Venous Compression for Prevention of Postthrombotic Syndrome: A Meta-analysis
|
|
|
- Dylan Green
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Venous Compression for Prevention of Postthrombotic Syndrome: A Meta-analysis Muzammil H. Musani, MD, a Fadi Matta, MD, b Abdo Y. Yaekoub, MD, c Jane Liang, MSc, d Russell D. Hull, MBBS, MSc, d Paul D. Stein, MD b a Department of Internal Medicine, St. Joseph Mercy Oakland, Pontiac, Mich; b Departments of Internal Medicine and Research and Advanced Studies Program, College of Osteopathic Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing; c Department of Internal Medicine, St. Mary Mercy, Livonia, Mich; d Department of Medicine, University of Calgary, Alberta, Canada. ABSTRACT PURPOSE: To determine the effectiveness of venous compression stockings or compression bandages on the reduction of postthrombotic syndrome in patients with deep venous thrombosis. METHODS: We attempted to identify all published trials in all languages identified by PubMed through June Meta-analysis was performed. RESULTS: Based on 5 randomized trials of patients with deep venous thrombosis comparing treatment with venous compression to controls, mild-to-moderate postthrombotic syndrome occurred in 64 of 296 (22%) treated with venous compression, compared with 106 of 284 (37%) in controls (relative risk 0.52). Severe postthrombotic syndrome occurred in 14 of 296 (5%) treated, compared with 33 of 284 (12%) controls (relative risk 0.38). Any postthrombotic syndrome occurred in 89 of 338 (26%) treated, compared with 150 of 324 (46%) controls (relative risk 0.54). CONCLUSION: Venous compression reduced the incidence of postthrombotic syndrome, particularly severe postthrombotic syndrome. Venous compression in patients with deep venous thrombosis would seem to be indicated for this purpose. There was, however, wide variation in the type of stockings used, time interval from diagnosis to application of stockings, and duration of treatment. Further investigation, therefore, is needed Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. The American Journal of Medicine (2010) 123, KEYWORDS: Deep venous thrombosis; Postthrombotic syndrome; Venous compression stockings The reported incidence of postthrombotic syndrome after symptomatic deep venous thrombosis varies widely and depends on the severity of the postthrombotic syndrome. Some reported that by the end of 1 month, among 347 patients with deep venous thrombosis, 34% developed mild postthrombotic syndrome, 10% moderate, and 4% severe. 1 Among patients with deep venous thrombosis who did not Funding: None. Conflict of Interest: None of the authors have any financial or other potential conflicts of interest relative to the data in this manuscript. Authorship: All authors had access to the data and a role in writing the manuscript. Requests for reprints should be addressed to Paul D. Stein, MD, Department of Internal Medicine, Michigan State University, College of Osteopathic Medicine, MSU Venous Thromboembolism Research Unit, Woodward Ave., Pontiac, MI address: steinp@trinity-health.org wear compression stockings, 20% to 82% developed postthrombotic syndrome of any severity. 2-6 Deep venous obstruction, calf muscle dysfunction, and venous reflux are contributing factors to the postthrombotic syndrome. 7 Venous hypertension developing due to venous reflux results in increased capillary filtration, leading to edema in the lower leg and skin changes, including dermatitis, lipodermatosclerosis, and white skin atrophy. 8 Local tissue hypoxia is associated with venous ulcers. 9 Disturbed microcirculation, perhaps due to precapillary fibrin cuffs, has been speculated to lead to a decrease of cutaneous oxygen concentration, contributing to spontaneous breakdown of the skin, but secondary hypoxia has not been demonstrated. 7 It has become common practice to prescribe graduated compression stockings for patients with deep venous thrombosis, particularly proximal deep venous thrombosis, to prevent postthrombotic syndrome. 10,11 Review in the clini /$ -see front matter 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. doi: /j.amjmed
2 736 The American Journal of Medicine, Vol 123, No 8, August 2010 cal guideline by Kearon et al 11 led them to conclude that graduated compression stockings were beneficial for the prevention of postthrombotic syndrome, although a randomized trial by Ginsberg et al 3 showed no benefit. A meta-analysis by Kolbach et al 8 that included 3 randomized trials showed an overall benefit of compression stockings in the prevention of any postthrombotic syndrome and of severe postthrombotic syndrome. A meta-analysis by Giannoukas et al 12 that included 4 randomized trials also showed an overall benefit of compression stockings in the reduction of any postthrombotic syndrome. Because of the potential importance of graduated compression stockings in the prevention of postthrombotic syndrome, we updated the literature review on this subject and performed a metaanalysis to include a randomized trial since the previous meta-analyses by Kolbach et al 8 and Giannoukas et al. 12 CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE METHODS Study Identification We attempted to identify all published trials in all languages that used compression stockings to prevent the postthrombotic syndrome. Studies were identified by searching PubMed through June Key words in the literature search were: postthrombotic syndrome combined with prevention, elastic stockings, or compression therapy. We augmented our searches by manually reviewing the reference lists of all original articles and all review articles. This was done by 2 of the authors, working separately. Each study was evaluated for inclusion by at least 2 authors. Studies were included if they met all of the following criteria: patients were randomized for comparison between treatment with compression stockings or compression bandages and no compression treatment; anticoagulant therapy was the same in compression therapy groups and the nostocking groups; the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis was made on the basis of objective tests; raw data were presented in sufficient detail to permit calculations of the incidence of postthrombotic syndrome. The literature search identified 257 citations. Among these, 64 were unrelated to postthrombotic syndrome, 69 were reviews or a guideline, 84 were related to prophylaxis or treatment without specific investigation of compression stockings, 23 were related to the pathophysiology and diagnosis of postthrombotic syndrome, 10 were case series or case reports, and 2 described methods of ongoing investigations. Complete versions of the articles were obtained if, Mild-to-moderate postthrombotic syndrome occurs in 37% of patients with deep venous thrombosis, and severe occurs in 12%. Venous compression, usually with belowknee compression stockings, reduced the incidence of mild postthrombotic syndrome to 22%, and severe to 5%. Venous compression stockings are effective in reducing the incidence of postthrombotic syndrome in patients with deep venous thrombosis. from the title or abstract, they satisfied the inclusion criteria. Five randomized trials evaluated the effects of graduated compression stockings or compression bandages on the prevention of postthrombotic syndrome, and these were included. Definitions of mild-to-moderate and severe postthrombotic syndrome used by Brandjes et al, 2 Partsch et al, 4 and Prandoni et al 5 were based on the Villalta scoring system, 13 which was summarized by Kahn and Ginsberg. 14 In the Villalta scoring system, a score of 5-14 indicated mild-tomoderate postthrombotic syndrome, and a score of 15 indicated severe. Aschwanden et al 6 used the Clinical-Etiology-Anatomic-Pathophysiologic (CEAP) scoring system, 15 also summarized by Kahn and Ginsberg. 14 Aschwanden et al 6 excluded from their results those with the lowest scores of 0-3. We interpreted a CEAP score of C4 (skin changes, pigmentation, eczema, lipodermatosclerosis) to indicate mild-to-moderate postthrombotic syndrome, and a CEAP score of C5 (skin changes with healed ulcer) and C6 (skin changes with active ulcer) to indicate severe postthrombotic syndrome. Ginsberg et al 3 did not quantify severity. Statistical Methods Meta-analysis was performed using the Metan procedure of Stata, release 8.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, Tex). Summary effects for the outcomes were calculated by using the fixed-effects model. The random-effects model produced similar results. We considered a probability of P.05 to be statistically significant for all statistical tests. RESULTS Age and sex of the patients in the 5 included trials are shown in Table 1. Among 338 treated patients, below-knee stockings were used in 308 (91%) patients, thigh-length stockings in 17 (5%), and thigh bandages in 13 (4%). 2-6 Characteristics of the stockings, time interval between diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis and application of stockings, duration of stocking use, duration of follow-up, the scoring system used, and the incidence of postthrombotic syndrome are shown in Table 2. Among patients treated with venous compression, mild to moderate postthrombotic syndrome occurred in 64 of 296 (22%), compared with 106 of 284 (37%) in controls. 2-6 The relative risk of mild-to-moderate postthrombotic syndrome was 0.52 (95% confidence interval [CI], ; P.001) (Figure 1).
