Temporal Bone Pneumatization in Cystic Fibrosis: A Correlation With Genotype?
|
|
|
- Fay Rich
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Temporal Bone Pneumatization in Cystic Fibrosis: A Correlation With Genotype? Maaike C. Berkhout, MD; Cornelis J. van Rooden, PhD, MD; Ralph C. Aalbers, MD; Lahssan H. el Bouazzaoui, MD; Wytske J. Fokkens, PhD, MD; Evert Rijntjes, PhD, MD; Harry G. M. Heijerman, PhD, MD Objectives/Hypothesis: Paranasal sinus pneumatization in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) is less extensive compared to the general population and seems to be correlated to CF genotype. Interestingly, in CF patients temporal bone pneumatization (TBP) is more extensive compared to the general population, and middle ear pathology is generally uncommon in CF. It is debated whether TBP is influenced environmentally or genetically. The aim of the present study was to investigate pneumatization of the temporal bone in patients with CF and to correlate this with genotype and paranasal sinus volume. Study Design: Prospective collection of data. Methods: In 104 adult CF patients, computed tomography of the temporal bone and the paranasal sinuses was performed. TBP was graded using a validated scoring system. Patients were divided into two groups, mild and severe CF, based on their mutations in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator gene. Results: Of the 31 patients with mild CF, 71% had extensive TBP, and of the 73 patients with severe CF, 82% had extensive pneumatization of the temporal bone. TBP did not differ significantly for CF genotype, and TBP was not correlated to paranasal sinus volume. Conclusions: Whereas paranasal sinus pneumatization in CF patients seems to be related to CF genotype among other influencing factors, this study showed no correlation between TBP and CF genotype. TBP was not correlated to paranasal sinus volume. Hypothetically, in CF, pneumatization of the temporal bone is under a different influence than paranasal sinus pneumatization. Key Words: Temporal bone pneumatization, cystic fibrosis, genotype, paranasal sinus volume. Level of Evidence: 4 Laryngoscope, 124: , 2014 INTRODUCTION Paranasal sinus pneumatization in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) is decreased in comparison to the general population. 1,2 This results in smaller maxillary sinuses and smaller or even absent frontal and sphenoid sinuses in CF patients. To date the pneumatization process in the human skull is not entirely understood. It is still debated whether the postnatal pneumatization is influenced environmentally or genetically. 3 A commonly held hypothesis is that an early onset of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) results in an impaired pneumatization of the paranasal sinuses. 1,4 Because many CF patients are From the Departments of Pulmonology (M.C.B., L.H.E.B., H.G.M.H.), Radiology (C.J.V.R.), the Hague, and Otorhinolaryngology (R.C.A., E.R.), Haga Teaching Hospital, the Hague, and Department of Otorhinolaryngology (W.J.F.), Academic Medical Center Amsterdam, Amsterdam, the Netherlands. Editor s Note: This Manuscript was accepted for publication December 23, This research was sponsored by Gilead through an investigatorsponsored research grant. Gilead was not involved in the study design, the data analysis, or the interpretation of the data. The authors have no other funding, financial relationships, or conflicts of interest to disclose. Send correspondence to Maaike C. Berkhout, MD, Department of Pulmonology, Haga Teaching Hospital, Leyweg 275, 2545 CH the Hague, the Netherlands. address: m.berkhout@hagaziekenhuis.nl DOI: /lary expected to have this early onset CRS, the decreased pneumatization could be explained. However, studies comparing CF CRS patients with non-cf CRS patients showed a difference in pneumatization of the paranasal sinuses between these groups. Pneumatization patterns in non-cf CRS patients were not comparable to the pneumatization patterns in CF CRS patients. 2,5 These results could suggest that the decreased pneumatization is not secondary to the sinonasal disease, but perhaps more genetically driven. Recently Chang and colleagues showed that in CF piglets the underdevelopment of the sinuses was seen prior to the onset of sinus disease. 6 According to the authors, these results suggest that sinus hypoplasia is a direct consequence of the CF mutation as opposed to a consequence of sinonasal disease. 6 Within the CF population, decreased pneumatized paranasal sinuses have been correlated to specific mutations in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. 4,7,8 Woodworth et al. demonstrated that DF508 homozygosity is related to smaller paranasal sinuses compared with other mutations in the CFTR gene. 7 Given that the temporal bone is also subjected to pneumatization, one might expect that in CF patients this pneumatization is different from the general population and might differ for CF genotypes. Temporal bone pneumatization (TBP) begins prenatally, but primarily occurs during postnatal growth. The pneumatization
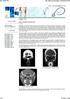
2 process starts at around 2 years of age and is completed between 10 and 15 years of age. 9 Chronic middle ear infections can impede pneumatization of the temporal bone. 10 Because the middle ear and the auditory tube are also lined with respiratory epithelium, viscous mucus and infection are expected to cause middle ear pathology in patients with CF. Moreover, one could hypothesize that sinonasal disease predisposes a CF patient to otitis media and consequently a decreased TBP. Interestingly, research in the pneumatization of the temporal bone showed a greater pneumatization in patients with CF compared to healthy controls. 8,11 Based on the abovementioned genetic influence of CF genotype on paranasal sinus pneumatization, one could hypothesize that the development of the temporal bone is also influenced by CF genotype. One study found that a greater TBP was related to delta F508 homozygosity when compared to other mutations in the CFTR gene. 8 In the present study, TBP in adult patients with CF was investigated and correlated with CF genotype and paranasal sinus volume (PSV) as a surrogate parameter of paranasal sinus pneumatization. MATERIALS AND METHODS Patients Adult patients treated in the Haga Teaching Hospital CF center, with a diagnosis of CF based on a positive sweat test and/ or genotype, were considered eligible for this study. The study was conducted from April 2011 to February 2012 and was approved by the medical ethics committee of South-West Holland. Genotype Participating patients were divided into subjects with mild CF and subjects with severe CF. Class I III mutations were considered as severe CF, and class IV V mutations were classified as mild CF. 12 Patients with two different mutations in the CFTR gene were allocated to one of these groups according to their mildest mutation. In patients with one or two unknown CFTR mutations, pancreatic status was used to allocate these patients to the mild or severe CF group. Research showed a strong relationship between CF genotype and pancreatic status, in which class I III mutations were associated with pancreatic insufficiency and class IV V mutations with pancreatic sufficiency. 13 Therefore, in this study subjects with a pancreatic insufficiency were considered to be patients with severe CF, and pancreatic-sufficient patients were assigned to the group with mild CF. Computed Tomography In every patient, computed tomography of the temporal bones and the paranasal sinuses was performed (Toshiba Aquilion 16; Toshiba Europe, London, UK). Patients were situated with their head tilted backward until the palatum durum was positioned perpendicular to the bench. Axial computed tomography was performed with a slice thickness of 0.5 mm, and images were reconstructed at 1.0 mm. The scan ranged from the upper border of the frontal sinuses to the lower part of the teeth in the maxilla. No intravenous contrast was used. TBP In this study, TBP was measured using the validated grading scale described by Han and coworkers. 