Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Masoud Mardani. M. D. MPH, FIDSA
|
|
|
- Anabel Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Masoud Mardani. M. D. MPH, FIDSA Professor Of Infectious Diseases Shahid Beheshti Medical University
3 URTI s Sinusitis Acute Otitis Media Pharyngitis
4 Question One: What percent of adults with common colds progress to acute bacterial sinusitis? A) 5-10% B) 2-5% C) 0.5-2% D) %
5 Sinusitis Most often a secondary infection of the paranasal sinuses which occurs because the outflow from one of the sinuses is decreased Common cold is really a viral rhinosinusitis 87% of patients with common colds have CT evidence of sinus cavity disease 0.5-2% will progress to acute bacterial sinusitis Maxillary sinus is most often affected [J Gen Int Med 1992; 7:481] & [Clin Inf Dis 1996; 23:1209]
6 Impact of Sinusitis in the US The estimated number of cases of acute bacterial sinusitis is million per year Approximately 10% seek medical care leading to 2 million office visits per year Cost of medications is more than $3 billion dollars per year, not including antibiotics Bartlett, 2001
7 Sinusitis: Predisposing Factors Impaired mucociliary function: > viral URTI s > cold or dry air > chemicals & drugs > cystic fibrosis > ciliary dysmotility syndrome Obstruction of sinus ostia: > anatomic abnormalities > allergic rhinitis > rhinitis medicamentosa > viral URTI s Vortel & Chow, 1992
8 Sinusitis: Predisposing Factors Immune defects: > IgA deficiency > AIDS > IgG subclass deficiency > diabetes > Wegener s granulomatosis Increased risk of microbial invasion: > odontogenic infection > head trauma > nasotracheal intubation > cocaine use > swimming or diving Vortel & Chow, 1992
9 Causes of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis Bacterial agents Mean Range S. pneumoniae 31% 20-35% H. influenzae 21% 6-26% S. pneumoniae & H. influenzae 5% 1-9% M. catarrhalis 2% 2-10% Viral agents Rhinovirus 15% Influenza 5% Parainfluenza 3% Gwaltney, 1996
10 Antibiotic Resistance S. pneumoniae mechanism: altered penicillin binding proteins high-level and overall resistance is on the rise incidence varies widely with location H. influenzae about 30% of isolates produce beta-lactamase M. catarrhalis over 90% of isolates produce beta-lactamase Bartlett, 1997
11 Microbial Causes of Sinusitis More than half of the cases of acute sinusitis are caused by S. pneumoniae & H. influenzae Anaerobes and S. aureus are uncommon but may be associated with chronic sinusitis Fungi seen in hosts with impaired immunity Nosocomial sinusitis is most often due to Gram-negative rods or S. aureus Bartlett, 1999
12 Acute Sinusitis is Overdiagnosed 174 patients clinically diagnosed with sinusitis, only 89 (53%) confirmed by sinus puncture In contrast to clinical features, ESR and CRP helped predict which patients had culture proven sinusitis For patients with abnormal ESR and CRP, sensitivity was 82% and specificity was 57% Hansen et al, 1995
13 Question Two : A 52 year old woman presents with 3 days of headache, tooth pain, and purulent nasal discharge unresponsive to decongestants. Her exam is normal. What do you believe? A) I m sure this is the the common cold B) Likelihood this is sinusitis is < 40% C) Likelihood this is sinusitis is > 60% D) Can t tell to any degree of certainty
14 Question Two (part 2): Would you treat this patient with an antibiotic? A) Yes B) No
15 Features That Predict Sinusitis Clinical Feature Likelihood ratio Maxillary toothache 2.5 ( ) Purulent secretion by exam 2.1 ( ) Poor response to decongestant 2.1 ( ) Abnormal transillumination 1.6 ( ) Hx of colored nasal discharge 1.5 ( ) [JAMA 1993; 270:1242-6]
16 Probability of Sinusitis Number of Predictors Probability (%) Williams et al, 1992
17 Diagnosing Acute Sinusitis If less than two of the five clinical features described by Williams and co-workers [Ann Intern Med 1992; 117: 705] are present, sinusitis is effectively ruled out If four of the five clinical features are present, sinusitis is effectively ruled in If 2-3 features present, consider x-rays Canadian Sinusitis Symposium, 1997
18 Sinus Transillumination In a dark room, place light source on infraorbital rim and look at roof of the mouth Result # of Sinuses Positive Aspirates Normal 18 1 (6%) Dull 26 7 (27%) Opaque (100%) Gwaltney et al, 1981
19
20 X-rays and Diagnosing Sinusitis A single Waters view is sufficient Williams et al, 1992 Good correlation seen in only 50% (major problem is many false positives with x-rays) Bartlett, 2001 Air-fluid level is most reliable: in 18 patients with this finding, 16 had positive aspirates Gwaltney et al, 1981
21
22 CT Scans in Diagnosing Sinusitis CT is best imaging technique & limited scans are now costing less Bartlett, 2001 CT may be too sensitive: Of 666 patients who had CT scan for either head trauma or seizures, % 43 had abnormal sinuses, %24 involving the maxillary sinuses Havas et al, 1988
23 Indications for Sinus CT Imaging Patient is considered a candidate for surgery Acute sinusitis with suspected intracranial or intraorbital extension Patient with severe facial pain or headache when nasal endoscopy is not diagnostic Patient fails to respond to standard therapy, including antibiotic treatment Bartlett, 2001
24 Cultures for Diagnosing Sinusitis Cultures of purulent nasal discharge contaminated by organisms in the nose Endoscopic collection: 65% sensitive and 40% specific compared to sinus aspirate Aspirate of sinus is definitive: obtain Gram stain as well as aerobic & anaerobic cultures (fungal stain & culture if compromised) [Clin Inf Dis 1996; 123:1209] & [ICAAC 1995; Abs D42]
25 Indications for Sinus Aspiration Septic or immunocompromised patient Nosocomial infection Poor response to therapy Complications > meningitis > brain abscess (frontal) > periorbital cellulitis > osteomyelitis > cavernous sinus thrombosis Bartlett, 1997
26 Management of Sinusitis Rule out dental source and complications Surgical management to promote drainage, remove diseased tissue, or correct ostial and/or intranasal abnormalities Consider hospitalization if patient is acutely ill or immunocompromised, if complication occurs, or if the frontal sinus is involved Goodman & Slavin, 1994
27 Medical Management of Sinusitis - Steam can prevent nasal crusting & liquefy secretions Steam can prevent nasal crusting & liquefy secretions steam inhalation several times daily Saline can prevent nasal crusting & liquefy secretions saline nasal spray qid Decongestants help to increase ostial diameter topical oxymetazoline (0.05%) 2-3 sprays in each nostril bid x 3 days at start of therapy; watch for rebound effect pseudoephedrine mg qid Goodman & Slavin, 1994
28 Medical Management of Sinusitis - 2 Topical steroids reduce mucosal inflammation; limit use to chronic sinusitis due to allergies beclomethasone 2 sprays in each nostril bid many other agents now available Mucoevacuants thin mucous secretions guaifenesin mg bid Antibiotics eradicate bacterial infection shown to be of benefit in numerous clinical trials Wald et al (1986) showed placebo effect is > 40% Goodman & Slavin, 1994
29 Question Three: First line therapy for acute sinusitis is: A) Amoxicillin-clavulanate B) Cefprozil C) Levofloxacin D) Azithromycin E) Amoxicillin
30 What is the correct duration for treating acute bacterial sinusitis with antibiotics? A) Three days B) Ten days C) Fourteen days D) Twenty-one days
31 Which Antibiotic to Choose? Historically established amoxicillin, doxycycline, TMP-SFX FDA-approved for sinusitis amoxicillin/clavulanate, cefdinir, cefpodoxime, cefprozil, cefuroxime axetil, ciprofloxacin, clarithromycin, gatifloxacin, loracarbef, levofloxacin, and moxifloxacin Bartlett, 2001
32 Antibiotics With Proven Efficacy* by Pre- and Posttreatment Aspiration Amoxicillin amoxicillin-clavulanate cefdinir cefuroxime axetil 500 mg po tid 875/125 mg po bid 300 mg po bid mg po bid cefpodoxime gatifloxacin loracarbef trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole levofloxacin moxifloxacin mg po bid 400 mg po q day 400 mg po bid one DS po bid 500 mg po q day 400 mg po q day *pathogen eradication in > 90% Bartlett, 2001