3 Musani et al Postthrombotic Syndrome 737 Table 1 First Author (Reference) Sex and Age of Included Patients Year Sex Brandjes M 55 F 44 Ginsberg M 70 F 90 Partsch M 7 F 4 Prandoni M 35 F 55 Aschwanden M 45 F 40 *Ages differed in study groups. Mean Age (Years) Control Stockings Stockings Control M 54 F 42 M 23 F 19 M 16 F 10 M 42 F 48 M 54 F * 40-60* Severe postthrombotic syndrome occurred in 14 of 296 (5%) patients treated with venous compression, compared with 33 of 284 (12%) controls. 2-6 The relative risk of severe postthrombotic syndrome, comparing stockings with no stockings, was 0.38 (95% CI, ; P.001) (Figure 2). Open lesions were found in 3 of 296 (1.0%) patients who used compression stockings and 9 of 284 (3.2%) controls. This difference was not significant. Any postthrombotic syndrome occurred in 89 of 338 (26%) treated with compression stockings compared with 150 of 324 (46%) controls. 2-6 The relative risk of any postthrombotic syndrome was 0.54 (95% CI, ; P.001) (Figure 3). Sensitivity analysis showed that the results for the outcomes of all episodes of postthrombotic syndrome, or cases of mild/moderate postthrombotic syndrome, were robust. Removal of individual studies did not alter our findings. The venous compression advantage was not lost for any of the outcomes when a single study was removed from the metaanalysis. Statistical tests did not detect heterogeneity in risk ratio among studies for the outcomes of all episodes of postthrombotic syndrome, or cases of mild/moderate postthrombotic syndrome, or cases of severe postthrombotic syndrome. DISCUSSION The risk of postthrombotic syndrome, on average, was reduced 46% by venous compression, usually by below-knee compression stockings. Venous compression was more effective in reducing the incidence of severe postthrombotic syndrome (62% risk reduction) than mild-to-moderate postthrombotic syndrome (48% risk reduction). One investigation (Ginsberg et al) 3 showed little benefit. In this investigation, the control patients received stockings that were 1-2 sizes too large. 3 We speculate that the unfitted stockings may have had a beneficial effect despite being 1-2 sizes too large. Also, these investigators waited 1 year after the episode of acute deep venous thrombosis before randomizing for patients for compression stockings. Whether this delay contributed to the failure to show an effect of compression stockings is uncertain. Patients in the control group in this investigation had nearly the same incidence of postthrombotic syndrome (28%) as patients in the treatment groups in the investigations by Prandoni et al (26%) and Brandjes et al (31%). 2,3,5 The time interval between diagnosis of acute deep venous thrombosis and the application of stockings, and the duration of application of compression stockings may have affected the results. The lowest relative risks for postthrombotic syndrome after the application of compression stockings were reported by Brandjes et al 2 (risk ratio 0.44) and by Prandoni et al 5 (risk ratio 0.52). These investigators applied stockings 2-3 weeks or within 5-10 days after the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis, and compression stockings were worn for 2 or more years. 3,5 In contrast, Partsch et al 4 treated patients with compression therapy immediately, but only for 9 days, whereas control patients received no compression treatment for only 9 days. 4 Thereafter, half or more of both controls and treated patients wore compression stockings for 2 years. These investigators showed a risk ratio of.66 with treatment, suggesting that the early application of venous compression is important. Both Ginsberg et al 3 and Aschwanden et al 6 showed no statistically significantly lower risk ratio for skin changes in those who wore compression stockings. Aschwanden et al 6 started randomization to compression stockings 6 months after the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis, and Ginsberg et al 3 waited 1 year before randomizing for treatment. This may have adversely affected the results. In addition to differences in time to application of stockings, and duration of use, some used below-knee stockings, 2,5,6 thigh-length stockings, 4 or either. 3 Strength of stockings varied (Table 2). There is no universal agreement on a definition of postthrombotic syndrome. 3 All definitions, however, include chronic complaints of the legs following deep venous thrombosis. 8 Symptoms may include pain, heaviness, pruritus, and paresthesia, and signs may include pretibial edema, erythema, induration, hyperpigmentation, new venous ectasia, pain during calf compression, and ulceration. 8 Definitions of severity differ, 3,13,15 and certain definitions, of necessity, are arbitrary. 15 The International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis recommended the Villalta scale as a standard scale for severity of postthrombotic-syndrome. 16 We used the definition of severity in the Villalta system when that system was used by the investigators. In the only study that used the CEAP scoring system, 6 we defined severe as showing healed or active ulcer. This corresponded to severe by the Villalta system, in which presence of ulcer was considered severe. Because of correspondence of the scoring systems for severe, we do not believe that differences in the scoring methods affected the results of the meta-analysis. The investigation by Aschwanden et al 6 excluded patients with the mildest signs, telangiectasias, reticular veins, malleolar flare (C1 classification), varicose veins (C2 clas-
4 Table 2 First Author, Year Brandjes Ginsberg Partsch Prandoni Aschwanden Stocking Characteristics, Study Protocol, and Results Group Patients (n) Stocking Pressure (mm Hg) Stocking Length and Type Interval Diagnosis to Stocking Stocking Duration (Years) Follow-up (Years) Scoring System Mild/ Moderate Severe Total Control 98 5 Villalta-Prandoni Scale* 46/98 (47) 23/98 (23) 69/98 (70) Stocking at ankle 36 at lower calf 21 at upper calf GCS below knee 2-3 weeks /96 (20) 11/96 (11) 30/96 (31) Control 40 Stockings 1-2 Below knee or thigh ( /40 (28) sizes too sizes too large) large Stocking below knee, n below knee, n thigh, n 4 ECS below knee, n 38 ECS thigh length, n 4 Control 11 No stockings for 9 days Stocking Thigh length ECS (n 13) or gauze-zinc oxide and calamine impregnated bandage on lower leg and firm thigh adhesive bandage (n 13) 1 year /42 (26) Immediate Bed rest 9 days, no stockings in all, then stockings in 8/11 (73%) 2 years 9 days stockings or Unna boot in all, then stockings in 13/26 (50%) 2 years 2 Villalta-Prandoni Scale* 9/11 (82) 0/11 (0) 9/11 (82) 2 14/26 (54) 0/26 (0) 14/26 (54) Control Villalta-Prandoni Scale* 34/90 (38) 10/90 (11) 44/90 (49) Stocking at ankle GSC below knee 5-10 days /90 (22) 3/90 (3) 23/90 (26) Control CEAP 17/85 (20) 0/85 (0) 17/85 (20) Classification Stocking at CS below knee 6 months /84 (13) 0/84 (0) 11/84 (13) ankle GCS graduate compression stockings; ECS elastic compression stockings; CS compression stockings. *Villalta-Prandoni Scale. 13 CEAP (Clinical-Etiology-Anatomic-Pathophysiologic) Classification. 15 Typical pain plus swelling ( 1 month duration) occurring 6 months after acute deep venous thrombosis The American Journal of Medicine, Vol 123, No 8, August 2010
5 Musani et al Postthrombotic Syndrome 739 Figure 1 Proportional effects of venous compression on prevention of mild-to-moderate postthrombotic syndrome. Overall relative risk with venous compression was 0.52 (P.001). Black squares point estimates (with area proportional to number of events) and horizontal lines 95% confidence interval (CI) for observed effects in different subgroups; diamonds point estimate and 95% CI for overall effects, with proportional reductions indicated alongside; long vertical line hazard ratio of 1.0 (ie, no effect of treatment), and shorter vertical line observed overall effect. Figure 3 Proportional effects of venous compression on prevention of mild to-severe postthrombotic syndrome. Overall relative risk with venous compression was 0.54 (P.001). Black squares point estimates (with area proportional to number of events) and horizontal lines 95% confidence interval (CI) for observed effects in different subgroups; diamonds point estimate and 95% CI for overall effects, with proportional reductions indicated alongside; long vertical line hazard ratio of 1.0 (ie, no effect of treatment), and shorter vertical line observed overall effect. sification), and edema with no skin changes (C3 classification). 