14 This scale used the sigmoid sinus as a reference structure. With this method, the section where the malleoincudal complex appeared as an ice cream cone shape was used. Three parallel lines angled at 45 in the anterolateral direction were applied at positions in which each line crossed the most anterior point of the sigmoid sinus, the most lateral aspect of the sigmoid sinus, and the most posterior point of the sigmoid sinus. TBP was classified in four categories: 1) pneumatization remained anterolateral to the line that was drawn at the most anterior point; 2) pneumatization extended beyond the most anterior line, but not beyond the line crossing the most lateral aspect of the sigmoid sinus; 3) pneumatization extended to the space between the lines drawn at the most lateral aspect and at the most posterior point; and 4) pneumatization extended beyond the line drawn at the most posterior point (Fig. 1). Left and right temporal bones were analyzed separately. Assessors Two assessors (M.C.B., R.C.A.) independently measured TBP. In case of disagreement between the TBP scores of the two assessors, an experienced radiologist (C.J.V.R.) gave a decisive opinion, which was considered as the final score for TBP. All assessors were blinded for the genotype of the patients and for previous outcome parameters, such as PSV. PSV To analyze whether the pneumatization process of the temporal bone was correlated to the pneumatization process of the paranasal sinuses, the correlation between TBP and paranasal sinus pneumatization was investigated. PSV was used as a surrogate parameter for paranasal sinus pneumatization. The volume of the sinuses was analyzed with Aquarius Intuition software (TeraRecon, Foster City, CA). For each sinus, the circumference on each slice was drawn manually, whereupon the software program calculated the surface. All these surfaces were added up to generate the total volume of the sinus. Only the frontal, sphenoid, and maxillary sinuses were measured. Together these volumes were used as total PSV. Aplastic sinuses were regarded as 0 cm 3. Data and Statistics Average TBP was calculated using the left and right TBP together. To ensure the patients TBP of the left and right side did not differ considerably, a Cohen j was calculated. In case of substantial difference between the two sides, both sides were analyzed separately. The interobserver correlation was assessed by Cohen j. Consensus on the value of j is that agreement is poor if j 0.20, fair if 0.21 j 0.40, moderate if 0.41 j 0.60, substantial if 0.61 j 0.80, and good if j > An insufficient number of patients would hinder proper statistical analyses; therefore, the four categories of TBP were divided into two groups: less extensive TBP 5 score 1 to 2 and extensive TBP 5 score 2.5 to 4. The Cohen j for interobserver correlation was applied to the original four categories of TBP. To evaluate a possible correlation between TBP and genotype, a v 2 test was used. The correlation between TBP and PSV was analyzed using a Mann-Whitney U test. RESULTS Patients One hundred and four patients gave informed consent and were included in the study. The mean age of all 1683
3 unknown. One of the three patients was pancreatic insufficient and therefore assigned to the class I III mutation group, and two patients were pancreatic sufficient and were allocated to the IV V mutation group. The subject with both unknown mutations was diagnosed at 42 years, but was pancreatic insufficient secondary to pancreatitis. Because this patient had typical characteristics of mild disease, he was assigned to the class IV V mutation group. In total, 31 patients were classified with mild CF and 73 patients with severe CF. Assessors In 17 of the 208 analyzed temporal bones (8.2%), the two observers disagreed and a deciding opinion was necessary. The Cohen j for interobserver correlation was 0.85 (P 5.000). Fig. 1. At the slide where the malleoincudal complex appeared as an ice cream cone shape, three parallel lines were drawn. (1) Pneumatization remained anterolateral to the line that was drawn at the most anterior point; (2) pneumatization extended beyond the most anterior line, but not beyond the line crossing the most lateral aspect of the sigmoid sinus; (3) pneumatization extended to the space between the lines drawn at the most lateral aspect and at the most posterior point; and (4) pneumatization extended beyond the line drawn at the most posterior point. subjects was 34.8 years (standard deviation ), and 52.9% was male. Table I shows the descriptive statistics of the 104 patients separated for the two severity groups. The mean age of the patients with mild CF was significantly higher compared to the mean age of the patients with severe CF. Genotype In three patients one CFTR mutation was unknown and in one patient both of the CFTR mutations were TBP and Genotype The average TBP separated for genotype is presented in Table II. Although the percentage of extensive TBP in patients with severe CF was higher compared to patients with mild CF, this difference did not reach statistical significance (P 5.20). Comparison between the left and right TBP within one patient showed a Cohen j of 0.48, which means a moderate agreement between both sides. For this reason, TBP was analyzed separately for the left and right side of the subject. Table III presents the TBP for patients with mild CF and patients with severe CF. For both sides, TBP was not significantly different between patients with mild CF and patients with severe CF (left: P 5.20; right: P 5.96). TBP and PSV The correlation between TBP and PSV was analyzed for average TBP as well as for the left and right side separately. For the latter analysis, PSV was also separated for the left and right side of the patient. Results are displayed in Table IV. Statistical analyses showed no correlation between PSV and TBP. DISCUSSION To our knowledge, this is the first study to compare TBP in a large group of adult patients with CF. The only study in which TBP was compared between CF patients with different genotypes is the study of Seifert and TABLE I. Descriptive Statistics of 104 Adult Patients With CF. Parameter Mild CF; n 5 31, Mutation Class IV V Severe CF; n 5 73, Mutation Class I III P Mean age, yr (SD) 40.5 (10.7) 32.4 (10.4).000* Male, No. [%] 14 [45.2] 41 [56.2].304 Lung function: Mean FEV1 % predicted (SD) 66.3 (25.4) 62.1 (25.5).389 Mean FVC % predicted (SD) 87.5 (18.1) 83.0 (19.0).265 *P <.05. CF 5 cystic fibrosis; FEV1 5 forced expiratory volume at 1 second; FVC 5 forced vital capacity; SD 5 standard deviation. 1684
