Renal Replacement Therapies in Kidney Disease
|
|
|
- Muriel Arlene Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sanjiv Mahajan* Chief Medical Officer, Department of Nephrology & Medicine, Safdarjung Hospital & Vardhman Mahavir Medical College, New Delhi, India ABSTRACT Renal replacement therapy (RRT) artificially replaces function of the kidney when it is damaged. Plethora of modalities has developed, each having its unique indication and advantages. The first step in choosing RRT is to establish whether damage is acute or chronic. There are specific indications in starting RRT in each. Hemodialysis and hemofiltration utilizes external filters while in peritoneal dialysis, peritoneal membrane of the patient is used for the purpose. Slow continuous therapies such as sustained low-efficiency dialysis and continuous renal replacement therapy have developed as variant of hemodialysis and hemofiltration making it possible to dialyze hemodynamically unstable patients. Except the transport characteristics of the peritoneum all other variables in RRT can be adjusted to achieve the desired response. Understanding of the underlying principles of each modality helps in choosing a right RRT for the patient. Various types of dialysis have been discussed in detail in the article. Key words: renal replacement therapy, hemodialysis, hemofiltration, peritoneal dialysis, sustained low-efficiency dialysis, continuous renal replacement therapy. INTRODUCTION Kidney is the only organ in the body whose function can be artificially replaced. If damage occurs to kidneys, the kidneys may become inefficient or may stop functioning altogether. Hemodialysis is the traditional method for replacing renal function. Over the last three decades, there has been rapid evolution of various modalities designated as renal replacement therapies (RRTs). RRTs, their indications, advantages and advances are reviewed in this article to help physicians chose a specific therapy as per patient s needs. DISCUSSION The first step in the administration of a specific RRT is to esablish whether the damage to kidney is acute or chronic. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI): An acute injury to kidneys can occur due to various causes such as toxins, drugs, infection or immune response. 1 The subsequent damage is largely reversible if the underlying cause is removed. However, the process may take days to weeks. Hence *Corresponding Author: Dr. Sanjiv Mahajan C-1-117, Lajpat Nagar, New Delhi Mobile No.: drsanjivmahajan@yahoo.com in the intermittent period RRT may be required for patient s survival in certain conditions. Table1: Indications for RRT in the patient with acute kidney injury 1. Uremic complications, such as pericarditis, encephalopathy, or gastrointestinal bleeding. 2. Volume overload not treatable with diuretics. 3. Severe hyperkalemia. 4. Resistant acidosis 5. Acute poisoning with a dialyzable substance Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): If an acute kidney injury does not reverse, it may progress to chronic stage. Chronic damage to kidneys also occur due to continuous insult from systemic diseases such as Diabetes & Hypertension. In such cases, the kidney function decreases progressively. Finally, a stage is reached when survival is compromised and RRT is mandated. Table-2: Indications for RRT in the patient with chronic kidney disease 1. GFR below 10mL/min 2. Fluid overload refractory to diuretics 3. Hypertension poorly responsive to antihypertensive medications 4. Refractory metabolic disturbances such as hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis, hypercalcemia, hypocalcemia, and hyperphosphatemia 5. Persistent nausea and vomiting 6. Evidence of malnutrition 7. Pericarditis or pleuritis 8. Uremic encephalopathy or neuropathy 9. Bleeding diathesis 1 Int J Res Med. 2016; 5(2); 1-5 e ISSN: p ISSN:
2 RRT can be done by Dialysis or Hemofiltration which have further evolved into various specific categories. Renal transplantation can also be said to be a type of RRT. Dialysis is divided into two broad categories: Hemodialysis & Peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis: In Hemodialysis, waste products & excess water are removed extra corporeally using a dialyser. A vascular access, dialyser, dialysate and a hemodialysis machine are the basic requirements. 1. Vascular access: It is the site on the body where blood is removed and returned during dialysis. The vascular access should allow continuous high volumes of blood flow. A vascular access may be temporary or permanent. a. Temporary vascular access: i. Venous catheter: A venous catheter is placed in jugular vein or femoral vein. In acute & emergency conditions and in non ambulatory patients, femoral vein may be used. Otherwise, jugular vein is used which is safer & lasts longer. Catheter in subclavian vein is now largely abandoned due to high incidence of stenosis. 2 ii. Arterio-venous graft: An arteriovenous graft is a synthetic tube made of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) that is grafted between an artery and vein. The graft becomes an artificial vein that can be used repeatedly for needle placement and blood access during hemodialysis. A graft can be used within 2 or 3 weeks after placement and can last several years. b. Permanent vascular access: Arterio-venous fistula (A-V fistula): It is made by joining an artery and a vein. Fistulas are usually made in the nondominant arm. They are generally created on the following sites: On the dorsum of the hand below the thumb: the 'snuffbox' fistula - the dorsal branch of the radial artery is anastomosed to the cephalic vein. The forearm: Brescia-Cimino fistula - the radial artery is anastomosed to the cephalic vein. The elbow: Brachiocephalic fistula - the brachial artery is anastomosed to the cephalic vein. A fistula takes on an average 4 6 weeks to mature. 2. Dialyser: A dialyser is different from a typical filter as the blood is not filtered out. Rather the undesirable elements in the blood and excess of water are absorbed. The main element in a dialyser is a semipermeable membrane through which small molecules can pass by diffusion. It consists of a cylindrical bundle of hollow fibers, whose walls are composed of semipermeable membrane. It is then assembled into a clear plastic cylindrical shell with four openings. One opening or blood port at each end of the cylinder communicates with each end of the bundle of hollow fibers. This forms the "blood compartment" of the dialyzer. Two other ports are cut into the side of the cylinder. These communicate with the space around the hollow fibers and forms the "dialysate compartment." Blood is pumped via the blood ports through this bundle of very thin capillary-like tubes and the dialysate is pumped through the space surrounding the fibers. Initial membranes were made of cellulose. Cellulose acetate and modified cellulose dialysers are still used. But most membranes are now made from synthetic materials, using polymers such as polyarylethersulfone, polyamide, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polycarbonate, and polyacrylonitrile. 3 The main advantage of synthetic membranes is that they activate complement to a lesser extent than cellulose membranes Dialysate: It is the fluid consisting of solutes that flow through the dialyser (Table-3). It helps in filtering out of the toxins from the blood. The composition can be varied depending upon the biochemical profile of the patient. 4. Hemodialysis Machine: It supplies the blood and the dialysate to the dialyser. The blood pump takes the blood from the patient via the vascular access and supplies it to the dialyser. The blood is confined to the disposable plastic tubing and does not come in contact with any part of the machine. The dialysate pump mixes the 2 Int J Res Med. 2016; 5(2); 1-5 e ISSN: p ISSN:
3 concentrate with water and moves the dialysate through the dialyser. The blood pump in the hemodialysis machine can control the rate of blood flow. It is generally kept in the range of ml/min. To prevent clotting, it is periodically mixed with heparin. Simultaneously, the dialysate pump mixes the concentrate with water thus making the dialysate of desired concentration. The dialysate is also pumped to the dialyser but from opposite end. In the dialyser, blood and dialysate flow in opposite direction (counter current). This counter current mechanism helps to maintain the concentration gradient along the whole length of the dialyser The dialysate pump also has adjustable flow rate and it is typically kept in the range of ml/min. In the dialyser, blood is pumped through the bundle of very thin capillary like tubes and the dialysate is pumped through the space surrounding the fibers. The impurities in the blood like urea diffuses to the dialysate. Pressure gradients are applied to move fluid from the blood to the dialysate compartment (ultrafiltration). During ultrafiltration, the solutes in the blood also move out by convection. The purified blood is then returned to the body. A typical hemodialysis session lasts 4 hours and needs to be repeated every hours. Table-3: Composition of a typical dialysate Glucose Sodium (Na) Potassium (K) Bicarbonate Calcium (Ca) Magnesium (Mg) 200mg/dL 140 meq/l 1-3 meq/l meq/l 2.5 meq/l 1mEq/L Hemofiltration: The procedure of hemofiltration is somewhat similar to hemodialysis but the principle involved is different. In hemofiltration, dialysate is not used. Solute movement with hemofiltration occurs by convection 5. When the blood flows through the dialyser, a positive hydrostatic pressure drives water and solutes across the filter membrane. This filtrate is drained. The excess fluid that is drained (after considering for required ultrafiltration) is replaced by an isotonic replacement fluid. The advantage of hemofiltration is that convection overcomes the reduced removal rate of larger solutes (due to their slow speed of diffusion) seen in hemodialysis. Thus clearance of phosphate, many uremic toxins such as complement factor D, leptin, erythropoiesis inhibitors is increased. 6 When hemofiltration is combined with hemodialysis, the process is known as hemodiafiltration. Slow Continuous Therapies: Slow Continuous Therapies are used for hemodynamically unstable, fluid overloaded, catabolic septic patients. 7 These patients are generally having AKI or multi organ failure. The following types of slow continuous therapies have developed. Sustained Low-efficiency Dialysis (SLED): In SLED, standard HD equipment is used with reduced dialysate and blood flow rates. The blood flow rate is kept at ml/min while dialysate flow rate is kept at 100 ml/min. The session is continued for 6-10 hours. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT): There are many variations of CRRT. They are categorized according to the access characteristics and also according to the modality chosen. In Arteriovenous (AV) an arterial catheter allows blood to flow into the extracorporeal circuit by the driving force of the systemic blood pressure. The blood is returned by the venous catheter. It does not require an extracorporeal blood pump. But there is risk of arterial embolization and blood flow may be unreliable in hypotensive patients. In Venovenous (VV) both catheters are placed in veins. An extracorporeal blood pump is required to circulate blood through the extracorporeal circuit. Irrespective of the access, any of the three modalities viz hemodialysis (HD), hemofiltration (H) or hemodiafiltration (HDF) can be used. Thus the possible variations are CAVHD, CAVH, CAVHDF, CVVHD, CVVH & CVVHDF. Peritoneal Dialysis: The Peritoneal dialysis utilizes the peritoneum as the dialyser. Peritoneal dialysis may be done acutely or chronically with different types of catheter and machines but the 3 Int J Res Med. 2016; 5(2); 1-5 e ISSN: p ISSN:
4 underlying basic principle is the same. To understand Peritoneal dialysis it is necessary to have a knowledge of structure of peritoneum. Structure of the Peritoneum: Peritoneum is a serous membrane of the abdominal cavity. It consists of two parts: Visceral, which forms 80% & covers the gut and other viscera. It also forms the omentum and the mesentry. Parietal forms 20% & lines the inner surface of the abdominal wall. Peritoneum consists of mesothelial cells resting on the basement membrane. Its Interstitium contains the peritoneal capillaries & lymphatics. Principle: All types of peritoneal dialysis are performed by introducing peritoneal dialysate in the peritoneal cavity. This is achieved by inserting peritoneal dialysis catheter which permits bi-directional flow of dialysate. 8 The passage of fluid or solutes from the blood vessels in the peritoneum to the dialysate in the peritoneal cavity or vice versa is met with six resistance sites viz fluid film, endothelial layer, capillary basement membrane, interstitium, mesothelium & fluid film of peritoneal cavity. The most important principle for solute removal in PD is diffusion, for which the driving force is the concentration gradient between the blood and the dialysis fluid. Small solutes move quickly through the membrane creating equilibrium during the dwell period. Larger solutes move slowly across the peritoneum, reaching equilibrium point takes a long time. Fluid removal in PD is by osmosis. Both solute and fluid removal in PD is controlled by various factors listed in. Table-4: Factors controlling solute and fluid removal in PD 1. Glucose concentration of the dialysate 2. Dwell time of the dialysate 3. Volume of the dialysate 4. Peritoneal membrane characteristics Types of Peritoneal Dialysis Acute Peritoneal Dialysis: It is done for acute kidney injury. For acute peritoneal dialysis, a short term, hard PVC catheter is used. Before insertion, patient's bladder is emptied to prevent accidental puncture. The catheter is inserted by puncturing the abdominal wall about 2.5 cm below the umbilicus in the midline. Through the catheter, the dialysate of 1-2 L is introduced over a 10 minute period (inflow time). The dialysate remains in the cavity for around 30 minutes (dwell time) after which it is allowed to drain over a 20 minute period (outflow time). The cycles are then repeated. During acute PD, it is essential to monitor electrolytes particularly Na & K. Potassium is generally required to be supplemented after 4-8 cycles. The cycles can be continued for hrs after which risk of peritonitis increases considerably. Long-term Peritoneal Dialysis: It is prescribed to CKD patients. It is of two main types: Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) and Continuous Cycling Peritoneal Dialysis (CCPD). The catheters inserted in both remain for many years and are softer and flexible. The double cuff straight Tenckhoff catheter, a silicone catheter, is the most commonly used catheter. The distal (intraabdominal) segment of the catheter is positioned freely in the intraabdominal pelvic area. The catheter's midportion is implanted within the wall of the abdomen via one to two Dacron velour cuffs. The deep cuff is embedded in the abdominal rectus muscle. The superficial cuff in both double cuff and single cuff catheters is placed subcutaneously approximately 2 cm from the catheter exit site on the abdominal wall. Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD): CAPD involves manual exchange of dialysate and does not require any machine. The patient may remain ambulatory while the dialysate remains in the peritoneal cavity. The fluid is allowed to stay in the abdomen for several hours allowing excess fluid and toxins to move from the blood to the dialysate. At the end of the dwell, the fluid is drained by gravity into a collecting bag and the same process is repeated. Draining dialysate and replacing it with fresh solution takes about 30 minutes and is repeated three to five times every day. The last exchange of the day may be done before going to sleep, and the dialysate is left in overnight. 4 Int J Res Med. 2016; 5(2); 1-5 e ISSN: p ISSN:
5 Continuous Cycling Peritoneal Dialysis (CCPD) / Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD): It uses a machine called a cycler. A cycler circulates dialysate solution in and out of the peritoneal cavity at evenly spaced intervals during the night for eight to 10 hours. In the morning, dialysate flows into the abdomen and the dialysate is carried in the peritoneal cavity during the day. During that time, patients do their daily activities. Before the patient goes to sleep, the catheter is reattached to the cycler, the fluid is drained out and the night exchanges are started. This cycle is repeated daily. CONCLUSION: RRT has evolved into a unique modality that provides both short and long term support for patient s survival in the absence of renal function. Except the transport characteristics of the peritoneum, all other variables in RRT can be adjusted to achieve the desired response. Specific type of RRT for a particular patient should be carefully chosen considering various factors such as residual renal function, co-morbidities, hemodynamic stability, access to hospital services, work profile of the patient, physical environment and patient s desire. REFERENCES 1. Zarbock A, Gomez H, Kellum JA. Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury revisited: pathophysiology, prevention and future therapies. Curr Opin Crit Care Dec;20(6): Agarwal AK. Central vein stenosis. Am J Kidney Dis Jun;61(6): Smeby LC, Widerøe TE, Balstad T, Jørstad S. Biocompatibility aspects of cellophane, cellulose acetate, polyacrylonitrile, polysulfone and polycarbonate hemodialyzers. Blood Purif. 1986;4(1-3): De Broe ME, van Waeleghem JP, Heyrman R, De Backer W. Biocompatibility of a polycarbonate membrane. A preliminary report. Blood Purif. 1986;4(1-3): Hall N, Fox A. Renal replacement therapies in critical care. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain. 2006;6(5): Van Laecke S., Wilde, K D, Vanholder R. Online Hemodiafiltration. Artificial Organs. 2006; 30: S Sarkar. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT). The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology. 2008;21: Tenckhoff H. Peritoneal Dialysis Today: A New Look. Nephron. 1974;12(5): Int J Res Med. 2016; 5(2); 1-5 e ISSN: p ISSN:
End-Stage Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology
 End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
Drug Use in Dialysis
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Drug Use in Dialysis Drambarean, B. (2017). Drug Use in Dialysis. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. DIALYSIS
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Drug Use in Dialysis Drambarean, B. (2017). Drug Use in Dialysis. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. DIALYSIS
Management of the patient with established AKI. Kelly Wright Lead Nurse for AKI King s College Hospital
 Management of the patient with established AKI Kelly Wright Lead Nurse for AKI King s College Hospital Medical management Medical management Respiratory- pulmonary oedema, repositioning- upright, oxygen
Management of the patient with established AKI Kelly Wright Lead Nurse for AKI King s College Hospital Medical management Medical management Respiratory- pulmonary oedema, repositioning- upright, oxygen
Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
 Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS St George Hospital Renal Department, reviewed 2017 St George Hospital Renal Department RENAL SELF LEARNING PACKAGE INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL
Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS St George Hospital Renal Department, reviewed 2017 St George Hospital Renal Department RENAL SELF LEARNING PACKAGE INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Peritoneal Dialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. There are 2 types of PD: continuous ambulatory
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
Renal Replacement Therapy in ICU. Dr. Sunil Sharma Senior Resident Dept of Pulmonary Medicine
 Renal Replacement Therapy in ICU Dr. Sunil Sharma Senior Resident Dept of Pulmonary Medicine Introduction Need for RRT in patients with ARF is a common & increasing problem in ICUs Leading cause of ARF
Renal Replacement Therapy in ICU Dr. Sunil Sharma Senior Resident Dept of Pulmonary Medicine Introduction Need for RRT in patients with ARF is a common & increasing problem in ICUs Leading cause of ARF
Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Renal Failure
 CHAPTER 82 Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Renal Failure R. Deshpande Introduction Acute renal failure (ARF) is defined as an abrupt decrease in renal function sufficient to result in retention of nitrogenous
CHAPTER 82 Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Renal Failure R. Deshpande Introduction Acute renal failure (ARF) is defined as an abrupt decrease in renal function sufficient to result in retention of nitrogenous
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
ECMO & Renal Failure Epidemeology Renal failure & effect on out come
 ECMO Induced Renal Issues Transient renal dysfunction Improvement in renal function ECMO & Renal Failure Epidemeology Renal failure & effect on out come With or Without RRT Renal replacement Therapy Utilizes
ECMO Induced Renal Issues Transient renal dysfunction Improvement in renal function ECMO & Renal Failure Epidemeology Renal failure & effect on out come With or Without RRT Renal replacement Therapy Utilizes
Kidney Decisions Aid
 Kidney Decisions Aid A G U I D E F O R P E O P L E W H O H A V E, O R K N O W S O M E O N E, W I T H C H R O N I C K I D N E Y D I S E A S E, A N D T O A I D I N T H E D E C I S I O N A B O U T W H I C
Kidney Decisions Aid A G U I D E F O R P E O P L E W H O H A V E, O R K N O W S O M E O N E, W I T H C H R O N I C K I D N E Y D I S E A S E, A N D T O A I D I N T H E D E C I S I O N A B O U T W H I C
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL. Living well with Kidney Disease
 HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
Patient Education Programme. Kidney Options Guiding you when kidneys fail
 Patient Education Programme Kidney Options Guiding you when kidneys fail About the kidneys What do healthy kidneys do? Your two kidneys work more than you realise. The kidneys remove excess body water
Patient Education Programme Kidney Options Guiding you when kidneys fail About the kidneys What do healthy kidneys do? Your two kidneys work more than you realise. The kidneys remove excess body water
PD In Acute Kidney Injury. February 7 th -9 th, 2013
 PD In Acute Kidney Injury February 7 th -9 th, 2013 Objectives PD as a viable initial therapy PD in AKI PD versus dhd PD versus CVVHD Why not PD first PD for AKI Early days (1970 s) PD was the option of
PD In Acute Kidney Injury February 7 th -9 th, 2013 Objectives PD as a viable initial therapy PD in AKI PD versus dhd PD versus CVVHD Why not PD first PD for AKI Early days (1970 s) PD was the option of
UNDERSTANDING THE CRRT MACHINE
 UNDERSTANDING THE CRRT MACHINE Helen Dickie Renal Sister Critical Care Unit Guy s and St.Thomas NHS Foundation Trust 18.10.14 RRT options - IHD vs CRRT (1) Intermittent HaemoDialysis e.g. 4hrs daily or
UNDERSTANDING THE CRRT MACHINE Helen Dickie Renal Sister Critical Care Unit Guy s and St.Thomas NHS Foundation Trust 18.10.14 RRT options - IHD vs CRRT (1) Intermittent HaemoDialysis e.g. 4hrs daily or
Kidney Failure. Haemodialysis
 Kidneys & Kidney Failure 2 Haemodialysis This booklet will help you to know the process of Haemodialysis in detail. It will also tell you about the disposables of Haemodialysis. In the end the advantages
Kidneys & Kidney Failure 2 Haemodialysis This booklet will help you to know the process of Haemodialysis in detail. It will also tell you about the disposables of Haemodialysis. In the end the advantages
Physiology of Blood Purification: Dialysis & Apheresis. Outline. Solute Removal Mechanisms in RRT
 Physiology of Blood Purification: Dialysis & Apheresis Jordan M. Symons, MD University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital Outline Physical principles of mass transfer Hemodialysis
Physiology of Blood Purification: Dialysis & Apheresis Jordan M. Symons, MD University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital Outline Physical principles of mass transfer Hemodialysis
KIDNEY FAILURE TREATMENT OPTIONS Choosing What s Best For You
 KIDNEY FAILURE TREATMENT OPTIONS Choosing What s Best For You What Kidneys Do The kidneys are a pair of bean shaped organs located below your ribcage near the middle of your back. Kidneys play a vital
KIDNEY FAILURE TREATMENT OPTIONS Choosing What s Best For You What Kidneys Do The kidneys are a pair of bean shaped organs located below your ribcage near the middle of your back. Kidneys play a vital