6 They showed no statistically significant reduction of postthrombotic syndrome (CEAP score 4 or greater). However, they showed fewer symptoms in those treated with stockings. A strength of this meta-analysis is that all included investigations were randomized. A weakness is that investigators used different methods of vein compression, different time intervals from diagnosis to application of stockings, different durations of treatment, different methods for quantifying severity of postthrombotic syndrome, and different definitions of control groups. Even with these differences, however, investigators showed a benefit of venous compression. In view of the importance of the postthrombotic syndrome, the potential benefit of compression stockings, and variability of the methods employed by previous investigators, a randomized, double-blind multicenter clinical trial (the SOX Trial) of 800 patients followed for 2 years is ongoing. 17 In conclusion, venous compression was effective in reducing the incidence of postthrombotic syndrome, particularly severe postthrombotic syndrome. Use of venous compression in patients with deep venous thrombosis would seem to be indicated for this purpose. However, there was wide variability in the methods employed by the various investigators. Further investigation, therefore, is needed. Figure 2 Proportional effects of venous compression on prevention of severe postthrombotic syndrome. Overall relative risk with venous compression was 0.38 (P.001). Black squares point estimates (with area proportional to number of events) and horizontal lines 95% confidence interval (CI) for observed effects in different subgroups; diamonds point estimate and 95% CI for overall effects, with proportional reductions indicated alongside; long vertical line hazard ratio of 1.0 (ie, no effect of treatment), and shorter vertical line observed overall effect. ACKNOWLEDGMENT We thank Muhammad Anis Musani, MD, for assisting in the literature search. References 1. Kahn SR, Shrier I, Julian JA, et al. Determinants and time course of the postthrombotic syndrome after acute deep venous thrombosis. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149: Brandjes DP, Büller HR, Heijboer H, et al. Randomized trial of effect of compression stockings in patients with symptomatic proximal-vein thrombosis. Lancet. 1997;349: Ginsberg JS, Hirsh J, Julian J, et al. Prevention and treatment of postphlebitic syndrome: results of a 3-part study. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:
6 740 The American Journal of Medicine, Vol 123, No 8, August Partsch H, Kaulich M, Mayer W. Immediate mobilisation in acute vein thrombosis reduces post-thrombotic syndrome. Int Angiol. 2004;23: Prandoni P, Lensing AW, Prins MH, et al. Below-knee elastic compression stockings to prevent the post-thrombotic syndrome: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2004;141: Aschwanden M, Jeanneret C, Koller MT, et al. Effect of prolonged treatment with compression stockings to prevent post-thrombotic sequelae: a randomized controlled trial. J Vasc Surg. 2008;47: Guex JJ. Physiopathology of post-thrombotic syndrome. Update 1994 [French]. J Mal Vasc. 1994;19: Kolbach DN, Sandbrink MW, Hamulyak K, et al. Non-pharmaceutical measures for prevention of post-thrombotic syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;CD Borzykowski M, Krahenbuhl B. Non-invasive measurement of skin oxygenation in chronic ulcers of the lower extremities [French]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1981;111: Kahn SR, Elman E, Rodger MA, Wells PS. Use of elastic compression stockings after deep venous thrombosis: a comparison of practices and perceptions of thrombosis physicians and patients. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1: Kearon C, Kahn SR, Agnelli G, et al. American College of Chest Physicians. Antithrombotic therapy for venous thromboembolic disease. American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 Suppl):454S-545S. 12. Giannoukas AD, Labropoulos N, Michaels JA. Compression with or without early ambulation in the prevention of post-thrombotic syndrome: a systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2006;32: Villalta S, Bagatella P, Piccioli A, et al. Assessment of validity and reproducibility of a clinical scale for the post-thrombotic syndrome. Haemostasis. 1994;24:158a. 14. Kahn SR, Ginsberg JS. Relationship between deep venous thrombosis and the postthrombotic syndrome. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164: Porter JM, Moneta GL. Reporting standards in venous disease: an update. International Consensus Committee on Chronic Venous Disease. J Vasc Surg. 1995;21: Kahn SR, Partsch H, Vedantham S, et al. Subcommittee on Control of Anticoagulation of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Definition of post-thrombotic syndrome of the leg for use in clinical investigations: a recommendation for standardization. J Thromb Haemost. 2009;7: Kahn SR, Shbaklo H, Shapiro S, et al. Effectiveness of compression stockings to prevent the post-thrombotic syndrome (the SOX Trial and Bio-SOX biomarker substudy): a randomized controlled trial. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2007;7:21.
Dr Paul Thibault. Phlebologist & Assistant Editor Phlebology (International Journal) Australasian College of Phlebology
 Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist & Assistant Editor Phlebology (International Journal) Australasian College of Phlebology Prescribing Effective Compression and PTS Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist, Newcastle,
Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist & Assistant Editor Phlebology (International Journal) Australasian College of Phlebology Prescribing Effective Compression and PTS Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist, Newcastle,
pressure of compression stockings matters (clinical importance of pressure)
 Classification of Compression Stockings ICC Meeting, Copenhagen, May 17, 2013. pressure of compression stockings matters (clinical importance of pressure) Giovanni Mosti; Lucca, Italy disclosure no conflict
Classification of Compression Stockings ICC Meeting, Copenhagen, May 17, 2013. pressure of compression stockings matters (clinical importance of pressure) Giovanni Mosti; Lucca, Italy disclosure no conflict
Compression Bulletin 36
 6 Compression Bulletin 36 In this issue: One versus two years of elastic compression stockings for prevention of postthrombotic syndrome (OCTAVIA study): randomised controlled trial The aim of this study
6 Compression Bulletin 36 In this issue: One versus two years of elastic compression stockings for prevention of postthrombotic syndrome (OCTAVIA study): randomised controlled trial The aim of this study
Scoring systems for the post-thrombotic syndrome
 Scoring systems for the post-thrombotic syndrome Arany Soosainathan, MB BChir, Hayley M. Moore, MRCS, MBBS, MA, Manjit S. Gohel, FRCS, MD, FEBVS, and Alun H. Davies, MA, DM, FRCS, London, United Kingdom
Scoring systems for the post-thrombotic syndrome Arany Soosainathan, MB BChir, Hayley M. Moore, MRCS, MBBS, MA, Manjit S. Gohel, FRCS, MD, FEBVS, and Alun H. Davies, MA, DM, FRCS, London, United Kingdom
Definition of the Post-thrombotic Syndrome, Differences Between Existing Classifications
 Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 30, 404 414 (2005) doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2005.06.006, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com on Definition of the Post-thrombotic Syndrome, Differences Between Existing
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 30, 404 414 (2005) doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2005.06.006, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com on Definition of the Post-thrombotic Syndrome, Differences Between Existing
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Prevention and Management. Dr. Ashwini Bennett
 Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Prevention and Management Dr. Ashwini Bennett Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this presentation Outline Importance of VTE and PTS Aetiology of PTS PTS risk factors PTS clinical
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Prevention and Management Dr. Ashwini Bennett Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this presentation Outline Importance of VTE and PTS Aetiology of PTS PTS risk factors PTS clinical
The purpose of this scientific statement is to provide an
 AHA Scientific Statement The Postthrombotic Syndrome: Evidence-Based Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association Susan R. Kahn, MD, MSc, FRCPC,
AHA Scientific Statement The Postthrombotic Syndrome: Evidence-Based Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association Susan R. Kahn, MD, MSc, FRCPC,
Compression therapy for prevention of post-thrombotic syndrome(review)
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Compression therapy for prevention of post-thrombotic syndrome(review) AppelenD,vanLooE,PrinsMH,NeumannMHAM,KolbachDN AppelenD,vanLooE,PrinsMH,NeumannMHAM,KolbachDN.
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Compression therapy for prevention of post-thrombotic syndrome(review) AppelenD,vanLooE,PrinsMH,NeumannMHAM,KolbachDN AppelenD,vanLooE,PrinsMH,NeumannMHAM,KolbachDN.
