Vasorelaxant e ect of nitric oxide releasing steroidal and nonsteroidal anti-in ammatory drugs
|
|
|
- Richard Rogers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 British Journal of Pharmacology (2001) 133, 1023 ± 1028 ã 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/01 $15.00 Vasorelaxant e ect of nitric oxide releasing steroidal and nonsteroidal anti-in ammatory drugs 1 J. Keeble, 2 O.A. Al-Swayeh & *,1 P.K. Moore 1 Messengers and Signalling Group, School of Biomedical Sciences, King's College London, Hodgkin Building, Guy's Campus, London SE1 9RT and 2 Department of Medicine King Saud University, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Keywords: Abbreviations: 1 The e ect of several nitric oxide releasing-non-steroidal anti-in ammatory drugs (NO-NSAID) and nitroprednisolone on blood vessel relaxation in vitro and in vivo was studied. Nitro urbiprofen (NOF; EC 50, mm), nitroaspirin (NOA; EC 50, mm), nitroparacetamol (NOPARA; EC 50, mm) and nitroprednisolone (EC 50, mm) caused concentration-related relaxation of noradrenaline (NA)-contracted rat aortic rings. All NO releasing compounds tested were approximately three orders of magnitude less potent than sodium nitroprusside (SNP, EC 50, nm). 2 The vasorelaxant e ect of NOF and NOPARA in the rat aorta was potentiated by zaprinast (5 mm) and reduced by ODQ (5 mm). Flurbiprofen and paracetamol (100 mm) caused minimal (510%) relaxation of the rat aorta and did not a ect the response to SNP. The e ect of NOF was unchanged in the presence of L-NAME (100 mm; EC 30, mm cf. EC 30, mm, P40.05) but increased by removal of the endothelium (EC 30, mm cf. EC 50, mm, P50.05). 3 NOF (0.1 ± 50 mm) produced a small but not concentration-related vasodilation of the NApreconstricted (i.e. `high tone') perfused rat mesentery preparation (cf. SNP, EC 30, mm). In contrast, NOF (1 ± 100 mm) produced concentration-related vasodilation of the `high tone' perfused rat kidney with an EC 50 of mm. 4 Neither NOF (74 mg kg 71, i.p.) nor NOA (91.9 mg kg 71, i.p.) nor equimolar doses of urbiprofen (50 mg kg 71, i.p.) or aspirin (50 mg kg 71, i.p.) a ected mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) or heart rate (HR) of pentobarbitone-anaesthetized rats over a 1 h period. 5 NO-NSAID relax blood vessels in vitro by an NO-dependent mechanism. The absolute vasorelaxant e ect of NO releasing drug varies greatly with the choice of compound and between blood vessel preparations. British Journal of Pharmacology (2001) 133, 1023 ± 1028 NO-NSAID; nitro urbiprofen; aorta; mesentery; kidney; nitroparacetamol; nitroaspirin; nitroprednisolone DMSO, dimethylsulphoxide; HR, heart rate; MAP, mean arterial blood pressure; NA, noradrenaline; NOA, nitroaspirin; NOF, nitro urbiprofen; NO-NSAID, nitro-non-steroidal anti-in ammatory drug(s); NOP, nitroprednisolone; NOPARA, nitroparacetamol; NSAID, non-steroidal anti-in ammatory drug(s); ODQ, oxadiazolo [4,3a] quinoxalin-1-one; SNP, sodium nitroprusside Introduction Aspirin and like nonsteroidal anti-in ammatory drugs (NSAID) have been employed, for many years, as a treatment for in ammation and hyperalgesia associated with such conditions as rheumatoid arthritis. However, the side e ects of NSAID in the gastrointestinal tract (e.g. haemorrhage, ulceration), resulting from reduced formation of vasodilator and cytoprotective prostanoids in the gastric mucosa, limit the usefulness of these compounds in the clinic (Wallace, 1997). In recent years, nitric oxide (NO)-releasing derivatives of NSAID (so-called `nitro-nonsteroidal anti-in ammatory drugs or NO-NSAID') have attracted considerable attention as possible therapeutic alternatives to the parent NSAID (reviewed by del Soldato et al., 1999). Thus, NO-NSAID cause signi cantly less gastrointestinal damage in experimental animals than do the parent NSAID (e.g. Muscara et *Author for correspondence; phillip.moore@kcl.ac.uk al., 1998; Takeuchi et al., 1998; Ukawa et al., 1997; Wallace et al., 1994). It has been suggested that nitro-nsaid most probably `spare' the gastrointestinal tract by the local release of NO resulting in increased stomach mucosal blood ow (Mariotto et al., 1995). Furthermore, NO released from NO-NSAID may also contribute to the anti-in ammatory e ect of this group of drugs. For example, nitroaspirin (but not aspirin) inhibits caspase 1 activity and thereby reduces formation of proin ammatory, interleukin-1b (Fiorucci et al., 1999). Such an action may contribute to the augmented anti-in ammatory (Al-Swayeh et al., 2000) and anti-thrombotic (Wallace et al., 1995) e ect of nitroaspirin (cf. aspirin). Thus, NO-NSAID may be considered as a novel class of `NO donor' drugs. With this in mind it is perhaps surprising that there is a paucity of published information concerning the cardiovascular e ects of NO-NSAID. For example, in vivo, nitro- urbiprofen (NOF), nitroaspirin (NOA) and nitronaproxen are reportedly without e ect on blood pressure of the
2 1024 J. Keeble et al NO-NSAID and aorta anaesthetized rat (Fujihara et al., 1998; Wallace et al., 1994; 1995, Yamamoto et al., 2000). Similarly, a newly reported NO releasing derivative of salicylic acid (B-NOD) has also recently been reported to be without e ect on rat blood pressure or heart rate following oral administration whilst potently inhibiting platelet aggregation in vitro (Bing et al., 2000). Furthermore, high concentrations of NOF have been shown to relax isolated rat aortic rings in vitro (Adami et al., 1996). However, to the best of our knowledge, there has been no systematic attempt to study the e ect of NOF (and other NO-NSAID) on vascular responsiveness in a range of blood vessel preparations in vitro. To this end, we now report the vasorelaxant e ect of NOF and urbiprofen in comparison with sodium nitroprusside (SNP) using a range of in vitro blood vessel preparations (i.e. rat aorta, perfused rat kidney and mesentery) and have additionally probed the mechanism of action of NOFinduced vasorelaxation and determined its potency (cf. other NO-NSAID) in the rat aorta preparation. Methods Effect of NO releasing compounds on rat aortic ring Rat aortic rings were prepared essentially as described previously (Moore et al., 1990). Brie y, rats (male, Wistar, 220 ± 300 g) were either killed by a blow to the head and exsanguination or by exposure to a gradually increasing concentration of CO 2. The thoracic aorta was removed and cleared of extraneous connective tissue. Rings (approx. 2 ± 4 mm diameter) were mounted using stainless steel clips under a tension of 1 g in 20 ml organ baths containing warmed (378C), oxygenated (95% O 2 : 5% CO 2 ) Krebs solution (composition, mm); NaCl 118, KCl 5.4, NaHCO 3 25, MgSO 4 1.2, CaCl 2 2.5, glucose 11.1, ph 7.4. Changes in tension were recorded using Grass-FT03 force transducers connected to a MacLab 2E (AD Instruments Inc.) attached to a Macintosh Performa 475 computer. After equilibration (1 h), rings were contracted with 1 mm noradrenaline (NA), a concentration that produces approximately 70% of the maximum contraction and thereafter relaxed by cumulative addition (dose cycle time, 6 min) of increasing concentrations (10 ± 1000 mm) of nitro urbiprofen (NOF), nitroaspirin (NOA), nitroprednisolone (NOP), nitroparacetamol (NO- PARA) or sodium nitroprusside (SNP: 0.01 ± 20 mm). The vasorelaxant e ect of urbiprofen, aspirin, prednisolone and paracetamol (all 10 ± 1000 mm) was also evaluated as was the e ect of SNP in the presence of paracetamol or urbiprofen (both 100 mm). In some experiments the vasorelaxant e ect of NOF and NOPARA in the rat aorta was additionally determined after preincubation (15 min) with either [1,2,4] oxadiazolo [4,3a] quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ; 5 mm), zaprinast (5 mm) orl-name (100 mm) or in rings gently rubbed on the intimal surface to remove the endothelial