33 Therapy for Acute Sinusitis Gold standard: Amoxicillin Bartlett, 2001 CDC Recommendation: Amoxicillin O Brien, 1998 Amoxicillin therapy should be the firstline treatment of acute bacterial sinusitis Canadian Sinusitis Symposium, 1997
34 How Good is Amoxicillin? Meta-analysis looking at effect of antibiotics versus lacebo (and amoxicillin or TMPSFX versus more expensive antimicrobials) 2717 patients with acute sinusitis from 27 trials Compared with placebo, antibiotics decreased the incidence of clinical failures by half (RR = 0.54 with 95% confidence interval ) amoxicillin and TMP-SFX equal to the rest [BMJ 1998; 317:632-7]
35
36 Duration of Antibiotic Therapy Most clinical trials have used days 1997 Canadian Sinusit is Symposium has formally recommended a 10 day course Evidence that three days may be enough: > trial of amoxicillin/clavulanate vs. amoxicillin in children with sinusitis [Wald et al, 1986] clinical response after 3 days was equal to 10 days > 80 adults treated with TMP-SFX [Williams et al, 1995] no difference between 3 and 10 days of therapy all received 3 days of oxymetazoline
37 Question Four: A 2 year old girl presents with a 1 day history of irritability, fever, and ear pain. On exam you see a bulging & red tympanic membrane. Do you treat her with antibiotics? A) Yes B) No
38 Acute Otitis Media Definition: presence of fluid in the middle ear accompanied by signs of acute illness Most common pediatric problem by age 3, more than 75% have been affected major cause of meningitis, sepsis, and hearing loss Predisposing factors include: eustachian tube obstruction (URTI s & allergies) anatomy of child s middle ear Klein, 1994
39
40 Causes of Acute Otitis Media S. pneumoniae 25-50% H. influenzae 15-30% M. catarrhalis 3-20% Respiratory viruses 20% S. pyogenes 2-3% S. aureus 2-3% [Clin Infect Dis 1994; 19:823-33]
41 Diagnosis of Acute Otitis Media Signs & symptoms: ear pain, ear drainage, hearing loss, lethargy, irritability, & fever Tympanic membrane is full & bulging, often red and immobile, occasionally perforated Middle ear effusion determined by exam, through pneumatic otoscopy, or impedance tympanometry Berman, 1995
42 A: Painful, retracted eardrum (due to negative pressure and not acute otitis media) B: Bulging eardrum with purulent fluid consistent with acute otitis media C: Red tympanic membrane without middle ear fluid is not otitis media
43 Indications for Tympanocentesis Neonates Immunocompromised patients septic patients Toxic patients despite > 2 days of therapy Recurrent disease Onset during antibiotic therapy Complications: meningitis or mastoiditis
44 Management of Acute Otitis Media Analgesics may help relieve symptoms Decongestants & antihistamines are unproven Role of antibiotics is becoming controversial concern with emergence of resistance (Berman, 1995) must treat 7 children to improve one (Rosenfeld, 1995) antibiotic use associated with decrease in incidence of mastoiditis & meningitis (Bluestone, 1995); but much of this decline is due to the Hib vaccine (CDC, 1996) Must follow-up patient to assess response
45 Therapy for Acute Otitis Media Amoxicillin is the drug currently preferred for initial empiric therapy of acute otitis media Bluestone, 1995 Amoxicillin remains the drug of choice for treatment of acute otitis media because of its 20-year record of clinical success, acceptability, limited side effects and relative low cost. Klein, 1994
46 1999 CDC Recommendations Amoxicillin is still first line, regardless of prevalence of penicillin resistance Increasing penicillin resistance seen with S. pneumoniae so use higher dose Dose is now mg/kg/day x 10 days Standard dose of mg/kg/day may be used if risk of resistance is low (e.g. age > 2, no day care, no antibiotics in past 3 months) [Pediatr Infect Dis J 1999; 18:1-9]
47 1999 CDC Recommendations Alternative agent should be considered after three days if amoxicillin fails Agent should cover H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis and penicillin resistant S. pneumoniae Cefuroxime 30 mg/kg divided bid, or Amoxicillin-clavulanate mg/kg/day (amoxicillin component mg/kg/day with clavulanate dosing remaining at approximately 10 mg/kg/day), or Ceftriaxone 50 mg/kg IM q day x three doses [Pediatr Infect Dis J 1999; 18:1-9]
48
49 Persistent Middle Ear Effusion Seen in 70% at 2 weeks, 20% at 2 months Associated with hearing loss If middle ear effusion persists at 12 weeks: antibiotic as in acute otitis media, but for 14-21days plus prednisone 1 mg/kg/d divided bid for 1 week If middle ear effusion persists at 16 weeks: check audiometry; refer for tympanostomy tubes if bilateral hearing threshold > 20 db Berman, 1995
50 New Vaccine for S. pneumoniae Conjugate 7-valent vaccine targeted at S. pneumoniae was approved in 2000 Doses at 2, 4, 6 and months Vaccine efficacy: 97% reduction in bacteremia and meningitis 73% reduction in pneumonia 34% reduction in otitis media [Infectious Disease News, 1999] [MMWR 2000; 49(RR-9):1-35]
51 Question five: An 18 year old man presents with sudden onset of fever and sore throat on Friday. You see patchy exudates over the tonsils but the rapid strep screen is negative. Do you get a culture in case the rapid detection test is negative? A) Yes B) No
52 Causes of Pharyngitis Rhinovirus 20% Coronavirus > 5% Adenovirus 5% Herpes simplex virus 4% Group A Streptococcus 15-30% Group C Streptococcus 5-10% Unknown 30%
53
54 Hints to Determine Cause of Pharyngitis Influenza: cough & constitutional symptoms Adenovirus: conjunctivitis EBV: splenomegaly & retrocervical nodes HIV: rash and diffuse lymphadenopathy HSV: stomatitis or vesicles Diphtheria: pseudomembrane Numerous viruses: hoarseness Bartlett, 1997
55 Streptococcal Pharyngitis Typical features include sudden onset of fever, chills, severe sore throat, dysphagia, malaise, and headache Examination typically shows pharyngeal erythema, exudative pharyngitis and anterior cervical lymphadenopathy None of these features are diagnostic Bartlett, 1997
56 Features Suggestive of S. pyogenes Scarlitiniform rash: tiny red papules initially involving the face; rash appears 1-2 days after sore throat and resolves in 7-10 days; desquamation of palms & soles may occur Age: S. pyogenes causes 50% of pharyngeal infections in school age children (6-17 years old), but less than 10% in adults over 30 Bartlett, 1997
57
58 Diagnosis of Streptococcal Pharyngitis Gold standard is throat culture 100% specific & 90-95% sensitive Rapid antigen detection tests (strep screens) > 95% specific but only 80-90% sensitive If rapid antigen screen negative, get culture Bottom line: treat if any test is positive!! IDSA, 1997
59 Complications of Streptococcal Pharyngitis Acute rheumatic fever Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis Scarlet fever Peritonsillar abscess Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome Epiglottitis
60 Management of Pharyngitis Treat if suspicion is high but confirm case Bisno et al, 1997 Treatment within 9 days from symptom onset will prevent acute rheumatic fever Catanzaro, 1954 Symptoms improve in 3 days, even when not treated, slightly less when treated (patients are non-infectious after 24 hrs) Bartlett, 1999
61 Therapy for Streptococcal Pharyngitis In children: penicillin 250 mg bid or tid x 10 days (amox ok) benzathine penicillin 0.6 million units IM once erythromycin mg/kg/d divided qid x 10 days in patients with penicillin allergy In adults: penicillin 250 mg tid (or 500 mg bid) x 10 days benzathine penicillin 1.2 million units IM once if allergic, erythromycin 250 mg qid x 10 days IDSA, 1997
