Maria Magdalena Jeleńska, Łukasz Romanowski
|
|
|
- Gilbert Barrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2010, 82, 11, /v Patients with upper extremity deep thrombosis in a clinical material of Warsaw Medical University Maria Magdalena Jeleńska, Łukasz Romanowski Department of General, Vascular and Transplant Surgery, Warsaw Medical University Kierownik: prof. dr hab. J. Szmidt The aim of the study was to analyze causes, location and signs and symptoms of the upper extremity deep thrombosis (UEDVP) in twelve patients who were referred for tests for trombophilia; these patients were treated from 2002 to 2009 in various Clinics of Warsaw Medical University. Material and methods. Retrospective analysis involved collection of clinical data of hospitalized patients related to signs and symptoms and location of the thrombosis, antithrombotic treatment and results of tests for thrombophilia. Patients with thrombosis caused by dialysis catheter, chemotherapy or paranteral nutrition and cardiac pacemaker electrode were excluded from the study. Results. Eight of the study subjects had a primary thrombosis: in as many as five of them this was an exercise-induced thrombosis. Secondary thrombosis was diagnosed in four patients, two of whom had a malignancy, the third one used oral contraceptives while the fourth, pregnant patient, had UEDVP associated with ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Conclusions. Pulmonary embolism (PE) without lower extremity thrombosis should prompt the search for UEDVT that can be asymptomatic. One of the study subjects underwent imaging studies that confirmed presence of thrombosis of the left brachiocephalic only after PE was detected. The study group contained many relatively young patients (five patients) with exercise-induced UEDVT, indicating possible thrombotic complications following too vigorous physical exercise. UEDVT that occurred in a pregnant patient was a complication of hormonal stimulation of ovaries used in the treatment of infertility. Pain and edema of the neck in such patients should prompt their attending physician to perform imaging studies. Should UEDVT be detected, antithrombotic heparin therapy should be started. Key words: venous thrombosis, upper extremity deep thrombosis, trombophilia Incidence of symptomatic upper extremity deep thrombosis (UEDVT) reported in the literature ranges from 4 to 10% of all deep thrombosis cases (1-5). However these data may be underestimated since UEDVT is often asymptomatic and pulmonary embolism is often its first manifestation (4, 6). Most risk factors of lower extremity deep thrombosis also increases the risk of UEDVT although to a variable degree. The most common predisposing factors to upper extremity deep thrombosis include foreign body in the vessel lumen (vascular catheter and sometimes cardiac pacemaker electrode) and active malignancy (1, 2, 5, 7-11). Congenital thrombophlilia is detected much less often in patients with upper than in lower extremity deep thrombosis (5, 12, 13, 14). Upper extremity thrombosis may also be caused by intensive physical exercise. In 1875 Paged in England and then in 1884 Schrötter in Germany were the first to report subclavian or axillary thrombosis after very dynamic physical exercise. This thrombosis, currently referred to as exercise-induced thrombosis, may be caused e.g. by weight lifting, rowing, wrestling (10, 15, 16, 17). Currently it is recognized that exercise-induced thrombosis is furthermore favored by anatomical anomalies. These anomalies, referred to as upper chest opening syndrome, were found in 4%
2 604 M. M. Jeleńska, Ł. Romanowski patients with UEDVT (12). They affect bones (abnormal structure of the first rib or clavicle), tendons (additional connective tissue bands) or muscles in the region where s that drain the upper extremity are located (scalenus anterior muscle and pectoris minor muscle) and result in slowing of blood flow through mechanical compression of the blood vessels (15, 17). Exercise-induced thrombosis of the sunclavian and/or axillary in patients with anatomical anomalies is referred to as Paget- Schrötter syndrome (15, 16). Exercise-induced thrombosis with or without accompanying anatomical anomalies and essential thrombosis are termed primary UEDVT. Thrombosis caused by risk factors, including the most common catheter and active malignancy, is termed secondary thrombosis and accounts for approximately 80% of all UEDVT cases (4, 18, 19). UEDVT complications similarly as for lower extremity thrombosis are not limited to pulmonary embolism, but also manifest as chronic, thrombosis-induced venous insufficiency and recurrent thrombosis; furthermore they may result in loss of vascular access (5, 9, 11, 17, 18, 20, 21, 22). The aim of this study was to analyze causes, location and signs and symptoms of UEDVT in twelve patients who were referred for tests for trombophilia; these patients were treated from 2002 to 2009 in various clinics of Warsaw Medical University (MUW). MATERIAL AND METHODS From 2002 to 2009, 12 patients (6 women and 6 men) with UEDVT, aged 18 to 58 years (average age 36 years) were hospitalized in various clinics of MUW (Department of General, Vascular and Transplantation Surgery; Department of General and Thoracic Surgery; Department of General, Gastroenterological and Oncological Surgery; Department of Hematology, Oncology and Internal Medicine; Department of Internal Medicine and Endocrinology; Department of Gastroenterology and Metabolic Disease) and were referred for tests for trombophilia. Patients with thrombosis caused by dialysis catheter, chemotherapy or paranteral nutrition and cardiac pacemaker electrode were excluded from the study. The thrombosis was diagnosed basing on imaging studies (US imaging, possibly CT), performed by radiologists. Complete blood cell count, fibrinogen concentration (colorimetric method), factor II, V and VII activity (one-step coagulometric methods), D-dimer concentration (ELISA, biomerieux, VIDAS D-dimer) were analyzed in all patients. Tests for trombophilia included: activity of antithrombin and protein C (amidolytic metod), resistance to active protein C (coagulometric method), and tests for lupus anticoagulant (coagulometric method). RESULTS Patient characteristics presented in tab. 1 indicates that eight patients developed UED- VT without detected risk factors (malignancy, pregnancy, vascular catheter, trombophilia). It was related to intensive physical exercise in five of them (bodybuilding, parachute jumping). Furthermore, thrombosis was diagnosed in four subjects: two of them had an active malignancy, the third one used oral contraceptives while the fourth patient was 11 weeks pregnant: her twin pregnancy was a result of in vitro conception preceded by hormonal stimulation of ovaries. The thrombosis occurred in the right extremity in seven of twelve patients. Neither patient was found to have a bilateral thrombosis. Most commonly the thrombosis was located in the subclavian, followed by the axillary, brachial s and jugular (tab. 1). More than one venous segment was affected by thrombosis in three patients. UEDVT was documented by ultrasound (US) imaging in nine patients. Results of US imaging in one patient were inconclusive and UEDVT was confirmed by computed tomography imaging. UEDVT was diagnosed using computed tomography imaging, without US imaging, in two patients (tab. 1). Neither patient required venography to confirm thrombosis. Lupus anticoagulant, antithrombin deficiency, protein C deficiency or resistance to an active protein C were found in none of the twelve patients. Table 2 summarizes other coagulation tests. Thrombocytosis was found only in one patient Ł.E. who had undergone hormonal stimulation of ovaries. She was found to have an increased activity of clotting factors II, V and VII and increased fibrinogen concentration. Fibrino-