cell layer (checked by failure to relax in response to 1 mm carbachol). All results are expressed as per cent relaxation of NA-induced tone. Effect of NOF on perfused rat mesentery and kidney Rat mesentery and kidney preparations were perfused as described previously (Moore et al., 1990). Brie y, rats (male, Wistar, 200 ± 250 g, Charles River Ltd) were killed by a blow to the head and exsanguination. The superior mesenteric artery and/or renal artery were cannulated and the mesenteric vascular bed and/or kidney were immediately removed and perfused (5 ml min 71 ) with warmed (378C), oxygenated (95% O 2 : 5% CO 2 ) Krebs solution. Perfusion pressure was monitored continuously by means of a Druck pressure transducer connected to a Devices pen recorder. In order to assess the vasorelaxant e ect of NOF (0.1 ± 100 mm), urbiprofen (1 ± 100 mm) and SNP (0.1 ± 100 mm) on perfusion pressure, NA at a concentration (31.3 mm) previously shown to cause approximately 70% maximal vasoconstrictor tone (Bhardwaj & Moore, 1988) was added to the perfusing Krebs solution. Under these circumstances no signi cant loss of vasoconstrictor tone in either mesentery or kidney was detected over a 3 h period which was the maximum length of each experiment. Experiments were carried out in a noncumulative manner i.e. drugs were added to the perfusing Krebs solution for a period of 15 min to allow development of a full vasodilator response after which time preparations were returned to NA-containing Krebs before exposure to a higher concentration of test drug. Results indicate change in perfusion pressure (mm Hg). Measurement of rat mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) Rats (male, Wistar, 200 ± 250 g, Tucks Ltd) were anaesthetized with sodium pentobarbitone (60 mg kg 71, i.p.). The right carotid artery was cannulated for measurement of blood pressure and heart rate via a Druck pressure transducer connected to a Powerlab (AD Instruments Ltd) attached to a Dell Inspiron 4000 computer running Chart for Windows. NOF (74 mg kg 71 ), NOA (91.9 mg kg 71 ), urbiprofen (50 mg kg 71 ), aspirin (50 mg kg 71 ), sodium nitroprusside (50 mg kg 71 ) or vehicle (0.5% w v 71 carboxymethylcellulose, 2mlkg 71 ) were administered i.p. and blood pressure and heart rate monitored continuously for 60 min thereafter. Drugs and chemicals Nitro urbiprofen (2- uoromethyl [1,1-biphenyl]-4-acetic acid 4-(nitrooxy) butyl ester), nitroparacetamol (4-(nitroxy)butanoic acid 4-acetylaminophenyl ester), nitroaspirin (2-(acetyloxy) benzoic acid 3-(nitrooxymethy) phenyl ester) and nitroprednisolone (prednisolone 21-[(4-nitrooxymethyl)benzoate]) were the generous gift of Dr P. del Soldato (NicOX Ltd, Sophia-Antipolis, France). Flurbiprofen, paracetamol, aspirin, noradrenaline bitartrate, prednisolone, ODQ, zaprinast, sodium nitroprusside and carboxymethylcellulose were purchased from Sigma Ltd. Noradrenaline and sodium nitroprusside were dissolved in distilled water and kept on ice throughout the experiment to minimize spontaneous breakdown. All other drugs were dissolved in DMSO. Statistical analysis Results indicate mean+s.e.mean with the number of observations shown in parenthesis. Statistical signi cance of di erences between groups was determined one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to compare means in the same group followed by unpaired student's t-tests to compare means between groups where necessary. In all cases a probability (P)
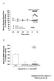
3 J. Keeble et al NO-NSAID and aorta 1025 value of less than 0.05 was taken to indicate statistical signi cance. Results The effect of NOF and other NO releasing compounds on rat aorta In this study, NA (1 mm) caused approximately 70% maximal contraction of the isolated rat aorta ( g, n=130). Increasing concentrations of NO- NSAID and nitroprednisolone (1 mm ±1 mm) caused graded relaxation of NA-precontracted aortic rings (Figure 1). The rank order of potency was NOP (EC 50, mm: E max, %, n=5 ± 12)4NOA (EC 50, mm: E max, %, n=12)4nopara (EC 50, mm: E max, %, n=6)4nof (EC 50, mm, n=15). Due to the limitations of solubility of the highest concentration of NOF tested (1 mm) the greatest relaxation of tone observed with this compound was % (n=15). In all cases, relaxation of rat aortic rings to these NO releasing compounds was a gradual process, which at higher concentrations, required 3 ± 4 min to complete. Control experiments were undertaken with SNP which also relaxed NA-precontracted aortic rings (EC 50, nm, E max, %, n=4). For comparison, SNP was therefore approximately three orders of magnitude more potent than the other NO releasing compounds tested. Mechanism of action of the vasorelaxant effect of NO-NSAID on rat aorta A number of separate experiments were undertaken to investigate the mechanism of the vasorelaxant e ect of NO- NSAID. Thus, relaxation of aortic rings in the presence of NO-NSAID is unlikely to be related to a vehicle e ect since DMSO at a concentration (0.3% v v 71 ) which represents the highest concentration of vehicle achieved in the organ bath in these experiments did not relax NA-precontracted aortic rings. Similarly, a direct e ect of prednisolone or NSAID (released by the cleavage of NO-NSAID in the organ bath) can be excluded since urbiprofen, paracetamol, prednisolone and aspirin (concentrations up to 100 mm) caused minimal relaxation of NA-precontracted rat aortic rings (data not shown). It is also unlikely that, following NO-NSAID breakdown, the presence of the NSAID moiety signi cantly a ected the vasorelaxant e ect of released NO since exposure of tissues to urbiprofen or paracetamol (both 100 mm) failed to a ect the response to SNP (EC 50, nm cf and nm in the presence of urbiprofen and paracetamol respectively, n=4, P40.05). Finally, pretreatment with L-NAME (100 mm) did not a ect the vasorelaxant response to either NOF (EC 30, mm cf , 17.0 mm, n=4, P40.05) or NOPARA ( mm cf mm, n=4, P40.05) suggesting that these NO-NSAID do not trigger the release of endogenous NO from aortic rings. In contrast, removal of endothelium signi cantly increased NOF-induced relaxation (EC 50, mm, n=7, P50.05). Moreover, preincubation of aortic rings with zaprinast (selective inhibitor of cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase) signi cantly potentiated the vasorelaxant e ect of NOF and NOPARA whilst ODQ (selective inhibitor of soluble guanylate cyclase) signi cantly reduced responses to both NO-NSAID (Figure 2). Effect of NOF on isolated, perfused rat mesentery Figure 1 Vasorelaxant e ect of a range of NO-NSAID on the rat aorta. Preparations were precontracted with NA (1 mm) and subsequently relaxed by cumulative addition of NO-NSAID. Results show per cent relaxation of NA-induced tone and are mean+ s.e.mean, n=5 ± 15. Perfusion of rat mesentery preparations with NA (31.3 mm) resulted in so-called `high tone' preparations in which perfusion pressure was increased by approximately 100 ± 180 mm Hg over basal values. Perhaps surprisingly, NOF (100 nm ±50 mm) exhibited negligible vasodilator activity in this vascular bed. Indeed, the response to NOF was not dose related with a small but consistent vasodilatation being observed at all concentrations used (e.g. 50 mm: % of NA-induced tone, n=5). In control experiments, both DMSO (0.2% v v 71 ; highest concentration achieved) and urbiprofen (100 mm) were without e ect on vascular tone in these preparations (data not shown). SNP was considerably more active than NOF producing a maximal relaxation of NA-induced tone of % (n=5) with an EC 30 of mm (n=5) (Figure 3). The failure of NOF to dilate the rat mesenteric vasculature in these experiments was not due to a non-speci c inhibitory e ect of the vehicle on the response to NO since DMSO (0.2% v v 71 ) did not a ect vasodilation due to SNP in this preparation (data not shown).