62 Once Daily Therapy for Strep Throat 152 children with strep throat randomized to receive either amoxicillin 750 mg po once daily or penicillin 250 mg po tid x 10 days Adherence monitored by urine testing and throats were cultured 1-3 weeks after Rx No difference between bacteriologic failures in either arm [Pediatrics 1999; 103:47-51]
63 Follow-up of Streptococcal Pharyngitis Only work up contacts if they have history of rheumatic fever, or if they have persistent or recurrent pharyngitis Follow-up cultures only indicated if symptoms persist, patient has history of rheumatic fever, or outbreak is present IDSA, 1997
64 Recurrent Streptococcal Pharyngitis Probably due to beta-lactamases produced by other organisms in oropharynx If recurrence does occur: clindamycin children: mg/kg/d divided tid x 10 days adults: 150 mg qid x 10 days amoxicillin/clavulanate 40 mg/kg/d divided tid x 10 days IDSA, 1997
65 Conclusions Upper respiratory tract infections cause a significant amount of morbidity in the US S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, and S. pyogenes are the major organisms involved Simple and inexpensive medications are still the agents of choice for these infections Judicious use of antibiotics will help control costs and minimize the spread of resistance
66 Thank You!!
Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent. 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens
 Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent Consider: 1) the host 2) the site of infection 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens 4) the likelihood that these pathogens are resistant to antimicrobial agents
Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent Consider: 1) the host 2) the site of infection 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens 4) the likelihood that these pathogens are resistant to antimicrobial agents
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections / 42
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections 1 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Acute tonsillitispharyngitis Acute otitis media Acute sinusitis Common cold Acute laryngitis Otitis externa Mastoiditis Acute apiglottis
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections 1 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Acute tonsillitispharyngitis Acute otitis media Acute sinusitis Common cold Acute laryngitis Otitis externa Mastoiditis Acute apiglottis
Prefe f rred d t e t rm: : rhi h no n s o inu n s u iti t s
 HELP It s my sinuses! An overview of pharmacologic treatment of sinusitis Objectives Identify types of sinusitis and underlying pathology Examine common evidence based pharmacologic treatment for sinusitis
HELP It s my sinuses! An overview of pharmacologic treatment of sinusitis Objectives Identify types of sinusitis and underlying pathology Examine common evidence based pharmacologic treatment for sinusitis
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS 1 INTRODUCTION Most common problem in children below 5 years. In this age group they get about 6 8 episodes per year. It includes infections of nasal cavity, throat,
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS 1 INTRODUCTION Most common problem in children below 5 years. In this age group they get about 6 8 episodes per year. It includes infections of nasal cavity, throat,
Acute Otitis Media, Acute Bacterial Sinusitis, and Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis
 Acute Otitis Media, Acute Bacterial Sinusitis, and Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis This guideline, developed by Larry Simmons, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 3, 2013, is a significantly
Acute Otitis Media, Acute Bacterial Sinusitis, and Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis This guideline, developed by Larry Simmons, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 3, 2013, is a significantly
Appropriate Use of Antibiotics for the Treatment of Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Adults
 Appropriate Use of Antibiotics for the Treatment of Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Adults Kyong Ran Peck, M.D. Division of Infectious Diseases Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung
Appropriate Use of Antibiotics for the Treatment of Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Adults Kyong Ran Peck, M.D. Division of Infectious Diseases Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung
Respiratory tract infections. Krzysztof Buczkowski
 Respiratory tract infections Krzysztof Buczkowski Etiology Viruses Rhinoviruses Adenoviruses Coronaviruses Influenza and Parainfluenza Viruses Respiratory Syncitial Viruses Enteroviruses Etiology Bacteria
Respiratory tract infections Krzysztof Buczkowski Etiology Viruses Rhinoviruses Adenoviruses Coronaviruses Influenza and Parainfluenza Viruses Respiratory Syncitial Viruses Enteroviruses Etiology Bacteria
Infections of the head, neck, and lower respiratory tract
 Infections of the head, neck, and lower respiratory tract Infections of the upper respiratory tract Common 25% bacteria antibiotics 75% viruses Diagnosis on clinical grounds Nonspecific infections of the
Infections of the head, neck, and lower respiratory tract Infections of the upper respiratory tract Common 25% bacteria antibiotics 75% viruses Diagnosis on clinical grounds Nonspecific infections of the
POLICY FOR TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS
 POLICY F TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATY TRACT INFECTIONS Written by: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Date: July 2013 Approved by: The Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Date: April 2016 Implementation
POLICY F TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATY TRACT INFECTIONS Written by: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Date: July 2013 Approved by: The Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Date: April 2016 Implementation
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani
 RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
Rhinosinusitis. John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD
 Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Update on Rhinosinusitis 2013 AAP Guidelines Review
 Update on Rhinosinusitis 2013 AAP Guidelines Review Carla M. Giannoni, MD Surgeon, Otolaryngology Texas Children's Hospital Professor, Surgery and Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine CDC: Acute Rhinosinusitis
Update on Rhinosinusitis 2013 AAP Guidelines Review Carla M. Giannoni, MD Surgeon, Otolaryngology Texas Children's Hospital Professor, Surgery and Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine CDC: Acute Rhinosinusitis
Upper Respiratory tract Infec1on. Gassem Gohal FAAP FRCPC
 Upper Respiratory tract Infec1on Gassem Gohal FAAP FRCPC Anatomy Contents Sinusitis Common Cold Otitis media pharyngitis Epiglottitis Croup Trachitis Sinuses Sinus development Born with ME ( Maxillary,
Upper Respiratory tract Infec1on Gassem Gohal FAAP FRCPC Anatomy Contents Sinusitis Common Cold Otitis media pharyngitis Epiglottitis Croup Trachitis Sinuses Sinus development Born with ME ( Maxillary,
MANAGEMENT of BACTERIAL RHINOSINUSITIS
 MANAGEMENT of BACTERIAL RHINOSINUSITIS Jennifer Le, PharmD Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice, College of Pharmacy, Western University of Health Sciences Martin S. Lipsky, MD Dean and Professor of
MANAGEMENT of BACTERIAL RHINOSINUSITIS Jennifer Le, PharmD Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice, College of Pharmacy, Western University of Health Sciences Martin S. Lipsky, MD Dean and Professor of
USAID Health Care Improvement Project. pneumonia) respiratory infections through improved case management (amb/hosp)
 Improvement objective: : decrease morbidity and mortality due to acute upper (rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis) and lower (bronchitis, pneumonia) respiratory infections through improved case management
