Brachioplasty by Power-Assisted Liposuction and Fat Transfer: A Novel Approach That Obviates Skin Excision
|
|
|
- Amice Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Aesthetic Surgery Journal Advance Access published February 23, 2016 Body Contouring Brachioplasty by Power-Assisted Liposuction and Fat Transfer: A Novel Approach That Obviates Skin Excision Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2016, The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, Inc. Reprints and permission: journals.permissions@oup.com DOI: /asj/sjv277 Marwan H. Abboud, MD; Nicolas M. Abboud; and Saad A. Dibo, MD Abstract Background: Current brachioplasty techniques include excisional surgery alone or in combination with liposuction. These techniques are associated with poor outcomes, such as residual contour deformities and unfavorable scarring. Objectives: The authors proposed a new classification system and treatment algorithm for brachial ptosis and described their experience with power-assisted liposuction and lipofilling to treat brachial ptosis without excisional surgery. Methods: Ninety-five patients with grades 1, 2, or 3 brachial ptosis who underwent brachioplasty were evaluated in a prospective study. Power-assisted liposuction was applied to the posterior arm and para-axillary region, and power-assisted lipofilling was applied to the so-called bicipital triangle of the medial arm. Results: The patients mean age was 39 years, mean body mass index was 28 kg/m 2, mean lipoaspirate volume was 240 ml per arm, and mean fatinjection volume was 110 ml per side. The mean operating time was 50 minutes, and the average follow-up period was 24 months. Hematoma developed in 2 patients who underwent brachioplasty in combination with another body contouring procedure (1 abdominal hematoma and 1 thigh hematoma; 2.1% complication rate). No other complications were recorded. Conclusions: Brachioplasty by means of power-assisted liposuction and lipofilling is a safe and reliable option that obviates excisional surgery in patients with mild to moderate brachial ptosis. Level of Evidence: 4 Accepted for publication December 31, Therapeutic Since the first descriptions of aesthetic brachioplasty in the 1950s, various surgical techniques and treatment algorithms have been proposed for brachial ptosis. 1,2 Treatment approaches vary according to the grade of the brachial deformity, which is derived from the amount of fat excess and the location and severity of skin redundancies. 1,3,4 Since the 1980s, surgical treatments for brachial ptosis have included liposuction, excisional surgery, or a combination of these techniques in a single session or as a staged procedure More recently, brachial implantation has been shown to improve the contour of the arm and tighten sagging skin. 13 However, postoperative complication rates as high as 40% have been reported with these surgeries, with residual contour deformities and unattractive scarring (eg, hypertrophic and widened scars or unfavorable scar locations) being the most common complications. 3,8,9,14,15 Surgical procedures that involve substantial liposuction (ie, 600 ml per arm) and minimize skin excision have been shown to improve the aesthetic results of brachioplasty. 1-3,9-12,16-22 We have observed that patients with brachial ptosis present with a minimal to severe contour depression of the medial arm. This contour depression usually is associated Dr Abboud is Head and Dr Dibo is a Fellow, Division of Plastic Surgery, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Tivoli, Brussels, Belgium. Mr Abboud is a fourth-year medical student, Universite Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium. Corresponding Author: Dr Saad A. Dibo, 23 Avenue Penelope, 1190 Brussels, Belgium saaddibo@gmail.com
2 2 Aesthetic Surgery Journal Figure 1. (A) Preoperative photograph of this 26-year-old woman who presented with brachial ptosis. The patient s shoulder is abducted 90 degrees and the elbow is extended. The anterior, medial, and posterior arm zones are indicated. (B) The bicipital triangle corresponds to a region of the medial arm (deemed zone 2) that is deficient in volume. The apex of the bicipital triangle is proximal to the medial epicondyle, and the base is at the axilla. with skin and fat excesses of the posterior arm, but occasionally occurs in patients with a normal posterior arm. The region of depression is triangular and is located at the bicipital groove; therefore, we refer to it as the bicipital triangle (Figure 1). The apex of the bicipital triangle is approximately 3 cm proximal to the medial epicondyle, and the base is at the axilla. Because the addition of volume in brachioplasty can resolve wrinkling and lift tissue, we presumed that fat grafting to the bicipital triangle could create an aesthetically pleasing contour of the medial arm. Fat grafting also could improve the shape of the posterior arm by lifting and tightening ptotic posterior skin and could obviate excisional surgery and associated wound complications. Similar assumptions have been made regarding fat grafting to the face 23 and implant placement in the arm. 13 We incorporated our observations of the bicipital triangle into a novel system for classifying brachial deformities (Figure 2 and Table 1) that is based on the following 4 treatment zones: the anteromedial/anterolateral arm (zone 1), the bicipital triangle (zone 2), the posteromedial/posterolateral arm (zone 3), and the para-axillary region (zone 4; Figure 3). Grade 1 brachial ptosis is characterized by minimal fat and skin excesses, grade 2 includes minimal skin sagging and fat excess, and grade 3 comprises moderate skin sagging and fat excess (Table 1). We also developed a treatment algorithm that includes: 1) liposuction of the posterior aspect of the arm and the para-axillary area with a power-assisted device; 2) tunnelization of the anterior and posterior zones of the arms to assist with posterior retraction of ptotic skin; and 3) lipofilling of the bicipital triangle to restore an aesthetically pleasing contour and lift the ptotic skin of the posterior arm. The surgical algorithm described in this study is indicated for patients with grade 2 or 3 ptosis. Patients with grade 1a or 1b ptosis could benefit from lipofilling or liposuction, respectively. Patients with grade 4 ptosis require a staged surgical procedure that involves liposuction, lipofilling, and skin excision to treat excessive sagging of the posterior arm. METHODS Patients and Study Design A total of 130 patients who presented with brachial ptosis and underwent brachioplasty from January 2009 to January 2013 were considered for a prospective study. Patients were evaluated clinically with regard to brachial ptosis and were stratified according to our classification system as follows: grade 1, 9 patients; grade 2, 32 patients; grade 3, 54 patients; and grade 4, 35 patients. Patients with grade 4 ptosis were excluded from the study. Also excluded were smokers, patients with lymphedema of the arms secondary to ancillary procedures, and patients with neurologic, vascular, or connectivetissue disorders of the upper extremities. Included in the study were patients with contour irregularities of the arm and grades 1, 2, or 3 brachial ptosis who wished to avoid a brachioplasty scar. All patients were supplied with detailed information regarding the surgical procedure and the risks and benefits of various surgical options. Patients were informed preoperatively that their surgical results would not be immediately apparent, that wrinkling of the posterior region of the arm
3 Abboud et al 3 Figure 2. Illustrations of the 4 grades of brachial ptosis described in this study. Images were generated with Maya 3D animation software (Autodesk, Inc, Mill Valley, CA), Photoshop (Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA), and Zbrush (Pixologic, Los Angeles, CA). (A) For patients with grade 1a ptosis, arm contour is inadequate, and a depression of the bicipital triangle (zone 2) can be observed. These patients do not have an excess of fatty deposits or skin laxity in the posterior part of the arm (zone 3). Treatment of these patients includes lipofilling of zone 2 to improve the aesthetic contour of the arm. (B) Patients with grade 1b ptosis present with minimal skin laxity, excess fat in zone 3, and a normal contour of zone 2. For these patients, simple liposuction of zone 3 is sufficient to restore the overall contour of the arm. (C) For patients with grade 2a ptosis, arm contour is lacking owing to minimal skin laxity and minimal to moderate fat excess in zone 3 as well as a flattened or depressed zone 2. These patients can be treated with liposuction of zone 3 combined with lipofilling of zone 2. (D) Compared with (C), patients with grade 2b ptosis have a more pronounced zone 3 and a flatter zone 2. Therefore, treatment of these patients involves more liposuction of zone 3 and more lipofilling of zone 2. (E) Patients with grade 3a ptosis have moderate amounts of skin laxity and fat excess in zone 3. These patients usually are obese and have good skin tone and a well-contoured zone 2. Therefore, liposuction of zone 3 is sufficient to restore arm contour. (F) For patients with grade 3b ptosis, arm contour is lacking owing to moderate skin laxity and fat excess in zone 3 as well as a moderately flattened zone 2. These patients can be treated by combining liposuction and lipofilling of zones 3 and 2, respectively, to restore arm contour. (G) Patients with grade 4a ptosis have moderate skin excess and severe fat excess in zone 3 as well as a flattened or depressed zone 2. Treatment of these patients may be carried out in 1 surgical session during which liposuction and skin excision are performed concurrently. Alternatively, these patients may undergo staged procedures in which liposuction and lipofilling are performed in 1 session, and excisional surgery is performed in a subsequent session. (H) In general, patients with grade 4b ptosis have undergone massive weight loss and present with severe wrinkling and skin excess, moderate fat excess in zone 3, and a severely depressed zone 2. As in (G), patients with grade 4b ptosis may undergo liposuction and excisional surgery in a single session, or they may chose to undergo liposuction and lipofilling in 1 session and excisional surgery in a subsequent session. (I) Patients with grade 4c ptosis usually are morbidly obese and present with a globally oversized arm, characterized by severe skin and fat excesses in zone 3 and an overfilled zone 2. These patients are not candidates for body contouring and should reduce their weight before undergoing brachioplasty.