Measurement properties of the Villalta scale to define and classify the severity of the post-thrombotic syndrome
 Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 7: 884 888 DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03339.x REVIEW ARTICLE Measurement properties of the Villalta scale to define and classify the severity of the post-thrombotic
Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 7: 884 888 DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03339.x REVIEW ARTICLE Measurement properties of the Villalta scale to define and classify the severity of the post-thrombotic
chronic venous disorders, varicose vein, CEAP classification, lipodermatosclerosis, Klippel- Trenaunay syndrome DVT CVD
 Online publication August 27, 2009 chronic venous disorders: CVD CEAP 4 CEAP CVD J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 201 205 chronic venous disorders, varicose vein, CEAP classification, lipodermatosclerosis,
Online publication August 27, 2009 chronic venous disorders: CVD CEAP 4 CEAP CVD J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 201 205 chronic venous disorders, varicose vein, CEAP classification, lipodermatosclerosis,
Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
 Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Thanainit Chotanaphuti Phramongkutklao College of Medicine Bangkok, Thailand President of CAOS Asia President of Thai Hip & Knee Society President of ASEAN Arthroplasty
Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Thanainit Chotanaphuti Phramongkutklao College of Medicine Bangkok, Thailand President of CAOS Asia President of Thai Hip & Knee Society President of ASEAN Arthroplasty
Long-term Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin and the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome: A Systematic Review
 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Long-term Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin and the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome: A Systematic Review Russell D. Hull, MBBS, MSc, a Jane Liang, MSc, a Grace Townshend, MSc b a University
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Long-term Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin and the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome: A Systematic Review Russell D. Hull, MBBS, MSc, a Jane Liang, MSc, a Grace Townshend, MSc b a University
Incidence and interventions for post-thrombotic syndrome
 Review Article Incidence and interventions for post-thrombotic syndrome Jeffrey J. Farrell, Christopher Sutter, Sidhartha Tavri, Indravadan Patel Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Cleveland
Review Article Incidence and interventions for post-thrombotic syndrome Jeffrey J. Farrell, Christopher Sutter, Sidhartha Tavri, Indravadan Patel Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Cleveland
One of every 3 to 4 patients with symptomatic proximal
 Annals of Internal Medicine Article Below-Knee Elastic Compression Stockings To Prevent the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome A Randomized, Controlled Trial Paolo Prandoni, MD, PhD; Anthonie W.A. Lensing, MD, PhD;
Annals of Internal Medicine Article Below-Knee Elastic Compression Stockings To Prevent the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome A Randomized, Controlled Trial Paolo Prandoni, MD, PhD; Anthonie W.A. Lensing, MD, PhD;
Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
 Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Catherine K. Chang, MD FACS Vascular Surgery San Diego Southern California Permanente Medical Group Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis Incidence & Outcomes
Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Catherine K. Chang, MD FACS Vascular Surgery San Diego Southern California Permanente Medical Group Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis Incidence & Outcomes
Deep Venous Pathology. Eberhard Rabe Department of Dermatology University of Bonn Germany
 Deep Venous Pathology Eberhard Rabe Department of Dermatology University of Bonn Germany Disclosures None for this presentation Consultant: Sigvaris, EUROCOM Speakers bureau: Bayer Vital, Aspen, Boehringer,
Deep Venous Pathology Eberhard Rabe Department of Dermatology University of Bonn Germany Disclosures None for this presentation Consultant: Sigvaris, EUROCOM Speakers bureau: Bayer Vital, Aspen, Boehringer,
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome(PTS) Conservative Treatment Options
 Post-Thrombotic Syndrome(PTS) Conservative Treatment Options Dr. S. Kundu Scarborough Hospital-General Division Scarborough Vascular Group Toronto Endovascular Centre The Vein Institute of Toronto Scarborough
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome(PTS) Conservative Treatment Options Dr. S. Kundu Scarborough Hospital-General Division Scarborough Vascular Group Toronto Endovascular Centre The Vein Institute of Toronto Scarborough
4/30/2018 CLOT+ In patients with an acute proximal deep vein thrombosis, pharmacomechanical catheter-directed thrombolysis does not reduce t
 In patients with an acute proximal deep vein thrombosis, pharmacomechanical catheter-directed thrombolysis does not reduce the rate of post-thrombotic syndrome Question In patients who have symptomatic
In patients with an acute proximal deep vein thrombosis, pharmacomechanical catheter-directed thrombolysis does not reduce the rate of post-thrombotic syndrome Question In patients who have symptomatic
Chronic Venous Disease: A Complex Disorder. A N Nicolaides
 Chronic Venous Disease: A Complex Disorder A N Nicolaides Emeritus Professor of Vascular Surgery, Imperial College, London. Hon. Professor of Surgery, University of Nicosia Medical School, Cyprus Disclosures
Chronic Venous Disease: A Complex Disorder A N Nicolaides Emeritus Professor of Vascular Surgery, Imperial College, London. Hon. Professor of Surgery, University of Nicosia Medical School, Cyprus Disclosures
A cost analysis of the treatment of patients with post-thrombotic syndrome in Brazil
 Thrombosis Research (2006) 118, 699 704 intl.elsevierhealth.com/journals/thre REGULAR ARTICLE A cost analysis of the treatment of patients with post-thrombotic syndrome in Brazil Eduardo Ramacciotti a,
Thrombosis Research (2006) 118, 699 704 intl.elsevierhealth.com/journals/thre REGULAR ARTICLE A cost analysis of the treatment of patients with post-thrombotic syndrome in Brazil Eduardo Ramacciotti a,
Keywords: compression stockings, deep venous thrombosis, exercise, post-thrombotic syndrome, randomized cross-over trial.
 Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 1: 494 499 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of graduated elastic compression s on leg symptoms and signs during exercise in patients with deep venous thrombosis: a randomized
Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 1: 494 499 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of graduated elastic compression s on leg symptoms and signs during exercise in patients with deep venous thrombosis: a randomized
The post-thrombotic syndrome
 MANAGING SEVERE THROMBOSIS AND SEQUELAE The post-thrombotic syndrome Susan R. Kahn 1,2 1 Division of Internal Medicine and Centre for Clinical Epidemiology, Jewish General Hospital, Montreal, QC, Canada;
MANAGING SEVERE THROMBOSIS AND SEQUELAE The post-thrombotic syndrome Susan R. Kahn 1,2 1 Division of Internal Medicine and Centre for Clinical Epidemiology, Jewish General Hospital, Montreal, QC, Canada;
Compression Bulletin 28
 8 Compression Bulletin 28 In this issue: Graduated compression stockings to treat acute leg pain associated with proximal DVT. A randomized controlled trial. This publication is a sub analysis of the SOX
8 Compression Bulletin 28 In this issue: Graduated compression stockings to treat acute leg pain associated with proximal DVT. A randomized controlled trial. This publication is a sub analysis of the SOX
Underlying factors influencing the development of the post-thrombotic limb
 Underlying factors influencing the development of the post-thrombotic limb Ann M. O Shaughnessy, MSc, RVT, AVT, a,b and Dermot E. FitzGerald, MD, PhD, MSc, a Dublin, Ireland Purpose: This study was designed
Underlying factors influencing the development of the post-thrombotic limb Ann M. O Shaughnessy, MSc, RVT, AVT, a,b and Dermot E. FitzGerald, MD, PhD, MSc, a Dublin, Ireland Purpose: This study was designed
Occasional pain or other discomfort (ie, not restricting regular daily activity)
 Revised Venous Clinical Severity Score Pain : 0 Mild: 1 or other discomfort (ie, aching, heaviness, fatigue, soreness, burning) Occasional pain or other discomfort (ie, not restricting regular daily activity)
Revised Venous Clinical Severity Score Pain : 0 Mild: 1 or other discomfort (ie, aching, heaviness, fatigue, soreness, burning) Occasional pain or other discomfort (ie, not restricting regular daily activity)
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. (PTS), a chronic condition consisting of leg pain, edema, venous ectasia, and skin induration
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Effect of Postthrombotic Syndrome on Health-Related Quality of Life After Deep Venous Thrombosis Susan R. Kahn, MD, MSc; Andrew Hirsch, MD; Ian Shrier, MD, PhD Background: Postthrombotic
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Effect of Postthrombotic Syndrome on Health-Related Quality of Life After Deep Venous Thrombosis Susan R. Kahn, MD, MSc; Andrew Hirsch, MD; Ian Shrier, MD, PhD Background: Postthrombotic
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers. Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities. Evidence of healed ulcers. Dermatitis. Normal ABI.
 Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
Efficacy of Velcro Band Devices in Venous and. Mixed Arterio-Venous Patients
 Efficacy of Velcro Band Devices in Venous and Mixed Arterio-Venous Patients T. Noppeney Center for Vascular Diseases: Outpatient Dept. Obere Turnstrasse, Dept. for Vascular Surgery Martha-Maria Hospital
Efficacy of Velcro Band Devices in Venous and Mixed Arterio-Venous Patients T. Noppeney Center for Vascular Diseases: Outpatient Dept. Obere Turnstrasse, Dept. for Vascular Surgery Martha-Maria Hospital
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
Medical Treatment for Postthrombotic Syndrome
 61 Medical Treatment for Postthrombotic Syndrome Federico Silva Palacios, MD 1 Suman Wasan Rathbun, MD, MS 1 1 Department of Vascular Medicine, Cardiovascular Section, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences
61 Medical Treatment for Postthrombotic Syndrome Federico Silva Palacios, MD 1 Suman Wasan Rathbun, MD, MS 1 1 Department of Vascular Medicine, Cardiovascular Section, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences
Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI
 Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI Cleveland Clinic Heart and Vascular Institute Heather L. Gornik, MD has the following relationships to disclose: CVR Global
Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI Cleveland Clinic Heart and Vascular Institute Heather L. Gornik, MD has the following relationships to disclose: CVR Global
Running head: PREVENTING PROGRESSION OF POST-THROMBOTIC SYNDROME
 1 Running head: PREVENTING PROGRESSION OF POST-THROMBOTIC SYNDROME Preventing Progression of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome for Patients Post-Deep Vein Thrombosis Author: Anne M. Schmidt, BSN, RN Creighton University,
1 Running head: PREVENTING PROGRESSION OF POST-THROMBOTIC SYNDROME Preventing Progression of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome for Patients Post-Deep Vein Thrombosis Author: Anne M. Schmidt, BSN, RN Creighton University,
Taken into account multidiscilinary aspect of Vascular Compression
 The Vascular Center : A model to improve patient care Taken into account multidiscilinary aspect of Vascular Compression F. Vin C. Gardon-Mollard Compression Therapy is an efficient treatment for the management
The Vascular Center : A model to improve patient care Taken into account multidiscilinary aspect of Vascular Compression F. Vin C. Gardon-Mollard Compression Therapy is an efficient treatment for the management
Additional Information S-55
 Additional Information S-55 Network providers are encouraged, but not required to participate in the on-line American Venous Forum Registry (AVR) - The First National Registry for the Treatment of Varicose
Additional Information S-55 Network providers are encouraged, but not required to participate in the on-line American Venous Forum Registry (AVR) - The First National Registry for the Treatment of Varicose
La compression Veineuse Elastique, Quelle évolution en 10 ans! Elastic Venous Compression, these last ten years evolution.
 La compression Veineuse Elastique, Quelle évolution en 10 ans! Elastic Venous Compression, these last ten years evolution. Dr Laure Perrissin-Chevalier Affaires Médicales INNOTHERA Disclosure INNOTHERA
La compression Veineuse Elastique, Quelle évolution en 10 ans! Elastic Venous Compression, these last ten years evolution. Dr Laure Perrissin-Chevalier Affaires Médicales INNOTHERA Disclosure INNOTHERA
Compression Bulletin Special Edition
 Compression Bulletin Special Edition Medical Compression Stockings in Venous and Lymphatic Disorders Consensus Group: Eberhard Rabe, Hugo Partsch, Juerg Hafner, Christopher Lattimer, Giovanni Mosti, Martino
Compression Bulletin Special Edition Medical Compression Stockings in Venous and Lymphatic Disorders Consensus Group: Eberhard Rabe, Hugo Partsch, Juerg Hafner, Christopher Lattimer, Giovanni Mosti, Martino
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is a common problem among
 Update When Can the Patient With Deep Venous Thrombosis Begin to Ambulate? Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is a common problem among hospitalized patients, 1 even those who receive prophylaxis. 2 Patients
Update When Can the Patient With Deep Venous Thrombosis Begin to Ambulate? Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is a common problem among hospitalized patients, 1 even those who receive prophylaxis. 2 Patients
Venous thromboembolism: What to do after anticoagulation is started
 REVIEW CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will prescribe anticoagulation for the appropriate length of time after venous thromboembolic events SCOTT KAATZ, DO, MSc, FACP a Clinical Associate Professor
REVIEW CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will prescribe anticoagulation for the appropriate length of time after venous thromboembolic events SCOTT KAATZ, DO, MSc, FACP a Clinical Associate Professor
ACR Appropriateness Criteria Suspected Lower Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis EVIDENCE TABLE
 . Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
. Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D.
 In low-risk patients with isolated calf DVT (IDDVT), what is the morbidity risk of treating with repeat ultrasound/observation versus anticoagulation? Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D. Clinical Scenario:
In low-risk patients with isolated calf DVT (IDDVT), what is the morbidity risk of treating with repeat ultrasound/observation versus anticoagulation? Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D. Clinical Scenario:
Bath, Philip M.W. and England, Timothy J. (2009) Thighlength compression stockings and DVT after stroke. Lancet. ISSN (In Press)
 Bath, Philip M.W. and England, Timothy J. (2009) Thighlength compression stockings and DVT after stroke. Lancet. ISSN 0140-6736 (In Press) Access from the University of Nottingham repository: http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/1087/1/lancet_clots_1_20090522_4.pdf
Bath, Philip M.W. and England, Timothy J. (2009) Thighlength compression stockings and DVT after stroke. Lancet. ISSN 0140-6736 (In Press) Access from the University of Nottingham repository: http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/1087/1/lancet_clots_1_20090522_4.pdf
Chronic Venous Insufficiency Compression and Beyond
 Disclosure of Conflict of Interest Chronic Venous Insufficiency Compression and Beyond Shawn Amyot, MD, CCFP Fellow of the Canadian Society of Phlebology Ottawa Vein Centre I do not have relevant financial
Disclosure of Conflict of Interest Chronic Venous Insufficiency Compression and Beyond Shawn Amyot, MD, CCFP Fellow of the Canadian Society of Phlebology Ottawa Vein Centre I do not have relevant financial
OHTAC Recommendation. Endovascular Laser Treatment for Varicose Veins. Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in November 2009
 OHTAC Recommendation Endovascular Laser Treatment for Varicose Veins Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in November 2009 April 2010 Issue Background The Ontario Health Technology
OHTAC Recommendation Endovascular Laser Treatment for Varicose Veins Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in November 2009 April 2010 Issue Background The Ontario Health Technology
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Prospective Evaluation of Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Deep Venous Thrombosis
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Prospective Evaluation of Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Deep Venous Thrombosis Susan R. Kahn, MSc, MD, FRCPC; Thierry Ducruet, MSc; Donna L. Lamping, PhD; Louise
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Prospective Evaluation of Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Deep Venous Thrombosis Susan R. Kahn, MSc, MD, FRCPC; Thierry Ducruet, MSc; Donna L. Lamping, PhD; Louise
Risk factors for the post-thrombotic syndrome. in patients with a first deep venous thrombosis CHAPTER 6
 CHAPTER 6 Risk factors for the post-thrombotic syndrome in patients with a first deep venous thrombosis L.W.Tick, M.H.H.Kramer, F.R. Rosendaal, W.R. Faber, C.J.M. Doggen Risk factors for the post-thrombotic
CHAPTER 6 Risk factors for the post-thrombotic syndrome in patients with a first deep venous thrombosis L.W.Tick, M.H.H.Kramer, F.R. Rosendaal, W.R. Faber, C.J.M. Doggen Risk factors for the post-thrombotic
Prevention of VTE Sequelae: Post-thrombotic Syndrome and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension
 Prevention of VTE Sequelae: Post-thrombotic Syndrome and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension Susan R. Kahn MD MSc Professor of Medicine, McGill University Director, Jewish General Hospital Centre
Prevention of VTE Sequelae: Post-thrombotic Syndrome and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension Susan R. Kahn MD MSc Professor of Medicine, McGill University Director, Jewish General Hospital Centre
Predictors of the post-thrombotic syndrome with non-invasive venous examinations
 CHAPTER 7 Predictors of the post-thrombotic syndrome with noninvasive venous examinations in patients six weeks after a first episode of deep venous thrombosis L.W.Tick, C.J.M. Doggen, W.R. Faber, F.R.
