Prevention of VTE Sequelae: Post-thrombotic Syndrome and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension
|
|
|
- Brandon Todd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prevention of VTE Sequelae: Post-thrombotic Syndrome and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension Susan R. Kahn MD MSc Professor of Medicine, McGill University Director, Jewish General Hospital Centre of Excellence in Thrombosis and Anticoagulation Care Montréal, Canada Thrombosis and Hemostasis Societies of North America 2018 San Diego, CA, March 8-10, 2018
2 Prevention of post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS)
3 Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) Occurs in 20-50% of DVT patients (severe in 5-10% of patients), in spite of receiving optimal anticoagulant therapy Costly to society Impairs QOL, causes disability and suffering to patients Prandoni 1996; Kahn 2008; Kahn 2015
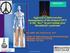
4 Clinical images of PTS
5 Risk factors (RF) for PTS 1. Those apparent at the time of DVT diagnosis 2. Those related to the treatment of acute DVT 3. Those apparent during follow-up after DVT
6 RF apparent at time of DVT diagnosis Risk factor DVT location Previous ipsilateral DVT Elevated body mass index (BMI > 30) Older age Pre-existing primary venous insufficiency (e.g. varicose veins) Magnitude of risk 2-3 fold risk after proximal DVT (especially iliac or common femoral vein) than distal (calf) DVT. 2-3 fold risk More than 2-fold risk risk from 30% to 3-fold. Up to 2-fold risk Little to no effect on the risk of developing PTS: Male vs. female; provoked vs. unprovoked DVT; genetic thrombophilia Galanaud JP et al. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord Rabinovich A et al. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord Kahn SR et al. Circulation 2014
7 J Thromb Haemost 2018 High risk predictors at baseline: 1 point: Iliac vein DVT 2 points: BMI >35 1 point: Villalta score 9-14 at baseline 2 points: Villalta score >14 at baseline Score of >4: 6-fold risk of PTS SOX-PTS index will be validated in ATTRACT study cohort
8 RF related to the treatment of acute DVT Risk factor Quality of oral anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonists (VKA) Choice of anticoagulant to treat DVT: DOAC vs. LMWH vs. VKA Thrombolysis to treat DVT (preventive?) Magnitude of risk 2-3 fold risk if level subtherapeutic INR >50% time during first 3 months of VKA treatment Not known if use of DOAC to treat DVT influences risk of PTS, vs. treatment with LMWH or VKA Metaanalysis suggests use of LMWH monotherapy to treat DVT may risk of PTS, compared to treatment with LMWH for 5-7 days followed by VKA To discuss later in talk Galanaud JP et al. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord Hull & Townshend, Thromb Haemost 2013 Cheung YW et al. Thromb Haemost. 2016
9 RF apparent during follow-up after DVT Risk factor Ipsilateral DVT recurrence Persistent venous symptoms and signs 1 month after acute DVT Residual thrombosis on ultrasound 3-6 months after acute DVT Magnitude of risk 4-6-fold risk (via damaging compromised venous valves or aggravating venous outflow obstruction) risk of subsequent PTS in graded fashion (may be a marker of persistent inflammation or venous outflow obstruction) 1.5 to 2-fold risk Persistent elevation of D-dimer in weeks to months after DVT Modest risk factor Kahn SR et al. Annals Intern Med 2008 Rabinovich A et al. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord Galanaud JP et al. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2016
10 Preventing PTS Prevent the initial DVT Improve systematic use of thromboprophylaxis in patients at risk for VTE (high-risk patients, high-risk settings) Prevent ipsilateral DVT recurrence Optimize treatment of initial DVT (ensure appropriate duration and intensity of anticoagulation) Ensure good quality of anticoagulation for DVT During 1 st 3 months, INR<2 more than 50% of time: 2-3-fold risk PTS (van Dongen, JTH 2005; Chitsike JTH 2012) Choice of anticoagulant Data insufficient to make specific recommendations re: VKA vs. DOAC vs. LMWH monotherapy on risk of developing PTS
11 Additional approaches to preventing PTS Elastic compression stockings (ECS)? Catheter directed thrombolysis (CDT)?
12 Do ECS prevent PTS? 2 older open-label RCTs reported that wearing mm Hg knee-high ECS for at least 2 years after proximal DVT reduced the risk of PTS by ½ (Brandjes 1997; Prandoni 2004) HOWEVER More recently, a large multicenter, placebo-controlled RCT of 803 patients with proximal DVT showed no benefit of mm Hg knee-high ECS, worn for two years, to 1) prevent PTS; 2) reduce recurrent VTE; or 3) improve quality of life (SOX Trial; Kahn Lancet 2014)
13 SOX Trial results: Primary outcome (ITT analysis) Active ECS (n=409) Placebo ECS (n=394) Hazard Ratio (95% CI) PTS (Ginsberg criteria) 44 Cumulative Incidence * 14.2% 37 Cumulative incidence 12.7% 1.13 (0.73, 1.76) p=0.58 SOX Trial. Kahn SR et al, Lancet 2014
14 SOX Trial results: Secondary outcomes Active ECS (n=409) Placebo ECS (n=394) Hazard Ratio (95% CI) PTS (Villalta criteria) Villalta score 5 at or after 6 month visit 176 Cumulative incidence 52.6% 168 Cumulative incidence 52.3% 1.0 ( ) p=0.96 Follow up, days SOX Trial. Kahn SR et al, Lancet 2014
15 ACCP 2016 Kearon et al, Chest 2016
16 2 recent ECS trials None designed to assess if ECS started at time of DVT diagnosis prevents PTS OCTAVIA study, 518 patients (BMJ 2016) All patients wore ECS for 1 year after prox DVT If free of PTS at 1 year, randomized to continue for 1 more year, or stop ECS IDEAL study, 865 patient (Lancet Haem 2017) All patients wore ECS for 6 mos. after prox DVT If free of PTS at 6 mos., randomized to continue for 18 more mos., or tailor continued use according to Villalta score
17 Mol GC et al. BMJ 2016 Results Developed PTS in 2 nd year after DVT % (95%CI) Stop ECS after 1 year (n=256) 19.9% (16%-24%) Continue ECS for total of 2 years (n=262) 13.0% (9.9%-17%) Difference, % (95% CI) 6.9% (0.6%, 12.3%) Adj HR 1.6 (1.0, 2.5) QOL did not differ between groups 1 year not non-inferior to 2 years Suggests if one has worn ECS for 1 year after DVT and have not developed PTS, may be benefit to continuing for 2 years, compare to stopping after 1 year.