Improvement objective: : decrease morbidity and mortality due to acute upper (rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis) and lower (bronchitis, pneumonia) respiratory infections through improved case management
Pathophysiology and Etiology
 Sinusitis Pathophysiology and Etiology Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucosa of one or more sinuses. It can be either acute chronic. Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed if symptoms are present for more than
Sinusitis Pathophysiology and Etiology Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucosa of one or more sinuses. It can be either acute chronic. Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed if symptoms are present for more than
COMMON UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN
 ١ ٢ COMMON UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr mostafavi SN Pediatric Infectious Disease Department Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Case 1 ٣ An 18 month old infant brought with high
١ ٢ COMMON UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr mostafavi SN Pediatric Infectious Disease Department Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Case 1 ٣ An 18 month old infant brought with high
High dose amoxicillin for sinusitis
 High dose amoxicillin for sinusitis Amoxil ( amoxicillin ) is a commonly used penicillin antibiotic. It is produced in tablets (500 mg 875 mg), capsules, chewable tablets and oral suspensions. 6-3-2018
High dose amoxicillin for sinusitis Amoxil ( amoxicillin ) is a commonly used penicillin antibiotic. It is produced in tablets (500 mg 875 mg), capsules, chewable tablets and oral suspensions. 6-3-2018
I have no disclosures
 Disclosures Streptococcal Pharyngitis: Update and Current Guidelines Richard A. Jacobs, MD, PhD Emeritus Professor of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases I have no disclosures CID 2012:55;e 86-102
Disclosures Streptococcal Pharyngitis: Update and Current Guidelines Richard A. Jacobs, MD, PhD Emeritus Professor of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases I have no disclosures CID 2012:55;e 86-102
Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology
 Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology Faculty: Evelyn Kluka, M.D. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's and other specialists' roles
Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology Faculty: Evelyn Kluka, M.D. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's and other specialists' roles
POLICY FOR TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS
 POLICY F TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATY TRACT INFECTIONS Written by: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Date: June 2018 Approved by: Date: July 2018 The Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Implementation
POLICY F TREATMENT OF UPPER RESPIRATY TRACT INFECTIONS Written by: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Date: June 2018 Approved by: Date: July 2018 The Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Implementation
Clinical Practice Guideline: Tonsillectomy in Children, Baugh et al Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, 2011 J and: 144 (1 supplement) S1 30.
 Pediatric ENT Guidelines Jane Cooper, FNP, CORLN References: Clinical Practice Guideline: Tympanostomy tubes in children, Rosenfeld et al., American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Foundation
Pediatric ENT Guidelines Jane Cooper, FNP, CORLN References: Clinical Practice Guideline: Tympanostomy tubes in children, Rosenfeld et al., American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Foundation
Acute Bacterial Sinusitis: The latest treatment recommendations. Objectives Having completed the learning activities, the participant will be able to:
 Acute Bacterial Sinusitis: The latest treatment recommendations Presented by: Monica Tombasco, MS, MSNA, FNP-BC, CRNA Senior Lecturer Fitzgerald Health Education Associates, Inc., North Andover, MA Emergency
Acute Bacterial Sinusitis: The latest treatment recommendations Presented by: Monica Tombasco, MS, MSNA, FNP-BC, CRNA Senior Lecturer Fitzgerald Health Education Associates, Inc., North Andover, MA Emergency
Common ENT Presentations
 Common ENT Presentations MD, BScMed, FRCSC Head Section of Otolaryngology St. Boniface Hospital Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada Assistant Professor Department of Otolaryngology University of Manitoba Winnipeg,
Common ENT Presentations MD, BScMed, FRCSC Head Section of Otolaryngology St. Boniface Hospital Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada Assistant Professor Department of Otolaryngology University of Manitoba Winnipeg,
Respiratory System Virology
 Respiratory System Virology Common Cold: Rhinitis. A benign self limited syndrome caused by several families of viruses. The most frequent acute illness in industrialized world. Mild URT illness involving:
Respiratory System Virology Common Cold: Rhinitis. A benign self limited syndrome caused by several families of viruses. The most frequent acute illness in industrialized world. Mild URT illness involving:
Evelyn A. Kluka, MD FAAP November 30, 2011
 Evelyn A. Kluka, MD FAAP November 30, 2011 > 80% of children will suffer from at least one episode of AOM by 3 years of age 40% will have > 6 recurrences by age 7 years Most common diagnosis for which
Evelyn A. Kluka, MD FAAP November 30, 2011 > 80% of children will suffer from at least one episode of AOM by 3 years of age 40% will have > 6 recurrences by age 7 years Most common diagnosis for which
Jimmy's Got Cooties! Common Childhood Infections and How Best to Treat Them
 Jimmy's Got Cooties! Common Childhood Infections and How Best to Treat Them Objectives:! Recognize and manage several infections commonly seen in Pediatric practice! Discuss best practices and current
Jimmy's Got Cooties! Common Childhood Infections and How Best to Treat Them Objectives:! Recognize and manage several infections commonly seen in Pediatric practice! Discuss best practices and current
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE
 PROFESSOR DR SALINA HUSAIN DEPUTY HEAD DEPARTMENT OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD NECK SURGERY UKM MEDICAL CENTRE MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT
PROFESSOR DR SALINA HUSAIN DEPUTY HEAD DEPARTMENT OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD NECK SURGERY UKM MEDICAL CENTRE MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT
+ Conflict of interest. + Sinus and Nasal Anatomy. + What is your diagnosis? 1) Allergic Rhinitis. 2) Non-Allergic rhinitis. 3) Chronic Rhinosinusitis
 Rhinitis & Sinusitis Conflict of interest I have no conflict of interest to declare for this lecture Al Chiodo, MD FRCSC Assistant Professor Director of Undergraduate Medical Education Department of Otolaryngology-Head
Rhinitis & Sinusitis Conflict of interest I have no conflict of interest to declare for this lecture Al Chiodo, MD FRCSC Assistant Professor Director of Undergraduate Medical Education Department of Otolaryngology-Head
Definition. Otitis Media with effusion (OME)
 Otitis Media. 1 Dr,wegdan saeed ALFHAL 2 Definition Acute Otitis Media (AOM) acute onset of symptoms, evidence of a middle ear effusion, and signs or symptoms of middle ear inflammation. Otitis Media with
Otitis Media. 1 Dr,wegdan saeed ALFHAL 2 Definition Acute Otitis Media (AOM) acute onset of symptoms, evidence of a middle ear effusion, and signs or symptoms of middle ear inflammation. Otitis Media with
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS
 MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Otorhinolaryngologist - Head & Neck Surgeons (MS)-HNS) Academy of Medicine Malaysia KEY MESSAGES
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Otorhinolaryngologist - Head & Neck Surgeons (MS)-HNS) Academy of Medicine Malaysia KEY MESSAGES
Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief.
