Prevalence of Radiologic Superior Canal Dehiscence in Normal Ears and Ears with Chronic Otitis Media
|
|
|
- Phoebe Alexander
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Prevalence of Radiologic Superior Canal Dehiscence in Normal Ears and Ears with Chronic Otitis Media Young W. Cho, MD; Byoung S. Shim, MD; Ji W. Kim, MD; Tae S. Kim, MD; Joong H. Ahn, MD; Jong W. Chung, MD; Kwang-Sun Lee, MD; Tae H. Yoon, MD; Hong J. Park, MD Objectives/Hypothesis: Although labyrinth fistulae are caused mostly by cholesteatoma, they can occur in longstanding chronic otitis media (COM) without cholesteatoma. We aimed to compare the prevalence of radiologic SCD on computed tomography (CT) between normal ears and contralateral COM ears in patients with unilateral COM and to assess the prevalence of superior canal dehiscence (SCD) according to the age. Study Design: Case series with comparison performed at a tertiary care academic referral center. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed consecutive temporal bone CT scans of 759 patients with unilateral COM between 2009 and The mean (6 standard deviation) age was 48 years (614 years). Images were independently evaluated by two otologists, and the bone overlying the superior canal was characterized as normal, suspicious, or definite SCD. Results: The prevalence (3.4%) of definite SCD in COM ears was significantly higher than that (0.3%) in normal ears. The prevalence (6.6%) of suspicious or definite SCD in COM ears was also higher than that (1.2%) in normal ears. There was no correlation between the prevalence of SCD and age in either normal or COM ears. All of the normal ears with suspicious or definite SCD also showed contralateral suspicious or definite SCD (bilateral involvement). Conclusions: Our present findings suggest that the COM is related to the presence of SCD. The roof of the temporal bone may become thin by the failure of postnatal bone development and susceptible to chronic brain pulsation and pressure exerted by the temporal lobe in COM ears. Key Words: Semicircular canals, dehiscence, chronic otitis media, radiology, computerized tomography. Level of Evidence: 4 Laryngoscope, 124: , 2014 INTRODUCTION Minor et al. first described superior canal dehiscence (SCD) syndrome, which is characterized by vertiginous symptoms induced by loud sounds and hyperacusis. 1 It is not clear whether SCD is a congenital or acquired condition, and it has been reported that developmental anomalies are a possible cause. 2,3 However, it has also been reported that the radiologic prevalence of SCD increases among older age groups, suggesting that SCD is an acquired condition. 3 Recently, it was reported that the mastoid air-cell volume in the SCD side was significantly smaller than the control From the Department of Otolaryngology (Y.W.C., J.W.K., J.H.A., J.W.C., K.-S.L. T.H.Y., H.J.P.), Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul; the Department of Otolaryngology (B.S.S.), Seogwipo Medical Center, Jeju; and the Department of Otolaryngology (T.S.K.), Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Republic of Korea. Editor s Note: This Manuscript was accepted for publication June 6, This study was supported by a grant ( ) from the Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Seoul, Korea. The authors have no other funding, financial relationships, or conflicts of interest to disclose. Young Wook Cho, MD, and Byoung Soo Shim, MD, contributed equally to this work. Send correspondence to Hong Ju Park, MD, Department of Otolaryngology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, 86 Asanbyeongwon-gil, Songpa-gu, Seoul, Korea dzness@amc.seoul.kr DOI: /lary group, which suggests that the decreased mastoid pneumatization possibly related to the otitis media is closely related to the generation of SCD. 4 Although labyrinth fistulae are caused almost exclusively by cholesteatoma, they can sometimes occur as a complication of longstanding suppurative chronic otitis media (COM) without cholesteatoma. 5,6 Nevertheless, there have been no previous studies that have investigated the radiologic prevalence of SCD in ears with COM. The aim of our current study was to compare the prevalence of radiologic SCD on computed tomography (CT) between normal ears and ears with COM in patients with unilateral COM, and to assess the prevalence of SCD according to age. MATERIALS AND METHODS Patients We reviewed 924 consecutive cases of mastoidectomy between January 2009 and December All of the patients had COM with/without cholesteatoma and underwent mastoidectomy to eliminate inflammation in the mastoid or to remove cholesteatoma. Of these patients, 165 patients with COM in both ears were excluded, and 759 patients with unilateral COM were included in this study. Contralateral healthy ears showed a normal tympanic membrane, and there was no conductive hearing loss (air-bone gaps < 10 db). Temporal bone CT scans of the 759 patients with unilateral COM were reviewed retrospectively. The mean (6 standard deviations) age of the patients
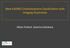
2 Fig. 1. Classification of the degrees of superior canal dehiscence (SCD) in three consecutive coronal computed tomography images. (A C) Normal: the bone overlying the superior canal is intact. (D F) Suspicious: SCD observed in only one section. (G I) Definite: SCD observed in two or more consecutive sections. Arrows indicate SCD. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.] was 48 years (614 years), ranging from 2 to 81 years. The patients consisted of 303 males and 456 females. Temporal Bone CT and Detection of SCD High-resolution temporal bone CT scans were performed using a 64-row detector CT scanner (Siemens Medical Systems, Erlanger, Germany). Images were helically acquired without contrast and were reconstructed using a bone plus algorithm. The axial plane images were acquired using a 0.6-mm-section thickness at 200 ma and kv. The coronal reconstruction image was acquired using 0.4-mm interval reconstructions. All of the images were evaluated on a diagnostic Petavision (Emsoma, Seoul, Korea) picture archiving and communication system. Dehiscence was assessed using coronal interactive reconstruction. This study was reviewed and approved by the institutional review board of Asan Medical Center. All CT images were independently evaluated by two otologists, and the thickness of the bone overlying the superior canal was categorized as either normal, suspicious SCD, or definite SCD (Fig. 1). Normal was defined as having intact bone on the superior canal, suspicious SCD was defined as having suspicious dehiscence in only one coronal section, and definite SCD was defined as having suspicious dehiscence in two or more consecutive coronal sections. Any discrepancies were resolved by consensus. Statistical Analysis Data were analyzed using SAS statistical system version 9.1 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). Statistical analysis comparing the observed counts between groups was performed using goodness of fit in a Fisher exact test. The radiologic prevalence of SCD was also assessed according to the patient s age. Age was categorized into four groups: 0 to 19 years, 20 to 39 years, 40 to 59 years, and 60 to 81 years. Log-linear regression models were used to estimate trends in prevalence ratios by age. The McNemar test was used to evaluate the association of SCD with contralateral involvement. RESULTS Of the 759 ears with COM analyzed in this study, 26 (3.4%) were identified as having definite SCD, and 747
