Peripheral arterial disease
|
|
|
- Tobias Adams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 clinical Kate Haigh John Bingley Jonathan Golledge Philip J Walker Peripheral arterial disease Screening in general practice Background As a manifestation of systemic atherosclerosis, peripheral arterial disease (PAD) signifies an increased risk of cardiovascular events. Peripheral arterial disease has received less attention than other atherosclerotic diseases, leading to under-diagnosis and under-treatment. Peripheral arterial disease affects approximately 10 15% of the general population, and approximately 50% of PAD patients are asymptomatic. Objective This article aims to review the literature on the rationale for screening for lower extremity PAD in the general practice setting, and to identify the barriers to screening for PAD experienced by general practitioners, with a focus on the Australian context. Discussion Screening for asymptomatic PAD among high risk groups has been recommended by major PAD authorities to increase early diagnosis. Screening for PAD using the ankle-brachial index can detect asymptomatic patients. Research into the effect of cardiovascular risk reduction therapies for asymptomatic patients is lacking, and available evidence is inconclusive. The prevalence of screening and barriers to screening experienced by Australian GPs has not yet been studied. Available data on the benefits of PAD screening is inconclusive, and further research is required to determine a survival benefit with treatment of asymptomatic PAD. Keywords screening; peripheral arterial disease Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the Western world, and is becoming increasingly common in developing nations. 1 A large body of data demonstrates that secondary prevention can reduce future cardiovascular morbidity and mortality indicating the potential value of early disease detection. 2 Atherosclerosis affects both coronary and peripheral arterial beds, typically developing in multiple vascular beds and remaining subclinical for many years before manifesting with clinical symptoms. 1 The risk factors for peripheral arterial disease (PAD) are similar to those for atherosclerosis in other beds with the strongest risk factors for PAD being increased age, smoking and diabetes. 3 Approximately 20% of people over the age of 65 years have symptomatic or asymptomatic PAD. 4 The age standardised population prevalence in men aged years of PAD in Australia is 15.6%. 5 A diagnosis of PAD holds important prognostic value as a marker of increased mortality and vascular event risk, but methods to identify PAD at an early stage are not widely used. 6 A diagnosis of PAD presents the opportunity to initiate secondary prevention by instituting atherosclerosis risk factor modification, and thus reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications. A failure to diagnose PAD misses this opportunity. 4 Factors postulated to be responsible for the current under-diagnosis of PAD include the asymptomatic nature of most PAD, the inappropriate use of recommended screening and diagnostic tools, and poor awareness of the prevalence, natural history and prognostic significance of PAD among public and medical communities. 7 This article aims to review the literature on the rationale for screening for lower extremity PAD in the general practice setting, and identify the barriers to screening for PAD experienced by general practitioners, with focus on the Australian context. Methods Databases searched included PubMed, Cochrane, EMBASE, Scopus, Web of Science and Informit Health Collection. The search was carried out in May The following search terms were used: peripheral arterial disease, screen, asymptomatic, detection, ankle brachial index, examination and general practice. Rationale for screening Asymptomatic PAD affects up to 12% of primary care patients aged 65 years and over. 4 Symptomatic PAD has been found in 8% of primary care patients aged more than 65 years, defined by an ankle-brachial index (ABI) of <0.9 in addition to intermittent claudication Reprinted from Australian Family Physician Vol. 42, No. 6, june
2 clinical Peripheral arterial disease screening in general practice (IC), ischaemic rest pain, ischaemic ulcers, or gangrene. 2,4 Typical characteristics of IC include exertional cramping or aching muscle discomfort, typically located in the calf, but may also include the buttock or thigh, that is not positional, has a reproducible onset, and is relieved within 10 minutes of rest. In addition to patients presenting with typical symptoms, it is increasingly recognised that a large portion of PAD patients have atypical leg symptoms and thus, many patients with PAD are easily missed in routine GP consultations. 8 Guidelines relating to PAD screening are presented in Table 1. Of note, there is no current Australian guideline relating to PAD screening. The World Health Organization criteria for an appropriate screening program are presented in Table 2 and discussed below in the context of screening for PAD with the ABI. 9 Table 1. Guidelines relating to screening for PAD Guidelines American College of Cardiologists and the American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) TransAtlantic InterSociety Consensus (TASC-II) United States Preventive Services Task Force 10 National Health and Medical Research Council 23 [rescinded 2004] The condition Asymptomatic PAD has long been disregarded because of the erroneous belief that it is benign. Contrary to this, asymptomatic and symptomatic PAD patients have a similarly increased cardiovascular mortality risk. 3,4 Compared to patients without PAD, asymptomatic patients without known cardiovascular disease in other arterial sites have a two-fold increased risk of premature death. 10 Screening methods Detection of PAD relying on history alone, or using a symptom based questionnaire, must necessarily miss all patients with asymptomatic PAD. 8 General practitioners commonly diagnose symptomatic and asymptomatic PAD using physical examination findings, such as absence Year of Recommendation and rationale publication 2011 Screen high risk patients with ABI Symptoms: exertional leg pain, non-healing ulcers Age >65 years Age >50 years PLUS either smoking or diabetes 2007 Screen high risk patients with ABI Symptoms: exertional leg pain Age years with cardiovascular risk factors Age >70 years 2006 Recommend against screening 1996 Recommend against screening Benefits of screening are outweighed by the harms; based on the outcome of PAD related morbidity, not cardiovascular risk Additional sensitivity and specificity data for detection tools required of pulses, femoral bruit and trophic skin changes. 8 While specific for PAD, these findings have low sensitivity (Table 3) The ABI is a simple test to effectively detect asymptomatic lower limb PAD. ABI measurement as a screening test The ABI is sensitive, symptom independent, non-invasive and cost effective, and has proven efficacy for community screening of high risk patients. 6 The ABI is calculated as the quotient of the higher of the posterior tibial or dorsalis pedis artery systolic pressures in the one leg, and the higher of the right and left brachial artery systolic pressures. 8 The ACC/AHA 2011 guidelines define values between as normal, as borderline PAD, <0.9 as diagnostic of PAD, and >1.4 indicates non-compressible arteries. 2 The diagnostic value of ABI is limited in diseases that cause arterial calcification and non-compressibility (eg. advanced diabetes, renal insufficiency and in the very elderly). 8 Measurement of the ABI and arterial waveform analysis using a hand-held Doppler ultrasound device currently attracts a Medicare fee of $63.75 (MBS Item Number 11610) provided a hard copy trace and report are supplied. 14 Treatment of asymptomatic PAD The desired outcome of early detection of PAD is to identify patients at increased risk of cardiovascular events and mortality and to take action to reduce their risk. As many PAD patients have involvement of multiple arterial sites and are likely to already be receiving secondary prevention therapies, it has been questioned whether detection of early PAD will significantly alter management. However, half of those Table 2. WHO principles of screening 21 Condition Important health problem Recognisable asymptomatic stage Known natural history of disease Test Suitable and acceptable test Treatment Treatment must be available Program Cost effective Table 3. Sensitivities and specificities of PAD detection methods Sensitivity Specificity Edinburgh Claudication Questionnaire 56% >90% Examination: absence of both pedal pulses 72% >90% Examination: femoral bruit 28% >90% Ankle-brachial index 77% >95% Duplex arterial ultrasound 96% >95% 392 Reprinted from Australian Family Physician Vol. 42, No. 6, june 2013
