Migraine, Tension, and Cluster Headache: Primary Care for Primary Headaches. Jonathon M. Firnhaber, MD, FAAFP
|
|
|
- Earl Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Migraine, Tension, and Cluster Headache: Primary Care for Primary Headaches Jonathon M. Firnhaber, MD, FAAFP
2 Learning objectives 1. Utilize evidence-based strategies to diagnose patients presenting with headache. 2. Identify associated conditions (e.g. depression), and red flags for potentially life threatening causes of headache. 3. Use evidence-based recommendations to prescribe treatment for patients presenting with acute or emergent headache pain. 4. Develop collaborate management plans, emphasizing patient education on avoiding triggers that cause headache, and adherence to prescribed treatment strategies. 2
3 Headache References to headache can be found in the Ebers Papyrus (1200 B.C.) Evidence of trepanation of 9000 year old Neolithic skulls suggests early headache treatment Lifetime prevalence: 96% Direct and indirect socioeconomic costs estimated at $14 billion annually 3
4 4 Tension headache
5 Tension headache: basics Lifetime prevalence in general population: 30-78%, depending on study Episodic (infrequent and frequent) and chronic 5
6 Tension frequency Infrequent episodic: At least 10 episodes of a headache occurring on <1 day per month on average (<12 days per year) Frequent episodic: At least 10 episodes of headache occurring on 1-14 days per month on average for >3 months (>12 and <180 days per year) 6
7 Tension headache: diagnosis B. Lasting from 30 minutes to 7 days C. At least two of the following four characteristics: 1. bilateral location 2. pressing or tightening (non-pulsating) quality 3. mild or moderate intensity 4. not aggravated by routine physical activity such as walking or climbing stairs D. Both of the following: 1. no nausea or vomiting 2. no more than one of photophobia or phonophobia 7
8 Tension headache: treatment Limited evidence base to support specific treatments Consider: Acetaminophen NSAIDs: short-acting (e.g. ibuprofen, diclofenac, naproxyn sodium) tend to have better efficacy Less preferable: Combination medications containing caffeine Narcotic analgesics, barbiturates 8
9 9 Cluster headache
10 Trigeminal autonomic cephalgias 3.1 Cluster headache Episodic cluster headache Chronic cluster headache 3.2 Paroxysmal hemicrania Episodic paroxysmal hemicrania Chronic paroxysmal hemicrania 3.3 Short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache attacks 3.4 Hemicrania continua 3.5 Probable trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia 10
11 Cluster headache: the basics Most common of the trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias Lifetime prevalence > 1 per 1000 Not easily recognized, which leads to diagnostic delay Age at onset typically years Male : female = 3:1 Attacks may be provoked by alcohol, histamine, nitroglycerin 11
12 Cluster headache: the basics Autosomal dominant in approximately 5% of cases Attacks occur in series/clusters lasting for weeks or months, separated by remission period of months or years 10-15% have chronic cluster headache without remission periods Approximately 25% have only one cluster period 12
13 Cluster headache: diagnosis A. At least five attacks fulfilling criteria B D B. Severe or very severe unilateral orbital, supraorbital and/or temporal pain lasting minutes (when untreated) 13
14 Cluster headache: diagnosis C. Either or both of the following: 1. At least one of the following symptoms or signs, ipsilateral to the headache: a) conjunctival injection and/or lacrimation b) nasal congestion and/or rhinorrhea c) eyelid edema d) forehead and facial sweating e) forehead and facial flushing f) sensation of fullness in the ear g) miosis and/or ptosis 2. a sense of restlessness or agitation 14
15 Cluster headache: diagnosis D. Attacks have a frequency between one every other day and eight per day for more than half of the time when the disorder is active E. Not better accounted for by another ICHD-3 diagnosis. 15
16 Cluster headache: treatment Established as effective: Sumatriptan (subcutaneous; 6 mg) Zolmitriptan (nasal spray; 5 and 10 mg) Oxygen (100%; 6-12 L/min flow) 16
17 Cluster headache: treatment Probably effective: Sumatriptan (nasal spray; 20 mg) Zolmitriptan (oral; 5 and 10 mg) Sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation 17
18 Cluster headache: treatment Possibly effective: Cocaine/lidocaine (nasal spray; 10% each) Octreotide (subcutaneous; 100 mcg) Insufficient evidence: Dihydroergotamine (nasal spray; 1 mg) Somatostatin Prednisone 18
19 Cluster headache: prophylaxis Established as effective: Suboccipital steroid injection Possibly effective: Lithium (oral; 900 mg daily) Verapamil (oral; 360 mg daily) Melatonin (oral; 10 mg every evening) Warfarin (oral; target INR ) 19
20 20 Migraine headache
21 Migraine: basics Approximately 12% of the general population affected Female : male = 3:1 Approximately one-third of patients have an initial aura of neurological symptoms, most often a visual scotoma Lifetime prevalence is at least 18% Most common in patients aged Family history of migraine is seen in at least 50% of migraine patients