CHAPTER 7 Predictors of the post-thrombotic syndrome with noninvasive venous examinations in patients six weeks after a first episode of deep venous thrombosis L.W.Tick, C.J.M. Doggen, W.R. Faber, F.R.
Current Management of C0s patient
 Current Management of C0s patient M. Perrin Vascular Surgery, Lyon, France 1 AIM of the PRESENTATION - 1 st to estimate the prevalence of C 0s patient - 2 d to evaluate its current management - 3d to suggest
Current Management of C0s patient M. Perrin Vascular Surgery, Lyon, France 1 AIM of the PRESENTATION - 1 st to estimate the prevalence of C 0s patient - 2 d to evaluate its current management - 3d to suggest
Segmental GSV reflux
 Segmental GSV reflux History of presentation A 43 year old female presented with right lower extremity varicose veins and swelling. She had symptoms of aching, heaviness and tiredness in the right leg.
Segmental GSV reflux History of presentation A 43 year old female presented with right lower extremity varicose veins and swelling. She had symptoms of aching, heaviness and tiredness in the right leg.
Classification for elastic tubes, medical socks and soft bandaging?
 Classification for elastic tubes, medical socks and soft bandaging? Dr. Martin Abel Head of Medical & Regulatory Affairs, Lohmann & Rauscher GmbH & Co KG Copenhagen, 17.05.2013 1 Standard Bandages in UK
Classification for elastic tubes, medical socks and soft bandaging? Dr. Martin Abel Head of Medical & Regulatory Affairs, Lohmann & Rauscher GmbH & Co KG Copenhagen, 17.05.2013 1 Standard Bandages in UK
Date: A. Venous Health History Form. Patient please complete questions Primary Care Physician:
 E S Insurance: 2 nd Insurance: Wait time: Date: A. Venous Health History Form Patient please complete questions 1-12 Patient Name: SSN#: Date of Birth: Primary Care Physician: What is the reason for your
E S Insurance: 2 nd Insurance: Wait time: Date: A. Venous Health History Form Patient please complete questions 1-12 Patient Name: SSN#: Date of Birth: Primary Care Physician: What is the reason for your
Prospective evaluation of chronic venous insufficiency based on foot venous pressure measurements and air plethysmography findings
 Prospective evaluation of chronic venous insufficiency based on foot venous pressure measurements and air plethysmography findings Masato Fukuoka, MD, Takaki Sugimoto, MD, and Yutaka Okita, MD, Kobe, Japan
Prospective evaluation of chronic venous insufficiency based on foot venous pressure measurements and air plethysmography findings Masato Fukuoka, MD, Takaki Sugimoto, MD, and Yutaka Okita, MD, Kobe, Japan
Validation of the new venous severity scoring system in varicose vein surgery
 Validation of the new venous severity scoring system in varicose vein surgery Stavros K. Kakkos, MD, MSc, a,b Marco A. Rivera, MD, MSc, a Miltiadis I. Matsagas, MD, a Miltos K. Lazarides, MD, c Peter Robless,
Validation of the new venous severity scoring system in varicose vein surgery Stavros K. Kakkos, MD, MSc, a,b Marco A. Rivera, MD, MSc, a Miltiadis I. Matsagas, MD, a Miltos K. Lazarides, MD, c Peter Robless,
Appendix D: Leg Ulcer Assessment Form
 Nursing Best Practice Guideline Appendix D: Ulcer Assessment Form Person Completing Assessment: Date: Client Name: Caf # CM# VON ID #: District CCAC ID # Address Telephone Home: Work: Date of Birth Y/M/D:
Nursing Best Practice Guideline Appendix D: Ulcer Assessment Form Person Completing Assessment: Date: Client Name: Caf # CM# VON ID #: District CCAC ID # Address Telephone Home: Work: Date of Birth Y/M/D:
Acute Venous Thrombosis: Thrombus Removal with Adjunctive Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis (ATTRACT Trial)
 Acute Venous Thrombosis: Thrombus Removal with Adjunctive Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis (ATTRACT Trial) N Engl J Med. Volume 377(23):2240-2252. December 7, 2017 Wednesday, July 11, 2018, 1:00pm ET Guest
Acute Venous Thrombosis: Thrombus Removal with Adjunctive Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis (ATTRACT Trial) N Engl J Med. Volume 377(23):2240-2252. December 7, 2017 Wednesday, July 11, 2018, 1:00pm ET Guest
How does compression really work?
 How does compression really work? Felizitas Pannier Private Practice Phlebology & Dermatology, Bonn, Germany Many thanks to Hugo Partsch, Horst Gerlach and Hans-Jürgen Thomä for some of the pictures Compression
How does compression really work? Felizitas Pannier Private Practice Phlebology & Dermatology, Bonn, Germany Many thanks to Hugo Partsch, Horst Gerlach and Hans-Jürgen Thomä for some of the pictures Compression
Below-knee deep vein thrombosis (DVT): diagnostic and treatment patterns
 Original Article Below-knee deep vein thrombosis (DVT): diagnostic and treatment patterns Drew Fleck, Hassan Albadawi, Alex Wallace, Grace Knuttinen, Sailendra Naidu, Rahmi Oklu Division of Interventional
Original Article Below-knee deep vein thrombosis (DVT): diagnostic and treatment patterns Drew Fleck, Hassan Albadawi, Alex Wallace, Grace Knuttinen, Sailendra Naidu, Rahmi Oklu Division of Interventional
New Guideline in venous ulcer treatment: dressing, medication, intervention
 New Guideline in venous ulcer treatment: dressing, medication, intervention Kittipan Rerkasem, FRCS(T), PhD Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University Topic Overview venous ulcer treatment
New Guideline in venous ulcer treatment: dressing, medication, intervention Kittipan Rerkasem, FRCS(T), PhD Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University Topic Overview venous ulcer treatment
Description and Management of C0s patient. M. Perrin, Vascular Surgery, Lyon, France
 Description and Management of C0s patient M. Perrin, Vascular Surgery, Lyon, France 1 No disclosure of interest to declare for this presentation 2 AIM of the PRESENTATION 1 st to estimate the prevalence
Description and Management of C0s patient M. Perrin, Vascular Surgery, Lyon, France 1 No disclosure of interest to declare for this presentation 2 AIM of the PRESENTATION 1 st to estimate the prevalence
The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT
 The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT Mr Chung Sim Lim Consultant Vascular Surgeon and Honorary Lecturer Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust and University College London NIHR UCLH Biomedical Research
The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT Mr Chung Sim Lim Consultant Vascular Surgeon and Honorary Lecturer Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust and University College London NIHR UCLH Biomedical Research
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
THE IMPACT OF MODIFYING OCCUPATIONAL RISK FACTORS ON THE OUTCOME OF TREATMENT OF CHRONIC VENOUS ULCER.
 Egyptian Journal of Occupational Medicine, 2011; 35 (2) : 277-287 THE IMPACT OF MODIFYING OCCUPATIONAL RISK FACTORS ON THE OUTCOME OF TREATMENT OF CHRONIC VENOUS ULCER. By Refaat T. M.*, Ewis A. A.*, Osman
Egyptian Journal of Occupational Medicine, 2011; 35 (2) : 277-287 THE IMPACT OF MODIFYING OCCUPATIONAL RISK FACTORS ON THE OUTCOME OF TREATMENT OF CHRONIC VENOUS ULCER. By Refaat T. M.*, Ewis A. A.*, Osman
Determine the patients relative risk of thrombosis. Be confident that you have had a meaningful discussion with the patient.