3 Patients with upper extremity deep thrombosis 605 Patient Age Gender Thrombosis location Table 1. Characteristics of UEDVT patients Signs and symptom sof the thrombosis Diagnostic procedures Risk factors Treatment W.A. 34 F left subclavian pain, edema TK / CT none detected nadroparin 170 IU/kg R.A. 34 F right subclavian pain, edema redness USG, TK / US CT oral contraception, cigarette smoking enoxaparin 1 mg/kg K.J. 30 M right axillary pain, edema USG / US none detected nadroparin 170 IU/kg W.K. 18 M right axillary pain, edema USG / US vigorous exercise nadroparin IU/kg P.P. 26 M right subclavian, axillary and brachial G.T. 44 M right subclavian Ł.E. 37 F left subclavian, left internal jugular G.B. 44 F left axillary, brachial s P.K. 22 F left subclavian W.K. 45 M right subclavian W.K. 53 M left brachiocephalic S.B. 36 F right subclavian pain, edema USG / US vigorous exercise enoxaparin 1,5 mg/kg pain, edema USG / US none detected enoxaparin 1,5 mg/kg pain, edema USG / US 11 weeks gestation, enoxaparin 1 mg/kg ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome pain, edema USG / US acute myelogenous leukemia, 2- u phenotypic pain, edema, cyanosis enoxaparin 1 mg/kg USG / US vigorous exercise nadroparin 170 IU/kg pain, edema USG / US parachute jumping nadroparin 170 IU/kg asymptomatic, TK / CT (metastatic) enoxaparin 1 mg/kg pe pancreatic cancer pain, edema USG / US vigorous exercise nadroparin 170 IU/kg gen concentration above the normal range was also found in two patients with malignancy (G.B., K.W.) and in one patient with exercise-induced thrombosis (P.P.). Increased D-dimer concentration, suggesting fibrinolytic degradation of intravascular fibrin deposits, was found in eight patients. Normal D-dimers were found in four patients who were receiving treatment with low molecular weight heparin (LMWH). All study patients received LMWH during their hospitalization according to Polish recommendations of treatment of lower extremity thrombosis, valid at the time of patient hospitalization. At discharge, five patients were advised to continue antithrombotic treatment with LMWH for three to six months while the pregnant patient (Ł.E.) was advised to continue her treatment until the end of her pregnancy. Five patients had an oral antagonist of vitamin K implemented during their hospitalization, under INR guidance, and advised to continue their treatment for at least three months. One patient with mild thrombosis was discharged and advised to take acetylsalicylic acid (2 mg/kg). DISCUSSION Currently there is no established definition of UEDVT, however it is generally believed to refer to thrombosis of subclavian, axillary and less often brachial as well as internal jugular. Vascular catheter is the most common cause of UEDVT. Patients with dialysis catheter, receiving chemotherapy or parenteral nutrition, were excluded from the study group. Therefore, secondary thrombosis rate was much lower than reported in the literature (4, 18, 19). However, a group of patients with exercise-induced UEDVT is clearly overrepresented in our study population versus literature data, which is the result of patient selection method used.
4 606 M. M. Jeleńska, Ł. Romanowski A limitation of this study is lack of comprehensive tests to detect a superior chest opening syndrome in patients with exercise induced thrombosis. A female Ł.E. with subclavian and internal jugular thrombosis in 11 weeks gestation (twin pregnancy) is an interesting and rare case in our study population. The patient had been treated for infertility with hormonal stimulation of ovaries and then underwent in vitro fertilization. A consulting gynecologist, after performing additional tests, diagnosed the patient with a mild ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. After two weeks of treatment with LMWH, pain and edema of the extremity resolved and the patient was discharged home and advised to continue LMWH therapy until the end of her pregnancy. Jugular and subclavian thrombosis, found in patient Ł.E., is one of the complications of hormonal stimulation of ovaries, used in the treatment of infertility. This thrombosis is a consequence of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome that occurs in 2-6% of the treated women (23, 24). This syndrome manifests as enlarged ovaries, massive ascites, pleural fluid and hemoconcentration (23-31). Hemoconcentration is caused by hypovolemia resulting from excessive blood vessel permeability mediated by rennin-angiotensin system activation (28). Patients with ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome were reported to have a tendency toward thrombocytosis that could facilitate thrombosis, increased concentration of fibrinogen and factor V and excess of fibrinolysis inhibitors (32). The patient Ł.E. had thrombocytosis, increased fibrinogen concentration and increased activity of clotting factors II, V and VII (tab. 2). However, these changes do not account for hormonal ovary stimulation predisposing to the upper extremity thrombosis instead of lower extremity thrombosis. According to Bauersachs et al. (31), high estrogen concentration is found in the peritoneal fluid in ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. These estrogens then migrate through lymphatic system, via thoracic duct, back to the venous system of the upper extremities, resulting in local activation of coagulation. Venous thrombosis accompanying infertility treatment is located almost exclusively in upper extremities and manifests as in patient Ł.E. a few weeks after resolution of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (23, 26-29). The thrombosis is more commonly found in the jugular than in subclavian s, but the reason behind it remains unknown (29). Recently the number of women who use the assisted reproduction has markedly increased, which is reflected by increased number of publications on the thrombotic complications that accompany this method. Therefore, there have been suggestions that severe of moderate ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome should be an indication to thrombotic prophylaxis for 1 2 months after symptom resolution (30). Hoverer, neck pain and edema should make the affected woman looking for imaging studies to Patient Table 2. Results of laboratory analyses in UEDVT patients fibrynogen (mg/dl) II (%) Clotting factor V (%) VII (%) D-dimer (ng/ml) Blond platelets (x10 3 /μl) W.A R.A K.J W.K P.P G.T Ł.E G.B P.K W.K W.K S.B Normal range <