3 TABLE I. Prevalence of SCD in Ears With COM and Normal Ears (N 5 759). 1 2 P * Definite SCD Ears with COM 26 (3.4%) 733 (96.6%) <.001 Normal ears 2 (0.3%) 757 (99.7%) Suspicious SCD Ears with COM 24 (3.2%) 735 (96.8%).003 Normal ears 7 (0.9%) 752 (99.1%) Definite or suspicious SCD Ears with COM 50 (6.6%) 709 (93.4%) <.001 Normal ears 9 (1.2%) 750 (98.8%) *Fisher exact test. COM 5 chronic otitis media; SCD 5 superior canal dehiscence. two ears (0.3%) out of 759 normal ears were identified as having definite SCD. The ears with COM had a significantly higher prevalence of definite SCD compared to normal ears (P <.001). Twenty-four (3.2%) out of 759 ears with COM were identified as having suspicious SCD, and seven (0.9%) of the 759 normal ears were characterized with suspicious SCD. Ears with COM also had a significantly higher prevalence of suspicious SCD than ears without COM (P 5.003). In terms of the summation of definite or suspicious SCD, the radiologic prevalence of definite or suspicious SCD in normal ears and ears with COM was 1.2% and 6.6%, respectively (P <.001, Table I). There was no discrepancy in determining normal SCD. There was discordance in determining the degrees of SCD in five (8%) of 59 ears with definite or suspicious SCD. Any discrepancies were resolved by consensus. Three patients who were finally decided to have definite SCD were assessed as having suspicious SCD by another examiner, and two patients who were finally decided to have suspicious SCD were assessed as having definite SCD by another examiner. The radiologic prevalence of suspicious or definite SCD was analyzed with respect to age. There was no correlation found between age and suspicious or definite SCD in both normal ears and in ears with COM (P >.05, Table II and Fig. 2). Interestingly, all of the normal ears with definite or suspicious SCD showed contralateral SCD (bilateral involvement). There were two patients with definite SCD in their healthy ears; one patient had definite SCD in both ears, and the other patient had definite SCD in one healthy ear and suspicious SCD in the other ear with COM. In addition, there were seven patients with suspicious SCD in their healthy ears; three patients had definite SCD, and the other four patients had suspicious SCD in the ear with COM. Therefore, there was a significant association found between SCD in normal ears and bilateral involvement (P <.0001, McNemar test, Table II). Of 759 patients, 164 patients were diagnosed with cholesteatoma. Among them, 18 (11%) had lateral semicircular canal fistula, which was in direct contact with the matrix of cholesteatoma. In 595 patients without cholesteatoma, one (0.002%) had lateral semicircular canal fistula, which was associated with soft tissue tympanosclerosis. There was no posterior semicircular canal fistula in COM ears. There was no lateral or posterior semicircular canal fistula in healthy ears. DISCUSSION Ears with COM in our study showed a prevalence of definite SCD (3.4%) and suspicious SCD (3.2%), which was significantly higher than the prevalence (0.3% and 0.9%, respectively) seen in contralateral normal ears. Our present data demonstrate that the presence of COM increased the prevalence of SCD, suggesting that chronic inflammation of the bone may play a role in the generation of SCD in ears with COM. Although labyrinthine fistulae are usually caused by cholesteatoma, with the lateral semicircular canal being the most commonly affected site, fistula could arise in ears with COM without cholesteatoma. 5 7 This suggests that COM might have a role in the development of SCD. Chronic osteomyelitis induces inflammatory processes, leading to compromised vascular channels and the activation of osteoclast activity, which results in bony destruction. 8 However, COM does not seem to be a direct cause of SCD according to our study, because the dehiscence in the ears with COM was found on the roof of superior canal but not in other sites. Because the superior canal is the only site of dehiscence, the role of COM seems to make the roof of the temporal bone susceptible to chronic brain pulsation and pressure exerted by the temporal lobe on the middle cranial fossa. 2,9 There was a report that the radiologic prevalence of SCD among older age groups increases, suggesting that TABLE II. The Prevalence of SCD in Normal Ears and Ears With COM According to Age. Definite SCD Suspicious SCD Definite or Suspicious SCD Age Group, yr Normal Ears COM Ears Normal Ears COM Ears Normal Ears COM Ears 0 19, n (0%) 1 (2.2%) 1 (2.2%) 3 (6.7%) 1 (2.2%)/1 * 4 (8.9%)/1 * 20 39, n (0%) 3 (2.5%) 0 (0%) 3 (2.5%) 0 (0%) 6 (5%)/ , n (0.2%) 17 (3.7%) 5 (1.1%) 11 (2.4%) 6 (1.3%)/6 * 28 (6.1%)/6 * 60, n (0.7%) 5 (3.6%) 1 (0.7%) 7 (5.1%) 2 (1.4%)/2 * 12 (8.8%)/2 * *Number of patients with bilateral SCD. COM 5 chronic otitis media; SCD 5 superior canal dehiscence. 748
4 Fig. 2. The prevalence of definite or suspicious superior canal dehiscence (SCD) in normal ears and ears with chronic otitis media (COM) according to age. There was no correlation found between age and suspicious or definite SCD in either normal ears or ears with COM. SCD is more commonly an acquired rather than a congenital condition. 3 However, we found no significant relationship between the age and the prevalence of SCD, and there was a significant association between SCD in normal ears and bilateral involvement, which is consistent with a congenital or developmental theory. This discrepancy may come from racial differences, or the former study might have included many patients with COM, especially in the elderly. In this study, we investigated the prevalence of radiologic SCD on CT between normal ears and contralateral COM ears in patients with unilateral COM through the same radiologic criteria. How can our findings be used for understanding the relationship between SCD and COM? There has been a report that mastoid volumes of both lesioned and normal ears in patients with unilateral SCD syndrome were significantly smaller than those of controls, 4 suggesting bilateral involvement and the significance of reduced mastoid volume in the generation of SCD. Reduction of mastoid volume was reported in ears with a history of otitis media with or even without middle ear fluid, suggesting that the reduced mastoid volume is genetically programmed (congenital) or developmental by a history of otitis media. 10,11 It has been reported that temporal bone specimens from infants show uniformly thin bone over the superior canal in the middle fossa at birth, with gradual thickening until 3 years of age, 2 and that SCD is not due to cephalic displacement or abnormally rotated orientation of the labyrinth but may arise from the failure of postnatal bone development. 12 All of the patients who were diagnosed with unilateral SCD syndrome had a normal tympanic membrane but decreased mastoid volumes in both ears, 4 suggesting that active inflammation is not directly responsible for the development of SCD, but a history of otitis media can be related to the reduced mastoid volume and the development of SCD. 10,11,13 A histopathological study of a temporal bone in a patient with SCD syndrome reported no osteoclastic process within the otic capsule bone surrounding the dehiscence. 14 It can be assumed that the reduced pneumatization, caused by a history of otitis media in early childhood, caused the roof of the superior canal to be thin enough and susceptible to brain pulsation and pressure to allow SCD to develop in a few normal subjects (0.3% in this study), suggesting a developmental theory. However, there is also a possibility that the temporal bone is congenitally thin, and previous history of otitis media enhances bony susceptibility to brain pulsation and pressure, resulting in SCD in COM ears. CONCLUSION Our findings showed that the presence of COM is closely related to the development of SCD, possibly making the roof of the temporal bone thin and susceptible to chronic brain pulsation and pressure exerted by the temporal lobe. Currently, the pathomechanism of SCD syndrome has not been known. Our findings suggest a hypothesis that SCD syndrome may arise in a few patients with a history of otitis media in early childhood that renders the bone overlying the superior canal to be thin due to the failure of postnatal bone development, 2 which is accompanied by decreased mastoid volume 4,10,11 and is susceptible to brain pulsation or pressure, resulting in the generation of SCD. This is an additional hypothesis to the previous hypothesis that SCD syndrome may arise from a failure of postnatal bone development, and that minor trauma may disrupt thin bone or stable dura over the superior canal. 2 In patients with 749
