Medical Thoracoscopy in Pleural Disease: Experience from a One-Center Study
|
|
|
- Gillian O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN: (Print)/ (Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2017;80: Medical Thoracoscopy in Pleural Disease: Experience from a One-Center Study Soo Jung Kim, M.D. 1, Sun Mi Choi, M.D. 2, Jinwoo Lee, M.D. 2, Chang-Hoon Lee, M.D. 2, Sang-Min Lee, M.D. 2, Jae-Joon Yim, M.D. 2, Chul-Gyu Yoo, M.D. 2, Young Whan Kim, M.D. 2, Sung Koo Han, M.D. 2 and Young Sik Park, M.D. 2 1 Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, 2 Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Background: Medical thoracoscopy (MT) is a minimally invasive, endoscopic procedure for exploration of the pleural cavity under conscious sedation and local anesthesia. MT has been performed at the Seoul National University Hospital since February This paper summarizes the findings and outcomes of MT cases at this hospital. Methods: Patients who had undergone MT were enrolled in the study. MT was performed by pulmonologists, using both rigid and semi-rigid thoracoscopes. During the procedure, patients were under conscious sedation with fentanyl and midazolam. Medical records were reviewed for clinical data. Results: From February 2014 to January 2016, 50 procedures (47 cases) were performed (diagnostic MT, 26 cases; therapeutic MT, 24 cases). The median age of patients was 66 years (59 73 years), and 38 patients (80.9%) were male. The median procedure duration from initial incision to insertion of the chest tube was 37 minutes. The median doses of fentanyl and midazolam were 50 μg and 5 mg, respectively. All procedures were performed without unexpected events. Of the 26 cases of pleural disease with an unknown cause, 19 were successfully diagnosed using MT. Additionally, diagnostic MT provided clinically useful information in the other six patients. Therapeutic MT was very effective for treatment of malignant pleural effusion or empyema. The median number of days with chest tube drainage was 6 (3 days for diagnostic MT and 8 days for therapeutic MT). Conclusion: MT is a useful and necessary procedure for both diagnosis and treatment of pleural diseases. Keywords: Thoracoscopy; Pleural Diseases Introduction Address for correspondence: Young Sik Park, M.D. Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 101 Daehak-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03080, Korea Phone: , Fax: mdyspark@gmail.com Received: May. 31, 2016 Revised: Oct. 18, 2016 Accepted: Jan. 24, 2017 cc It is identical to the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( Copyright 2017 The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights reserved. Medical thoracoscopy (MT) is a minimally invasive, endoscopic procedure for exploration of the pleural cavity under conscious sedation and local anesthesia 1,2. MT, performed by pulmonologists, is useful as both a diagnostic and a therapeutic tool for various pleural diseases. According to currently available data, the diagnostic sensitivity of MT using rigid thoracoscopy ranges from 85% to 93% 3. More recent metaanalyses have reported that the sensitivity and specificity of semi-rigid thoracoscopy are 91% and 100%, respectively 4, with efficacy being as high as for surgical thoracoscopy. As a therapeutic procedure, chemical pleurodesis performed during or after MT for recurrent and symptomatic malignant pleural effusions has a success rate of ~90% 2. Furthermore, MT is useful for the treatment of pleural infection as 194
2 Medical thoracoscopy in pleural disease it allows division of septations and adhesions and facilitates accurate tube placement and drainage 5. In this report, we summarize the findings and outcomes of MT performed at Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, South Korea since February Patients Materials and Methods Patients who underwent at least one MT procedure at Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, South Korea from February 2014 to January 2016 were included in the study. MT was performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in patients with various pleural diseases. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Seoul National University Hospital (IRB number: ) and was conducted in accordance with the amended Declaration of Helsinki. 2. Thoracoscopy equipment and procedure All MT procedures were performed by pulmonologists under conscious sedation in the bronchoscopy room. All patients received oxygen by nasal cannula and were placed in the lateral decubitus position with the ipsilateral arm abducted and elevated over the head to maximize access to the hemithorax 2. After patients were positioned, thoracic ultrasound (TUS) was used to assess the ideal entry site for the trocar. For conscious sedation, fentanyl (50 μg) and midazolam (2 mg) were administered before commencing the procedure, and an additional dose of midazolam was injected to maintain the desired level of sedation during the procedure. Local anesthesia was administered with lidocaine, and a 2 3-cm incision was made parallel to the upper margin of the rib. Blunt dissection was performed using a mosquito or Kelly clamp in the chest wall as far as the parietal pleura. Following penetration of the parietal pleura with the clamp, a trocar was introduced and the thoracoscope was placed through the trocar. A rigid thoracoscope (Olympus, Jena, Germany) or semi-rigid thoracoscope (LTF-240; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) was used on the basis of the surgeon s preference. Upon completion of the procedure, a chest tube was inserted through the trocar, and the trocar was removed. 