4 1026 J. Keeble et al NO-NSAID and aorta Figure 3 Vasodilator e ect of NOF and SNP in the isolated, perfused rat mesentery. Preparations were preconstricted with NA (31.3 mm) and subsequently relaxed by non-cumulative addition of drug. Results show per cent reduction in NA-induced perfusion pressure and are mean+s.e.mean, n=5. Effect of NOF on MAP Figure 2 Vasorelaxant e ect of NOF (A) and NOPARA (B) on the NA (1 mm) precontracted rat aorta following pretreatment (15 min) with either ODQ (5 mm) or zaprinast (5 mm). Results show per cent relaxation of NA-induced tone and are mean+s.e.mean, n=4 ± 7. Effect of NOF on isolated, perfused rat kidney Perfusion of rat kidney preparations with NA (31.3 mm) resulted in so-called `high tone' preparations in which perfusion pressure was increased by approximately 80 ± 150 mm Hg over basal values. Both NOF (1 ± 100 mm) and SNP (1 ± 100 mm), but not urbiprofen (10 ± 100 mm), caused concentrationdependent relaxation of the NA-preconstricted renal vasculature (Figure 4). In contrast to data obtained using both rat aorta and rat mesentery, the maximum relaxation response following exposure to NOF (100 mm; %, n=5) was considerably greater than that observed with SNP (100 mm; %, n=5, P50.05). In these experiments, the EC 50 for NOF was mm (n=5). Unfortunately, due to the lack of e ect of SNP, no direct comparison of the potency of NOF and SNP is possible. Resting MAP (heart rate in parenthesis) of pentobarbitoneanaesthetized rats in these experiments was mm Hg and beats min 71 respectively (n=25). Injection (i.p.) of NOF (74 mg kg 71 ), NOA (91.9 mg kg 71 ), urbiprofen (50 mg kg 71 ), aspirin (50 mg kg 71 ) or vehicle did not signi cantly a ect MAP or heart rate over the following 60 min period (Table 1). In contrast, i.p. injection of a much lower dose of SNP (50 mg kg 71 ) signi cantly reduced MAP at 5 min post-injection. Discussion NO-NSAID have been proposed as alternatives to the parent NSAID for the treatment of a number of clinical conditions associated with in ammation, pain and/or thrombosis (del Soldato et al., 1999). In this context, it is of interest that nitroprednisolone has also been reported to exhibit more potent anti-in ammatory activity than the parent compound, prednisolone (Paul-Clark et al., 2000). The major perceived therapeutic advantage of NO-NSAID (cf. NSAID) is that these compounds cause much reduced gastrointestinal haemorrhage and ulceration (Elliot et al., 1995; Muscara et al., 1998; Ukawa et al., 1997; Wallace et al., 1994). The mechanism of such gastroprotection has been proposed to
5 J. Keeble et al NO-NSAID and aorta 1027 Figure 4 Vasodilator e ect of NOF, SNP and urbiprofen in the isolated, perfused rat kidney. Preparations were preconstricted with NA (31.3 mm) and subsequently relaxed by non-cumulative addition of drug. Results show per cent reduction in NA-induced perfusion pressure and are mean+s.e.mean, n=5. involve NO-mediated dilatation of the gastric vasculature (del Soldato et al., 1999; Wallace et al., 1995). However, this possibility is not consistent with previous reports that NO- NSAID have no e ect on MAP of the anaesthetized rat (Fujihara et al., 1998; Wallace et al., 1994; 1995, Yamamoto et al., 2000) and raise the intriguing possibility of a di erential e ect of NO-NSAID on vascular beds throughout the body. In the present series of experiments we have extended our preliminary observation that NOF exhibits no vasodepressor activity in the urethane-anaesthetized rat (McLoughlin et al., 1999). We now report that NOA (in addition to NOF) is devoid of vasodepressor activity in this species and have also employed pentobarbitone as the anaesthetic in order to avoid any potential inhibition of cardiovascular re exes associated with urethane. In contrast, a 1000 fold lower dose of the NO donor, SNP, did as expected cause a marked but relatively transient fall in MAP in these animals. It should be pointed out that, at doses shown to be without e ect on MAP in the present study, both NOF and NOA exhibit pronounced antiin ammatory activity in the carrageenan-induced rat hindpaw oedema test (Al-Swayeh et al., 1999, 2000) and NOF attenuates endotoxin-induced gastric and intestinal lesions in the rat (Wallace et al., 1995). Thus, it may be concluded that pharmacologically active doses of NOF and NOA are devoid of hypotensive activity in vivo at least in the anaesthetized rat. Similarly, chronic oral dosing of conscious rats with nitro urbiprofen also failed to reduce MAP (Fujihara et al., 1998). Interestingly, chronic treatment with nitronaproxen has been reported to reduce MAP in the hypertensive rat (Muscara et al., 2000). Thus, the consensus of published information (see Introduction for additional references) strongly suggests a lack of vasodepressor activity of the NO-NSAID class of compounds in normotensive rats. Although beyond the scope of the present investigation, it would clearly be of interest to probe further the mechanism(s) underlying the fall in MAP elicited by nitronaproxen in the hypertensive rat. All of the NO-releasing compounds tested (i.e. NOF, NOA, NOP and NOPARA) relaxed the NA-precontracted rat aorta. Relaxation of aortic rings due to both NOF and NOPARA was increased by zaprinast and reduced by ODQ thereby suggesting that NO release from NOF and NOPARA was a pre-requisite for blood vessel relaxation to take place. This conclusion was supported by the weak vasorelaxant e ect of urbiprofen, paracetamol and prednisolone coupled with the inability of urbiprofen and paracetamol to in uence the vasorelaxant e ect of SNP-derived NO in this preparation. The nding that the vasorelaxant e ect of NOF and NOPARA was not reduced by L-NAME, taken together with the above ndings, strongly suggest that NO-NSAID act as endothelium-independent, NO donors in this preparation. In this context, the augmented vasorelaxant e ect of NOF in endothelium-denuded aortic rings is probably explained by improved access to the underlying smooth muscle cells in the absence of an endothelial barrier. An interesting feature of the present study is that pronounced di erences in the vasorelaxant potency of the various NO-releasing compounds used in this study are apparent. Thus, the rank order of potency to relax the NAprecontracted rat aorta was NOP 4 NOA 4 NOPARA 4 NOF. Based upon a comparison of EC 50 measurements it is clear that NOP is approximately 50 times more potent than NOF in this preparation. In this context, it is also of interest that the vasorelaxant e ect of one of the NO-NSAID tested, NOF, varied considerably between blood vessel preparations. Thus, NOF was markedly less potent than SNP in the rat aorta and also in the perfused rat mesentery but was considerably more potent than SNP in the perfused rat kidney. The disparity in potency both between di erent NO- NSAID (and nitroprednisolone) in the same tissue and for the same NO-NSAID in di erent tissues is somewhat unexpected. To the best of our knowledge, release of NO from NO-NSAID and like drugs is stochiometric and as such NO-mediated blood vessel relaxation would be expected to be similar between di erent NO-NSAID and within di erent tissues. One possible explanation for these observations is that the absolute amount and/or the time course of NO release varies from one NO-releasing compound to the next and also between vascular beds. The mechanism(s) by which NO release from these compounds take place are not fully understood. It is clear that the molecule comprises NO linked via a `spacer' molecule and an ester bridge to the parent NSAID (or prednisolone) and it is also clear that this ester linkage is broken by cell/tissue esterase enzymes in order to liberate free NO (see del Soldato et al., 1999). However, the identity, and tissue distribution of these endogenous
6 1028 J. Keeble et al NO-NSAID and aorta esterases remains unknown. One interpretation of the present data is therefore that the rate of esterase-mediated cleavage of NO di ers between compounds. Thus, we hypothesize that NOP is cleaved more e ciently by esterase enzyme(s) present in rat aortic rings than is NOF and the other NO-NSAID studied and consequently causes relaxation at lower concentrations. Similar di erences in esterase activity (i.e. high in kidney, low in mesentery and aorta) may account for the variability in vasorelaxant activity of NOF between di erent blood vessel preparations. In conclusion, NO-NSAID (and nitroprednisolone) relax isolated blood vessel preparations in vitro with a potency which varies with the individual compound and with choice of blood vessel preparation. The possibility that the activity and selectivity of the endogenous, tissue-based esterase enzyme(s) which release NO from NOA, NOF, NOPARA and NOP play a critical role in the cardiovascular response to these compounds is suggested. Further experiments to investigate the mechanism of NO release from NO-NSAID and related compounds both in vitro and in vivo are required. J. Keeble was sponsored by the British Pharmacological Society. We would like to thank Dr P. del Soldato (NicOx Ltd, Sophia- Antipolis, France) for the generous gift of NO-NSAID and nitroprednisolone. References ADAMI, A., CUZZOLIN, L., MINUZ, P., CRIVELLENTE, F., LECHI, A. & BENONI, G.(1996). Vasodilating properties of a new nonsteroidal anti-in ammatory drug, nitro urbiprofen, on rat aortic rings. Pharmacol. Res., 33, 239 ± 244. Al-SWAYEH, O.A., CLIFFORD, R.H., DEL SOLDATO, P. & MOORE, P.K. (2000). A comparison of the anti-in ammatory and antinociceptive activity of nitroaspirin and aspirin. Br. J. Pharmacol., 129, 343 ± 350. Al-SWAYEH, O.A., CLIFFORD, R.H. & MOORE, P.K. (1999). Antioedema and antinociceptive e ect of nitroprednisone and nitro urbiprofen. Br.J.Pharmacol.,127, 84. BHARDWAJ, R. & MOORE, P.K. (1988). Endothelium derived relaxing factor and the e ects of acetylcholine and histamine on resistance blood vessels. Br.J.Pharmacol.,95, 835 ± 843. BING, R.J., YAMAMOTO, T., KIM, H. & GRUBBS, R.H. (2000). The pharmacology of a new nitric oxide donor: B-NOD. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 275, 350 ± 353. DEL SOLDATO, P., SORRENTINO, R. & PINTO, A. (1999). NOaspirins: a class of new anti-in ammatory and antithrombotic agents. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 20, 319 ± 323. ELLIOT, S.N., MCKNIGHT, W., CIRINO, G. & WALLACE, J.L. (1995). A nitric oxide releasing non-steroid anti-in ammatory drug accelerates gastric ulcer healing in rats. Gastroenterology, 109, 524 ± 530. FIORUCCI, S., ANTONELLI, E., SANTUCCI, L., MORELLI, O., MIGLIETTI, M., FEDERICI, B., MANNUCCI, R., DEL SOLDATO, P. & MORELLI, A. (1999). Gastrointestinal safety of nitric oxide derived aspirin is related to inhibition of ICE-like cysteine proteases in rats. Gastroenterology, 116, 1089 ± FUJIHARA, C.K., MALHEIROS, D.M.A.C., DONATO, J.L., POLI, A., DE NUCCI, G. & ZATZ, R. (1998). Nitro urbiprofen, a new nonsteroidal anti-in ammatory, ameliorates structural injury in the remnant kidney. Am. J. Physiol., 274, F573 ± F579. MARIOTTO, S., MENEGAZZI, M., CARCERAN DE PRATI, A., CUZZOLIN, L., ADAMI, A., SUZUKI, H. & BENONI, G. (1995). Protective e ect of NO on gastric lesions and inhibition of expression of gastric inducible NOS by urbiprofen and its nitroderivative, nitro urbiprofen. Br.J.Pharmacol.,116, 1713 ± MCLOUGHLIN, C., KEEBLE, J. & MOORE, P.K. (1999). E ect of nitro urbiprofen on lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis. Mediators of In ammation, 8 (suppl 1), P MOORE, P.K., AL-SWAYEH, O.A., CHONG, N.W.S., EVANS, R.A. & GIBSON, A. (1990). L-N G -nitro arginine (L-NOARG) - a novel, L- arginine reversible inhibitor of endothelium-dependent vasodilatation. Br.J.Pharmacol.,99, 408 ± 412. MUSCARA, M.N., MCKNIGHT, W., DEL SOLDATO, P. & WALLACE, J.L. (1998). E ect of a nitric oxide-releasing naproxen derivative on hypertension and gastric damage induced by chronic nitric oxide inhibition in the rat. Life Sci., 62, PL235 ± PL240. MUSCARA, M.N., MCKNIGHT, W., LOVREN, F., TRIGGLE, C.R., CIRINO,G.&WALLACE,J.L.(2000). Antihypertensive properties of a nitric oxide releasing naproxen derivative in two-kidney, one-clip rat. Am.J.Physiol.,279, H528 ± H535. PAUL-CLARK, M., DEL SOLDATO,P.,FIORUCCI,S.,FLOWER,R.J.& PERRETTI, M. (2000). 21-NO-prednisolone is a novel nitric oxide-releasing derivative of prednisolone with enhanced antiin ammatory properties. Br.J.Pharmacol.,137, 1345 ± TAKEUCHI, K., UKAWA, H., KONAKA, A., KITAMURA, M. & SUGAWA, Y. (1998). E ect of nitric oxide-releasing aspirin derivative on gastric functional and ulcerogenic responses in rats: comparison with plain aspirin. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther., 286, 115 ± 121. UKAWA, H., YAMAKUNI, H., KATO, S. & TAKEUCHI, K. (1997). E ects of cycloxygenase-2 selective and nitric oxide releasing nonsteroidal anti-in ammatory drugs on gastric ulcerogenic and healing responses in experimental animals. Dig. Dis. Sci., 43, 2003 ± WALLACE, J.L. (1997). Nonsteroidal antiin ammatory drugs and gastroenteropathy: the second hundred years. Gastroenterology, 112, 1000 ± WALLACE, J.L., MCKNIGHT, W., DEL SOLDATO, P., BAYDOUN, A.R. & CIRINO, G.(1995). Antithrombotic e ects of a nitric oxide releasing gastric sparing aspirin derivative. J. Clin. Invest., 96, 2711 ± WALLACE, J.L., REUTER, B., CICALA, C., MCKNIGHT, W., GRI- SHAM, M. & CIRINO, G. (1994). Novel non-steroidal antiin- ammatory derivatives with markedly reduced ulcerogenic properties in the rat. Gastroenterology, 107, 173 ± 179. YAMAMOTO,T.,KAKAR,N.R.,VINA,E.R.,JOHNSON,P.E.&BING, R.J. (2000). The e ect of aspirin and two nitric oxide donors on the infarcted heart in situ. Life Sci., 67, 839 ± 846. (Received March 19, 2001 Accepted May 10, 2001)
Vasorelaxant e ects of a nitric oxide-releasing aspirin derivative in normotensive and hypertensive rats
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2001) 133, 1314 ± 1322 ã 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp Vasorelaxant e ects of a nitric oxide-releasing aspirin
British Journal of Pharmacology (2001) 133, 1314 ± 1322 ã 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp Vasorelaxant e ects of a nitric oxide-releasing aspirin
A comparison of the anti-in ammatory and anti-nociceptive activity of nitroaspirin and aspirin
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2000) 129, 343 ± 350 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp A comparison of the anti-in ammatory and anti-nociceptive
British Journal of Pharmacology (2000) 129, 343 ± 350 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp A comparison of the anti-in ammatory and anti-nociceptive
Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate
 Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
J.E. Keeble & *,1 P.K. Moore
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2002) 137, 295 ± 310 ã 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/bjp REVIEW Pharmacology and potential therapeutic applications
British Journal of Pharmacology (2002) 137, 295 ± 310 ã 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/bjp REVIEW Pharmacology and potential therapeutic applications
NCX 4016, a nitric oxide-releasing aspirin, modulates adrenergic vasoconstriction in the perfused rat tail artery
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2002) 137, 229 ± 236 ã 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/bjp NCX 4016, a nitric oxide-releasing aspirin, modulates adrenergic
British Journal of Pharmacology (2002) 137, 229 ± 236 ã 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/bjp NCX 4016, a nitric oxide-releasing aspirin, modulates adrenergic
Effect of a nitric oxide releasing derivative of paracetamol in a rat model of endotoxaemia
 British Journal of Pharmacology (6) 149, 516 522 & 6 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Effect of a nitric oxide releasing derivative of paracetamol
British Journal of Pharmacology (6) 149, 516 522 & 6 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Effect of a nitric oxide releasing derivative of paracetamol
Studies on the effects of viprostol in isolated small blood vessels and thoracic aorta of the rat
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1988), 93, 613-617 Studies on the effects of viprostol in isolated small blood vessels and thoracic aorta of the rat Fong M. Lai, Tarak Tanikella, Agnes Cobuzzi & Peter Cervoni Cardiovascular
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1988), 93, 613-617 Studies on the effects of viprostol in isolated small blood vessels and thoracic aorta of the rat Fong M. Lai, Tarak Tanikella, Agnes Cobuzzi & Peter Cervoni Cardiovascular
LOW-DOSE ASPIRIN AND CLOPIDOGREL ATTENUATE REFLEX CUTANEOUS VASODILATION IN MIDDLE AGED SKIN Lacy A. Holowatz, John Jennings, and W.
 Holowatz et al. 1 LOW-DOSE ASPIRIN AND CLOPIDOGREL ATTENUATE REFLEX CUTANEOUS VASODILATION IN MIDDLE AGED SKIN Lacy A. Holowatz, John Jennings, and W. Larry Kenney Department of Kinesiology and Graduate
Holowatz et al. 1 LOW-DOSE ASPIRIN AND CLOPIDOGREL ATTENUATE REFLEX CUTANEOUS VASODILATION IN MIDDLE AGED SKIN Lacy A. Holowatz, John Jennings, and W. Larry Kenney Department of Kinesiology and Graduate
Cooling effects on nitric oxide production by rabbit ear and femoral arteries during cholinergic stimulation
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1994), 113, 55-554 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1994 Cooling effects on nitric oxide production by rabbit ear and femoral arteries during cholinergic stimulation N. Fernandez, L. Monge,
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1994), 113, 55-554 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1994 Cooling effects on nitric oxide production by rabbit ear and femoral arteries during cholinergic stimulation N. Fernandez, L. Monge,
This laboratory exercise uses a simple preparation and a straightforward
 LABORATORY DEMONSTRATION OF VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE FUNCTION USING RAT AORTIC RING SEGMENTS Rayna J. Gonzales, Rebecca W. Carter, and Nancy L. Kanagy Vascular Physiology Group, Department of Cell Biology
LABORATORY DEMONSTRATION OF VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE FUNCTION USING RAT AORTIC RING SEGMENTS Rayna J. Gonzales, Rebecca W. Carter, and Nancy L. Kanagy Vascular Physiology Group, Department of Cell Biology
Cyclooxygenase (COX), the primary enzyme responsible
 Aspirin-Triggered, Cyclooxygenase-2 Dependent Lipoxin Synthesis Modulates Vascular Tone Pierre-Yves von der Weid, PhD; Morley D. Hollenberg, MD, PhD; Stefano Fiorucci, MD; John L. Wallace, PhD Background
Aspirin-Triggered, Cyclooxygenase-2 Dependent Lipoxin Synthesis Modulates Vascular Tone Pierre-Yves von der Weid, PhD; Morley D. Hollenberg, MD, PhD; Stefano Fiorucci, MD; John L. Wallace, PhD Background
hypoxic pulmonary hypertension
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1992), 17, 47-413 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1992 Reduced relaxant potency of nitroprusside on pulmonary artery preparations taken from rats during the development of hypoxic pulmonary
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1992), 17, 47-413 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1992 Reduced relaxant potency of nitroprusside on pulmonary artery preparations taken from rats during the development of hypoxic pulmonary
Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats
 Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 27(December 12) 117 122 www.njps.com.ng Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats 1 Oloyo, Ahmed
Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 27(December 12) 117 122 www.njps.com.ng Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats 1 Oloyo, Ahmed
Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats
 Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats Orachorn Boonla 1, Phattharaphon Tuangpolkrung 1, Poungrat Pakdeechote 1, Upa Kukongviriyapan
Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats Orachorn Boonla 1, Phattharaphon Tuangpolkrung 1, Poungrat Pakdeechote 1, Upa Kukongviriyapan
Supplemental Figure I
 Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous Herbal Supplement?