5 Patients with upper extremity deep thrombosis 607 explain whether jugular or subclavian thrombosis is the cause for the above mentioned signs and symptoms (27, 28). In the event of documented UEDVT, antithrombotic heparin therapy (29) should be started immediately and continued until the end of her pregnancy. The patient Ł.E. was managed in such manner. Clinical characteristics of patients with UEDVT and lower extremity deep thrombosis differ. Patients with upper extremity thrombosis are younger, have lower body weight and less often have a family history of thrombotic disease (5). Patients with UEDVT analyzed by us were relatively young (average and 36 years) and were not overweight; only one study subject was a cigarette smoker. According to the literature, the most common signs and symptoms of UEDVT include: edema (82% of patients) and pain (37% of patients) of the extremity and sometimes neck and shoulder erythema and edema, cyanosis of the extremity (2, 11, 17, 18). Due to the fact that these signs and symptoms in approximately 50% of patients are not caused by UEDVT, differential diagnostics is often required (11, 21), including superficial thrombosis, cellulitis, lymphatic edema and local disease conditions that result in secondary thrombosis (e.g. malignant infiltrate around a, fibro-muscular hypertrophy of venous walls). Eleven of our study subjects presented with both pain and edema of the extremity. Furthermore, edema and cyanosis of the extremity occurred in two patients. The twelfth patient developed pulmonary embolism caused by asymptomatic UEDVT (tab. 1). Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a life threatening complication of UEDVT. Symptomatic PE is definitely less common in patients with upper than lower extremity thrombosis (5). One of the study subjects (Z.P.) developed respiratory insufficiency caused by P.E., confirmed both by computed tomography imaging as well as by subsequent autopsy. Asymptomatic thrombosis of the left brachiocephalic was the cause of this thrombosis. The patient died of multiorgan failure caused by metastatic malignancy. Example of this patient supports literature reports that pulmonary embolism is often the first sign of UEDVT (4, 6). Currently, most common diagnostic procedure used to demonstrate thrombosis, is US imaging with compression tests often accompanied by flow examination using Doppler imaging. On the other hand, computed tomography imaging is used to assess lumen of thoracic s. Venography is the ultimate study considered as a gold standard (33). Upper extremity deep thrombosis most often affects the subclavian, followed by axillary, brachial and other upper extremity s, usually affecting simultaneously more than one venous segment (11, 12). In patients with UEDVT hospitalized in MUW clinics, the thrombosis most often affected the subclavian (8/12 patients), followed by axillary (4/12 patients), brachial s (2/12 patients) and brachiocephalic in one case. The thrombosis affected more than one venous segment in three patients. Thrombosis developed slightly more often in the right extremity (seven cases) and there was no bilateral thrombosis in our study. Studies of congenital thrombophilia in patients with UEDVT are very limited. Linnermann et al. compared a series of 150 patients with the upper extremity thrombosis from a single-site register MAISTHRO with a group of 300 patients with the lower extremity thrombosis, matched for gender and age (12). Thrombophilia was found in 55% of patients with the lower extremity thrombosis and only in 34% of patients with UEDVT which may account for less common family history of thrombosis in these patients (2, 12). We did not find lupus anticoagulant or antithrombin deficiency, protein C deficiency or resistance to active protein C in our study subjects. However, we did not assay activity of protein S inhibitor or prothrombin gene mutations (G A). Since no prospective, comparative studies are available (due to difficulties in enrollment of large number of patients), there is no consensus with regard to optimal antithrombotic treatment of UEDVT. Joffe et al. analyzed risk factors in the largest group of 592 patients with UEDVT did not present long-term results of treatment (2). According to ACCP (American College of Chest Physicians) suggestions updated periodically, patients with UEDVT should receive the same treatment as patients with lower extremity thrombosis. However, a large retrospective study by Spencer et al. (7) demonstrated that only 56 per cent of patients received antithrombotic treatment following their discharge from a hospital. This may re-
6 608 M. M. Jeleńska, Ł. Romanowski flect quite common belief that the upper extremity thrombosis does not require long-term anticoagulation (1). All our hospitalized study subjects received LMWH treatment at therapeutic doses, according to Polish guidelines of prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic disease. Gradual resolution of complaints was noted in eleven patients while one patient died for multiorgan failure resulting from metastatic pancreatic cancer. At discharge the patients were advised to continue their antithrombotic treatment for at least three months. Five patients were to continue LMWH treatment and another five were advised to continue their treatment with oral vitamin K antagonists. One patient (W.K.) with mild thrombosis who furthermore did not consent to any of the above mentioned therapies was discharged home and advised to take acetylsalicylic acid at a dose of 2 mg/kg every 24 hours. The decision of a clinician with regard to antithrombotic treatment of patients with upper extremity thrombosis often is additionally dictated by the presence of malignancy. In RIETE (1) study, patients with UEDVT, following initial LMWH treatment, received long-term LMWH treatment if they had a malignancy (75% of patients) or at least three months of vitamin K antagonist treatment if they had no malignancy (76% of patients). ACCP recommends avoidance of thrombolysis and surgical procedures in most of UEDVT patients due to numerous possible complications (34). Patients with Paget-Schrötter are an exception to this rule because antithrombotic treatment preceded by thrombolysis is often successful in these patients. However, further surgical procedures in these pa- tients are dependent on the type of detected anatomical anomaly (16). CONCLUSIONS 1. Pulmonary embolism (P.E.) without lower extremity thrombosis should prompt the search for UEDVT that can be asymptomatic. One of the study subjects (with malignancy) underwent imaging studies that confirmed presence of thrombosis of the left brachiocephalic only after P.E. was detected. 2. The study group contained many relatively young patients (five patients) with exerciseinduced UEDVT, indicating possible thrombotic complications following too vigorous physical exercise. 3. UEDVT that occurred in a patient at 11 weeks gestation (twin pregnancy) was a complication of hormonal stimulation of ovaries used in the treatment of infertility. Pain and edema of the neck in such patients should prompt their attending physician to perform imaging studies. Should UEDVT be detected, antithrombotic heparin therapy should be started and continued until the end of the pregnancy what was the case in our patient. 4. Currently there is no consensus with regard to optimal antithrombotic treatment of UEDVT. All study subjects with UEDVT received LMWH during their hospitalization, according to Polish guidelines of treatment of the lower extremity thrombosis. Acknowledgements. We would like to tank heads of individual clinics of MUW for their consent to the access to medical records of the discussed patients and to publish data contained in them. PIŚMIENNICTWO / references 1. Muñoz J, Mismetti P, Loggio R et al.: Clinical outcome of patients with upper-extremity deep thrombosis. Results from the RIETE registry. CHEST 2008; 133: Joffe HV, Kuchner N, Tapson VF et al.: Upperextremity deep thrombosis. A prospective registry of 592 patients. Circulation 2004; 110: Martinelli I, De Stefano V: Rare thromboses of cerebral, splachnic and upper-extremity s. Thromb Haemost 2010; 103: Flinterman LE, van der Meer FJM, Rosendaal FR et al.: Current perspective of venous thrombosis in the upper extremity. J Thromb Haemost 2008; 6: Lechner D, Wiener C, Weltermann A et al.: Comparison between idiopathic deep thrombosis of the upper and lower extremity regarding risk factors and recurrence. J Thromb Haemost 2008; 6: Spaniolas K, Velmahos GC, Wicky S et al.: Is upper extremity deep venous thrombosis underdiagnosed in trauma patients? American Surg 2008; 74: Spencer FA, Emery C, Lessard D et al.: for the Worcester Venous Thromboembolism Study: Upper
