Multiple factors contributing to lipopolysaccharide-induced reactivity changes in rabbit pulmonary artery
|
|
|
- Arnold Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Physiologica Sinica, December 25, 2005, 57 (6): Research Paper Multiple factors contributing to lipopolysaccharide-induced reactivity changes in rabbit pulmonary artery HUANG Xin-Li, LING Yi-Qun, ZHU Tie-Nian, ZHANG Jun-Lan, LING Yi-Ling * Department of Pathophysiology, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang , China Abstract: To explore the underlying mechanism(s) of pulmonary arterial hypertension in endotoxic shock, the roles of N-acetylcysteine (NAC), nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide (CO) were investigated. Pulmonary arterial rings (3-mm width) were prepared from 24 rabbits. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), after 7- hour incubation, decreased the endothelium-dependent relaxation response of the arterial ring (pre-contracted with phenylephrine) to acetylcholine (1 µmol/l), but did not affect the endothelium-independent relaxation response to sodium nitroprusside. The LPS effects were reduced by a concomitant incubation with the free radical scavenger (NAC), NO donor (L-arginine), and CO donor (hemin), respectively. On the other hand, the LPS effects were enhanced by applying heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) inhibitor (zinc protoporphyrin) to block CO production. The response to acetylcholine changed from relaxation to contraction, however, the contractile response to phenylephrine increased significantly after pre-incubation with nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor (L-NAME) to block NO production, confirming the importance of CO and NO. These results show that LPS impairs endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pulmonary artery, which can be greatly reduced by the antioxidant, or by supplying with NO and CO. Thus, multiple factors are involved in this model of endotoxin-induced pulmonary hypertension. Key words: N-acetylcysteine; lipopolysaccharide; nitric oxide; carbon monoxide; pulmonary artery * N- (N-acetylcysteine, NAC) NO CO (lipopolysaccharide LPS) 24 3 mm LPS 7 h 1 µmol/l (NAC) L- (NO ) (CO ) LPS -1(heme oxygenase-1, HO-1) CO LPS N- -L- (L-NAME ) NO 1 µmol/l NO CO NO CO LPS N - Q954.6; R363.2 Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a main component of Gramnegative bacterial endotoxin [1], is the leading cause of endotoxic shock. The early stage of endotoxic shock is characterized by systemic hypotension and pulmonary arterial hypertension, and further, the degree and duration of pulmonary arterial hypertension may contribute to the acute Received Accepted * Corresponding author. Tel: ; lingyiling@ tom.com
2 738 lung injury during endotoxic shock [2]. Overproduction of endothelial nitric oxide (NO) has been identified to play an important role in the increased pulmonary artery pressure [3, 4]. In vivo study indicated that LPS could increase inducible nitric oxide synthase (inos) at mrna and protein level [5], however, its role in pulmonary arterial hypertension has not been fully understood. Heme oxygenase (HO) catalyzes the oxidation of heme to carbon monoxide (CO) and biliverdin, which is then converted to bilirubin by biliverdin reductase. So far three isoforms of HO have been identified: the inducible HO-1, 2 and 3 [6]. And study revealed that HO-1 was a NO/cGMPsensitive endothelial gene and CO released by HO-1 conferred protection against vasoconstriction induced by hypoxia [7]. In addition, N-acetylcysteine (NAC) treatment has been shown to ameliorate structural lung damage by reducing pulmonary vascular resistance in endotoxin-exposed rats [8], but its role in the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension induced by LPS has not been well understood. In the present study, we hypotheses that NAC, NO and CO are all involved in the pathologenesis of pulmonary hypertension induced by endotoxin. 1 MATERIALS AND METHODS 1.1 Animals and tissues Adult male New Zealand white rabbits (2.0~3.0 kg) were sacrificed, and the pulmonary arteries were rapidly isolated as described before [9]. In brief, the pulmonary arteries were placed in 4 o C modified Krebs solution containing (in mmol/l) NaCl 118, KCl 4.7, CaCl 2 2.5, MgSO 4 1.2, KH 2 PO 4 1.2, NaHCO 3 25, and glucose 11.1 (ph 7.2~7.4). Once cleaned of adventitia, the pulmonary artery was cut into 3-mm width rings. Care was taken during this process to avoid endothelial injury. Then pulmonary arterial rings were maintained in RPMI-1640 medium (GibcoBRL) supplemented with 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin and were randomly divided into four groups incubated at 37 o C with different agents in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO 2. Pulmonary artery rings were divided into four groups at random: Vehicle group (medium containing saline as vehicle), LPS group (medium containing 4 µg/ml LPS, LPS+NAC group (medium containing 4 µg/ml LPS and 0.5 mmol/l NAC) and NAC group (medium containing 0.5 mmol/l NAC). After being incubated for 7 h, each ring was threaded between two stainless steel parallel hooks and suspended in tissue bath (37 o C) filled with 6 ml Krebs solution for the measurement of isometric Acta Physiologica Sinica, December 25, 2005, 57 (6): tension. The top hook was connected to an isometric forcedisplacement transducer, and the bottom hook was anchored to an immovable support. Tissue baths were continuously bubbled with 95% O 2 and 5% CO 2. Artery rings from 4 to 6 rabbits were studied in each group. Rings were stretched to resting tension of 4.0 g and allowed to equilibrate for 1 h, during which time Krebs solution was changed every 15 min before experiment. The experiments were conducted after the rings were rinsed with Krebs solution and the tension returned to the baseline. 1.2 Experiment protocols Demonstration of vasoreactive changes to acetylcholine and phenylephrine After equilibration, endothelium-intact rings from all groups were challenged with 1 µmol/l α 1 -adrenocepter agonist phenylephrine. At the peak of contraction, the endothelium-dependent relaxation response to 1 µmol/l acetylcholine (ACh) and the endothelium-independent relaxation response to 1 µmol/l sodium nitroprusside were tested. Four to six rabbits (8~12 rings) were studied in all groups. Rings were rinsed with Krebs solution and returned to baseline tension, followed by the following experiment Role of NO in the vasoreactive changes To determine whether NO contributed to the decreased relaxant responsiveness induced by LPS, NO donor L- arginine (2 mmol/l), inos inhibitor aminoguanidine (0.1 mmol/l) and NOS inhibitor L-NAME (0.1 mmol/l) were added to the tissue bath respectively and then was repeated 15 min after every agent added Role of CO in the vasoreactive changes To determine the role of CO in the decreased relaxant responsiveness induced by LPS, CO donor hemin (0.02 mmol/l) and HO-1 inhibitor zinc protoporphyrin (0.01 mmol/l) were added to the tissue bath respectively and then was repeated 20 min after every agent added. 1.3 Drugs LPS (0111:B4), NAC, L-arginine, aminoguanidine, L- NAME, hemin, zinc protoporphyrin, sodium nitroprusside, acetylcholine and phenylephrine were purchased from Sigma. RPMI-1640 medium was purchased from GibcoBRL. All the other chemicals were purchased from Chinese Chemical Co. 1.4 Data analysis Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS software. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Relaxation is expressed as percentage of the active tension generated by phenylephrine. Statistical significance was obtained by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Newman-Keuls q test. P<0.05 was accepted to be statistically significant.