 Sinus Sinus Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief. So what is sinusitis? Although many individuals interpret
Sinus Sinus Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief. So what is sinusitis? Although many individuals interpret
CAREFUL ANTIBIOTIC USE
 Make promoting appropriate antibiotic use part of your routine clinical practice When parents ask for antibiotics to treat viral infections: PRACTICE TIPS Create an office environment to promote the reduction
Make promoting appropriate antibiotic use part of your routine clinical practice When parents ask for antibiotics to treat viral infections: PRACTICE TIPS Create an office environment to promote the reduction
ANTIBIOTICS ACUTE RHINOSINUSITIS IN CHILDREN
 MARCH 2016 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
MARCH 2016 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
Sinusitis in Adults UP TO DATE
 Sinusitis in Adults UP TO DATE Acute sinusitis and rhinosinusitis in adults: Treatment Authors Peter H Hwang, MD Anne Getz, MD Section Editors Daniel G Deschler, MD, FACS Stephen B Calderwood, MD Deputy
Sinusitis in Adults UP TO DATE Acute sinusitis and rhinosinusitis in adults: Treatment Authors Peter H Hwang, MD Anne Getz, MD Section Editors Daniel G Deschler, MD, FACS Stephen B Calderwood, MD Deputy
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Anatomy of the Respiratory System Respiratory Infections Respiratory tract can be divided into: Upper Respiratory Tract (URT): Sinuses Nasopharynx,.
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Anatomy of the Respiratory System Respiratory Infections Respiratory tract can be divided into: Upper Respiratory Tract (URT): Sinuses Nasopharynx,.
Molina Healthcare of Washington, Inc. Guideline for the Judicious use of Antibiotics
 Molina Healthcare of Washington, Inc. Guideline for the Judicious use of Antibiotics The Washington State Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Judicious Use of Antibiotics in URI (Sinusitis, Otitis Media,
Molina Healthcare of Washington, Inc. Guideline for the Judicious use of Antibiotics The Washington State Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Judicious Use of Antibiotics in URI (Sinusitis, Otitis Media,
Paediatric ENT problems
 Paediatric ENT problems Ears Otitis media Otitis media with effusion FBs Otitis externa Ruptured TM Nose FBs Allergic rhinitis Septal perforation expistaxis Throat FB Croup Stidor Tonsillitis Paediatric
Paediatric ENT problems Ears Otitis media Otitis media with effusion FBs Otitis externa Ruptured TM Nose FBs Allergic rhinitis Septal perforation expistaxis Throat FB Croup Stidor Tonsillitis Paediatric
Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults Guideline
 Member Groups Requesting Changes: Lakeview Clinic Marshfield Clinic Mayo Clinic South Lake Pediatrics Response Report for Review and Comment January 2013 Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness
Member Groups Requesting Changes: Lakeview Clinic Marshfield Clinic Mayo Clinic South Lake Pediatrics Response Report for Review and Comment January 2013 Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness
DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC
 MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS DR ZULKEFLI HUSSEIN CONSULTANT EAR NOSE & THROAT SURGEON PANTAI HOSPITAL PENANG DISCLAIMER Nothing to disclose PENANG ISLAND, MALAYSIA
MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS DR ZULKEFLI HUSSEIN CONSULTANT EAR NOSE & THROAT SURGEON PANTAI HOSPITAL PENANG DISCLAIMER Nothing to disclose PENANG ISLAND, MALAYSIA
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Otolaryngology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Otolaryngology 1. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Otolaryngology 1. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's
Infectious Disease. Chloe Duke
 Infectious Disease Chloe Duke Learning Objectives Essential - Causes, recognition and Treatment of: Meningitis Sepsis Purpura Important Cervical Adenopathy Tonsillitis and Pharyngitis Otitis Media Pneumonia
Infectious Disease Chloe Duke Learning Objectives Essential - Causes, recognition and Treatment of: Meningitis Sepsis Purpura Important Cervical Adenopathy Tonsillitis and Pharyngitis Otitis Media Pneumonia
Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
 Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Robin Jump, MD, PhD Cleveland Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center Case Western Reserve University
Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Robin Jump, MD, PhD Cleveland Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center Case Western Reserve University
Comparative Efficacy and Safety Evaluation of Cefaclor VS Amoxycillin + Clavulanate in Children with Acute Otitis Media (AOM)
 Special Article Comparative Efficacy and Safety Evaluation of Cefaclor VS Amoxycillin + Clavulanate in Children with Acute Otitis Media (AOM) Mukesh Aggarwal, Ramanuj Sinha 1, M. Vasudeva Murali 2, Prita
Special Article Comparative Efficacy and Safety Evaluation of Cefaclor VS Amoxycillin + Clavulanate in Children with Acute Otitis Media (AOM) Mukesh Aggarwal, Ramanuj Sinha 1, M. Vasudeva Murali 2, Prita
Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults
 Page 1 of 9 Main Algorithm Annotations 1. Patient Reports Some Combination of Symptoms Patients may present for an appointment, call into a provider to schedule an appointment or nurse line presenting
Page 1 of 9 Main Algorithm Annotations 1. Patient Reports Some Combination of Symptoms Patients may present for an appointment, call into a provider to schedule an appointment or nurse line presenting
4/7/13 SINUSITIS WHO ARE WE TREATING? AMANDA SAM CONLEY RN, MSN, CFN, LNC, FNP- BC
 SINUSITIS WHO ARE WE TREATING? AMANDA SAM CONLEY RN, MSN, CFN, LNC, FNP- BC 1 DefiniGons Anatomy Review Signs and Symptoms OBJECTIVES Acute Viral vrs. Acute Bacterial Treatment Guidelines ANATOMY REVIEW
SINUSITIS WHO ARE WE TREATING? AMANDA SAM CONLEY RN, MSN, CFN, LNC, FNP- BC 1 DefiniGons Anatomy Review Signs and Symptoms OBJECTIVES Acute Viral vrs. Acute Bacterial Treatment Guidelines ANATOMY REVIEW
BLOCK 12 Viruses of the ENT
 BLOCK 12 Viruses of the ENT Acute infections Introduction Pharyngitis, Common cold, Sinusitis, Otitis media Recurrent infections Herpes zoster oticus Chronic infections HIV and ENT manifestations Neoplasms
BLOCK 12 Viruses of the ENT Acute infections Introduction Pharyngitis, Common cold, Sinusitis, Otitis media Recurrent infections Herpes zoster oticus Chronic infections HIV and ENT manifestations Neoplasms
General Surgery >>>>>[[ sheet # 4]]