18 IDEAL Study results Individualized duration ECS non-inferior to standard 2 years duration 66% in intervention group able to stop wearing stockings before 2 years ten Cate-Hoek A, Lancet Haematol 2017
19 How I use ECS Do I prescribe ECS for 2 years or longer to all my proximal DVT patients? No. ECS hard to apply, uncomfortable, expensive, must be replaced every few months. Many patients don t wear them in real life, especially if no symptoms Not clear if ECS prevents vs. palliates PTS à may be as effective, more convenient (and achieve better compliance) to start using ECS at time of PTS onset Based on current state of evidence: I prescribe mm Hg or mm Hg below-knee ECS to patients who have residual leg pain or swelling after proximal or distal DVT I continue them for as long as the patient derives symptomatic benefit or is able to tolerate them. Contraindications: symptomatic claudication due to PAD, allergy to material
20 Thrombolysis to prevent PTS Anticoagulant drugs do not eliminate thrombus Endogenous fibrinolysis slow and often incomplete Could immediate thrombus removal at time of acute DVT open veins, save venous valves, and prevent PTS?
21 ATTRACT Trial Acute venous Thrombosis Thrombus Removal with Adjunctive Catheter- Directed Thrombolysis Hypothesis PCDT will reduce future PTS by 33% (30% to 20%, assessed from 6 to 24 months) Patients randomized to PCDT vs. no PCDT; all patients received AC and ECS Not blinded: Healthcare providers, patients Blinded: Randomization; outcome assessors
22 Patients studied Proximal DVT ( femoral) 691 common femoral or iliac 57% not common femoral or iliac 43% Age 53 yrs Males 62 % Symptoms 6 days Exclusions: <16 and >75 yrs; symptoms 14 d; high bleeding risk; cancer
23 Study Outcomes Primary: PTS (Villalta Scale 5, 6-24m) Secondary: Many Short & Long-term
24 PCDT Used Initial PCDT Infuse-First 58% Single Session 38% AngioJet (22%) Trellis (15%) Adjunctive (88%) Baloon maceration 62% Baloon venoplasty 62% AngioJet 61% Stent 28% Aspiration 21% Trellis 5%
25 Short-Term Results Outcome PCDT n=336 No-PCDT n=355 P Value Major Bleeding (10 d)* 1.7% 0.3% Any Bleeding (10 d) 4.5% 1.7% Leg Pain (10 d) Leg Pain (30 d) Leg Swelling (10 d) Leg Swelling (30 d) Recurrent VTE (10d) 1.8% 1.1% 0.5
26 Long-Term Results Outcome (24 months) PCDT n=336 No-PCDT n=355 P Value Any PTS 47% 48% 0.56 Recurrent VTE 13% 8% 0.09 Generic QOL (SF-36 PCS) Venous QOL (VEINES) Moderate/Severe PTS 18% 24% MS-PTS: IF-DVT 18% 28% MS-PTS: FP-DVT 17% 18%
27 Conclusions PCDT Does not prevent PTS May reduce the severity of PTS Increases bleeding Modestly reduces acute symptoms
28 ACCP 2012 and 2016 recommendations Use of CDT requires substantial resources and expertise. Patients who are most likely to benefit have iliofemoral DVT, symptoms <14 days, good functional status, life expectancy > 1 year, and low risk of bleeding. Kearon C et al, Chest 2012, Chest 2016 Because the balance of risks and benefits is uncertain, anticoagulant therapy alone is an acceptable alternative to CDT in all patients with acute DVT who do not have impending venous gangrene.
29 CTEPH (Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension)
30 Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH): Overview Late complication of Pulmonary Embolism (PE): - 1-4% of patients after acute PE cases/million (general population) More common cause of pulmonary hypertension (PH) than idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension If untreated: life-threatening disease with poor prognosis leading to death (refractory RV failure) within a few years
31 How does CTEPH develop after PE? (current pathophysiology concept) (Infection, inflammation, immunity, genetics, in situ thrombosis) Acute PE CTEPH 1. Incomplete resolution and organisation of thrombus 2. Development of fibrotic stenoses/occlusions 3. Adaptative vascular remodelling of resistance vessels Lang IM, Eur Respir J. 2013; 41 ( )
32 Clinical Features of CTEPH Progressive dyspnea and exercise intolerance Clinical presentation of CTEPH may mimic acute PE or other conditions (asthma, physical deconditioning, older age, interstitial lung disease, CAD, or psychogenic dyspnea) Non-specific presentation and, early in its natural history, subtle physical examination findings Fernandes T, Thromb Res. 2018
33 How often does CTEPH develop after PE? Recent meta-analysis 16 studies (4047 pts) Type of PE All comers with symptomatic PE Survivors* of symptomatic PE Survivors* of Symptomatic PE, no major comorbidities Non-objective diagnostic criteria Number of studies CTEPH Incidence % (95% CI) 2 studies 0.56% ( ) 4 studies 3.2% ( ) 9 studies 2.8% ( ) 12 studies 6.3% ( ) * Only patients that were alive after an initial treatment period of 6 months Ende-Verhaar YM, Eur Respir J. 2017; 49 (1-11)
34 Occurrence of CTEPH: Known risk factors
35 Demographic or medical factors associated with occurrence of CTEPH (none modifiable) Age > 60 Previous splenectomy Antiphospholipid antibodies Increased levels of lipoprotein(a) Hypothyroidism, thyroid replacement therapy Non-O blood groups Malignancy Known chronic inflammatory conditions (osteomyelitis, inflammatory bowel disease, infected intravascular devices) Fernandes T, Thromb Res. 2018
36 Risk factors related to initial PE (some modifiable) Acute PE: up to 25% of CTEPH patients have no known documented history of PE Characteristics of the initial episode of acute PE: unprovoked PE (OR 4.1) recurrent PE (OR 3.2) larger initial perfusion defects RV dysfunction at diagnosis delay in PE diagnosis persistent PH after therapy with a PAsP > 50 mm Hg Fernandes T, Thromb Res Ende-Verhaar YM, Eur Respir J. 2017
37 Prevention
38 Prevention of CTEPH Modality Methods Data Thrombolysis of acute PE AC therapy duration DOAC vs. warfarin New therapeutic targets Urokinase, streptokinase, Tenecteplase Extended anticoagulant therapy for at least 24 months Pharmacokinetics and antithrombotic effect, Safety None identified Not effective Unknown No data available No data available
39 Thrombolysis of acute PE for prevention of CTEPH Thrombolysis of acute PE is associated with significantly lower PA pressure and vascular resistance compared to those initially treated with heparin alone. Evidence based on two small RCTs 40 patients (Sharma GV, N Engl J Med. 1980) 23 patients (Sharma GV, Vasc Med 2000) Pesavento R, Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2015; 13 ( )
40 Thrombolysis of acute PE for the prevention of CTEPH PEITHO trial: Most recent long-term results Outcome (Median 37.8 months) T n=144 No-T n=146 P Value CTEPH 2.1% 3.2% 0.79 Residual PH and/or RV dysfunction 44.1% 36.6% 0.20 Konstantinides SV, J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017; 69 ( )
41 Treatment Options
42 Treatment options: Overview In patients with established CTEPH: Surgery Endovascular interventions Medical treatment Lung transplant in highly selected patients Time to diagnosis is a key factor in selection of treatment options!!!