 Grand Valley State University ScholarWorks@GVSU Student Summer Scholars Undergraduate Research and Creative Practice 2010 Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous
Grand Valley State University ScholarWorks@GVSU Student Summer Scholars Undergraduate Research and Creative Practice 2010 Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous
Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation
 6 The Open Circulation and Vascular Journal, 2011, 4, 6-11 Open Access Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation Induced by R-PIA Gonzalo Allende* and Salvador Acevedo
6 The Open Circulation and Vascular Journal, 2011, 4, 6-11 Open Access Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation Induced by R-PIA Gonzalo Allende* and Salvador Acevedo
PCTH 400. Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases. Blood vessel LAST LECTURE. Endothelium. High blood pressure
 PCTH 400 LAST LECTURE Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases. Classic Vascular pharmacology -chronic -systemic Local Vascular pharmacology -acute -targeted High blood pressure Blood pressure
PCTH 400 LAST LECTURE Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases. Classic Vascular pharmacology -chronic -systemic Local Vascular pharmacology -acute -targeted High blood pressure Blood pressure
Name: Class: "Pharmacology NSAIDS (1) Lecture
 I Name: Class: "Pharmacology NSAIDS (1) Lecture د. احمد الزهيري Inflammation is triggered by the release of chemical mediators from injured tissues and migrating cells. The specific mediators vary with
I Name: Class: "Pharmacology NSAIDS (1) Lecture د. احمد الزهيري Inflammation is triggered by the release of chemical mediators from injured tissues and migrating cells. The specific mediators vary with
Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 139-143. Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline I. R. INNES AND R. MAILHOT* Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 139-143. Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline I. R. INNES AND R. MAILHOT* Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine,
Mechanisms of simvastatin-induced vasodilatation of rat superior mesenteric arteries
 BIOMEDICAL REPORTS 5: 491-496, 2016 Mechanisms of simvastatin-induced vasodilatation of rat superior mesenteric arteries YULONG CHEN 1,2*, HONGMEI ZHANG 3*, HUANHUAN LIU 2 and AILAN CAO 1,4 1 Shaanxi Pharmaceutical
BIOMEDICAL REPORTS 5: 491-496, 2016 Mechanisms of simvastatin-induced vasodilatation of rat superior mesenteric arteries YULONG CHEN 1,2*, HONGMEI ZHANG 3*, HUANHUAN LIU 2 and AILAN CAO 1,4 1 Shaanxi Pharmaceutical
The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function in vitro
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 811-818 L-arginine on airway smooth muscle ISSN -879X 811 The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 811-818 L-arginine on airway smooth muscle ISSN -879X 811 The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function
Magnesium is a key ionic modulator of blood vessel
 Hypomagnesemia Inhibits Nitric Oxide Release From Coronary Endothelium: Protective Role of Magnesium Infusion After Cardiac Operations Paul J. Pearson, MD, PhD, Paulo R. B. Evora, MD, PhD, John F. Seccombe,
Hypomagnesemia Inhibits Nitric Oxide Release From Coronary Endothelium: Protective Role of Magnesium Infusion After Cardiac Operations Paul J. Pearson, MD, PhD, Paulo R. B. Evora, MD, PhD, John F. Seccombe,
Preservation of vascular function in rat mesenteric resistance arteries following cold storage, studied by small vessel myography
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1998) 123, 1555 ± 1560 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Preservation of vascular function in rat mesenteric
British Journal of Pharmacology (1998) 123, 1555 ± 1560 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Preservation of vascular function in rat mesenteric
J.D. Mo att & 1 T.M. Cocks
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1998) 125, 591 ± 594 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp SPECIAL REPORT Endothelium-dependent and -independent
British Journal of Pharmacology (1998) 125, 591 ± 594 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp SPECIAL REPORT Endothelium-dependent and -independent
Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) 30: 891-895 Perfused rat tail vascular bed ISSN 0100-879X 891 Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed A.S. França, L.V. Rossoni,
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) 30: 891-895 Perfused rat tail vascular bed ISSN 0100-879X 891 Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed A.S. França, L.V. Rossoni,
Involvement of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in a model of a delayed vascular hyporeactivity induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 127, 1447 ± 1453 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Involvement of ATP-sensitive potassium channels
British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 127, 1447 ± 1453 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Involvement of ATP-sensitive potassium channels
John L. Wallace, Marcelo N. Muscará, Gilberto de Nucci, Stella Zamuner, Giuseppe Cirino, Piero del Soldato, and Ennio Ongini
 0022-3565/04/3092-626 633$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 309, No. 2 Copyright 2004 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 63453/1144306
0022-3565/04/3092-626 633$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 309, No. 2 Copyright 2004 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 63453/1144306
Anti-Thrombotic Effects of a Nitric Oxide-releasing, Gastric-sparing
 Anti-Thrombotic Effects of a Nitric Oxide-releasing, Gastric-sparing Aspirin Derivative John L. Wallace,* Webb McKnight,* Piero Del Soldato,t Anwar R. Baydoun,' and Giuseppe Cirino11 *Department of Pharmacology
Anti-Thrombotic Effects of a Nitric Oxide-releasing, Gastric-sparing Aspirin Derivative John L. Wallace,* Webb McKnight,* Piero Del Soldato,t Anwar R. Baydoun,' and Giuseppe Cirino11 *Department of Pharmacology
A. HOLiiCYOVA, J. TOROK, I. BERNATOVA, O. PECHANOVA
 Physiol. Res. 45: 317-321, 1996 Restriction of Nitric Oxide Rather than Elevated Blood Pressure is Responsible for Alterations of Vascular Responses in Nitric Oxide-Deficient Hypertension A. HOLiiCYOVA,
Physiol. Res. 45: 317-321, 1996 Restriction of Nitric Oxide Rather than Elevated Blood Pressure is Responsible for Alterations of Vascular Responses in Nitric Oxide-Deficient Hypertension A. HOLiiCYOVA,
In the name of GOD. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension
 In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
RAPID COMMUNICATION. Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension
 Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Modulation of vascular reactivity in normal, hypertensive and diabetic rat aortae by a non-antioxidant flavonoid
 Pharmacological Research 55 (2007) 385 391 Modulation of vascular reactivity in normal, hypertensive and diabetic rat aortae by a non-antioxidant flavonoid Machha Ajay a,,1, Francis I. Achike b, Mohd Rais
Pharmacological Research 55 (2007) 385 391 Modulation of vascular reactivity in normal, hypertensive and diabetic rat aortae by a non-antioxidant flavonoid Machha Ajay a,,1, Francis I. Achike b, Mohd Rais
NO-naproxen modulates in ammation, nociception and downregulates T cell response in rat Freund's adjuvant arthritis
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2000) 130, 1399 ± 1405 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp NO-naproxen modulates in ammation, nociception and downregulates
British Journal of Pharmacology (2000) 130, 1399 ± 1405 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp NO-naproxen modulates in ammation, nociception and downregulates
EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1981), 73,829-835 EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE RESPONSES TO CHOLINOMIMETICS IN THE RAT ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE SHEILA A. DOGGRELL Department of Pharmacology & Clinical
Br. J. Pharmac. (1981), 73,829-835 EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE RESPONSES TO CHOLINOMIMETICS IN THE RAT ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE SHEILA A. DOGGRELL Department of Pharmacology & Clinical
THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1974), 46, 473 THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO M. R. WASSEF, H. LAL AND BARBARA J. PLEUVRY SUMMARY The cardiovascular effects
Br. J. Anaesth. (1974), 46, 473 THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO M. R. WASSEF, H. LAL AND BARBARA J. PLEUVRY SUMMARY The cardiovascular effects
A comparison of e ects measured with isotonic and isometric recording: II. Concentration-e ect curves for physiological antagonists
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2001) 133, 1087 ± 1095 ã 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/01 $15.00 A comparison of e ects measured with isotonic and isometric recording: II.
British Journal of Pharmacology (2001) 133, 1087 ± 1095 ã 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/01 $15.00 A comparison of e ects measured with isotonic and isometric recording: II.