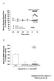
3 HUANG Xin-Li et al: Multiple Factors Contributing to LPS-induced Reactivity Changes in PA RESULTS 2.1 Effect of NAC on pulmonary artery exposed to LPS Pulmonary artery rings contraction in response to α 1 -adrenergic receptor phenylephrine (1 µmol/l) agonist was not impaired by in vitro LPS administration. In contrast, the endothelium-dependent relaxation response of pulmonary artery rings to 1 µmol/l ACh was significantly decreased by LPS, which, however, could be reversed by a concomitant exposure to NAC. NAC alone had no affection on the pulmonary artery vasoreactivity (Fig.1, 2). The endothelium-independent relaxation response of pulmonary artery to sodium nitroprusside was unaffected by LPS (data not shown). 2.2 Effect of L-arginine, aminoguanidine, L-NAME, hemin or zinc protoporphyrin on the vasoreactivity of pulmonary artery rings The endothelium-dependent relaxation response of pulmonary artery to acetylcholine can be totally or partially restored by L-arginine and hemin in the LPS group, and L- arginine and hemin had synergic effect. Neither the relaxation response to ACh nor the contractile response to phenylephrine was affected by aminoguanidine in each group. Pretreatment with L-NAME led to switch from the relaxation response to ACh to contractile response, and the contractile response to phenylephrine was significantly increased as well (Fig.3, 4). In LPS group, pretreatment with zinc protoporphyrin led to significantly decreased relaxation response to ACh and increased contraction response to phenylephrine (Fig. 5, 6). Fig. 1. Representative tracings showing tension of relaxation to acetylcholine in isolated rabbit pulmonary artery rings. Relaxation responses of pulmonary artery rings to acetylcholine after incubation with vehicle (A), LPS (B), NAC+ LPS (C) and NAC (D) for 7 h. W, wash with Krebs solution. 0, 1 µmol/l phenylephrine; 1, 1 µmol/l ACh. Fig. 3. Effect of L-Arg (L-arginine), AG (aminoguanidine) and L- NAME on endothelium-dependent relaxation responses of pulmonary artery rings to acetylcholine. n=8. * P<0.05 vs control, # P<0.01 vs AG. Fig. 2. Effect of NAC on LPS-induced decrease in the relaxation responses of pulmonary artery rings to ACh after incubation for 7 h. * P<0.05 vs vehicle, # P<0.05 vs LPS. Fig. 4. Effect of AG (aminoguanidine) and L-NAME on contraction responses of pulmonary artery rings to phenylephrine. n=6. * P< 0.05 vs control, # P<0.01 vs AG.
4 740 Fig. 5. Effect of hemin and ZnPP (zinc protoporphyrin) on endothelium-dependent relaxation responses of pulmonary artery rings to acetylcholine. n=8. * P<0.05 vs control, # P<0.01 vs hemin. Fig. 6. Effect of ZnPP (zinc protoporphyrin) on contraction responses of pulmonary artery rings to phenylephrine. n=6. * P<0.05 vs pre-znpp. 3 DISCUSSION Acta Physiologica Sinica, December 25, 2005, 57 (6): Previous studies showed that LPS injection in the rat resulted in a kind of acute lung injury characterized by lung neutrophile accumulation, edema, increase of pulmonary vascular resistance, and dysfunction of vasorelaxation to cgmp-mediated agonists [10,11]. Although early production of NO by endothelial NOS (enos) after LPS administration appears to play a protective role in acute lung injury, the later phase of endotoxemia or endotoxic shock results in the induction of inos in pulmonary artery, with subsequent production of NO and its cytotoxic derivative peroxynitrite [12,13]. Increase of pulmonary inos activity induced by LPS has been extensively studied, however, its role in the pulmonary circulation has not been well understood. In the present study, we found that pulmonary artery with LPS exposure had decreased endothelium-dependent relaxation response to ACh, however, the endothelium-independent relaxation response to sodium nitroprusside and vasoconstriction to phenylephrine were not significantly affected. The LPS effects could be reduced by a concomitant incubation with NO donor (Larginine). Neither the relaxation response nor the augment of contractile response was observed with aminoguanidine, the selective inos inhibitor in all groups. The response to ACh changed from relaxation to contraction, however, the contractile response to phenylephrine increased significantly after pre-incubation with NOS inhibitor (L-NAME) to block NO production. This finding was likely due to inhibition of enos, and confirmed the importance of endothelial-derived NO in maintaining a low basal tone in the pulmonary circulation. Although in our present experiment it seems that inos inhibitor aminoguanidine has no effect on the pulmonary artery vasomotor function during LPS exposure, it might be important to attenuate or even abrogate other aspects of acute lung injury [14]. Selective inos inhibition by either aminoguanidine or S-methylisothiourea can prevent the increase of lung inos activity and the reduction of lung vascular leak [15, 16] in animal models of LPS-induced acute lung injury. In addition, inos knockout mice has no significant changes in lung NOS activity, lactate dehydrogenase activity, lung wet/dry ratio, or pulmonary nitrotyrosine staining after LPS injection, indicating that inos deficiency mice in gene are more resistant to LPSinduced acute lung injury than wild-type mice [17]. These data suggest that the decreased relaxation response of pulmonary artery contributes to the development of pulmonary artery hypertension in endotoxic shock, and the reduced production of NO by enos might be critical. The discovery of endogenous gaseous messenger, CO, has been moving the research of pulmonary arterial hypertension induced by LPS to a very new phase. But the effect and significance of HO/CO on the development of pulmonary artery hypertension have not been fully understood. In this study, we observed that the decreased endothelium-dependent relaxation of pulmonary artery induced by LPS can be partially reversed by CO donor, and hemin and L-arginine showed synergistic effect. On the other hand, the LPS effects could be enhanced by HO-1 inhibitor (zinc protoporphyrin) through blocking the CO production. Our findings suggested an important protective function of HO-1/CO was as a vasorelaxant to supply the place of NO by enos whose function has been impaired by LPS in endotoxic shock. In addition, the free radical scavenger (NAC) could also reduce the LPS effects. In summary, these results show that LPS impairs endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pulmonary artery, which can be greatly reduced by the antioxidant, or by supplying with NO and CO. Thus, multiple factors are involved in this model of endotoxin-induced pulmonary hypertension.
