management of Common Sinonasal Symptoms Kristina Haralambides, MS, RN, FNP-C Disclosures The content of this presentation
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
 Measure #334: Adult Sinusitis: More than One Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan Within 90 Days for Chronic Sinusitis (Overuse) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS
Measure #334: Adult Sinusitis: More than One Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan Within 90 Days for Chronic Sinusitis (Overuse) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS
A CASE OF SINONASAL CHONDROSARCOMA CASE REPORT
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 A CASE OF SINONASAL CHONDROSARCOMA CASE REPORT SankaraNarayanan Gopalakrishnan K.M Elango Swarna Saravanan Government Royepettah Hospital Chennai ABSTRACT Introduction:
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 A CASE OF SINONASAL CHONDROSARCOMA CASE REPORT SankaraNarayanan Gopalakrishnan K.M Elango Swarna Saravanan Government Royepettah Hospital Chennai ABSTRACT Introduction:
Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation
 246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
Chronic Sinusitis. Acute Sinusitis. Sinusitis. Anatomy of the Paranasal Sinuses. Sinusitis. Medical Topics - Sinusitis
 1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
Extranasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Of The Cartilaginous Nasal Septum: Possible Origin From Ectopic Tissue Trapped During Septal Development
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 14 Number 1 Extranasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Of The Cartilaginous Nasal Septum: Possible Origin From Ectopic Tissue Trapped During Septal Development
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 14 Number 1 Extranasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Of The Cartilaginous Nasal Septum: Possible Origin From Ectopic Tissue Trapped During Septal Development
Case 2. Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset
 Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
Pott s Puffy Tumor. Shahad Almohanna 15/1/2018
 Pott s Puffy Tumor Shahad Almohanna R2 15/1/2018 Definition First described in 1760 by Sir Percival Pott. s he originally suggested that trauma of the frontal bone was causative for this lesion, but later,
Pott s Puffy Tumor Shahad Almohanna R2 15/1/2018 Definition First described in 1760 by Sir Percival Pott. s he originally suggested that trauma of the frontal bone was causative for this lesion, but later,
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013
 FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
Sinus Surgery. Middle Meatus
 Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
Risk Factors of Chronic Rhinosinusitis After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.900421 Received: 2016.07.05 Accepted: 2016.07.22 Published: 2017.02.28 Risk Factors of Chronic Rhinosinusitis After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Authors Contribution:
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.900421 Received: 2016.07.05 Accepted: 2016.07.22 Published: 2017.02.28 Risk Factors of Chronic Rhinosinusitis After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Authors Contribution:
Schwannoma of the nasal septum-a case report
 Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN: 2250-0359 Schwannoma of the nasal septum-a case report *SUNIL JANARDHANAN *KULOTHUNGAN *VINOD FELIX * KERF ENT HOSPITAL TRIVANDRUM KERALA Abstract: Schwannomas of the nasal
Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN: 2250-0359 Schwannoma of the nasal septum-a case report *SUNIL JANARDHANAN *KULOTHUNGAN *VINOD FELIX * KERF ENT HOSPITAL TRIVANDRUM KERALA Abstract: Schwannomas of the nasal
The advent of high-resolution computerized tomography
 An anatomic classification of the ethmoidal bulla REUBEN C. SETLIFF, III, MD, PETER J. CATALANO, MD, FACS, LISA A. CATALANO, MPH, and CHAD FRANCIS, BA, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and Burlington, Massachusetts
An anatomic classification of the ethmoidal bulla REUBEN C. SETLIFF, III, MD, PETER J. CATALANO, MD, FACS, LISA A. CATALANO, MPH, and CHAD FRANCIS, BA, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and Burlington, Massachusetts
Isolated sphenoid inflammatory diseases
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2454-5929.ijohns20183688
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2454-5929.ijohns20183688
CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS
 CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS SCOPE OF THE PRACTICE GUIDELINE This clinical practice guideline is for use by the Philippine Society of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. It covers the diagnosis and
CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS SCOPE OF THE PRACTICE GUIDELINE This clinical practice guideline is for use by the Philippine Society of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. It covers the diagnosis and
Case Report A 65- year old female with synchronous HIV and Extramedullary Plasmacytoma of Maxillary sinus. Abstract. Keywords.
 Case Report A 65- year old female with synchronous HIV and Extramedullary Plasmacytoma of Maxillary sinus H. Sabir 1, S. Kumbhare 2, A. Parate 2, S. Gupta 3, Ravi Tale 4 1 Raj Multispeciality Dental Clinic,
Case Report A 65- year old female with synchronous HIV and Extramedullary Plasmacytoma of Maxillary sinus H. Sabir 1, S. Kumbhare 2, A. Parate 2, S. Gupta 3, Ravi Tale 4 1 Raj Multispeciality Dental Clinic,
CASE REPORT PLASMA CELL GRANULOMA OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW
 CASE REPORT Dennis H. Kraus, MD, Section Editor PLASMA CELL GRANULOMA OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW Heather E. Newlin, BS, 1 John W. Werning, MD, 2 William M. Mendenhall,
CASE REPORT Dennis H. Kraus, MD, Section Editor PLASMA CELL GRANULOMA OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW Heather E. Newlin, BS, 1 John W. Werning, MD, 2 William M. Mendenhall,