5 SCD syndrome accompanied by reduced mastoid volume but without any trauma history, our hypothesis can help to explain how SCD develops. BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. Minor LB, Solomon D, Zinreich JS, Zee DS. Sound- and/or pressureinduced vertigo due to bone dehiscence of the superior semicircular canal. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1998;124: Carey JP, Minor LB, Nager GT. Dehiscence or thinning of bone overlying the superior semicircular canal in a temporal bone survey. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2000;126: Nadgir RN, Ozonoff A, Devaiah AK, Halderman AA, Sakai O. Superior semicircular canal dehiscence: congenital or acquired condition? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2011;32: Shim BS, Kim CH, Kim TS, et al. Superior canal dehiscence patients have smaller mastoid volume than age and sex-matched otosclerosis and temporal bone fracture patients. Korean J Audiol 2012;16: Grewal DS, Hathiram BT, Dwivedi A, Kumar L, Sheth K, Srivastava S. Labyrinthine fistula: a complication of chronic suppurative otitis media. J Laryngol Otol 2003;117: Jang CH, Merchant SN. Histopathology of labyrinthine fistulae in chronic otitis media with clinical implications. Am J Otol 1997;18: Chole RA. Osteoclasts in chronic otitis media, cholesteatoma, and otosclerosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1988;97: Marriott I, Miller JR, Sahraei M. Therapeutic strategies against inflammation and bone loss associated with osteomyelitis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2007;8: Sanna M, Fois P, Russo A, Falcioni M. Management of meningoencephalic herniation of the temporal bone: Personal experience and literature review. Laryngoscope 2009;119: Swarts JD, Foley S, Alper CM, Doyle WJ. Mastoid geometry in a crosssection of humans from infancy through early adulthood with a confirmed history of otitis media. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2012;76: Csakanyi Z, Katona G, Josvai E, Mohos F, Sziklai I. Volume and surface of the mastoid cell system in otitis media with effusion in children: a casecontrol study by three-dimensional reconstruction of computed tomographic images. Otol Neurotol 2011;32: Potyagaylo VL, Della Santina CC, Minor LB, Carey JP. Superior canal dehiscence is not due to cephalic displacement of the labyrinth. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2005;1039: Andreasson L. Correlation of tubal function and volume of mastoid and middle ear space as related to otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1976;85: Teixido M, Kung B, Rosowski JJ, Merchant SN. Histopathology of the temporal bone in a case of superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2012;121:
Gerard J. Gianoli, MD, FACS The Ear and Balance Institute Baton Rouge, Louisiana
 Gerard J. Gianoli, MD, FACS The Ear and Balance Institute Baton Rouge, Louisiana SSCD is defined anatomically as the absence of bone between the SSC and the middle fossa dura PSCD is a defect of the PSC
Gerard J. Gianoli, MD, FACS The Ear and Balance Institute Baton Rouge, Louisiana SSCD is defined anatomically as the absence of bone between the SSC and the middle fossa dura PSCD is a defect of the PSC
Clinical Experience in Diagnosis and Management of Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence in Children
 The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Clinical Experience in Diagnosis and Management of Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence in Children Gi
The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Clinical Experience in Diagnosis and Management of Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence in Children Gi
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Journal of the New Zealand Medical Association Bilateral superior canal dehiscence syndrome Jeremy Hornibrook, David O Neill-Kerr, Latham Berry, Grant Carroll Superior canal
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Journal of the New Zealand Medical Association Bilateral superior canal dehiscence syndrome Jeremy Hornibrook, David O Neill-Kerr, Latham Berry, Grant Carroll Superior canal
Relationship between Severity of Nasal Septum Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Cells and Chronic Otitis Media
 Original Article J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 20, Issu 2; Feb 2018. P:27-32 Relationship between Severity of Nasal Septum Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Cells and Chronic Otitis Media E. Shobeiri
Original Article J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 20, Issu 2; Feb 2018. P:27-32 Relationship between Severity of Nasal Septum Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Cells and Chronic Otitis Media E. Shobeiri
ISSN: Volume 5 Issue CASE REPORT. Anju Chauhan, Vikram Wadhwa, Samuel Rajan, P.K. Rathore
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 5 Issue 2 2015 CONGENITAL CHOLESTEATOMA ISOLATED TO MASTOID PROCESS : A CASE REPORT Anju Chauhan, Vikram Wadhwa, Samuel Rajan, P.K. Rathore Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi,
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 5 Issue 2 2015 CONGENITAL CHOLESTEATOMA ISOLATED TO MASTOID PROCESS : A CASE REPORT Anju Chauhan, Vikram Wadhwa, Samuel Rajan, P.K. Rathore Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi,
Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Mimicking Otosclerotic Hearing Loss
 Arnold W, Häusler R (eds): Otosclerosis and Stapes Surgery. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. Basel, Karger, 7, vol 65, pp 137 145 Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Mimicking Otosclerotic Hearing Loss Saumil
Arnold W, Häusler R (eds): Otosclerosis and Stapes Surgery. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. Basel, Karger, 7, vol 65, pp 137 145 Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Mimicking Otosclerotic Hearing Loss Saumil
Congenital Middle Ear Cholesteatoma in Children; Retrospective Review of 35 Cases
 J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24: 126-31 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.126 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Congenital Middle Ear Cholesteatoma in Children; Retrospective Review of
J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24: 126-31 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.126 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Congenital Middle Ear Cholesteatoma in Children; Retrospective Review of
Meniere s disease and Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
 Meniere s disease and Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Tsutomu Nakashima 1,2 1 Ichinomiya Medical Treatment & Habilitation Center, Ichinomiya, Japan 2 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Nagoya University,
Meniere s disease and Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Tsutomu Nakashima 1,2 1 Ichinomiya Medical Treatment & Habilitation Center, Ichinomiya, Japan 2 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Nagoya University,
Clinical Utility of MRI for Cholesteatoma Recurrence
 Curr Surg Rep (2014) 2:63 DOI 10.1007/s40137-014-0063-0 EAR SURGERY (CJ LIMB, SECTION EDITOR) Clinical Utility of MRI for Cholesteatoma Recurrence Jonathan McJunkin Richard Chole Published online: 24 June
Curr Surg Rep (2014) 2:63 DOI 10.1007/s40137-014-0063-0 EAR SURGERY (CJ LIMB, SECTION EDITOR) Clinical Utility of MRI for Cholesteatoma Recurrence Jonathan McJunkin Richard Chole Published online: 24 June
Surgical intervention in middle-ear cholesterol granuloma
 Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2003 Surgical intervention in middle-ear cholesterol granuloma Manabu Maeta Ryusuke Saito Fumio Nakagawa Takakazu Miyahara Okayama University
Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2003 Surgical intervention in middle-ear cholesterol granuloma Manabu Maeta Ryusuke Saito Fumio Nakagawa Takakazu Miyahara Okayama University
New EAONO Cholesteatoma Classification with imaging illustration. Milan Profant, Katarina Sláviková
 New EAONO Cholesteatoma Classification with imaging illustration Milan Profant, Katarina Sláviková EAONO/JOS Joint Consensus Statements on the Definitions, Classification and Staging of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma
New EAONO Cholesteatoma Classification with imaging illustration Milan Profant, Katarina Sláviková EAONO/JOS Joint Consensus Statements on the Definitions, Classification and Staging of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma
Cochlear-Facial Dehiscence A Newly Described Entity
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Case Report Cochlear-Facial Dehiscence A Newly Described Entity Danielle M. Blake, BA; Senja Tomovic, MD;
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Case Report Cochlear-Facial Dehiscence A Newly Described Entity Danielle M. Blake, BA; Senja Tomovic, MD;
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Temporal Lobe Injury in Temporal Bone Fractures. imaging (MRI) to evaluate lesions of the temporal
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Temporal Lobe Injury in Temporal Bone Fractures Richard M. Jones, MD; Michael I. Rothman, MD; William C. Gray, MD; Gregg H. Zoarski, MD; Douglas E. Mattox, MD Objective: To determine the
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Temporal Lobe Injury in Temporal Bone Fractures Richard M. Jones, MD; Michael I. Rothman, MD; William C. Gray, MD; Gregg H. Zoarski, MD; Douglas E. Mattox, MD Objective: To determine the
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma. Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal
 Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(1) 63-68 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal Alexandria Ear Hospital Alexandria Egypt (AB,
Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(1) 63-68 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal Alexandria Ear Hospital Alexandria Egypt (AB,
The close anatomic relationship between the cochlea and
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.J. Young D.R. Shatzkes J.S. Babb A.K. Lalwani The Cochlear-Carotid Interval: Anatomic Variation and Potential Clinical Implications BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: A temporal bone CT study
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.J. Young D.R. Shatzkes J.S. Babb A.K. Lalwani The Cochlear-Carotid Interval: Anatomic Variation and Potential Clinical Implications BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: A temporal bone CT study
The Value of Computed Tomography Scanning in Assessment of Aditus ad Antrum Patency and Choice of Treatment Line in Revision Myringoplasty
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 2, September: 53-57, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com The Value of Computed Tomography Scanning in Assessment of Aditus ad Antrum Patency and Choice of Treatment
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 2, September: 53-57, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com The Value of Computed Tomography Scanning in Assessment of Aditus ad Antrum Patency and Choice of Treatment
Congenital Absence of the Oval Window: Radiologic Diagnosis and Associated Anomalies
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:322 327, February 2000 Congenital Absence of the Oval Window: Radiologic Diagnosis and Associated Anomalies Barbara Zeifer, Paul Sabini, and Jonathan Sonne BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:322 327, February 2000 Congenital Absence of the Oval Window: Radiologic Diagnosis and Associated Anomalies Barbara Zeifer, Paul Sabini, and Jonathan Sonne BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
DOI: / ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Tomographic evaluation of the contralateral ear in patients with severe chronic otitis media
 Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;79(4):475-9. DOI: 10.5935/1808-8694.20130085 ORIGINAL ARTICLE.org BJORL Tomographic evaluation of the contralateral ear in patients with severe chronic otitis media Maurício
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;79(4):475-9. DOI: 10.5935/1808-8694.20130085 ORIGINAL ARTICLE.org BJORL Tomographic evaluation of the contralateral ear in patients with severe chronic otitis media Maurício
ACUTE MASTOIDITIS IN CHILDREN: SUSCEPTIBILITY FACTORS AND MANAGEMENT
 & ACUTE MASTOIDITIS IN CHILDREN: SUSCEPTIBILITY FACTORS AND MANAGEMENT Slobodan Spremo*, Biljana Udovčić Clinic for Otorhinolaryngology, Clinic Center in Banja Luka, Zdrave Korde 1, 78000 Banja Luka, Bosnia
& ACUTE MASTOIDITIS IN CHILDREN: SUSCEPTIBILITY FACTORS AND MANAGEMENT Slobodan Spremo*, Biljana Udovčić Clinic for Otorhinolaryngology, Clinic Center in Banja Luka, Zdrave Korde 1, 78000 Banja Luka, Bosnia
Abnormal direction of internal auditory canal and vestibulocochlear nerve
 Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2004 Abnormal direction of internal auditory canal and vestibulocochlear nerve Shin Kariya kazunori Nishizaki Hirofumi Akagi Michael M. Paparella
Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2004 Abnormal direction of internal auditory canal and vestibulocochlear nerve Shin Kariya kazunori Nishizaki Hirofumi Akagi Michael M. Paparella
Clinical Study The Dehiscent Facial Nerve Canal
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 679708, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/679708 Clinical Study The Dehiscent Facial Nerve Canal Sertac Yetiser Department of ORL and HNS, Anadolu Medical Center,
International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 679708, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/679708 Clinical Study The Dehiscent Facial Nerve Canal Sertac Yetiser Department of ORL and HNS, Anadolu Medical Center,
On Signal Analysis of Three-Dimensional Nystagmus
 846 Medical Informatics in a United and Healthy Europe K.-P. Adlassnig et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 29 29 European Federation for Medical Informatics. All rights reserved. doi:1.3233/978-1-675-44-5-846 On
846 Medical Informatics in a United and Healthy Europe K.-P. Adlassnig et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 29 29 European Federation for Medical Informatics. All rights reserved. doi:1.3233/978-1-675-44-5-846 On
Surgical and Non-Surgical Causes of Progressive Hearing Loss in Children: What can be done about it?
 Surgical and Non-Surgical Causes of Progressive Hearing Loss in Children: What can be done about it? Daniela Carvalho, MD, MMM, FAAP Professor, Surgery Department UCSD Pediatric Otolaryngology Rady Children
Surgical and Non-Surgical Causes of Progressive Hearing Loss in Children: What can be done about it? Daniela Carvalho, MD, MMM, FAAP Professor, Surgery Department UCSD Pediatric Otolaryngology Rady Children
Shape of the Osseous External Auditory Canal and Its Relationship to Troublesome Cavities
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Shape of the Osseous External Auditory Canal and Its Relationship to Troublesome Cavities Erik van Spronsen,
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Shape of the Osseous External Auditory Canal and Its Relationship to Troublesome Cavities Erik van Spronsen,
High resolution computed tomography of temporal bone in the evaluation of otologic diseases
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Handi PS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jan;4(1):87-92 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Handi PS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jan;4(1):87-92 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence, Not Only Vestibular Symptoms.
 Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence, Not Only Vestibular Symptoms. Poster No.: C-1397 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Grive 1, A. M. Garcia Correa 1, A. A. MARIN SUAREZ 2, I.
Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence, Not Only Vestibular Symptoms. Poster No.: C-1397 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Grive 1, A. M. Garcia Correa 1, A. A. MARIN SUAREZ 2, I.
Dizziness Handicap After Cartilage Cap Occlusion for Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence
 Otology & Neurotology 34:135Y140 Ó 2012, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Dizziness Handicap After Cartilage Cap Occlusion for Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Jamie M. Bogle, Larry B. Lundy, David A.
Otology & Neurotology 34:135Y140 Ó 2012, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Dizziness Handicap After Cartilage Cap Occlusion for Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Jamie M. Bogle, Larry B. Lundy, David A.
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Commonly Occurs Following Repair of Superior Canal Dehiscence
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Commonly Occurs Following Repair of Superior Canal Dehiscence Samuel
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Commonly Occurs Following Repair of Superior Canal Dehiscence Samuel
Clinical Course of Pediatric Congenital Inner Ear Malformations
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2000 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Clinical Course of Pediatric Congenital Inner Ear Malformations
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2000 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Clinical Course of Pediatric Congenital Inner Ear Malformations
Vestibular and auditory symptoms can be caused. Clinical outcomes of middle fossa craniotomy for superior semicircular canal dehiscence repair
 clinical article J Neurosurg 125:1187 1193, 2016 Clinical outcomes of middle fossa craniotomy for superior semicircular canal dehiscence repair Lawrance K. Chung, BS, 1 Nolan Ung, BS, 1 Marko Spasic, BA,
clinical article J Neurosurg 125:1187 1193, 2016 Clinical outcomes of middle fossa craniotomy for superior semicircular canal dehiscence repair Lawrance K. Chung, BS, 1 Nolan Ung, BS, 1 Marko Spasic, BA,
Combined TBH / GSH meeting. 11 September 2007 Eric F Post
 Combined TBH / GSH meeting 11 September 2007 Eric F Post Case 32 yo male Presenting: Vertigo x since a.m. Tinnitus 5/7 Hearing loss worsened 4/7 Otorhea (L) x 2/ 52 Case History Ear surgery 1990 @ Umtata
Combined TBH / GSH meeting 11 September 2007 Eric F Post Case 32 yo male Presenting: Vertigo x since a.m. Tinnitus 5/7 Hearing loss worsened 4/7 Otorhea (L) x 2/ 52 Case History Ear surgery 1990 @ Umtata
Do the Angle and Length of the Eustachian Tube Influence the Development of Chronic Otitis Media?