5 HUANG Xin-Li et al: Multiple Factors Contributing to LPS-induced Reactivity Changes in PA 741 REFERENCES 1 Meng AH, Ling YL, Zhang XP, Zhang JL. Anti-inflammatory effect of cholecystokinin and its signal transduction mechanism in endotoxic shock rat. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8: Sheridan BC, McIntyre RC Jr, Moore EE, Meldrum DR, Agrafojo J, Fullerton DA. Neutrophils mediate pulmonary vasomotor dysfunction in endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. J Trauma 1997; 42: Pulido EJ, Shames BD, Fullerton DA, Sheridan BC, Selzman CH, Gamboni-Robertson F, Bensard DD, McIntyre RC Jr. Differential inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in systemic and pulmonary vessels after endotoxin. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2000; 278: Matsuda N, Hattori Y, Zhang XH, Fukui H, Kemmotsu O, Gando S. Contractions to histamine in pulmonary and mesenteric arteries from endotoxemic rabbits: modulation by vascular expressions of inducible nitric-oxide synthase and histamine H1- receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003; 307: Agorreta J, Garayoa M, Montuenga LM, Zulueta JJ. Effects of acute hypoxia and lipopolysaccharide on nitric oxide synthase-2 expression in acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003; 168: Wunder C, Potter RF. The heme oxygenase system: its role in liver inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord 2003; 3: Gonzales RJ, Walker BR. Role of CO in attenuated vasoconstrictor reactivity of mesenteric resistance arteries after chronic hypoxia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2002; 282: Rocksen D, Lilliehook B, Larsson R, Johansson T, Bucht A. Differential anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of dexamethasone and N-acetylcysteine in endotoxin-induced lung inflammation. Clin Exp Immunol 2000; 122: Meng AH ( ), Ling YL, Wang DH, Guo ZY, Li SJ, Zhu TN. Role of nitric oxide in cholecystokinin-octapeptide alleviation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced changes in rabbit pulmonary arterial reactivity. Acta Physiol Sin ( ) 2001; 53: (Chinese, English abstract). 10 Sheridan BC, McIntyre RC Jr, Meldrum DR, Fullerton DA. L- arginine prevents lung neutrophil accumulation and preserves pulmonary endothelial function after endotoxin. Am J Physiol 1998; 274: Sheridan BC, McIntyre RC, Meldrum DR, Meng X, Fullerton DA. Endotoxin stuns cgmp-mediated pulmonary vasorelaxation. Shock 1997; 8: Sheridan BC, McIntyre RC Jr, Meldrum DR, Fullerton DA. L- arginine attenuates endothelial dysfunction in endotoxin-induced lung injury. Surgery 1999; 125: Muzaffar S, Jeremy JY, Angelini GD, Stuart-Smith K, Shukla N. Role of the endothelium and nitric oxide synthases in modulating superoxide formation induced by endotoxin and cytokines in porcine pulmonary arteries. Thorax 2003; 58: Albertini M, Lafortuna CL, Clement MG, Mazzola S, Radice S, Hussain SN. Effect of NO synthase inhibition on cardiovascular and pulmonary dysfunction in a porcine short-term model of endotoxic shock. Prost Leuk Essent Fatty Acids 2002; 67: Evgenov OV, Hevroy O, Bremnes KE, Bjertnaes LJ. Effect of aminoguanidine on lung fluid filtration after endotoxin in awake sheep. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 162: Arkovitz MS, Wispe JR, Garcia VF, Szabo C. Selective inhibition of the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase prevents pulmonary transvascular flux during acute endotoxemia. J Pediatr Surg 1996; 31: Kristof AS, Goldberg P, Laubach V, Hussain SN. Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 158:
Melatonin improves vascular reactivity of endotoxemia rats
 Acta Physiologica Sinica, June 25, 2005, 57 (3): 367-372 http://www.actaps.com.cn 367, *,,,, 050017 (melatonin, MT) (lipopolysaccharide LPS) LPS LPS+MT MT (phenylephrine PE) (acetylcholine ACh) (malondialhyde
Acta Physiologica Sinica, June 25, 2005, 57 (3): 367-372 http://www.actaps.com.cn 367, *,,,, 050017 (melatonin, MT) (lipopolysaccharide LPS) LPS LPS+MT MT (phenylephrine PE) (acetylcholine ACh) (malondialhyde
Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate
 Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
This laboratory exercise uses a simple preparation and a straightforward
 LABORATORY DEMONSTRATION OF VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE FUNCTION USING RAT AORTIC RING SEGMENTS Rayna J. Gonzales, Rebecca W. Carter, and Nancy L. Kanagy Vascular Physiology Group, Department of Cell Biology
LABORATORY DEMONSTRATION OF VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE FUNCTION USING RAT AORTIC RING SEGMENTS Rayna J. Gonzales, Rebecca W. Carter, and Nancy L. Kanagy Vascular Physiology Group, Department of Cell Biology
Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats
 Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats Y. Zhu 1, H.-S. Wang 1, X.-M. Li 1 and C. Qu 2 1 Department of Cardiac Surgery, General
Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats Y. Zhu 1, H.-S. Wang 1, X.-M. Li 1 and C. Qu 2 1 Department of Cardiac Surgery, General
Vascular action of the hypoglycaemic agent gliclazide in diabetic rabbits
 Diabetologia (1998) 41: 9--15 Springer-Verlag 1998 Vascular action of the hypoglycaemic agent gliclazide in diabetic rabbits P. J. Pagano 1, M. C. Griswold 1, D. Ravel 2, R. A. Cohen 1 1 Vascular Biology
Diabetologia (1998) 41: 9--15 Springer-Verlag 1998 Vascular action of the hypoglycaemic agent gliclazide in diabetic rabbits P. J. Pagano 1, M. C. Griswold 1, D. Ravel 2, R. A. Cohen 1 1 Vascular Biology
The analysis on the expression of gasotransmitters in early trauma patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Wang Z et al. The analysis on the expression of gasotransmitters in early trauma patients Zhiyong Wang 1, Mignxing Fang 1, Jianying Guo 1, Yong Yang 1, Fengjun Tian 2 * 1 Department of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Wang Z et al. The analysis on the expression of gasotransmitters in early trauma patients Zhiyong Wang 1, Mignxing Fang 1, Jianying Guo 1, Yong Yang 1, Fengjun Tian 2 * 1 Department of
The Role of Massage in Blood Circulation, Pain Relief, and the Recovery Process: Implications of Existing Research
 The Role of Massage in Blood Circulation, Pain Relief, and the Recovery Process: Implications of Existing Research I. Basic Physiology of Circulation A. The Vascular Endothelium The endothelium is a complex
The Role of Massage in Blood Circulation, Pain Relief, and the Recovery Process: Implications of Existing Research I. Basic Physiology of Circulation A. The Vascular Endothelium The endothelium is a complex
PCTH 400. Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases. Blood vessel LAST LECTURE. Endothelium. High blood pressure
 PCTH 400 LAST LECTURE Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases. Classic Vascular pharmacology -chronic -systemic Local Vascular pharmacology -acute -targeted High blood pressure Blood pressure
PCTH 400 LAST LECTURE Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases. Classic Vascular pharmacology -chronic -systemic Local Vascular pharmacology -acute -targeted High blood pressure Blood pressure
Reversal by L-arginine of a dysfunctional arginine/nitric oxide pathway in the endothelium of the genetic diabetic BB rat
 Diabetologia (1997) : 91 915 Springer-Verlag 1997 Reversal by L-arginine of a dysfunctional arginine/nitric oxide pathway in the endothelium of the genetic diabetic BB rat G.M. Pieper, W. Siebeneich, G.
Diabetologia (1997) : 91 915 Springer-Verlag 1997 Reversal by L-arginine of a dysfunctional arginine/nitric oxide pathway in the endothelium of the genetic diabetic BB rat G.M. Pieper, W. Siebeneich, G.
Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats
 Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 27(December 12) 117 122 www.njps.com.ng Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats 1 Oloyo, Ahmed
Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 27(December 12) 117 122 www.njps.com.ng Differential responses to endothelial dependent relaxation of the thoracic and abdominal aorta from male Sprague-Dawley rats 1 Oloyo, Ahmed
Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous Herbal Supplement?
 Grand Valley State University ScholarWorks@GVSU Student Summer Scholars Undergraduate Research and Creative Practice 2010 Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous
Grand Valley State University ScholarWorks@GVSU Student Summer Scholars Undergraduate Research and Creative Practice 2010 Hawthorn Extract - Viable Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease or Unscrupulous
H 2 S: Synthesis and functions
 H 2 S: Synthesis and functions 1 Signaling gas molecules: O 2, NO and CO Then, H 2 S - Fourth singling gas molecule after O 2, NO and CO 2 Nothing Rotten About Hydrogen Sulfide s Medical Promise Science
H 2 S: Synthesis and functions 1 Signaling gas molecules: O 2, NO and CO Then, H 2 S - Fourth singling gas molecule after O 2, NO and CO 2 Nothing Rotten About Hydrogen Sulfide s Medical Promise Science
Supplemental Figure I
 Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) 30: 891-895 Perfused rat tail vascular bed ISSN 0100-879X 891 Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed A.S. França, L.V. Rossoni,
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) 30: 891-895 Perfused rat tail vascular bed ISSN 0100-879X 891 Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed A.S. França, L.V. Rossoni,
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) is a potent immunosuppressant (antiinflammatory
 Vascular Effects of Lipopolysaccharide Are Enhanced in Interleukin-10 Deficient Mice Carol A. Gunnett, PhD; Daniel J. Berg, MD; Frank M. Faraci, PhD Background and Purpose The role in blood vessels of
Vascular Effects of Lipopolysaccharide Are Enhanced in Interleukin-10 Deficient Mice Carol A. Gunnett, PhD; Daniel J. Berg, MD; Frank M. Faraci, PhD Background and Purpose The role in blood vessels of
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators
 Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats
 Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats Orachorn Boonla 1, Phattharaphon Tuangpolkrung 1, Poungrat Pakdeechote 1, Upa Kukongviriyapan
Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats Orachorn Boonla 1, Phattharaphon Tuangpolkrung 1, Poungrat Pakdeechote 1, Upa Kukongviriyapan
Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and. -independent mechanisms
 Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and -independent mechanisms Yang-Kai WANG 1 #, An-Jing REN 1 #, Xiang-Qun YANG 1, Li-Gang WANG 1, Wei-Fang RONG 3, Chao-Shu TANG 4, Wen-Jun YUAN
Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and -independent mechanisms Yang-Kai WANG 1 #, An-Jing REN 1 #, Xiang-Qun YANG 1, Li-Gang WANG 1, Wei-Fang RONG 3, Chao-Shu TANG 4, Wen-Jun YUAN
Cooling effects on nitric oxide production by rabbit ear and femoral arteries during cholinergic stimulation
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1994), 113, 55-554 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1994 Cooling effects on nitric oxide production by rabbit ear and femoral arteries during cholinergic stimulation N. Fernandez, L. Monge,
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1994), 113, 55-554 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1994 Cooling effects on nitric oxide production by rabbit ear and femoral arteries during cholinergic stimulation N. Fernandez, L. Monge,
In the name of GOD. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension
 In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
LOW-DOSE ASPIRIN AND CLOPIDOGREL ATTENUATE REFLEX CUTANEOUS VASODILATION IN MIDDLE AGED SKIN Lacy A. Holowatz, John Jennings, and W.