3 Peripheral arterial disease screening in general practice clinical Table 4. National Heart Foundation recommendations for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease 22 Secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease Smoking Complete cessation Exercise Moderate level activity (brisk walking) 30 min/day at least 5 days per week Diet Mediterranean diet: emphasis on fruits, vegetables, healthy oils, nuts/seeds and fish; limit sugar, saturated fats and salt Weight Target BMI <25 kg/m 2 ; waist measurement <94 cm for men and <80 cm for women; recommend weight loss 5 10% of starting weight or 1 4 kg/month Alcohol No more than two standard drinks per day for men and women, and no more than four standard drinks on a single occasion Blood pressure Lifestyle modification ± drug therapy to achieve BP <140/90 mmhg Lipid management Diabetes Antiplatelet therapy Dietary modification and statin therapy is recommended for all people with clinical evidence of vascular disease. Targets: LDL-C <2.5 mmol/l HDL-C >1 mmol/l TC <4 mmol/l Triglycerides <1.5 mmol/l HbA1c <7%; fasting blood glucose 4 8 mmol/l mg/day aspirin is advised for all patients with symptomatic cardiovascular disease patients with undiagnosed, asymptomatic PAD have no known cardiovascular disease in other vascular beds. 1 Secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease is detailed in Table 4. Despite the known benefit of these therapies in reducing cardiovascular risk in symptomatic coronary artery disease and stroke patients, limited data exists on the impact of early intervention on asymptomatic PAD patients. There is little data supporting the use of aspirin for cardiovascular risk reduction amongst PAD patients. 2,8 Available evidence from two studies suggests that 100 mg of aspirin daily has no benefit in preventing fatal or non-fatal cardiovascular events among asymptomatic PAD patients (Table 5). 15,16 The Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) evaluated the impact of ramipril, an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI), on the prevention of fatal or non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI) or stroke among patients with PAD, including those described as having subclinical PAD. The investigators demonstrated a reduction Table 5. Summary of evidence for early intervention Treatment Study title Year Study type Study size Study population (inclusion) Aspirin Aspirin for Asymptomatic Atherosclerosis (AAA) Trialists 15 Prevention Of Progression of Arterial Disease And Diabetes (POPADAD) Randomised 2008 Randomised ACEI HOPE Randomised Multiple preventive therapies NHANES Crosssectional 3350 Age years + ABI no history of CVD 1276 Age >40 years + type 1 or 2 diabetes + ABI no symptomatic CVD 2118 with asymptomatic PAD Age 55 years + existing CVD or other CV risk factors + ABI <0.9 + no clinical symptoms 7458 General population aged 40 years included in NHANES without previously established CVD Intervention 100 mg vs placebo 100 mg aspirin ± antioxidants vs placebo 10 mg ramipril vs placebo + vitamin E vs placebo Nil Finding/results HR=1.03 ( ) for fatal or nonfatal MI or stroke or revascularisation HR=0.98 ( ) for fatal or nonfatal MI or stroke or amputation RR: 0.72 ( ) for patients with asymptomatic PAD (ABI ) for fatal or non-fatal MI or stroke Two or more preventive therapies (aspirin, ACEI, and/ or statin) were associated with 65% reduced risk of all-cause mortality HR=0.35, 95% CI: , p=0.02 Reprinted from Australian Family Physician Vol. 42, No. 6, june
4 clinical Peripheral arterial disease screening in general practice in vascular events amongst subjects with subclinical PAD randomised to ACEI. 17 The effect of lipid lowering therapy for PAD patients with asymptomatic disease has not been studied. Data from the National Health and Nutrition Evaluation Survey (NHANES) suggested that secondary prevention in asymptomatic PAD patients without known atherosclerotic disease carries a survival benefit, with a 65% reduction in the risk of all cause mortality in the patients treated with multiple preventive therapies compared to no prevention. 10 Screening program No studies have been published to date regarding the cost effectiveness of PAD screening with an ABI or whether widespread implementation of a PAD screening program and appropriate treatment results in survival benefit. Barriers to screening In view of their position in the community as primary carers, GPs are best positioned to detect patients at high risk of PAD. 2 However, international studies indicate that screening is rarely practiced. 2 There is no literature concerning the prevalence of PAD screening in Australia. European and American reports suggest that this may be due to poor community and physician awareness of PAD, lack of familiarity with guidelines, and underutilisation of screening tools contribute. 7 Studies have revealed suboptimal awareness of PAD and its consequences amongst both the public and medical community, with only half of GPs aware of their patient s PAD diagnosis. 18 Education interventions can effectively improve physician awareness of PAD and have resulted in significant changes to the number of GPs regularly measuring ABI. 18 The ABI is underutilised, and research into the barriers to ABI use is lacking. A study of 886 American primary care physicians found that time constraints, lack of reimbursement and staff availability were identified as major barriers to ABI use. 19 Most GPs measure ABI within 15 minutes, however, over half regarded this as prohibitively too long. 19 The automated oscillometric measurement of ABI is a novel technology that is quick and easy to perform in the office setting and demonstrates high accuracy for detecting PAD. 23 Conclusion Cardiovascular disease remains the major cause of mortality in the developed world. Despite the attendant cardiovascular risk associated with even asymptomatic disease, PAD is underdiagnosed and under-treated. Early detection offers the advantage of early intervention to reduce the risk of future cardiovascular events. While there are guidelines for screening for PAD in high risk groups in the United States and Europe, there are currently no Australian guidelines relating to PAD screening. Screening is rarely performed in general practice and there is a deficit in research on this subject in the Australian context. Data on the benefits of screening are inconclusive and more evidence of a survival benefit associated with treatment of asymptomatic PAD is needed in order to confidently recommend PAD screening. There is a clear need for further research and Australian guidelines in this area. At this time, in the absence of Australian guidelines, it may be reasonable to recommend screening for PAD with ABI measurement in Australia in high risk groups as outlined by the ACC/AHA; ie. in patients with symptoms of lower extremity PAD, age 65 years and over, or 50 years and over with a history of smoking or diabetes. 2 Authors Kate Haigh MBBS(Hons), is an intern, Toowoomba Hospital, Toowoomba, Queensland. kate.haigh@uqconnect.edu.au John Bingley MBBS, FRACS(Vasc), is Director of Surgical Services, Division of Surgical Services, Mater Adults Hospital, Brisbane, Queensland Jonathan Golledge BA, MA, MChir, FRCS, FRACS, is Professor of Vascular Surgery, Queensland Research Centre for Peripheral Vascular Disease, James Cook University, Townsville, Queensland Philip J Walker MBBS, FRACS(Vasc), is Professor of Clinical Surgery and Head, Discipline of Surgery, University of Queensland, School of Medicine and Centre for Clinical Research and Department of Vascular Surgery, Royal Brisbane and Women s Hospital, Herston, Queensland. Competing interests: None. Funding: National Health and Medical Research Council (Project Grants and Centre of Research Excellence) and the Queensland government. John Golledge holds fellowships from the NHMRC and Queensland Government. Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed. References 1. Sabouret P, Cacoub P, Dallongeville J, et al. REACH: international prospective observational registry in patients at risk of atherothrombotic events. Results for the French arm at baseline and one year. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 2008;101: Rooke TW, Hirsch AT, Misra S, et al ACCF/AHA Focused Update of the Guideline for the Management of Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease (updating the 2005 guideline): a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;58: Hooi JD, Kester AD, Stoffers HE, Overdijk MM, van Ree JW, Knottnerus JA. Incidence of and risk factors for asymptomatic peripheral arterial occlusive disease: a longitudinal study. Am J Epidemiol 2001;153: Diehm C, Allenberg JR, Pittrow D, et al. Mortality and vascular morbidity in older adults with asymptomatic versus symptomatic peripheral artery disease. Circulation 2009;120: Fowler B, Jamrozik K, Norman P, Allen Y. Prevalence of peripheral arterial disease: persistence of excess risk in former smokers. Aust N Z J Public Health 2002;26: Hayoz D, Bounameaux H, Canova CR. Swiss Atherothrombosis Survey: a field report on the occurrence of symptomatic and asymptomatic peripheral arterial disease. J Intern Med 2005;258: Cimminiello C, Kownator S, Wautrecht JC, et al. The PANDORA study: peripheral arterial disease in patients with non-high cardiovascular risk. Intern Emerg Med 2011;6: Norgren L, Hiatt WR, Dormandy JA, Nehler MR, Harris KA, Fowkes FG. Inter-Society Consensus for the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease (TASC II). J Vasc Surg 2007;45(Suppl S):S Australian Population Health Development Principal Committee Screening Subcommittee. Population Based Screening Framework. Canberra: Commonwealth of Australia, Pande RL, Perlstein TS, Beckman JA, Creager MA. Secondary prevention and mortality in peripheral artery disease: National Health and Nutrition Examination Study, 1999 to Circulation 2011;124: Dachun X, Jue L, Liling Z, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of the ankle-brachial index to diagnose peripheral artery disease: a structured review. Vasc Med 2010;15: Khan NA, Rahim SA, Anand SS, Simel DL, Panju A. Does the clinical examination predict lower extremity peripheral arterial disease? JAMA 2006;295: Collins R, Burch J, Cranny G, et al. Duplex ultra- 394 Reprinted from Australian Family Physician Vol. 42, No. 6, june 2013