Renal Replacement Therapies
 Renal Replacement Therapies M I H Á L Y T A P O L Y A I, M D, F A S N, F A C P A s s o c i a t e P r o f e s s o r D e p a r t m e n t o f N e p h r o l o g y L o u i s i a n a S t a t e U n i v e r s
Renal Replacement Therapies M I H Á L Y T A P O L Y A I, M D, F A S N, F A C P A s s o c i a t e P r o f e s s o r D e p a r t m e n t o f N e p h r o l o g y L o u i s i a n a S t a t e U n i v e r s
- SLED Sustained Low-Efficiency Dialysis
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD 1 Definition of Terms - SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD 1 Definition of Terms - SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
Acute Kidney Injury- What Is It and How Do I Treat It?
 Acute Kidney Injury- What Is It and How Do I Treat It? Jayant Kumar, MD Renal Medicine Assoc., Albuquerque, NM Incidence of ARF in ICU Causes of ARF Non -ICU ICU 1 KDIGO criteria for AKI Increase in serum
Acute Kidney Injury- What Is It and How Do I Treat It? Jayant Kumar, MD Renal Medicine Assoc., Albuquerque, NM Incidence of ARF in ICU Causes of ARF Non -ICU ICU 1 KDIGO criteria for AKI Increase in serum
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy. Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD 1 Definition of Terms SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD 1 Definition of Terms SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD Definition of Terms SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD Definition of Terms SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Hemodialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
Treatment Options Not Not access
 Treatment Options Treatment options for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) CKD is a permanent condition. Treatment will: Help the patient feel better Not cure the disease Not make the kidneys start working again
Treatment Options Treatment options for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) CKD is a permanent condition. Treatment will: Help the patient feel better Not cure the disease Not make the kidneys start working again
Sid Bhende MD Sentara Vascular Specialists April 28 th Dialysis Access Review: Understanding the Access Options our Patients Face
 Sid Bhende MD Sentara Vascular Specialists April 28 th 2018 Dialysis Access Review: Understanding the Access Options our Patients Face Disclosures Dialysis Background Why is it important? Outline National
Sid Bhende MD Sentara Vascular Specialists April 28 th 2018 Dialysis Access Review: Understanding the Access Options our Patients Face Disclosures Dialysis Background Why is it important? Outline National
Kidney Disease Treatment Options
 Page 1 Fact sheet The kidneys play a number of important roles in your body such as: extracting excess water to make urine (wee) controlling your blood pressure filtering waste products and toxins from
Page 1 Fact sheet The kidneys play a number of important roles in your body such as: extracting excess water to make urine (wee) controlling your blood pressure filtering waste products and toxins from
Introduction to the Native Arteriovenous Fistula: A primer for medical students and radiology residents
 Introduction to the Native Arteriovenous Fistula: A primer for medical students and radiology residents Jesus Contreras, D.O. PGY-4 John Yasmer, D.O. Department of Radiology No Disclosures Objectives Introduce
Introduction to the Native Arteriovenous Fistula: A primer for medical students and radiology residents Jesus Contreras, D.O. PGY-4 John Yasmer, D.O. Department of Radiology No Disclosures Objectives Introduce
RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN ACUTE KIDNEY FAILURE - AN OVERVIEW
 RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN ACUTE KIDNEY FAILURE - AN OVERVIEW Treesa P. Varghese, Department of pharmacy practice St. James College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Thrissure treesapv510@gmail.com Abstract
RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN ACUTE KIDNEY FAILURE - AN OVERVIEW Treesa P. Varghese, Department of pharmacy practice St. James College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Thrissure treesapv510@gmail.com Abstract
UNDERSTANDING PROCESS OF DIALYSIS
 UNDERSTANDING PROCESS OF DIALYSIS Introduction: End-stage renal disease (ESRD), the final stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD), occurs when the kidneys have deteriorated to the point that they are no
UNDERSTANDING PROCESS OF DIALYSIS Introduction: End-stage renal disease (ESRD), the final stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD), occurs when the kidneys have deteriorated to the point that they are no
ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1
 ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1 This document is a supplement to the Online Training. Do not reproduce. Copyright Dialysis4Career. All Rights Reserved. The Renal System - A highly sophisticated
ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1 This document is a supplement to the Online Training. Do not reproduce. Copyright Dialysis4Career. All Rights Reserved. The Renal System - A highly sophisticated
Symposium. Principles of Renal Replacement Therapy in Critically ill children- Indian Perspective
 Symposium DOI- 10.21304/2018.0502.00376 in Critically ill children- Indian Perspective Sidharth Kumar Sethi *, Aliza Mittal**, Rupesh Raina***, Manindar Dhaliwal**** * Senior Consultant, Pediatric Nephrology
Symposium DOI- 10.21304/2018.0502.00376 in Critically ill children- Indian Perspective Sidharth Kumar Sethi *, Aliza Mittal**, Rupesh Raina***, Manindar Dhaliwal**** * Senior Consultant, Pediatric Nephrology
Peritoneal dialysis. Overview. Preparing for dialysis. Links to sections in topic Other topics available on website
 Peritoneal dialysis This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. Visit www.infokid.org.uk to find more topics about conditions, tests & diagnosis, treatments and supporting
Peritoneal dialysis This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. Visit www.infokid.org.uk to find more topics about conditions, tests & diagnosis, treatments and supporting
Recent advances in CRRT
 Recent advances in CRRT JAE IL SHIN, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children s Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Pediatric AKI epidemiology and demographics
Recent advances in CRRT JAE IL SHIN, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children s Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Pediatric AKI epidemiology and demographics
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN CHILDREN. Bashir Admani KPA Precongress 24/4/2018
 ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN CHILDREN Bashir Admani KPA Precongress 24/4/2018 Case presentation SP 11month old Presenting complaint: bloody diarrhea, lethargy On exam: dehydration,
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN CHILDREN Bashir Admani KPA Precongress 24/4/2018 Case presentation SP 11month old Presenting complaint: bloody diarrhea, lethargy On exam: dehydration,
MODALITIES of Renal Replacement Therapy in AKI
 MODALITIES of Renal Replacement Therapy in AKI Jorge Cerdá, MD, MS, FACP, FASN Clinical Professor of Medicine Albany Medical College Albany, NY, USA cerdaj@mail.amc.edu In AKI, RRT is a multidimensional
MODALITIES of Renal Replacement Therapy in AKI Jorge Cerdá, MD, MS, FACP, FASN Clinical Professor of Medicine Albany Medical College Albany, NY, USA cerdaj@mail.amc.edu In AKI, RRT is a multidimensional
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) How Wise is Early Dialysis in Critically Ill Patients? Modalities of Dialysis
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) How Wise is Early Dialysis in Critically Ill Patients? A common condition in ICU patients Associated with high mortality and morbidity Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) is the cornerstone
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) How Wise is Early Dialysis in Critically Ill Patients? A common condition in ICU patients Associated with high mortality and morbidity Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) is the cornerstone
Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family.