43 Curative Treatment: Pulmonary Endarterectomy (PEA) Surgical procedure Mechanical removal of the proximal fibrous pulmonary artery obstruction Treatment of choice for patients with CTEPH Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to improve the prognosis: up to 30% of CTEPH patients are already inoperable at time of diagnosis Complications Short-term: postoperative residual PH (up to 40% of operated patients) and mortality (<5%) Long-term: recurrent CTEPH, survival rates (> 90% at 1 year, 89% at 3 years and >70% at 10 years), residual PH. Hoeper MM, Lancet Respir Med 2014; 2 ( ) Galiè N, Eur Respir J. 2015; 46 ( ) Delcroix M, Circulation 2016; 133 ( )
44
45 Pulmonary Endarterectomy (PEA) Advantages Best therapeutic option 1. Relevant improvement in symptoms in majority of patients 2. Almost complete normalization of most important hemodynamic parameters; only potentially curative treatment option for early-stage CTEPH Hybrid intervention: PEA and BPA promising Balloon Pulmonary Angioplasty (BPA) performed in highly selected patients after unsuccessful PEA or for late recurrent CTEPH after PEA Disadvantages Assessment of operability is a complex task 1. Multidisciplinary, devoted team (expert surgeons, radiologists, anesthesiologists, cardiologists, pulmonologists, internists) 2. Expert surgical centre, performing at least 20 PEAs per year with mortality rate < 10%. Surgical procedure is complex Highly specialized training level and complex protocols of postoperative care. Galiè N, Eur Respir J. 2015; 46 ( ) - Wiedenroth CB, J Heart Lung Transplant 2016; 35 ( )
46 Medical therapy as an alternative effective treatment Recommended in symptomatic patients with persistent or recurrent CTEPH after surgery and in those considered inoperable Life-long anticoagulation is recommended, once the diagnosis of CTEPH is established for the prevention of in situ thrombosis and recurrent VTE: VKA (well known), DOAC as the first choice treatment (No RCT data available) Alternatives to anticoagulant therapy: IVC filters sometimes used in patients with clots in known location: e.g. lower limbs, pelvic region Usual supportive therapy for heart or respiratory failure is also recommended to reduce arterial PH: prostacyclin analogues, endothelin receptor antagonists, PDE-5 inhibitors, riociguat Galiè N, Eur Respir J. 2015; 46 ( ) Kearon C, Chest 2016; 149 ( )
47 Palliative treatment: Balloon pulmonary angioplasty (BPA) For patients with technically non-operable and unfavourable risk-benefit ratio for PEA, (+/- residual lesions, recurrent/ residual PH after PEA). Used in association with medical therapy or PEA Complications: reperfusion pulm edemea; +/- PA injury with hemorrhage due to artery rupture or dissection, wire perforation, high-pressure perfusion haemoptysis. Disadvantages: Multiple sessions are required to treat all lesions (usually at intervals of one or more weeks). Potential adverse effects from repeated exposure to radiation and contrast media. Feinstein JA, Circulation 2001;103 (10-13) - Taniguchi Y, EuroIntervention 2014;10 ( ) Roik M, Int J Cardiol 2016; 203 ( ) - Ogo T, Eur J Radiol 2017; 89 ( )
48 End-stage treatment option: Lung transplantation Bilateral lung or heart/lung transplantation in highly selected young patients for whom no other therapeutic option is available. Effectiveness: data are lacking and an indirect comparison with other treatment options might be inappropriate. Threshold for unrecoverable RV systolic dysfunction and/or LV diastolic dysfunction is unknown. Disadvantages: delays in referral, shortage of organ donors (length of waiting time), limited success (survival rates: 52 75% at 5 years and 45 66% at 10 years) Galiè N, Eur Respir J. 2015; 46 ( )
49 Areas for Future Research Better understanding of underlying pathology of CTEPH Better characterization of true incidence of CTEPH Better identification of risk factors and predictors Assess efficacy and safety of hybrid intervention and novel molecules in operable and non-operable patients Assess the potential preventive role of DOAC Identify new therapeutic and preventive targets
Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
 Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Catherine K. Chang, MD FACS Vascular Surgery San Diego Southern California Permanente Medical Group Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis Incidence & Outcomes
Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Catherine K. Chang, MD FACS Vascular Surgery San Diego Southern California Permanente Medical Group Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis Incidence & Outcomes
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2017 Toronto, ON
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2017 Toronto, ON How to Prevent and Manage the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome? Jean-Philippe Galanaud Clinical Thromboembolism & Division of GIM Sunnybrook,
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2017 Toronto, ON How to Prevent and Manage the Post-Thrombotic Syndrome? Jean-Philippe Galanaud Clinical Thromboembolism & Division of GIM Sunnybrook,
Acute Venous Thrombosis: Thrombus Removal with Adjunctive Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis (ATTRACT Trial)
 Acute Venous Thrombosis: Thrombus Removal with Adjunctive Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis (ATTRACT Trial) N Engl J Med. Volume 377(23):2240-2252. December 7, 2017 Wednesday, July 11, 2018, 1:00pm ET Guest
Acute Venous Thrombosis: Thrombus Removal with Adjunctive Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis (ATTRACT Trial) N Engl J Med. Volume 377(23):2240-2252. December 7, 2017 Wednesday, July 11, 2018, 1:00pm ET Guest
The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT
 The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT Mr Chung Sim Lim Consultant Vascular Surgeon and Honorary Lecturer Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust and University College London NIHR UCLH Biomedical Research
The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT Mr Chung Sim Lim Consultant Vascular Surgeon and Honorary Lecturer Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust and University College London NIHR UCLH Biomedical Research
Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Case 1:
 12/16/2015 Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Constantino S.Peña, FSIR, FSCCT, FAHA Interventional Radiologist Medical Director, Vascular Imaging Miami
12/16/2015 Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Constantino S.Peña, FSIR, FSCCT, FAHA Interventional Radiologist Medical Director, Vascular Imaging Miami
Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach
 Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach Hae Giu Lee, MD Professor, Dept of Radiology Seoul St. Mary s Hospital The Catholic University of Korea Introduction Incidence High incidence: 250,000-1,000,000/year
Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach Hae Giu Lee, MD Professor, Dept of Radiology Seoul St. Mary s Hospital The Catholic University of Korea Introduction Incidence High incidence: 250,000-1,000,000/year
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
Should We Be More Aggressive in the Treatment of Acute DVT?