3. Outcome and follow-up Procedure duration was defined as the time from skin incision to insertion of the chest tube. Tissue biopsies and/or microbiological results of samples were reviewed. Clinicians assessed the effectiveness of therapeutic MT. Major and minor complications were recorded. 4. Statistical analysis Continuous variables are presented as median values (interquartile range); categorical variables, relative frequencies, and percentages. Comparison of MT for diagnosis and treatment was evaluated using the Mann-Whitney U test for continuous variables, or the chi-square test for categorical variables. A two-tailed p-value less than <0.05 indicated statistical significance. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). 1. Baseline characteristics Results During a 2-year period, 47 patients underwent 50 procedures, including 26 diagnostic and 24 therapeutic MT (Figure Medical thoracoscopy (n=50) Specific diagnosis (n=19) For diagnosis (n=26) Malignant pleural effusion (n=12) TB pleurisy (n=1) NTM pleural disease (n=1) Subplural abscess (n=1) GVHD (n=1) Amyloiosis (n=1) Foreign body (n=1)* IgG4-related disease (n=1) Undiagnosed (n=7) For treatment (n=24) Atypical cell (n=3) Nonspecific inflammation (n=4) Malignant pleural effusion (n=11) Empyema (n=13) Figure 1. Flow diagram of patients undergoing medical thoracoscopy. *Guidewire. Adenocarcinoma was diagnosed via video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) in one patient; two patients were clinically diagnosed with malignant pleural effusion. Mesothelioma was diagnosed via VATS in one patient, and pleural effusion was spontaneously resolved in another three patients. TB: tuberculosis; NTM: nontuberculous mycobacteria; GVHD: graft-versus-host disease
3 SJ Kim et al. 1). Median age of the study patients was 66 years (range, years), and 38 patients (80.9%) were male. Almost 70% of patients had a history of smoking, and 21 had a history of malignancy (Table 1). 2. Procedure-related parameters The median procedure time was 37 minutes, although the duration of the procedure was generally longer for patients who underwent therapeutic MT. The doses of fentanyl and midazolam that were used were different for diagnostic and therapeutic MT; fentanyl was used at a dose of 50 μg for both Table 1. Characteristics of the study population Characteristic Value (n=47) Age, yr 66 (59 73) Male sex 38 (80.9) Smoking status Current 10 (21.3) Former 22 (46.8) Never 14 (29.8) Unknown 1 (2.1) Pack-year 15.0 (0 32.5) History of tuberculosis 6 (12.8) History of malignancy Solid tumor 21 (44.7) Hematologic malignancy 2 (4.3) Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%). diagnostic and therapeutic MT, whereas midazolam was used at a dose of 5 mg for therapeutic MT and 4.5 mg for diagnostic MT (4.5 mg vs. 5 mg, p=0.048) (Table 2). All procedures were completed without unexpected events. 3. Results of diagnostic MT Nineteen of 26 cases of unexplained pleural disease were successfully diagnosed. Twelve patients were diagnosed with pleural metastases: pulmonary adenocarcinoma (five patients), non-pulmonary adenocarcinoma (one patient), squamous cell carcinoma (one patient), sarcomatoid carcinoma (one patient), small cell carcinoma (two patients), epithelioid sarcoma (one patient), and metastasis of unknown origin (one patient) (Table 2). Seven patients were diagnosed with nonmalignant diseases: subpleural abscess (one patient), tuberculous pleurisy (one patient), nontuberculous mycobacterial pleurisy (one patient), amyloidosis (one patient), graft-versushost disease (one patient), foreign body (one patient), and immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related disease (one patient) (Figure 1). Seven patients remained undiagnosed even after MT; however, three had pleural biopsy findings that showed the presence of atypical cells, and they were clinically diagnosed with malignant pleural effusion. Finally, one patient was finally diagnosed with adenocarcinoma via video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS). Among four patients who showed nonspecific inflammation, pleural effusion was spontaneously resolved without specific treatment in three, whereas one was finally diagnosed with mesothelioma using VATS after 3 months of MT. Although a specific diagnosis was established in 19 of 26 patients, diagnostic MT provided clinically useful information in the other six. Overall diagnostic yield in the Table 2. Medical thoracoscopy procedure parameters Parameter Total procedures Diagnostic procedure Therapeutic procedure (n=50) (n=26) (n=24) p-value Procedure time*, min 37:29 (27:15 55:29) 33:59 (24:44 40:00) 51:29 (37:14 1:07:44) Instruments Rigid scope 29 (58.0) 16 (61.5) 13 (54.2) Semi-rigid scope 21 (42.0) 10 (38.5) 11 (45.8) TUS-guided 39 (78.0) 19 (73.1) 20 (83.3) Doses of sedatives/analgesics Fentanyl, μg 50 (50 50) 50 (50 50) 50 (50 50) Midazolam, mg 5 ( ) 4.5 ( ) 5.0 ( ) Duration of post-procedure chest tube drainage, day 6.0 ( ) (n=41) 3.0 ( ) 8.0 ( ) (n=18) Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%). *Procedure time: from lidocaine injection to chest tube insertion. TUS: thoracic ultrasound. 196 Tuberc Respir Dis 2017;80:
4 Medical thoracoscopy in pleural disease study was 96.2%. 4. Results of therapeutic MT For therapeutic purposes, 21 patients underwent 24 procedures. Ten patients with malignant pleural effusion underwent 11 procedures. One patient underwent MT twice because pleural effusion had progressed on both sides. Eleven patients with empyema underwent 13 procedures. With the exception of one procedure, therapeutic MT was generally determined to be helpful according to clinicians. 5. Other outcomes For 41 patients, the median number of days with chest tube drainage was 6 (3 days for patients who underwent diagnostic MT and 8 days for those who underwent therapeutic MT) (Table 2). The remaining patients were either discharged with the chest tube intact or died before chest tube removal. Three patients died within 30 days of MT, and underlying cancer progression was a potential cause of death. 6. Complications Re-expansion pulmonary edema occurred in one patient and required drainage of 3.03 L of pleural fluid over a 3 4 hour period (Figure 2A C). After the patient received supportive care, resolution of the edema was observed by chest radiography after 3 days (Figure 2D). Discussion MT is a minimally invasive procedure for inspection and A B C D Figure 2. Re-expansion pulmonary edema. Chest radiography immediately (A), 4 hours (B), 6 hours (C), and 3 days (D) after medical thoracoscopy
5 SJ Kim et al. biopsy of the pleural space and therapeutic intervention 2. MT is generally performed by pulmonologists under moderate sedation with local anesthesia in a spontaneously breathing patient; it generally takes place outside a bronchoscopy room and requires one single port of entry into the thoracic cavity. Surgical thoracoscopy, better known as VATS, is performed by a surgeon in an operating room in a patient under general anesthesia with selective intubation, and it requires at least three ports of entry into the thoracic cavity. Compared with surgical thoracoscopy, the major advantage of MT is its cost-effectiveness for patients with poor tolerance for general anesthesia 6. Patients who need therapeutic MT usually have poor lung function or performance status. MT can be performed in patients with poor lung function or those with a high anesthetic risk associated with an open procedure. Migliore et al. 7 reported that MT can safely be used for patients with compromised pulmonary function. In their study, 20% of patients had a preoperative forced expiratory volume in 1 second of <1 L. Additionally, more than 60% of these patients had poor performance status (American Society of Anesthesiologists status 3 or greater) 7. Therefore, MT may be a good diagnostic or therapeutic option for patients intolerant to VATS under general anesthesia. TUS can be performed at the bedside and is very useful during MT. TUS can safely and reliably identify entry sites for trocar placement during MT, and a TUS exam adds only minutes to the duration of the procedure 8. The entry site for the trocar was assessed with TUS in 78% of patients in our study, and the trocar was inserted safely without any complications. Additionally, since TUS can elucidate pleural loculations at an early stage, mechanical adhesiolysis via MT may be used as a first-line treatment without delay in patients with clear septation 5. A recent study demonstrated that TUS accurately identifies intrathoracic adhesions and, in experienced hands, can guide MT access even in the complete absence of pleural effusion 9. MT is typically performed under local anesthesia, although premedication with an intravenous anxiolytic or analgesic may be accommodated 10. Although sedation requirements for MT are quite low, a combination of a short-acting benzodiazepine like midazolam and an opioid, such as fentanyl, is the most commonly used strategy for moderate sedation during MT 6. Previous studies have shown that the dose of midazolam used for MT is 1 to 10 mg 2,11-14 and 50 to 100 μg for fentanyl 2,11, which is consistent with the doses used in our study. In addition, meticulous attention to administration of local anesthesia at the entry site, especially along the periosteum, is important to achieve patient comfort and reduce pain during manipulation of the thoracoscope 1,2,10. In this retrospective, descriptive study, we investigated the outcomes of patients who underwent MT, over a 2-year period. Our findings showed that MT had a high diagnostic yield and was effective for treatment of malignant pleural effusion and empyema. MT allows direct visual assessment of the pleura and subsequent biopsy of visually abnormal areas, which maximizes diagnostic yield 3. Previous studies have reported a diagnostic yield for MT that ranges from 85% to 100%. In our study, the diagnostic yield was 96.2%, which was comparable to previous studies 