4 Average TBP* TABLE II. Average TBP Separated for Genotype. Mild CF; n 5 31, Mutation Class IV V Severe CF; n 5 73, Mutation Class I III Less extensive TBP, 9 (29.0) 13 (17.8) category 1 2, No. (%) Extensive TBP, 22 (71.0) 60 (82.2) category 2.5 4, No. (%) Total 31 (100) 73 (100).20 *Average TBP was calculated using the left and right TBP together. CF 5 cystic fibrosis; TBP 5 temporal bone pneumatization. coworkers. 8 They found that DF508 homozygosity correlated with greater TBP. In contrast with their results, we did not find a significant difference in TBP between patients with mild CF and patients with severe CF. However, the percentage of extensive TBP in patients with severe CF was higher compared to the patients with mild CF, thereby showing the same trend as in the study of Seifert et al. The difference in statistical results could be due to the groups used in both studies not being similar. Classification in severe and mild CF is based on the CFTR mutation classes, as mentioned in the study design. Patients with DF508 homozygosity belong to the group of severe CF patients. However, many other mutations result in severe CF. Therefore, the study of Seifert et al. is in theory not comparing patients with severe CF and patients with mild CF. Moreover, we had to subdivide the TBP into two categories, because statistical analysis was not possible using the original four categories. Seifert et al., however, did use the original four categories. For these reasons we have to be careful when comparing both studies. Whereas we did not find a correlation between genotype and TBP, in the same study population we did find a correlation between paranasal sinus pneumatization and genotype. 15 Because the mastoid air cells and the sinuses are in close contact with each other and are lined with similar mucosa, one would expect the pneumatization processes to be correlated. However, the present study did not show a correlation between PSV and TBP. This is confirmed by other studies showing no correlation between the volume of the paranasal sinuses and the mastoid air cells. 16,17 P TBP TABLE IV. Paranasal Sinus Volume and Temporal Bone Pneumatization. Paranasal Sinus Volume, cm 3, Mean (SD) Average TBP Left Right Less extensive (12.92) (7.47) (5.04) TBP, category 1 2 Extensive TBP, (11.92) (5.93) (6.88) category P SD 5 standard deviation; TBP 5 temporal bone pneumatization. To date the pneumatization process in the human skull is not entirely understood. It is debated whether the postnatal pneumatization is influenced genetically or environmentally. 3 Seifert et al. hypothesize that the defective CFTR protein directly influences the function of the mastoid air cell mucosa, with changes in gas exchange and pressure and consequently an influence on TBP. 8 Todd and Martin studied TBP in patients with CF and in the general population and found an increased TBP in patients with CF. 11 They hypothesize that the mucosa of the auditory tube and the middle ear in CF patients is different in, for example, composition of goblet cells compared to non-cf patients. Twelve years later this was confirmed by the results of Yildirim and coworkers. 10 They performed histologic examination of the temporal bone of patients with CF and found lower densities of goblet cells in the mucosa of the auditory tube and middle ear of patients with CF compared to the middle ear mucosa and auditory tube of a non-cf population. This could explain the low prevalence of ear pathology in CF patients. Moreover, they suggest a role for expression of mucin genes. Differences between mucin gene expression in the epithelium of the sinuses and in the epithelium of the middle ear might explain the discrepancy between sinonasal pathology and middle ear pathology in CF patients. The degree of pneumatization of the temporal bone does not have direct clinical implications. Indirectly, however, the results of this study can be meaningful for clinicians treating patients with CF. A decreased TBP is an objective measure for a history of chronic ear infection. 10,11 No difference in TBP between patients with mild CF and severe CF could indicate that these patients do not differ in middle ear pathology. Moreover, the overall well-preserved TABLE III. Temporal Bone Pneumatization for Left and Right Side Separately. Left* Right* TBP Mild CF, No. (%) Severe CF, No. (%) Mild CF, No. (%) Severe CF, No. (%) Less extensive TBP, category (29.0) 13 (17.8) 13 (41.9) 31 (42.5) Extensive TBP, category (71.0) 60 (82.2) 18 (58.1) 42 (57.5) Total 31 (100) 73 (100) 31 (100) 73 (100) P *Because the left and right TBP in one patient often were not identical, the left and right TBP were analyzed separately. This results in two TBP scores per patient and therefore in a total of 208 temporal bones analyzed. CF 5 cystic fibrosis; TBP 5 temporal bone pneumatization. 1685
5 TBP in CF patients 11 might indicate that CF patients do not suffer from middle ear pathology often. Furthermore, these findings challenge the belief that poor mucociliary transport induces middle ear disease. A limitation of this study was the scale that is used for grading TBP. The grading scale is based on pneumatization that is in the posterior direction. However, during analysis in some patients, the investigators noticed pneumatization in a more anterior direction. Sometimes this pneumatization was more extensive in the anterior direction than in the posterior direction. Therefore, these patients would be graded as having less extensive TBP, although they had an extensively pneumatized temporal bone. Another limitation was that information on the otologic history of the patients was not collected. Therefore, we could not correlate these retrospective data to the pneumatization of the temporal bone. However, we did investigate the middle ear on the same day the CT scan was performed. Only two of the 104 patients had signs of unilateral otitis media with effusion. From an article of Hadfield and coworkers, we learned that otitis media with effusion is scarce among patients with CF. 18 CONCLUSION Data from 104 adult patients with CF showed no difference in TBP between patients with mild CF and patients with severe CF. Moreover, no correlation between PSV and TBP was found. Hypothetically, the TBP is under a different influence than the paranasal sinus pneumatization. The exact mechanism has not yet been elucidated. BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. Gysin C, Alothman GA, Papsin BC. Sinonasal disease in cystic fibrosis: clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and management. Pediatr Pulmonol 2000;30: Kim HJ, Friedman EM, Sulek M, Duncan NO, McCluggage C. Paranasal sinus development in chronic sinusitis, cystic fibrosis, and normal comparison population: a computerized tomography correlation study. Am J Rhinol 1997;11: Lee DH, Shin JH, Lee DC. Three-dimensional morphometric analysis of paranasal sinuses and mastoid air cell system using computed tomography in pediatric population. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2012;76: Eggesbo HB, Sovik S, Dolvik S, Eiklid K, Kolmannskog F. CT characterization of developmental variations of the paranasal sinuses in cystic fibrosis. Acta Radiol 2001;42: April MM, Zinreich SJ, Baroody FM, Naclerio RM. Coronal CT scan abnormalities in children with chronic sinusitis. Laryngoscope 1993;103: Chang EH, Pezzulo AA, Meyerholz DK, et al. Sinus hypoplasia precedes sinus infection in a porcine model of cystic fibrosis. Laryngoscope 2012; 122: Woodworth BA, Ahn C, Flume PA, Schlosser RJ. The delta F508 mutation in cystic fibrosis and impact on sinus development. Am J Rhinol 2007; 21: Seifert CM, Harvey RJ, Mathews JW, et al. Temporal bone pneumatization and its relationship to paranasal sinus development in cystic fibrosis. Rhinology 2010;48: Hill CA. Ontogenetic change in temporal bone pneumatization in humans. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 2011;294: Yildirim N, Sone M, Mutlu C, Schachern PA, Paparella MM, Le CT. Histopathologic features of the temporal bone in patients with cystic fibrosis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2000;126: Todd NW, Martin WS. Temporal bone pneumatization in cystic fibrosis patients. Laryngoscope 1988;98: Zielenski J. Genotype and phenotype in cystic fibrosis. Respiration 2000; 67: Castellani C, Cuppens H, Macek M Jr, et al. Consensus on the use and interpretation of cystic fibrosis mutation analysis in clinical practice. J Cyst Fibros 2008;7: Han SJ, Song MH, Kim J, Lee WS, Lee HK. Classification of temporal bone pneumatization based on sigmoid sinus using computed tomography. Clin Radiol 2007;62: Berkhout MC, van Rooden CJ, Rijntjes E, Fokkens WJ, el Bouazzaoui LH, Heijerman HG. Sinonasal manifestations of cystic fibrosis: a correlation between genotype and phenotype? J Cyst Fibros (2013) /j.jcj Thomas A, Raman R. A comparative study of the pneumatization of the mastoid air cells and the frontal and maxillary sinuses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1989;10:S Kim J, Song SW, Cho JH, Chang KH, Jun BC. Comparative study of the pneumatization of the mastoid air cells and paranasal sinuses using three-dimensional reconstruction of computed tomography scans. Surg Radiol Anat 2010;32: Hadfield PJ, Rowe-Jones JM, Mackay IS. The prevalence of nasal polyps in adults with cystic fibrosis. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 2000;25:
Chronic osteitic rhinosinusitis as a manifestation of cystic fibrosis: A case report
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2014; 44: 243-7 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2014.44.3.243 Chronic osteitic rhinosinusitis as a manifestation of cystic fibrosis: A case report Aniket B. Jadhav 1, *, Alan
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2014; 44: 243-7 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2014.44.3.243 Chronic osteitic rhinosinusitis as a manifestation of cystic fibrosis: A case report Aniket B. Jadhav 1, *, Alan
Relationship between Severity of Nasal Septum Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Cells and Chronic Otitis Media
 Original Article J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 20, Issu 2; Feb 2018. P:27-32 Relationship between Severity of Nasal Septum Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Cells and Chronic Otitis Media E. Shobeiri
Original Article J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 20, Issu 2; Feb 2018. P:27-32 Relationship between Severity of Nasal Septum Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Cells and Chronic Otitis Media E. Shobeiri
OSTEITIS IN CRS. Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a
 OSTEITIS IN CRS Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a ROAD MAP Definition. pathophysiology. Diagnosis. Grading systems. Clinical implications. Management. OSTEITIS Presence of new bone formation,
OSTEITIS IN CRS Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a ROAD MAP Definition. pathophysiology. Diagnosis. Grading systems. Clinical implications. Management. OSTEITIS Presence of new bone formation,
Crista galli sinusitis a radiological impression or a real clinical entity
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 6, No. 23, July - September 2016 ORIGINAL STUDY Crista galli sinusitis a radiological impression or a real clinical entity Claudiu Manea 1,2, Ranko Mladina 3 1 CESITO
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 6, No. 23, July - September 2016 ORIGINAL STUDY Crista galli sinusitis a radiological impression or a real clinical entity Claudiu Manea 1,2, Ranko Mladina 3 1 CESITO
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Cystic Fibrosis and Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cystic Fibrosis and Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Relationship Between Nasal Polyposis and Likelihood of Revision Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Cystic Fibrosis Scott Rickert, MD;
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cystic Fibrosis and Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Relationship Between Nasal Polyposis and Likelihood of Revision Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Cystic Fibrosis Scott Rickert, MD;
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013
 FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
Prevalence of Radiologic Superior Canal Dehiscence in Normal Ears and Ears with Chronic Otitis Media
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Prevalence of Radiologic Superior Canal Dehiscence in Normal Ears and Ears with Chronic Otitis Media Young
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Prevalence of Radiologic Superior Canal Dehiscence in Normal Ears and Ears with Chronic Otitis Media Young
Canine Fossa Puncture for Severe Maxillary Disease in Unilateral Chronic Sinusitis With Nasal Polyp
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Canine Fossa Puncture for Severe Maxillary Disease in Unilateral Chronic Sinusitis With Nasal Polyp Jang
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Canine Fossa Puncture for Severe Maxillary Disease in Unilateral Chronic Sinusitis With Nasal Polyp Jang
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page 1390-1394 Anatomical Variations of Nasal Structures in Chronic Rhinosinusitis as Detected by Computed Tomography Scan Omar Adnan Hasan,
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page 1390-1394 Anatomical Variations of Nasal Structures in Chronic Rhinosinusitis as Detected by Computed Tomography Scan Omar Adnan Hasan,
Review Article The Prevalence of Concha Bullosa and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship to Maxillary Sinusitis by Volumetric Tomography
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Computed Tomographic Staging and the Fate of the Dependent Sinuses in Revision Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 Computed Tomographic Staging and the Fate of the Dependent es in Revision Endoscopic Surgery Neil Bhattacharyya, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objectives: To determine the patterns of disease recurrence in chronic
Computed Tomographic Staging and the Fate of the Dependent es in Revision Endoscopic Surgery Neil Bhattacharyya, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objectives: To determine the patterns of disease recurrence in chronic
Paranasal sinuses are empty spaces located within
 Total aplasia of the paranasal sinuses Hakan Korkmaz, M.D. and Mukadder Korkmaz, M.D. ABSTRACT Although a variety of theories have been proposed about functions of the paranasal sinuses, not one is clear
Total aplasia of the paranasal sinuses Hakan Korkmaz, M.D. and Mukadder Korkmaz, M.D. ABSTRACT Although a variety of theories have been proposed about functions of the paranasal sinuses, not one is clear
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 09 Page September 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i9.52 Relationship of Agger Nasi Cell and Uncinate
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i9.52 Relationship of Agger Nasi Cell and Uncinate
The Relation between Anatomical Variations of Osteomeatal Complex & Nasal Structures and Chronic Sinusitis by Computed Tomography
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2015; 3(2): 16-20 Published online March 6, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20150302.12 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN:
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2015; 3(2): 16-20 Published online March 6, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20150302.12 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN:
Mai ElMallah,MD Updates in Pediatric Pulmonary Care XII: An Interdisciplinary Program April 13, 2012
 Mai ElMallah,MD Updates in Pediatric Pulmonary Care XII: An Interdisciplinary Program April 13, 2012 Recognize the importance of Pulmonary Function Testing in Cystic Fibrosis Be aware of different types
Mai ElMallah,MD Updates in Pediatric Pulmonary Care XII: An Interdisciplinary Program April 13, 2012 Recognize the importance of Pulmonary Function Testing in Cystic Fibrosis Be aware of different types
Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma Nasal Type: Detection by Computed Tomography Features
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma Nasal Type: Detection by Computed Tomography Features Yin-Ping
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma Nasal Type: Detection by Computed Tomography Features Yin-Ping
Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells, Temporal Bone, Ethmoid and Sphenoid Sinuses. Any Correlation?