7 Patients with upper extremity deep thrombosis 609 extremity deep thrombosis: A communitybased perspective. Am J Med 2007; 120: Van Roden CJ, Tesslaar MET, Osanto S et al.: Deep thrombosis associated with central venous catheters a review. J Thromb Haemost 2005; 3: Ong B, Gibbs H, Hetherington R et al.: Peripherally inserted central catheters and upper extremity deep thrombosis. Australasian Radiol 2006; 50: Blom JW, Doggen CJM, Osanto S et al.: Old and new risk factors for upper extremity deep venous thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost 2005; 3: Bernardi E, Pesavento R, Prandoni P: Upper extremity deep venous thrombosis. Semin Thromb Haemost 2006; 32: Linnemann B, Meister F, Schwonberg J et al.: Hereditary and acquired thrombophilia in patients with upper extremity deep- thrombosis. Results from the MAISTHRO registry. Thromb Haemost 2008; 100: Hoffman U, Spannagl M: Deep venous thrombosis of the upper extremity: Is thrombophilia a relevant clinical issue? Thromb Haemost 2008; 100: Martinelli I, Battaglioli T, Buccirelli P et al.: Risk factors and recurrence rate of primary deep thrombosis of the upper extremities. Circulation 2004; 110: Zell L, Kinderman W, Marschal F et al.: Paget- Schroetter syndrome in sport activities. Case study and literature review. Angiology 2001; 52: Chin-Wo W, Haw-Chong C, Cheng-Ooi L: Paget-Schroetter syndrome: Case report and review of the literature. Internet J Orthopedic Surg TM ISSN: Gaffar M: Upper extremity deep thrombosis. Hospital Physician 2005; June: Sajid MS, Ahmed N, Desai M et al.: Upper limb deep thrombosis : A literature review to streamline the protocol for management. Acta Haematol 2007; 118: Lancaster SL, Owens A, Ramey LS et al.: Upper-extremity deep thrombosis. AJN 2010; 110: Elman EE, Kahn SR: The post-thrombotic syndrome after upper extremity deep venous thrombosis in adults: A systematic review. Thromb Res 2006; 117: Prandoni P, Polistena P, Brrnardi E et al.: Upper-extremity deep thrombosis. Risk factors, diagnosis, and complications. Arch Intern Med 1997; 157: Prandoni P, Bernardi E, Marchiori A et al.: The long term clinical course of acute deep thrombosis of the arm: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2004; 329: Salomon O, Schiby G, Heiman Z et al.: Combined jugular and subclavian thrombosis following assisted reproductive technology new observation. Fert Steril 2009; 92: Abramov Y, Elchalal U, Schenker JG: An epidemic of severe OHSS: a price we have to pay? Human Reprod 1999; 14: Papanikolaou EG, Pozzobon C, Kolibianakis EM et al.: Incidence and prediction of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome in women undergoing gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist in vitro fertilization cycles. Fertility and Sterility 2006; 85: Stewart JA, Hamilton PJ, Murdoch AP: Thromboembolic disease associated with ovarian stimulation and assisted conception techniques. Hum Reprod 1997; 12: Scanzer A, Rochman CB, Rockman B et al.: Internal jagular thrombosis in association with the ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. J Vasc Surg 2000; 31: Chipwete E, Bugren S, Rafla N: Thrombosis post ovarian hyperstimulation. Fertil Steril 2009; 91: 1956.e13-e Chan WS Ginsberg JS: A review of upper extremity deep thrombosis in pregnancy: unmasking the ART behind the clot. J Thromb Haemost 2006; 4: Chan WS: The ART of thrombosis: a review of arterial and venous thrombosis in assisted reproductive technology. Curr Opinion Obstet Gynecol 2009; 21: Bauersachs RM, Manolopoulos K, Hoppe I et al.: More on: the ART behind the clot: solving the mystery. J Thromb Haemost 2007; 5: Phillips LL, Gladstone W, van de Wiele R: Studies of the coagulation and fibrinolytic system in hyperstymulation syndrome after administration of human gonadotrophins. J Reprod Med 1975; 14: Di Nisio M, Van Sluis GL, Bossuyt PMM et al.: Accuracy of diagnostic tests for clinical suspected upper extremity deep thrombosis: a systematic review. J Thromb Haemost 2010; 8: Kearon C, Kahn SR, Agnelli G et al.: Therapy for venous thromboembolic disease: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (8 th edition). Chest 2008; 133(6Suppl): 454S-545S. Received: r. Adress correspondence: Warszawa, ul. Banacha 1a
Risk stratification and incidence of acute complications in upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) patients.
 Risk stratification and incidence of acute complications in upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) patients. Dr. Santosh Yatam Ganesh MBBS, MPH., Mentors: Dr. Khalid J. Qazi MD, MACP., Dr. Paul Anain
Risk stratification and incidence of acute complications in upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) patients. Dr. Santosh Yatam Ganesh MBBS, MPH., Mentors: Dr. Khalid J. Qazi MD, MACP., Dr. Paul Anain
5/5/15. Overview. Deep vein thrombosis of the upper extremity (UEDVT) Classification of UEDVT Epidemiology. Primary UEDVT.
 Deep vein thrombosis of the upper extremity (UEDVT) Hong H. Keo, MD, MSc Angiologie Kantonsspital Aarau 07.05.2015 06. Symposium venöse Insuff. und arterielle Gefässerkr. Glarus Overview Epidemiology Classification/Risk
Deep vein thrombosis of the upper extremity (UEDVT) Hong H. Keo, MD, MSc Angiologie Kantonsspital Aarau 07.05.2015 06. Symposium venöse Insuff. und arterielle Gefässerkr. Glarus Overview Epidemiology Classification/Risk
Oddities of Medical School: A Case Report of Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis (Paget-Schroetter Syndrome) in a 27-Year-Old Female
 1 www.acofp.org Oddities of Medical School: A Case Report of Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis (Paget-Schroetter Syndrome) in a 27-Year-Old Female Peter F. Bidey, DO, MSEd Department of Family Medicine,
1 www.acofp.org Oddities of Medical School: A Case Report of Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis (Paget-Schroetter Syndrome) in a 27-Year-Old Female Peter F. Bidey, DO, MSEd Department of Family Medicine,
Strenuous sport activities involving the upper extremities increase the risk of venous thrombosis of the arm
 Chapter 5 Strenuous sport activities involving the upper extremities increase the risk of venous thrombosis of the arm KJ van Stralen, JW Blom, CJM Doggen, FR Rosendaal. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis,
Chapter 5 Strenuous sport activities involving the upper extremities increase the risk of venous thrombosis of the arm KJ van Stralen, JW Blom, CJM Doggen, FR Rosendaal. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis,
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein
 Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein Yang Jin Park Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine CASE A 32-year-old male patient 3-day history of
Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein Yang Jin Park Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine CASE A 32-year-old male patient 3-day history of
Venous thrombosis is common and often occurs spontaneously, but it also frequently accompanies medical and surgical conditions, both in the community
 Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form.
 : Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Medicine Type of Article: Case Report Title: Use of new oral
: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Medicine Type of Article: Case Report Title: Use of new oral
VTE in Children: Practical Issues
 VTE in Children: Practical Issues Wasil Jastaniah MBBS,FAAP,FRCPC Consultant Pediatric Hem/Onc/BMT May 2012 Top 10 Reasons Why Pediatric VTE is Different 1. Social, ethical, and legal implications. 2.
VTE in Children: Practical Issues Wasil Jastaniah MBBS,FAAP,FRCPC Consultant Pediatric Hem/Onc/BMT May 2012 Top 10 Reasons Why Pediatric VTE is Different 1. Social, ethical, and legal implications. 2.
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
 Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
UC SF. Division of General Internal Medicine UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA SAN FRANCISCO, DIVISION OF HOSPITAL MEDICINE
 Updates in the Management of Venous Thromboembolism Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical Director, Anticoagulation Clinic Venous Thromboembolism
Updates in the Management of Venous Thromboembolism Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical Director, Anticoagulation Clinic Venous Thromboembolism
Characterizing resolution of catheter-associated upper extremity deep venous thrombosis
 Characterizing resolution of catheter-associated upper extremity deep venous thrombosis Mark A. Jones, MD, a Dae Y. Lee, MD, b Jocelyn A. Segall, MD, c Gregory J. Landry, MD, b Timothy K. Liem, MD, b Erica
Characterizing resolution of catheter-associated upper extremity deep venous thrombosis Mark A. Jones, MD, a Dae Y. Lee, MD, b Jocelyn A. Segall, MD, c Gregory J. Landry, MD, b Timothy K. Liem, MD, b Erica
Approach to Thrombosis
 Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
ESIM 2014 Clinical Case Presentation Israel. Ben-Sasson Maayan Bnei-Zion medical center Haifa
 ESIM 2014 Clinical Case Presentation Israel Ben-Sasson Maayan Bnei-Zion medical center Haifa Presentation A 24 YO male,a ping-pong player, presented to the ER with acute onset of right upper extremity
ESIM 2014 Clinical Case Presentation Israel Ben-Sasson Maayan Bnei-Zion medical center Haifa Presentation A 24 YO male,a ping-pong player, presented to the ER with acute onset of right upper extremity
Disclosures. DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Questions To Ask. Dr. Susanna Shin - DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) None
 Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
Upper Extremity Venous Duplex. Michigan Sonographers Society Fall Ultrasound Symposium October 15, 2016
 Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Michigan Sonographers Society Fall Ultrasound Symposium October 15, 2016 Patricia A. (Tish) Poe, BA RVT FSVU Director of Quality Assurance Navix Diagnostix Patricia A. Poe
Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Michigan Sonographers Society Fall Ultrasound Symposium October 15, 2016 Patricia A. (Tish) Poe, BA RVT FSVU Director of Quality Assurance Navix Diagnostix Patricia A. Poe
Thrombophilia. Diagnosis and Management. Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI
 Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Genetic Tests for the Better Outcome of VTE? 서울대학교병원혈액종양내과윤성수
 Genetic Tests for the Better Outcome of VTE? 서울대학교병원혈액종양내과윤성수 Thrombophilia A hereditary or acquired disorder predisposing to thrombosis Questions Why should we test? Who should we test For what disorders?
Genetic Tests for the Better Outcome of VTE? 서울대학교병원혈액종양내과윤성수 Thrombophilia A hereditary or acquired disorder predisposing to thrombosis Questions Why should we test? Who should we test For what disorders?
Epidemiologia e clinica del tromboembolismo venoso. Maria Ciccone Sezione di Ematologia e Fisiopatologia della Coagulazione
 Epidemiologia e clinica del tromboembolismo venoso Maria Ciccone Sezione di Ematologia e Fisiopatologia della Coagulazione Thrombophilia may present clinically as one or more of several thrombotic manifestations
Epidemiologia e clinica del tromboembolismo venoso Maria Ciccone Sezione di Ematologia e Fisiopatologia della Coagulazione Thrombophilia may present clinically as one or more of several thrombotic manifestations
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM. Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow
 CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
Causative factors of deep vein thrombosis of lower limb in Indian population
 International Surgery Jthisnal Khadilkar R et al. Int Surg J. 18 Jan;(1):3-3 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 39-33 eissn 39-9 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.183/39-9.isj17919 Causative
International Surgery Jthisnal Khadilkar R et al. Int Surg J. 18 Jan;(1):3-3 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 39-33 eissn 39-9 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.183/39-9.isj17919 Causative
Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein
 416507JDMXXX10.1177/8756479311416507Wash ko et al.journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 27(5) 231 235 The Author(s) 2011
416507JDMXXX10.1177/8756479311416507Wash ko et al.journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 27(5) 231 235 The Author(s) 2011
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT?
 How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism
 Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism Ethan Cumbler M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Hospitalist Medicine Section University of Colorado Denver May 2010 No Conflicts of Interest Objectives
Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism Ethan Cumbler M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Hospitalist Medicine Section University of Colorado Denver May 2010 No Conflicts of Interest Objectives
Menopausal Hormone Therapy & Haemostasis
 Menopausal Hormone Therapy & Haemostasis The Haematologist Perspective Dr. Batia Roth-Yelinek Coagulation unit Hadassah MC Menopausal Hormone Therapy & Hemostasis Hemostatic mechanism Mechanism of estrogen
Menopausal Hormone Therapy & Haemostasis The Haematologist Perspective Dr. Batia Roth-Yelinek Coagulation unit Hadassah MC Menopausal Hormone Therapy & Hemostasis Hemostatic mechanism Mechanism of estrogen
Clinical Policy: Dalteparin (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date:
 Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 11.17 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 11.17 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
Chapter. A higher risk of recurrent venous thrombosis in men is due to hormonal risk factors in women in thrombophilic families
 Chapter A higher risk of recurrent venous thrombosis in men is due to hormonal risk factors in women in thrombophilic families Willem M. Lijfering Nic J.G.M. Veeger Saskia Middeldorp Karly Hamulyák Martin
Chapter A higher risk of recurrent venous thrombosis in men is due to hormonal risk factors in women in thrombophilic families Willem M. Lijfering Nic J.G.M. Veeger Saskia Middeldorp Karly Hamulyák Martin
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20915 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Flinterman, Linda Elisabeth Title: Risk factors for a first and recurrent venous
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20915 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Flinterman, Linda Elisabeth Title: Risk factors for a first and recurrent venous
Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT?
 Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Epidemiology of Thrombosis in Patients with Malignancy. Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism. Chew HK, Arch Int Med, Feb Blom et al, JAMA, Feb 2005
 Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism Objectives 1. Epidemiology of thrombosis in patients with malignancy 2. Anticancer agents and thrombosis 3. Current treatment protocols at UHN 4. Prevention of DVT 5.
Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism Objectives 1. Epidemiology of thrombosis in patients with malignancy 2. Anticancer agents and thrombosis 3. Current treatment protocols at UHN 4. Prevention of DVT 5.
Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism. Rajat Deo, MD, MTR
 Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism Rajat Deo, MD, MTR Director of Translational Research in Cardiac Arrhythmias Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism Rajat Deo, MD, MTR Director of Translational Research in Cardiac Arrhythmias Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
A 50-year-old woman with syncope
 Hira Shahzad 1, Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi 2 1 Medical College, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi 2 Department of Medicine, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi Associate
Hira Shahzad 1, Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi 2 1 Medical College, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi 2 Department of Medicine, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi Associate
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS. Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital My Talk Today 1.Introduction 2. Are All Cancer Patients at Risk of VTE? 3. Should All VTE Patients Be Screened
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital My Talk Today 1.Introduction 2. Are All Cancer Patients at Risk of VTE? 3. Should All VTE Patients Be Screened
Risk factors for DVT. Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Anticoagulation (cont d) Diagnosis 1/5/2018. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/188/20915 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Flinterman, Linda Elisabeth Title: Risk factors for a first and recurrent venous
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/188/20915 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Flinterman, Linda Elisabeth Title: Risk factors for a first and recurrent venous
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy. Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016
 Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. PE - Clinical
 Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
10/24/2013. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy:
 Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy: Heparin-Induced (HIT) Michael H. Creer, MD Professor of Pathology Director, Clinical Laboratories, Medical Co- Director, Hematopathology and Chief, Division
Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy: Heparin-Induced (HIT) Michael H. Creer, MD Professor of Pathology Director, Clinical Laboratories, Medical Co- Director, Hematopathology and Chief, Division
Inherited Thrombophilia Testing. George Rodgers, MD, PhD Kristi Smock MD
 Inherited Thrombophilia Testing George Rodgers, MD, PhD Kristi Smock MD Prevalence and risk associated with inherited thrombotic disorders Inherited Risk Factor % General Population % Patients w/ Thrombosis
Inherited Thrombophilia Testing George Rodgers, MD, PhD Kristi Smock MD Prevalence and risk associated with inherited thrombotic disorders Inherited Risk Factor % General Population % Patients w/ Thrombosis
Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism
 Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism An Educational Slide Set American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism Slide set authors: Eric Tseng MD MScCH, University of
Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism An Educational Slide Set American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism Slide set authors: Eric Tseng MD MScCH, University of
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Outline of This Presentation
 Slide 1 Current Approaches to Venous Thromboembolism Prevention in Orthopedic Patients Hujefa Vora, MD Maria Fox, RN June 9, 2017 Slide 2 Slide 3 Outline of This Presentation Pathophysiology of venous
Slide 1 Current Approaches to Venous Thromboembolism Prevention in Orthopedic Patients Hujefa Vora, MD Maria Fox, RN June 9, 2017 Slide 2 Slide 3 Outline of This Presentation Pathophysiology of venous
Clinical Policy: Dalteparin (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date:
 Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 02.18 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 02.18 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
VTE in the Trauma Population
 VTE in the Trauma Population Erik Peltz, D.O. February 11 th, 2015 * contributions from Eduardo Gonzalez, M.D. University of Colorado T-32 Research Fellow The problem. VTE - Scope of the Problem One of
VTE in the Trauma Population Erik Peltz, D.O. February 11 th, 2015 * contributions from Eduardo Gonzalez, M.D. University of Colorado T-32 Research Fellow The problem. VTE - Scope of the Problem One of
Thyroid disease and haemostasis: a relationship with clinical implications? Squizzato, A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Thyroid disease and haemostasis: a relationship with clinical implications? Squizzato, A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Squizzato, A.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Thyroid disease and haemostasis: a relationship with clinical implications? Squizzato, A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Squizzato, A.
Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis
 Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis A Summary Sinus and cerebral vein clots are uncommon. They can lead to severe headaches, confusion, and stroke-like symptoms. They may lead to bleeding into the surrounding
Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis A Summary Sinus and cerebral vein clots are uncommon. They can lead to severe headaches, confusion, and stroke-like symptoms. They may lead to bleeding into the surrounding
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information
 Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism
 Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK?