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Do the Angle and Length of the Eustachian Tube Influence the Development of Chronic Otitis Media? Aykut Erdem
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Do the Angle and Length of the Eustachian Tube Influence the Development of Chronic Otitis Media? Aykut Erdem
Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study
 Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study Mark C. DeLano, F. Y. Fun, and S. James Zinreich PURPOSE: To delineate the relationship between the optic nerves
Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study Mark C. DeLano, F. Y. Fun, and S. James Zinreich PURPOSE: To delineate the relationship between the optic nerves
Pediatric Ear Diseases
 Pediatric Ear Diseases Yasushi Naito Pediatric Ear Diseases Diagnostic Imaging Atlas and Case Reports 242 figures, 7 in color and 5 tables, 2013 Basel Freiburg Paris London New York New Delhi Bangkok
Pediatric Ear Diseases Yasushi Naito Pediatric Ear Diseases Diagnostic Imaging Atlas and Case Reports 242 figures, 7 in color and 5 tables, 2013 Basel Freiburg Paris London New York New Delhi Bangkok
A Clicking Larynx: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges
 The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Case Report A Clicking Larynx: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges Derrek A. Heuveling, MD, PhD ; Maarten
The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Case Report A Clicking Larynx: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges Derrek A. Heuveling, MD, PhD ; Maarten
Facial Nerve Paralysis due to Chronic Otitis Media: Prognosis in Restoration of Facial Function after Surgical Intervention
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.49/ymj.2012.5..642 pissn: 051-596, eissn: 196-24 Yonsei Med J 5():642-648, 2012 Facial Nerve Paralysis due to Chronic Otitis Media: Prognosis in Restoration of Facial
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.49/ymj.2012.5..642 pissn: 051-596, eissn: 196-24 Yonsei Med J 5():642-648, 2012 Facial Nerve Paralysis due to Chronic Otitis Media: Prognosis in Restoration of Facial
Public Statement: Medical Policy Statement:
 Medical Policy Title: Implantable Bone ARBenefits Approval: 09/28/2011 Conduction Hearing Aids Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0190 Revision Date: Code(s): 69714 Implantation, osseointegrated implant,
Medical Policy Title: Implantable Bone ARBenefits Approval: 09/28/2011 Conduction Hearing Aids Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0190 Revision Date: Code(s): 69714 Implantation, osseointegrated implant,
Relationship of Pure Tone Audiometry and Ossicular Discontinuity in Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media
 Silver Anniversary Issue Vol. Nos. & January June; July December Ryner Jose C. Carrillo, MD, Nathaniel W. Yang, MD,, Generoso T. Abes, MD, MPH, Department of Otorhinolaryngology Philippine General Hospital
Silver Anniversary Issue Vol. Nos. & January June; July December Ryner Jose C. Carrillo, MD, Nathaniel W. Yang, MD,, Generoso T. Abes, MD, MPH, Department of Otorhinolaryngology Philippine General Hospital
Clinical Significance of Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
 Otology & Neurotology 29:1162Y1166 Ó 2008, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Clinical Significance of Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo *Won Sun Yang, Sung Huhn Kim,
Otology & Neurotology 29:1162Y1166 Ó 2008, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Clinical Significance of Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo *Won Sun Yang, Sung Huhn Kim,
Editorial Manager(tm) for European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology and Head & Neck Manuscript Draft
 Editorial Manager(tm) for European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology and Head & Neck Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: EAORL-D-07-00196 Title: Usefulness of CT scans in malignant external otitis: Effective
Editorial Manager(tm) for European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology and Head & Neck Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: EAORL-D-07-00196 Title: Usefulness of CT scans in malignant external otitis: Effective
Incus Footplate Assembly: Indication and Surgical Outcome
 The Laryngoscope VC 2016 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Incus Footplate Assembly: Indication and Surgical Outcome Mina Park, MD; Sungjun Han, MD; Byung Yoon Choi,
The Laryngoscope VC 2016 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Incus Footplate Assembly: Indication and Surgical Outcome Mina Park, MD; Sungjun Han, MD; Byung Yoon Choi,
Characteristics of Patients Who Underwent Mastoidectomy: A Two Years Experience
 474 AMJ September 2017 AMJ. 2017;4(3):474 8 Characteristics of Patients Who Underwent Mastoidectomy: A Two Years Experience Ashwini Gunasekaran, 1 Sally Mahdiani, 2 Fifi Veronica 3 1 Faculty of Medicine
474 AMJ September 2017 AMJ. 2017;4(3):474 8 Characteristics of Patients Who Underwent Mastoidectomy: A Two Years Experience Ashwini Gunasekaran, 1 Sally Mahdiani, 2 Fifi Veronica 3 1 Faculty of Medicine
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE
 Belyea et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2016) 45:44 DOI 10.1186/s40463-016-0157-z ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Middle ear ventilation status postoperatively after translabyrinthine
Belyea et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2016) 45:44 DOI 10.1186/s40463-016-0157-z ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Middle ear ventilation status postoperatively after translabyrinthine
Delayed Endolymphatic Hydrops: Episodic Vertigo of Delayed Onset after Profound Inner Ear Hearing Loss
 Delayed Endolymphatic Hydrops: Episodic Vertigo of Delayed Onset after Profound Inner Ear Hearing Loss Tamio Kamei 1, MD, PhD and Kenji Watanabe 2, MD 1 Professor emeritus at Gunma University, Japan 2
Delayed Endolymphatic Hydrops: Episodic Vertigo of Delayed Onset after Profound Inner Ear Hearing Loss Tamio Kamei 1, MD, PhD and Kenji Watanabe 2, MD 1 Professor emeritus at Gunma University, Japan 2
European Journal of Medicine, 2015, Vol.(10), Is. 4
 Copyright 2015 by Academic Publishing House Researcher Published in the Russian Federation European Journal of Medicine Has been issued since 2013. ISSN: 2308-6513 E-ISSN: 2310-3434 Vol. 10, Is. 4, pp.
Copyright 2015 by Academic Publishing House Researcher Published in the Russian Federation European Journal of Medicine Has been issued since 2013. ISSN: 2308-6513 E-ISSN: 2310-3434 Vol. 10, Is. 4, pp.