22 Migraine: pathophysiology A neurovascular headache: Neural events trigger dilation of blood vessels, resulting in pain and further nerve activation Aura is characterized by a short phase of hyperemia, followed by a wave of oligemia or spreading depression that passes across the cortex at 2-6mm/min
23 Migraine: pathophysiology Trigeminal nerve activation occurs Referred pain in the parietal, occipital and high cervical regions If treatment is delayed or ineffective, central sensitization may occur with associated cutaneous allodynia
24 Important historical questions Age at onset Presence or absence of aura and prodrome Frequency, intensity and duration of attack Number of headache days per month Time and mode of onset Associated symptoms and abnormalities Family history of migraine Quality, site, and radiation of pain Precipitating and relieving factors
25 Important historical questions Effect of activity on pain Relationship with food/alcohol Response to any previous treatment Any recent change in vision Association with recent trauma State of general health Any recent changes in sleep, exercise, weight, or diet Change in work or lifestyle (disability) Change in method of birth control (women) Possible association with environmental factors Effects of menstrual cycle and exogenous hormones
26 Four questions from the American Association of Neurology 1. How often do you get severe headaches (i.e., without treatment it is difficult to function)? 2. How often do you get other (milder) headaches? 3. How often do you take headache relievers or pain pills? 4. Has there been any recent change in your headaches?
27 Accuracy of four-question approach In one validation study, the presence of episodic disabling headache correctly identified migraine in 136 of 146 patients (93 percent) with episodic migraine, and 154 of 197 patients (78 percent) with chronic headache with migraine, with a specificity of 63 percent. Only 6 of 343 patients (1.7 percent) with migraine were not identified by disabling headache.
28 Migraine: diagnosis A. At least five attacks fulfilling criteria B D E. Not better accounted for by another ICHD-3 diagnosis. 28
29 Migraine: diagnosis B. Headache attacks lasting 4-72 hours (untreated or unsuccessfully treated) C. Headache has at least two of the following four characteristics: 1. unilateral location 2. pulsating quality 3. moderate or severe pain intensity 4. aggravation by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity (e.g. walking or climbing stairs) D. During headache at least one of the following: 1. nausea and/or vomiting 2. photophobia and phonophobia 29
30 Other potential features Vascular changes: cold hands and feet, tenderness over the superficial vessels where the headache occurs, pale skin of face Weight increase, Na + retention, oliguria Hyperesthesia of scalp
31 Other potential features Trigeminal activation may also cause: Nasal congestion Rhinorrhea Lacrimation Facial pain, especially in maxillary region Tooth pain, especially maxillary
32 Prodrome Premonitory symptoms occur in migraine with and without aura, and may precede headache by up to 24 hours; present in up to 60% of patients Mood changes: depression, hyperactivity, irritability, euphoria Increased appetite / food cravings Excessive yawning, fatigue Neck stiffness/pain
33 Aura Aura occurs in about 35% of migraines Typically precedes attack by minutes Not every patient who has migraine with aura has aura with every headache Negative visual: Scotomata, or blind spots Positive visual: Scintillations Paresthesias Visual and auditory hallucinations
34 Postdrome A sort of post-ictal phase, which may last hours to a day or more Na + retention and oliguria reverse with subsequent diuresis Many patients report a period when they are refractory to subsequent migraine
35 Migraine and cardiovascular risk Physicians Health Study Prospective cohort study of year old male physicians The 7.2% who self-reported migraine had multivariableadjusted hazard ratios of 1.24 for major CVD, 1.42 for myocardial infarction Age-adjusted HR for ischemic stroke was 1.84 in men <55 years; no significant association in older age groups Information on aura was not recorded, nor was information about use of migraine-specific drugs 35
36 Migraine and cardiovascular risk Nurses Health Study II 115,541 women aged years at baseline and free of angina and cardiovascular disease Cumulative follow-up rates were more than 90% 17,531 (15.2%) women reported a physician s diagnosis of migraine 36
37 Migraine and cardiovascular risk After adjustment for potential confounding factors, migraine was associated with an increased risk for: major cardiovascular disease (HR 1.50; 95% CI 1.33 to 1.69) myocardial infarction (1.39; 1.18 to 1.64) stroke (1.62; 1.37 to 1.92) angina/coronary revascularization procedures (1.73; 1.29 to 2.32) risk for cardiovascular disease mortality (HR 1.37; 1.02 to 1.83)