 Holowatz et al. 1 LOW-DOSE ASPIRIN AND CLOPIDOGREL ATTENUATE REFLEX CUTANEOUS VASODILATION IN MIDDLE AGED SKIN Lacy A. Holowatz, John Jennings, and W. Larry Kenney Department of Kinesiology and Graduate
Holowatz et al. 1 LOW-DOSE ASPIRIN AND CLOPIDOGREL ATTENUATE REFLEX CUTANEOUS VASODILATION IN MIDDLE AGED SKIN Lacy A. Holowatz, John Jennings, and W. Larry Kenney Department of Kinesiology and Graduate
ulcer healing role 118 Bicarbonate, prostaglandins in duodenal cytoprotection 235, 236
 Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
HIGH ALTITUDE PHYSIOLOGY AND PHYSIOPATHOLOGY, FROM THE ORGANISM TO THE MOLECULE - HAPPOM PREGNANGY AND HIGH ALTITUDE
 HIGH ALTITUDE PHYSIOLOGY AND PHYSIOPATHOLOGY, FROM THE ORGANISM TO THE MOLECULE - HAPPOM PREGNANGY AND HIGH ALTITUDE DR. ANÍBAL LLANOS FACULTAD DE MEDICINA, UNIVERSIDAD DE CHILE APRIL 18, 25 ATMOSPHERIC
HIGH ALTITUDE PHYSIOLOGY AND PHYSIOPATHOLOGY, FROM THE ORGANISM TO THE MOLECULE - HAPPOM PREGNANGY AND HIGH ALTITUDE DR. ANÍBAL LLANOS FACULTAD DE MEDICINA, UNIVERSIDAD DE CHILE APRIL 18, 25 ATMOSPHERIC
(NA) [112 ] ,, NA. Acta Physiologica Sinica imp/ s Tsinghua Tongfang Optical Disc Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
![(NA) [112 ] ,, NA. Acta Physiologica Sinica imp/ s Tsinghua Tongfang Optical Disc Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. (NA) [112 ] ,, NA. Acta Physiologica Sinica imp/ s Tsinghua Tongfang Optical Disc Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.](/thumbs/93/113818017.jpg) , 1999 8, 51 (4), 407 412 407 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 (, 050021) 30 2 (CSN), 39 (NA) : (1) (MTS), 19 0113 0106 0125 0112 imp/ s ( P < 01001) ; (2), 19 0114 0108 0123 0113 imp/ s ( P < 0101) ; (3) 4
, 1999 8, 51 (4), 407 412 407 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 (, 050021) 30 2 (CSN), 39 (NA) : (1) (MTS), 19 0113 0106 0125 0112 imp/ s ( P < 01001) ; (2), 19 0114 0108 0123 0113 imp/ s ( P < 0101) ; (3) 4
Differential Effects of Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors on Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction and Pulmonary Artery Cytokine Expression
 Differential Effects of Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors on Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction and Pulmonary Artery Cytokine Expression Ben M. Tsai, MD, Mark W. Turrentine, MD, Brett C. Sheridan, MD, Meijing
Differential Effects of Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors on Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction and Pulmonary Artery Cytokine Expression Ben M. Tsai, MD, Mark W. Turrentine, MD, Brett C. Sheridan, MD, Meijing
Potassium-Induced Release of Endothelium- Derived Relaxing Factor From Canine Femoral Arteries
 1098 Potassium-Induced Release of Endothelium- Derived Relaxing Factor From Canine Femoral Arteries Gabor M. Rubanyi and Paul M. Vanhoutte Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on January 13, 2019
1098 Potassium-Induced Release of Endothelium- Derived Relaxing Factor From Canine Femoral Arteries Gabor M. Rubanyi and Paul M. Vanhoutte Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on January 13, 2019
Magnesium is a key ionic modulator of blood vessel
 Hypomagnesemia Inhibits Nitric Oxide Release From Coronary Endothelium: Protective Role of Magnesium Infusion After Cardiac Operations Paul J. Pearson, MD, PhD, Paulo R. B. Evora, MD, PhD, John F. Seccombe,
Hypomagnesemia Inhibits Nitric Oxide Release From Coronary Endothelium: Protective Role of Magnesium Infusion After Cardiac Operations Paul J. Pearson, MD, PhD, Paulo R. B. Evora, MD, PhD, John F. Seccombe,
Prestretched airway smooth muscle response to length oscillation
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiological Reports ISSN 2051-817X Prestretched airway smooth muscle response to length oscillation Ahmed M. Al-Jumaily, Kevin Roos, Sandy Bessaguet & Miguel Jo Avila Institute of Biomedical
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiological Reports ISSN 2051-817X Prestretched airway smooth muscle response to length oscillation Ahmed M. Al-Jumaily, Kevin Roos, Sandy Bessaguet & Miguel Jo Avila Institute of Biomedical
, L2Arg NO. (ischemia reperfusion injury, IRI) (L2arginine/ nitric oxide, L2Arg/ NO) IRI g Wistar,, g/ kg) ip, Acta Physiologica Si nica
 , 1999 2, 51 (1), 25 30 25 Acta Physiologica Si nica L2Arg/ NO 1997212227 1998203230 3 3 (, 524023 ; 3, 100083) ( IRI) (NO), 15 min, 45 min, 30 ml KH 15 min, (LDH) NO2 - NOS L2 (L2Arg), IRI LDH 411, 514
, 1999 2, 51 (1), 25 30 25 Acta Physiologica Si nica L2Arg/ NO 1997212227 1998203230 3 3 (, 524023 ; 3, 100083) ( IRI) (NO), 15 min, 45 min, 30 ml KH 15 min, (LDH) NO2 - NOS L2 (L2Arg), IRI LDH 411, 514
Acta Physiologica Sinica
 , 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
, 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
A. HOLiiCYOVA, J. TOROK, I. BERNATOVA, O. PECHANOVA
 Physiol. Res. 45: 317-321, 1996 Restriction of Nitric Oxide Rather than Elevated Blood Pressure is Responsible for Alterations of Vascular Responses in Nitric Oxide-Deficient Hypertension A. HOLiiCYOVA,
Physiol. Res. 45: 317-321, 1996 Restriction of Nitric Oxide Rather than Elevated Blood Pressure is Responsible for Alterations of Vascular Responses in Nitric Oxide-Deficient Hypertension A. HOLiiCYOVA,
A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets
 Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Part-I: Screening. 3.1 Assessment of non-toxic concentration of test compounds in RAW cells. Results
 Part-I: Screening Our strategy was to look for compounds which can inhibit HMGB1 (high mobility group box 1) release in activated macrophages and check effect of screened compound on endotoxemic mice.