3,4,15. Interestingly, one case was diagnosed as IgG4- related pleural disease in our study, and MT findings were very similar to those from a previous study 16. Figure 3 shows representative features of IgG4-related pleural disease, such as severe adhesions in the pleural space (Figure 3A), thickened parietal pleura (Figure 3B), and inflamed parietal pleura with proliferating blood vessels (Figure 3C). IgG4-related disease is a recently described systemic fibro-inflammatory disease associated with elevated circulating levels of IgG4 17. The diagnosis of IgG4-related disease rests on the combined presence of a characteristic histopathological appearance and increased numbers of IgG4 + plasma cells 18. It is known that pleural effusion is an uncommon feature of IgG4-related disease 17,19. However, a recent study by Murata et al. 20 reported that the A B C Figure 3. IgG4-related disease: findings during medical thoracoscopy. (A) Adhesions in the pleural space. (B) Thickened parietal pleura. (C) Inflamed parietal pleura with proliferating blood vessels. 198 Tuberc Respir Dis 2017;80:
6 Medical thoracoscopy in pleural disease proportion of cases of IgG4-related pleural lesions in undiagnosed pleural effusion is estimated to be 8.3%. Therefore, IgG4-related disease in a setting of pleural effusion should be considered as a differential diagnosis of unknown cause. Although MT has become more readily available in Europe and North America over the past two decades 2, it is still an unfamiliar procedure in Korea, and only a few reports have been published there 15,21. Yang et al. 15 reported that it was a safe method for diagnosing patients with unknown pleural effusions and had a relatively high diagnostic accuracy. However, they did not include therapeutic MT. In our study, we included patients who received therapeutic MT, which was effective in treating malignant pleural effusion and empyema. Traditionally, diagnoses of the causes of pleural effusion or pleurodesis in patients with malignant disease are the two major indications for MT 22,23. According to guidelines of the British Thoracic Society, MT is not currently used in the United Kingdom either as primary or rescue therapy for pleural infection 3. However, MT may be effective for managing empyema by experienced respiratory physicians 23. Brutsche et al. 5 reported that multiloculated empyema, as identified by ultrasonography, can safely and successfully be treated with MT. Additionally, Ravaglia et al. 24 demonstrated that MT successfully treated 22 of 24 patients with multiloculated empyema (91.7%) and four of eight patients with organizing effusion (50%). In our study, more than half of the patients who underwent therapeutic MT had empyema, and one patient with empyema underwent MT twice, as this was effective for relieving symptoms such as dyspnea. Fibrinopurulent membranes of multiloculated empyema were mechanically removed with forceps to facilitate drainage of pus. A single thoracentesis procedure using TUS rarely provides long-lasting relief. MT is more effective than conventional thoracentesis using TUS, in draining pus to provide palliation. Some patients with malignant pleural effusion have adhesions in the pleural space 25, and the use of thoracoscopic adhesiolysis could manage pleural effusion more effectively. Moreover, a pleurodesis could be performed through a chest tube placed at the time of the MT procedure. Additionally, diagnostic and therapeutic MT could be performed simultaneously to treat the malignant pleural effusion. Even in patients with a known malignancy, a firm diagnosis of malignant pleural effusion is important for determining proper management because up to 50% of pleural effusions could be benign 26. In summary, MT is a useful and necessary procedure for both the diagnosis and treatment of various pleural diseases. Conflicts of Interest No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. References 1. Lee P, Mathur PN, Colt HG. Advances in thoracoscopy: 100 years since Jacobaeus. Respiration 2010;79: Michaud G, Berkowitz DM, Ernst A. Pleuroscopy for diagnosis and therapy for pleural effusions. Chest 2010;138: Rahman NM, Ali NJ, Brown G, Chapman SJ, Davies RJ, Downer NJ, et al. Local anaesthetic thoracoscopy: British Thoracic Society Pleural Disease Guideline Thorax 2010;65 Suppl 2:ii Agarwal R, Aggarwal AN, Gupta D. Diagnostic accuracy and safety of semirigid thoracoscopy in exudative pleural effusions: a meta-analysis. Chest 2013;144: Brutsche MH, Tassi GF, Gyorik S, Gokcimen M, Renard C, Marchetti GP, et al. Treatment of sonographically stratified multiloculated thoracic empyema by medical thoracoscopy. Chest 2005;128: Shojaee S, Lee HJ. Thoracoscopy: medical versus surgicalin the management of pleural diseases. J Thorac Dis 2015;7(Suppl 4):S Migliore M, Giuliano R, Aziz T, Saad RA, Sgalambro F. Four-step local anesthesia and sedation for thoracoscopic diagnosis and management of pleural diseases. Chest 2002;121: Hersh CP, Feller-Kopman D, Wahidi M, Garland R, Herth F, Ernst A. Ultrasound guidance for medical thoracoscopy: a novel approach. Respiration 2003;70: Marchetti G, Valsecchi A, Indellicati D, Arondi S, Trigiani M, Pinelli V. Ultrasound-guided medical