38 You ve got the clinical diagnosis But doctor, what if I have a brain tumor?
39 Neuroimaging Neuroimaging is not usually warranted for patients with migraine and normal neurologic exam (Grade B) Symptoms that significantly increase odds of finding a significant abnormality on neuroimaging: Rapidly increasing headache frequency History of dizziness or lack of coordination History of subjective numbness or tingling History of headache causing awakening from sleep
40 Neuroimaging: How much to spend? MRI may be more sensitive than CT for identifying clinically insignificant abnormalities, but may not be more sensitive for identifying clinically significant pathology that is relevant to the cause of headache
41 Medication options: NSAIDs NSAIDs are reasonable for mild to moderate pain Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis prevents neurogenically mediated inflammation in the trigeminovascular system May also interfere with serotonin neurotransmission and modulate vasoconstriction
42 Medication options: Dihydroergotamine Differs from ergotamine: less nausea and increased venoconstrictive effects DHE-45: 1mg IM; may repeat hourly up to 3mg daily Minimum of 5 days between treatment days Also available as a nasal spray (Migranal): 2mg dose, 1 spray in each nostril; repeat in 15min, up to 3mg per day
43 The triptans Serotonin is thought to have a pivotal role in migraine pathogenesis 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists Potential mechanisms of action: Normalization of dilated intracranial arteries Peripheral neuronal inhibition Neuronal inhibition of second-order neurons of the trigemino-cervical complex
44 Triptans: individual characteristics Sumatriptan (Imitrex): available for longest, most number of dosing forms, given successfully to most number of patients (oral 25-50mg; nasal 20mg; SQ 6mg) Zolmitriptan (Zomig): only triptan proven effective when repeated for persistent headache (oral/odt 2.5-5mg; nasal 2.5-5mg) Naratriptan (Amerge): slower onset but favorable adverse event profile and lower recurrence rate (oral 1-2.5mg)
45 Triptans: individual characteristics Rizatriptan (Maxalt): highest 2-hour and sustained pain-free rates, fastest time to response of any oral tablet (oral/odt 5-10mg) Almotriptan (Axert): slightly better adverse event profile, less chest pain than sumatriptan (oral 12.5mg) Eletriptan (Relpax): clear dose-response curve, good sustained response rates (oral 20-40mg) Frovatriptan (Frova): slower acting, longest half-life in class (oral 2.5mg)
46 Despite the individual characteristics Oral triptans within each group are more similar than different It is not possible to predict which triptan will work best for any given patient Tolerability problems as a reason for discontinuation are relatively rare for all triptans
47 Triptans: dosing strategies Avoid starting with baby doses Try a med for 2-3 headaches before concluding it s not effective, unless side effects are the problem Rizatriptan (Maxalt) and eletriptan (Axert) tend to offer the best combination of efficacy and tolerability; the other five are excellent choices as well
48 Migraine: prophylaxis Should be considered in patients: Who experience 2 or more migraines per month Whose migraines greatly affect quality of life and ability to function For whom abortive therapies have been unsuccessful For whom abortive therapies are contraindicated
49 Migraine prophylaxis: beta-blockers Propranolol (80-160mg daily divided or mg ER) and timolol (5-30mg daily) are FDA-approved Metoprolol, atenolol and nebivolol have limited supporting evidence Beta-blockers with ISA (intrinsic sympathomimetic activity) have been shown ineffective as prophylaxis (oxprenolol, pindolol, penbutolol and acebutolol)
50 Migraine prophylaxis: antidepressants Amitriptyline (50-100mg hs) is the only antidepressant with consistent evidence supporting its effectiveness; it is more beneficial in mixed migraine-tension headache While not as well studied, nortriptyline and desipramine are typically better tolerated SSRIs consistently demonstrate no effect on migraine frequency/severity
51 Migraine prophylaxis: antiepileptic drugs Divalproex sodium Depakote ER: 500mg qhs for 1 week, then increase to 1000mg qhs Side effects may include: Nausea Sedation Appetite increase (transient) Hair thinning
52 Migraine prophylaxis: antiepileptic drugs Topiramate Topamax 25 mg qhs for 1 week, then titrate by 25 mg weekly either split or hs dosing to target of 100 mg daily Side effects may include: Paresthesias Appetite decrease Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
53 Migraine prophylaxis: antiepileptic drugs Doses lower than target may still be effective if tolerability becomes an issue Intermittent difficulty with word finding is frequently seen with AEDs Virtually all AEDs can cause hepatotoxicity and suppression of one or more blood cell line Divalproex has a black box warning for hepatotoxicity; LFT monitoring is recommended at baseline and frequently for the first 6 months Periodic CBC and chemistry is advisable