 PEP CONNECT PEP Talk Outline P a t i e n t E d u c a t i o n P r o g r a m Your Treatment Options Part 1 Peritoneal Dialysis Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family. This
PEP CONNECT PEP Talk Outline P a t i e n t E d u c a t i o n P r o g r a m Your Treatment Options Part 1 Peritoneal Dialysis Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family. This
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses
 Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses A Primer ABCs of PD R x Betty Kelman RN-EC MEd CNeph (C) Toronto General Hospital University Health Network Toronto, Ontario, Canada A moment to remember
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses A Primer ABCs of PD R x Betty Kelman RN-EC MEd CNeph (C) Toronto General Hospital University Health Network Toronto, Ontario, Canada A moment to remember
Objectives. Peritoneal Dialysis vs. Hemodialysis 02/27/2018. Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring
 Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring Christine B. Sethna, MD, EdM Division Director, Pediatric Nephrology Cohen Children s Medical Center Associate Professor Hofstra Northwell School
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring Christine B. Sethna, MD, EdM Division Director, Pediatric Nephrology Cohen Children s Medical Center Associate Professor Hofstra Northwell School
Salma Hindy Mahum Qureshi
 Salma Hindy Mahum Qureshi 1 There are two kidneys in the human body and both are identical in structure and function Located in the abdominal cavity Each kidney is 10 cm long and 6.5 cm wide Weights 125-170
Salma Hindy Mahum Qureshi 1 There are two kidneys in the human body and both are identical in structure and function Located in the abdominal cavity Each kidney is 10 cm long and 6.5 cm wide Weights 125-170
Nurse-Pharmacist Collaboration in the Delivery of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
 Cedarville University DigitalCommons@Cedarville Pharmacy Faculty Presentations School of Pharmacy 2-23-2012 Nurse-Pharmacist Collaboration in the Delivery of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Jeb Ballentine
Cedarville University DigitalCommons@Cedarville Pharmacy Faculty Presentations School of Pharmacy 2-23-2012 Nurse-Pharmacist Collaboration in the Delivery of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Jeb Ballentine
CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test. AKI & CRRT Conference 2018
 CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test AKI & CRRT Conference 2018 Question 1 Which ONE of the following statements regarding solute clearance in CRRT is MOST correct? A. Convective and diffusive solute
CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test AKI & CRRT Conference 2018 Question 1 Which ONE of the following statements regarding solute clearance in CRRT is MOST correct? A. Convective and diffusive solute
What is renal failure?
 What is renal failure? The kidney is a very important organ, and cannot be restored to health once it fails. However, it is possible to avoid or retard the deterioration of its functionality if therapy
What is renal failure? The kidney is a very important organ, and cannot be restored to health once it fails. However, it is possible to avoid or retard the deterioration of its functionality if therapy
Dialysis in the Acute Setting
 Dialysis in the Acute Setting medicine2.missouri.edu/jahm/dialysis-in-the-acute-setting/ October 8, 2015 Kunal Malhotra, MD Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, University of Missouri School
Dialysis in the Acute Setting medicine2.missouri.edu/jahm/dialysis-in-the-acute-setting/ October 8, 2015 Kunal Malhotra, MD Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, University of Missouri School
Nursing Care of the Dialysis Patient. Adrian Hordon, MSN, RN
 Nursing Care of the Dialysis Patient Adrian Hordon, MSN, RN Understand principles of hemodialysis Recognize different access ports Identify side effects and complications Discuss nursing care for pre and
Nursing Care of the Dialysis Patient Adrian Hordon, MSN, RN Understand principles of hemodialysis Recognize different access ports Identify side effects and complications Discuss nursing care for pre and
Oxford Kidney Unit. Treatment options for chronic kidney disease A brief overview
 Oxford Kidney Unit Treatment options for chronic kidney disease A brief overview You may feel well at the moment and may not have any symptoms from your kidney disease, but it is important that you understand
Oxford Kidney Unit Treatment options for chronic kidney disease A brief overview You may feel well at the moment and may not have any symptoms from your kidney disease, but it is important that you understand
Continuous renal replacement therapy. David Connor
 Continuous renal replacement therapy David Connor Overview Classification of AKI Indications Principles Types of CRRT Controversies RIFL criteria Stage GFR Criteria Urine Output Criteria Risk Baseline
Continuous renal replacement therapy David Connor Overview Classification of AKI Indications Principles Types of CRRT Controversies RIFL criteria Stage GFR Criteria Urine Output Criteria Risk Baseline
UAB CRRT Primer Ashita Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham
 UAB CRRT Primer 2018 Ashita Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham 1 CRRT Primer Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) is a "catch all" term used for all the continuous modes of renal
UAB CRRT Primer 2018 Ashita Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham 1 CRRT Primer Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) is a "catch all" term used for all the continuous modes of renal
* It is proportionate to body size and the reference value is usually expressed after correction for body surface area as 120 ± 25 ml/min/1.