 DOI 10.1007/s12070-014-0745-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells, Temporal Bone, Ethmoid and Sphenoid Sinuses. Any Correlation? Khalid Hindi Sarmad Alazzawi Rajagopalan Raman Narayanan
DOI 10.1007/s12070-014-0745-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells, Temporal Bone, Ethmoid and Sphenoid Sinuses. Any Correlation? Khalid Hindi Sarmad Alazzawi Rajagopalan Raman Narayanan
An epidemiologic study of factors associated with nasal septum deviation by computed tomography scan: a cross sectional study
 Mohebbi et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders 2012, 12:15 RESEARCH ARTICLE An epidemiologic study of factors associated with nasal septum deviation by computed tomography scan: a cross sectional study
Mohebbi et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders 2012, 12:15 RESEARCH ARTICLE An epidemiologic study of factors associated with nasal septum deviation by computed tomography scan: a cross sectional study
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Ighodaro O. Emmanuel, Ehigiamusoe O. Festus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lund-Mackay Scoring of Incidental Paranasal Sinus Collection on Computed Tomography Scan of Head and Neck in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Nigeria Ighodaro O. Emmanuel, Ehigiamusoe
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lund-Mackay Scoring of Incidental Paranasal Sinus Collection on Computed Tomography Scan of Head and Neck in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Nigeria Ighodaro O. Emmanuel, Ehigiamusoe
Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem
 Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
CT of the paranasal sinuses is not a valid indicator for sinus surgery in CF patients
 Journal of Cystic Fibrosis 11 (2012) 93 99 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcf Original Article CT of the paranasal sinuses is not a valid indicator for sinus surgery in CF patients Jacob Rasmussen a,1, Kasper
Journal of Cystic Fibrosis 11 (2012) 93 99 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcf Original Article CT of the paranasal sinuses is not a valid indicator for sinus surgery in CF patients Jacob Rasmussen a,1, Kasper
Evaluation of the Change in Recent Diagnostic Criteria of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Cross-sectional Study
 Abhishek Ramadhin REVIEW ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1246 Evaluation of the Change in Recent Diagnostic Criteria of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Cross-sectional Study Abhishek Ramadhin ABSTRACT There
Abhishek Ramadhin REVIEW ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1246 Evaluation of the Change in Recent Diagnostic Criteria of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Cross-sectional Study Abhishek Ramadhin ABSTRACT There
"The prevalence and CT detection of Onodi cell types."
 "The prevalence and CT detection of Onodi cell types." Poster No.: C-1566 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Chmielik 1, L. Chmielik 2, R. Boguslawska-Walecka 1 ; 1 Warszawa/ PL, 2
"The prevalence and CT detection of Onodi cell types." Poster No.: C-1566 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Chmielik 1, L. Chmielik 2, R. Boguslawska-Walecka 1 ; 1 Warszawa/ PL, 2
Variation in frontal cells in relation to chronic frontal sinusitis
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 244-71 P-ISJN: A472-04, E -ISJN: A472-01 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume, Issue 1-2019 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2019.0.01.00
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 244-71 P-ISJN: A472-04, E -ISJN: A472-01 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume, Issue 1-2019 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2019.0.01.00
Practice patterns regarding noninvasive rhinosinusitis in the immunosuppressed patient population
 Practice patterns regarding noninvasive rhinosinusitis in the immunosuppressed patient population Zara M. Patel, Emory University Journal Title: Allergy & Rhinology Volume: Volume 4, Number 3 Publisher:
Practice patterns regarding noninvasive rhinosinusitis in the immunosuppressed patient population Zara M. Patel, Emory University Journal Title: Allergy & Rhinology Volume: Volume 4, Number 3 Publisher:
Study of correlation between patient symptomatology and incidental paranasal sinus abnormalities detected on CT & MRI Brain imaging
 Original article Study of correlation between patient symptomatology and incidental paranasal sinus abnormalities detected on CT & MRI Brain imaging 1 DR. SHAIKH IMRAN NIZAMUDDIN, 2 DR. Y.P.SACHDEV*, 3
Original article Study of correlation between patient symptomatology and incidental paranasal sinus abnormalities detected on CT & MRI Brain imaging 1 DR. SHAIKH IMRAN NIZAMUDDIN, 2 DR. Y.P.SACHDEV*, 3
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
Reliability of computed tomography scans in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis
 Original papers Reliability of computed tomography scans in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis Marcin Frączek 1, A D, F, Marcin Masalski 1, B, B, E, Maciej Guziński 1 Department of Otolaryngology,
Original papers Reliability of computed tomography scans in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis Marcin Frączek 1, A D, F, Marcin Masalski 1, B, B, E, Maciej Guziński 1 Department of Otolaryngology,
Frontal Sinus Drillout (Modified Lothrop Procedure): Long-Term Results in 204 Patients
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Frontal Sinus Drillout (Modified Lothrop Procedure): Long-Term Results in 204 Patients Jonathan Y. Ting,
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Frontal Sinus Drillout (Modified Lothrop Procedure): Long-Term Results in 204 Patients Jonathan Y. Ting,
2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Efficiency
 Measure #334: Adult Sinusitis: More than One Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan Within 90 Days for Chronic Sinusitis (Overuse) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2017 OPTIONS
Measure #334: Adult Sinusitis: More than One Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan Within 90 Days for Chronic Sinusitis (Overuse) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2017 OPTIONS
Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision
 THIEME Original Research 73 Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision Jan Alessandro Socher 1 Jonas Mello 2 Barbara Batista Baltha 2 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
THIEME Original Research 73 Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision Jan Alessandro Socher 1 Jonas Mello 2 Barbara Batista Baltha 2 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
 Measure #334: Adult Sinusitis: More than One Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan Within 90 Days for Chronic Sinusitis (Overuse) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS
Measure #334: Adult Sinusitis: More than One Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan Within 90 Days for Chronic Sinusitis (Overuse) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS
Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Videler, W.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Videler, W.
Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses
 14. Sommerschule Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses Bettlach 24.08.2018 Christoph Schlegel Conventional Radiology NNH-Status: okzipito-frontal: frontal sinus, anterior ethmoid okzipito-nasal : maxillary
14. Sommerschule Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses Bettlach 24.08.2018 Christoph Schlegel Conventional Radiology NNH-Status: okzipito-frontal: frontal sinus, anterior ethmoid okzipito-nasal : maxillary
Image quality and dose reduction in sinus computed tomography using iterative reconstruction: a cadaver study*
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Image quality and dose reduction in sinus computed tomography using iterative reconstruction: a cadaver study* Adam J. Kimple 1, Stanley W. McClurg 1, Benjamin Y. Huang 2, Satyan
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Image quality and dose reduction in sinus computed tomography using iterative reconstruction: a cadaver study* Adam J. Kimple 1, Stanley W. McClurg 1, Benjamin Y. Huang 2, Satyan
Rhinosinusitis. John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD
 Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study
 Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study Mark C. DeLano, F. Y. Fun, and S. James Zinreich PURPOSE: To delineate the relationship between the optic nerves
Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study Mark C. DeLano, F. Y. Fun, and S. James Zinreich PURPOSE: To delineate the relationship between the optic nerves
Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
Inter-Observer and Intra-Observer Variability In the Assessment of The Paranasal Sinuses Radiographs
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 5 Number 2 Inter-Observer and Intra-Observer Variability In the Assessment of The Paranasal Sinuses Radiographs A Norie, R Ahmad, W Liew, M
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 5 Number 2 Inter-Observer and Intra-Observer Variability In the Assessment of The Paranasal Sinuses Radiographs A Norie, R Ahmad, W Liew, M
A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis.