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF VERAPAMIL AND CIMETIDINE ON ISOLATED RAT STOMACH STRIP
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF VERAPAMIL AND CIMETIDINE ON ISOLATED RAT STOMACH STRIP ABSTRACT Pages with reference to book, From 263 To 266 Talat Ahmed Nishat ( Department of Pharmacology, Rawalpindi
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF VERAPAMIL AND CIMETIDINE ON ISOLATED RAT STOMACH STRIP ABSTRACT Pages with reference to book, From 263 To 266 Talat Ahmed Nishat ( Department of Pharmacology, Rawalpindi
Streptozotocin Diabetes-Induced Changes in Aorta, Peripheral Nerves and Stomach of Wistar Rats
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1999), 18, Focus Issue, 155 162 155 Streptozotocin Diabetes-Induced Changes in Aorta, Peripheral Nerves and Stomach of Wistar Rats R. SOTNÍKOVÁ, V. NosÁĽovÁ, M. ŠTEFEK, S. ŠTOLC,
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1999), 18, Focus Issue, 155 162 155 Streptozotocin Diabetes-Induced Changes in Aorta, Peripheral Nerves and Stomach of Wistar Rats R. SOTNÍKOVÁ, V. NosÁĽovÁ, M. ŠTEFEK, S. ŠTOLC,
Reduced capacitative calcium entry in the mesenteric vascular bed of bile duct-ligated rats
 European Journal of Pharmacology 525 (2005) 117 122 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejphar Reduced capacitative calcium entry in the mesenteric vascular bed of bile duct-ligated rats Noemí M. Atucha, F. Javier
European Journal of Pharmacology 525 (2005) 117 122 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejphar Reduced capacitative calcium entry in the mesenteric vascular bed of bile duct-ligated rats Noemí M. Atucha, F. Javier
Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 1-7 Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog B. N. DAVIES ADi P. G. WITHRINGTON Department of Physiology, Medical College of
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 1-7 Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog B. N. DAVIES ADi P. G. WITHRINGTON Department of Physiology, Medical College of
Evidence for speci c regional patterns of responses to di erent vasoconstrictors and vasodilators in sheep isolated pulmonary arteries and veins
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1997) 121, 441 ± 45 1997 Stockton Press All rights reserved 7 ± 1188/97 $12. Evidence for speci c regional patterns of responses to di erent vasoconstrictors and vasodilators
British Journal of Pharmacology (1997) 121, 441 ± 45 1997 Stockton Press All rights reserved 7 ± 1188/97 $12. Evidence for speci c regional patterns of responses to di erent vasoconstrictors and vasodilators
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Ibuprofen versus other non-steroidal anti-in ammatory drugs: use in general practice and patient perception
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000; 14: 187±191. Ibuprofen versus other non-steroidal anti-in ammatory drugs: use in general practice and patient perception C. J. HAWKEY 1,D.J.E.CULLEN 1,9,G.PEARSON 1,S.HOLMES
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000; 14: 187±191. Ibuprofen versus other non-steroidal anti-in ammatory drugs: use in general practice and patient perception C. J. HAWKEY 1,D.J.E.CULLEN 1,9,G.PEARSON 1,S.HOLMES
Reversal by L-arginine of a dysfunctional arginine/nitric oxide pathway in the endothelium of the genetic diabetic BB rat
 Diabetologia (1997) : 91 915 Springer-Verlag 1997 Reversal by L-arginine of a dysfunctional arginine/nitric oxide pathway in the endothelium of the genetic diabetic BB rat G.M. Pieper, W. Siebeneich, G.
Diabetologia (1997) : 91 915 Springer-Verlag 1997 Reversal by L-arginine of a dysfunctional arginine/nitric oxide pathway in the endothelium of the genetic diabetic BB rat G.M. Pieper, W. Siebeneich, G.
27 part 2. Laith Abu Shekha. Mamoon Al-qatameen
 27 part 2 Laith Abu Shekha Mamoon Al-qatameen Ebaa Alzayadneh In this sheet we will continue talking about second messengers for hormone that can t cross PM. D. Ca +2 as a second messenger: Another second
27 part 2 Laith Abu Shekha Mamoon Al-qatameen Ebaa Alzayadneh In this sheet we will continue talking about second messengers for hormone that can t cross PM. D. Ca +2 as a second messenger: Another second
Clonidine-induced nitric oxide-dependent vasorelaxation mediated by endothelial a 2 -adrenoceptor activation
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2001) 134, 957 ± 968 ã 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/01 $15.00 Clonidine-induced nitric oxide-dependent vasorelaxation mediated by endothelial
British Journal of Pharmacology (2001) 134, 957 ± 968 ã 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/01 $15.00 Clonidine-induced nitric oxide-dependent vasorelaxation mediated by endothelial
Functional regulation of vascular and platelet activity during thrombosis by nitric. Christopher Moore, Charalambos Tymvios and Michael Emerson
 Page of Thrombosis and Haemostasis Functional regulation of vascular and platelet activity during thrombosis by nitric oxide and endothelial nitric oxide synthase Christopher Moore, Charalambos Tymvios
Page of Thrombosis and Haemostasis Functional regulation of vascular and platelet activity during thrombosis by nitric oxide and endothelial nitric oxide synthase Christopher Moore, Charalambos Tymvios
Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and. -independent mechanisms
 Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and -independent mechanisms Yang-Kai WANG 1 #, An-Jing REN 1 #, Xiang-Qun YANG 1, Li-Gang WANG 1, Wei-Fang RONG 3, Chao-Shu TANG 4, Wen-Jun YUAN
Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and -independent mechanisms Yang-Kai WANG 1 #, An-Jing REN 1 #, Xiang-Qun YANG 1, Li-Gang WANG 1, Wei-Fang RONG 3, Chao-Shu TANG 4, Wen-Jun YUAN
Vascular action of the hypoglycaemic agent gliclazide in diabetic rabbits
 Diabetologia (1998) 41: 9--15 Springer-Verlag 1998 Vascular action of the hypoglycaemic agent gliclazide in diabetic rabbits P. J. Pagano 1, M. C. Griswold 1, D. Ravel 2, R. A. Cohen 1 1 Vascular Biology
Diabetologia (1998) 41: 9--15 Springer-Verlag 1998 Vascular action of the hypoglycaemic agent gliclazide in diabetic rabbits P. J. Pagano 1, M. C. Griswold 1, D. Ravel 2, R. A. Cohen 1 1 Vascular Biology
PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE OF
 Br. J. Pharmac. (198). 71, 35-4 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF TH ANOCOCCYGUS MUSCL OF TH DOG A.R. DHPOUR, M.A. KHOYI, H. KOUTCHKI & M.R. ZARRINDAST Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Br. J. Pharmac. (198). 71, 35-4 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF TH ANOCOCCYGUS MUSCL OF TH DOG A.R. DHPOUR, M.A. KHOYI, H. KOUTCHKI & M.R. ZARRINDAST Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Posted: 11/27/2011 on Medscape; Published Br J Anaesth. 2011;107(2): Oxford University Press
 Posted: 11/27/2011 on Medscape; Published Br J Anaesth. 2011;107(2):209-217. 2011 Oxford University Press Effect of Phenylephrine and Ephedrine Bolus Treatment on Cerebral Oxygenation in Anaesthetized
Posted: 11/27/2011 on Medscape; Published Br J Anaesth. 2011;107(2):209-217. 2011 Oxford University Press Effect of Phenylephrine and Ephedrine Bolus Treatment on Cerebral Oxygenation in Anaesthetized
blood-vessels of the isolated perfused lungs of the rat. Both Hirakawa
 547.435-292: 547.781.5: 577.174.5: 612.215 THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE, ACETYLCHOLINE, AND HIS- TAMINE ON THE LUNGS OF THE RAT. By P. FoGGIE. From the Physiology Department, University of Edinburgh. (Received
547.435-292: 547.781.5: 577.174.5: 612.215 THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE, ACETYLCHOLINE, AND HIS- TAMINE ON THE LUNGS OF THE RAT. By P. FoGGIE. From the Physiology Department, University of Edinburgh. (Received
In uence of the CB 1 receptor antagonist, AM 251, on the regional haemodynamic e ects of WIN or HU 210 in conscious rats
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2002) 136, 581 ± 587 ã 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/bjp In uence of the CB 1 receptor antagonist, AM 251, on the
British Journal of Pharmacology (2002) 136, 581 ± 587 ã 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/bjp In uence of the CB 1 receptor antagonist, AM 251, on the
The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products
 Bulletin of saka University of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (2007) Brief Reviews *,a b c The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products Daisuke NAKAN, *, a Yoshinobu KIS, b Yasuo MATSUMURA c
Bulletin of saka University of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (2007) Brief Reviews *,a b c The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products Daisuke NAKAN, *, a Yoshinobu KIS, b Yasuo MATSUMURA c
Antinociception and the New COX Inhibitors: Research Approaches and Clinical Perspectives
 CNS Drug Reviews Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 227 252 2003 Neva Press, Branford, Connecticut Antinociception and the New COX Inhibitors: Research Approaches and Clinical Perspectives Juan F. Herrero, E. Alfonso