54 Migraine prophylaxis: onabotulinumtoxin A 155 units IM divided over 7 specific head/neck muscle areas every 12 weeks FDA-approved for prevention of chronic migraine (>15 headache days per month with headache lasting 4 hours per day or longer) 54
55 Migraine prophylaxis: other drugs Weak evidence or efficacy in small trials: Verapamil Lisinopril Candesartan Venlafaxine XR Duloxetine 55
56 Feature Migraine Tension Cluster Location Unilateral in 60 to 70 percent; bifrontal or global in 30 percent Bilateral Always unilateral, typically begins around eye or temple Characteristics Gradual in onset, crescendo pattern; pulsating; moderate or severe intensity; aggravated by routine physical activity Pressure or tightness which waxes and wanes Pain begins quickly, reaches a crescendo within minutes; pain is deep, continuous, excruciating, and explosive in quality Pt appearance Patient prefers to rest in a dark, quiet room Patient may remain active or may need to rest Patient remains active Duration 4 to 72 hours Variable 30 minutes to 3 hours Associated symptoms Nausea, vomiting, photophobia, phonophobia; may have aura (usually visual, but can involve other senses or cause speech or motor deficits) None Ipsilateral lacrimation and redness of the eye; stuffy nose; rhinorrhea; pallor; sweating; Horner's syndrome; focal neurologic symptoms rare; sensitivity to alcohol
57 References Of the (IHS) H. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia. 2013;33(9): doi: / Rizzoli P, Mullally W. Headache. The American Journal of Medicine doi: /j.amjmed Robbins M, Starling A, Pringsheim T, Becker W, Schwedt T. Treatment of Cluster Headache: The American Headache Society Evidence-Based Guidelines. Headache J Head Face Pain. 2016;56(7): doi: /head
58 References Hu X, Zhou Y, Zhao H, Peng C. Migraine and the risk of stroke: an updated meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.neurol Sci. 2017;38(1): doi: /s z Moore A, Derry S, Wiffen P, Straube S, Bendtsen L. Evidence for efficacy of acute treatment of episodic tension-type headache: Methodological critique of randomised trials for oral treatments. Pain. 2014;155(11): doi: /j.pain Kurth T, Gaziano M, Cook N, et al. Migraine and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Men. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(8): doi: /archinte
59 References Robbins M, Starling A, Pringsheim T, Becker W, Schwedt T. Treatment of Cluster Headache: The American Headache Society Evidence-Based Guidelines. Headache J Head Face Pain. 2016;56(7): Of the (IHS) H. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia. 2013;33(9):
60
Disclosures. Objectives 6/2/2017
 Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
MIGRAINE UPDATE. Objectives & Disclosures. Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment.
 MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
A case of a patient with chronic headache. Focus on Migraine. None related to the presentation Grants to conduct clinical trials from: Speaker bureau:
 Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Truths about Headaches (2017) Most headaches were muscle-tension headaches
 Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
Chronic Daily Headaches
 Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT
 ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
Faculty Disclosure. Karen L. Bremer, MD. Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest.
 Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Headache. Section 1. Migraine headache. Clinical presentation
 Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE
 Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines
 How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE
 MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias. Disclosures. Objectives 6/20/2018. Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018
 Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
OH, MY ACHING HEAD! I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING SECONDARY HEADACHES
 1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care
 Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates
 Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Anti-Migraine Agents
 DRUG POLICY BENEFIT APPLICATION Anti-Migraine Agents Benefit determinations are based on the applicable contract language in effect at the time the services were rendered. Exclusions, limitations or exceptions
DRUG POLICY BENEFIT APPLICATION Anti-Migraine Agents Benefit determinations are based on the applicable contract language in effect at the time the services were rendered. Exclusions, limitations or exceptions
Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D.
 Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D. Objectives Present patient case Review epidemiology/pathophysiology
Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D. Objectives Present patient case Review epidemiology/pathophysiology
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
Disclosures. Triptans for Kids 5/16/13
 5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
Index. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Headache Questionnaire
 Date: All Headache Patients We would appreciate your cooperation in filling out this form. In our evaluation of headache, your history is typically our most valuable tool for diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
Date: All Headache Patients We would appreciate your cooperation in filling out this form. In our evaluation of headache, your history is typically our most valuable tool for diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
Headache and Facial Pain. Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology
 Headache and Facial Pain Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology Introduction It is the most common neurologic complain The diagnosis usually
Headache and Facial Pain Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology Introduction It is the most common neurologic complain The diagnosis usually
10/17/2017 CHRONIC MIGRAINES BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES PATIENT CASE EPIDEMIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY
 BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
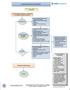 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
Headache A Practical Approach
 Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder
 ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
Management of headache
 Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care. December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary
 Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines
 Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Clinical case. Clinical case 3/15/2018 OVERVIEW. Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment. Refractory headache.
 OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: occipital_nerve_stimulation 8/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Occipital nerve
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: occipital_nerve_stimulation 8/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Occipital nerve
Subject: CGRP Inhibitors
 ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Archived: 08/01/18 09-J2000-98 Original Effective Date: 06/15/18 Reviewed: 05/09/18 Revised: 08/01/18 Next Review: ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Subject: CGRP Inhibitors THIS
ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Archived: 08/01/18 09-J2000-98 Original Effective Date: 06/15/18 Reviewed: 05/09/18 Revised: 08/01/18 Next Review: ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Subject: CGRP Inhibitors THIS
6/4/2018. Headache. Headaches. Headache. Migraine Headaches. Headache. Red Flag signs and symptoms. Imaging CT without contrast.
 Presented by M.D. Shepherd, M.D. OH MY ACHING HEAD! Estimated that one half of the adult population is affected by a headache disorder International Society Classification Primary : Tension s 40% of the
Presented by M.D. Shepherd, M.D. OH MY ACHING HEAD! Estimated that one half of the adult population is affected by a headache disorder International Society Classification Primary : Tension s 40% of the
Headache Pain Generators
 Objectives 1. Define the major categories of headache. 2. Take a history directed at characterizing a headache pattern in an individual patient and identify the cause or triggers of the headache. 3. Understand
Objectives 1. Define the major categories of headache. 2. Take a history directed at characterizing a headache pattern in an individual patient and identify the cause or triggers of the headache. 3. Understand
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline. Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN
 A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
Short Clinical Guidelines: Headache, Key Points for Diagnosis and Treatment
 Clinical Highlights 1. Headache is diagnosed by history and physical examination with limited need for imaging or laboratory tests. 2. Warning signs of possible disorder other than primary headache are:
Clinical Highlights 1. Headache is diagnosed by history and physical examination with limited need for imaging or laboratory tests. 2. Warning signs of possible disorder other than primary headache are:
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in
 HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
Migraine: Past, Present and Future Edward O Sullivan September 12 th 2015 Dublin 12/09/2015
 1 Migraine: Past, Present and Future Edward O Sullivan September 12 th 2015 Dublin Tour de France 2015: Mark Renshaw Yesterday at the end of the stage 17 I came down with a migraine before the final climb
1 Migraine: Past, Present and Future Edward O Sullivan September 12 th 2015 Dublin Tour de France 2015: Mark Renshaw Yesterday at the end of the stage 17 I came down with a migraine before the final climb
Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017
 Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor
 By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
10/13/17. Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD
 Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD } Depomed Consultant 2014 to present } Avanir Consultant 2014 to present } Amgen
Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD } Depomed Consultant 2014 to present } Avanir Consultant 2014 to present } Amgen
MIGRAINE CLASSIFICATION
 MIGRAINE CLASSIFICATION Nada Šternić At most, only 30% of migraineurs have classic aura The same patient may have migraine headache without aura, migraine headache with aura as well as migraine aura without
MIGRAINE CLASSIFICATION Nada Šternić At most, only 30% of migraineurs have classic aura The same patient may have migraine headache without aura, migraine headache with aura as well as migraine aura without
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, II. Management of Refractory Headaches