5 Peripheral arterial disease screening in general practice clinical sonography, magnetic resonance angiography, and computed tomography angiography for diagnosis and assessment of symptomatic, lower limb peripheral arterial disease: systematic review. BMJ 2007;334: Australian Government Department of Health and Aging. Measurement of ankle brachial indices and arterial waveform analysis. Commonwealth of Australia, Available at gov.au/internet/mbsonline [Accessed 12 April 2013]. 15. Fowkes FG, Price JF, Stewart MC, et al. Aspirin for prevention of cardiovascular events in a general population screened for a low ankle brachial index: a randomized. JAMA 2010;303: Belch J, MacCuish A, Campbell I, et al. The prevention of progression of arterial disease and diabetes (POPADAD) : factorial randomised placebo of aspirin and antioxidants in patients with diabetes and asymptomatic peripheral arterial disease. BMJ 2008;337:a Ostergren J, Sleight P, Dagenais G, et al. Impact of ramipril in patients with evidence of clinical or subclinical peripheral arterial disease. Eur Heart J 2004;25: McDermott MM, Mandapat AL, Moates A, et al. Knowledge and attitudes regarding cardiovascular disease risk and prevention in patients with coronary or peripheral arterial disease. Arch Intern Med 2003;163: Mohler ER 3rd, Treat-Jacobson D, Reilly MP, et al. Utility and barriers to performance of the anklebrachial index in primary care practice. Vasc Med 2004;9: Beckman JA, Higgins CO, Gerhard-Herman M. Automated oscillometric determination of the ankle-brachial index provides accuracy necessary for office practice. Hypertension 2006;47: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for peripheral arterial disease: recommendation statement. Am Fam Physician 2006;73: Heart Foundation of Australia. Information for professionals Available at Pages/information-professionals.aspx [Accessed 15 June 2011]. 23. National Health and Medical Research Council. Guidelines for preventive interventions in primary health care. Canberra: Commonwealth of Australia,1996; pp Reprinted from Australian Family Physician Vol. 42, No. 6, june
Case Study: Chris Arden. Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Case Study: Chris Arden Peripheral Arterial Disease Patient Presentation Diane is a 65-year-old retired school teacher She complains of left calf pain when walking 50 metres; the pain goes away after she
Case Study: Chris Arden Peripheral Arterial Disease Patient Presentation Diane is a 65-year-old retired school teacher She complains of left calf pain when walking 50 metres; the pain goes away after she
Peripheral Arterial Disease Management A Practical Guide for Internists. EFIM Vascular Working Group
 2 Peripheral Arterial Disease Management A Practical Guide for Internists EFIM Vascular Working Group 1 Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a growing concern among our aging population. More than 27 million
2 Peripheral Arterial Disease Management A Practical Guide for Internists EFIM Vascular Working Group 1 Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a growing concern among our aging population. More than 27 million
Peripheral arterial disease: prognostic significance and prevention of atherothrombotic complications
 Peripheral arterial disease: prognostic significance and prevention of atherothrombotic complications Paul E Norman, John W Eikelboom and Graeme J Hankey Peripheral arterial disease, whether symptomatic
Peripheral arterial disease: prognostic significance and prevention of atherothrombotic complications Paul E Norman, John W Eikelboom and Graeme J Hankey Peripheral arterial disease, whether symptomatic
Peripheral Arterial Disease: Objectives. Disclosure. Definition: Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
 Geriatric Grand Rounds Tuesday, April 21, 2009 12:00 noon Dr. Bill Black Auditorium Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital In keeping with Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital policy, speakers participating in this
Geriatric Grand Rounds Tuesday, April 21, 2009 12:00 noon Dr. Bill Black Auditorium Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital In keeping with Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital policy, speakers participating in this
USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential
 USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential MEASURE STEWARD: The US Wound Registry [Note: This measure
USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential MEASURE STEWARD: The US Wound Registry [Note: This measure
Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI
 PAD Diagnosis Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Metro Health / University of Michigan Health, Wyoming, MI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI University Hospitals Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, Cleveland, OH PAD:
PAD Diagnosis Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Metro Health / University of Michigan Health, Wyoming, MI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI University Hospitals Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, Cleveland, OH PAD:
A new era in the treatment of peripheral artery disease (PAD)?
 A new era in the treatment of peripheral artery disease (PAD)? Prof. Dr. Jan Beyer-Westendorf Head of Thrombosis Research, University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus, TU Dresden; Germany Senior Lecturer Thrombosis
A new era in the treatment of peripheral artery disease (PAD)? Prof. Dr. Jan Beyer-Westendorf Head of Thrombosis Research, University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus, TU Dresden; Germany Senior Lecturer Thrombosis
Peripheral Arterial Disease. Westley Smith MD Vascular Fellow
 Peripheral Arterial Disease Westley Smith MD Vascular Fellow Background (per 10,000) Goodney P, et al. Regional intensity of vascular care and lower extremity amputation rates. JVS. 2013; 6: 1471-1480.
Peripheral Arterial Disease Westley Smith MD Vascular Fellow Background (per 10,000) Goodney P, et al. Regional intensity of vascular care and lower extremity amputation rates. JVS. 2013; 6: 1471-1480.
Goals of Screening Programs. What is Vascular Screening? Assumptions Regarding the Potential Benefits of Screening Programs PAD
 Conflict of Interest Disclosure (Relationships with Industry) An Epidemic of : The Debate Over Population Screening Membership on an advisory board, consultant, or recipient of a research grant from the
Conflict of Interest Disclosure (Relationships with Industry) An Epidemic of : The Debate Over Population Screening Membership on an advisory board, consultant, or recipient of a research grant from the
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE QUALITY AND OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK (QOF) INDICATOR DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME Briefing paper QOF indicator area: Peripheral arterial disease Potential output:
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE QUALITY AND OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK (QOF) INDICATOR DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME Briefing paper QOF indicator area: Peripheral arterial disease Potential output:
The Changing Landscape of Managing Patients with PAD- Update on the Evidence and Practice of Care in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease
 Interventional Cardiology and Cath Labs The Changing Landscape of Managing Patients with PAD- Update on the Evidence and Practice of Care in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Manesh R. Patel MD Chief,
Interventional Cardiology and Cath Labs The Changing Landscape of Managing Patients with PAD- Update on the Evidence and Practice of Care in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Manesh R. Patel MD Chief,
- Lecture - Recommandations ESC : messages importants P. MEYER (Saint Laurent du Var) - Controverse - Qui doit faire l'angioplastie périphérique?