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
Evaluation of Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis Risk Factors and Management
 Research Article Evaluation of Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis Risk Factors and Management Heena Sheth 1*, Rahim Remtulla 2, Abuzar Moradi 2 and Roy Smith 2 1 Department of Medicine, University of
Research Article Evaluation of Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis Risk Factors and Management Heena Sheth 1*, Rahim Remtulla 2, Abuzar Moradi 2 and Roy Smith 2 1 Department of Medicine, University of
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
Upper extremity deep vein thrombosis
 Intern Emerg Med (2010) 5:103 109 DOI 10.1007/s11739-009-0320-x IM - REVIEW Upper extremity deep vein thrombosis Luca Spiezia Æ Paolo Simioni Received: 18 May 2009 / Accepted: 7 September 2009 / Published
Intern Emerg Med (2010) 5:103 109 DOI 10.1007/s11739-009-0320-x IM - REVIEW Upper extremity deep vein thrombosis Luca Spiezia Æ Paolo Simioni Received: 18 May 2009 / Accepted: 7 September 2009 / Published
Frequently Asked Questions about Cancer Associated Thrombosis
 + Frequently Asked Questions about Cancer Associated Thrombosis Atlantic Canada Oncology Group Annual Meeting June 13 th, 2015 Sudeep Shivakumar, Dalhousie University + Conflict of Interest Disclosures
+ Frequently Asked Questions about Cancer Associated Thrombosis Atlantic Canada Oncology Group Annual Meeting June 13 th, 2015 Sudeep Shivakumar, Dalhousie University + Conflict of Interest Disclosures
Correspondence should be addressed to Tawfik Khoury;
 Hindawi Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2017, Article ID 7290945, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7290945 Case Report Upper Limb Deep Vein Thrombosis in Patient with Hemophilia A and Heterozygosity
Hindawi Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2017, Article ID 7290945, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7290945 Case Report Upper Limb Deep Vein Thrombosis in Patient with Hemophilia A and Heterozygosity
DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE)
 DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE) Introduction VTE (DVT/PE) is an important complication in hospitalized patients Hospitalization for acute medical illness
DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE) Introduction VTE (DVT/PE) is an important complication in hospitalized patients Hospitalization for acute medical illness
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients. David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center
 DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Parker Truong, D.O. Interventional Cardiology Oklahoma Heart Hospital Physicians RELEVANT DISCLOSURE Under the Oklahoma State Medical Association CME guidelines disclosure must be
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Parker Truong, D.O. Interventional Cardiology Oklahoma Heart Hospital Physicians RELEVANT DISCLOSURE Under the Oklahoma State Medical Association CME guidelines disclosure must be
AN AUDIT: THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PATIENTS AT NORTHWICK PARK AND CENTRAL MIDDLESEX HOSPITALS
 The West London Medical Journal 2010 Vol 2 No 4 pp 19-24 AN AUDIT: THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PATIENTS AT NORTHWICK PARK AND CENTRAL MIDDLESEX HOSPITALS Soneji ND Agni NR Acharya MN Anjari
The West London Medical Journal 2010 Vol 2 No 4 pp 19-24 AN AUDIT: THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PATIENTS AT NORTHWICK PARK AND CENTRAL MIDDLESEX HOSPITALS Soneji ND Agni NR Acharya MN Anjari
ASH 2011: Clinically Relevant Highlights Regarding Venous Thromboembolism and Anticoagulation
 ASH 2011: Clinically Relevant Highlights Regarding Venous Thromboembolism and Anticoagulation Stephan Moll Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology-Oncology, University of North Carolina School of
ASH 2011: Clinically Relevant Highlights Regarding Venous Thromboembolism and Anticoagulation Stephan Moll Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology-Oncology, University of North Carolina School of
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Draft Agreed by Cardiovascular Working Party 28 September Adoption by CHMP for release for consultation 12 October 2017
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 October 2017 EMA/230866/2017 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Concept paper on the need for a paediatric addendum of the guideline on clinical investigation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 October 2017 EMA/230866/2017 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Concept paper on the need for a paediatric addendum of the guideline on clinical investigation
1. SCOPE of GUIDELINE:
 Page 1 of 35 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention Guideline: Thromboprophylaxis AUTHORIZATION: VP, Medicine Date Approved: May 17, 2012 Date Revised: Vancouver Coastal Health
Page 1 of 35 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention Guideline: Thromboprophylaxis AUTHORIZATION: VP, Medicine Date Approved: May 17, 2012 Date Revised: Vancouver Coastal Health
Clinical Policy Title: Genetic testing for G1691A polymorphism factor V Leiden
 Clinical Policy Title: Genetic testing for G1691A polymorphism factor V Leiden Clinical Policy Number: 05.01.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: July 15, 2015 Most Recent Review Date:
Clinical Policy Title: Genetic testing for G1691A polymorphism factor V Leiden Clinical Policy Number: 05.01.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: July 15, 2015 Most Recent Review Date:
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40114 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Exter, Paul L. den Title: Diagnosis, management and prognosis of symptomatic and
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40114 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Exter, Paul L. den Title: Diagnosis, management and prognosis of symptomatic and
Updates in Anticoagulation for Atrial Fibrillation and Venous Thromboembolism
 Disclosures Updates in Anticoagulation for Atrial Fibrillation and Venous Thromboembolism No financial conflicts of interest Member of the ABIM Focused- Practice in Hospital Medicine Self Examination Process
Disclosures Updates in Anticoagulation for Atrial Fibrillation and Venous Thromboembolism No financial conflicts of interest Member of the ABIM Focused- Practice in Hospital Medicine Self Examination Process
Current issues in the management of Superficial Vein Thrombosis - SVT
 Current issues in the management of Superficial Vein Thrombosis - SVT Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, School of Health Sciences,
Current issues in the management of Superficial Vein Thrombosis - SVT Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, School of Health Sciences,
ACR Appropriateness Criteria Suspected Lower Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis EVIDENCE TABLE
 . Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
. Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY
 CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting Calgary, Alberta, October 2014 Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update Benjamin Bell, MD FRCPC James Douketis, MD FRCPC On Behalf of Thrombosis Canada
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting Calgary, Alberta, October 2014 Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update Benjamin Bell, MD FRCPC James Douketis, MD FRCPC On Behalf of Thrombosis Canada
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis. Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS
 Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Catheter-based thrombolysis Local administration of lytic agent Higher local
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Catheter-based thrombolysis Local administration of lytic agent Higher local
Updates in Medical Management of Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis. By: Justin Youtsey, Elliott Reiff, William Montgomery, Grant Finlan
 Updates in Medical Management of Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis By: Justin Youtsey, Elliott Reiff, William Montgomery, Grant Finlan Objectives Describe the prevalence of PE and DVT as it relates
Updates in Medical Management of Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis By: Justin Youtsey, Elliott Reiff, William Montgomery, Grant Finlan Objectives Describe the prevalence of PE and DVT as it relates
Primary Care practice clinics within the Edmonton Southside Primary Care Network.