 DISCLOSURES Consultant Penumbra, Inc. UCSF Vascular Surgery Symposium April 6, 2017 K. Pallav Kolli, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology University of California, San Francisco 17 yo male, DVT
DISCLOSURES Consultant Penumbra, Inc. UCSF Vascular Surgery Symposium April 6, 2017 K. Pallav Kolli, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology University of California, San Francisco 17 yo male, DVT
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT?
 How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
Real life management of CTEPH: patient case
 2 nd International Congress on cardiovascular imaging in clinical practice k Real life management of CTEPH: patient case Anastasia Anthi Pulmonary Hypertension Clinic, Attikon University Hospital, Athens
2 nd International Congress on cardiovascular imaging in clinical practice k Real life management of CTEPH: patient case Anastasia Anthi Pulmonary Hypertension Clinic, Attikon University Hospital, Athens
New Guidance in AT10 Clive Kearon, MD, PhD,
 New Guidance in AT10 Clive Kearon, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Medicine, McMaster University; Program Director, McMaster Clinical Investigator Program, McMaster University Head, Clinical Thromboembolism
New Guidance in AT10 Clive Kearon, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Medicine, McMaster University; Program Director, McMaster Clinical Investigator Program, McMaster University Head, Clinical Thromboembolism
Venous interventions in DVT
 Venous interventions in DVT Sriram Narayanan Chief of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Tan Tock Seng Hospital A/Prof of Surgery, National University of Singapore ANTI-COAGULATION LMWH Warfarin x 6m Acute
Venous interventions in DVT Sriram Narayanan Chief of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Tan Tock Seng Hospital A/Prof of Surgery, National University of Singapore ANTI-COAGULATION LMWH Warfarin x 6m Acute
Implications from the ACCP 2012 Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Thrombosis: a case based approach
 Implications from the ACCP 2012 Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Thrombosis: a case based approach Prof. I. Baumgartner Head Clinical and Interventional Angiology About the ACCP guidelines Widely
Implications from the ACCP 2012 Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Thrombosis: a case based approach Prof. I. Baumgartner Head Clinical and Interventional Angiology About the ACCP guidelines Widely
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Prevention and Management. Dr. Ashwini Bennett
 Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Prevention and Management Dr. Ashwini Bennett Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this presentation Outline Importance of VTE and PTS Aetiology of PTS PTS risk factors PTS clinical
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Prevention and Management Dr. Ashwini Bennett Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this presentation Outline Importance of VTE and PTS Aetiology of PTS PTS risk factors PTS clinical
With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis
 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital April
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital April
Aggressive endovascular management of ilio-femoral DVT. thrombotic syndrome. is the key in preventing post
 CACVS 2017 Aggressive endovascular management of ilio-femoral DVT is the key in preventing post thrombotic syndrome ALI AMIN MD, FACS,FACC, RVT CHIEF OF ENDOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS READING HEALTH SYSTEM
CACVS 2017 Aggressive endovascular management of ilio-femoral DVT is the key in preventing post thrombotic syndrome ALI AMIN MD, FACS,FACC, RVT CHIEF OF ENDOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS READING HEALTH SYSTEM
- Our patients with iliofemoral DVT - Effective thrombus removal with purely mechanical thrombectomy can lead to better outcomes
 - Our patients with iliofemoral DVT - Effective thrombus removal with purely mechanical thrombectomy can lead to better outcomes Michael K. W. Lichtenberg, FESC Conflict of Interest - Disclosure Within
- Our patients with iliofemoral DVT - Effective thrombus removal with purely mechanical thrombectomy can lead to better outcomes Michael K. W. Lichtenberg, FESC Conflict of Interest - Disclosure Within
Dr Paul Thibault. Phlebologist & Assistant Editor Phlebology (International Journal) Australasian College of Phlebology
 Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist & Assistant Editor Phlebology (International Journal) Australasian College of Phlebology Prescribing Effective Compression and PTS Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist, Newcastle,
Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist & Assistant Editor Phlebology (International Journal) Australasian College of Phlebology Prescribing Effective Compression and PTS Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist, Newcastle,
Disclosures. DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Questions To Ask. Dr. Susanna Shin - DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) None
 Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
4/30/2018 CLOT+ In patients with an acute proximal deep vein thrombosis, pharmacomechanical catheter-directed thrombolysis does not reduce t
 In patients with an acute proximal deep vein thrombosis, pharmacomechanical catheter-directed thrombolysis does not reduce the rate of post-thrombotic syndrome Question In patients who have symptomatic
In patients with an acute proximal deep vein thrombosis, pharmacomechanical catheter-directed thrombolysis does not reduce the rate of post-thrombotic syndrome Question In patients who have symptomatic
Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus
 Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus Michael R. Jaff, DO Paul and Phyllis Fireman Endowed Chair in Vascular Medicine Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard
Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus Michael R. Jaff, DO Paul and Phyllis Fireman Endowed Chair in Vascular Medicine Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard
Acute and long-term treatment of PE. Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia
 Acute and long-term treatment of PE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE What is the optimal acute phase treatment for the patient? Intravenous thrombolysis One
Acute and long-term treatment of PE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE What is the optimal acute phase treatment for the patient? Intravenous thrombolysis One
Anticoagulation therapy following endovascular treatment of iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis
 Anticoagulation therapy following endovascular treatment of iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis Tim Sebastian, M.D. University Hospital Zurich Clinic for Angiology Disclosure Speaker name: Tim Sebastian I
Anticoagulation therapy following endovascular treatment of iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis Tim Sebastian, M.D. University Hospital Zurich Clinic for Angiology Disclosure Speaker name: Tim Sebastian I
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM. Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow
 CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI
 Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI Cleveland Clinic Heart and Vascular Institute Heather L. Gornik, MD has the following relationships to disclose: CVR Global
Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI Cleveland Clinic Heart and Vascular Institute Heather L. Gornik, MD has the following relationships to disclose: CVR Global
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy. Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016
 Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
Mark H. Meissner, MD Peter Gloviczki Professor of Venous & Lymphatic Disorders University of Washington School of Medicine
 Pulmonary Embolism Response Teams Not So Fast Early Interventions is a House of Cards Mark H. Meissner, MD Peter Gloviczki Professor of Venous & Lymphatic Disorders University of Washington School of Medicine
Pulmonary Embolism Response Teams Not So Fast Early Interventions is a House of Cards Mark H. Meissner, MD Peter Gloviczki Professor of Venous & Lymphatic Disorders University of Washington School of Medicine
Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144
 Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144 Appendix A: Summary of new evidence from Summary of evidence from previous year Diagnosis Diagnostic
Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144 Appendix A: Summary of new evidence from Summary of evidence from previous year Diagnosis Diagnostic
Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
 Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Thanainit Chotanaphuti Phramongkutklao College of Medicine Bangkok, Thailand President of CAOS Asia President of Thai Hip & Knee Society President of ASEAN Arthroplasty
Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Thanainit Chotanaphuti Phramongkutklao College of Medicine Bangkok, Thailand President of CAOS Asia President of Thai Hip & Knee Society President of ASEAN Arthroplasty
Risk-Based Evaluation and Management of VTE
 12:50-1:50pm Risk-Based Evaluation and Management of VTE SPEAKER Gregory Piazza, MD, MS BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Risk-Based Evaluation and Management of VTE Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Assistant Professor
12:50-1:50pm Risk-Based Evaluation and Management of VTE SPEAKER Gregory Piazza, MD, MS BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Risk-Based Evaluation and Management of VTE Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Assistant Professor
Risk factors for DVT. Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Anticoagulation (cont d) Diagnosis 1/5/2018. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Duration of Anticoagulation? Peter Verhamme MD, PhD Department of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Leuven Belgium
 Duration of Anticoagulation? Peter Verhamme MD, PhD Department of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Leuven Belgium Disclosures Honoraria and research support: Daiichi-Sankyo, Boehringer Ingelheim,
Duration of Anticoagulation? Peter Verhamme MD, PhD Department of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Leuven Belgium Disclosures Honoraria and research support: Daiichi-Sankyo, Boehringer Ingelheim,
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
Ileo Femoral DVT Review and Update
 Ileo Femoral DVT Review and Update Ammar Safar, MD, FSCAI, FACC, FACP, RPVI Interventional Cardiology & Endovascular Medicine Deep Vein Thrombosis Venous thromboembolism is a major national health problem,
Ileo Femoral DVT Review and Update Ammar Safar, MD, FSCAI, FACC, FACP, RPVI Interventional Cardiology & Endovascular Medicine Deep Vein Thrombosis Venous thromboembolism is a major national health problem,
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
THERE IS NO ROLE FOR SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DVT
 THERE IS NO ROLE FOR SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DVT Tara D. Balint, MD FACS Sentara RMH Thursday, June 14, 2018 1 Objectives of treatment for DVT Prevent death from PE Prevent recurrent VTE Prevent post-thrombotic
THERE IS NO ROLE FOR SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DVT Tara D. Balint, MD FACS Sentara RMH Thursday, June 14, 2018 1 Objectives of treatment for DVT Prevent death from PE Prevent recurrent VTE Prevent post-thrombotic
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
Disclosures. Objectives
 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Treatment of Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Staff Physician, Cardiovascular Division
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Treatment of Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Staff Physician, Cardiovascular Division
Aspirex for Upper and Lower Extremity DVT
 Aspirex for Upper and Lower Extremity DVT Steven Kum MD Vascular & Endovascular Surgeon Director of Vascular Service Changi General Hospital Singapore Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following potential
Aspirex for Upper and Lower Extremity DVT Steven Kum MD Vascular & Endovascular Surgeon Director of Vascular Service Changi General Hospital Singapore Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following potential
Pulmonary embolism: Acute management. Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia, Italy
 Pulmonary embolism: Acute management Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia, Italy Acute pulmonary embolism: Acute management Diagnosis Risk stratification Treatment Non-high risk PE: diagnosis 3-mo VTE
Pulmonary embolism: Acute management Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia, Italy Acute pulmonary embolism: Acute management Diagnosis Risk stratification Treatment Non-high risk PE: diagnosis 3-mo VTE
Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting Calgary, Alberta, October 2014 Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update Benjamin Bell, MD FRCPC James Douketis, MD FRCPC On Behalf of Thrombosis Canada
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting Calgary, Alberta, October 2014 Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update Benjamin Bell, MD FRCPC James Douketis, MD FRCPC On Behalf of Thrombosis Canada
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES
 DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES Jose M. Borromeo M.D. Vascular Surgeon Iowa Heart Center Disclosures: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals Cook CVRx LeMaitre Vascular,
DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES Jose M. Borromeo M.D. Vascular Surgeon Iowa Heart Center Disclosures: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals Cook CVRx LeMaitre Vascular,
Duration of Therapy for Venous Thromboembolism
 Duration of Therapy for Venous Thromboembolism Michael B Streiff, MD FACP Associate Professor of Medicine and Pathology Medical Director, Johns Hopkins Anticoagulation Service Chairman, VTE Guideline Committee
Duration of Therapy for Venous Thromboembolism Michael B Streiff, MD FACP Associate Professor of Medicine and Pathology Medical Director, Johns Hopkins Anticoagulation Service Chairman, VTE Guideline Committee
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients. David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center
 DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism. João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal
 Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal Disclosures João Morais On the last year JM received honoraria
Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal Disclosures João Morais On the last year JM received honoraria
Surgical approach for DVT. Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine
 Surgical approach for DVT Seung-Kee Min Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine Treatment Options for Venous Thrombosis Unfractionated heparin &
Surgical approach for DVT Seung-Kee Min Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine Treatment Options for Venous Thrombosis Unfractionated heparin &
Copy Here. The Easy One.. What is the Role of Thrombus Removal in Acute Proximal DVT after ATTRACT? Deep Venous Thrombosis Spectrum
 What is the Role of Thrombus Removal in Acute Proximal DVT after ATTRACT? Mitchell J. Silver DO FACC FSVM RPVI Director, Center for Critical Limb Care Riverside Methodist Hospital Ohio Health Heart and
What is the Role of Thrombus Removal in Acute Proximal DVT after ATTRACT? Mitchell J. Silver DO FACC FSVM RPVI Director, Center for Critical Limb Care Riverside Methodist Hospital Ohio Health Heart and
PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) in Myeloma. Christine Chen May 2017
 Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) in Myeloma Christine Chen May 2017 Objectives 1. Review the magnitude of the problem and why myeloma patients are at risk of VTE 2. Discuss thromboprophylaxis approaches in
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) in Myeloma Christine Chen May 2017 Objectives 1. Review the magnitude of the problem and why myeloma patients are at risk of VTE 2. Discuss thromboprophylaxis approaches in
Results from RE-COVER RE-COVER II RE-MEDY RE-SONATE EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 Assessment of the safety and efficacy of dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa ) in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) and the prevention of recurrent DVT and PE Results from
Assessment of the safety and efficacy of dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa ) in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) and the prevention of recurrent DVT and PE Results from
This chapter will describe the effectiveness of antithrombotic
 Antithrombotic Therapy for Venous Thromboembolic Disease The Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy Harry R. Büller, MD, Chair; Giancarlo Agnelli, MD; Russel D. Hull, MBBS,
Antithrombotic Therapy for Venous Thromboembolic Disease The Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy Harry R. Büller, MD, Chair; Giancarlo Agnelli, MD; Russel D. Hull, MBBS,
Updates in venous thromboembolism. Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia
 Updates in venous thromboembolism Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia News for VTE Diagnosis Treatment the acute phase the agents Pulmonary embolism: diagnosis Vein ultrasonography Meta-analysis 15
Updates in venous thromboembolism Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia News for VTE Diagnosis Treatment the acute phase the agents Pulmonary embolism: diagnosis Vein ultrasonography Meta-analysis 15
Anticoagulation Forum: Management of Tiny Clots
 Anticoagulation Forum: Management of Tiny Clots Casey O Connell, MD FACP Associate Professor Jane Anne Nohl Division of Hematology Keck School of Medicine USC DISCLOSURES None 4/11/2017 Objectives Define
Anticoagulation Forum: Management of Tiny Clots Casey O Connell, MD FACP Associate Professor Jane Anne Nohl Division of Hematology Keck School of Medicine USC DISCLOSURES None 4/11/2017 Objectives Define
Μακροχρόνια παρακολούθηση ασθενών με πνευμονική εμβολή
 Μακροχρόνια παρακολούθηση ασθενών με πνευμονική εμβολή Ευφροσύνη Δ. Μάναλη Λέκτορας Β Πανεπιστημιακή Πνευμονολογική Κλινική ΓΝΑ «Αττικόν» Εθνικό και Καποδιστριακό Πανεπιστήμιο Αθηνών Existing guidelines
Μακροχρόνια παρακολούθηση ασθενών με πνευμονική εμβολή Ευφροσύνη Δ. Μάναλη Λέκτορας Β Πανεπιστημιακή Πνευμονολογική Κλινική ΓΝΑ «Αττικόν» Εθνικό και Καποδιστριακό Πανεπιστήμιο Αθηνών Existing guidelines
Ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis: Does it really work? The BERNUTIFUL trial
 Ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis: Does it really work? The BERNUTIFUL trial Rolf P. Engelberger Division of Angiology CHUV, Lausanne & Inselspital, Bern Switzerland Disclosure Speaker
Ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis: Does it really work? The BERNUTIFUL trial Rolf P. Engelberger Division of Angiology CHUV, Lausanne & Inselspital, Bern Switzerland Disclosure Speaker
EXTENDING VTE PROPHYLAXIS IN ACUTELY ILL MEDICAL PATIENTS
 EXTENDING VTE PROPHYLAXIS IN ACUTELY ILL MEDICAL PATIENTS Samuel Z. Goldhaber, MD Director, VTE Research Group Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical
EXTENDING VTE PROPHYLAXIS IN ACUTELY ILL MEDICAL PATIENTS Samuel Z. Goldhaber, MD Director, VTE Research Group Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical
What is the real place of venous echo Doppler in aircrew member flying rehabilitation after a thromboembolism event?
 89 th ASMA ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING DALLAS- May 6-10, 2018 What is the real place of venous echo Doppler in aircrew member flying rehabilitation after a thromboembolism event? S BISCONTE (1), V MARICOURT
89 th ASMA ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING DALLAS- May 6-10, 2018 What is the real place of venous echo Doppler in aircrew member flying rehabilitation after a thromboembolism event? S BISCONTE (1), V MARICOURT
DVT - initial management NSCCG
 Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis. Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS
 Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Catheter-based thrombolysis Local administration of lytic agent Higher local
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Catheter-based thrombolysis Local administration of lytic agent Higher local
Duration of anticoagulation
 Duration of anticoagulation P. Fontana Service d angiologie et d hémostase Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Pomeriggio formativo in coagulazione, Bellinzona, 19.10.2017 Conflict of interest AstraZeneca,
Duration of anticoagulation P. Fontana Service d angiologie et d hémostase Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Pomeriggio formativo in coagulazione, Bellinzona, 19.10.2017 Conflict of interest AstraZeneca,
Focus: l embolia polmonare Per quanto la terapia anticoagulante orale? Giulia Magnani 27 Gennaio, 2018
 Focus: l embolia polmonare Per quanto la terapia anticoagulante orale? Giulia Magnani 27 Gennaio, 2018 NO DISCLOSURE Pulmonary Embolism Venous thromboembolism (VT) is the third most common cause of cardiovascular
Focus: l embolia polmonare Per quanto la terapia anticoagulante orale? Giulia Magnani 27 Gennaio, 2018 NO DISCLOSURE Pulmonary Embolism Venous thromboembolism (VT) is the third most common cause of cardiovascular
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
A Review of the Role of Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants in the Acute and Long-Term Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism
 Cardiol Ther (2018) 7:1 13 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40119-018-0107-0 REVIEW A Review of the Role of Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants in the Acute and Long-Term Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Andrew
Cardiol Ther (2018) 7:1 13 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40119-018-0107-0 REVIEW A Review of the Role of Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants in the Acute and Long-Term Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Andrew
Venous Thrombosis. Magnitude of the Problem. DVT 2 Million PE 600,000. Death 60,000. Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year.