 - Lecture - Recommandations ESC : messages importants P. MEYER (Saint Laurent du Var) - Controverse - Qui doit faire l'angioplastie périphérique? Un chirurgien E. DUCASSE (Bordeaux) Un interventionnel
- Lecture - Recommandations ESC : messages importants P. MEYER (Saint Laurent du Var) - Controverse - Qui doit faire l'angioplastie périphérique? Un chirurgien E. DUCASSE (Bordeaux) Un interventionnel
Peripheral Arterial Disease: the growing role of endovascular management
 Peripheral Arterial Disease: the growing role of endovascular management Poster No.: C-1931 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. M. C. Guedes Pinto, E. Rosado, D. Penha, P. Cabral,
Peripheral Arterial Disease: the growing role of endovascular management Poster No.: C-1931 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. M. C. Guedes Pinto, E. Rosado, D. Penha, P. Cabral,
7 th Munich Vascular Conference
 7 th Munich Vascular Conference Secondary prevention of major cardiovascular events in patients with CHD or PAD - What can we learn from EUCLID and COMPASS, evaluating Clopidogrel, Ticagrelor and Univ.-Prof.
7 th Munich Vascular Conference Secondary prevention of major cardiovascular events in patients with CHD or PAD - What can we learn from EUCLID and COMPASS, evaluating Clopidogrel, Ticagrelor and Univ.-Prof.
Peripheral Arterial Disease Extremity
 Peripheral Arterial Disease Lower Extremity 05 Contributor Dr Steven Chong Advisors Dr Ashish Anil Dr Tay Jam Chin Introduction Risk Factors Clinical Presentation Classification History PHYSICAL examination
Peripheral Arterial Disease Lower Extremity 05 Contributor Dr Steven Chong Advisors Dr Ashish Anil Dr Tay Jam Chin Introduction Risk Factors Clinical Presentation Classification History PHYSICAL examination
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu Indicator area: Pulse rhythm assessment for AF Indicator: NM146 Date: June 2017 Introduction There is evidence
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu Indicator area: Pulse rhythm assessment for AF Indicator: NM146 Date: June 2017 Introduction There is evidence
Peripheral Artery Disease Role of Exercise, Endovascular and Surgical Options
 Peripheral Artery Disease Role of Exercise, Endovascular and Surgical Options Jeffrey W. Olin, D.O., F.A.C.C., F.A.H.A. Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) Director of Vascular Medicine & the Vascular Diagnostic
Peripheral Artery Disease Role of Exercise, Endovascular and Surgical Options Jeffrey W. Olin, D.O., F.A.C.C., F.A.H.A. Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) Director of Vascular Medicine & the Vascular Diagnostic
John E. Campbell, MD. Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division
 John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
Peripheral arterial disease: A growing problem for the internist
 European Journal of Internal Medicine 20 (2009) 132 138 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejim Review article Peripheral arterial disease: A growing problem for the internist Coen D.A. Stehouwer a,, Denis Clement
European Journal of Internal Medicine 20 (2009) 132 138 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejim Review article Peripheral arterial disease: A growing problem for the internist Coen D.A. Stehouwer a,, Denis Clement
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease
 Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
Introduction. Risk factors of PVD 5/8/2017
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease
 What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Sibu P. Saha, MD, MBA Professor of Surgery Chairman, Directors Council Gill Heart Institute University of Kentucky Lexington, KY Disclosure My
What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Sibu P. Saha, MD, MBA Professor of Surgery Chairman, Directors Council Gill Heart Institute University of Kentucky Lexington, KY Disclosure My
Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes
 Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes Ashok Handa Reader in Surgery and Consultant Surgeon Nuffield Department of Surgery University of Oxford Introduction Vascular
Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes Ashok Handa Reader in Surgery and Consultant Surgeon Nuffield Department of Surgery University of Oxford Introduction Vascular
OUTPATIENT DEPARTMENT
 1 This chapter outlines the main arterial and venous diseases that are likely to be seen within a vascular outpatient setting. It also highlights the role of the vascular nurse specialist wherever appropriate.
1 This chapter outlines the main arterial and venous diseases that are likely to be seen within a vascular outpatient setting. It also highlights the role of the vascular nurse specialist wherever appropriate.
2013 ACC/AHA Guidelines on the Assessment of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk: Overview and Commentary
 2013 ACC/AHA Guidelines on the Assessment of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk: Overview and Commentary The Johns Hopkins Ciccarone Center for the Prevention of Heart Disease Becky McKibben, MPH; Seth
2013 ACC/AHA Guidelines on the Assessment of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk: Overview and Commentary The Johns Hopkins Ciccarone Center for the Prevention of Heart Disease Becky McKibben, MPH; Seth
Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease. Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August
 Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August 20 2014 Outline (and for the ABIM board exam * ** ***) Prevalence* Definitions Lower Extremity: Aorta*** Claudication***
Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August 20 2014 Outline (and for the ABIM board exam * ** ***) Prevalence* Definitions Lower Extremity: Aorta*** Claudication***
Clinical Features and Subtypes of Ischemic Stroke Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Research Article Clinical Features and Subtypes of Ischemic Stroke Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease Jin Ok Kim, Hyung-IL Kim, Jae Guk Kim, Hanna Choi, Sung-Yeon
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Research Article Clinical Features and Subtypes of Ischemic Stroke Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease Jin Ok Kim, Hyung-IL Kim, Jae Guk Kim, Hanna Choi, Sung-Yeon
Garland Green, MD Interventional Cardiologist. Impact of PAD: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Testing, and Medical Management
 Garland Green, MD Interventional Cardiologist Impact of PAD: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Testing, and Medical Management Peripheral Arterial Disease Affects over 8 million Americans Affects 12% of the general
Garland Green, MD Interventional Cardiologist Impact of PAD: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Testing, and Medical Management Peripheral Arterial Disease Affects over 8 million Americans Affects 12% of the general
Ankle brachial index measured by palpation for the diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease
 Ó The Author 2008. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org. doi:10.1093/fampra/cmn035 Family Practice Advance
Ó The Author 2008. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org. doi:10.1093/fampra/cmn035 Family Practice Advance
Ankle Brachial Index as a Marker of Atherosclerosis in Chinese Patients with High Cardiovascular Risk
 23 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.29 (2006) No.1 p.23-28 Ankle Brachial Index as a Marker of Atherosclerosis in Chinese Patients with High Cardiovascular Risk Buaijiaer HASIMU 1), Jue LI 1), Tomohiro
23 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.29 (2006) No.1 p.23-28 Ankle Brachial Index as a Marker of Atherosclerosis in Chinese Patients with High Cardiovascular Risk Buaijiaer HASIMU 1), Jue LI 1), Tomohiro
PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE (PAD); Frequency in diabetics.
 PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE (PAD); Frequency in diabetics. ORIGINAL PROF-2084 Dr. Qaiser Mahmood, Dr. Nasreen Siddique, Dr. Affan Qaiser ABSTRACT Objectives: (1) To determine the frequency of PAD in diabetic
PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE (PAD); Frequency in diabetics. ORIGINAL PROF-2084 Dr. Qaiser Mahmood, Dr. Nasreen Siddique, Dr. Affan Qaiser ABSTRACT Objectives: (1) To determine the frequency of PAD in diabetic
Prevalence, Progression and Associated Risk Factors of Asymptomatic Peripheral Arterial Disease
 ORIGINAL PAPER ORIGINAL PAPER The ANNALS of AFRICAN SURGERY www.annalsofafricansurgery.com Prevalence, Progression and Associated Risk Factors of Asymptomatic Peripheral Arterial Disease Nikita Mehta 1,
ORIGINAL PAPER ORIGINAL PAPER The ANNALS of AFRICAN SURGERY www.annalsofafricansurgery.com Prevalence, Progression and Associated Risk Factors of Asymptomatic Peripheral Arterial Disease Nikita Mehta 1,
Is there an association between atherosclerosis and chronic venous disease?
 Is there an association between atherosclerosis and chronic venous disease? Karel Roztocil, IKEM, Praha Hungarian Society of Angiology and Vascular Surgery Congress, Szombathely 2017 Disclosure Nothing
Is there an association between atherosclerosis and chronic venous disease? Karel Roztocil, IKEM, Praha Hungarian Society of Angiology and Vascular Surgery Congress, Szombathely 2017 Disclosure Nothing
Early Identification of PAD: Evidence to Refute USPSTF Position on Screening
 Early Identification of PAD: Evidence to Refute USPSTF Position on Screening Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, MPH, PhD Director Endovascular Services Interventional Cardiology & Vascular Medicine Department of
Early Identification of PAD: Evidence to Refute USPSTF Position on Screening Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, MPH, PhD Director Endovascular Services Interventional Cardiology & Vascular Medicine Department of
Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital
 Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital Deep Venous Thrombosis Varicose Veins Venous insufficiency Phlebitis Lymphedema Elephantiasis nostras
Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital Deep Venous Thrombosis Varicose Veins Venous insufficiency Phlebitis Lymphedema Elephantiasis nostras
ACC NY Cardiovascular Symposium
 ACC NY Cardiovascular Symposium Peripheral Vascular Disease: Watch the Heart and the Brain Evolving Role of Exercise, ACE-Inhibitors, Interventional and Surgical Options Mark A. Creager, M.D President,
ACC NY Cardiovascular Symposium Peripheral Vascular Disease: Watch the Heart and the Brain Evolving Role of Exercise, ACE-Inhibitors, Interventional and Surgical Options Mark A. Creager, M.D President,
Joshua A. Beckman, MD. Brigham and Women s Hospital
 Peripheral Vascular Disease: Overview, Peripheral Arterial Obstructive Disease, Carotid Artery Disease, and Renovascular Disease as a Surrogate for Coronary Artery Disease Joshua A. Beckman, MD Brigham
Peripheral Vascular Disease: Overview, Peripheral Arterial Obstructive Disease, Carotid Artery Disease, and Renovascular Disease as a Surrogate for Coronary Artery Disease Joshua A. Beckman, MD Brigham
When to screen for PAD? Prof. Dr.Tine De Backer Prof. Dr. Jean-Claude Wautrecht
 When to screen for PAD? Prof. Dr.Tine De Backer Prof. Dr. Jean-Claude Wautrecht How do we define asymptomatic PAD? A. ABI < 1 B. ABI < 0.9 C. ABI < 0.8 D. ABI > 1 How do we define asymptomatic PAD? A.
When to screen for PAD? Prof. Dr.Tine De Backer Prof. Dr. Jean-Claude Wautrecht How do we define asymptomatic PAD? A. ABI < 1 B. ABI < 0.9 C. ABI < 0.8 D. ABI > 1 How do we define asymptomatic PAD? A.
Treatment Strategies For Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease
 Treatment Strategies For Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Presented by Schuyler Jones, MD Duke University Medical Center & Duke Clinical Research Institute AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Review
Treatment Strategies For Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Presented by Schuyler Jones, MD Duke University Medical Center & Duke Clinical Research Institute AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Review
STATINS FOR PAD Long - term prognosis
 STATINS FOR PAD Long - term prognosis Prof. Pavel Poredos, MD, PhD Department of Vascular Disease University Medical Centre Ljubljana Slovenia DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST No conflict of interest
STATINS FOR PAD Long - term prognosis Prof. Pavel Poredos, MD, PhD Department of Vascular Disease University Medical Centre Ljubljana Slovenia DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST No conflict of interest
Nephrology Unit- CHU Liège- Ulg- Belgium
 Are the complications of arteriovenous fistulas associated with an abnormal Ankle-Brachial Index in Hemodialysis? A 4y study P. Xhignesse, A. Saint-Remy, B. Dubois, JC. Philips, JM. Krzesinski Nephrology
Are the complications of arteriovenous fistulas associated with an abnormal Ankle-Brachial Index in Hemodialysis? A 4y study P. Xhignesse, A. Saint-Remy, B. Dubois, JC. Philips, JM. Krzesinski Nephrology
The aching, cramping pain of
 Screening Identifying and treating intermittent claudication in people with diabetes Edward Jude, Judith Gibbons ARTICLE POINTS 1The most important risk factor for intermittent claudication (IC) is diabetes.
Screening Identifying and treating intermittent claudication in people with diabetes Edward Jude, Judith Gibbons ARTICLE POINTS 1The most important risk factor for intermittent claudication (IC) is diabetes.
Is there a role for a Vascular Specialist Podiatrist in the diabetes MDfT / FPT?
 Is there a role for a Vascular Specialist Podiatrist in the diabetes MDfT / FPT? Martin Fox BSc FFPM RCPS(Glasg) Vascular Specialist Podiatrist North Manchester Leg Circulation Service Pennine Acute Hospitals
Is there a role for a Vascular Specialist Podiatrist in the diabetes MDfT / FPT? Martin Fox BSc FFPM RCPS(Glasg) Vascular Specialist Podiatrist North Manchester Leg Circulation Service Pennine Acute Hospitals
Thank you for the opportunity to provide expert advice on the Draft Research Plan on Screening for Peripheral Artery Disease.
 January 12, 2012 Robert L. Cosby, Ph.D., MSW Senior Coordinator, USPSTF Department of Health and Human Services Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Center for Primary Care, Prevention and Clinical
January 12, 2012 Robert L. Cosby, Ph.D., MSW Senior Coordinator, USPSTF Department of Health and Human Services Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Center for Primary Care, Prevention and Clinical
Antiplatelet Therapy in Primary CVD Prevention and Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Καρακώστας Γεώργιος Διευθυντής Καρδιολογικής Κλινικής, Γ.Ν.