thoracoscopy in the absence of pleural effusion. Chest 2015;147: Havelock T, Teoh R, Laws D, Gleeson F; BTS Pleural Disease Guideline Group. Pleural procedures and thoracic ultrasound: British Thoracic Society Pleural Disease Guideline Thorax 2010;65 Suppl 2:ii Hallifax RJ, Corcoran JP, Ahmed A, Nagendran M, Rostom H, Hassan N, et al. Physician-based ultrasound-guided biopsy for diagnosing pleural disease. Chest 2014;146: Lee P, Hsu A, Lo C, Colt HG. Prospective evaluation of flex-rigid pleuroscopy for indeterminate pleural effusion: accuracy, safety and outcome. Respirology 2007;12: Dhooria S, Singh N, Aggarwal AN, Gupta D, Agarwal R. A randomized trial comparing the diagnostic yield of rigid and semirigid thoracoscopy in undiagnosed pleural effusions. Respir Care 2014;59: Willendrup F, Bodtger U, Colella S, Rasmussen D, Clementsen PF. Diagnostic accuracy and safety of semirigid thoracoscopy in exudative pleural effusions in Denmark. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol 2014;21: Yang JK, Lee JH, Kwon MH, Jeong JH, Lee GE, Cho HM, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and safety of medical thoracoscopy. Tuberc Respir Dis 2007;63: Ishida A, Furuya N, Nishisaka T, Mineshita M, Miyazawa T. IgG4-related pleural disease presenting as a massive bilateral
7 SJ Kim et al. effusion. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol 2014;21: Ryu JH, Sekiguchi H, Yi ES. Pulmonary manifestations of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease. Eur Respir J 2012;39: Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato Y, Yoshino T, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol 2012;25: Zen Y, Inoue D, Kitao A, Onodera M, Abo H, Miyayama S, et al. IgG4-related lung and pleural disease: a clinicopathologic study of 21 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33: Murata Y, Aoe K, Murakami T, Oishi K, Matsumoto T, Ueoka H, et al. Involvement of IgG4 in pleural effusions of unknown cause. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014;189:A Kim WJ, Lee HY, Lee SH, Cho SJ, Park WS, Kim JK, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of 2-mm minithoracoscopic pleural biopsy for pleural effusion. Tuberc Respir Dis 2004;57: Lee P, Colt HG. Pleuroscopy in Clin Chest Med 2013;34: Froudarakis ME. Medical thoracoscopy: the green shapes of grey. Chest 2015;147: Ravaglia C, Gurioli C, Tomassetti S, Casoni GL, Romagnoli M, Gurioli C, et al. Is medical thoracoscopy efficient in the management of multiloculated and organized thoracic empyema? Respiration 2012;84: Bielsa S, Martin-Juan J, Porcel JM, Rodriguez-Panadero F. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of pleural adhesions in malignant effusions. J Thorac Oncol 2008;3: Heffner JE, Klein JS. Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of malignant pleural effusions. Mayo Clin Proc 2008;83: Tuberc Respir Dis 2017;80:
Ultrasound-Guided Medical Thoracoscopy in the Absence of Pleural Effusion
 [ Original Research Pulmonary Procedures ] Ultrasound-Guided Medical Thoracoscopy in the Absence of Pleural Effusion Giampietro Marchetti, MD, FCCP ; Alberto Valsecchi, MD ; Davide Indellicati, MD ; Sabrina
[ Original Research Pulmonary Procedures ] Ultrasound-Guided Medical Thoracoscopy in the Absence of Pleural Effusion Giampietro Marchetti, MD, FCCP ; Alberto Valsecchi, MD ; Davide Indellicati, MD ; Sabrina
Role of medical Thoracoscopy in the Management of Multiloculated Empyema
 Sumalani et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018) 18:179 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0745-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Role of medical Thoracoscopy in the Management of Multiloculated Empyema Kamran Khan Sumalani
Sumalani et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018) 18:179 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0745-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Role of medical Thoracoscopy in the Management of Multiloculated Empyema Kamran Khan Sumalani
Initial experience of medical pleuroscopy via the peel-away introducer of the indwelling pleural catheter using a thin bronchoscope
 Surgical Technique of Interventional Pulmonology Corner Initial experience of medical pleuroscopy via the peel-away introducer of the indwelling pleural catheter using a thin bronchoscope Kassem Harris
Surgical Technique of Interventional Pulmonology Corner Initial experience of medical pleuroscopy via the peel-away introducer of the indwelling pleural catheter using a thin bronchoscope Kassem Harris
Thoracoscopic Management of Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions in Young Children. Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 31, No. 4, December 2009 Thoracoscopic Management of Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions in Young Children Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Objective: To evaluate the role
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 31, No. 4, December 2009 Thoracoscopic Management of Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions in Young Children Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Objective: To evaluate the role
Post Pneumonic Empyema: Is There Still a Role for Surgery?