 Patient Assessment :Venous History, Examination and Introduction to Doppler and PPG Dr Louis Loizou The 11 th Annual Scientific Meeting and Workshops of the Australasian College of Phlebology Tuesday 18
Patient Assessment :Venous History, Examination and Introduction to Doppler and PPG Dr Louis Loizou The 11 th Annual Scientific Meeting and Workshops of the Australasian College of Phlebology Tuesday 18
PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
Review Article Association between Thrombophilia and the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
 International Vascular Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 643036, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/643036 Review Article Association between Thrombophilia and the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Anat Rabinovich
International Vascular Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 643036, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/643036 Review Article Association between Thrombophilia and the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Anat Rabinovich
Date: A. Venous Health History Form. Patient please complete questions Primary Care Physician:
 E S Insurance: 2 nd Insurance: Wait time: Date: A. Venous Health History Form Patient please complete questions 1-12 Patient Name: SSN#: Date of Birth: Primary Care Physician: What is the reason for your
E S Insurance: 2 nd Insurance: Wait time: Date: A. Venous Health History Form Patient please complete questions 1-12 Patient Name: SSN#: Date of Birth: Primary Care Physician: What is the reason for your
Epidemiologia e clinica del tromboembolismo venoso. Maria Ciccone Sezione di Ematologia e Fisiopatologia della Coagulazione
 Epidemiologia e clinica del tromboembolismo venoso Maria Ciccone Sezione di Ematologia e Fisiopatologia della Coagulazione Thrombophilia may present clinically as one or more of several thrombotic manifestations
Epidemiologia e clinica del tromboembolismo venoso Maria Ciccone Sezione di Ematologia e Fisiopatologia della Coagulazione Thrombophilia may present clinically as one or more of several thrombotic manifestations
The use of compression stockings for venous disorders in Brazil
 The use of compression stockings for venous disorders in Brazil J L Cataldo*, J M Pereira de Godoy and N de Barros Jr *Service of Peripheral Vascular Disease, University of Campinas UNICAMP; Department
The use of compression stockings for venous disorders in Brazil J L Cataldo*, J M Pereira de Godoy and N de Barros Jr *Service of Peripheral Vascular Disease, University of Campinas UNICAMP; Department
Current Management of Varicose Veins
 Current Management of Varicose Veins Michael J. Heidenreich, MD St. Joseph Mercy Hospital Ann Arbor, MI March 23, 2013 Nothing to disclose History Prevalence Anatomy Risk factors Clinical manifestations
Current Management of Varicose Veins Michael J. Heidenreich, MD St. Joseph Mercy Hospital Ann Arbor, MI March 23, 2013 Nothing to disclose History Prevalence Anatomy Risk factors Clinical manifestations
Identification and recommended management of leg ulcers Jill Robson RGN and Gerard Stansby MA, MChir, FRCS
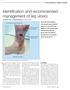 Identification and recommended management of leg ulcers Jill Robson RGN and Gerard Stansby MA, MChir, FRCS thickened skin, lipodermatosclerosis skin stained haemosiderin shallow ulcer irregular shape Our
Identification and recommended management of leg ulcers Jill Robson RGN and Gerard Stansby MA, MChir, FRCS thickened skin, lipodermatosclerosis skin stained haemosiderin shallow ulcer irregular shape Our
H. PARTSCH, M.D. SUMMARY. Results: Compression stockings worn for two years after deep CLINICAL SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
 Le RÔLE de la COMPRESSION dans la PRÉVENTION du SYNDROME POST-THROMBOTIQUE après THROMBOSE VEINEUSE AIGÜE : REVUE de la LITTÉRATURE The ROLE of COMPRESSION THERAPY in the PREVENTION of the POSTTHROMBOTIC
Le RÔLE de la COMPRESSION dans la PRÉVENTION du SYNDROME POST-THROMBOTIQUE après THROMBOSE VEINEUSE AIGÜE : REVUE de la LITTÉRATURE The ROLE of COMPRESSION THERAPY in the PREVENTION of the POSTTHROMBOTIC
Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) is one the most serious. occurring as competing processes. In fact, the lack of
 Effect of the anticoagulant therapy in the incidence of post-thrombotic syndrome and recurrent thromboembolism: Comparative study of enoxaparin versus coumarin José A. González-Fajardo, MD, PhD, a Miguel
Effect of the anticoagulant therapy in the incidence of post-thrombotic syndrome and recurrent thromboembolism: Comparative study of enoxaparin versus coumarin José A. González-Fajardo, MD, PhD, a Miguel
Alberta Health. Alberta Aids to Daily Living Compression Stockings and Lymphedema Sleeves Ready Made Benefits Policy & Procedures Manual
 Alberta Health Alberta Aids to Daily Living Compression Stockings and Lymphedema Sleeves Ready Made Benefits Policy & Procedures Manual March 7, 2016 Revision History Description Date N-03, N 05 and N-07:
Alberta Health Alberta Aids to Daily Living Compression Stockings and Lymphedema Sleeves Ready Made Benefits Policy & Procedures Manual March 7, 2016 Revision History Description Date N-03, N 05 and N-07:
Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), often the
 Revascularization of Chronic Venous Occlusion in the Setting of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Jon George, MD; Deepakraj Gajanana; Sean Janzer; Vincent Figueredo; Dennis Morris From the Einstein Heart and Vascular
Revascularization of Chronic Venous Occlusion in the Setting of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Jon George, MD; Deepakraj Gajanana; Sean Janzer; Vincent Figueredo; Dennis Morris From the Einstein Heart and Vascular
The legally binding text is the original French version. Opinion 15 May 2013
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 15 May 2013 ARIXTRA 2.5 mg/0.5 ml, solution for injection in pre-filled syringe B/2 (CIP: 34009 359 225 4 0) B/7 (CIP:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 15 May 2013 ARIXTRA 2.5 mg/0.5 ml, solution for injection in pre-filled syringe B/2 (CIP: 34009 359 225 4 0) B/7 (CIP:
Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders
 SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
Deep vein thrombosis resolution, recurrence and post-thrombotic syndrome: a prospective observational study protocol
 Bonfield et al. BMC Hematology (2016) 16:24 DOI 10.1186/s12878-016-0063-7 STUDY PROTOCOL Deep vein thrombosis resolution, recurrence and post-thrombotic syndrome: a prospective observational study protocol
Bonfield et al. BMC Hematology (2016) 16:24 DOI 10.1186/s12878-016-0063-7 STUDY PROTOCOL Deep vein thrombosis resolution, recurrence and post-thrombotic syndrome: a prospective observational study protocol
Mechanical treatment for acute DVT. Laurent Casbas, MD Toulouse, France
 Laurent Casbas, MD Toulouse, France Disclosure of Interest Speaker name: Laurent Casbas I have the following potential conflicts of interest to report: Consulting Medtronic General Electric Acute Venous
Laurent Casbas, MD Toulouse, France Disclosure of Interest Speaker name: Laurent Casbas I have the following potential conflicts of interest to report: Consulting Medtronic General Electric Acute Venous
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40114 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Exter, Paul L. den Title: Diagnosis, management and prognosis of symptomatic and
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40114 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Exter, Paul L. den Title: Diagnosis, management and prognosis of symptomatic and
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2017 Toronto, ON
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2017 Toronto, ON How to Prevent and Manage the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome? Jean-Philippe Galanaud Clinical Thromboembolism & Division of GIM Sunnybrook,
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2017 Toronto, ON How to Prevent and Manage the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome? Jean-Philippe Galanaud Clinical Thromboembolism & Division of GIM Sunnybrook,
Compression stockings for the treatment of post-thrombotic syndrome Protocol information
 Compression stockings for the treatment of post-thrombotic syndrome Protocol information Authors Christopher F Berntsen 1, Annette Kristiansen 1, Elie A. Akl 2, Per Olav Vandvik 1 1 Department of Internal
Compression stockings for the treatment of post-thrombotic syndrome Protocol information Authors Christopher F Berntsen 1, Annette Kristiansen 1, Elie A. Akl 2, Per Olav Vandvik 1 1 Department of Internal
DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE)
 DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE) Introduction VTE (DVT/PE) is an important complication in hospitalized patients Hospitalization for acute medical illness
DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE) Introduction VTE (DVT/PE) is an important complication in hospitalized patients Hospitalization for acute medical illness
Clinical/Duplex Evaluation of Varicose Veins: Who to Treat?