 Antiplatelet Therapy in Primary CVD Prevention and Stable Coronary Artery Disease Καρακώστας Γεώργιος Διευθυντής Καρδιολογικής Κλινικής, Γ.Ν.Κιλκίς Primary CVD Prevention A co-ordinated set of actions,
Antiplatelet Therapy in Primary CVD Prevention and Stable Coronary Artery Disease Καρακώστας Γεώργιος Διευθυντής Καρδιολογικής Κλινικής, Γ.Ν.Κιλκίς Primary CVD Prevention A co-ordinated set of actions,
American Diabetes Association: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2015
 American Diabetes Association: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2015 Synopsis of ADA standards relevant to the 11 th Scope of Work under Task B.2 ASSESSMENT OF GLYCEMIC CONTROL Recommendations: Perform
American Diabetes Association: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2015 Synopsis of ADA standards relevant to the 11 th Scope of Work under Task B.2 ASSESSMENT OF GLYCEMIC CONTROL Recommendations: Perform
Reducing risk in heart disease
 Reducing risk in heart disease An expert guide to clinical practice for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease Prof Patricia Davidson (chair) Prof Nigel Stocks Dr Anu Aggarwal Ms Jill Waddell Ms
Reducing risk in heart disease An expert guide to clinical practice for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease Prof Patricia Davidson (chair) Prof Nigel Stocks Dr Anu Aggarwal Ms Jill Waddell Ms
Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)
 Original article: Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) 1DR Anu N Gaikwad, 2 Dr Vikrant V Rasal, 3 Dr S A Kanitkar, 4 Dr Meenakshi Kalyan
Original article: Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) 1DR Anu N Gaikwad, 2 Dr Vikrant V Rasal, 3 Dr S A Kanitkar, 4 Dr Meenakshi Kalyan
Guidelines on cardiovascular risk assessment and management
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement L), L5 L10 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui079 Guidelines on cardiovascular risk assessment and management David A. Wood 1,2 * 1 Cardiovascular Medicine
European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement L), L5 L10 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui079 Guidelines on cardiovascular risk assessment and management David A. Wood 1,2 * 1 Cardiovascular Medicine
Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot. Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017
 Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017 Case Male 67 years old Underlying DM, HTN, TVD Present with gangrene
Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017 Case Male 67 years old Underlying DM, HTN, TVD Present with gangrene
Diabetes Mellitus: A Cardiovascular Disease
 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cardiovascular Disease Nestoras Mathioudakis, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism September 30, 2013 1 The ABCs of cardiovascular
Diabetes Mellitus: A Cardiovascular Disease Nestoras Mathioudakis, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism September 30, 2013 1 The ABCs of cardiovascular
Predictors of an abnormal postexercise ankle brachial index: Importance of the lowest ankle pressure in calculating the resting ankle brachial index
 Received: 14 May 2017 Revised: 18 August 2017 Accepted: 4 September 2017 DOI: 10.1002/clc.22808 CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Predictors of an abnormal postexercise ankle brachial index: Importance of the lowest
Received: 14 May 2017 Revised: 18 August 2017 Accepted: 4 September 2017 DOI: 10.1002/clc.22808 CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Predictors of an abnormal postexercise ankle brachial index: Importance of the lowest
Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Role of Vascular Surgeon Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai University
Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Role of Vascular Surgeon Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai University
Asymptomatic peripheral arterial occlusive disease predicted cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in a 7-year follow-up study
 Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 57 (2004) 294 300 Asymptomatic peripheral arterial occlusive disease predicted cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in a 7-year follow-up study J.D. Hooi a, A.D.M. Kester
Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 57 (2004) 294 300 Asymptomatic peripheral arterial occlusive disease predicted cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in a 7-year follow-up study J.D. Hooi a, A.D.M. Kester
Peripheral Arterial Disease: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics
 Peripheral Arterial Disease: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics ii Colloquium Digital Library of Life Sciences This e-book is a copyrighted work in the Colloquium Digital Library an innovative collection
Peripheral Arterial Disease: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics ii Colloquium Digital Library of Life Sciences This e-book is a copyrighted work in the Colloquium Digital Library an innovative collection
Evaluation of Medical Treatment for Peripheral Arterial Disease in Chinese High-Risk Patients
 Circ J 2007; 71: 95 99 Evaluation of Medical Treatment for Peripheral Arterial Disease in Chinese High-Risk Patients Buaijiaer Hasimu, MD, PhD*,, ; Jue Li, MD, PhD*; Jinming Yu, MD, PhD*; Yitong Ma, MD,
Circ J 2007; 71: 95 99 Evaluation of Medical Treatment for Peripheral Arterial Disease in Chinese High-Risk Patients Buaijiaer Hasimu, MD, PhD*,, ; Jue Li, MD, PhD*; Jinming Yu, MD, PhD*; Yitong Ma, MD,
April 20, USPSTF Coordinator c/o USPSTF 540 Gaither Road Rockville, MD Dear Sir or Madam:
 April 20, 2016 USPSTF Coordinator c/o USPSTF 540 Gaither Road Rockville, MD 20850 Dear Sir or Madam: Thank you for the opportunity to comment on the Draft Research Plan for Peripheral Artery Disease in
April 20, 2016 USPSTF Coordinator c/o USPSTF 540 Gaither Road Rockville, MD 20850 Dear Sir or Madam: Thank you for the opportunity to comment on the Draft Research Plan for Peripheral Artery Disease in
1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia:
 Questions: 1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia: a) Diabetes mellitus b) Hypertension c) Family history of premature coronary disease (first degree relatives:
Questions: 1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia: a) Diabetes mellitus b) Hypertension c) Family history of premature coronary disease (first degree relatives:
Blood Pressure LIMBO How Low To Go?
 Blood Pressure LIMBO How Low To Go? Joseph L. Kummer, MD, FACC Bryan Heart Spring Conference April 21 st, 2018 Hypertension Epidemiology Over a billion people have hypertension Major cause of morbidity
Blood Pressure LIMBO How Low To Go? Joseph L. Kummer, MD, FACC Bryan Heart Spring Conference April 21 st, 2018 Hypertension Epidemiology Over a billion people have hypertension Major cause of morbidity
Arteriopatie periferiche. Trattamento delle arteriopatie periferiche: AVK versus Antiaggregante
 Arteriopatie periferiche Trattamento delle arteriopatie periferiche: AVK versus Antiaggregante Anna Falanga USC Immunoematologia e Medicina Trasfusionale ASST Papa Giovanni XXIII, Bergamo Obiettivi della
Arteriopatie periferiche Trattamento delle arteriopatie periferiche: AVK versus Antiaggregante Anna Falanga USC Immunoematologia e Medicina Trasfusionale ASST Papa Giovanni XXIII, Bergamo Obiettivi della
Module 2. Global Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Reduction in Women with Hypertension
 Module 2 Global Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Reduction in Women with Hypertension 1 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored,
Module 2 Global Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Reduction in Women with Hypertension 1 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored,
Coronary Heart Disease in Women Go Red for Women
 Coronary Heart Disease in Women Go Red for Women Dr Fiona Stewart Green Lane Cardiovascular Service and National Women s Health Auckland City Hospital Auckland Heart Group Women are Different from Men
Coronary Heart Disease in Women Go Red for Women Dr Fiona Stewart Green Lane Cardiovascular Service and National Women s Health Auckland City Hospital Auckland Heart Group Women are Different from Men
National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD
 National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD No relevant financial relationships to disclose Wound Care Referral The patient has been maximized from a vascular standpoint. She has no other options.
National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD No relevant financial relationships to disclose Wound Care Referral The patient has been maximized from a vascular standpoint. She has no other options.
Epidemiology and Prevention
 Epidemiology and Prevention Secondary Prevention and Mortality in Peripheral Artery Disease National Health and Nutrition Examination Study, 1999 to 2004 Reena L. Pande, MD; Todd S. Perlstein, MD, MMSc;
Epidemiology and Prevention Secondary Prevention and Mortality in Peripheral Artery Disease National Health and Nutrition Examination Study, 1999 to 2004 Reena L. Pande, MD; Todd S. Perlstein, MD, MMSc;
Due to Perimed s commitment to continuous improvement of our products, all specifications are subject to change without notice.