 DOI: 10.2127/aimdr.201..2.EN1 Original Article ISSN (O):239-222; ISSN (P):239-21 A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Smruti Swain 1 1 Associate Professor, Department
DOI: 10.2127/aimdr.201..2.EN1 Original Article ISSN (O):239-222; ISSN (P):239-21 A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Smruti Swain 1 1 Associate Professor, Department
The frequency of nasal septal deviation and concha bullosa and their relationship with maxillary sinusitis based on CBCT finding
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 11:152-156 The frequency of nasal septal deviation and concha bullosa and their
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 11:152-156 The frequency of nasal septal deviation and concha bullosa and their
Abnormal direction of internal auditory canal and vestibulocochlear nerve
 Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2004 Abnormal direction of internal auditory canal and vestibulocochlear nerve Shin Kariya kazunori Nishizaki Hirofumi Akagi Michael M. Paparella
Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2004 Abnormal direction of internal auditory canal and vestibulocochlear nerve Shin Kariya kazunori Nishizaki Hirofumi Akagi Michael M. Paparella
Spheno-Ethmoidectomy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Endoscopic Management Of A Giant Ethmoid Mucocele
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
RoleofAllergyinNasalPolyposis. Role of Allergy in Nasal Polyposis
 Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Relation between Nasal Septal Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells A Computerised Tomographic Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between Nasal Septal Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells A Computerised Tomographic Study N. Vinay Kumar 1, T. S. Gugapriya 2 ISSN (0): 2455-5274; ISSN (P): 2617-5207
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between Nasal Septal Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells A Computerised Tomographic Study N. Vinay Kumar 1, T. S. Gugapriya 2 ISSN (0): 2455-5274; ISSN (P): 2617-5207
International Journal of Biological & Medical Research
 Int J Biol Med Res.2015;6(1):4775-4781 Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International Journal of Biological & Medical Research Journal homepage: www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect
Int J Biol Med Res.2015;6(1):4775-4781 Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International Journal of Biological & Medical Research Journal homepage: www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect
A radiological study of anatomical variations in ostiomeatal complex in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Rajneesh et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):528-533 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Rajneesh et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):528-533 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
Article ID: WMC ISSN Cystic Fibrosis Otolaryngologist Perspective
 Article ID: WMC003278 ISSN 2046-1690 ENT Scholar Cystic Fibrosis Otolaryngologist Perspective Corresponding Author: Dr. Balasubramanian Thiagarajan, Professor, Department of otolaryngology, Stanley Medical
Article ID: WMC003278 ISSN 2046-1690 ENT Scholar Cystic Fibrosis Otolaryngologist Perspective Corresponding Author: Dr. Balasubramanian Thiagarajan, Professor, Department of otolaryngology, Stanley Medical
The sinonasal involvement is one of the most common
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol. V.71, n.6, 698-704, nov./dec. 2005 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis in patients with cystic fibrosis: correlation between anamnesis, nasal endoscopy and computed
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol. V.71, n.6, 698-704, nov./dec. 2005 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis in patients with cystic fibrosis: correlation between anamnesis, nasal endoscopy and computed
Investigation of the incidence of Eustachian tube dysfunction in patients with sinonasal disease*
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Investigation of the incidence of Eustachian tube dysfunction in patients with sinonasal disease* C.E. Rennie 1, M. Gutierrez 2, Y. Darby 1, V.J. Lund 1 Rhinology Online, Vol 1: 85-89,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Investigation of the incidence of Eustachian tube dysfunction in patients with sinonasal disease* C.E. Rennie 1, M. Gutierrez 2, Y. Darby 1, V.J. Lund 1 Rhinology Online, Vol 1: 85-89,
Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases
 Original article: Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases 1 Dr. Vijay Kumar Kalra, 2 Dr. Samar Pal Singh Yadav, 3 Dr. Swati 1Assistant Professor, 2 Senior Professor
Original article: Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases 1 Dr. Vijay Kumar Kalra, 2 Dr. Samar Pal Singh Yadav, 3 Dr. Swati 1Assistant Professor, 2 Senior Professor
Pediatric Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in a Tertiary Government Hospital: Patient Profile and Surgical Indications
 Philippine Journal Of Otolaryngology-Head And Neck Surgery Vol. 4 No. January June ichael Joseph C. David, D Gil. Vicente, D, Antonio H. Chua, D, Jose R. Reyes emorial edical Center St. Luke s edical Center
Philippine Journal Of Otolaryngology-Head And Neck Surgery Vol. 4 No. January June ichael Joseph C. David, D Gil. Vicente, D, Antonio H. Chua, D, Jose R. Reyes emorial edical Center St. Luke s edical Center
ORIGINAL ARTICLE RELATIONSHIP OF CONCHA BULLOSA WITH OSTEOMEATAL UNIT BLOCKAGE. TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY IN 200 PATIENTS.