4 4 Aesthetic Surgery Journal Table 1. Algorithm for Brachioplasty by Power-Assisted Liposuction and Fat Transfer Ptosis Grade Skin Excess Fat Excess Contour Depression of Bicipital Triangle Approach for Surgical Treatment 1a None None Minimal Lipofilling 1b Minimal Minimal None Liposuction 2a Minimal Minimal to Moderate Minimal Liposuction (0-100 ml) and lipofilling 2b Minimal Moderate Moderate Liposuction ( ml) and lipofilling 3a Moderate Moderate None Liposuction ( ml) 3b Moderate Moderate Moderate Liposuction ( ml) and lipofilling a 4a b Moderate Severe Moderate to severe Single session or staged procedure of liposuction (>400 ml), lipofilling, and skin excision 4b b Severe Moderate Severe Single session or staged procedure of liposuction (<400 ml), lipofilling, and skin excision 4c c Severe Severe None Weight reduction a If revisional surgery is warranted following liposuction/lipofilling to address grade 3b ptosis, the resulting scar is smaller than with traditional excisional brachioplasty. b If the patient does not wish to undergo a staged procedure consisting of liposuction and lipofilling first and excisional surgery second, then liposuction and excisional surgery can be performed in a single session. The resulting scar would extend to the elbow. c Patients with grade 4c ptosis typically are morbidly obese with massive skin and fat excesses. These patients should be advised to lose weight before undergoing brachioplasty. was likely to occur in the early postoperative period, and that skin retraction would occur gradually over a three month period. The possibility of persistent residual wrinkling following the procedure, potentially requiring revisional surgery, was discussed. Patients were advised to make financial arrangements to support a secondary brachioplasty if deemed necessary. Patients who declined to undergo the procedure after receiving this information were excluded from the study. Because this was not a comparative study, we did not evaluate patients who wished to undergo traditional brachioplasty (ie, with skin excision) rather than our proposed technique (ie, without skin excision). The 95 patients included in the study provided written informed consent. Medical charts were reviewed preoperatively, and patient demographics, including age, gender, method of weight loss, body mass index, and comorbidities, were recorded. Because all patients underwent surgery in a private practice, approval from an institutional review board or ethics committee was not obtained. This study was conducted in accordance with the principles set forth in the Declaration of Helsinki. Surgical Procedures and Postoperative Care Each patient was asked to stand with shoulders abducted 90 degrees and with elbows extended and then flexed. The 4 treatment zones of the arm and contiguous para-axillary regions were marked preoperatively (Figure 3). Zone 1 comprised the anteromedial and anterolateral arm and was treated with subcutaneous tunnelization. Zone 2 comprised the bicipital triangle, which is characterized by a contour depression in patients with grades 1a, 2a, 2b, 3b, 4a, and 4b ptosis. This zone was treated with lipofilling. Zone 3 included the posteromedial and posterolateral aspects of the arm, in which excess subcutaneous fat and ptotic skin are located. Liposuction and tunnelization were applied to zone 3; conventional brachioplasty techniques typically involve skin and subcutaneous fat excision in this zone. Zone 4 comprised the para-axillary region (ie, the lateral pectoral zone and the upper back); this zone was treated with liposuction and subcutaneous tunnelization. In addition, the primary fat-donor sites were marked along the posterior zone of the arm. The flanks and/or thighs also were marked when additional fat was needed for injection into the bicipital triangle. The patient was positioned supine for the entire operation. Intraoperative and postoperative parameters, including the lipoaspirate volume, the volume of fat injected, the operating time, and the incidence of complications, were recorded. A single power-assisted liposuction system (Lipomatic Eva SP, Euromi SA, Verviers, Belgium) was employed to infiltrate tissue with Klein s solution, perform liposuction, and transfer fat. A video demonstrating these preoperative markings and surgical procedures in a 26-year-old woman may be viewed at Zone 3 was infiltrated with Klein s solution and was subsequently deflated by means of a customized, multiplehole, v-shaped cannula (diameter, 3 mm) attached to a handpiece and set to 3 bars handpiece pressure and 0.7 atm suction pressure. Liposuction was performed in the deep and superficial subcutaneous planes until the results of a pinch test were approximately 1 cm. When necessary, zone 4 was infiltrated and deflated by the same approach. Thelipoaspiratewasplacedundergentlepressureonanabdominalpadtorapidlyseparatetheadiposetissuefromblood
5 Abboud et al 5 Figure 3. Illustrations of the 4 treatment zones of the arm as viewed from (A) the front and (B) the back. Images were generated with Maya 3D animation software (Autodesk, Inc), Photoshop (Adobe Systems), and Zbrush (Pixologic). Zone 1 (green) corresponds to the anteromedial/anterolateral arm and is treated with subcutaneous tunnelization. Zone 2 (yellow) corresponds to the bicipital triangle and is treated by lipofilling. Zone 3 (red) and zone 4 ( purple) correspond to the posteromedial/posterolateral arm and the para-axillary region, respectively. These zones are treated with liposuction and subcutaneous tunnelization. (C) Front-view and (D) rear-view photographs of this 26-year-old woman who presented with grade 3b brachial ptosis. The patient underwent preoperative marking of the treatment zones, as follows: black, zone 1; green, zone 2; and red, zone 3. Zone 4 was not marked for this patient because treatment of this region was not required. and crystalloids without destroying fat cells. The remaining solution of adipose tissue was collected into sterile 60-mL syringes. To shorten the time that harvested fat was kept outside the body and to decrease the overall operating time, 2 surgical teams performed these procedures. Specifically, the surgeon performed liposuction of the arm and harvested the lipoaspirate while the assistant strained the lipoaspirate and transferred adipose tissue to the syringes. When needed, this procedure was applied to harvest and prepare additional fat from the flanks or thighs. Aspiration was disabled in the power-assisted liposuction system, and multilayered and multidirectional tunnelization was achieved through multiple access points in the subcutaneous plane of zones 1, 2, 3, and 4. Tunnelization in zone 2 was performed to prepare a matrix for fat injection. Harvested fat was grafted into zone 2 through a customized v-shaped cannula (3 holes, 3 mm in diameter) with simultaneous vibration of the recipient site. Fat also was injected in the subcutaneous plane along access points at the apex and anterior and posterior edges of the bicipital triangle. This region was carefully overfilled to accommodate some resorption of injected fat. Patients were advised to utilize compression garments for 2 weeks postoperatively. If deemed tolerable by the
6 6 Aesthetic Surgery Journal Table 2. Patient Demographics and Surgical Data patient, deep lymphatic massage was recommended to decrease contour deformities and resolve edema more quickly. Assessment of Patient Satisfaction At 6 months postoperatively, patients were asked to complete a nonanonymous questionnaire prepared by the authors (a blank copy of the questionnaire is available as Supplementary Material at The results of the questionnaire were analyzed to determine the psychological and physical well-being of each patient preoperatively and at 6 months postoperatively and to assess patient satisfaction with the surgical outcomes. RESULTS Study Group (N = 95) Mean age (range), years 39 (19-58) Mean BMI (range), kg/m 2 28 (21-36) Mean lipoaspirate volume per arm (range), ml 240 (0-450) Mean arm fat injection volume per side (range), ml 100 (0-220) Mean operating time (range), minutes 50 (45-60) Mean no. of sessions (range) 1.1 (1-2) Mean follow-up (range), months 24 (12-48) BMI, body mass index. Of 95 women who underwent brachioplasty by means of liposuction and fat transfer, 45 patients (47.4%) underwent brachioplasty as the sole procedure, and 50 patients (52.6%) underwent brachioplasty combined with another body contouring procedure (abdominoplasty, thighlift, back lift, and mastopexy). Prior to undergoing brachioplasty, 41 patients (43.1%) underwent a bariatric procedure for weight loss, whereas 26 patients (27.3%) lost weight through diet and exercise alone. No men presented to our practice for brachioplasty during the study period. It is important to inform patients that skin retraction occurs gradually after power-assisted liposuction and lipofilling of the arm. Wrinkling of the posterior arm also may be observed while edema and inflammation resolve, especially for patients who present with grade 3 ptosis. In our experience, the grade of brachial ptosis did not correlate with patient preference for a specific surgical procedure (ie, with or without skin excision). Three patients with grade 3 ptosis and 3 patients with grade 2 ptosis declined to undergo our novel brachioplasty technique. The mean age of the patients was 39 years (range, years), and the mean body mass index was 28 kg/m 2 (range, kg/m 2 )(Table2). The mean lipoaspirate volume was 240 ml per arm (range, ml per arm), and the mean fat injection volume was 100 ml per side per session (range, ml per side per session). The mean operating time for brachioplasty was 50 minutes (range, minutes), and an average of 1.1 sessions (range, 1-2 sessions) were required to achieve the desired outcome. The mean follow-up period was 24 months (range, months). Patients who underwent only brachioplasty were discharged the same day as the surgery, returned to sedentary activities at 7 days postoperatively, and resumed full activity at 3 weeks postoperatively. The average hospital stay for patients who underwent brachioplasty in combination with another procedure was 2.3 days (range, 1-4 days; Figures 4-5 and Supplemental Figures 1-2 [available online at The overall complication rate was 2.1% (2 of 95 patients). None of the patients experienced major complications, such as lymphedema, skin necrosis, or nerve injuries. No complications developed in patients who underwent brachioplasty alone. Abdominal hematoma occurred in 1 patient who underwent brachioplasty in combination with lipoabdominoplasty, and unilateral thigh hematoma developed in 1 patient who received brachioplasty in combination with thigh lift (Table 3). Eighty-seven of the 95 patients (91.6%) completed a questionnaire 6 months postoperatively (Figure 6). Six patients (6.3%) declined to complete the questionnaire at the beginning of the study (ie, before undergoing surgery), citing personal reasons. Two patients (2.1%) withdrew from the study before the questionnaire was administered. Therefore, the results of this study were not affected by selection bias. Of 87 survey respondents, 79 (90.8%) indicated that they would repeat the surgical procedure or recommend it to a friend, 78 patients (89.6%) were satisfied with the final shape of their arms, and 80 patients (91.9%) reported improved psychological well-being as a result of the operation (Figure 6). The overall rate of revision was 9.5% (9 of 95 patients). The 9 patients who underwent revisional surgery originally presented with grade 3b brachial ptosis. Despite improvements in arm shape following power-assisted liposuction and lipofilling, these patients had concerns regarding residual ptosis and persistent wrinkling in the posterior proximal region of the arm and in the para-axillary area. Two of these patients (2.1%) refused revisional surgery consisting of combined liposuction and lipofilling and instead underwent excisional brachioplasty. The remaining 7 patients underwent revisional brachioplasty for contour enhancement by means of power-assisted liposuction and lipofilling. The 9 patients who underwent revisional surgery were asked to complete an additional questionnaire to assess their satisfaction 6 months after the secondary procedure. All 9 patients reported improvements in arm shape following the revisional procedure, and none of the patients sought additional arm surgery.