Part-I: Screening Our strategy was to look for compounds which can inhibit HMGB1 (high mobility group box 1) release in activated macrophages and check effect of screened compound on endotoxemic mice.
Calcium-dependent mechanisms mediate the vasorelaxant effects of Tridax procumbens
 DOI 1.1515/jbcpp-213-3 J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 214; 25(2): 161 166 Hussein M. Salahdeen, Gbolahan O. Idowu, Omoniyi K. Yemitan, Babatunde A. Murtala and Abdul-Rasak A. Alada Calcium-dependent mechanisms
DOI 1.1515/jbcpp-213-3 J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 214; 25(2): 161 166 Hussein M. Salahdeen, Gbolahan O. Idowu, Omoniyi K. Yemitan, Babatunde A. Murtala and Abdul-Rasak A. Alada Calcium-dependent mechanisms
Studies on the effects of viprostol in isolated small blood vessels and thoracic aorta of the rat
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1988), 93, 613-617 Studies on the effects of viprostol in isolated small blood vessels and thoracic aorta of the rat Fong M. Lai, Tarak Tanikella, Agnes Cobuzzi & Peter Cervoni Cardiovascular
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1988), 93, 613-617 Studies on the effects of viprostol in isolated small blood vessels and thoracic aorta of the rat Fong M. Lai, Tarak Tanikella, Agnes Cobuzzi & Peter Cervoni Cardiovascular
Systemic inflammation after myocardial infarction
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Systemic inflammation after myocardial infarction Rudiger, Alain DOI:
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Systemic inflammation after myocardial infarction Rudiger, Alain DOI:
hypoxic pulmonary hypertension
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1992), 17, 47-413 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1992 Reduced relaxant potency of nitroprusside on pulmonary artery preparations taken from rats during the development of hypoxic pulmonary
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1992), 17, 47-413 '." Macmillan Press Ltd, 1992 Reduced relaxant potency of nitroprusside on pulmonary artery preparations taken from rats during the development of hypoxic pulmonary
Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection. All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention. Infusates/ drugs. hub/lines Dressing
 Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention catheter hematogeneous Infusates/ drugs hub/lines Dressing skin Critically ill patient: 2-4 vascular
Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention catheter hematogeneous Infusates/ drugs hub/lines Dressing skin Critically ill patient: 2-4 vascular
The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber
 INVITED BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber Colleen M. Brophy, MD, Augusta, Ga BACKGROUND The flow of blood to organs is regulated by changes in the diameter of the blood
INVITED BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber Colleen M. Brophy, MD, Augusta, Ga BACKGROUND The flow of blood to organs is regulated by changes in the diameter of the blood
Pregnanolone effects on the blood pressure of stress-induced hypertension in rats
 Acta Physiologica Sinica August June 25 25 2004 2004 56 56 (3) (4) 269-274 471-475 http//www.actaps.com.cn 471 * 130021 (pregnanolone ) (stress-induced hypertension SIH) (0.24 mg/kg) (angiotensin Ang )
Acta Physiologica Sinica August June 25 25 2004 2004 56 56 (3) (4) 269-274 471-475 http//www.actaps.com.cn 471 * 130021 (pregnanolone ) (stress-induced hypertension SIH) (0.24 mg/kg) (angiotensin Ang )
Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy
 Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy J. Guan 1,2, L. Long 1, Y.-Q. Chen 1, Y. Yin 1, L. Li 1, C.-X. Zhang 1, L. Deng 1 and L.-H. Tian
Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy J. Guan 1,2, L. Long 1, Y.-Q. Chen 1, Y. Yin 1, L. Li 1, C.-X. Zhang 1, L. Deng 1 and L.-H. Tian
Interactions Between Gasotransmitters
 Gasotransmitter Interactions 33 2 Interactions Between Gasotransmitters Ray J. Carson, Gunter Seyffarth, Rubina Mian, and Helen Maddock CONTENTS INTRODUCTION COMPARISON OF CELLULAR EFFECTS OF NO, CO, AND
Gasotransmitter Interactions 33 2 Interactions Between Gasotransmitters Ray J. Carson, Gunter Seyffarth, Rubina Mian, and Helen Maddock CONTENTS INTRODUCTION COMPARISON OF CELLULAR EFFECTS OF NO, CO, AND
Effects of ascorbic acid on impaired vascular reactivity in aortas isolated from age-matched hypertensive and diabetic rats
 University of Malaya From the SelectedWorks of Mohd Rais Mustafa 2006 Effects of ascorbic acid on impaired vascular reactivity in aortas isolated from age-matched hypertensive and diabetic rats Mohd Rais
University of Malaya From the SelectedWorks of Mohd Rais Mustafa 2006 Effects of ascorbic acid on impaired vascular reactivity in aortas isolated from age-matched hypertensive and diabetic rats Mohd Rais
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
RAPID COMMUNICATION. Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension
 Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Modulation of vascular reactivity in normal, hypertensive and diabetic rat aortae by a non-antioxidant flavonoid
 Pharmacological Research 55 (2007) 385 391 Modulation of vascular reactivity in normal, hypertensive and diabetic rat aortae by a non-antioxidant flavonoid Machha Ajay a,,1, Francis I. Achike b, Mohd Rais
Pharmacological Research 55 (2007) 385 391 Modulation of vascular reactivity in normal, hypertensive and diabetic rat aortae by a non-antioxidant flavonoid Machha Ajay a,,1, Francis I. Achike b, Mohd Rais
Neue Wirkungsmechanismen von Transfusionsplasma
 Neue Wirkungsmechanismen von Transfusionsplasma Lorenzo ALBERIO Médecin chef Hématologie générale et Hémostase Service et Laboratoire centrale d Hématologie CHUV, Lausanne Trauma patient Bleeding Thrombosis
Neue Wirkungsmechanismen von Transfusionsplasma Lorenzo ALBERIO Médecin chef Hématologie générale et Hémostase Service et Laboratoire centrale d Hématologie CHUV, Lausanne Trauma patient Bleeding Thrombosis
Generation of Nitric Oxide in the Opossum Lower Esophageal Sphincter during Physiological Experimentation
 Yonsei Medical Journal Vol. 47, No. 2, pp. 223-229, 2006 Generation of Nitric Oxide in the Opossum Lower Esophageal Sphincter during Physiological Experimentation Se-Joon Lee, 1 Hyojin Park, 1 Jin Hyuck
Yonsei Medical Journal Vol. 47, No. 2, pp. 223-229, 2006 Generation of Nitric Oxide in the Opossum Lower Esophageal Sphincter during Physiological Experimentation Se-Joon Lee, 1 Hyojin Park, 1 Jin Hyuck
TITLE: Alcohol Intoxication Impact on Outcome from Traumatic Injury
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0236 TITLE: Alcohol Intoxication Impact on Outcome from Traumatic Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Patricia Molina, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Louisiana State University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0236 TITLE: Alcohol Intoxication Impact on Outcome from Traumatic Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Patricia Molina, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Louisiana State University
Intravenous Vitamin C. Severe Sepsis Acute Lung Injury
 Intravenous Vitamin C Severe Sepsis Acute Lung Injury Alpha A. (Berry) Fowler, III, MD Professor of Medicine VCU Pulmonary Disease and Critical Care Medicine I Have No Disclosures Bacterial Sepsis Approximately
Intravenous Vitamin C Severe Sepsis Acute Lung Injury Alpha A. (Berry) Fowler, III, MD Professor of Medicine VCU Pulmonary Disease and Critical Care Medicine I Have No Disclosures Bacterial Sepsis Approximately
We also tested the hypothesis that the inhibitory effects of etomidate and ketamine involved a decrease in
 Anesthesiology 2003; 98:104 13 2003 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Inhibitory Effects of Etomidate and Ketamine on Adenosine Triphosphate Sensitive Potassium
Anesthesiology 2003; 98:104 13 2003 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Inhibitory Effects of Etomidate and Ketamine on Adenosine Triphosphate Sensitive Potassium
Establishment of a rabbit model of coronary artery bypass graft and endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene transfection