 Ahmad Al-zoubi Glomerular filtration rate : is the sum of the ultrafiltration rates from plasma into the Bowman s space in each nephron and is a measure of renal excretory function *co : 6L *renal blood
Ahmad Al-zoubi Glomerular filtration rate : is the sum of the ultrafiltration rates from plasma into the Bowman s space in each nephron and is a measure of renal excretory function *co : 6L *renal blood
egfr 34 ml/min egfr 130 ml/min Am J Kidney Dis 2002;39(suppl 1):S17-S31
 Update on Renal Therapeutics Caroline Ashley Lead Pharmacist Renal Services UCL Centre for Nephrology, Royal Free Hospital, London Kongress für Arzneimittelinformation January 2011 What are we going to
Update on Renal Therapeutics Caroline Ashley Lead Pharmacist Renal Services UCL Centre for Nephrology, Royal Free Hospital, London Kongress für Arzneimittelinformation January 2011 What are we going to
Implementing therapy-delivery, dose adjustments and fluid balance. Eileen Lischer MA, BSN, RN, CNN University of California San Diego March 6, 2018
 Implementing therapy-delivery, dose adjustments and fluid balance. Eileen Lischer MA, BSN, RN, CNN University of California San Diego March 6, 2018 Objectives By the end of this session the learner will
Implementing therapy-delivery, dose adjustments and fluid balance. Eileen Lischer MA, BSN, RN, CNN University of California San Diego March 6, 2018 Objectives By the end of this session the learner will
Treatment choices for someone with Stage 5 kidney disease are:
 Information for patients about advanced kidney disease Dialysis and non-dialysis treatments DOCUMENT PREPARED FOR This information is to help you understand some key issues about dialysis; it is designed
Information for patients about advanced kidney disease Dialysis and non-dialysis treatments DOCUMENT PREPARED FOR This information is to help you understand some key issues about dialysis; it is designed
Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
 Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Farahnak Assadi Fatemeh Ghane Sharbaf Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Principles and Practice Farahnak Assadi, M.D. Professor Emeritus Department
Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Farahnak Assadi Fatemeh Ghane Sharbaf Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Principles and Practice Farahnak Assadi, M.D. Professor Emeritus Department
Fundamentals of DIALYSIS
 Fundamentals of DIALYSIS Knowing Your Kidneys Healthy Kidneys are the body s cleaning crew These are twin bean shaped organs, of the size of fist They make up a filter system for the blood & reabsorb almost
Fundamentals of DIALYSIS Knowing Your Kidneys Healthy Kidneys are the body s cleaning crew These are twin bean shaped organs, of the size of fist They make up a filter system for the blood & reabsorb almost
Peritoneal Dialysis Program King Campus 2757 King Street East Hamilton, Ontario ext
 Peritoneal Dialysis Program King Campus 2757 King Street East Hamilton, Ontario 905-522-1155 ext. 38275 1 Table of Contents Page What is peritoneal dialysis? 1 How does this happen? 1 What are the types
Peritoneal Dialysis Program King Campus 2757 King Street East Hamilton, Ontario 905-522-1155 ext. 38275 1 Table of Contents Page What is peritoneal dialysis? 1 How does this happen? 1 What are the types
Haemodialysis. Overview. Preparing for haemodialysis. Links to sections in topic Other topics available on website. Fistula
 Haemodialysis This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. Visit www.infokid.org.uk to find more topics about conditions, tests & diagnosis, treatments and supporting
Haemodialysis This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. Visit www.infokid.org.uk to find more topics about conditions, tests & diagnosis, treatments and supporting
Utopia Health Career Center, LLC. Do not distribute without permission.
 Introduction What is dialysis and a brief history. What laws govern dialysis treatments. How to ensure high quality care for patients. How to behave in a professional way. How to become certified. We don
Introduction What is dialysis and a brief history. What laws govern dialysis treatments. How to ensure high quality care for patients. How to behave in a professional way. How to become certified. We don
Who? Dialysis for Acute Renal Failure: Who, What, How, and When? Kathleen D. Liu, MD, PhD, MAS June 2011
 Dialysis for Acute Renal Failure: Who, What, How, and When? Kathleen D. Liu, MD, PhD, MAS June 2011 Dorre Nicholau MD PhD Clinical Professor Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care University of
Dialysis for Acute Renal Failure: Who, What, How, and When? Kathleen D. Liu, MD, PhD, MAS June 2011 Dorre Nicholau MD PhD Clinical Professor Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care University of
CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test. AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT
 CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling at home. He
CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling at home. He
AV Fistula for Dialysis
 AV Fistula for Dialysis Introduction Before starting regular hemodialysis sessions, you must first prepare a vascular access. A vascular access is the site on your body where blood is removed and returned
AV Fistula for Dialysis Introduction Before starting regular hemodialysis sessions, you must first prepare a vascular access. A vascular access is the site on your body where blood is removed and returned
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT)
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 21 Number 1 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) S Sarkar Citation S Sarkar. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT). The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 21 Number 1 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) S Sarkar Citation S Sarkar. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT). The Internet Journal
Kidney Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
 Cheshire and Merseyside Kidney Care Services Renal Replacement Therapy Options for Kidney Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 Renal Replacement Therapy Options for Kidney Patients with Chronic
Cheshire and Merseyside Kidney Care Services Renal Replacement Therapy Options for Kidney Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 Renal Replacement Therapy Options for Kidney Patients with Chronic
Understanding. Your Kidneys. Laurie Biel, RN,BSN, CNN The MGH Center For Renal Education March 28, 2016
 Understanding Your Kidneys Laurie Biel, RN,BSN, CNN The MGH Center For Renal Education March 28, 2016 Today s Discussion - The Role of your kidneys Common causes of kidney disease Treatment for kidney
Understanding Your Kidneys Laurie Biel, RN,BSN, CNN The MGH Center For Renal Education March 28, 2016 Today s Discussion - The Role of your kidneys Common causes of kidney disease Treatment for kidney
Ana Paula Bernardo. CHP Hospital de Santo António ICBAS/ Universidade do Porto
 Ana Paula Bernardo CHP Hospital de Santo António ICBAS/ Universidade do Porto Clinical relevance of hyperphosphatemia Phosphate handling in dialysis patients Phosphate kinetics in PD peritoneal phosphate
Ana Paula Bernardo CHP Hospital de Santo António ICBAS/ Universidade do Porto Clinical relevance of hyperphosphatemia Phosphate handling in dialysis patients Phosphate kinetics in PD peritoneal phosphate
A PATIENT S GUIDE. Author: Dr. A. Patel. Editor: Dr. A. Kadri
 A PATIENT S GUIDE Author: Dr. A. Patel Editor: Dr. A. Kadri 1 ACKNOWLEDGMENT I would like to thank all of those individuals involved in producing this educational book for patients. The printing of this
A PATIENT S GUIDE Author: Dr. A. Patel Editor: Dr. A. Kadri 1 ACKNOWLEDGMENT I would like to thank all of those individuals involved in producing this educational book for patients. The printing of this
Your Kidney Health. Your Choices. Chronic Kidney Disease
 Your Kidney Health Your Choices Your doctor may have told you that you have chronic kidney disease (CKD or advanced kidney disease; or, you may be in kidney failure, and may have to make a decision about
Your Kidney Health Your Choices Your doctor may have told you that you have chronic kidney disease (CKD or advanced kidney disease; or, you may be in kidney failure, and may have to make a decision about
Decision making in acute dialysis
 Decision making in acute dialysis Geoffrey Bihl MB.BCh M.MED FCP(SA) Nephrologist and Director Winelands Kidney and Dialysis Centre Somerset West South Africa Important questions in AKI What is the cause?