 RELATIONSHIP OF CONCHA BULLOSA WITH OSTEOMEATAL UNIT BLOCKAGE. TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY IN 200 PATIENTS. Shrikrishna B H 1, Jyothi A C 2, Sanjay G 3, Sandeep Samson G 4. 1. Associate Professor, Department of
RELATIONSHIP OF CONCHA BULLOSA WITH OSTEOMEATAL UNIT BLOCKAGE. TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY IN 200 PATIENTS. Shrikrishna B H 1, Jyothi A C 2, Sanjay G 3, Sandeep Samson G 4. 1. Associate Professor, Department of
Eosinophilic Rhinosinusitis is Not a Disease of Ostiomeatal Occlusion
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Eosinophilic Rhinosinusitis is Not a Disease of Ostiomeatal Occlusion Kornkiat Snidvongs, MD; David Chin,
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Eosinophilic Rhinosinusitis is Not a Disease of Ostiomeatal Occlusion Kornkiat Snidvongs, MD; David Chin,
A Computer-Assisted Anatomical Study of the Nasofrontal Region
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. A Computer-Assisted Anatomical Study of the Nasofrontal Region
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. A Computer-Assisted Anatomical Study of the Nasofrontal Region
High-Frequency Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. High-Frequency Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children Kaalan Johnson, MD; Meredith Tabangin, MPH; Jareen
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. High-Frequency Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children Kaalan Johnson, MD; Meredith Tabangin, MPH; Jareen
The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Association with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Deviated Nasal Septum and Osteomeatal Complex Obstruction
 1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Association with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Deviated Nasal Septum and Osteomeatal Complex Obstruction Fatma
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Association with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Deviated Nasal Septum and Osteomeatal Complex Obstruction Fatma
Limitations of balloon sinuplasty in frontal sinus surgery
 Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2011) 268:1463 1467 DOI 10.1007/s00405-011-1626-7 RHINOLOGY Limitations of balloon sinuplasty in frontal sinus surgery S. Heimgartner J. Eckardt D. Simmen H. R. Briner A. Leunig
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2011) 268:1463 1467 DOI 10.1007/s00405-011-1626-7 RHINOLOGY Limitations of balloon sinuplasty in frontal sinus surgery S. Heimgartner J. Eckardt D. Simmen H. R. Briner A. Leunig
2016 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Sinusitis (for patients aged 18 and older)
 2016 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Sinusitis (for patients aged 18 and older) IMPORTANT: Any measure with a 0% performance rate (100% for inverse measures) is not considered
2016 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Sinusitis (for patients aged 18 and older) IMPORTANT: Any measure with a 0% performance rate (100% for inverse measures) is not considered
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Anatomical Study of the Middle Meatus with Emphasis to the Maxillary Ostium and Their Clinical
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Anatomical Study of the Middle Meatus with Emphasis to the Maxillary Ostium and Their Clinical
3D Cone beam CT & Digital Radiography Dedicated to Otorhinolaryngology
 3D Cone beam CT & Digital Radiography Dedicated to Otorhinolaryngology Multi-functional imaging solution3 RAYSCAN m is an unique 2-in-1 imaging solution, combining Cone Beam CT and Digital Radiography,
3D Cone beam CT & Digital Radiography Dedicated to Otorhinolaryngology Multi-functional imaging solution3 RAYSCAN m is an unique 2-in-1 imaging solution, combining Cone Beam CT and Digital Radiography,
Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS
 Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN 2250-0359 A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS * Sankaranaryanan Gopalakrishnan, * Satheesh kumar * Kilpaulk Medical College, Royepettah
Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN 2250-0359 A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS * Sankaranaryanan Gopalakrishnan, * Satheesh kumar * Kilpaulk Medical College, Royepettah
Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis: A 15-Year Experience With 29 Patients
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis: A 15-Year Experience With 29 Patients Marcus M. Monroe, MD; Max McLean, BA;
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis: A 15-Year Experience With 29 Patients Marcus M. Monroe, MD; Max McLean, BA;
Modification of the Lund-Kennedy Endoscopic Scoring System Improves Its Reliability and Correlation With Patient-Reported Outcome Measures
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Modification of the Lund-Kennedy Endoscopic Scoring System Improves Its Reliability and Correlation With
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Modification of the Lund-Kennedy Endoscopic Scoring System Improves Its Reliability and Correlation With
Mucocele of paranasal sinuses
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Efficiency
 Quality ID #333: Adult Sinusitis: Computerized Tomography (CT) for Acute Sinusitis (Overuse) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
Quality ID #333: Adult Sinusitis: Computerized Tomography (CT) for Acute Sinusitis (Overuse) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
Agenesis of paranasal sinuses and nasal nitric oxide in primary ciliary dyskinesia
 Eur Respir J 2011; 37: 566 571 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00068810 CopyrightßERS 2011 Agenesis of paranasal sinuses and nasal nitric oxide in primary ciliary dyskinesia M. Pifferi*, A. Bush #, D. Caramella
Eur Respir J 2011; 37: 566 571 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00068810 CopyrightßERS 2011 Agenesis of paranasal sinuses and nasal nitric oxide in primary ciliary dyskinesia M. Pifferi*, A. Bush #, D. Caramella
ACUTE MASTOIDITIS IN CHILDREN: SUSCEPTIBILITY FACTORS AND MANAGEMENT
 & ACUTE MASTOIDITIS IN CHILDREN: SUSCEPTIBILITY FACTORS AND MANAGEMENT Slobodan Spremo*, Biljana Udovčić Clinic for Otorhinolaryngology, Clinic Center in Banja Luka, Zdrave Korde 1, 78000 Banja Luka, Bosnia
& ACUTE MASTOIDITIS IN CHILDREN: SUSCEPTIBILITY FACTORS AND MANAGEMENT Slobodan Spremo*, Biljana Udovčić Clinic for Otorhinolaryngology, Clinic Center in Banja Luka, Zdrave Korde 1, 78000 Banja Luka, Bosnia
Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
1. Introduction. Obstructive lung disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in cystic fibrosis
 1. Introduction Obstructive lung disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in cystic fibrosis (CF) [1]. With time it has become increasingly clear that CF lung disease is present very
1. Introduction Obstructive lung disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in cystic fibrosis (CF) [1]. With time it has become increasingly clear that CF lung disease is present very
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Factors for Maxillary Sinus Volume and Craniofacial Anatomical Features in Adults With Chronic Rhinosinusitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors for Maxillary Sinus Volume and Craniofacial Anatomical Features in Adults With Chronic Rhinosinusitis Seok Hyun Cho, MD; Tae Heon Kim, MD; Kyung Rae Kim, MD; Jong-Min Lee, hd;
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors for Maxillary Sinus Volume and Craniofacial Anatomical Features in Adults With Chronic Rhinosinusitis Seok Hyun Cho, MD; Tae Heon Kim, MD; Kyung Rae Kim, MD; Jong-Min Lee, hd;
A Cross Sectional Study of Normal Variations of Sphenoid Sinus Through CT-Scan in North Karnataka, India
 Original Article A Cross Sectional Study of Normal Variations of Sphenoid Sinus Through CT-Scan in North Karnataka, India DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2016/20940.2180 Anatomy Section Manisha S. Chougule, Preetam
Original Article A Cross Sectional Study of Normal Variations of Sphenoid Sinus Through CT-Scan in North Karnataka, India DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2016/20940.2180 Anatomy Section Manisha S. Chougule, Preetam
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 10 Page October 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v6i1.145 Role of VR 3D Imaging in temporal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v6i1.145 Role of VR 3D Imaging in temporal
Preface... Contributors... 1 Embryology... 3
 Contents Preface... Contributors... vii xvii I. Pediatrics 1 Embryology... 3 Pearls... 3 Branchial Arch Derivatives... 3 Branchial Arch Anomalies: Cysts, Sinus, Fistulae... 4 Otologic Development... 4
Contents Preface... Contributors... vii xvii I. Pediatrics 1 Embryology... 3 Pearls... 3 Branchial Arch Derivatives... 3 Branchial Arch Anomalies: Cysts, Sinus, Fistulae... 4 Otologic Development... 4
Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment
 Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment INFECTION INFLAMMATION Predisposing Factors Anatomical variations Allergic rhinitis Acute sinusitis Immune deficiency Rhinosinusitis Non-allergic rhinitis Chronic sinusitis
Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment INFECTION INFLAMMATION Predisposing Factors Anatomical variations Allergic rhinitis Acute sinusitis Immune deficiency Rhinosinusitis Non-allergic rhinitis Chronic sinusitis
Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis
 Original article: Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis G.S. Thalor Senior Specialist (MS) (department of Oto Rhino Laryngology), Govt. S.K. Hospital, Sikar, Rajasthan, India. Corresponding
Original article: Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis G.S. Thalor Senior Specialist (MS) (department of Oto Rhino Laryngology), Govt. S.K. Hospital, Sikar, Rajasthan, India. Corresponding
Transnasal Endoscopic Medial Maxillary Sinus Wall Transposition With Preservation of Structures
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Transnasal Endoscopic Medial Maxillary Sinus Wall Transposition With Preservation of Structures Alice Z.