 Venous Thrombosis Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Postthrombotic Syndrome 800,000 PE 600,000 Death 60,000 Silent PE 1 Million Pulmonary Hypertension 30,000 Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year
Venous Thrombosis Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Postthrombotic Syndrome 800,000 PE 600,000 Death 60,000 Silent PE 1 Million Pulmonary Hypertension 30,000 Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year
Meissner MH, Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ, Dalsing MC, Eklof BG, Gillespie DL, et al. J Vasc Surg. 2012;55:
 Early thrombus removal strategies for acute deep venous thrombosis: Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery and the American Venous Forum Meissner MH, Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ,
Early thrombus removal strategies for acute deep venous thrombosis: Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery and the American Venous Forum Meissner MH, Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ,
Keynote lecture: Oral anticoagulation and DVT
 Keynote lecture: Oral anticoagulation and DVT What is the evidence? Is there a need to anticoagulate every lower leg DVT? Disclosure Speaker name:...sebastian Schellong... I have the following potential
Keynote lecture: Oral anticoagulation and DVT What is the evidence? Is there a need to anticoagulate every lower leg DVT? Disclosure Speaker name:...sebastian Schellong... I have the following potential
Acute and long-term treatment of VTE. Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia
 Acute and long-term treatment of VTE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE The goals The acute PE phase After the acute phase Treatment for VTE Goals of acute treatment
Acute and long-term treatment of VTE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE The goals The acute PE phase After the acute phase Treatment for VTE Goals of acute treatment
The evidence for venous interventions is evolving- many patients do actually benefit. Nils Kucher University Hospital Bern Switzerland
 The evidence for venous interventions is evolving- many patients do actually benefit Nils Kucher University Hospital Bern Switzerland Disclosure Speaker name: Nils Kucher X X I have the following potential
The evidence for venous interventions is evolving- many patients do actually benefit Nils Kucher University Hospital Bern Switzerland Disclosure Speaker name: Nils Kucher X X I have the following potential
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis - Why Should We Care? Harry Gibbs FRACP FCSANZ Vascular Physician The Alfred Hospital
 Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis - Why Should We Care? Harry Gibbs FRACP FCSANZ Vascular Physician The Alfred Hospital VTE is common and dangerous 5 VTE is Common VTE Incidence: 1.5 / 1000 per year
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis - Why Should We Care? Harry Gibbs FRACP FCSANZ Vascular Physician The Alfred Hospital VTE is common and dangerous 5 VTE is Common VTE Incidence: 1.5 / 1000 per year
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE
 Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE-SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE-SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
Current issues in the management of Superficial Vein Thrombosis - SVT
 Current issues in the management of Superficial Vein Thrombosis - SVT Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, School of Health Sciences,
Current issues in the management of Superficial Vein Thrombosis - SVT Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, School of Health Sciences,
The post-thrombotic syndrome
 MANAGING SEVERE THROMBOSIS AND SEQUELAE The post-thrombotic syndrome Susan R. Kahn 1,2 1 Division of Internal Medicine and Centre for Clinical Epidemiology, Jewish General Hospital, Montreal, QC, Canada;
MANAGING SEVERE THROMBOSIS AND SEQUELAE The post-thrombotic syndrome Susan R. Kahn 1,2 1 Division of Internal Medicine and Centre for Clinical Epidemiology, Jewish General Hospital, Montreal, QC, Canada;
Use of EKOS Catheter in the management of Venous Mr. Manoj Niverthi, Mr. Sarang Pujari, and Ms. Nupur Dandavate, The GTF Group
 Use of EKOS Catheter in the management of Venous Thromboembolism @ Mr. Manoj Niverthi, Mr. Sarang Pujari, and Ms. Nupur Dandavate, The GTF Group Introduction Georgia Thrombosis Forum (GTF, www.gtfonline.net)
Use of EKOS Catheter in the management of Venous Thromboembolism @ Mr. Manoj Niverthi, Mr. Sarang Pujari, and Ms. Nupur Dandavate, The GTF Group Introduction Georgia Thrombosis Forum (GTF, www.gtfonline.net)
Approach to Thrombosis
 Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49:
 Online publication August 27, 2009 1 2 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 247 254 deep vein thrombosis, thrombolytic therapy, catheter-directed thrombolysis, inferior vena cava filter, pulmonary thromboembolism
Online publication August 27, 2009 1 2 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 247 254 deep vein thrombosis, thrombolytic therapy, catheter-directed thrombolysis, inferior vena cava filter, pulmonary thromboembolism
Status of anticoagulation therapy in 2016: Is there a need for venous revascularization?
 Status of anticoagulation therapy in 2016: Is there a need for venous revascularization? Rupert M. Bauersachs Dept. of Vascular Medicine, Darmstadt Center of Thrombosis Hemostasis, Mainz Status of anticoagulation
Status of anticoagulation therapy in 2016: Is there a need for venous revascularization? Rupert M. Bauersachs Dept. of Vascular Medicine, Darmstadt Center of Thrombosis Hemostasis, Mainz Status of anticoagulation
Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis. Barbara LeVarge MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Pulmonary Hypertension Center COPYRIGHT
 Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis Barbara LeVarge MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Pulmonary Hypertension Center Acute PE and DVT No disclosures. Acute PE and DVT Learning objectives
Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis Barbara LeVarge MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Pulmonary Hypertension Center Acute PE and DVT No disclosures. Acute PE and DVT Learning objectives
What is the impact of Superficial Vein Thrombosis?
 What is the impact of Superficial Vein Thrombosis? Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, University of Thessalia, Greece Chairman,
What is the impact of Superficial Vein Thrombosis? Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, University of Thessalia, Greece Chairman,
Pharmaco-mechanical techniques stand alone procedures? Peter Neglén, MD, PhD SP Vascular Center Limassol Cyprus
 Pharmaco-mechanical techniques stand alone procedures? Peter Neglén, MD, PhD SP Vascular Center Limassol Cyprus Faculty Disclosure Peter Neglén, M.D., Ph.D Stockholder/Founder of Veniti, Inc. Member, Medical
Pharmaco-mechanical techniques stand alone procedures? Peter Neglén, MD, PhD SP Vascular Center Limassol Cyprus Faculty Disclosure Peter Neglén, M.D., Ph.D Stockholder/Founder of Veniti, Inc. Member, Medical
Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related. Iliocaval Thrombosis
 Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related Iliocaval Thrombosis Faiz D. Francis, DO; Gianvito Salerno, MD; Sabbah D. Butty, MD Abstract In the setting of
Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related Iliocaval Thrombosis Faiz D. Francis, DO; Gianvito Salerno, MD; Sabbah D. Butty, MD Abstract In the setting of
Αγγειοπλαστική των πνευμονικών αρτηριών στην χρόνια θρομβοεμβολική πνευμονική υπέρταση. Παρόν και μέλλον
 Αγγειοπλαστική των πνευμονικών αρτηριών στην χρόνια θρομβοεμβολική πνευμονική υπέρταση. Παρόν και μέλλον Παναγιώτης Καρυοφύλλης Επιμελητής Β Ωνάσειο Καρδιοχ/κό Κέντρο CTEPH is an obstructive disease Pulmonary
Αγγειοπλαστική των πνευμονικών αρτηριών στην χρόνια θρομβοεμβολική πνευμονική υπέρταση. Παρόν και μέλλον Παναγιώτης Καρυοφύλλης Επιμελητής Β Ωνάσειο Καρδιοχ/κό Κέντρο CTEPH is an obstructive disease Pulmonary
Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D.