 Establishment of a rabbit model of coronary artery bypass graft and endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene transfection Y. Zhu, H.-S. Wang, X.-M. Li and Z.-W. Wang Department of Cardiovascular Surgery,
Establishment of a rabbit model of coronary artery bypass graft and endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene transfection Y. Zhu, H.-S. Wang, X.-M. Li and Z.-W. Wang Department of Cardiovascular Surgery,
MMM. Topic The use of Tadalafil 5mg daily for the treatment of BPH-LUTS
 Dr Tan & Partners MMM Vol. 1 No. 1 Morbidity & Mortality Meeting 14 th November 2014 Introduction Topic The use of Tadalafil 5mg daily for the treatment of BPH-LUTS Tadalafil 5mg daily is a well established
Dr Tan & Partners MMM Vol. 1 No. 1 Morbidity & Mortality Meeting 14 th November 2014 Introduction Topic The use of Tadalafil 5mg daily for the treatment of BPH-LUTS Tadalafil 5mg daily is a well established
Endothelial Injury and Repair as a Working Paradigm
 Endothelial Injury and Repair as a Working Paradigm A. Linke ESC Meeting 2010 UNIVERSITÄTLEIPZIG H ERZZEN TRUM Physiology of Endothelial Function: Regulation of Vascular Tone L-Arg. L-Arg. Agonists Shear
Endothelial Injury and Repair as a Working Paradigm A. Linke ESC Meeting 2010 UNIVERSITÄTLEIPZIG H ERZZEN TRUM Physiology of Endothelial Function: Regulation of Vascular Tone L-Arg. L-Arg. Agonists Shear
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors potentiate subthreshold preconditioning through NO and mitok ATP. channel
 Acta Physiologica Sinica, August 25, 2005, 57 (4): 453-460 http://www.actaps.com.cn 453 ATP 1 1 1 2 2 2,* 1 313000 2 310006 Langendorff ( ) ( ) (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, ACEI) (nitric
Acta Physiologica Sinica, August 25, 2005, 57 (4): 453-460 http://www.actaps.com.cn 453 ATP 1 1 1 2 2 2,* 1 313000 2 310006 Langendorff ( ) ( ) (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, ACEI) (nitric
How does Exercise Work at the Cellular/Molecular Level
 How does Exercise Work at the Cellular/Molecular Level Volker Adams, PhD ESC, Paris 28. Aug. 211 UNIVERSITÄT LEIPZIG H E R Z Z E N T R U M Nothing to disclose Survival Exercise Training in Patients With
How does Exercise Work at the Cellular/Molecular Level Volker Adams, PhD ESC, Paris 28. Aug. 211 UNIVERSITÄT LEIPZIG H E R Z Z E N T R U M Nothing to disclose Survival Exercise Training in Patients With
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
The role of angiotensin II (AngII) in maintaining
 AJH 1999;12:705 715 Chronic Captopril Administration Decreases Vasodilator Responses in Skeletal Muscle Arterioles Jefferson C. Frisbee, David S. Weber, and Julian H. Lombard Changes in arteriolar reactivity
AJH 1999;12:705 715 Chronic Captopril Administration Decreases Vasodilator Responses in Skeletal Muscle Arterioles Jefferson C. Frisbee, David S. Weber, and Julian H. Lombard Changes in arteriolar reactivity
Effects of Total Alkaloids in Buxus microphylla Leaves on Aorta Smooth Muscle of Rats and Their Mechanisms
 136 Zhang HQ et al. Chinese Herbal Medicines, 212, 4(2): 136-141 Effects of Total Alkaloids in Buxus microphylla Leaves on Aorta Smooth Muscle of Rats and Their Mechanisms ZHANG Hui-qin 1, LIU Yan-yan
136 Zhang HQ et al. Chinese Herbal Medicines, 212, 4(2): 136-141 Effects of Total Alkaloids in Buxus microphylla Leaves on Aorta Smooth Muscle of Rats and Their Mechanisms ZHANG Hui-qin 1, LIU Yan-yan
PUBLICATIONS. cells. J. Physiol. (London) 517P:91P (Manchester, England, UK).
 277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
Histamine Develops Homologous Desensitization under Ca 2+ -free Conditions with Increase in Basal Tone in Smooth Muscle of Guinea Pig Taenia Caeci
 YAKUGAKU ZASSHI 130(3) 451 455 (2010) 2010 The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan 451 Notes Histamine Develops Homologous Desensitization under Ca 2+ -free Conditions with Increase in Basal Tone in Smooth
YAKUGAKU ZASSHI 130(3) 451 455 (2010) 2010 The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan 451 Notes Histamine Develops Homologous Desensitization under Ca 2+ -free Conditions with Increase in Basal Tone in Smooth
Research Article The Inhibition of Ureteral Motility by Periureteral Adipose Tissue
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Urology Volume, Article ID 37, 7 pages doi:1.5//37 Research Article The Inhibition of Ureteral Motility by Periureteral Adipose Tissue Lyndsey M. Killian and
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Urology Volume, Article ID 37, 7 pages doi:1.5//37 Research Article The Inhibition of Ureteral Motility by Periureteral Adipose Tissue Lyndsey M. Killian and
Lactate and force production in skeletal muscle
 J Physiol 562.2 (2005) pp 521 526 521 Lactate and force production in skeletal muscle Michael Kristensen, Janni Albertsen, Maria Rentsch and Carsten Juel Copenhagen Muscle Research Centre, University of
J Physiol 562.2 (2005) pp 521 526 521 Lactate and force production in skeletal muscle Michael Kristensen, Janni Albertsen, Maria Rentsch and Carsten Juel Copenhagen Muscle Research Centre, University of
Lipoteichoic Acid from Staphylococcus aweus Depresses Contractile Function of Human Arteries In Vitro Due to the Induction of Nitric Oxide Synthase
 Lipoteichoic Acid from Staphylococcus aweus Depresses Contractile Function of Human Arteries In Vitro Due to the Induction of Nitric Oxide Synthase Isao Tsuneyoshi, MD, Yuichi Kanmura, MD, PhD, and Nozomu
Lipoteichoic Acid from Staphylococcus aweus Depresses Contractile Function of Human Arteries In Vitro Due to the Induction of Nitric Oxide Synthase Isao Tsuneyoshi, MD, Yuichi Kanmura, MD, PhD, and Nozomu
The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products
 Bulletin of saka University of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (2007) Brief Reviews *,a b c The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products Daisuke NAKAN, *, a Yoshinobu KIS, b Yasuo MATSUMURA c
Bulletin of saka University of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (2007) Brief Reviews *,a b c The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products Daisuke NAKAN, *, a Yoshinobu KIS, b Yasuo MATSUMURA c
SILDENAFIL IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION TREATMENT: Effects in a chronic hypoxic newborn sheep. Emilio Herrera V. DMV, PhD
 HAPPOM - ALFA June 26, 2007 SILDENAFIL IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION TREATMENT: Effects in a chronic hypoxic newborn sheep. Emilio Herrera V. DMV, PhD Laboratorio de Fisiología y Fisiopatología del Desarrollo
HAPPOM - ALFA June 26, 2007 SILDENAFIL IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION TREATMENT: Effects in a chronic hypoxic newborn sheep. Emilio Herrera V. DMV, PhD Laboratorio de Fisiología y Fisiopatología del Desarrollo
Relaxant Effects of Matrine on Aortic Smooth Muscles of Guinea Pigs 1
 BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 22, 327-332 (2009) www.besjournal.com Relaxant Effects of Matrine on Aortic Smooth Muscles of Guinea Pigs 1 JIE ZHENG #, PING ZHENG #, XU ZHOU *, LIN YAN #, RU ZHOU
BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 22, 327-332 (2009) www.besjournal.com Relaxant Effects of Matrine on Aortic Smooth Muscles of Guinea Pigs 1 JIE ZHENG #, PING ZHENG #, XU ZHOU *, LIN YAN #, RU ZHOU
Role of Nitric Oxide in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension
 PHYSIOLOGICAL REVIEWS Vol. 80, No. 4, October 2000 Printed in U.S.A. Role of Nitric Oxide in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension VÁCLAV HAMPL AND JAN HERGET Department of Physiology, Charles
PHYSIOLOGICAL REVIEWS Vol. 80, No. 4, October 2000 Printed in U.S.A. Role of Nitric Oxide in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension VÁCLAV HAMPL AND JAN HERGET Department of Physiology, Charles
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period January 1, 2012 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period January 1, 2012 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine
Correlations among copeptin, ischemia-modified albumin, and the extent of myocardial injury in patients with acute carbon monoxide poisoning
 Correlations among copeptin, ischemia-modified albumin, and the extent of myocardial injury in patients with acute carbon monoxide poisoning J. Li, J.S. Wang, Z.X. Xie, W.Z. Wang, L. Wang, G.Y. Ma, Y.Q.