 Post Pneumonic Empyema: Is There Still a Role for Surgery? M. Blair Marshall, MD Ismael Matus, MD Chief, Thoracic Surgery Interventional Pulmonary Professor of Surgery Medicine MedStar Georgetown University
Post Pneumonic Empyema: Is There Still a Role for Surgery? M. Blair Marshall, MD Ismael Matus, MD Chief, Thoracic Surgery Interventional Pulmonary Professor of Surgery Medicine MedStar Georgetown University
The Portsmouth thoracoscopy experience, an evaluation of service by retrospective case note analysis
 Respiratory Medicine (2007) 101, 1021 1025 The Portsmouth thoracoscopy experience, an evaluation of service by retrospective case note analysis Sophie V. Fletcher,1, Robin J. Clark Respiratory Centre,
Respiratory Medicine (2007) 101, 1021 1025 The Portsmouth thoracoscopy experience, an evaluation of service by retrospective case note analysis Sophie V. Fletcher,1, Robin J. Clark Respiratory Centre,
Interventional Pulmonary Case Based Discussions (ATS) Ali Imran Saeed, MD University of New Mexico
 Interventional Pulmonary Case Based Discussions (ATS) Ali Imran Saeed, MD University of New Mexico Objectives Interventional Pulmonary in New Mexico Interventional Pulmonary and Advanced Diagnostic Cases
Interventional Pulmonary Case Based Discussions (ATS) Ali Imran Saeed, MD University of New Mexico Objectives Interventional Pulmonary in New Mexico Interventional Pulmonary and Advanced Diagnostic Cases
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS. Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP
 APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore Catheter in the Patients with Iatrogenic Pneumothorax
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 20;44:48-422 ISSN: 2233-60X (Print) ISSN: 2093-656 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/0.5090/kjtcs.20.44.6.48 Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 20;44:48-422 ISSN: 2233-60X (Print) ISSN: 2093-656 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/0.5090/kjtcs.20.44.6.48 Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore
Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications of Pleural Adhesions in Malignant Effusions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications of Pleural Adhesions in Malignant Effusions Silvia Bielsa, MD,* José Martín-Juan, MD, José M. Porcel, MD,* and Francisco Rodríguez-Panadero, MD Background
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications of Pleural Adhesions in Malignant Effusions Silvia Bielsa, MD,* José Martín-Juan, MD, José M. Porcel, MD,* and Francisco Rodríguez-Panadero, MD Background
Medical thoracoscopy and its evolving role in the diagnosis and treatment of pleural disease
 Review Article Medical thoracoscopy and its evolving role in the diagnosis and treatment of pleural disease Vivek Murthy, Jamie L. Bessich Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, New York
Review Article Medical thoracoscopy and its evolving role in the diagnosis and treatment of pleural disease Vivek Murthy, Jamie L. Bessich Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, New York
PAKISTAN JOURNAL OF CHEST MEDICINE. Volume 18, No 1, January-March REVIEW ARTICLE MEDICAL PLEUROSCOPY
 82 REVIEW ARTICLE MEDICAL PLEUROSCOPY Pyng Lee MD,* Henri G Colt,**Ali I. Musani MD*** ABSTRACT Pleuroscopy or medical thoracoscopy are terms used interchangeably to describe a minimally invasive procedure
82 REVIEW ARTICLE MEDICAL PLEUROSCOPY Pyng Lee MD,* Henri G Colt,**Ali I. Musani MD*** ABSTRACT Pleuroscopy or medical thoracoscopy are terms used interchangeably to describe a minimally invasive procedure
Medical Thoracoscopy When to Choose Over a General Anaesthetic VATS
 Medical Thoracoscopy When to Choose Over a General Anaesthetic VATS SpR Training Day 07.07.14 Dr Alex West Consultant Chest/Pleural Physician Guy s and St Thomas Hospital Medical Thoracoscopy? No Just
Medical Thoracoscopy When to Choose Over a General Anaesthetic VATS SpR Training Day 07.07.14 Dr Alex West Consultant Chest/Pleural Physician Guy s and St Thomas Hospital Medical Thoracoscopy? No Just
A randomized trial comparing the diagnostic yield of rigid and semirigid thoracoscopy in undiagnosed pleural effusions
 0 0 0 A randomized trial comparing the diagnostic yield of rigid and semirigid thoracoscopy in undiagnosed pleural effusions [Running title: RISE trial] Sahajal Dhooria Navneet Singh Ashutosh N Aggarwal
0 0 0 A randomized trial comparing the diagnostic yield of rigid and semirigid thoracoscopy in undiagnosed pleural effusions [Running title: RISE trial] Sahajal Dhooria Navneet Singh Ashutosh N Aggarwal
Flex-rigid pleuroscopic biopsy with the SB knife Jr is a novel technique for diagnosis of malignant or benign fibrothorax
 Case Report Flex-rigid pleuroscopic biopsy with the SB knife Jr is a novel technique for diagnosis of malignant or benign fibrothorax Xiao-Bo Wang 1, Yan Yin 1, Yuan Miao 2, Ralf Eberhardt 3, Gang Hou