 INR Monitoring and Warfarin Dose Adjustment Last Review: November 2016 Intervention(s) and/or Procedure: Registered Nurses (RNs) adjust warfarin dosage according to individual patient International Normalized
INR Monitoring and Warfarin Dose Adjustment Last Review: November 2016 Intervention(s) and/or Procedure: Registered Nurses (RNs) adjust warfarin dosage according to individual patient International Normalized
Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Thrombophilia testing: who is it good for? F.R. Rosendaal, Leiden
 Thrombophilia testing: who is it good for? F.R. Rosendaal, Leiden Inaugural meeting of Iranian Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis Mofid Children Hospital Tehran, 24 December 2015 Chest. 2012;141(2_suppl):e48S-e801S
Thrombophilia testing: who is it good for? F.R. Rosendaal, Leiden Inaugural meeting of Iranian Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis Mofid Children Hospital Tehran, 24 December 2015 Chest. 2012;141(2_suppl):e48S-e801S
Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease
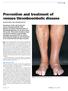 REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
THROMBOPHILIA TESTING: PROS AND CONS SHANNON CARPENTER, MD MS CHILDREN S MERCY HOSPITAL KANSAS CITY, MO
 THROMBOPHILIA TESTING: PROS AND CONS SHANNON CARPENTER, MD MS CHILDREN S MERCY HOSPITAL KANSAS CITY, MO DISCLAIMER I m a pediatrician I will be discussing this issue primarily from a pediatric perspective
THROMBOPHILIA TESTING: PROS AND CONS SHANNON CARPENTER, MD MS CHILDREN S MERCY HOSPITAL KANSAS CITY, MO DISCLAIMER I m a pediatrician I will be discussing this issue primarily from a pediatric perspective
Venous Thrombo-Embolism. John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH
 Venous Thrombo-Embolism John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH overview The statistics Pathogenesis Prophylaxis Treatment Agent Duration Incidental VTE Recurrence of VTE IVC filters CVC related thrombosis
Venous Thrombo-Embolism John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH overview The statistics Pathogenesis Prophylaxis Treatment Agent Duration Incidental VTE Recurrence of VTE IVC filters CVC related thrombosis
Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism
 Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Benjamin Hohlfelder Samuel Z. Goldhaber Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Cardiovascular Division Harvard Medical School Brigham and
Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Benjamin Hohlfelder Samuel Z. Goldhaber Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Cardiovascular Division Harvard Medical School Brigham and
Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders
 SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
Anticoagulation Forum: Management of Tiny Clots
 Anticoagulation Forum: Management of Tiny Clots Casey O Connell, MD FACP Associate Professor Jane Anne Nohl Division of Hematology Keck School of Medicine USC DISCLOSURES None 4/11/2017 Objectives Define
Anticoagulation Forum: Management of Tiny Clots Casey O Connell, MD FACP Associate Professor Jane Anne Nohl Division of Hematology Keck School of Medicine USC DISCLOSURES None 4/11/2017 Objectives Define
Recurrence risk after anticoagulant treatment of limited duration for late, second venous thromboembolism
 ARTICLES Coagulation & its Disorders Recurrence risk after anticoagulant treatment of limited duration for late, second venous thromboembolism Tom van der Hulle, Melanie Tan, Paul L. den Exter, Mark J.G.
ARTICLES Coagulation & its Disorders Recurrence risk after anticoagulant treatment of limited duration for late, second venous thromboembolism Tom van der Hulle, Melanie Tan, Paul L. den Exter, Mark J.G.
Use of EKOS Catheter in the management of Venous Mr. Manoj Niverthi, Mr. Sarang Pujari, and Ms. Nupur Dandavate, The GTF Group
 Use of EKOS Catheter in the management of Venous Thromboembolism @ Mr. Manoj Niverthi, Mr. Sarang Pujari, and Ms. Nupur Dandavate, The GTF Group Introduction Georgia Thrombosis Forum (GTF, www.gtfonline.net)
Use of EKOS Catheter in the management of Venous Thromboembolism @ Mr. Manoj Niverthi, Mr. Sarang Pujari, and Ms. Nupur Dandavate, The GTF Group Introduction Georgia Thrombosis Forum (GTF, www.gtfonline.net)
Prevention of thrombosis
 Prevention of thrombosis Massimo Lamperti MD, MBA Chief of General Anaesthesia Department Anaesthesiology Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Clinical Professor of Anaesthesiology Cleveland Clinic Lerner
Prevention of thrombosis Massimo Lamperti MD, MBA Chief of General Anaesthesia Department Anaesthesiology Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Clinical Professor of Anaesthesiology Cleveland Clinic Lerner
IRB protocol Yair Lev, MD 11/25/08
 IRB protocol Yair Lev, MD 11/25/08 Abdominal and Pelvic CT as a screening modality for occult malignant disease in unprovoked Venous Thromboembolism: A randomized, controlled prospective study. A. Study
IRB protocol Yair Lev, MD 11/25/08 Abdominal and Pelvic CT as a screening modality for occult malignant disease in unprovoked Venous Thromboembolism: A randomized, controlled prospective study. A. Study
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin
 Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2016 Section: Prescription Drugs
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2016 Section: Prescription Drugs
Thrombophilia. Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC. GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, Disclosures. Conflicts of interest: NONE
 LA APLA 1 3 ACA Anti-ß2-GP I 2 45 Thrombophilia Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, 2017 Disclosures Conflicts of interest: NONE Off-label product use discussion:
LA APLA 1 3 ACA Anti-ß2-GP I 2 45 Thrombophilia Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, 2017 Disclosures Conflicts of interest: NONE Off-label product use discussion:
What is the impact of Superficial Vein Thrombosis?
 What is the impact of Superficial Vein Thrombosis? Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, University of Thessalia, Greece Chairman,
What is the impact of Superficial Vein Thrombosis? Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, University of Thessalia, Greece Chairman,
THROMBOPHILIA SCREENING
 THROMBOPHILIA SCREENING Introduction The regulation of haemostasis Normally, when a clot occurs, it exactly occurs where it has to be and does not grow more than necessary due to the action of the haemostasis
THROMBOPHILIA SCREENING Introduction The regulation of haemostasis Normally, when a clot occurs, it exactly occurs where it has to be and does not grow more than necessary due to the action of the haemostasis
Arterial Ischemic Stroke with Protein S Deficiency in Pakistan
 Case Reports Arterial Ischemic Stroke with Protein S Deficiency in Pakistan Faika Usman, Ali Hassan, Arsalan Ahmad From Section of Neurology, Department of Medicine, Shifa International Hospitals and College
Case Reports Arterial Ischemic Stroke with Protein S Deficiency in Pakistan Faika Usman, Ali Hassan, Arsalan Ahmad From Section of Neurology, Department of Medicine, Shifa International Hospitals and College
Clinical Policy: Dalteparin (Fragmin) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.225
 Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.225 Effective Date: 05/16 Last Review Date: 05/17 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.225 Effective Date: 05/16 Last Review Date: 05/17 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Perioperative Management of the Anticoagulated Patient
 Perioperative Management of the Anticoagulated Patient Citywide Resident Perioperative Medical Consultation Conference 5/5/17 Matthew Eisen, MD Director, Anticoagulation Services MetroHealth Medical Center
Perioperative Management of the Anticoagulated Patient Citywide Resident Perioperative Medical Consultation Conference 5/5/17 Matthew Eisen, MD Director, Anticoagulation Services MetroHealth Medical Center
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 16 December 1999 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON CLINICAL
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 16 December 1999 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON CLINICAL