CNS Drug Reviews Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 227 252 2003 Neva Press, Branford, Connecticut Antinociception and the New COX Inhibitors: Research Approaches and Clinical Perspectives Juan F. Herrero, E. Alfonso
The role of angiotensin II (AngII) in maintaining
 AJH 1999;12:705 715 Chronic Captopril Administration Decreases Vasodilator Responses in Skeletal Muscle Arterioles Jefferson C. Frisbee, David S. Weber, and Julian H. Lombard Changes in arteriolar reactivity
AJH 1999;12:705 715 Chronic Captopril Administration Decreases Vasodilator Responses in Skeletal Muscle Arterioles Jefferson C. Frisbee, David S. Weber, and Julian H. Lombard Changes in arteriolar reactivity
Endothelium-dependent vasodilator effects of platelet activating factor on rat resistance vessels
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1989), 98, 136-1364 Endothelium-dependent vasodilator effects of platelet activating factor on rat resistance vessels 'Katsuo Kamata, Tatsuya Mori, *Koki Shigenobu & Yutaka Kasuya Department
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1989), 98, 136-1364 Endothelium-dependent vasodilator effects of platelet activating factor on rat resistance vessels 'Katsuo Kamata, Tatsuya Mori, *Koki Shigenobu & Yutaka Kasuya Department
Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l)
 A 18 16 14 1 8 6 4 Vehicle BCTC (.8 mmol/l) Sensory deafferentation Time (min) Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l) N=3 4 * P
A 18 16 14 1 8 6 4 Vehicle BCTC (.8 mmol/l) Sensory deafferentation Time (min) Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l) N=3 4 * P
Effects of Aging and Hypertension on Endothelium-Dependent Vascular Relaxation in Rat Carotid Artery
 892 Effects of Aging and Hypertension on Endothelium-Dependent Vascular Relaxation in Rat Carotid Artery Kazuhiro Hongo, MD, Tadayoshi Nakagomi, MD, Neal F. Kassell, MD, Tomio Sasaki, MD, Michael Lehman,
892 Effects of Aging and Hypertension on Endothelium-Dependent Vascular Relaxation in Rat Carotid Artery Kazuhiro Hongo, MD, Tadayoshi Nakagomi, MD, Neal F. Kassell, MD, Tomio Sasaki, MD, Michael Lehman,
Calcium-dependent mechanisms mediate the vasorelaxant effects of Tridax procumbens
 DOI 1.1515/jbcpp-213-3 J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 214; 25(2): 161 166 Hussein M. Salahdeen, Gbolahan O. Idowu, Omoniyi K. Yemitan, Babatunde A. Murtala and Abdul-Rasak A. Alada Calcium-dependent mechanisms
DOI 1.1515/jbcpp-213-3 J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 214; 25(2): 161 166 Hussein M. Salahdeen, Gbolahan O. Idowu, Omoniyi K. Yemitan, Babatunde A. Murtala and Abdul-Rasak A. Alada Calcium-dependent mechanisms
Diphasic Effects of Astragalus membranaceus BUNGE (Leguminosae) on Vascular Tone in Rat Thoracic Aorta
 1450 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28(8) 1450 1454 (2005) Vol. 28, No. 8 Diphasic Effects of Astragalus membranaceus BUNGE (Leguminosae) on Vascular Tone in Rat Thoracic Aorta Bi-Qi ZHANG, a Shen-Jiang HU,*,a,d Li-Hong
1450 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28(8) 1450 1454 (2005) Vol. 28, No. 8 Diphasic Effects of Astragalus membranaceus BUNGE (Leguminosae) on Vascular Tone in Rat Thoracic Aorta Bi-Qi ZHANG, a Shen-Jiang HU,*,a,d Li-Hong
E ects of the soluble guanylyl cyclase activator, YC-1, on vascular tone, cyclic GMP levels and phosphodiesterase activity
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 127, 195 ± 203 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp E ects of the soluble guanylyl cyclase activator,
British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 127, 195 ± 203 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp E ects of the soluble guanylyl cyclase activator,
Effect of ageing on ƒ 1A-adrenoceptor mechanisms in rabbit. Issei TAKAYANAGI, Mann MORIYA and Katsuo KOIKE
 J. Smooth Muscle Res. 28: 63-68, 1992. Effect of ageing on ƒ 1A-adrenoceptor mechanisms in rabbit isolated bronchial preparations Issei TAKAYANAGI, Mann MORIYA and Katsuo KOIKE Department of Chemical Pharmacology,
J. Smooth Muscle Res. 28: 63-68, 1992. Effect of ageing on ƒ 1A-adrenoceptor mechanisms in rabbit isolated bronchial preparations Issei TAKAYANAGI, Mann MORIYA and Katsuo KOIKE Department of Chemical Pharmacology,
Interrelationship between Angiotensin Catecholamines. Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D.
 Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
Critical dependence of the NO-mediated component of cyclic AMP-induced vasorelaxation on extracellular L-arginine in pulmonary arteries of the rat
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2000) 130, 997 ± 1004 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp Critical dependence of the NO-mediated component of cyclic
British Journal of Pharmacology (2000) 130, 997 ± 1004 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp Critical dependence of the NO-mediated component of cyclic
Role of Endothelial Nitric Oxide in Shear Stress Induced Vasodilation of Human Microvasculature
 Role of Endothelial Nitric Oxide in Shear Stress Induced Vasodilation of Human Microvasculature Diminished Activity in Hypertensive and Hypercholesterolemic Patients Oscar A. Paniagua, MD; Melissa B. Bryant,
Role of Endothelial Nitric Oxide in Shear Stress Induced Vasodilation of Human Microvasculature Diminished Activity in Hypertensive and Hypercholesterolemic Patients Oscar A. Paniagua, MD; Melissa B. Bryant,
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
ambrisentan, bosentan, BQ788, endothelin-1, ET A receptors, ET B receptor-mediated clearance mechanism, ET B receptors, macitentan, sarafotoxin S6c
 Received: 9 October 2017 Accepted: 23 October 2017 DOI: 10.1002/prp2.374 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distortion of K B estimates of endothelin-1 ET A and ET B receptor antagonists in pulmonary arteries: Possible
Received: 9 October 2017 Accepted: 23 October 2017 DOI: 10.1002/prp2.374 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distortion of K B estimates of endothelin-1 ET A and ET B receptor antagonists in pulmonary arteries: Possible
Chapter V. Evaluation of the Effects of d-fenfluramine on the Cutaneous Vasculature and Total Metabolic Heat Production
 Chapter V. Evaluation of the Effects of d-fenfluramine on the Cutaneous Vasculature and Total Metabolic Heat Production Experiments presented in this chapter were designed to investigate the possible mechanisms
Chapter V. Evaluation of the Effects of d-fenfluramine on the Cutaneous Vasculature and Total Metabolic Heat Production Experiments presented in this chapter were designed to investigate the possible mechanisms
Gastrointestinal Safety and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Hydrogen Sulfide Releasing Diclofenac Derivative in the Rat
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2007;132:261 271 Gastrointestinal Safety and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Hydrogen Sulfide Releasing Diclofenac Derivative in the Rat JOHN L. WALLACE,* GIUSEPPE CALIENDO, VINCENZO SANTAGADA,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2007;132:261 271 Gastrointestinal Safety and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Hydrogen Sulfide Releasing Diclofenac Derivative in the Rat JOHN L. WALLACE,* GIUSEPPE CALIENDO, VINCENZO SANTAGADA,
Endothelial function is preserved in pregnant women with well-controlled type 1 diabetes
 BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology June 2002, Vol. 109, pp. 699 707 Endothelial function is preserved in pregnant women with well-controlled type 1 diabetes Christine Ang a, Chris
BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology June 2002, Vol. 109, pp. 699 707 Endothelial function is preserved in pregnant women with well-controlled type 1 diabetes Christine Ang a, Chris
Novel role for P2X receptor activation in endothelium-dependent vasodilation
 British Journal of Pharmacology (24) 143, 611 617 & 24 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/4 $3. www.nature.com/bjp Novel role for P2X receptor activation in endothelium-dependent vasodilation
British Journal of Pharmacology (24) 143, 611 617 & 24 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/4 $3. www.nature.com/bjp Novel role for P2X receptor activation in endothelium-dependent vasodilation
A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: INCREASED MAXIMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATIVE NORADREN- ALINE IN THE ISOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 171-176. A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: NCREASED MAXMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATVE NORADREN- ALNE N THE SOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS BY A. BARNETT, D. D. GREENHOUSE AND R..
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 171-176. A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: NCREASED MAXMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATVE NORADREN- ALNE N THE SOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS BY A. BARNETT, D. D. GREENHOUSE AND R..