The Best Candidates for Nerve-Sparing Stripping Surgery for Facial Nerve Schwannoma
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Best Candidates for Nerve-Sparing Stripping Surgery for Facial Nerve Schwannoma Soon H. Park, MD; Jin
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Best Candidates for Nerve-Sparing Stripping Surgery for Facial Nerve Schwannoma Soon H. Park, MD; Jin
The Relationship Between Endolymphatic Hydrops in the Vestibule and Low-Frequency Air-Bone Gaps
 The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Relationship Between Endolymphatic Hydrops in the Vestibule and Low-Frequency Air-Bone Gaps Satofumi
The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Relationship Between Endolymphatic Hydrops in the Vestibule and Low-Frequency Air-Bone Gaps Satofumi
Indications for canal wall down mastoidectomy in. Acetic Acid Instillation after Canal Wall Down Mastoidectomy. Main Article
 Acetic Acid Instillation after Canal Wall Down Mastoidectomy Hamsa Shetty, 1 Gangadhara K S 1 ABSTRACT Introduction Persistent otorrhoea and granulation tissue in the mastoid cavity are common post-operative
Acetic Acid Instillation after Canal Wall Down Mastoidectomy Hamsa Shetty, 1 Gangadhara K S 1 ABSTRACT Introduction Persistent otorrhoea and granulation tissue in the mastoid cavity are common post-operative
Monitoring of Caloric Response and Outcome in Patients With Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
 Otology & Neurotology 28:798Y800 Ó 2007, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Monitoring of Caloric Response and Outcome in Patients With Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo *Maria I. Molina, *Jose A. López-Escámez,
Otology & Neurotology 28:798Y800 Ó 2007, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Monitoring of Caloric Response and Outcome in Patients With Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo *Maria I. Molina, *Jose A. López-Escámez,
Modern Imaging & Current Controversies
 Temporal Bone: Modern Imaging & Current Controversies Suresh K. Mukherji, MD, FACR Professor and Chief of Neuroradiology Professor of Radiology, Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery, Radiation i Oncology,
Temporal Bone: Modern Imaging & Current Controversies Suresh K. Mukherji, MD, FACR Professor and Chief of Neuroradiology Professor of Radiology, Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery, Radiation i Oncology,
Audiological outcome of tympanoplasties a single center experience
 Original article Audiological outcome of tympanoplasties a single center experience Selma Hodžić-Redžić*, Lana Kovač-Bilić, Srećko Branica Department of Ear, Nose and Throat and Head and Neck Surgery,
Original article Audiological outcome of tympanoplasties a single center experience Selma Hodžić-Redžić*, Lana Kovač-Bilić, Srećko Branica Department of Ear, Nose and Throat and Head and Neck Surgery,
HRCT in Conductive Hearing Loss: A Study of One Hundred Cases
 HRCT in Conductive Hearing Loss: A Study of One Hundred Cases Dr Minutha R 1 Associate Professor ENT MVJ medical college Bangalore/ India Email:minuthar@yahoo.com * Dr.Sriram Nathan 2 Senior Consultant
HRCT in Conductive Hearing Loss: A Study of One Hundred Cases Dr Minutha R 1 Associate Professor ENT MVJ medical college Bangalore/ India Email:minuthar@yahoo.com * Dr.Sriram Nathan 2 Senior Consultant
High-Frequency Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. High-Frequency Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children Kaalan Johnson, MD; Meredith Tabangin, MPH; Jareen
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. High-Frequency Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children Kaalan Johnson, MD; Meredith Tabangin, MPH; Jareen
Clinical Characteristics of Labyrinthine Concussion
 online ML Comm ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Audiol 2013;17:13-17 pissn 2092-9862 / eissn 2093-3797 http://dx.doi.org/10.7874/kja.2013.17.1.13 Clinical Characteristics of Labyrinthine Concussion Mi Suk Choi,
online ML Comm ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Audiol 2013;17:13-17 pissn 2092-9862 / eissn 2093-3797 http://dx.doi.org/10.7874/kja.2013.17.1.13 Clinical Characteristics of Labyrinthine Concussion Mi Suk Choi,
Anna Lisa Giannuzzi, MD, PhD; Paul Merkus, MD, PhD; Abdelkader Taibah, MD; Maurizio Falcioni, MD
 1145-061-D Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology 11?(?):??-??. 2011 Annals Publishing Company. All rights reserved. Congenital Mastoid Cholesteatoma: Case Series, Definition, Surgical Key Points,
1145-061-D Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology 11?(?):??-??. 2011 Annals Publishing Company. All rights reserved. Congenital Mastoid Cholesteatoma: Case Series, Definition, Surgical Key Points,
Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Middle Ear a Complication of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media?
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Middle Ear a Complication of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media? B Vikram, S Saimanohar, G Narayanaswamy
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Middle Ear a Complication of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media? B Vikram, S Saimanohar, G Narayanaswamy
Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Perforated Otitis Media in Different Age Groups
 J Int Adv Otol 2017; 13(2): 176-80 DOI: 10.5152/iao.2017.3513 Original Article Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Perforated Otitis Media in Different s Masayo Hasegawa, Akihiro Shinnabe, Hiromi Kanazawa,
J Int Adv Otol 2017; 13(2): 176-80 DOI: 10.5152/iao.2017.3513 Original Article Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Perforated Otitis Media in Different s Masayo Hasegawa, Akihiro Shinnabe, Hiromi Kanazawa,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Utku Aydil, Ali Koksal, Tuncay Ozcelik, Nuri Ozgirgin
 Int. Adv. Otol. 2010; 6:(3) 337-341 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Reformatted Two-Dimensional Images with Three-Dimensional Reconstructions Based on Images from Multi-Detector Computed Tomography of the
Int. Adv. Otol. 2010; 6:(3) 337-341 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Reformatted Two-Dimensional Images with Three-Dimensional Reconstructions Based on Images from Multi-Detector Computed Tomography of the
Middle ear CT imaging: Review of anatomy and common pathology
 Middle ear CT imaging: Review of anatomy and common pathology Poster No.: C-0665 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. R. Campos Arenas, M. C. Sánchez-Porro, J. Garrido Rull ; 1 1 2
Middle ear CT imaging: Review of anatomy and common pathology Poster No.: C-0665 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. R. Campos Arenas, M. C. Sánchez-Porro, J. Garrido Rull ; 1 1 2
Temporal Bone Carcinoma: Results of Surgery for Primary and Secondary Malignancies
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Temporal Bone Carcinoma: Results of Surgery for Primary and Secondary Malignancies Milan Stankovic, M.D. From the Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Medical Faculty Nis, Serbia. Correspondence:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Temporal Bone Carcinoma: Results of Surgery for Primary and Secondary Malignancies Milan Stankovic, M.D. From the Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Medical Faculty Nis, Serbia. Correspondence:
OTOLOGY. 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF OTOLOGIC TRAINING Rotations that include otologic training are a component of each of the four years of training.
 OTOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF OTOLOGIC TRAINING Rotations that include otologic training are a component of each of the four years of training. Longwood Rotation PGY-2 through PGY-5 years o Clinic experience
OTOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF OTOLOGIC TRAINING Rotations that include otologic training are a component of each of the four years of training. Longwood Rotation PGY-2 through PGY-5 years o Clinic experience
ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST
 www.manchesterchildrensent.com ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST A CHILD WITH EARACHE UNCOMPLICATED AOM ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA Acute otitis media
www.manchesterchildrensent.com ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST A CHILD WITH EARACHE UNCOMPLICATED AOM ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA Acute otitis media
CLASSIFICATION OF CONGENITAL MIDDLE AND EXTERNAL EAR MALFORMATIONS: CT STUDY
 VolumeS Medicalloumal of the Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3,4 Payiz & Zemestan 1370 Fall & Winter 1991 CLASSIFICATION OF CONGENITAL MIDDLE AND EXTERNAL EAR MALFORMATIONS: CT STUDY D. SAYIC, MD, DMS:
VolumeS Medicalloumal of the Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3,4 Payiz & Zemestan 1370 Fall & Winter 1991 CLASSIFICATION OF CONGENITAL MIDDLE AND EXTERNAL EAR MALFORMATIONS: CT STUDY D. SAYIC, MD, DMS:
Correlation of HRCT mastoid with clinical presentation and operative findings in ear diseases
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chintale SG et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):656-660 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chintale SG et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):656-660 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
syndrome (LEDS) and its associated anomalies, with clinical features.