![General Surgery >>>>>[[ sheet # 4]] General Surgery >>>>>[[ sheet # 4]]](/thumbs/82/86768776.jpg) General Surgery 11-3-2014 >>>>>[[ sheet # 4]] *Note *: this sheet includes the slides and extra notes >> and what the dr were mentioned are in the bold font Acute Rhinosinusitis Sinusitis commonly used
General Surgery 11-3-2014 >>>>>[[ sheet # 4]] *Note *: this sheet includes the slides and extra notes >> and what the dr were mentioned are in the bold font Acute Rhinosinusitis Sinusitis commonly used
NECK MASS. Clinical history and examination: Document detail history of mass. Imaging: US or CT of neck
 ENT ENT Referral Referral Guidelines Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment
ENT ENT Referral Referral Guidelines Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Otitis Media
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Otitis Media Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Otitis Media Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in
Clindamycin strep throat dose
 Clindamycin strep throat dose User Reviews for Clindamycin. Also known as: Cleocin, Cleocin HCl, Cleocin Pediatric, Cleocin Phosphate, Cleocin Phosphate ADD-Vantage. The following information is. 1 Answer
Clindamycin strep throat dose User Reviews for Clindamycin. Also known as: Cleocin, Cleocin HCl, Cleocin Pediatric, Cleocin Phosphate, Cleocin Phosphate ADD-Vantage. The following information is. 1 Answer
Mohammed El-Khateeb MSVL-4 Nov 26 th 2013
 Mohammed El-Khateeb MSVL-4 Nov 26 th 2013 The respiratory system is the most commonly infected system. Health care providers will see more respiratory infections than any other type. Geography of the
Mohammed El-Khateeb MSVL-4 Nov 26 th 2013 The respiratory system is the most commonly infected system. Health care providers will see more respiratory infections than any other type. Geography of the
27/11/2012. Parainfuenza 1, 2 3 Rhinovirus Coronavirus Adenovirus Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) Chlamydophila pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumonite
 8 «Evidence-based Medicine-» 27/11/2012,,,, : :,,,,,,,, (30%-50%) () (5%-10%) (40%-50%) 20% Infuenza A B Parainfuenza 1, 2 3 Rhinovirus Coronavirus Adenovirus Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) Chlamydophila
8 «Evidence-based Medicine-» 27/11/2012,,,, : :,,,,,,,, (30%-50%) () (5%-10%) (40%-50%) 20% Infuenza A B Parainfuenza 1, 2 3 Rhinovirus Coronavirus Adenovirus Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) Chlamydophila
NOVEMBER 2016 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS ACUTE RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS
 NOVEMBER 2016 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
NOVEMBER 2016 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
Community Acquired Pneumonia
 April 2014 References: 1. Bradley JS, Byington CL, Shah SS, Alverson B, Carter ER, Harrison C, Kaplan SL Mace SE, McCracken Jr. GH, Moor MR, St. Peter SD, Stockwell JA, and Swanson JT. The Management of
April 2014 References: 1. Bradley JS, Byington CL, Shah SS, Alverson B, Carter ER, Harrison C, Kaplan SL Mace SE, McCracken Jr. GH, Moor MR, St. Peter SD, Stockwell JA, and Swanson JT. The Management of
ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST
 www.manchesterchildrensent.com ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST A CHILD WITH EARACHE UNCOMPLICATED AOM ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA Acute otitis media
www.manchesterchildrensent.com ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST A CHILD WITH EARACHE UNCOMPLICATED AOM ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA Acute otitis media
Drugs Used to Treat Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Drugs Used to Treat Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) COPD COPD is a chronic, irreversible obstruction of airflow that is usually progressive. Symptoms include cough, excess mucus production,
Drugs Used to Treat Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) COPD COPD is a chronic, irreversible obstruction of airflow that is usually progressive. Symptoms include cough, excess mucus production,
Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis in Children Aged 1 to 18 Years
 Organizational Principles to Guide and Define the Child Health Care System and/or Improve the Health of all Children CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management
Organizational Principles to Guide and Define the Child Health Care System and/or Improve the Health of all Children CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum
 The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Acute Otitis Media. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Acute Otitis Media. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The
Chronic Sinusitis. Acute Sinusitis. Sinusitis. Anatomy of the Paranasal Sinuses. Sinusitis. Medical Topics - Sinusitis
 1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
Current Trend in URTI
 Current Trend in URTI Dr Chow Chun Kuen Specialist in Otorhinolaryngology Upper respiratory tract infection Nonspecific Most common cause of physician visits & sick leaves Acute infection of noes, sinuses,
Current Trend in URTI Dr Chow Chun Kuen Specialist in Otorhinolaryngology Upper respiratory tract infection Nonspecific Most common cause of physician visits & sick leaves Acute infection of noes, sinuses,
Dine & Learn - Victoria May 2015 Otolaryngology
 Dine & Learn - Victoria May 2015 Otolaryngology Allergic rhinitis Allergic rhinitis guidelines (Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 2015) Diagnosis: history: allergen + either nasal congestion or runny
Dine & Learn - Victoria May 2015 Otolaryngology Allergic rhinitis Allergic rhinitis guidelines (Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 2015) Diagnosis: history: allergen + either nasal congestion or runny
Journal of Pediatric Sciences
 Journal of Pediatric Sciences Buccal Cellulitis in 3 Infants Martin W Stallings Journal of Pediatric Sciences 2016;8:e252 http://dx.doi.org/10.17334/jps.78460 How to cite this article: Stallings MW. Buccal
Journal of Pediatric Sciences Buccal Cellulitis in 3 Infants Martin W Stallings Journal of Pediatric Sciences 2016;8:e252 http://dx.doi.org/10.17334/jps.78460 How to cite this article: Stallings MW. Buccal
Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders
 F.A. Davis: Advantage Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders (11.16.15) Page 1 Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders The respiratory system is an interconnected network of organs, tissues, and
F.A. Davis: Advantage Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders (11.16.15) Page 1 Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders The respiratory system is an interconnected network of organs, tissues, and