 A summary Disclaimer The information contained in this document is intended to provide general information only. It is not intended to be, nor does it constitute, medical advice. Under no circumstances
A summary Disclaimer The information contained in this document is intended to provide general information only. It is not intended to be, nor does it constitute, medical advice. Under no circumstances
World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device
 World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device Accurate and objective Peripheral Arterial Disease diagnosis E S S E N T I A L T O H E A LT H NOTE: Brošura - A4 format na poli A3 What is Peripheral
World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device Accurate and objective Peripheral Arterial Disease diagnosis E S S E N T I A L T O H E A LT H NOTE: Brošura - A4 format na poli A3 What is Peripheral
Medical Management of Vascular Disease KEITH E SWANSON MD ND ACADEMY OF FAMILY PHYSICIANS FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE JANUARY 2017
 Medical Management of Vascular Disease KEITH E SWANSON MD ND ACADEMY OF FAMILY PHYSICIANS FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE JANUARY 2017 Objectives 1. Appreciate the long term implications of PAD 2. Appreciate the
Medical Management of Vascular Disease KEITH E SWANSON MD ND ACADEMY OF FAMILY PHYSICIANS FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE JANUARY 2017 Objectives 1. Appreciate the long term implications of PAD 2. Appreciate the
Objectives. Abdominal Aortic Aneuryms 11/16/2017. The Vascular Patient: Diagnosis and Conservative Treatment
 The Vascular Patient: Diagnosis and Conservative Treatment Ferrell-Duncan Clinic Zachary C. Schmittling, M.D., F.A.C.S. Vascular and General Surgery Ferrell-Duncan Clinic Cox Health Systems Objectives
The Vascular Patient: Diagnosis and Conservative Treatment Ferrell-Duncan Clinic Zachary C. Schmittling, M.D., F.A.C.S. Vascular and General Surgery Ferrell-Duncan Clinic Cox Health Systems Objectives
Guidelines for Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Guidelines for Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Subhash Banerjee, MD, FACC, FSCAI Professor of Medicine, Univ. of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Chief, Division of Cardiology, VA North Texas
Guidelines for Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Subhash Banerjee, MD, FACC, FSCAI Professor of Medicine, Univ. of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Chief, Division of Cardiology, VA North Texas
A Healthy Heart. IN BRIEF: Your Guide to
 IN BRIEF: Your Guide to A Healthy Heart If you re like most people, you may think of heart disease as a problem for other folks. If you re a woman, you may believe that being female protects you from heart
IN BRIEF: Your Guide to A Healthy Heart If you re like most people, you may think of heart disease as a problem for other folks. If you re a woman, you may believe that being female protects you from heart
Coronary Artery Disease Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Coronary Artery Disease Clinical Practice Guidelines Guidelines are systematically developed statements to assist patients and providers in choosing appropriate healthcare for specific clinical conditions.
Coronary Artery Disease Clinical Practice Guidelines Guidelines are systematically developed statements to assist patients and providers in choosing appropriate healthcare for specific clinical conditions.
Complications of Diabetes: Screening and Prevention
 Complications of Diabetes: Screening and Prevention Dr Steve Cleland Consultant Physician GGH and QEUH Diabetes Staff Education Course June 17 Diabetic Complications Microvascular: Retinopathy Nephropathy
Complications of Diabetes: Screening and Prevention Dr Steve Cleland Consultant Physician GGH and QEUH Diabetes Staff Education Course June 17 Diabetic Complications Microvascular: Retinopathy Nephropathy
CVD Prevention, Who to Consider
 Continuing Professional Development 3rd annual McGill CME Cruise September 20 27, 2015 CVD Prevention, Who to Consider Dr. Guy Tremblay Excellence in Health Care and Lifelong Learning Global CV risk assessment..
Continuing Professional Development 3rd annual McGill CME Cruise September 20 27, 2015 CVD Prevention, Who to Consider Dr. Guy Tremblay Excellence in Health Care and Lifelong Learning Global CV risk assessment..
Ankle brachial index performance among internal medicine residents
 Ankle brachial index performance among internal medicine residents Vascular Medicine 15(2) 99 105 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: http://www. sagepub.co.uk/journalspermission.nav DOI: 10.1177/1358863X09356015
Ankle brachial index performance among internal medicine residents Vascular Medicine 15(2) 99 105 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: http://www. sagepub.co.uk/journalspermission.nav DOI: 10.1177/1358863X09356015
TABLE OF CONTENTS. 2. LOWER EXTREMITY PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE 2.1. Epidemiology Risk Factors
 LOWER EXTREMITY PAD The following is one of three extracted sections lower extremity, renal/mesenteric, and abdominal aortic of the ACC/AHA 2005 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Peripheral
LOWER EXTREMITY PAD The following is one of three extracted sections lower extremity, renal/mesenteric, and abdominal aortic of the ACC/AHA 2005 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Peripheral
Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds
 Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds American Society of Podiatric Surgeons Surgical Conference September 22, 2018 Michael Maier, DPM, FACCWS Cardiovascular Medicine Cleveland Clinic Disclosures Speaker,
Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds American Society of Podiatric Surgeons Surgical Conference September 22, 2018 Michael Maier, DPM, FACCWS Cardiovascular Medicine Cleveland Clinic Disclosures Speaker,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/30/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 79 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/30/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 79 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Perceptions of the ankle brachial index amongst podiatrists registered in Western Australia
 Chen et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2012, 5:19 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access Perceptions of the ankle brachial index amongst podiatrists registered in Western Australia
Chen et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2012, 5:19 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access Perceptions of the ankle brachial index amongst podiatrists registered in Western Australia
Αντιθρομβωτική αγωγή σε ασθενείς με περιφερική αρτηριακή νόσο των κάτω άκρων
 Αντιθρομβωτική αγωγή σε ασθενείς με περιφερική αρτηριακή νόσο των κάτω άκρων Μ. Ματσάγκας, MD, PhD, FEBVS Καθηγητής Αγγειοχειρουργικής Πανεπιστήμιο Θεσσαλίας Prevalence (millions) PAD Affects Millions
Αντιθρομβωτική αγωγή σε ασθενείς με περιφερική αρτηριακή νόσο των κάτω άκρων Μ. Ματσάγκας, MD, PhD, FEBVS Καθηγητής Αγγειοχειρουργικής Πανεπιστήμιο Θεσσαλίας Prevalence (millions) PAD Affects Millions
PAD Characterization Within A Healthcare System" RAPID Face-to-Face Meeting Schuyler Jones, MD September 14, 2016
 PAD Characterization Within A Healthcare System" RAPID Face-to-Face Meeting Schuyler, MD September 14, 2016 Interventional Cardiology and Cath Labs Disclosures Research Grants: Agency for Healthcare Research
PAD Characterization Within A Healthcare System" RAPID Face-to-Face Meeting Schuyler, MD September 14, 2016 Interventional Cardiology and Cath Labs Disclosures Research Grants: Agency for Healthcare Research
The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography
 Research imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2572-5483.100036 Journal of Preventive Medicine The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography Andrew
Research imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2572-5483.100036 Journal of Preventive Medicine The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography Andrew
World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device
 World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device Accurate and objective Peripheral Arterial Disease diagnosis From secondary to primary healthcare with the help of technology. MESI founders identified
World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device Accurate and objective Peripheral Arterial Disease diagnosis From secondary to primary healthcare with the help of technology. MESI founders identified
ANKLE BRACHIAL PRESSURE INDEX: AS A PREDICTOR OF PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE IN DIABETIC & NON DIABETIC SUBJECTS
 RESEARCH ARTICLE ANKLE BRACHIAL PRESSURE INDEX: AS A PREDICTOR OF PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE IN DIABETIC & NON DIABETIC SUBJECTS Dharmesh Patel 1, MB Jani 2 1 Department of Physiology, GMERS Medical College,
RESEARCH ARTICLE ANKLE BRACHIAL PRESSURE INDEX: AS A PREDICTOR OF PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE IN DIABETIC & NON DIABETIC SUBJECTS Dharmesh Patel 1, MB Jani 2 1 Department of Physiology, GMERS Medical College,
Prevalence of peripheral arterial disease and its association with smoking in a population-based study in Beijing, China
 of peripheral arterial disease and its association with smoking in a population-based study in Beijing, China Yao He, MD, PhD, a,b Yong Jiang, MD, a Jie Wang, MD, PhD, c Li Fan, MD, d XiaoYing Li, MD,
of peripheral arterial disease and its association with smoking in a population-based study in Beijing, China Yao He, MD, PhD, a,b Yong Jiang, MD, a Jie Wang, MD, PhD, c Li Fan, MD, d XiaoYing Li, MD,
Diabetes, Diet and SMI: How can we make a difference?