Case Report Flex-rigid pleuroscopic biopsy with the SB knife Jr is a novel technique for diagnosis of malignant or benign fibrothorax Xiao-Bo Wang 1, Yan Yin 1, Yuan Miao 2, Ralf Eberhardt 3, Gang Hou
A Randomized Trial Comparing the Diagnostic Yield of Rigid and Semirigid Thoracoscopy in Undiagnosed Pleural Effusions
 A Randomized Trial Comparing the Diagnostic Yield of Rigid and Semirigid Thoracoscopy in Undiagnosed Pleural Effusions Sahajal Dhooria MD DM, Navneet Singh MD DM, Ashutosh N Aggarwal MD DM, Dheeraj Gupta
A Randomized Trial Comparing the Diagnostic Yield of Rigid and Semirigid Thoracoscopy in Undiagnosed Pleural Effusions Sahajal Dhooria MD DM, Navneet Singh MD DM, Ashutosh N Aggarwal MD DM, Dheeraj Gupta
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion
 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
Diagnostic value of medical thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusions
 4590 Diagnostic value of medical thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusions RUI LIN CHEN, YONG QING ZHANG, JUN WANG, HUA WU and SHU MEI YANG Department of Respiratory Medicine, Shaanxi Provincial People's
4590 Diagnostic value of medical thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusions RUI LIN CHEN, YONG QING ZHANG, JUN WANG, HUA WU and SHU MEI YANG Department of Respiratory Medicine, Shaanxi Provincial People's
A Repeat Case of Idiopathic Spontaneous Hemothorax
 Case Report A Repeat Case of Idiopathic Spontaneous Hemothorax Felix R. Gaw, MD Jack H. Bloch, MD, PhD, FACS Nolan J. Anderson, MD, FACS Spontaneous hemothorax, a collection of blood in the pleural cavity
Case Report A Repeat Case of Idiopathic Spontaneous Hemothorax Felix R. Gaw, MD Jack H. Bloch, MD, PhD, FACS Nolan J. Anderson, MD, FACS Spontaneous hemothorax, a collection of blood in the pleural cavity
Medical thoracoscopy for exudative pleural effusion: an eight-year experience from a country with a young population
 Thomas et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017) 17:151 DOI 10.1186/s12890-017-0499-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Medical thoracoscopy for exudative pleural effusion: an eight-year experience from a country with a young
Thomas et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017) 17:151 DOI 10.1186/s12890-017-0499-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Medical thoracoscopy for exudative pleural effusion: an eight-year experience from a country with a young
Clinical Study Safety and Complications of Medical Thoracoscopy
 Advances in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3794791, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3794791 Clinical Study Safety and Complications of Medical Thoracoscopy Shimaa Nour Moursi Ahmed, 1,2 Hideo
Advances in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3794791, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3794791 Clinical Study Safety and Complications of Medical Thoracoscopy Shimaa Nour Moursi Ahmed, 1,2 Hideo
Management of Pleural Effusion
 Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Modern Approaches to Empyema
 Modern Approaches to Empyema Amit Bhargava, MD Attending Thoracic Surgeon Assistant Professor Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery 1 Principles of Treatment Adequate drainage Sterilization
Modern Approaches to Empyema Amit Bhargava, MD Attending Thoracic Surgeon Assistant Professor Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery 1 Principles of Treatment Adequate drainage Sterilization
Early Outcomes of Single-Port Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery for Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2014;47:384-388 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2014.47.4.384 Early Outcomes of Single-Port Video-Assisted
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2014;47:384-388 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2014.47.4.384 Early Outcomes of Single-Port Video-Assisted
Alper Toker, MD. VATS decortication. Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery
 VATS decortication Alper Toker, MD Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery Pleural space infection is a common pathology causing morbidity and mortality. It is a collection
VATS decortication Alper Toker, MD Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery Pleural space infection is a common pathology causing morbidity and mortality. It is a collection
The Role of Thoracoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion of Unknown Origin
 Short Communication J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 20, Issu 8; Aug 2018. P:31-36 The Role of Thoracoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion of Unknown Origin R. Mahmodlou (MD) 1, J. Sarbazzadeh (MD) 1, S.A.