Correlations among copeptin, ischemia-modified albumin, and the extent of myocardial injury in patients with acute carbon monoxide poisoning J. Li, J.S. Wang, Z.X. Xie, W.Z. Wang, L. Wang, G.Y. Ma, Y.Q.
Brief Definitive Communications
 88 Brief Definitive Communications Negative Feedback Regulation of Endothelial Cell Function by Nitric Oxide Georgette M. Buga, Jeanette M. Griscavage, Norma E. Rogers, Louis J. Ignarro The objective of
88 Brief Definitive Communications Negative Feedback Regulation of Endothelial Cell Function by Nitric Oxide Georgette M. Buga, Jeanette M. Griscavage, Norma E. Rogers, Louis J. Ignarro The objective of
Mol Biotechnol Sep;37(1):31-7. Bioenergetic and antioxidant properties of coenzyme Q10: recent developments. Littarru GP, Tiano L.
 Mol Biotechnol. 2007 Sep;37(1):31-7. Bioenergetic and antioxidant properties of coenzyme Q10: recent developments. Littarru GP, Tiano L. Source : Institute of Biochemistry, Polytechnic University of the
Mol Biotechnol. 2007 Sep;37(1):31-7. Bioenergetic and antioxidant properties of coenzyme Q10: recent developments. Littarru GP, Tiano L. Source : Institute of Biochemistry, Polytechnic University of the
Effects of Resveratrol on Ileal Smooth Muscle Reactivity in Polymicrobial Sepsis Model
 Journal of Surgical Research 174, 339 343 (212) doi:1.116/j.jss.21.12.15 Effects of Resveratrol on Ileal Smooth Muscle Reactivity in Polymicrobial Sepsis Model Nejat Gacar, Ph.D., Selcen Gocmez, Ph.D.,
Journal of Surgical Research 174, 339 343 (212) doi:1.116/j.jss.21.12.15 Effects of Resveratrol on Ileal Smooth Muscle Reactivity in Polymicrobial Sepsis Model Nejat Gacar, Ph.D., Selcen Gocmez, Ph.D.,
Buffering a Permissive Hypercapnia The Evidence
 Buffering a Permissive Hypercapnia The Evidence John Laffey Department of Anesthesia, St Michael s Hospital, University of Toronto, CANADA Disclosures Funding European Research Council [FP-7] Health Research
Buffering a Permissive Hypercapnia The Evidence John Laffey Department of Anesthesia, St Michael s Hospital, University of Toronto, CANADA Disclosures Funding European Research Council [FP-7] Health Research
Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l)
 A 18 16 14 1 8 6 4 Vehicle BCTC (.8 mmol/l) Sensory deafferentation Time (min) Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l) N=3 4 * P
A 18 16 14 1 8 6 4 Vehicle BCTC (.8 mmol/l) Sensory deafferentation Time (min) Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l) N=3 4 * P
The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function in vitro
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 811-818 L-arginine on airway smooth muscle ISSN -879X 811 The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 811-818 L-arginine on airway smooth muscle ISSN -879X 811 The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Role of Endothelial Nitric Oxide in Shear Stress Induced Vasodilation of Human Microvasculature
 Role of Endothelial Nitric Oxide in Shear Stress Induced Vasodilation of Human Microvasculature Diminished Activity in Hypertensive and Hypercholesterolemic Patients Oscar A. Paniagua, MD; Melissa B. Bryant,
Role of Endothelial Nitric Oxide in Shear Stress Induced Vasodilation of Human Microvasculature Diminished Activity in Hypertensive and Hypercholesterolemic Patients Oscar A. Paniagua, MD; Melissa B. Bryant,
Role of GABA B Receptor and L-Arg in GABA- Induced Vasorelaxation in Non-diabetic and Streptozotocin- Induced Diabetic Rat Vessels
 Iranian Biomedical Journal 19 (2): 91-95 (April 2015) DOI: 10.6091/ibj.1461.2015 Role of GABA B Receptor and L-Arg in GABA- Induced Vasorelaxation in Non-diabetic and Streptozotocin- Induced Diabetic Rat
Iranian Biomedical Journal 19 (2): 91-95 (April 2015) DOI: 10.6091/ibj.1461.2015 Role of GABA B Receptor and L-Arg in GABA- Induced Vasorelaxation in Non-diabetic and Streptozotocin- Induced Diabetic Rat
ino in neonates with cardiac disorders
 ino in neonates with cardiac disorders Duncan Macrae Paediatric Critical Care Terminology PAP Pulmonary artery pressure PVR Pulmonary vascular resistance PHT Pulmonary hypertension - PAP > 25, PVR >3,
ino in neonates with cardiac disorders Duncan Macrae Paediatric Critical Care Terminology PAP Pulmonary artery pressure PVR Pulmonary vascular resistance PHT Pulmonary hypertension - PAP > 25, PVR >3,
Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN THE -GALACTOSIDASE A-KNOCKOUT MOUSE IS AN ENDOTHELIAL CELL-, PLASMA MEMBRANE-BASED DEFECT
 Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology (2008) 35, 1156 1163 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.04984.x Blackwell Endothelial-based JL Park et Publishing al. defect Asiain Fabry disease VASCULAR
Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology (2008) 35, 1156 1163 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.04984.x Blackwell Endothelial-based JL Park et Publishing al. defect Asiain Fabry disease VASCULAR
Role of Ion Fluxes in Hydrogen Peroxide Pulmonary Vasoconstriction
 Physiol. Res. 44: 31-3 7, 1995 Role of Ion Fluxes in Hydrogen Peroxide Pulmonary Vasoconstriction J. W ILHELM, J. H E R G E T 1 Department of Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry and department of Physiology,
Physiol. Res. 44: 31-3 7, 1995 Role of Ion Fluxes in Hydrogen Peroxide Pulmonary Vasoconstriction J. W ILHELM, J. H E R G E T 1 Department of Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry and department of Physiology,
Supplemental Materials
 Supplemental Methods Spin trap and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy Hypoxanthine (1 mmol=l) plus xanthine oxidase (.1 u=ml) were incubated in Krebs solution at 378C bubbled with 95% O 2 and
Supplemental Methods Spin trap and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy Hypoxanthine (1 mmol=l) plus xanthine oxidase (.1 u=ml) were incubated in Krebs solution at 378C bubbled with 95% O 2 and
Bronchial epithelium-associated pulmonary arterial muscle relaxation in the rat is absent in the fetus and suppressed by postnatal hypoxia
 Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288: L384 L389, 2005. First published October 29, 2004; doi:10.1152/ajplung.00309.2004. Bronchial epithelium-associated pulmonary arterial muscle relaxation in the rat
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288: L384 L389, 2005. First published October 29, 2004; doi:10.1152/ajplung.00309.2004. Bronchial epithelium-associated pulmonary arterial muscle relaxation in the rat
Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 139-143. Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline I. R. INNES AND R. MAILHOT* Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 139-143. Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline I. R. INNES AND R. MAILHOT* Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine,