 Relationship of the rea Measurement of the Large Endolymphatic Duct and Sac Syndrome as well as the Clinical Symptoms with CT and MR Imaging Results 1 Ji-Sang Park, M.D., Hyun Sook Hong, M.D., Jong-Sea
Relationship of the rea Measurement of the Large Endolymphatic Duct and Sac Syndrome as well as the Clinical Symptoms with CT and MR Imaging Results 1 Ji-Sang Park, M.D., Hyun Sook Hong, M.D., Jong-Sea
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE
 RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
Study on Hearing Status of Elderly Patients attending a Specialized ENT Hospital (SAHIC)
 Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2015; 21(2): 80-84 Original Article Study on Hearing Status of Elderly Patients attending a Specialized ENT Hospital (SAHIC) Mohammad Wakilur Rahman 1, Ali Imam Ahasan 2,
Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2015; 21(2): 80-84 Original Article Study on Hearing Status of Elderly Patients attending a Specialized ENT Hospital (SAHIC) Mohammad Wakilur Rahman 1, Ali Imam Ahasan 2,
Congenital aural atresia (CAA) is a rare disorder of the temporal
 Published July 3, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4022 CLINICAL REPORT HEAD & NECK The Boomerang Malleus-Incus Complex in Congenital Aural Atresia S. Mukherjee, B.W. Kesser, and P. Raghavan ABSTRACT SUMMARY: Boomerang
Published July 3, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4022 CLINICAL REPORT HEAD & NECK The Boomerang Malleus-Incus Complex in Congenital Aural Atresia S. Mukherjee, B.W. Kesser, and P. Raghavan ABSTRACT SUMMARY: Boomerang
"The prevalence and CT detection of Onodi cell types."
 "The prevalence and CT detection of Onodi cell types." Poster No.: C-1566 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Chmielik 1, L. Chmielik 2, R. Boguslawska-Walecka 1 ; 1 Warszawa/ PL, 2
"The prevalence and CT detection of Onodi cell types." Poster No.: C-1566 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Chmielik 1, L. Chmielik 2, R. Boguslawska-Walecka 1 ; 1 Warszawa/ PL, 2
Key words: Chronic suppurative otitis media, High resolution Computed tomography, cholesteatoma,
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Study of Radiological findings in High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) temporal bone in Chronic suppurative otitis Media (CSOM): A hospital Based cross sectional study. Vijay vaidya
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Study of Radiological findings in High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) temporal bone in Chronic suppurative otitis Media (CSOM): A hospital Based cross sectional study. Vijay vaidya
Evaluation of hearing loss in relation to site & size of tympanic membrane perforation
 Original article: Evaluation of hearing loss in relation to site & size of tympanic membrane perforation 1 Dr. Anup Agrawal, 2 Dr. Beni Prasad*, 3 Dr. Sunil Sharma 1Resident, 2 Head of Department, 3 Senior
Original article: Evaluation of hearing loss in relation to site & size of tympanic membrane perforation 1 Dr. Anup Agrawal, 2 Dr. Beni Prasad*, 3 Dr. Sunil Sharma 1Resident, 2 Head of Department, 3 Senior
No conflicts of interest were identified by the planning committee, faculty, authors and reviewers for this program.
 Disclosure: Is that a Hole? Evaluation and Treatment of TM Perforations Kristi McGowin, MSN, CPNP Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, MO No conflicts of interest were identified by the planning committee,
Disclosure: Is that a Hole? Evaluation and Treatment of TM Perforations Kristi McGowin, MSN, CPNP Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, MO No conflicts of interest were identified by the planning committee,
Chronic Ear Disease. Daekeun Joo Resident Lecture Series 11/18/09
 Chronic Ear Disease Daekeun Joo Resident Lecture Series 11/18/09 ETD URIs Viral-induced damage to ET lining resulting in decreased mucociliary clearance Viral invasion of ME mucosa results in inflamm Reflux
Chronic Ear Disease Daekeun Joo Resident Lecture Series 11/18/09 ETD URIs Viral-induced damage to ET lining resulting in decreased mucociliary clearance Viral invasion of ME mucosa results in inflamm Reflux
Tympanogenic Labyrinthitis (Cochlear Deafness) due to chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM)
 Tympanogenic Labyrinthitis (Cochlear Deafness) due to chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) * Dr. Raad A AlObaydi (FICS MBChB) Background: It has been accepted that in patients with CSOM, conductive
Tympanogenic Labyrinthitis (Cochlear Deafness) due to chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) * Dr. Raad A AlObaydi (FICS MBChB) Background: It has been accepted that in patients with CSOM, conductive
Imaging Profile of the Ear in Hearing Loss Patients in Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia: 5 year Cross Sectional Analysis at a Tertiary
 Imaging Profile of the Ear in Hearing Loss Patients in Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia: 5 year Cross Sectional Analysis at a Tertiary Otologic Centre Rohaizam bin Japar 1, Dinsuhaimi bin Sidek 1, Suzina
Imaging Profile of the Ear in Hearing Loss Patients in Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia: 5 year Cross Sectional Analysis at a Tertiary Otologic Centre Rohaizam bin Japar 1, Dinsuhaimi bin Sidek 1, Suzina
Size of Tympanic Membrane Perforation and Hearing Loss
 J Nep Med Assoc 2006; 45: 167-172 Size of Tympanic Membrane Perforation and Hearing Loss Bhusal C L *, Guragain R P S *, Shrivastav R P * * Tribhuvan University, Institute of Medicine, Maharajgunj, Kathmandu,
J Nep Med Assoc 2006; 45: 167-172 Size of Tympanic Membrane Perforation and Hearing Loss Bhusal C L *, Guragain R P S *, Shrivastav R P * * Tribhuvan University, Institute of Medicine, Maharajgunj, Kathmandu,
The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology John R. Hesselink, M.D. Temporal Bone Axial View Temporal Bone Coronal View Longitudinal Fracture The Temporal
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology John R. Hesselink, M.D. Temporal Bone Axial View Temporal Bone Coronal View Longitudinal Fracture The Temporal
Assessment of Hearing Loss in Tympanic Membrane Perforation at Tertiary Care Hospitals
 Assessment of Hearing Loss in Tympanic Membrane Perforation at Tertiary Care Hospitals ABSTRACT Muhammad Rafique, Muhammed Shujah Farrukh, Arsalan Ahmed Shaikh OBJECTIVE: To evaluate and analyze the degree
Assessment of Hearing Loss in Tympanic Membrane Perforation at Tertiary Care Hospitals ABSTRACT Muhammad Rafique, Muhammed Shujah Farrukh, Arsalan Ahmed Shaikh OBJECTIVE: To evaluate and analyze the degree
Received 20 June 2006
 American Journal of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Medicine and Surgery 28 (2007) 230 234 www.elsevier.com/locate/amjoto Value of high-resolution computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in the
American Journal of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Medicine and Surgery 28 (2007) 230 234 www.elsevier.com/locate/amjoto Value of high-resolution computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in the
Clinical analysis of secondary acquired cholesteatoma.
 Research Article Clinical analysis of secondary acquired cholesteatoma. http://www.alliedacademies.org/archives-of-general-internal-medicine/ ISSN : 2591-7951 Takashi Yamatodani 1 *, Kunihiro Mizuta 2,
Research Article Clinical analysis of secondary acquired cholesteatoma. http://www.alliedacademies.org/archives-of-general-internal-medicine/ ISSN : 2591-7951 Takashi Yamatodani 1 *, Kunihiro Mizuta 2,
Pediatric Temporal Bone
 Pediatric Temporal Bone Suresh K. Mukherji, MD, FACR Professor and Chief of Neuroradiology Professor of Radiology, Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery, Radiation Oncology and Periodontics & Oral Medicine
Pediatric Temporal Bone Suresh K. Mukherji, MD, FACR Professor and Chief of Neuroradiology Professor of Radiology, Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery, Radiation Oncology and Periodontics & Oral Medicine
PRIMARY SQUAMOUS cell carcinoma
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Temporal Bone A Radiographic-Pathologic Correlation ORIGINAL ARTICLE M. Boyd Gillespie, MD; Howard W. Francis, MD; Nelson Chee, MD; David W. Eisele, MD Objective: To assess
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Temporal Bone A Radiographic-Pathologic Correlation ORIGINAL ARTICLE M. Boyd Gillespie, MD; Howard W. Francis, MD; Nelson Chee, MD; David W. Eisele, MD Objective: To assess
CT of Postmeningitic Deafness: Observations and Predictive Value for Cochlear Implants in Children
 CT of Postmeningitic Deafness: Observations and Predictive Value for Cochlear Implants in Children Michele H. Johnson, M. Suzanne Hasenstab, Michael A. Seicshnaydre, and George H. Williams PURPOSE: To
CT of Postmeningitic Deafness: Observations and Predictive Value for Cochlear Implants in Children Michele H. Johnson, M. Suzanne Hasenstab, Michael A. Seicshnaydre, and George H. Williams PURPOSE: To
J.P.S. Bakshi Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat
 J.P.S. Bakshi Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat Reading excerpt Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat of J.P.S. Bakshi Publisher: B. Jain http://www.narayana-publishers.com/b5603 Copying excerpts is not permitted.