 Clinical/Duplex Evaluation of Varicose Veins: Who to Treat? Sanjoy Kundu MD, FASA, FCIRSE, FSIR The Vein Institute of Toronto Scarborough Vascular Group Scarborough Vascular Ultrasound Scarborough Vascular
Clinical/Duplex Evaluation of Varicose Veins: Who to Treat? Sanjoy Kundu MD, FASA, FCIRSE, FSIR The Vein Institute of Toronto Scarborough Vascular Group Scarborough Vascular Ultrasound Scarborough Vascular
Patient assessment and strategy making for endovenous treatment
 Patient assessment and strategy making for endovenous treatment Raghu Kolluri, MD Director Vascular Medicine OhioHealth Riverside Methodist Hospital Columbus, OH Disclosures Current Medtronic Consultant/
Patient assessment and strategy making for endovenous treatment Raghu Kolluri, MD Director Vascular Medicine OhioHealth Riverside Methodist Hospital Columbus, OH Disclosures Current Medtronic Consultant/
AWARENESS PREVENTION TREATMENT SUPPORT
 N ATT The National Alliance for Thrombosis and Thrombophilia Postthrombotic Syndrome (Venous Stress Disorder) An In-Depth Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers AWARENESS PREVENTION TREATMENT SUPPORT
N ATT The National Alliance for Thrombosis and Thrombophilia Postthrombotic Syndrome (Venous Stress Disorder) An In-Depth Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers AWARENESS PREVENTION TREATMENT SUPPORT
What is the real place of venous echo Doppler in aircrew member flying rehabilitation after a thromboembolism event?
 89 th ASMA ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING DALLAS- May 6-10, 2018 What is the real place of venous echo Doppler in aircrew member flying rehabilitation after a thromboembolism event? S BISCONTE (1), V MARICOURT
89 th ASMA ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING DALLAS- May 6-10, 2018 What is the real place of venous echo Doppler in aircrew member flying rehabilitation after a thromboembolism event? S BISCONTE (1), V MARICOURT
Indications for medical compression stockings in venous and lymphatic disorders: An evidence-based consensus statement
 Review Article Indications for medical compression stockings in venous and lymphatic disorders: An evidence-based consensus statement Phlebology 2018, Vol. 33(3) 163 184! The Author(s) 2017 Reprints and
Review Article Indications for medical compression stockings in venous and lymphatic disorders: An evidence-based consensus statement Phlebology 2018, Vol. 33(3) 163 184! The Author(s) 2017 Reprints and
EFFICACY OF ELECTRICAL MUSCLE STIMULATION IN CLINICAL PRACTICE
 EFFICACY OF ELECTRICAL MUSCLE STIMULATION IN CLINICAL PRACTICE V.N. Obolenskiy 1,2 1 City Hospital #13 (Moscow, Russia), 2 RNRMU (Moscow, Russia) Disclosures Nothing to disclose Relevance The thromboembolic
EFFICACY OF ELECTRICAL MUSCLE STIMULATION IN CLINICAL PRACTICE V.N. Obolenskiy 1,2 1 City Hospital #13 (Moscow, Russia), 2 RNRMU (Moscow, Russia) Disclosures Nothing to disclose Relevance The thromboembolic
Compression Bulletin 26
 6 Compression Bulletin 26 In this issue: Chronic venous disease progression and modification of predisposing factors Non-compliance in wearing MCS increases the risk of progression of chronic venous disease
6 Compression Bulletin 26 In this issue: Chronic venous disease progression and modification of predisposing factors Non-compliance in wearing MCS increases the risk of progression of chronic venous disease
With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis
 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital April
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital April
Secondary chronic venous disease progresses faster than primary
 Secondary chronic venous disease progresses faster than primary Nicos Labropoulos, PhD, DIC, DVT, a Antonios P. Gasparis, MD, RVT, a Dina Pefanis, MBBS, a Luis R. Leon Jr, MD, RVT, b and Apostolos K. Tassiopoulos,
Secondary chronic venous disease progresses faster than primary Nicos Labropoulos, PhD, DIC, DVT, a Antonios P. Gasparis, MD, RVT, a Dina Pefanis, MBBS, a Luis R. Leon Jr, MD, RVT, b and Apostolos K. Tassiopoulos,
Evolution of deep venous thrombosis: A 2-year follow-up using duplex ultrasound scan and strain-gauge plethysmography
 Evolution of deep venous thrombosis: A 2-year follow-up using duplex ultrasound scan and strain-gauge plethysmography José H. Haenen, PhD, a Hub Wollersheim, MD, PhD, b Mirian C. H. Janssen, MD, PhD, b
Evolution of deep venous thrombosis: A 2-year follow-up using duplex ultrasound scan and strain-gauge plethysmography José H. Haenen, PhD, a Hub Wollersheim, MD, PhD, b Mirian C. H. Janssen, MD, PhD, b
Current issues in the management of Superficial Vein Thrombosis - SVT
 Current issues in the management of Superficial Vein Thrombosis - SVT Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, School of Health Sciences,
Current issues in the management of Superficial Vein Thrombosis - SVT Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, School of Health Sciences,
Disclosures. What is a Specialty Vein Clinic? Prevalence of Venous Disease. Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach.
 Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach Disclosures Ed Boyle, MD Andrew Jones, MD Dr. Ed Boyle and Dr. Andrew Jones disclose Grants/research support: Medtronic, BTG International, Clearflow,
Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach Disclosures Ed Boyle, MD Andrew Jones, MD Dr. Ed Boyle and Dr. Andrew Jones disclose Grants/research support: Medtronic, BTG International, Clearflow,
Compression Bulletin 35
 5 Compression Bulletin 35 In this issue: Control of lower extremity edema in patients with diabetes: double blind randomized controlled trial assessing the efficacy of mild compression diabetic socks The
5 Compression Bulletin 35 In this issue: Control of lower extremity edema in patients with diabetes: double blind randomized controlled trial assessing the efficacy of mild compression diabetic socks The
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Risk factors and underlying mechanisms for venous stasis syndrome: a population-based case control study
 Risk factors and underlying mechanisms for venous stasis syndrome: a population-based case control study Aneel A Ashrani Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Mayo
Risk factors and underlying mechanisms for venous stasis syndrome: a population-based case control study Aneel A Ashrani Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Mayo
- Our patients with iliofemoral DVT - Effective thrombus removal with purely mechanical thrombectomy can lead to better outcomes
 - Our patients with iliofemoral DVT - Effective thrombus removal with purely mechanical thrombectomy can lead to better outcomes Michael K. W. Lichtenberg, FESC Conflict of Interest - Disclosure Within
- Our patients with iliofemoral DVT - Effective thrombus removal with purely mechanical thrombectomy can lead to better outcomes Michael K. W. Lichtenberg, FESC Conflict of Interest - Disclosure Within
Graduated compression stockings are universally
 Efficacy of Graduated Compression Stockings for an Additional 3 Weeks after Sclerotherapy Treatment of Reticular and Telangiectatic Leg Veins PAVAN K. NOOTHETI, MD, KRISTIAN M. CADAG, BS, ANGELA MAGPANTAY,
Efficacy of Graduated Compression Stockings for an Additional 3 Weeks after Sclerotherapy Treatment of Reticular and Telangiectatic Leg Veins PAVAN K. NOOTHETI, MD, KRISTIAN M. CADAG, BS, ANGELA MAGPANTAY,