 Diabetes, Diet and SMI: How can we make a difference? Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Relative
Diabetes, Diet and SMI: How can we make a difference? Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Relative
Heart health CHD management gaps in general practice
 professional practice Nancy Huang MBBS, DipRACOG, MPH, is National Manager Clinical Programs, Heart Foundation, Melbourne, Victoria. nancy.huang@heartfoundation.org.au Marcus Daddo BSc(Hons), is Manager
professional practice Nancy Huang MBBS, DipRACOG, MPH, is National Manager Clinical Programs, Heart Foundation, Melbourne, Victoria. nancy.huang@heartfoundation.org.au Marcus Daddo BSc(Hons), is Manager
How Do We Optimize the Medical Therapy of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia?
 How Do We Optimize the Medical Therapy of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia? Ehrin J. Armstrong, MD MSc MAS Director, Interventional Cardiology Director, Vascular Laboratory VA Eastern Colorado Healthcare
How Do We Optimize the Medical Therapy of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia? Ehrin J. Armstrong, MD MSc MAS Director, Interventional Cardiology Director, Vascular Laboratory VA Eastern Colorado Healthcare
Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease
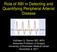 Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease Difference in AAA size between US and Surgeon 2 1 0-1 -2-3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean AAA size between US and Surgeon Kathleen G. Raman MD,
Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease Difference in AAA size between US and Surgeon 2 1 0-1 -2-3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean AAA size between US and Surgeon Kathleen G. Raman MD,
Medical Therapy for Peripheral Artery Disease
 Medical Therapy for Peripheral Artery Disease Beau M. Hawkins, MD, FSCAI University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK Sahil A. Parikh, MD, FSCAI Columbia University Medical Center,
Medical Therapy for Peripheral Artery Disease Beau M. Hawkins, MD, FSCAI University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK Sahil A. Parikh, MD, FSCAI Columbia University Medical Center,
Macrovascular Residual Risk. What risk remains after LDL-C management and intensive therapy?
 Macrovascular Residual Risk What risk remains after LDL-C management and intensive therapy? Defining Residual Vascular Risk The risk of macrovascular events and microvascular complications which persists
Macrovascular Residual Risk What risk remains after LDL-C management and intensive therapy? Defining Residual Vascular Risk The risk of macrovascular events and microvascular complications which persists
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD): Presentation, Diagnosis, and Treatment
 Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD): Presentation, Diagnosis, and Treatment Prepared and Presented by Jon Manocchio, Pharm D Blanchard Valley Hospital October 2011 Introduction PAD is a condition that is
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD): Presentation, Diagnosis, and Treatment Prepared and Presented by Jon Manocchio, Pharm D Blanchard Valley Hospital October 2011 Introduction PAD is a condition that is
Peripheral arterial disease versus other localizations of vascular disease: The ATTEST study
 Peripheral arterial disease versus other localizations of vascular disease: The ATTEST study Jacques Blacher, MD, PhD, a Patrice Cacoub, MD, PhD, b François Luizy, MD, a Jean-Jacques Mourad, MD, PhD, c
Peripheral arterial disease versus other localizations of vascular disease: The ATTEST study Jacques Blacher, MD, PhD, a Patrice Cacoub, MD, PhD, b François Luizy, MD, a Jean-Jacques Mourad, MD, PhD, c
Eugene Barrett M.D., Ph.D. University of Virginia 6/18/2007. Diagnosis and what is it Glucose Tolerance Categories FPG
 Diabetes Mellitus: Update 7 What is the unifying basis of this vascular disease? Eugene J. Barrett, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine and Pediatrics Director, Diabetes Center and GCRC Health System
Diabetes Mellitus: Update 7 What is the unifying basis of this vascular disease? Eugene J. Barrett, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine and Pediatrics Director, Diabetes Center and GCRC Health System
Controversies in Preventative Cardiology
 Controversies in Preventative Cardiology Francisco Lopez-Jimenez, M.D., M.Sc, FACC, FAHA Professor of Medicine, Mayo Medical School Chair, Division of Preventive Cardiology Co-Director, Artificial Intelligence
Controversies in Preventative Cardiology Francisco Lopez-Jimenez, M.D., M.Sc, FACC, FAHA Professor of Medicine, Mayo Medical School Chair, Division of Preventive Cardiology Co-Director, Artificial Intelligence
Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease Aditya M. Sharma 1 and Herbert D. Aronow 2 1 Saint Joseph Mercy Hospital, Department of Internal Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI, 2 Michigan Heart and Vascular Institute,
Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease Aditya M. Sharma 1 and Herbert D. Aronow 2 1 Saint Joseph Mercy Hospital, Department of Internal Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI, 2 Michigan Heart and Vascular Institute,
Consensus document: Screening and Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation
 Consensus document: Screening and Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation Yong-Seog Oh, M.D.,Ph.D. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary s Hospital, College of Medicine, The
Consensus document: Screening and Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation Yong-Seog Oh, M.D.,Ph.D. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary s Hospital, College of Medicine, The
LLL Session - Nutrition support in diabetes and dyslipidemia. Dyslipidemia: targeting the management of cardiovascular risk factors. M.
 ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 LLL Session - Nutrition support in diabetes and dyslipidemia Dyslipidemia: targeting the management of cardiovascular risk factors M. Leon Sanz (ES) Dyslipidemia: Targeting
ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 LLL Session - Nutrition support in diabetes and dyslipidemia Dyslipidemia: targeting the management of cardiovascular risk factors M. Leon Sanz (ES) Dyslipidemia: Targeting
Dyslipidemia in women: Who should be treated and how?
 Dyslipidemia in women: Who should be treated and how? Lale Tokgozoglu, MD, FACC, FESC Professor of Cardiology Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Ankara, Turkey. Cause of Death in Women: European
Dyslipidemia in women: Who should be treated and how? Lale Tokgozoglu, MD, FACC, FESC Professor of Cardiology Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Ankara, Turkey. Cause of Death in Women: European
Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Frank J. Green, M.D., F.A.C.C. St. Vincent Medical Group
 Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Frank J. Green, M.D., F.A.C.C. St. Vincent Medical Group AHA Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations Balance calorie intake and physical activity to
Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Frank J. Green, M.D., F.A.C.C. St. Vincent Medical Group AHA Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations Balance calorie intake and physical activity to
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease. Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010
 Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