Sinusitis & its complication. MOHAMMED ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC Assistant Professor,Consultant Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery King Saud University
 Sinusitis & its complication MOHAMMED ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC Assistant Professor,Consultant Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery King Saud University Definition Types Clinical manifestation Complications Diagnosis
Sinusitis & its complication MOHAMMED ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC Assistant Professor,Consultant Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery King Saud University Definition Types Clinical manifestation Complications Diagnosis
Upper Respiratory Infections. Mehreen Arshad, MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases Duke University
 Upper Respiratory Infections Mehreen Arshad, MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases Duke University Disclosures None Objectives Know the common age- and season-specific causes of pharyngitis
Upper Respiratory Infections Mehreen Arshad, MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases Duke University Disclosures None Objectives Know the common age- and season-specific causes of pharyngitis
Management of URTI s in Children
 Management of URTI s in Children Robin J Green PhD Antibiotics - Dilemmas for General Practitioners Antibiotic overuse = Resistance Delay in antibiotic use = Mortality Patient expectation Employer expectation
Management of URTI s in Children Robin J Green PhD Antibiotics - Dilemmas for General Practitioners Antibiotic overuse = Resistance Delay in antibiotic use = Mortality Patient expectation Employer expectation
Evidence-based Strategies to Avoid Prescribing Unnecessary Antibiotics
 Evidence-based Strategies to Avoid Prescribing Unnecessary Antibiotics Robert Redwood MD, MPH Emergency & Preventive Medicine Physician June 11, 2018. WHA Journal Club #2 Conflict of Interest Disclosure
Evidence-based Strategies to Avoid Prescribing Unnecessary Antibiotics Robert Redwood MD, MPH Emergency & Preventive Medicine Physician June 11, 2018. WHA Journal Club #2 Conflict of Interest Disclosure
SINUSITIS. HAVAS ENT CLINICS Excellence in otolaryngology
 JULY 2015 SINUSITIS WHAT IS IT? WHAT SHOULD YOU DO? WHAT WORKS? THOMAS E HAVAS MBBS (SYD) MD (UNSW) FRCSE, FRACS, FACS CONJOINT ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNSW OTOLARNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY HAVAS ENT CLINICS
JULY 2015 SINUSITIS WHAT IS IT? WHAT SHOULD YOU DO? WHAT WORKS? THOMAS E HAVAS MBBS (SYD) MD (UNSW) FRCSE, FRACS, FACS CONJOINT ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNSW OTOLARNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY HAVAS ENT CLINICS
Patricia M. Wegner, BS Pharm, PharmD, FASHP PEER REVIEWERS: Nathaniel James Rhodes, PharmD, BCPS Linda O. Martinez, CPhT
 Pharmacy Tech Topics VOLUME 18 NO. 2 APRIL 2013 Cough, Sneeze, Sniffle: Management of Respiratory Tract Infections AUTHOR: Sarah M. Wieczorkiewicz, PharmD, BCPS EDITOR: Patricia M. Wegner, BS Pharm, PharmD,
Pharmacy Tech Topics VOLUME 18 NO. 2 APRIL 2013 Cough, Sneeze, Sniffle: Management of Respiratory Tract Infections AUTHOR: Sarah M. Wieczorkiewicz, PharmD, BCPS EDITOR: Patricia M. Wegner, BS Pharm, PharmD,
ب ه نام خد ا فارماکوویژیالنس و عوارض ناخواسته داروها آذر ماه 1396
 ب ه نام خد ا فارماکوویژیالنس و عوارض ناخواسته داروها آذر ماه 1396 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Z. Sahraei Pharm. D., Ph.D. Infectious Disease Clinical Pharmacist Rhinosinusitis Definition Acute rhinosinusitis
ب ه نام خد ا فارماکوویژیالنس و عوارض ناخواسته داروها آذر ماه 1396 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Z. Sahraei Pharm. D., Ph.D. Infectious Disease Clinical Pharmacist Rhinosinusitis Definition Acute rhinosinusitis
ENT Referral Guidelines
 ENT Referral Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment of patients with cancerous
ENT Referral Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment of patients with cancerous
Recognize the broad impact of hearing impairment on child and family, including social, psychological, educational and financial consequences.
 Otolaryngology Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Otolaryngology Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Appropriate Antibiotic Prescribing. Frank Romanelli, Pharm.D., MPH, AAHIVP Professor & Associate Dean Paul F. Parker Endowed Professor of Pharmacy
 Appropriate Antibiotic Prescribing Frank Romanelli, Pharm.D., MPH, AAHIVP Professor & Associate Dean Paul F. Parker Endowed Professor of Pharmacy Objectives Discuss CDCs Core Elements of abx stewardship.
Appropriate Antibiotic Prescribing Frank Romanelli, Pharm.D., MPH, AAHIVP Professor & Associate Dean Paul F. Parker Endowed Professor of Pharmacy Objectives Discuss CDCs Core Elements of abx stewardship.
Index. Infect Dis Clin N Am 21 (2007) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Infect Dis Clin N Am 21 (2007) 591 599 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess(es) epidural, subdural empyema and, 584 586 periotonsillar, microbiologic investigations
Infect Dis Clin N Am 21 (2007) 591 599 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess(es) epidural, subdural empyema and, 584 586 periotonsillar, microbiologic investigations
Welcome to Big Sky Country. Pediatrics Infectious disease update. Todd TwogoodMD
 Welcome to Big Sky Country Pediatrics Infectious disease update Todd TwogoodMD My kid is always sick!! We have to deal with parents Snotty nose kids Average number of colds in children from Oct to March
Welcome to Big Sky Country Pediatrics Infectious disease update Todd TwogoodMD My kid is always sick!! We have to deal with parents Snotty nose kids Average number of colds in children from Oct to March
INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Return to Syllabus INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES General Goal: To know the major mechanisms of defense in the URT, the major mechanisms invaders use
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Return to Syllabus INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES General Goal: To know the major mechanisms of defense in the URT, the major mechanisms invaders use
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Rapenin (phenoxymethylpenicillin potassium) is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by penicillin-sensitive bacteria.
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Rapenin (phenoxymethylpenicillin potassium) is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by penicillin-sensitive bacteria.
My kid is always sick!!