Decision making in acute dialysis Geoffrey Bihl MB.BCh M.MED FCP(SA) Nephrologist and Director Winelands Kidney and Dialysis Centre Somerset West South Africa Important questions in AKI What is the cause?
RENAL FAILURE IN ICU. Jo-Ann Vosloo Department Critical Care SBAH
 RENAL FAILURE IN ICU Jo-Ann Vosloo Department Critical Care SBAH DEFINITION: RIFLE criteria Criteria for initiation of RRT Modes of RRT (options) CRRT = continuous renal replacement therapy SCUF : Ultra-filtration
RENAL FAILURE IN ICU Jo-Ann Vosloo Department Critical Care SBAH DEFINITION: RIFLE criteria Criteria for initiation of RRT Modes of RRT (options) CRRT = continuous renal replacement therapy SCUF : Ultra-filtration
Renal Disease and PK/PD. Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology
 Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Dialyzing challenging patients: Patients with hepato-renal conditions
 Dialyzing challenging patients: Patients with hepato-renal conditions Nidyanandh Vadivel MD Medical Director for Living kidney Donor and Pancreas Transplant Programs Swedish Organ Transplant, Seattle Acute
Dialyzing challenging patients: Patients with hepato-renal conditions Nidyanandh Vadivel MD Medical Director for Living kidney Donor and Pancreas Transplant Programs Swedish Organ Transplant, Seattle Acute
Fistula First? Vascular Symposium 4/28/18
 Fistula First? Vascular Symposium 4/28/18 Disclosure I have no financial interest to disclose connected to any of the information presented in this discussion Objectives Scope of Problem Benefits of PD
Fistula First? Vascular Symposium 4/28/18 Disclosure I have no financial interest to disclose connected to any of the information presented in this discussion Objectives Scope of Problem Benefits of PD
PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST. AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences
 PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences INTRODUCTION The peritoneal equilibration test (PET) is a semiquantitative assessment of peritoneal membrane transport
PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences INTRODUCTION The peritoneal equilibration test (PET) is a semiquantitative assessment of peritoneal membrane transport
Home Dialysis. Peritoneal Dialysis. Home Hemodialysis
 Home Dialysis The information provided is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. A licensed healthcare professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and
Home Dialysis The information provided is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. A licensed healthcare professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and
oxiris A single CRRT set with multiple benefits for managing critically ill patients with AKI Adsorption of inflammatory mediators
 oxiris A single CRRT set with multiple benefits for managing critically ill patients with AKI Adsorption of inflammatory mediators Heparin-grafted for reduced thrombogenicity Supports renal function POWERED
oxiris A single CRRT set with multiple benefits for managing critically ill patients with AKI Adsorption of inflammatory mediators Heparin-grafted for reduced thrombogenicity Supports renal function POWERED
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in PICU: explanation/definitions/rationale/background
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in PICU: explanation/definitions/rationale/background Index: 1. Introduction Pg. 1 1.1 Definitions Pg. 2 1.2 Renal replacement therapy principles Pg. 2 2. Continuous
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in PICU: explanation/definitions/rationale/background Index: 1. Introduction Pg. 1 1.1 Definitions Pg. 2 1.2 Renal replacement therapy principles Pg. 2 2. Continuous
Blood Purification Methods
 Blood Purification Methods Kidney function: Excretory (removal of small and middle size molecules) Metabolic (acid- base balance, removal of molecules of higher molecular weight) Endocrine (erythropoetin,
Blood Purification Methods Kidney function: Excretory (removal of small and middle size molecules) Metabolic (acid- base balance, removal of molecules of higher molecular weight) Endocrine (erythropoetin,
Know The Facts About Home Dialysis Choices
 Know The Facts About Home Dialysis Choices Fact Sheet www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents What are my choices for dialysis at home?...3 Why consider home hemodialysis?...4 What are the different types of
Know The Facts About Home Dialysis Choices Fact Sheet www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents What are my choices for dialysis at home?...3 Why consider home hemodialysis?...4 What are the different types of
Active UMMC Protocols
 UMMC CRRT 2018 Active UMMC Protocols 1. Standard CRRT Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with Fixed Ratio Regional Citrate Anticoagulation 2. No Anticoagulation Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with
UMMC CRRT 2018 Active UMMC Protocols 1. Standard CRRT Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with Fixed Ratio Regional Citrate Anticoagulation 2. No Anticoagulation Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with
Gambrosol Trio, clinical studies 91 Glitazone, malnutrition-inflammationatherosclerosis
 Subject Index Acidosis, see Metabolic acidosis Activated carbon, sorbents 337 Adipokines adipose tissue and systemic inflammation 169 functions 167 169 prospects for study in renal patients 171 Adiponectin,
Subject Index Acidosis, see Metabolic acidosis Activated carbon, sorbents 337 Adipokines adipose tissue and systemic inflammation 169 functions 167 169 prospects for study in renal patients 171 Adiponectin,
Rationale for renal replacement therapy in ICU: indications, approaches and outcomes. Richard Beale
 Rationale for renal replacement therapy in ICU: indications, approaches and outcomes Richard Beale RIFLE classification (ADQI group) 2004 Outcome AKIN classification Definition: Abrupt (within 48 hrs)
Rationale for renal replacement therapy in ICU: indications, approaches and outcomes Richard Beale RIFLE classification (ADQI group) 2004 Outcome AKIN classification Definition: Abrupt (within 48 hrs)
Timing, Dosing and Selecting of modality of RRT for AKI - the ERBP position statement
 Timing, Dosing and Selecting of modality of RRT for AKI - the ERBP position statement Prof. Dr. Achim Jörres Dept. of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care Charité University Hospital Campus Virchow Klinikum
Timing, Dosing and Selecting of modality of RRT for AKI - the ERBP position statement Prof. Dr. Achim Jörres Dept. of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care Charité University Hospital Campus Virchow Klinikum
Section 3: Prevention and Treatment of AKI
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2012 KDIGO Summary of ommendation Statements Kidney International Supplements (2012) 2, 8 12; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.7 Section 2: AKI Definition 2.1.1: AKI is defined
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2012 KDIGO Summary of ommendation Statements Kidney International Supplements (2012) 2, 8 12; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.7 Section 2: AKI Definition 2.1.1: AKI is defined
Continuous renal replacement therapy Gulzar Salman Amlani Aga Khan University, School of Nursing, Karachi.