Augmentation of Cysteamine and Mepirizole-Induced Lesions in the Rat Duodenum and Stomach by Histamine or Indomethacin
 Augmentation of Cysteamine and Mepirizole-Induced Lesions in the Rat Duodenum and Stomach by Histamine or Indomethacin Hironori TANAKA, Yoshimi KUWAHARA and Susumu OKABE Department of Applied Pharmacology,
Augmentation of Cysteamine and Mepirizole-Induced Lesions in the Rat Duodenum and Stomach by Histamine or Indomethacin Hironori TANAKA, Yoshimi KUWAHARA and Susumu OKABE Department of Applied Pharmacology,
The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science
 Advance Publication The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science Accepted Date: Nov 0 J-STAGE Advance Published Date: Nov 0 FULL PAPER Pharmacology Eukaryotic elongation factor kinase inhibitor, A inhibits
Advance Publication The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science Accepted Date: Nov 0 J-STAGE Advance Published Date: Nov 0 FULL PAPER Pharmacology Eukaryotic elongation factor kinase inhibitor, A inhibits
Cardiovascular System. Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
British Journal of Pharmacology (2002) 137, 1031 ± 1038 ã 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/02 $25.00
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2002) 137, 1031 ± 1038 ã 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/bjp E ects of non-steroidal anti-in ammatory drugs on cyclooxygenase
British Journal of Pharmacology (2002) 137, 1031 ± 1038 ã 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/bjp E ects of non-steroidal anti-in ammatory drugs on cyclooxygenase
Multiple factors contributing to lipopolysaccharide-induced reactivity changes in rabbit pulmonary artery
 Acta Physiologica Sinica, December 25, 2005, 57 (6): 737-741 http://www.actaps.com.cn 737 Research Paper Multiple factors contributing to lipopolysaccharide-induced reactivity changes in rabbit pulmonary
Acta Physiologica Sinica, December 25, 2005, 57 (6): 737-741 http://www.actaps.com.cn 737 Research Paper Multiple factors contributing to lipopolysaccharide-induced reactivity changes in rabbit pulmonary
THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS
 Br. J. Phannac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 531-536. THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS BY A. L. BARTLET AND T. HASSAN From the Department of Veterinary
Br. J. Phannac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 531-536. THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS BY A. L. BARTLET AND T. HASSAN From the Department of Veterinary
Coronary Circulation Under normal conditions cardiac muscle metabolism is almost exclusively aerobic depending on oxidative phosorylation to
 Coronary Circulation Under normal conditions cardiac muscle metabolism is almost exclusively aerobic depending on oxidative phosorylation to resynthesis the ATP continuously utilized by repetitive, excitation,
Coronary Circulation Under normal conditions cardiac muscle metabolism is almost exclusively aerobic depending on oxidative phosorylation to resynthesis the ATP continuously utilized by repetitive, excitation,
vascular smooth muscle and platelet aggregation
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1989), 98, 1275-1280 Interactions of iloprost and sodium nitroprusside on vascular smooth muscle and platelet aggregation 1 Paul S. Lidbury, 2Edson Antunes, 2Gilberto de Nucci & John
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1989), 98, 1275-1280 Interactions of iloprost and sodium nitroprusside on vascular smooth muscle and platelet aggregation 1 Paul S. Lidbury, 2Edson Antunes, 2Gilberto de Nucci & John
Different Effects of Verapamil on Cytosolic Ca 2+ and Contraction in Norepinephrine-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle
 Japan. J. Pharmacol. 55, 35-42 (1991) Different Effects of Verapamil on Cytosolic Ca 2+ and Contraction in Norepinephrine-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Hideaki Karaki, Koichi Sato and Hiroshi Ozaki
Japan. J. Pharmacol. 55, 35-42 (1991) Different Effects of Verapamil on Cytosolic Ca 2+ and Contraction in Norepinephrine-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Hideaki Karaki, Koichi Sato and Hiroshi Ozaki
The Role of Massage in Blood Circulation, Pain Relief, and the Recovery Process: Implications of Existing Research
 The Role of Massage in Blood Circulation, Pain Relief, and the Recovery Process: Implications of Existing Research I. Basic Physiology of Circulation A. The Vascular Endothelium The endothelium is a complex
The Role of Massage in Blood Circulation, Pain Relief, and the Recovery Process: Implications of Existing Research I. Basic Physiology of Circulation A. The Vascular Endothelium The endothelium is a complex
Ex vivo Reactivity of the Ovarian Vascular Bed to Noradrenaline and Carbachol during Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
 Original Paper Med Princ Pract 2004;13:115 121 DOI: 10.1159/000076948 Received: November 20, 2002 Revised: February 22, 2003 Ex vivo Reactivity of the Ovarian Vascular Bed to Noradrenaline and Carbachol
Original Paper Med Princ Pract 2004;13:115 121 DOI: 10.1159/000076948 Received: November 20, 2002 Revised: February 22, 2003 Ex vivo Reactivity of the Ovarian Vascular Bed to Noradrenaline and Carbachol
Classification of tachykinin receptors in muscularis mucosae of opossum oesophagus
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1989), 97, 1013-1018 Classification of tachykinin receptors in muscularis mucosae of opossum oesophagus 'E.E. Daniel, S. Cipris, Y. Manaka, P. Bowker & *D. Regoli Smooth Muscle Program,
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1989), 97, 1013-1018 Classification of tachykinin receptors in muscularis mucosae of opossum oesophagus 'E.E. Daniel, S. Cipris, Y. Manaka, P. Bowker & *D. Regoli Smooth Muscle Program,
Modulation of synovial blood ow by the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist, CGRP (8 ± 37)
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1997) 121, 175 ± 18 1997 Stockton Press All rights reserved 7 ± 1188/97 $12. Modulation of synovial blood ow by the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist,
British Journal of Pharmacology (1997) 121, 175 ± 18 1997 Stockton Press All rights reserved 7 ± 1188/97 $12. Modulation of synovial blood ow by the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist,
Lecture 1 and 2 ONE. Definitions. Pharmacology: the study of the interaction of drugs within living systems
 Lecture 1 and 2 ONE 1. Explain what pharmacology encompasses and how it relates to other disciplines 2. Discuss the types of drug target and the factors that influence the binding of drugs to these targets
Lecture 1 and 2 ONE 1. Explain what pharmacology encompasses and how it relates to other disciplines 2. Discuss the types of drug target and the factors that influence the binding of drugs to these targets
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators
 Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Effects of indomethacin, piroxicam and selected prostanoids on gastric acid secretion by the rat isolated gastric mucosa
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1985), 86, 677-684 Effects of indomethacin, piroxicam and selected prostanoids on gastric acid secretion by the rat isolated gastric mucosa J.J. Reeves & R. Stables Department of Neuropharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1985), 86, 677-684 Effects of indomethacin, piroxicam and selected prostanoids on gastric acid secretion by the rat isolated gastric mucosa J.J. Reeves & R. Stables Department of Neuropharmacology,
PDGF-BB decreases systolic blood pressure through an increase in macrovascular compliance in rats
 PDGF-BB decreases systolic blood pressure through an increase in macrovascular compliance in rats MASAHIRO IKEDA, 1 CHIZURU MORITA, 1 MAKOTO MIZUNO, 1 TOSHIO SADA, 1 HIROYUKI KOIKE, 1 AND KIYOSHI KUROKAWA
PDGF-BB decreases systolic blood pressure through an increase in macrovascular compliance in rats MASAHIRO IKEDA, 1 CHIZURU MORITA, 1 MAKOTO MIZUNO, 1 TOSHIO SADA, 1 HIROYUKI KOIKE, 1 AND KIYOSHI KUROKAWA
Chapter 15: The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 15: The Cardiovascular System McArdle, W. D., Katch, F. I., & Katch, V. L. (2010). Exercise Physiology: Nutrition, Energy, and Human Performance (7 ed.). Baltimore, MD.: Lippincott Williams and
Chapter 15: The Cardiovascular System McArdle, W. D., Katch, F. I., & Katch, V. L. (2010). Exercise Physiology: Nutrition, Energy, and Human Performance (7 ed.). Baltimore, MD.: Lippincott Williams and
SPECIAL REPORT Anandamide activates peripheral nociceptors in normal and arthritic rat knee joints
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2001) 132, 617 ± 621 ã 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/01 $15.00 SPECIAL REPORT Anandamide activates peripheral nociceptors in normal and arthritic
British Journal of Pharmacology (2001) 132, 617 ± 621 ã 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/01 $15.00 SPECIAL REPORT Anandamide activates peripheral nociceptors in normal and arthritic
Inhibition of neuronal M 2 muscarinic receptor function in the lungs by extracellular nitric oxide
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2000) 131, 312 ± 318 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp Inhibition of neuronal M 2 muscarinic receptor function
British Journal of Pharmacology (2000) 131, 312 ± 318 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp Inhibition of neuronal M 2 muscarinic receptor function
Endothelium-Dependent Responses in Small Human Mesenteric Arteries
 Physiol. Res. 53: 255-263, 2004 Endothelium-Dependent Responses in Small Human Mesenteric Arteries A. TØTTRUP, K. KRAGLUND Department of Surgery L, University Hospital of Aarhus, Amtssygehuset, Aarhus,
Physiol. Res. 53: 255-263, 2004 Endothelium-Dependent Responses in Small Human Mesenteric Arteries A. TØTTRUP, K. KRAGLUND Department of Surgery L, University Hospital of Aarhus, Amtssygehuset, Aarhus,
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
 2. MATERIALS AND METHODS 2.1 Materials [ 3 H]-Digoxin (37Ci/mmol) was purchased from Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences Inc. (Boston, USA) and [U- 14 C]-Sucrose (660mCi/mmol) was purchased from Amersham Bioscience
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS 2.1 Materials [ 3 H]-Digoxin (37Ci/mmol) was purchased from Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences Inc. (Boston, USA) and [U- 14 C]-Sucrose (660mCi/mmol) was purchased from Amersham Bioscience
NSAIDs: Side Effects and Guidelines
 NSAIDs: Side Effects and James J Hale FY1 Department of Anaesthetics Introduction The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a diverse group of drugs that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory
NSAIDs: Side Effects and James J Hale FY1 Department of Anaesthetics Introduction The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a diverse group of drugs that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory
Evidence that di erent mechanisms underlie smooth muscle relaxation to nitric oxide and nitric oxide donors in the rabbit isolated carotid artery
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1998) 123 1351 ± 1358 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 7 ± 1188/98 $12. Evidence that di erent mechanisms underlie smooth muscle relaxation to nitric oxide and nitric
British Journal of Pharmacology (1998) 123 1351 ± 1358 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 7 ± 1188/98 $12. Evidence that di erent mechanisms underlie smooth muscle relaxation to nitric oxide and nitric
ulcer healing role 118 Bicarbonate, prostaglandins in duodenal cytoprotection 235, 236
 Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