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
1. On how many days in the last 3 months did you miss work or school because of your headaches?
 The Migraine Disability Assessment Test The MIDAS (Migraine Disability Assessment) questionnaire was put together to help you measure the impact your headaches have on your life. The information on this
The Migraine Disability Assessment Test The MIDAS (Migraine Disability Assessment) questionnaire was put together to help you measure the impact your headaches have on your life. The information on this
Page: 1 of 6. Aimovig (erenumab-aooe) injection, Ajovy (fremanezumab-vfrm) injection, Emgality (galcanezumab-gnim)
 Page: 1 of 6 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Description Aimovig (erenumab-aooe) injection, Ajovy (fremanezumab-vfrm)
Page: 1 of 6 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Description Aimovig (erenumab-aooe) injection, Ajovy (fremanezumab-vfrm)
Migraine Management. Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital
 Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Treatments for migraine
 Treatments for migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Contents Page About this leaflet Abortive medication for migraine Painkillers Antisickness medication
Treatments for migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Contents Page About this leaflet Abortive medication for migraine Painkillers Antisickness medication
ARxCH. Annual Review of Changes in Healthcare. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptors and the Prevention of Migraines. Abstract
 Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptors and the Prevention of Migraines Brian Schuler, PharmD Candidate 2018 1 1 University of Findlay College of Pharmacy Abstract Migraines are the third most prevalent
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptors and the Prevention of Migraines Brian Schuler, PharmD Candidate 2018 1 1 University of Findlay College of Pharmacy Abstract Migraines are the third most prevalent
ABORTIVE AGENTS. Average cost per 30 days. Form Limits SEROTONIN AGONISTS $ $ Reserved for treatment failure to either Sumatriptan PA; QL
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Migraine Therapy P&T DATE: 12/11/2018 CLASS: Neurological Disorders REVIEW HISTORY 9/17, 12/16, 9/15, 2/15, 2/10, LOB: MCL
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Migraine Therapy P&T DATE: 12/11/2018 CLASS: Neurological Disorders REVIEW HISTORY 9/17, 12/16, 9/15, 2/15, 2/10, LOB: MCL
Headache evaluation and management after concussion. Assistant Professor
 Headache evaluation and management after concussion Juliette Preston, M.D. Assistant Professor OHSU Headache Center OVERVIEW Introduction Definition Acute post-traumatic headache Red flags Persistent post-traumatic
Headache evaluation and management after concussion Juliette Preston, M.D. Assistant Professor OHSU Headache Center OVERVIEW Introduction Definition Acute post-traumatic headache Red flags Persistent post-traumatic
Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE 1-13,14,23,24 Agents Amerge (naratriptan) 1, 2.5 tablets Axert (almotriptan) 6.25, 12.5 tablets migraine attacks with/without
Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE 1-13,14,23,24 Agents Amerge (naratriptan) 1, 2.5 tablets Axert (almotriptan) 6.25, 12.5 tablets migraine attacks with/without
Clinical Policy: Triptans Reference Number: CP.CPA.217 Effective Date: Last Review Date: Line of Business: Commercial
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.CPA.217 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Commercial Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.CPA.217 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Commercial Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Managing Headache in Acute Medicine. Ben Lovell Consultant Physician in Acute Medicine University College London Hospital
 Managing Headache in Acute Medicine Ben Lovell Consultant Physician in Acute Medicine University College London Hospital Some ED headache stats Arrive by ambulance 31% Median age 39 Worst ever headache
Managing Headache in Acute Medicine Ben Lovell Consultant Physician in Acute Medicine University College London Hospital Some ED headache stats Arrive by ambulance 31% Median age 39 Worst ever headache
Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes
 Presenter Disclosure Information 2:45 3:45pm Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes SPEAKER Gerald W. Smetana, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gerald W.Smetana, MD,
Presenter Disclosure Information 2:45 3:45pm Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes SPEAKER Gerald W. Smetana, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gerald W.Smetana, MD,
The trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) are a group of. Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias By Mark Burish, MD, PhD
 Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by SruuCyaLiGD/095xRqJ2PzgDYuM98ZB494KP9rwScvIkQrYai2aioRZDTyulujJ/fqPksscQKqke3QAnIva1ZqwEKekuwNqyUWcnSLnClNQLfnPrUdnEcDXOJLeG3sr/HuiNevTSNcdMFp1i4FoTX9EXYGXm/fCfrbTavvQSUHUH4eazE11ptLzgCyEpzDoF
Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by SruuCyaLiGD/095xRqJ2PzgDYuM98ZB494KP9rwScvIkQrYai2aioRZDTyulujJ/fqPksscQKqke3QAnIva1ZqwEKekuwNqyUWcnSLnClNQLfnPrUdnEcDXOJLeG3sr/HuiNevTSNcdMFp1i4FoTX9EXYGXm/fCfrbTavvQSUHUH4eazE11ptLzgCyEpzDoF
23, 2005 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN:
 TITLE: Migraine SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: March 23, 2005 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Jeffrey Buyten, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: David C. Teller, MD SERIES EDITORS: Francis
TITLE: Migraine SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: March 23, 2005 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Jeffrey Buyten, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: David C. Teller, MD SERIES EDITORS: Francis
Strategies in Migraine Care
 Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy
 HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
Migraine. What are the symptoms of a migraine attack?