7 Abboud et al 7 Figure 4. (A, C) This 47-year-old woman presented with grade 1a brachial ptosis. She underwent power-assisted transfer of 140 ml of autologous fat to the bicipital triangle of each arm. (B, D) Two years postoperatively. DISCUSSION Despite numerous studies aimed at classifying and surgically correcting brachial deformities, unfavorable scarring and considerable complication rates have persisted. 3,8,9,14,15 Many authors have described liposuction of the arm as a safe and effective treatment strategy for brachial ptosis. 3,5,6,9-12,16-19 Liposuction may be performed alone or in combination with skin excision to improve the contour of the arm, decrease bulkiness, loosen subcutaneous tissue, and enhance the aesthetic results of brachioplasty. 1-3,20 Gilliland and Lyos 9,10 have advocated circumferential para-axillary liposuction in the superficial and/or subdermal planes to improve skin retraction. These authors also demonstrated the reliability of liposuction to effect skin retraction in the posteromedial and posterolateral aspects of the arm. Herein we described a novel surgical treatment for patients with mild to moderate brachial ptosis (ie, grades 1, 2, or 3) that combines liposuction and lipofilling of the arm and obviates skin excision. This procedure involves deflation of the ptotic region of the arm (zone 3) and lipofilling of the bicipital triangle (zone 2). Liposuction of zone 3 helps to tighten the skin. Fat transfer to zone 2 fills the depression at the bicipital triangle and places upward
8 8 Aesthetic Surgery Journal Figure 5. (A, C, E) This 26-year-old woman presented with grade 3b brachial ptosis and underwent liposuction of zone 3 of each arm (lipoaspirate, 300 ml per arm) and transfer of autologous fat (180 ml per arm) to the bicipital triangle of each arm. (B, D, F) One year postoperatively. Table 3. Complications of Brachioplasty Alone or Combined With Additional Body Contouring Procedures (N = 95) Complication No. of patients (%) Hematoma a 2 (2.1) Seroma 0 (0) Infection 0 (0) Wound dehiscence 0 (0) Embolism 0 (0) There were no complications among patients who underwent brachioplasty as the only procedure. a An abdominal hematoma developed in 1 patient who underwent brachioplasty combined with lipoabdominoplasty. A unilateral thigh hematoma occurred in 1 patient who underwent brachioplasty combined with thigh lift. tension on zone 3, thereby supporting and redraping ptotic skin and restoring a pleasing contour of the arm in patients with grade 2 or 3 ptosis. Lipofilling also lifts the posterior ptotic skin of the arm through volumization effects that recruit skin from the deflated region of the posterior arm. Because the subcutaneous space of the bicipital triangle is large, upward tension on the abundant skin excess skin of the posterior arm is unlikely to be problematic. Our technique of power-assisted fat injection expands the recipient site by means of vibration and multilayered tunnelization. We suggest that the process of thrusting the cannula in the superficial subcutaneous spaces of the arm releases tethered tissues in this region and facilitates postoperative skin retraction. These maneuvers maximize the dispersal and expansion of fat in the subcutaneous space, thereby creating an ideal substrate for fat grafting 24,25 and optimizing graft survival by minimizing tension and preventing fat lobules from crowding. A moderate volume of fat must be injected for sufficient brachial rejuvenation. We cannot rule out that conventional methods of fat preparation 23 and injection might be as effective as our method of power-assisted fat transfer. We chose to adapt power-assisted fat grafting to brachial ptosis because we previously demonstrated favorable results when applying this procedure to augment the breasts 24 and gluteal region. 25 Because our technique obviates skin excision and consequent scarring, it is likely to have lower rates of complication and morbidity. Patients who undergo power-assisted fat grafting recover more quickly and can resume daily activities in a timely fashion. Our technique shortens the operating time and decreases surgical risks and complications for patients who undergo
9 Abboud et al 9 was to validate this technique for patients with mild to moderate ptosis (ie, grades 1, 2, or 3). An evaluation of the utility of this technique for patients with grade 4 ptosis is warranted. Finally, the effects of tunnelization and vibration detailed in this study are based on the authors observations. A clinical study involving a control group is needed to determine the precise benefits of these surgical maneuvers. CONCLUSIONS Figure 6. Results of the patient satisfaction questionnaire, which was administered at 6 months postoperatively and was completed by 87 of 95 patients (91.6%). Seventy-nine respondents (90.8%) indicated that they would repeat the surgical procedure or recommend it to a friend. Blue bars indicate responses of very dissatisfied/not good, red bars indicate responses of somewhat dissatisfied/not good, green bars indicate responses of somewhat dissatisfied/good, and purple bars indicate responses of very satisfied/good. A dissatisfied rating comprised responses of very/somewhat dissatisfied and not good/somewhat good. Satisfied ratings comprised responses of very satisfied/somewhat satisfied and somewhat good/very good. brachioplasty in combination with other body contouring procedures. Patients with grade 4 ptosis often have poor skin quality. For these patients, liposuction combined with dermolipectomy of the arm have been shown to decrease the amount of skin excision needed and thus the length of the scar. 9,10,16,17,21 For patients with massive brachial ptosis and poor skin tone, the benefits of liposuction are questionable, especially if skin retraction is likely to be insufficient. However, skin excision with a short scar can be performed at a second surgical session if the outcomes of liposuction alone include residual contour deformities or if the patient requests additional treatment. Study Limitations Patient satisfaction was evaluated 6 months postoperatively by means of a nonanonymous questionnaire that was prepared by the authors. The timing of this assessment may have been premature. An evaluation of patient satisfaction at 1 or 2 years postoperatively would further validate the present study and might yield different results. In addition, power-assisted liposuction and lipofilling are not indicated for all grades of brachial ptosis. Patients with grade 4 ptosis require excisional surgery alone or as a staged procedure with liposuction and lipofilling. We did not include patients with grade 4 ptosis in the present study because our aim We described a classification system and treatment algorithm for rejuvenation of the arm, associated with minimal complications. The ptotic brachial region is delineated into 4 zones that are treated by liposuction or lipofilling to achieve an aesthetically pleasing contour. The bicipital triangle (zone 2) is addressed by lipofilling to improve retraction and redraping of the ptotic skin at the posterior arm. Liposuction and fat transfer yield satisfactory results for patients with mild to moderate (grades 1, 2, or 3) brachial ptosis and eliminate the need for excisional surgery. Additional studies are needed to validate this technique for patients with grade 4 brachial ptosis, and patients must be adequately informed and carefully selected for this surgical procedure. To our knowledge, this is the first study to involve a bicipital triangle in the classification and treatment of brachial ptosis and to employ power-assisted fat injection into the arm. Supplementary Material This article contains supplementary material located online at Acknowledgments The authors thank Mr Emilio Kheir for creating the illustrations presented in this article. Disclosures The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article. Funding The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and publication of this article. REFERENCES 1. Appelt EA, Janis JE, Rohrich RJ. An algorithmic approach to upper arm contouring. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;118: Mahmoud AS, Sadek EY, Salem BZ, Elmeligy AA. A new algorithm for brachioplasty.: Egypt, J Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;34:
10 10 Aesthetic Surgery Journal 3. El Khatib HA. Classification of brachial ptosis: strategy for treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119: de Souza Pinto EB, Erazo PJ, Matsuda CA, Regazzini DV, Burgos DS, Acosta HAP, do Amaral AG. Brachioplasty technique with the use of molds. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;105: , discussion Teimourian B, Malekzadeh S. Rejuvenation of the upper arm. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998;102: , discussion Richards ME. Minimal-incision brachioplasty: a firstchoice option in arm reduction surgery. Aesthet Surg J. 2001;21: Lockwood T. Contouring of the arms, trunk and thighs. Plastic Surgery: Indications, Operations, and Outcomes. Vol. 5: Aesthetic Surgery. Achauer BM, Eriksson E, Gjyuron B, et al., eds. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; Goddio AS. A new technique for brachioplasty.: Plast Reconstr Surg. 1989;84: Gilliland MD, Lyos AT. CAST liposuction of the arm improves aesthetic results. Aesthet Plast Surg. 1997;21: Gilliland MD, Lyos AT. CAST liposuction: an alternative to brachioplasty. Aesthet Plast Surg. 1997;21: Vogt PA. Brachial suction assisted lipoplasty and brachioplasty. Aesthet Surg J. 2001;21: Nguyen AT, Rohrich RJ. Liposuction assisted posterior brachioplasty: technical refinements in upper arm contouring. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126: Abadesso I, Serra F. Augmentation brachioplasty: surgery for improving the appearance of the arms. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 2012;27: Knoetgen J 3rd, Moran SL. Long-term outcomes and complications associated with brachioplasty: a retrospective review and cadaveric study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117: Gusenoff JA, Coon D, Rubin JP. Brachioplasty and concomitant procedures after massive weight loss: a statistical analysis from a prospective registry. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;122: Gasparotti M. Superficial liposuction: a new application of the technique for aged and flaccid skin. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1992;16: Hong YG, Sim HB, Lee MY, Seo SW, Chang CH, Yeo KK, Kim JK. Three-dimensional circumferential liposuction of the overweight or obese upper arm. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2012;36: Ambrason DL. Minibrachioplasty: minimizing scars while maximizing results. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;114: , discussion Trussler AP, Rohrich RJ. Limited incision medial brachioplasty: technical refinements in upper arm contouring. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;121: Capella JF, Trovato MJ, Woebrle S. Brachioplasty. The Art of Aesthetic Surgery: Principles and Techniques. 2nded. Nahai F, ed. St. Louis, MO: Quality Medical Publishing; 2010: Lillis PJ.: Liposuction of the arms.: Dermatol Clin. 1999;17: Bossert RP, Dreifuss S, Coon D, Wollstein A, Clavijo-Alvarez J, Gusenoff JA, Rubin JP.: Liposuction of the arm concurrent with brachioplasty in the massive weight loss patient: is it safe? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131: Coleman SR. Infraorbital and check region. Structural fat grafting. Coleman SR, ed. St. Louis, MO: Quality Medical Publishing;2004: Abboud MH, Dibo SA.: Immediate large-volume grafting of autologous fat to the breast following implant removal.: Aesthet Surg J. 2015;35: Abboud MH, Dibo SA, Abboud NM. Power-assisted gluteal augmentation: a new technique for sculpting, harvesting, and transferring fat. Aesthet Surg J. 2015;35(8):
Power-Assisted Gluteal Augmentation: A New Technique for Sculpting, Harvesting, and Transferring Fat
 Body Contouring Power-Assisted Gluteal Augmentation: A New Technique for Sculpting, Harvesting, and Transferring Fat Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2015, Vol 35(8) 987 994 2015 The American Society for Aesthetic
Body Contouring Power-Assisted Gluteal Augmentation: A New Technique for Sculpting, Harvesting, and Transferring Fat Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2015, Vol 35(8) 987 994 2015 The American Society for Aesthetic
Mons Pubis Ptosis: Classification and Strategy for Treatment
 Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:24 30 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9552-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mons Pubis Ptosis: Classification and Strategy for Treatment Hamdy A. El-Khatib Received: 2 April 2010 / Accepted: 25 June
Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:24 30 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9552-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mons Pubis Ptosis: Classification and Strategy for Treatment Hamdy A. El-Khatib Received: 2 April 2010 / Accepted: 25 June
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Surgical Pearls in the Management of Body Contouring by Liposculpture from Fournier s Syringe to Lipomatic
 Surgical Pearls in the Management of Body Contouring by Liposculpture from Fournier s Syringe to Lipomatic By Constantin STAN, M.D. The MEDICAL SERVICE Clinic - Romania PEARLS little concepts that can
Surgical Pearls in the Management of Body Contouring by Liposculpture from Fournier s Syringe to Lipomatic By Constantin STAN, M.D. The MEDICAL SERVICE Clinic - Romania PEARLS little concepts that can
Is There an Ideal Donor Site of Fat for Secondary Breast Reconstruction?
 526751AESXXX10.1177/1090820X14526751Aesthetic Surgery JournalSmall et al research-article2014 Breast Surgery Is There an Ideal Donor Site of Fat for Secondary Breast Reconstruction? Kevin Small, MD; Mihye
526751AESXXX10.1177/1090820X14526751Aesthetic Surgery JournalSmall et al research-article2014 Breast Surgery Is There an Ideal Donor Site of Fat for Secondary Breast Reconstruction? Kevin Small, MD; Mihye
Champagne Groove Lipectomy: A Safe Technique to Contour the Upper Abdomen in Abdominoplasty
 Champagne Groove Lipectomy: A Safe Technique to Contour the Upper Abdomen in Abdominoplasty Ron Brooks, MD, Jonathan Nguyen, MD, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, John Paul Tutela, MD, Sean Kelishadi, MD, David Yonick,
Champagne Groove Lipectomy: A Safe Technique to Contour the Upper Abdomen in Abdominoplasty Ron Brooks, MD, Jonathan Nguyen, MD, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, John Paul Tutela, MD, Sean Kelishadi, MD, David Yonick,
Aesthetic Surgery Journal
 Aesthetic Surgery Journal http://aes.sagepub.com/ Aesthetic and Functional Satisfaction After Monsplasty in the Massive Weight Loss Population Jacob M. P. Bloom, Emily Van Kouwenberg, Michael Davenport,
Aesthetic Surgery Journal http://aes.sagepub.com/ Aesthetic and Functional Satisfaction After Monsplasty in the Massive Weight Loss Population Jacob M. P. Bloom, Emily Van Kouwenberg, Michael Davenport,
Abdominoplasty with Scarpa s Fascia Advancement Flap to Enhance the Waistline
 My Way Abdominoplasty with Scarpa s Fascia Advancement Flap to Enhance the Waistline Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2016, Vol 36(7) 852 857 2016 The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, Inc. Reprints
My Way Abdominoplasty with Scarpa s Fascia Advancement Flap to Enhance the Waistline Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2016, Vol 36(7) 852 857 2016 The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, Inc. Reprints
CHAPTER 19 BODY CONTOURING. Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Sachin M. Shridharani, MD
 CHAPTER 19 BODY CONTOURING Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Sachin M. Shridharani, MD Body contouring is an umbrella term for aesthetic surgery of the body that includes the breasts, abdomen/trunk and upper and
CHAPTER 19 BODY CONTOURING Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Sachin M. Shridharani, MD Body contouring is an umbrella term for aesthetic surgery of the body that includes the breasts, abdomen/trunk and upper and
Vertical mammaplasty has been developed
 BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
See Before & After Gallery and Other Procedures at Open Body Contour
 Open Body Contour Despite the great advances which have been achieved since the advent of suction lipoplasty, surgeons and patients are still unable to restore skin elasticity. Skin becomes loose for several
Open Body Contour Despite the great advances which have been achieved since the advent of suction lipoplasty, surgeons and patients are still unable to restore skin elasticity. Skin becomes loose for several
Post-bariatric body contouring: our experience
 Acta Biomed 2016; Vol. 87, N. 1: 70-75 Mattioli 1885 Original article Post-bariatric body contouring: our experience Michele P. Grieco 1, Eugenio Grignaffini 1, Francesco Simonacci 1, Donatello Di Mascio
Acta Biomed 2016; Vol. 87, N. 1: 70-75 Mattioli 1885 Original article Post-bariatric body contouring: our experience Michele P. Grieco 1, Eugenio Grignaffini 1, Francesco Simonacci 1, Donatello Di Mascio
The Changing Body After Bariatric Surgery Plastic Surgery & Other Options. Al Aly, MD, FACS
 The Changing Body After Bariatric Surgery Plastic Surgery & Other Options Al Aly, MD, FACS Professor of Plastic Surgery Director of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery University of California Irvine Overview Why
The Changing Body After Bariatric Surgery Plastic Surgery & Other Options Al Aly, MD, FACS Professor of Plastic Surgery Director of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery University of California Irvine Overview Why
Drains are Not Needed in Body Contouring Procedures. Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS
 Drains are Not Needed in Body Contouring Procedures Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Drains are Not Needed in Body Contouring Procedures Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures The Doctors Company - Advisory
Drains are Not Needed in Body Contouring Procedures Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Drains are Not Needed in Body Contouring Procedures Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures The Doctors Company - Advisory
Various Surgical Techniques for Improving Body Contour
 Aesth. Plast. Surg. 29:446 455, 2005 DOI: 10.1007/s00266-005-0037-9 Various Surgical Techniques for Improving Body Contour La zaro Ca rdenas-camarena, M.D. Jalisco, Me xico Abstract. Body contouring surgery
Aesth. Plast. Surg. 29:446 455, 2005 DOI: 10.1007/s00266-005-0037-9 Various Surgical Techniques for Improving Body Contour La zaro Ca rdenas-camarena, M.D. Jalisco, Me xico Abstract. Body contouring surgery
Breast reduction surgery reduction mammaplasty Is it right for me? What to expect during your consultation Be prepared to discuss:
 This guide is for women who are considering having an operation to lift their breasts. We advise that you talk to a plastic surgeon and only use this information as a guide to the procedure. Breast reduction