J.P.S. Bakshi Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat Reading excerpt Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat of J.P.S. Bakshi Publisher: B. Jain http://www.narayana-publishers.com/b5603 Copying excerpts is not permitted.
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2009), Vol. 7, No. 4, Issue 28,
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2009), Vol. 7, No. 4, Issue 28, 397-401 Original Article Observation of hearing loss in patients with chronic suppurative otitis media tubotympanic type Maharjan M
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2009), Vol. 7, No. 4, Issue 28, 397-401 Original Article Observation of hearing loss in patients with chronic suppurative otitis media tubotympanic type Maharjan M
Otosclerosis affects approximately 1% of the population
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Surgical and Clinical Confirmation of Temporal Bone CT Findings in Patients with Otosclerosis with Failed Stapes Surgery J. Whetstone, A. Nguyen, A. Nguyen-Huynh, and B.E.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Surgical and Clinical Confirmation of Temporal Bone CT Findings in Patients with Otosclerosis with Failed Stapes Surgery J. Whetstone, A. Nguyen, A. Nguyen-Huynh, and B.E.
Pseudo-Spontaneous Nystagmus in Lateral Semicircular Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
 Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 5, No. 4: 201-206, December 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2012.5.4.201 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Pseudo-Spontaneous Nystagmus
Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 5, No. 4: 201-206, December 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2012.5.4.201 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Pseudo-Spontaneous Nystagmus
Temporal Bone Pneumatization in Cystic Fibrosis: A Correlation With Genotype?
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Temporal Bone Pneumatization in Cystic Fibrosis: A Correlation With Genotype? Maaike C. Berkhout, MD; Cornelis
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Temporal Bone Pneumatization in Cystic Fibrosis: A Correlation With Genotype? Maaike C. Berkhout, MD; Cornelis
Outcomes and Complications in Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Surgery: A Systematic Review
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Systematic Review Outcomes and Complications in Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Surgery: A Systematic
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Systematic Review Outcomes and Complications in Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Surgery: A Systematic
Aberrant sylvian vein: A newly described cause of pulsatile tinnitus
 Special Issue: Systemic disease and otolaryngology-related disease Aberrant sylvian vein: A newly described cause of pulsatile tinnitus Journal of International Medical Research 2017, Vol. 45(5) 1481 1485!
Special Issue: Systemic disease and otolaryngology-related disease Aberrant sylvian vein: A newly described cause of pulsatile tinnitus Journal of International Medical Research 2017, Vol. 45(5) 1481 1485!
Minor: Manifestations of Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. 2005 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Clinical Manifestations of Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Lloyd
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. 2005 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Clinical Manifestations of Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Lloyd
B. CT protocols for the spine
 B. CT protocols for the spine Poster No.: A-003 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Neuro Authors: B. Tins; Oswestry/UK Keywords: CT, spine, diagnostic imaging protocol DOI: 10.1594/ecr2010/A-003
B. CT protocols for the spine Poster No.: A-003 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Neuro Authors: B. Tins; Oswestry/UK Keywords: CT, spine, diagnostic imaging protocol DOI: 10.1594/ecr2010/A-003
Relation between Nasal Septal Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells A Computerised Tomographic Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between Nasal Septal Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells A Computerised Tomographic Study N. Vinay Kumar 1, T. S. Gugapriya 2 ISSN (0): 2455-5274; ISSN (P): 2617-5207
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between Nasal Septal Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells A Computerised Tomographic Study N. Vinay Kumar 1, T. S. Gugapriya 2 ISSN (0): 2455-5274; ISSN (P): 2617-5207
Study of Mastoid Air Cells Diseases using Spiral CT
 Global Journal of Medical research Diseases Volume 13 Issue 3 Version 1. Year 13 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
Global Journal of Medical research Diseases Volume 13 Issue 3 Version 1. Year 13 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 10 Page October 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v6i1.145 Role of VR 3D Imaging in temporal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v6i1.145 Role of VR 3D Imaging in temporal
Radiologic Evaluation of Petrous Apex Masses. Pavan Kavali, MS-IV Morehouse School of Medicine November 16, 2009
 Radiologic Evaluation of Petrous Apex Masses Pavan Kavali, MS-IV Morehouse School of Medicine November 16, 2009 Roadmap Petrous Apex Anatomy Patient D.S.: Clinical Presentation Differential diagnosis of
Radiologic Evaluation of Petrous Apex Masses Pavan Kavali, MS-IV Morehouse School of Medicine November 16, 2009 Roadmap Petrous Apex Anatomy Patient D.S.: Clinical Presentation Differential diagnosis of
Results of single stage ossicular reconstruction by incus transposition in patients with chronic otitis media
 Original Article Results of single stage ossicular reconstruction by incus transposition in patients with chronic otitis media Masoud Naderpour, 1 Yalda Jabbari-Moghaddam, 1 Reza Radfar, 2 Sina Zarrintan,
Original Article Results of single stage ossicular reconstruction by incus transposition in patients with chronic otitis media Masoud Naderpour, 1 Yalda Jabbari-Moghaddam, 1 Reza Radfar, 2 Sina Zarrintan,
Intratympanic Steroid Therapy in Moderate Sudden Hearing Loss: A Randomized, Triple-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Intratympanic Steroid Therapy in Moderate Sudden Hearing Loss: A Randomized, Triple-Blind, Placebo-Controlled
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Intratympanic Steroid Therapy in Moderate Sudden Hearing Loss: A Randomized, Triple-Blind, Placebo-Controlled
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Efficacy of the 2-Staged Procedure in the Management of Cholesteatoma. paradigms have been published
 Efficacy of the 2-Staged Procedure in the Management of Cholesteatoma Steven Y. Ho, MD; John F. Kveton, MD ORIGAL ARTICLE Objective: To demonstrate the efficacy of intact canal wall procedure coupled with
Efficacy of the 2-Staged Procedure in the Management of Cholesteatoma Steven Y. Ho, MD; John F. Kveton, MD ORIGAL ARTICLE Objective: To demonstrate the efficacy of intact canal wall procedure coupled with
Tympanoplasty With Or Without Cortical Mastoidectomy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tympanoplasty With Or Without Cortical Mastoidectomy Padam Singh Jamwal, Om Prakash, Monika Khajuria, Manish Sharma, Mohit Goel Abstract Tympanoplasty is the treatment of choice for non-cholesteatomatous
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tympanoplasty With Or Without Cortical Mastoidectomy Padam Singh Jamwal, Om Prakash, Monika Khajuria, Manish Sharma, Mohit Goel Abstract Tympanoplasty is the treatment of choice for non-cholesteatomatous