 Special Communication Continuous renal replacement therapy Gulzar Salman Amlani Aga Khan University, School of Nursing, Karachi. Abstract Acute renal failure refers to sudden deterioration in biochemical
Special Communication Continuous renal replacement therapy Gulzar Salman Amlani Aga Khan University, School of Nursing, Karachi. Abstract Acute renal failure refers to sudden deterioration in biochemical
Technical Considerations for Renal Replacement Therapy in Children
 Technical Considerations for Renal Replacement Therapy in Children Timothy E. Bunchman, MD,* Patrick D. Brophy, MD, and Stuart L. Goldstein, MD Summary: Provision of renal replacement therapy to the critically
Technical Considerations for Renal Replacement Therapy in Children Timothy E. Bunchman, MD,* Patrick D. Brophy, MD, and Stuart L. Goldstein, MD Summary: Provision of renal replacement therapy to the critically
Chapter 2 Peritoneal Equilibration Testing and Application
 Chapter 2 Peritoneal Equilibration Testing and Application Francisco J. Cano Case Presentation FW, a recently diagnosed patient with CKD Stage 5, is a 6-year-old boy who has been recommended to initiate
Chapter 2 Peritoneal Equilibration Testing and Application Francisco J. Cano Case Presentation FW, a recently diagnosed patient with CKD Stage 5, is a 6-year-old boy who has been recommended to initiate
You can sleep while I dialyze
 You can sleep while I dialyze Nocturnal Peritoneal Dialysis Dr. Suneet Singh Medical Director, PD, VGH Division of Nephrology University of British Columbia Acknowledgements Melissa Etheridge You can sleep
You can sleep while I dialyze Nocturnal Peritoneal Dialysis Dr. Suneet Singh Medical Director, PD, VGH Division of Nephrology University of British Columbia Acknowledgements Melissa Etheridge You can sleep
Starting Peritoneal Dialysis
 PD Education Booklet 1 Starting Peritoneal Dialysis What you will learn: What your kidneys do Uremia (kidney disease) and its symptoms How Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) helps The two types of PD: Automated
PD Education Booklet 1 Starting Peritoneal Dialysis What you will learn: What your kidneys do Uremia (kidney disease) and its symptoms How Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) helps The two types of PD: Automated
CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test Answers. AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT
 CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test Answers AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling
CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test Answers AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling
Peritoneal Dialysis. Choosing your logo. V2.0 logos. information. you can trust. Certified Member. The Information Standard
 Use of The Information Standard s Member Logos Peritoneal Dialysis Patient Information Choosing your logo The Information Standard has four logo versions for its members. They are designed to fit neatly
Use of The Information Standard s Member Logos Peritoneal Dialysis Patient Information Choosing your logo The Information Standard has four logo versions for its members. They are designed to fit neatly
A Review of Renal Diseases
 A Review of Renal Diseases NDFS 356 Amber McArthur April 3, 2014 0 INTRODUCITON Tom Harkin stated, America s health care system is in crisis precisely because we systematically neglect wellness and prevention.
A Review of Renal Diseases NDFS 356 Amber McArthur April 3, 2014 0 INTRODUCITON Tom Harkin stated, America s health care system is in crisis precisely because we systematically neglect wellness and prevention.
Renal replacement therapy in Pediatric Acute Kidney Injury
 Renal replacement therapy in Pediatric Acute Kidney Injury ASCIM 2014 Dr Adrian Plunkett Consultant Paediatric Intensivist Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Aims of the presentation Important topic: AKI
Renal replacement therapy in Pediatric Acute Kidney Injury ASCIM 2014 Dr Adrian Plunkett Consultant Paediatric Intensivist Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Aims of the presentation Important topic: AKI
Staff-Assisted Home Hemodialysis
 Medical Coverage Policy Staff-Assisted Home Hemodialysis Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 Overview... 1 General Background... 2 Coding/Billing Information... 4 References... 4 Effective Date...11/15/2017
Medical Coverage Policy Staff-Assisted Home Hemodialysis Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 Overview... 1 General Background... 2 Coding/Billing Information... 4 References... 4 Effective Date...11/15/2017
Excretory System Workbook
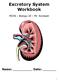 Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Dialysis technologies
 Moscow Institute of Electronic Technology Dialysis technologies Kidneys Remove toxic by-products of the metabolism and molecules smaller than 69000Da Regulate body fluid composition and volume Provide
Moscow Institute of Electronic Technology Dialysis technologies Kidneys Remove toxic by-products of the metabolism and molecules smaller than 69000Da Regulate body fluid composition and volume Provide
Renal Physiology Intro to CRRT Concepts. Catherine Jones September 2017
 Renal Physiology Intro to CRRT Concepts Catherine Jones September 2017 Learning Outcomes To revise anatomy & physiology of kidney in health: To understand basic principles of continuous renal replacement
Renal Physiology Intro to CRRT Concepts Catherine Jones September 2017 Learning Outcomes To revise anatomy & physiology of kidney in health: To understand basic principles of continuous renal replacement
Your life will need to change, however, and you have some big decisions to make concerning your treatment options.
 Project: Dialysis Center Educational Video Assignment: In conjunction with CAPA Production, develop a script to educate newly diagnosed kidney disease patients about their treatment options. The technical
Project: Dialysis Center Educational Video Assignment: In conjunction with CAPA Production, develop a script to educate newly diagnosed kidney disease patients about their treatment options. The technical
Choices. Patient Education. Making the treatment decision. Overview. How do you define quality of life?
 Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 6 Making the treatment decision Objectives: 1. List the 3 main options to supplement or replace failing kidney function. 2. Review steps for each of the main kidney replacement
Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 6 Making the treatment decision Objectives: 1. List the 3 main options to supplement or replace failing kidney function. 2. Review steps for each of the main kidney replacement
STARTING PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
 STARTING PERITONEAL DIALYSIS What you will learn: What your kidneys do What uremia (kidney disease) is and what the symptoms are How Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) helps What the two types of PD are: automated
STARTING PERITONEAL DIALYSIS What you will learn: What your kidneys do What uremia (kidney disease) is and what the symptoms are How Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) helps What the two types of PD are: automated
CRRT: The Technical Questions Modality & Dose. Ashita J. Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham 2018
 CRRT: The Technical Questions Modality & Dose Ashita J. Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham 2018 Case A 24YOM with HTN and OSA presents with acute pancreatitis. Despite aggressive fluid
CRRT: The Technical Questions Modality & Dose Ashita J. Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham 2018 Case A 24YOM with HTN and OSA presents with acute pancreatitis. Despite aggressive fluid