This guide is for women who are considering having an operation to lift their breasts. We advise that you talk to a plastic surgeon and only use this information as a guide to the procedure. Breast reduction
Body contouring by combined abdominoplasty and medial vertical thigh reduction: experience of 14 cases
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 222 227 Body contouring by combined abdominoplasty and medial vertical thigh reduction: experience of 14 cases M.G. Ellabban*, N.B. Hart Plastic Surgery
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 222 227 Body contouring by combined abdominoplasty and medial vertical thigh reduction: experience of 14 cases M.G. Ellabban*, N.B. Hart Plastic Surgery
Body Contouring After Major Weight Loss
 Body Contouring After Major Weight Loss Dramatic weight loss, whether achieved by proper nutrition and exercise, or as the result of bariatric surgery, or from other forms of medical treatment, has many
Body Contouring After Major Weight Loss Dramatic weight loss, whether achieved by proper nutrition and exercise, or as the result of bariatric surgery, or from other forms of medical treatment, has many
No Drain Abdominoplasty with Progressive Tension Sutures. Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS
 No Drain Abdominoplasty with Progressive Tension Sutures Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures Suneva Medical Instructor Merz Advisory Board NO financial interests in any suture company Will use brand
No Drain Abdominoplasty with Progressive Tension Sutures Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures Suneva Medical Instructor Merz Advisory Board NO financial interests in any suture company Will use brand
Lipoabdominoplasty: The Saldanha Technique
 Lipoabdominoplasty: The Saldanha Technique Osvaldo R. Saldanha, MD a, *,Sergio F.D. Azevedo, MD a,b,c, Pablo S.F. Delboni, MD a,b,c, Osvaldo R. Saldanha Filho, MD a,d, Cristianna B. Saldanha a,e, Luis
Lipoabdominoplasty: The Saldanha Technique Osvaldo R. Saldanha, MD a, *,Sergio F.D. Azevedo, MD a,b,c, Pablo S.F. Delboni, MD a,b,c, Osvaldo R. Saldanha Filho, MD a,d, Cristianna B. Saldanha a,e, Luis
Case Studies in Asian Blepharoplasty
 Aesthetic Surgery Journal XX(X) Takayanagi INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Oculoplastic Surgery Review Article Case Studies in Asian Blepharoplasty Aesthetic Surgery Journal 31(2) 171 179 2011 The American
Aesthetic Surgery Journal XX(X) Takayanagi INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Oculoplastic Surgery Review Article Case Studies in Asian Blepharoplasty Aesthetic Surgery Journal 31(2) 171 179 2011 The American
COSMETIC SURGERY: BREAST LIFT (MASTOPEXY)
 PROCEDURE FACT SHEET PLASTIC SURGERY COSMETIC SURGERY: BREAST LIFT (MASTOPEXY) This guide is for women who are considering having an operation to lift their breasts. We advise that you talk to a plastic
PROCEDURE FACT SHEET PLASTIC SURGERY COSMETIC SURGERY: BREAST LIFT (MASTOPEXY) This guide is for women who are considering having an operation to lift their breasts. We advise that you talk to a plastic
Augmentation of the Ptotic Breast: Simultaneous Periareolar Mastopexy/Breast Augmentation By: Laurence Kirwan, M.D., F.R.C.S
 Augmentation of the Ptotic Breast: Simultaneous Periareolar Mastopexy/Breast Augmentation By: Laurence Kirwan, M.D., F.R.C.S Background: Submusculofascial augmentation of the ptotic breast can result in
Augmentation of the Ptotic Breast: Simultaneous Periareolar Mastopexy/Breast Augmentation By: Laurence Kirwan, M.D., F.R.C.S Background: Submusculofascial augmentation of the ptotic breast can result in
Reducing Seroma in Outpatient Abdominoplasty: Analysis of 516 Consecutive Cases
 Body Contouring Reducing Seroma in Outpatient Abdominoplasty: Analysis of 516 Consecutive Cases Aesthetic Surgery Journal 30(3) 418 427 2010 The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, Inc. Reprints
Body Contouring Reducing Seroma in Outpatient Abdominoplasty: Analysis of 516 Consecutive Cases Aesthetic Surgery Journal 30(3) 418 427 2010 The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, Inc. Reprints
Anti-aging treatments that harness the hands of time
 www.cosmeticsurgerytimes.com Part of the Modified Avelar abdominoplasty 34 SEPTEMBER 2011 Vol. 14 No. 8 Flap resection for inner thigh lifting 36 Anti-aging treatments that harness the hands of time Facelifting
www.cosmeticsurgerytimes.com Part of the Modified Avelar abdominoplasty 34 SEPTEMBER 2011 Vol. 14 No. 8 Flap resection for inner thigh lifting 36 Anti-aging treatments that harness the hands of time Facelifting
Cleft lip is the most common craniofacial
 Ideas and Innovations Fat Grafting in Primary Cleft Lip Repair Elizabeth Gordon Zellner, M.D. Miles J. Pfaff, M.D. Derek M. Steinbacher, M.D., D.M.D. New Haven, Conn. Summary: The goal of primary cleft
Ideas and Innovations Fat Grafting in Primary Cleft Lip Repair Elizabeth Gordon Zellner, M.D. Miles J. Pfaff, M.D. Derek M. Steinbacher, M.D., D.M.D. New Haven, Conn. Summary: The goal of primary cleft
Reduction mammoplasty techniques in post-bariatric patients: our experience
 Acta Biomed 2017; Vol. 88, N. 2: 156-160 DOI: 10.23750/abm.v88i2.5085 Mattioli 1885 Original article Reduction mammoplasty techniques in post-bariatric patients: our experience Susanna Polotto 1, Michele
Acta Biomed 2017; Vol. 88, N. 2: 156-160 DOI: 10.23750/abm.v88i2.5085 Mattioli 1885 Original article Reduction mammoplasty techniques in post-bariatric patients: our experience Susanna Polotto 1, Michele
The latest statistics from the National Center for. Correlation of Complications of Body Contouring Surgery With Increasing Body Mass Index
 Correlation of Complications of Body Contouring Surgery With Increasing Body Mass Index The latest statistics from the National Center for Health Statistics state that 30% of U.S. adults over the age of
Correlation of Complications of Body Contouring Surgery With Increasing Body Mass Index The latest statistics from the National Center for Health Statistics state that 30% of U.S. adults over the age of
Truncal body contouring surgery in the massive weight loss patient
 Clin Plastic Surg 31 (2004) 611 624 Truncal body contouring surgery in the massive weight loss patient Al S. Aly, MD, FACS*, Albert E. Cram, MD, FACS, Claudette Heddens, MA, ARNP, CPSN, BSN Plastic Surgery,
Clin Plastic Surg 31 (2004) 611 624 Truncal body contouring surgery in the massive weight loss patient Al S. Aly, MD, FACS*, Albert E. Cram, MD, FACS, Claudette Heddens, MA, ARNP, CPSN, BSN Plastic Surgery,
No Drain Abdominoplasty: No More Excuses. Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS
 No Drain Abdominoplasty: No More Excuses Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures NO financial interests in any suture company Will use brand names due to lack of distinguishing generic names Objectives
No Drain Abdominoplasty: No More Excuses Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures NO financial interests in any suture company Will use brand names due to lack of distinguishing generic names Objectives
Combined Use of Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction and Limited-Incision Platysmaplasty for Treatment of the Aging Neck
 Aesth Plast Surg (2008) 32:790 794 DOI 10.1007/s00266-008-9215-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Combined Use of Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction and Limited-Incision Platysmaplasty for Treatment of the Aging Neck Patrick
Aesth Plast Surg (2008) 32:790 794 DOI 10.1007/s00266-008-9215-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Combined Use of Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction and Limited-Incision Platysmaplasty for Treatment of the Aging Neck Patrick
F ORUM. Is One-Stage Breast Augmentation With Mastopexy Safe and Effective? A Review of 186 Primary Cases
 Is One-Stage Breast Augmentation With Mastopexy Safe and Effective? A Review of 186 Primary Cases W. Grant Stevens, MD; David A. Stoker, MD; Mark E. Freeman, MD; Suzanne M. Quardt, MD; Elliot M. Hirsch,
Is One-Stage Breast Augmentation With Mastopexy Safe and Effective? A Review of 186 Primary Cases W. Grant Stevens, MD; David A. Stoker, MD; Mark E. Freeman, MD; Suzanne M. Quardt, MD; Elliot M. Hirsch,
What vascular access for which patient : obesity
 What vascular access for which patient : obesity C. Sessa, J. Coudurier A. De Lambert, C. Ducos, M. Guergour, O. Pichot Department of Vascular Surgery Grenoble France Controversies & Updates in Vascular
What vascular access for which patient : obesity C. Sessa, J. Coudurier A. De Lambert, C. Ducos, M. Guergour, O. Pichot Department of Vascular Surgery Grenoble France Controversies & Updates in Vascular
No Drain Abdominoplasty: No More Excuses. Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Instructional Course
 No Drain Abdominoplasty: No More Excuses Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Instructional Course Disclosures Angiotech/Surgical Specialties - Advisory Board AxcelRx Pharmacuticals - Advisory Board Suneva Medical
No Drain Abdominoplasty: No More Excuses Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Instructional Course Disclosures Angiotech/Surgical Specialties - Advisory Board AxcelRx Pharmacuticals - Advisory Board Suneva Medical
Personal Evolution in Thighplasty Techniques for Patients Following Massive Weight Loss
 Body Contouring Personal Evolution in Thighplasty Techniques for Patients Following Massive Weight Loss Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2017, 1 12 2017 The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, Inc.