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Transnasal Endoscopic Medial Maxillary Sinus Wall Transposition With Preservation of Structures Alice Z.
Dose-dependent effects of tobramycin in an animal model of Pseudomonas sinusitis Am J Rhino Jul-Aug; 21(4):423-7
 AMINOGLYCOSIDES Dose-dependent effects of tobramycin in an animal model of Pseudomonas sinusitis Am J Rhino. 2007 Jul-Aug; 21(4):423-7 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17882910 Evaluation of the in-vivo
AMINOGLYCOSIDES Dose-dependent effects of tobramycin in an animal model of Pseudomonas sinusitis Am J Rhino. 2007 Jul-Aug; 21(4):423-7 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17882910 Evaluation of the in-vivo
Histopathology of Nasal Masses
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Hemant Chopra, 2 Kapil Dua, 3 Neha Chopra, 4 Vikrant Mittal AIJCR Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Professor and Head, Dayanand Medical College, Ludhiana,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Hemant Chopra, 2 Kapil Dua, 3 Neha Chopra, 4 Vikrant Mittal AIJCR Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Professor and Head, Dayanand Medical College, Ludhiana,
Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis Involving Frontal Sinus: A Prospective Study comparing Surgical Modalities
 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1141 H Verma et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis Involving Frontal Sinus: A Prospective Study comparing Surgical Modalities H Verma, Rijuneeta, AK Gupta, A Chakrabarti
10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1141 H Verma et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis Involving Frontal Sinus: A Prospective Study comparing Surgical Modalities H Verma, Rijuneeta, AK Gupta, A Chakrabarti
ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma. Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal
 Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(1) 63-68 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal Alexandria Ear Hospital Alexandria Egypt (AB,
Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(1) 63-68 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal Alexandria Ear Hospital Alexandria Egypt (AB,
A review of endoscopic sinus surgery in the management of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis in pediatric cystic fibrosis patients
 Borgis New Med 2016; 20(4): 119-125 DOI: 10.5604/14270994.1228142 A review of endoscopic sinus surgery in the management of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis in pediatric cystic fibrosis patients
Borgis New Med 2016; 20(4): 119-125 DOI: 10.5604/14270994.1228142 A review of endoscopic sinus surgery in the management of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis in pediatric cystic fibrosis patients
Human, Child (15-16 months)
 Human, Child (15-16 months) Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-111 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations: In general, the molding process has
Human, Child (15-16 months) Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-111 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations: In general, the molding process has
Reproducibility of 3 mm-slice-thick Reconstruction of Paranasal Sinus Computed Tomography Scans. Karjalainen, Matti.
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Reproducibility of 3 mm-slice-thick Reconstruction of Paranasal Sinus Computed Tomography Scans Karjalainen, Matti 2016 Karjalainen, M, Julkunen, A, Markkola, A, Prasun, D, Huhtala,
https://helda.helsinki.fi Reproducibility of 3 mm-slice-thick Reconstruction of Paranasal Sinus Computed Tomography Scans Karjalainen, Matti 2016 Karjalainen, M, Julkunen, A, Markkola, A, Prasun, D, Huhtala,
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
Original Article Effect of lamina papyracea ingression on orbito-ocular complications after functional endoscopic sinus surgery
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):10317-10321 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0025371 Original Article Effect of lamina papyracea ingression on orbito-ocular complications after functional endoscopic sinus
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):10317-10321 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0025371 Original Article Effect of lamina papyracea ingression on orbito-ocular complications after functional endoscopic sinus
Introduction. Ophthalmic manifestations can result from a myriad of Non Sinogenic and Sinogenic Disease :
 Ophthalmic Manifestations of Paranasal Sinus Disease; A Clinical Grading System Surayie Al Dousary, MD Associate Professor Director Rhinology Research Chair & Fatma Al Anazy, MD Associate Professor Rhinology
Ophthalmic Manifestations of Paranasal Sinus Disease; A Clinical Grading System Surayie Al Dousary, MD Associate Professor Director Rhinology Research Chair & Fatma Al Anazy, MD Associate Professor Rhinology
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.102 Pneumatization of the Sphenoid Sinus:
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.102 Pneumatization of the Sphenoid Sinus:
A Clicking Larynx: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges
 The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Case Report A Clicking Larynx: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges Derrek A. Heuveling, MD, PhD ; Maarten
The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Case Report A Clicking Larynx: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges Derrek A. Heuveling, MD, PhD ; Maarten
Chapter Five. 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM.
 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
Review Article The Prevalence of Concha Bullosa and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship to Maxillary Sinusitis by Volumetric Tomography
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE
 PROFESSOR DR SALINA HUSAIN DEPUTY HEAD DEPARTMENT OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD NECK SURGERY UKM MEDICAL CENTRE MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT
PROFESSOR DR SALINA HUSAIN DEPUTY HEAD DEPARTMENT OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD NECK SURGERY UKM MEDICAL CENTRE MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT
Major inflammatory patterns of chronic sinonasal diseases and their. accompanied anatomical variations; CT scan review
 Major inflammatory patterns of chronic sinonasal diseases and their accompanied anatomical variations; CT scan review Dr. Qays Ahmed Hassan AL-Timimy ABSTRACT Background: Because of wide use of Functional
Major inflammatory patterns of chronic sinonasal diseases and their accompanied anatomical variations; CT scan review Dr. Qays Ahmed Hassan AL-Timimy ABSTRACT Background: Because of wide use of Functional
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP SINUS CT Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70486, 70487, 70488, 76380
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP SINUS CT Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70486, 70487, 70488, 76380
NASAL OBSTRUCTION. Andy Whyte PERTH RADIOLOGICAL CLINIC UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE UNIVERSITY OF WA
 NASAL OBSTRUCTION Andy Whyte PERTH RADIOLOGICAL CLINIC UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE UNIVERSITY OF WA INTRODUCTION sinonasal imaging focuses on structural abnormalities of the POSTERIOR (BONY 3/4 ) of the nose
NASAL OBSTRUCTION Andy Whyte PERTH RADIOLOGICAL CLINIC UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE UNIVERSITY OF WA INTRODUCTION sinonasal imaging focuses on structural abnormalities of the POSTERIOR (BONY 3/4 ) of the nose