 Welcome to Big Sky Country My kid is always sick!! Pediatrics Infectious disease update Todd Twogood MD We have to deal with parents Snotty nose kids Average number of colds in children from Oct to March
Welcome to Big Sky Country My kid is always sick!! Pediatrics Infectious disease update Todd Twogood MD We have to deal with parents Snotty nose kids Average number of colds in children from Oct to March
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Impetigo. This document should be read in conjunction with this DISCLAIMER
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Impetigo Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Impetigo Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS. Clinical Practice Guideline: Management of Sinusitis
 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Subcommittee on Management of Sinusitis and Committee on Quality Improvement Clinical Practice Guideline: Management of Sinusitis ABSTRACT. This clinical practice guideline
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Subcommittee on Management of Sinusitis and Committee on Quality Improvement Clinical Practice Guideline: Management of Sinusitis ABSTRACT. This clinical practice guideline
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTION
 UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTION OVERVIEW To learn the epidemiology and various clinical presentation of URT To identify the common etiological agents causing these syndromes To study the laboratory diagnosis
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTION OVERVIEW To learn the epidemiology and various clinical presentation of URT To identify the common etiological agents causing these syndromes To study the laboratory diagnosis
Five New Clinical Guidelines in Primary Care: What we all need to know. Learning Objectives. Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Five New Clinical Guidelines in Primary Care: What we all need to know Annie Abraham, MSN, RN, FNP-BC Assistant Clinical Professor Texas Woman s University Dallas, TX Learning Objectives Discuss up-to-date
Five New Clinical Guidelines in Primary Care: What we all need to know Annie Abraham, MSN, RN, FNP-BC Assistant Clinical Professor Texas Woman s University Dallas, TX Learning Objectives Discuss up-to-date
The Nose and Sinuses. Ophir Ilan, MD, PhD Department of Otolaryngology/Head&Neck surgery Hadassah University Hospital
 The Nose and Sinuses Ophir Ilan, MD, PhD Department of Otolaryngology/Head&Neck surgery Hadassah University Hospital Nasal Mucociliary System Function of the Nasal Mucosa warming and humidifying the
The Nose and Sinuses Ophir Ilan, MD, PhD Department of Otolaryngology/Head&Neck surgery Hadassah University Hospital Nasal Mucociliary System Function of the Nasal Mucosa warming and humidifying the
Swedish guidelines for the treatment of rhinosinusitis, pharyngotonsillitis and acute media otitis in children.
 Swedish guidelines for the treatment of rhinosinusitis, pharyngotonsillitis and acute media otitis in children. The guidelines are produced by STRAMA in collaboration with the Swedish Medical Products
Swedish guidelines for the treatment of rhinosinusitis, pharyngotonsillitis and acute media otitis in children. The guidelines are produced by STRAMA in collaboration with the Swedish Medical Products
Reducing Antibiotic Use in Common Infections in Family Practice
 Reducing Antibiotic Use in Common Infections in Family Practice W. Rosser Emeritus Professor Department of Family Medicine Queen s University Discussion with Honorary Teachers, University of Hong Kong
Reducing Antibiotic Use in Common Infections in Family Practice W. Rosser Emeritus Professor Department of Family Medicine Queen s University Discussion with Honorary Teachers, University of Hong Kong
DEFINITION Cellulitis is an acute, spreading inflammation of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, often complicating a wound or other skin condition.
 DEFINITION Cellulitis is an acute, spreading inflammation of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, often complicating a wound or other skin condition. Cellulitis may be further classified by the unique area
DEFINITION Cellulitis is an acute, spreading inflammation of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, often complicating a wound or other skin condition. Cellulitis may be further classified by the unique area
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS COPD CT MRI IG PID Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Computed tomography
PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS COPD CT MRI IG PID Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Computed tomography
FEATURE. 8 EMERGENCY MEDICINE I JANUARY
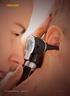 FEATURE 8 EMERGENCY MEDICINE I JANUARY 2017 www.emed-journal.com Pediatric ENT Complaints: An Update Melanie A. Weller, MD; Joel M. Clingenpeel, MD, MPH, MS.MEdL This review highlights the diagnosis and
FEATURE 8 EMERGENCY MEDICINE I JANUARY 2017 www.emed-journal.com Pediatric ENT Complaints: An Update Melanie A. Weller, MD; Joel M. Clingenpeel, MD, MPH, MS.MEdL This review highlights the diagnosis and
Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis
 IDSA GUIDELINES Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis Alan L. Bisno, 1 Michael A. Gerber, 2 Jack M. Gwaltney, Jr., 3 Edward L. Kaplan, 5 and Richard
IDSA GUIDELINES Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis Alan L. Bisno, 1 Michael A. Gerber, 2 Jack M. Gwaltney, Jr., 3 Edward L. Kaplan, 5 and Richard
Research articles last 5 years- ENT
 Research articles last 5 years- ENT Throats and tonsils Tonsillectomy versus antibiotics in children for recurrent tonsillitis Randomised controlled trial (BMJ May 2007) Tonsillectomy is more beneficial
Research articles last 5 years- ENT Throats and tonsils Tonsillectomy versus antibiotics in children for recurrent tonsillitis Randomised controlled trial (BMJ May 2007) Tonsillectomy is more beneficial
Guidelines for the Antibiotic Use in Adults with Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
 Special Article https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2017.49.4.326 Infect Chemother 2017;49(4):326-352 ISSN 2093-2340 (Print) ISSN 2092-6448 (Online) Infection & Chemotherapy Guidelines for the Antibiotic Use in
Special Article https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2017.49.4.326 Infect Chemother 2017;49(4):326-352 ISSN 2093-2340 (Print) ISSN 2092-6448 (Online) Infection & Chemotherapy Guidelines for the Antibiotic Use in
Objectives. Pneumonia. Pneumonia. Epidemiology. Prevalence 1/7/2012. Community-Acquired Pneumonia in infants and children
 Objectives Community-Acquired in infants and children Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America - 2011 Sabah Charania,
Objectives Community-Acquired in infants and children Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America - 2011 Sabah Charania,
Facilitator s Guide. Prescription Writing/Patient Safety Author: Benjamin Estrada, MD, University of South Alabama. Active Learning Module
 Facilitator s Guide Prescription Writing/Patient Safety Author: Benjamin Estrada, MD, University of South Alabama Active Learning Module Core Concepts In order to master this topic area, students must
Facilitator s Guide Prescription Writing/Patient Safety Author: Benjamin Estrada, MD, University of South Alabama Active Learning Module Core Concepts In order to master this topic area, students must
Haemophilus influenzae, Invasive Disease rev Jan 2018
 Haemophilus influenzae, Invasive Disease rev Jan 2018 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) is a small, Gram-negative bacillus, a bacterium capable of causing a range
Haemophilus influenzae, Invasive Disease rev Jan 2018 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) is a small, Gram-negative bacillus, a bacterium capable of causing a range
The Throat. Image source:
 The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
9/18/2018. Disclosures. Objectives
 Is It Really Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis? Assessment, Differential Diagnosis and Management of Common Sinonasal Symptoms Kristina Haralambides, MS, RN, FNP-C Disclosures The content of this presentation
Is It Really Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis? Assessment, Differential Diagnosis and Management of Common Sinonasal Symptoms Kristina Haralambides, MS, RN, FNP-C Disclosures The content of this presentation