 In low-risk patients with isolated calf DVT (IDDVT), what is the morbidity risk of treating with repeat ultrasound/observation versus anticoagulation? Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D. Clinical Scenario:
In low-risk patients with isolated calf DVT (IDDVT), what is the morbidity risk of treating with repeat ultrasound/observation versus anticoagulation? Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D. Clinical Scenario:
Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: 2017 Update and Future Directions
 Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: 2017 Update and Future Directions Kush R Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, IL Disclosures
Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: 2017 Update and Future Directions Kush R Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, IL Disclosures
VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies
 VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies VTE in Surgical Patients: Recognizing the Patients at Risk Pathogenesis of thrombosis: Virchow s triad and VTE Risk Hypercoagulability
VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies VTE in Surgical Patients: Recognizing the Patients at Risk Pathogenesis of thrombosis: Virchow s triad and VTE Risk Hypercoagulability
UPDATE ON TREATMENT OF ACUTE VENOUS THROMBOSIS
 UPDATE ON TREATMENT OF ACUTE VENOUS THROMBOSIS Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS 16 th National Congress of the Italian Society of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Bologna, 2017 Disclosure I have the following
UPDATE ON TREATMENT OF ACUTE VENOUS THROMBOSIS Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS 16 th National Congress of the Italian Society of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Bologna, 2017 Disclosure I have the following
Clinical Cases with Deep Venous Thrombosis - The position of Apixaban Stavros KAKKOS, MD, MSc, PhD, RVT
 Clinical Cases with Deep Venous Thrombosis - The position of Apixaban Stavros KAKKOS, MD, MSc, PhD, RVT Department of Vascular Surgery. University Hospital of Patras Chairman: Ioannis Tsolakis DISCLAIMER
Clinical Cases with Deep Venous Thrombosis - The position of Apixaban Stavros KAKKOS, MD, MSc, PhD, RVT Department of Vascular Surgery. University Hospital of Patras Chairman: Ioannis Tsolakis DISCLAIMER
Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism. Rajat Deo, MD, MTR
 Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism Rajat Deo, MD, MTR Director of Translational Research in Cardiac Arrhythmias Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism Rajat Deo, MD, MTR Director of Translational Research in Cardiac Arrhythmias Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Judith Hurdman Consultant Respiratory Physician
 Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism Judith Hurdman Consultant Respiratory Physician Judith.hurdman@sth.nhs.uk Overview Risk Stratification Who can be managed as an outpatient? To thrombolyse or not
Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism Judith Hurdman Consultant Respiratory Physician Judith.hurdman@sth.nhs.uk Overview Risk Stratification Who can be managed as an outpatient? To thrombolyse or not
Anjali Vaidya, MD, FACC, FASE, FACP Associate Director, Pulmonary Hypertension, Right Heart Failure, and Pulmonary Thromboendarterectomy Program
 Anjali Vaidya, MD, FACC, FASE, FACP Associate Director, Pulmonary Hypertension, Right Heart Failure, and Pulmonary Thromboendarterectomy Program Advanced Heart Failure & Cardiac Transplant Temple University
Anjali Vaidya, MD, FACC, FASE, FACP Associate Director, Pulmonary Hypertension, Right Heart Failure, and Pulmonary Thromboendarterectomy Program Advanced Heart Failure & Cardiac Transplant Temple University
Objectives. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis. Case VTE WHY DO IT? Question: Who Is At Risk?
 Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Management of Cancer Associated Thrombosis (CAT) where data is lacking. Tim Nokes Haematologist, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth
 Management of Cancer Associated Thrombosis (CAT) where data is lacking Tim Nokes Haematologist, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth Contents Overview of the statistics and aetiology for Cancer Associated Thrombosis
Management of Cancer Associated Thrombosis (CAT) where data is lacking Tim Nokes Haematologist, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth Contents Overview of the statistics and aetiology for Cancer Associated Thrombosis
Techniques for thrombus removal in acute DVT Benefits of an Endovascular Approach for Rapid Flow Restoration in DVT
 Techniques for thrombus removal in acute DVT Benefits of an Endovascular Approach for Rapid Flow Restoration in DVT Michael K. W. Lichtenberg, MD, FESC Vascular Centre Arnsberg, Germany Disclosure Speaker
Techniques for thrombus removal in acute DVT Benefits of an Endovascular Approach for Rapid Flow Restoration in DVT Michael K. W. Lichtenberg, MD, FESC Vascular Centre Arnsberg, Germany Disclosure Speaker
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE
 Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE Financial Disclosures-NONE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE- SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA,
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE Financial Disclosures-NONE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE- SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA,
BC Vascular Day. Contents. November 3, Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3. Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6. Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8
 BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
The latest on the diagnosis and treatment of venous thromboembolism
 The latest on the diagnosis and treatment of venous thromboembolism Vicky Tagalakis MD FRCP Division of General Internal Medicine Jewish General Hospital McGill University Disclosures Advisory board Pfizer
The latest on the diagnosis and treatment of venous thromboembolism Vicky Tagalakis MD FRCP Division of General Internal Medicine Jewish General Hospital McGill University Disclosures Advisory board Pfizer
The Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): Has Warfarin Met Its Match? Michael P. Gulseth, Pharm. D., BCPS, FASHP Program Director for
 The Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): Has Warfarin Met Its Match? Michael P. Gulseth, Pharm. D., BCPS, FASHP Program Director for Anticoagulation Services Sanford USD Medical Center Sioux Falls,
The Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): Has Warfarin Met Its Match? Michael P. Gulseth, Pharm. D., BCPS, FASHP Program Director for Anticoagulation Services Sanford USD Medical Center Sioux Falls,
Optimal Utilization of Thrombolytics
 April 8-9, 2011 New York LaGuardia Marriott COMPLETE MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS DISEASE Optimal Utilization of Thrombolytics Anthony J. Comerota, MD, FACS, FACC Director, Jobst Vascular Institute Adjunct Professor
April 8-9, 2011 New York LaGuardia Marriott COMPLETE MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS DISEASE Optimal Utilization of Thrombolytics Anthony J. Comerota, MD, FACS, FACC Director, Jobst Vascular Institute Adjunct Professor