Body Contouring Personal Evolution in Thighplasty Techniques for Patients Following Massive Weight Loss Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2017, 1 12 2017 The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, Inc.
Scientific Forum. Extreme Cosmetic Surgery: A Retrospective Study of Morbidity in Patients Undergoing Combined Procedures
 W. Grant Stevens, MD; Steven D. Vath, MD; and David A. Stoker, MD Dr. Stevens is Associate Clinical Professor, Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery, University of Southern
W. Grant Stevens, MD; Steven D. Vath, MD; and David A. Stoker, MD Dr. Stevens is Associate Clinical Professor, Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery, University of Southern
FOR THE HARMONY OF THE BODY
 FOR THE HARMONY OF THE BODY AND THE PLEASURE TO SEDUCE OUR TECHNICS FOR A nutational infrasonic liposculpture TABLE OF CONT 01 THE NUTATIONAL LIPOFILLING SYSTEM n.l.f. System 1 & 2... Surgeons share their
FOR THE HARMONY OF THE BODY AND THE PLEASURE TO SEDUCE OUR TECHNICS FOR A nutational infrasonic liposculpture TABLE OF CONT 01 THE NUTATIONAL LIPOFILLING SYSTEM n.l.f. System 1 & 2... Surgeons share their
COSMETIC SURGERY: BREAST REDUCTION FOR MEN (GYNAECOMASTIA)
 PROCEDURE FACT SHEET PLASTIC SURGERY COSMETIC SURGERY: BREAST REDUCTION FOR MEN (GYNAECOMASTIA) This is a guide for men who are considering having a breast reduction operation. We advise that you talk
PROCEDURE FACT SHEET PLASTIC SURGERY COSMETIC SURGERY: BREAST REDUCTION FOR MEN (GYNAECOMASTIA) This is a guide for men who are considering having a breast reduction operation. We advise that you talk
Liposuction. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on or your weight management. All decisions about or weight management must be made in conjunction with your
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on or your weight management. All decisions about or weight management must be made in conjunction with your
Patient Safety in Postbariatric Body Contouring. Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS
 Patient Safety in Postbariatric Body Contouring Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures The Doctors Company - Advisory Board Angiotech/Quill - Advisory Board Suneva Medical Instructor Viora - Speaker Will
Patient Safety in Postbariatric Body Contouring Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures The Doctors Company - Advisory Board Angiotech/Quill - Advisory Board Suneva Medical Instructor Viora - Speaker Will
MICHAEL J. BROWN, M.D., P.L.L.C. Aesthetic Cosmetic Plastic Surgery
 MICHAEL J. BROWN, M.D., P.L.L.C. Aesthetic Cosmetic Plastic Surgery INFORMED-CONSENT SUCTION ASSISTED LIPECTOMY SURGERY WITH FAT RE-INJECTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document that has
MICHAEL J. BROWN, M.D., P.L.L.C. Aesthetic Cosmetic Plastic Surgery INFORMED-CONSENT SUCTION ASSISTED LIPECTOMY SURGERY WITH FAT RE-INJECTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document that has
Remodeling Bodylift with High Lateral Tension
 Aesth. Plast. Surg. 26:223 230, 2002 DOI: 10.1007/s00266-002-1478-z 2002 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Remodeling Bodylift with High Lateral Tension J.F. Pascal, 1 and C. Le Louarn 1 Lyon, France 2 Paris,
Aesth. Plast. Surg. 26:223 230, 2002 DOI: 10.1007/s00266-002-1478-z 2002 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Remodeling Bodylift with High Lateral Tension J.F. Pascal, 1 and C. Le Louarn 1 Lyon, France 2 Paris,
Barbed Sutures in Progressive Tension Suture Technique Abdominoplasty. Karol A Gutowski, MD
 Barbed Sutures in Progressive Tension Suture Technique Abdominoplasty Karol A Gutowski, MD 1 Disclosures Speakers Bureau for AngioTech since April 2011 (Makers of Quill bi-directional barbed sutures) Technique
Barbed Sutures in Progressive Tension Suture Technique Abdominoplasty Karol A Gutowski, MD 1 Disclosures Speakers Bureau for AngioTech since April 2011 (Makers of Quill bi-directional barbed sutures) Technique
Despite breast reduction being one of the BREAST. Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction?
 BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
ALTERNATIVE TREATMENT
 INFORMED CONSENT LIPOSUCTION (SUCTION- ASSISTED LIPECTOMY SURGERY) (ULTRASOUND- ASSISTED LIPECTOMY SURGERY) (LASER ASSISTED LIPOSUCTION SURGERY) INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed- consent document that
INFORMED CONSENT LIPOSUCTION (SUCTION- ASSISTED LIPECTOMY SURGERY) (ULTRASOUND- ASSISTED LIPECTOMY SURGERY) (LASER ASSISTED LIPOSUCTION SURGERY) INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed- consent document that
Clinical Policy Title: Abdominoplasty, panniculectomy and brachioplasty
 Clinical Policy Title: Abdominoplasty, panniculectomy and brachioplasty Clinical Policy Number: 18.03.03 Effective Date: July 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: April 27, 2016 Most Recent Review Date: April
Clinical Policy Title: Abdominoplasty, panniculectomy and brachioplasty Clinical Policy Number: 18.03.03 Effective Date: July 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: April 27, 2016 Most Recent Review Date: April
Article Outline Abstract. Patients and Methods Surgical Technique Results Discussion Acknowledgments REFERENCES
 Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery: Volume 104(6) November 1999 pp 1887-1899 Large-Volume Circumferential Liposuction with Tumescent Technique: A Sure and Viable Procedure [Cosmetic Special Topic] Cárdenas-Camarena,
Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery: Volume 104(6) November 1999 pp 1887-1899 Large-Volume Circumferential Liposuction with Tumescent Technique: A Sure and Viable Procedure [Cosmetic Special Topic] Cárdenas-Camarena,
Fat Grafting Technique, A Paradigm Shift in the Treatment of Tuberous Breast
 7 Fat grafting in tuberous breast Original Article Fat Grafting Technique, A Paradigm Shift in the Treatment of Tuberous Breast Downloaded from wjps.ir at 5:45 +040 on Sunday September 9th 08 Claudio Silva-Vergara*,
7 Fat grafting in tuberous breast Original Article Fat Grafting Technique, A Paradigm Shift in the Treatment of Tuberous Breast Downloaded from wjps.ir at 5:45 +040 on Sunday September 9th 08 Claudio Silva-Vergara*,
Abdominal contour surgery has undergone a number of refinements as our understanding
 bdominal Contour Surgery: Treating ll esthetic Units, Including the Mons Pubis lan Matarasso, MD; and Steven G. Wallach, MD ackground: Many patients who seek abdominal contour surgery also desire improvement
bdominal Contour Surgery: Treating ll esthetic Units, Including the Mons Pubis lan Matarasso, MD; and Steven G. Wallach, MD ackground: Many patients who seek abdominal contour surgery also desire improvement
Fat Transfer
 Fat Transfer For those who would like to decrease unwanted fat in specific body areas while restoring or adding volume to other areas of the body, a fat transfer can improve body contours and revitalize
Fat Transfer For those who would like to decrease unwanted fat in specific body areas while restoring or adding volume to other areas of the body, a fat transfer can improve body contours and revitalize
Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
11. I realize that not having the operation is an option.
 Consent Body Lift Surgery 1. I hereby authorize Dr. John P. Stratis and such assistants as may be selected to perform the following procedure or treatment. BODY LIFT (Circumferential abdominoplasty, lower
Consent Body Lift Surgery 1. I hereby authorize Dr. John P. Stratis and such assistants as may be selected to perform the following procedure or treatment. BODY LIFT (Circumferential abdominoplasty, lower
LIPOPLASTY. About Fat
 LIPOPLASTY LIPOSUCTION AND FAT REMOVAL Liposuction in all its various guises has always been one of the most popular cosmetic surgical procedures. But before we go into details about how Liposuction is
LIPOPLASTY LIPOSUCTION AND FAT REMOVAL Liposuction in all its various guises has always been one of the most popular cosmetic surgical procedures. But before we go into details about how Liposuction is
Transgender body surgeries
 Transgender body surgeries Overview Sometimes you may find consuming hormones and hard exercise huge a challenge to keep you in a perfect feminine shape. To eliminate the challenge, body plastic surgery
Transgender body surgeries Overview Sometimes you may find consuming hormones and hard exercise huge a challenge to keep you in a perfect feminine shape. To eliminate the challenge, body plastic surgery
The Tumescent Technique TUMESCENT TECHNIQUE. by itself We strongly recommend that you consult with one of our nutrition and
 procedures. Body sculpting can be performed on virtually any area of the body. If there is a body area of concern not mentioned, please ask specifically about these areas at the time of consultation. The
procedures. Body sculpting can be performed on virtually any area of the body. If there is a body area of concern not mentioned, please ask specifically about these areas at the time of consultation. The
Thames Valley Priorities Committee Commissioning Policy Statement
 Bracknell and Ascot Clinical Commissioning Group Slough Clinical Commissioning Group Windsor, Ascot and Maidenhead Clinical Commissioning Group Thames Valley Priorities Committee Commissioning Policy Statement
Bracknell and Ascot Clinical Commissioning Group Slough Clinical Commissioning Group Windsor, Ascot and Maidenhead Clinical Commissioning Group Thames Valley Priorities Committee Commissioning Policy Statement
Mommy Makeover
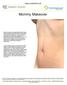 Mommy Makeover Many women experience significant physical changes following pregnancy and breast-feeding, many of which can be persistent and difficult to correct with diet and exercise alone. Changes
Mommy Makeover Many women experience significant physical changes following pregnancy and breast-feeding, many of which can be persistent and difficult to correct with diet and exercise alone. Changes
Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate surgical options
 A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
world [2]. One product of such innovative engineering in is the ultrasound-assisted liposuction
![world [2]. One product of such innovative engineering in is the ultrasound-assisted liposuction world [2]. One product of such innovative engineering in is the ultrasound-assisted liposuction](/thumbs/76/73846474.jpg) Taewoo Kim Dr. Ramsey WRIT 340 4/12/2013 Sculpting the Human Body with VASER Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction Abstract Traditional liposuction methods often involved direct mechanical cutting of the fat
Taewoo Kim Dr. Ramsey WRIT 340 4/12/2013 Sculpting the Human Body with VASER Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction Abstract Traditional liposuction methods often involved direct mechanical cutting of the fat
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
INFORMATION SHEET MODIFIED (MINI) ABDOMINOPLASTY
 INFORMATION SHEET MODIFIED (MINI) ABDOMINOPLASTY INTRODUCTION There is not much which is mini about a mini-abdominoplasty because it can take as long and can be as complicated as a standard abdominoplasty
INFORMATION SHEET MODIFIED (MINI) ABDOMINOPLASTY INTRODUCTION There is not much which is mini about a mini-abdominoplasty because it can take as long and can be as complicated as a standard abdominoplasty
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Clinical Policy Title: Body contouring surgery after massive weight loss
 Clinical Policy Title: Body contouring surgery after massive weight loss Clinical Policy Number: 18.03.03 Effective Date: July 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: April 27, 2016 Most Recent Review Date: April
Clinical Policy Title: Body contouring surgery after massive weight loss Clinical Policy Number: 18.03.03 Effective Date: July 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: April 27, 2016 Most Recent Review Date: April
THE INEVITABLE DECLINE IN THE ATTRACTIVENESS OF FEMALE SCARLESS SCALPEL FREE BREAST LIFTING ADVANTAGES AND LIMITATIONS
 SCARLESS SCALPEL FREE BREAST LIFTING ADVANTAGES AND LIMITATIONS Diane Irvine Duncan presents six cases of scarless breast lifting using an energy-based approach DIANE IRVINE DUNCAN, M.D., FACS, Plastic
SCARLESS SCALPEL FREE BREAST LIFTING ADVANTAGES AND LIMITATIONS Diane Irvine Duncan presents six cases of scarless breast lifting using an energy-based approach DIANE IRVINE DUNCAN, M.D., FACS, Plastic
The Desire for Body Contouring Surgery after Bariatric Surgery
 OBES SURG (8) 18:18 1312 DOI.7/s11695-8-9557- RESEARCH ARTICLE The Desire for Body Contouring Surgery after Bariatric Surgery James E. Mitchell & Ross D. Crosby & Troy W. Ertelt & Joanna M. Marino & David
OBES SURG (8) 18:18 1312 DOI.7/s11695-8-9557- RESEARCH ARTICLE The Desire for Body Contouring Surgery after Bariatric Surgery James E. Mitchell & Ross D. Crosby & Troy W. Ertelt & Joanna M. Marino & David
Prognostication for Body Contouring Surgery After Bariatric Surgery
 Prognostication for Body Contouring Surgery After Bariatric Surgery Devinder Singh, MD, a Antonio J. V. Forte, MD, b Hamid R. Zahiri, DO, a Lindsay E. Janes, BS, a Jennifer Sabino, MD, a Jamil A. Matthews,
Prognostication for Body Contouring Surgery After Bariatric Surgery Devinder Singh, MD, a Antonio J. V. Forte, MD, b Hamid R. Zahiri, DO, a Lindsay E. Janes, BS, a Jennifer Sabino, MD, a Jamil A. Matthews,
The progress in microsurgical procedures has led
 Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
INFORMED CONSENT BODY LIFT SURGERY
 INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document that has been prepared to help inform you concerning body lift surgery (also commonly called lower body lift, belt lipectomy, circumferential lipectomy,
INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document that has been prepared to help inform you concerning body lift surgery (also commonly called lower body lift, belt lipectomy, circumferential lipectomy,
INFORMED-CONSENT-THIGH LIFT INSTRUCTIONS
 INFORMED-CONSENT-THIGH LIFT INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document that has been prepared to help the Doctor inform you of thigh lift surgery, its risks, as well as alternative treatments. At
INFORMED-CONSENT-THIGH LIFT INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document that has been prepared to help the Doctor inform you of thigh lift surgery, its risks, as well as alternative treatments. At
Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop
 Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:333 340 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9612-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop André Auersvald Luiz Augusto Auersvald Received: 28 April
Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:333 340 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9612-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop André Auersvald Luiz Augusto Auersvald Received: 28 April
INFORMED-CONSENT-ABDOMINOPLASTY SURGERY
 INFORMED-CONSENT-ABDOMINOPLASTY SURGERY 2000 American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify documents contained herein
INFORMED-CONSENT-ABDOMINOPLASTY SURGERY 2000 American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify documents contained herein
Unsatisfactory Results of Liposuction
 Unsatisfactory Results of Liposuction Editor s note: My thanks to the moderator, Joseph P. Hunstad, MD (board-certified plastic surgeon and SPS member, Charlotte, NC), and to panelists Richard. D mico,
Unsatisfactory Results of Liposuction Editor s note: My thanks to the moderator, Joseph P. Hunstad, MD (board-certified plastic surgeon and SPS member, Charlotte, NC), and to panelists Richard. D mico,
The history of face lift surgery encompasses a wide
 Richard Ellenbogen, MD; Anthony Youn, MD; Dan Yamini, MD; and Steven Svehlak, MD Dr. Ellenbogen, Dr. Yamini, and Dr. Svehlak are in private practice in Los Angeles, CA. Dr. Youn is in private practice
Richard Ellenbogen, MD; Anthony Youn, MD; Dan Yamini, MD; and Steven Svehlak, MD Dr. Ellenbogen, Dr. Yamini, and Dr. Svehlak are in private practice in Los Angeles, CA. Dr. Youn is in private practice
Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts
 Aesth. Plast. Surg. 24:90 96, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002660010017 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts Ozan Sozer, M.D., and Thomas M. Biggs, M.D. İstanbul, Turkey and
Aesth. Plast. Surg. 24:90 96, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002660010017 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts Ozan Sozer, M.D., and Thomas M. Biggs, M.D. İstanbul, Turkey and
Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons
 Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons Options for reconstruction after mastectomy Implants Autologous tissue = from your own body: skin
Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons Options for reconstruction after mastectomy Implants Autologous tissue = from your own body: skin
Tummy Tuck (Abdominoplasty)
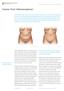 Tummy Tuck (Abdominoplasty) Fitness and the appearance of fitness has become an obsession in our culture. Our torso shapes are revealed in form fitting clothing, in athletic garments and in the minimalist
Tummy Tuck (Abdominoplasty) Fitness and the appearance of fitness has become an obsession in our culture. Our torso shapes are revealed in form fitting clothing, in athletic garments and in the minimalist
The overlap of lipoplasty and abdominoplasty: indication, classification, and treatment
 Clin Plastic Surg 31 (2004) 539 553 The overlap of lipoplasty and abdominoplasty: indication, classification, and treatment Luiz S. Toledo, MD Private Practice, Av. Brg. Luiz Antônio, 4442, São Paulo,
Clin Plastic Surg 31 (2004) 539 553 The overlap of lipoplasty and abdominoplasty: indication, classification, and treatment Luiz S. Toledo, MD Private Practice, Av. Brg. Luiz Antônio, 4442, São Paulo,
Abdominal Wall Modification for the Difficult Ostomy
 Abdominal Wall Modification for the Difficult Ostomy David E. Beck, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT A select group of patients with major stomal problems may benefit from operative modification of the abdominal wall.
Abdominal Wall Modification for the Difficult Ostomy David E. Beck, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT A select group of patients with major stomal problems may benefit from operative modification of the abdominal wall.
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty?
 Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
Getting Your Body Back:
 Getting Your Body Back: The Mommy Makeover Guide 1 introduction The hard part is over. You ve given birth to a beautiful baby. You can finally have a few drinks at a gettogether. It s all smooth sailing
Getting Your Body Back: The Mommy Makeover Guide 1 introduction The hard part is over. You ve given birth to a beautiful baby. You can finally have a few drinks at a gettogether. It s all smooth sailing
Brachioplasty (Arm Lift) Information Sheet
 Brachioplasty (Arm Lift) Information Sheet Brachioplasty (pronounced brack-ee-o-plasty) is the medical term used for an upper arm lift operation. Upper arms can be prone to drooping or sagging thanks to
Brachioplasty (Arm Lift) Information Sheet Brachioplasty (pronounced brack-ee-o-plasty) is the medical term used for an upper arm lift operation. Upper arms can be prone to drooping or sagging thanks to
Controlled Results with Abdominoplasty
 Aesth. Plast. Surg. 25:357 364, 2001 DOI: 10.1007/s00266-001-0010-1 2001 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Controlled Results with Abdominoplasty Richard A. Baxter, M.D., F.A.C.S. Mountlake Terrace, WA, USA
Aesth. Plast. Surg. 25:357 364, 2001 DOI: 10.1007/s00266-001-0010-1 2001 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Controlled Results with Abdominoplasty Richard A. Baxter, M.D., F.A.C.S. Mountlake Terrace, WA, USA
THE VIDEO SESSIONS PRACTICAL SURGICAL TECHNIQUES FACE AND TOTAL BODY SCULPTING
 WWW.ASTONBAKERSYMPOSIUM.COM 2014 THE VIDEO SESSIONS PRACTICAL SURGICAL TECHNIQUES FACE AND TOTAL BODY SCULPTING 34 TH AESTHETIC SURGERY SYMPOSIUM THE WALDORF ASTORIA HOTEL GRAND BALLROOM NEW YORK, NEW
WWW.ASTONBAKERSYMPOSIUM.COM 2014 THE VIDEO SESSIONS PRACTICAL SURGICAL TECHNIQUES FACE AND TOTAL BODY SCULPTING 34 TH AESTHETIC SURGERY SYMPOSIUM THE WALDORF ASTORIA HOTEL GRAND BALLROOM NEW YORK, NEW
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Breast Lift (Mastopexy) Breast Lift (Mastopexy) Houston
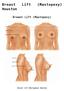 Breast Lift (Mastopexy) Houston Breast Lift (Mastopexy) Breast Lift (Mastopexy) Houston Breast Lift (Mastopexy) is a procedure that tightens firms and lifts the breasts. Patients who are satisfied with
Breast Lift (Mastopexy) Houston Breast Lift (Mastopexy) Breast Lift (Mastopexy) Houston Breast Lift (Mastopexy) is a procedure that tightens firms and lifts the breasts. Patients who are satisfied with
BraLineBackLift A Safe, Reliable, and Effective Method for Achieving Dramatic Results for Comprehensive Back Contouring
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 BraLineBackLift A Safe, Reliable, and Effective Method for Achieving Dramatic Results for Comprehensive Back Contouring Q2Q3 Joseph P. Hunstad, MD*, Phillip D. Khan, MD 10 Q4 11 12 KEYWORDS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 BraLineBackLift A Safe, Reliable, and Effective Method for Achieving Dramatic Results for Comprehensive Back Contouring Q2Q3 Joseph P. Hunstad, MD*, Phillip D. Khan, MD 10 Q4 11 12 KEYWORDS
INFORMED CONSENT-BREAST RECONSTRUCTION WITH TRAM ABDOMINAL MUSCLE FLAP
 INFORMED CONSENT-BREAST RECONSTRUCTION WITH TRAM ABDOMINAL MUSCLE FLAP 2000 American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify
INFORMED CONSENT-BREAST RECONSTRUCTION WITH TRAM ABDOMINAL MUSCLE FLAP 2000 American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify
The question Which face lift technique is COSMETIC. A Comparison of Face Lift Techniques in Eight Consecutive Sets of Identical Twins
 COSMETIC A Comparison of Face Lift Techniques in Eight Consecutive Sets of Identical Twins Darrick E. Antell, M.D., D.D.S. Michael J. Orseck, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Selecting the correct face
COSMETIC A Comparison of Face Lift Techniques in Eight Consecutive Sets of Identical Twins Darrick E. Antell, M.D., D.D.S. Michael J. Orseck, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Selecting the correct face
From ancient times to the present day, the aesthetic female breast has been portrayed. A Classification and Algorithm for Treatment of Breast Ptosis
 lassification and lgorithm for Treatment of reast Ptosis Laurence Kirwan, M ackground: The Regnault classification of breast ptosis is insufficient for determining surgical strategies for different stages
lassification and lgorithm for Treatment of reast Ptosis Laurence Kirwan, M ackground: The Regnault classification of breast ptosis is insufficient for determining surgical strategies for different stages
ALTERNATIVE TREATMENTS
 INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document that has been prepared to help inform you concerning body lift surgery (also commonly called lower body lift, belt lipectomy, circumferential lipectomy,
INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document that has been prepared to help inform you concerning body lift surgery (also commonly called lower body lift, belt lipectomy, circumferential lipectomy,
KAROL A. GUTOWSKI, MD, FACS AESTHETIC SURGERY CERTIFIED BY THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PLASTIC SURGERY MEMBER AMERICAN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS
 INFORMED CONSENT FOR LIPOSUCTION INCLUDES: TUMESCENT LIPOSUCTION ULTRASOUND ASSISTED LIPOSUCTION (UAL) WATER ASSISTED LIPOSUCTION (WAL) POWER ASSISTED LIPOSUCTION (PAL) LASER ASSISTED LIPOSUCTION (LAL)
INFORMED CONSENT FOR LIPOSUCTION INCLUDES: TUMESCENT LIPOSUCTION ULTRASOUND ASSISTED LIPOSUCTION (UAL) WATER ASSISTED LIPOSUCTION (WAL) POWER ASSISTED LIPOSUCTION (PAL) LASER ASSISTED LIPOSUCTION (LAL)
GENERAL CONSENT FOR THIGH LIFT
 GENERAL CONSENT FOR THIGH LIFT GENERAL INFORMATION A medial thigh lift is a surgical procedure to remove excess skin and fatty tissue from the medial thighs. A medial thigh lift is not a surgical treatment
GENERAL CONSENT FOR THIGH LIFT GENERAL INFORMATION A medial thigh lift is a surgical procedure to remove excess skin and fatty tissue from the medial thighs. A medial thigh lift is not a surgical treatment
Clinical Accuracy of Portrait 3D Surgical Simulation Platform in Breast Augmentation. Ryan K. Wong MD, David T Pointer BS, Kamran Khoobehi MD FACS
 Clinical Accuracy of Portrait 3D Surgical Simulation Platform in Breast Augmentation Ryan K. Wong MD, David T Pointer BS, Kamran Khoobehi MD FACS Division of Plastic, Reconstructive & Reconstructive Surgery,
Clinical Accuracy of Portrait 3D Surgical Simulation Platform in Breast Augmentation Ryan K. Wong MD, David T Pointer BS, Kamran Khoobehi MD FACS Division of Plastic, Reconstructive & Reconstructive Surgery,
Goals of Care. Restore shape and function after cancer
 Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps
 Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
The introduction of lipoplasty into the surgical armamentarium by Illouz1 has. Lipoabdominoplasty Without Undermining
 Lipoabdominoplasty Without Undermining Osvaldo Ribeiro Saldanha, MD; Ewaldo olivar de Souza Pinto, MD; Wilson Novaes Matos, Jr., MD; Reynaldo L. Lucon, MD; Felipe Magalhães, MD; and Érika Mônica Lopes
Lipoabdominoplasty Without Undermining Osvaldo Ribeiro Saldanha, MD; Ewaldo olivar de Souza Pinto, MD; Wilson Novaes Matos, Jr., MD; Reynaldo L. Lucon, MD; Felipe Magalhães, MD; and Érika Mônica Lopes
Cosmetic Surgery: Breast Reduction
 PROCEDURE FACT SHEET PLASTIC SURGERY Cosmetic Surgery: Breast Reduction This guide is for women who are considering having an operation to lift their breasts. We advise that you talk to a plastic surgeon
PROCEDURE FACT SHEET PLASTIC SURGERY Cosmetic Surgery: Breast Reduction This guide is for women who are considering having an operation to lift their breasts. We advise that you talk to a plastic surgeon
CONSENT FOR LIPOSUCTION SURGERY
 CONSENT FOR LIPOSUCTION SURGERY Liposuction is a surgical technique to remove unwanted deposits of fat from specific areas of the body, including the face and neck, upper arms, trunk, abdomen, buttocks,
CONSENT FOR LIPOSUCTION SURGERY Liposuction is a surgical technique to remove unwanted deposits of fat from specific areas of the body, including the face and neck, upper arms, trunk, abdomen, buttocks,
Tumescent Liposuction
 Standards & Guidelines October 2015 v5 Serving the public by guiding the medical profession Revision date: October 2015 v5 Approval date: September 1999 Originating Committee: Advisory Committee on Non-Hospital
Standards & Guidelines October 2015 v5 Serving the public by guiding the medical profession Revision date: October 2015 v5 Approval date: September 1999 Originating Committee: Advisory Committee on Non-Hospital