 Migraine Migraine causes attacks of headaches, often with feeling sick or vomiting. Treatment options include: avoiding possible 'triggers', painkillers, antiinflammatory painkillers, anti-sickness medicines,
Migraine Migraine causes attacks of headaches, often with feeling sick or vomiting. Treatment options include: avoiding possible 'triggers', painkillers, antiinflammatory painkillers, anti-sickness medicines,
Headache. Headache Case. Migraine Headache. Eric Kraus, MD. Types» Without aura (common)» With aura (classic)
 Headache Eric Kraus, MD Headache Case This 23 year-old female has headaches behind the right eye that cause her to lay down in a quiet room. They have a throbbing quality and she may vomit. Migraine Headache
Headache Eric Kraus, MD Headache Case This 23 year-old female has headaches behind the right eye that cause her to lay down in a quiet room. They have a throbbing quality and she may vomit. Migraine Headache
Clinical Policy: Triptans Reference Number: CP.HNMC.217 Effective Date: Last Review Date: Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.HNMC.217 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.HNMC.217 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE. No relevant financial relationships
 Sleep and Headache Paul Mathew, MD, FAHS Director of Continuing Medical Education John R. Graham Headache Center Brigham & Women s Hospital Director of Headache Medicine Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard
Sleep and Headache Paul Mathew, MD, FAHS Director of Continuing Medical Education John R. Graham Headache Center Brigham & Women s Hospital Director of Headache Medicine Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert
 Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Triptan Quantity Limit
 *- Florida Healthy Kids Triptan Quantity Limit Override(s) Quantity Limit Approval Duration 1 year Oral Tablets Axert (almotriptan) tablets Relpax (eletriptan) tablets 6 tablets (6.25 mg) 12 tablets (12.5
*- Florida Healthy Kids Triptan Quantity Limit Override(s) Quantity Limit Approval Duration 1 year Oral Tablets Axert (almotriptan) tablets Relpax (eletriptan) tablets 6 tablets (6.25 mg) 12 tablets (12.5
SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection
 SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit
SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit
Goals. Primary Headache Syndromes. One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders
 Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Zomig. Zomig / Zomig-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
Understanding Migraines and Treatment Options. Simplified Diagnosis of Migraine. Migraine Prevalence American Migraine Study II
 Understanding Migraines and Treatment Options Deborah C. Zajac, RN-BC Center for Headache and Pain Neurological Institute Cleveland Clinic Simplified Diagnosis of Migraine Any person with a stable pattern
Understanding Migraines and Treatment Options Deborah C. Zajac, RN-BC Center for Headache and Pain Neurological Institute Cleveland Clinic Simplified Diagnosis of Migraine Any person with a stable pattern
Migraine in Children. Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014
 Migraine in Children Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014 Headaches in Children One of the most common concerns reported by children 3% for children age 3-7 years 4-11% for children age 7-11
Migraine in Children Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014 Headaches in Children One of the most common concerns reported by children 3% for children age 3-7 years 4-11% for children age 7-11
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital
 Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
Migranal Nasal Spray. Migranal Nasal Spray (dihydroergotamine) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Migranal Nasal Spray
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Migranal Nasal Spray
Maxalt. Maxalt / Maxalt-MLT (rizatriptan) Description. Section: Prescription Drugs Effective Date: April 1, 2016
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Maxalt Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 18, 2016 Maxalt Description Maxalt / Maxalt-MLT (rizatriptan)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Maxalt Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 18, 2016 Maxalt Description Maxalt / Maxalt-MLT (rizatriptan)
10/31/2017 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE DISCLOSURES WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Primary Care 67%
 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
Controlling Migraine Pain
 Migraine Stats Controlling Migraine Pain Alan Zacharias, M.D. Associated Neurologists, Boulder Community Health 303-622-3365 Women 15% Men 5% Usually starts in 2 nd and 3 rd Decade Major Impact on days
Migraine Stats Controlling Migraine Pain Alan Zacharias, M.D. Associated Neurologists, Boulder Community Health 303-622-3365 Women 15% Men 5% Usually starts in 2 nd and 3 rd Decade Major Impact on days
Headache Syndrome. Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL
 Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
Adult & Pediatric Patients. Stanford Health Care, Division Pain Medicine
 Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Zomig. Zomig / Zomig-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present
 23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present Henrik Winther Schytz 1. Cristina Tassorelli 2. Messoud Ashina 1 1 Glostrup Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Glostrup, Copenhagen,
23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present Henrik Winther Schytz 1. Cristina Tassorelli 2. Messoud Ashina 1 1 Glostrup Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Glostrup, Copenhagen,
Abortive Agents. Available Strengths. Formulary Limits. Tablet: 5mg, 10mg ODT: 5mg, 10 mg 25mg, 50mg, 100mg. 5mg/act, 20mg/act
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Migraine Therapy P&T DATE: 9/12/2017 CLASS: Neurological Disorders REVIEW HISTORY 12/16, 9/15, 2/15, 2/10, 5/07 LOB: MCL
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Migraine Therapy P&T DATE: 9/12/2017 CLASS: Neurological Disorders REVIEW HISTORY 12/16, 9/15, 2/15, 2/10, 5/07 LOB: MCL
How could I be having migraine when I don't have a headache?
 Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
Regulatory Status FDA approved indication: Migranal Nasal Spray is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine headaches with or without aura (1).
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Migranal Nasal Spray
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Migranal Nasal Spray
General Patient Information Dr. David A. Branch, M.D.
 General Patient Information Dr. David A. Branch, M.D. **Please Print** Patient Name: Date of Birth: Social Security # Email Address: Patient Address: _ City: State: Zip Code: Phone : Marital Status: S
General Patient Information Dr. David A. Branch, M.D. **Please Print** Patient Name: Date of Birth: Social Security # Email Address: Patient Address: _ City: State: Zip Code: Phone : Marital Status: S
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
GENERAL APPROACH AND CLASSIFICATION OF HEADACHES
 GENERAL APPROACH AND CLASSIFICATION OF HEADACHES CLASSIFICATION Headache is one of the most common medical complaints. Most of the population will have experienced headache, and over 5% will seek medical
GENERAL APPROACH AND CLASSIFICATION OF HEADACHES CLASSIFICATION Headache is one of the most common medical complaints. Most of the population will have experienced headache, and over 5% will seek medical
Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE
 Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture
 Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture Toomas Toomsoo, M.D. Head of the Center of Neurology East Tallinn Central Hospital 1 INTRODUCTION Cluster headache - known as trigeminal
Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture Toomas Toomsoo, M.D. Head of the Center of Neurology East Tallinn Central Hospital 1 INTRODUCTION Cluster headache - known as trigeminal
Migraine Clinical Guideline
 Migraine Clinical Guideline Definition: Migraine refers to a chronic neurological disorder characterized by episodic attacks often in association with enhanced sensitivity of the nervous system and activation
Migraine Clinical Guideline Definition: Migraine refers to a chronic neurological disorder characterized by episodic attacks often in association with enhanced sensitivity of the nervous system and activation
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Atypical presentations of cluster headache
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleAtypical presentations in cluster headachetd Rozen Atypical presentations of cluster headache TD Rozen Department
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleAtypical presentations in cluster headachetd Rozen Atypical presentations of cluster headache TD Rozen Department
The Pediatric Headache Handbook
 The Pediatric Headache Handbook For the Primary Care Physician Brought to you by the Division of Pediatric Neurology cardinalglennon.com Classification of headache patterns in children Acute onset of worst
The Pediatric Headache Handbook For the Primary Care Physician Brought to you by the Division of Pediatric Neurology cardinalglennon.com Classification of headache patterns in children Acute onset of worst
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache
 MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
Outline. Etiology. General information. Definition 4/13/2012
 Outline Dr. Susan Fralick-Ball, PsyD, MSN, RN, CH, CLNC PsychMedEd for Advance 2012 Etiology, Stages & Classifications of Migraines Differential Pathophysiology from other Headaches Current Treatment Therapies
Outline Dr. Susan Fralick-Ball, PsyD, MSN, RN, CH, CLNC PsychMedEd for Advance 2012 Etiology, Stages & Classifications of Migraines Differential Pathophysiology from other Headaches Current Treatment Therapies
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins
 Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins Page a Analgesics (painkillers) Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Prescription required Brand Name Formulation
Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins Page a Analgesics (painkillers) Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Prescription required Brand Name Formulation
COMPLEXITIES OF MIGRAINE HEADACHES
 COMPLEXITIES OF MIGRAINE HEADACHES Michael A. Rogawski, MD, PhD Professor and Chair Department of Neurology University of California, Davis Sacramento, CA MICHAEL A. ROGAWSKI, MD, PHD Disclosures Research/Grants:
COMPLEXITIES OF MIGRAINE HEADACHES Michael A. Rogawski, MD, PhD Professor and Chair Department of Neurology University of California, Davis Sacramento, CA MICHAEL A. ROGAWSKI, MD, PHD Disclosures Research/Grants:
Paediatric headaches. Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services. Brevity, levity, repetition
 Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