Reactive oxygen species: Importance for ischemia/reperfusion (injury)
 Physiologisches Institut Reactive oxygen species: Importance for ischemia/reperfusion (injury) Prof. Dr. Rainer Schulz Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) ROS GOOD: Endogenous
Physiologisches Institut Reactive oxygen species: Importance for ischemia/reperfusion (injury) Prof. Dr. Rainer Schulz Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) ROS GOOD: Endogenous
ca2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in the rabbit isolated pulmonary artery
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1993), 18, 155-161 d" Macmillan Press Ltd, 1993 Influences of the endothelium and hypoxia on ac- and ca2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in the rabbit isolated pulmonary artery 'Margaret
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1993), 18, 155-161 d" Macmillan Press Ltd, 1993 Influences of the endothelium and hypoxia on ac- and ca2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in the rabbit isolated pulmonary artery 'Margaret
Topical application of a Rho-kinase inhibitor in rats causes penile erection
 (2004) 16, 294 298 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijir Topical application of a Rho-kinase inhibitor in rats causes penile erection Y Dai 1,2,3, K
(2004) 16, 294 298 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijir Topical application of a Rho-kinase inhibitor in rats causes penile erection Y Dai 1,2,3, K
Moh Tarek + Faisal Massad. Tala Saleh ... Naif
 19 Moh Tarek + Faisal Massad Tala Saleh... Naif Last lecture we ve talked about the main antioxidant system which are the enzymes found in our body, mainly: 1. Glutathione peroxidase 2. Super oxide dismutase(sod)
19 Moh Tarek + Faisal Massad Tala Saleh... Naif Last lecture we ve talked about the main antioxidant system which are the enzymes found in our body, mainly: 1. Glutathione peroxidase 2. Super oxide dismutase(sod)
Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation
 6 The Open Circulation and Vascular Journal, 2011, 4, 6-11 Open Access Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation Induced by R-PIA Gonzalo Allende* and Salvador Acevedo
6 The Open Circulation and Vascular Journal, 2011, 4, 6-11 Open Access Evidence for a Role of Cyclic AMP and Endothelium in Rat Aortic Relaxation Induced by R-PIA Gonzalo Allende* and Salvador Acevedo
CHAPTER 5 Bradykinin Potentiation by ACE Inhibitors: A Matter of Metabolism
 CHAPTER 5 Bradykinin Potentiation by ACE Inhibitors: A Matter of Metabolism Summary Studies in isolated cells overexpressing ACE and B 2 receptors suggest that ACE inhibitors potentiate bradykinin by inhibiting
CHAPTER 5 Bradykinin Potentiation by ACE Inhibitors: A Matter of Metabolism Summary Studies in isolated cells overexpressing ACE and B 2 receptors suggest that ACE inhibitors potentiate bradykinin by inhibiting
Mechanisms of simvastatin-induced vasodilatation of rat superior mesenteric arteries
 BIOMEDICAL REPORTS 5: 491-496, 2016 Mechanisms of simvastatin-induced vasodilatation of rat superior mesenteric arteries YULONG CHEN 1,2*, HONGMEI ZHANG 3*, HUANHUAN LIU 2 and AILAN CAO 1,4 1 Shaanxi Pharmaceutical
BIOMEDICAL REPORTS 5: 491-496, 2016 Mechanisms of simvastatin-induced vasodilatation of rat superior mesenteric arteries YULONG CHEN 1,2*, HONGMEI ZHANG 3*, HUANHUAN LIU 2 and AILAN CAO 1,4 1 Shaanxi Pharmaceutical
NAOYUKI MATSUDA, YUICHI HATTORI, XIAO-HONG ZHANG, HIROYUKI FUKUI, OSAMU KEMMOTSU, and SATOSHI GANDO
 0022-3565/03/3071-175 181$7.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 307, No. 1 Copyright 2003 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 54163/1095232
0022-3565/03/3071-175 181$7.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 307, No. 1 Copyright 2003 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 54163/1095232
CURCUMIN AMELIORATES HIGH GLUCOSE-INDUCED ACUTE VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION IN RAT THORACIC AORTA
 Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology (2009) 36, 1177 1182 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2009.05210.x CURCUMIN AMELIORATES HIGH GLUCOSE-INDUCED ACUTE VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION IN RAT
Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology (2009) 36, 1177 1182 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2009.05210.x CURCUMIN AMELIORATES HIGH GLUCOSE-INDUCED ACUTE VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION IN RAT
The 1,4-dihydropyridine known as nifedipine is a commonly
 Synergistic Antihypertensive Effects of Nifedipine on Endothelium Concurrent Release of NO and Scavenging of Superoxide Viktor Brovkovych, Leszek Kalinowski, Reiner Muller-Peddinghaus, Tadeusz Malinski
Synergistic Antihypertensive Effects of Nifedipine on Endothelium Concurrent Release of NO and Scavenging of Superoxide Viktor Brovkovych, Leszek Kalinowski, Reiner Muller-Peddinghaus, Tadeusz Malinski
Role of nitric oxide and cgmp in the modulation of vascular contraction induced by angiotensin II and Bay K8644 during ischemia/reperfusion
 616 Role of nitric oxide and cgmp in the modulation of vascular contraction induced by angiotensin II and Bay K8644 during ischemia/reperfusion KATARZYNA SZADUJKIS-SZADURSKA, GRZEGORZ GRZESK, LESZEK SZADUJKIS
616 Role of nitric oxide and cgmp in the modulation of vascular contraction induced by angiotensin II and Bay K8644 during ischemia/reperfusion KATARZYNA SZADUJKIS-SZADURSKA, GRZEGORZ GRZESK, LESZEK SZADUJKIS
Role of protein kinase G on the post-shock mesenteric lymph blockage ameliorating vascular calcium sensitivity 1
 Role of protein kinase G on the post-shock mesenteric lymph blockage ameliorating vascular calcium sensitivity 1 10 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SHOCK Zi-gang Zhao I, Yan-ling Wei II, Chun-yu Niu III, Yu-ping Zhang
Role of protein kinase G on the post-shock mesenteric lymph blockage ameliorating vascular calcium sensitivity 1 10 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SHOCK Zi-gang Zhao I, Yan-ling Wei II, Chun-yu Niu III, Yu-ping Zhang
Gadolinium Effect of Experimental Orthostatic Hypotension
 [Index FAC] [FVCC Index] Otras Unidades Temáticas /Other Thematics Units Gadolinium Effect of Experimental Orthostatic Hypotension Zarco Olvera G., Pastelín Hernández G. Departamento de Farmacología, Instituto
[Index FAC] [FVCC Index] Otras Unidades Temáticas /Other Thematics Units Gadolinium Effect of Experimental Orthostatic Hypotension Zarco Olvera G., Pastelín Hernández G. Departamento de Farmacología, Instituto