Short Communication J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 20, Issu 8; Aug 2018. P:31-36 The Role of Thoracoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion of Unknown Origin R. Mahmodlou (MD) 1, J. Sarbazzadeh (MD) 1, S.A.
Diagnostic Utility of Indigenous Technique of Pleuroscopy in Undiagnosed Cases of Exudative Pleural Effusions
 Journal of Health Science 6 (2018) 304-309 doi: 10.17265/2328-7136/2018.04.009 D DAVID PUBLISHING Diagnostic Utility of Indigenous Technique of Pleuroscopy in Undiagnosed Cases of Exudative Pleural Effusions
Journal of Health Science 6 (2018) 304-309 doi: 10.17265/2328-7136/2018.04.009 D DAVID PUBLISHING Diagnostic Utility of Indigenous Technique of Pleuroscopy in Undiagnosed Cases of Exudative Pleural Effusions
Chapter 8. Other Important Tests and Procedures. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax
 Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Interventional Pulmonology
 Interventional Pulmonology The Division of Thoracic Surgery Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical College p: 212-746-6275 f: 212-746-8223 https://weillcornell.org/eshostak
Interventional Pulmonology The Division of Thoracic Surgery Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical College p: 212-746-6275 f: 212-746-8223 https://weillcornell.org/eshostak
North West London Trauma Network. Management of Chest Drains
 North West London Trauma Network Management of Chest Drains Contents Introduction... 2 What is a chest drain?... 2 Indications for insertion:... 2 Insertion of drain:... 3 Equipment:... 3 Procedure...
North West London Trauma Network Management of Chest Drains Contents Introduction... 2 What is a chest drain?... 2 Indications for insertion:... 2 Insertion of drain:... 3 Equipment:... 3 Procedure...
Some clinical conditions such as congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, acute. Bleomycin in the treatment of 50 cases with malignant pleural effusion
 Original Article Bleomycin in the treatment of 5 cases with malignant pleural effusion Novin Nikbakhsh (MD) *1 Ali Pourhasan Amiri (MD) 2 Danial Hoseinzadeh (MD) 3 1- Department of Surgery, Babol University
Original Article Bleomycin in the treatment of 5 cases with malignant pleural effusion Novin Nikbakhsh (MD) *1 Ali Pourhasan Amiri (MD) 2 Danial Hoseinzadeh (MD) 3 1- Department of Surgery, Babol University
Different characteristics of tuberculous pleural effusion according to pleural fluid cellular predominance and loculation
 Original Article Different characteristics of tuberculous pleural effusion according to pleural fluid cellular predominance and loculation Jaehee Lee 1, Jae Kwang Lim 2, Seung Soo Yoo 1, Shin Yup Lee 1,
Original Article Different characteristics of tuberculous pleural effusion according to pleural fluid cellular predominance and loculation Jaehee Lee 1, Jae Kwang Lim 2, Seung Soo Yoo 1, Shin Yup Lee 1,
EMPYEMA. Catheter Based Treatment vs. VATS. UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds August 27 th, Jeremy Hedges, M.D.
 EMPYEMA Catheter Based Treatment vs. VATS UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds August 27 th, 2007 Jeremy Hedges, M.D. OVERVIEW Empyema Pathogenesis Treatment Catheter based treatment Fibrinolytics
EMPYEMA Catheter Based Treatment vs. VATS UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds August 27 th, 2007 Jeremy Hedges, M.D. OVERVIEW Empyema Pathogenesis Treatment Catheter based treatment Fibrinolytics
Thoracoscopy: medical versus surgical in the management of pleural diseases
 Review Article on Pleural Disease Thoracoscopy: medical versus surgical in the management of pleural diseases Samira Shojaee 1, Hans J. Lee 2 1 Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA 23219, USA;
Review Article on Pleural Disease Thoracoscopy: medical versus surgical in the management of pleural diseases Samira Shojaee 1, Hans J. Lee 2 1 Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA 23219, USA;
Bao-An Gao 1, Gang Zhou 2 *, Li Guan 1, Ling-Yun Zhang 1, Guang-Ming Xiang 1. Introduction
 Original Article Effectiveness and safety of diagnostic flexi-rigid thoracoscopy in differentiating exudative pleural effusion of unknown etiology: a retrospective study of 215 patients Bao-An Gao 1, Gang
Original Article Effectiveness and safety of diagnostic flexi-rigid thoracoscopy in differentiating exudative pleural effusion of unknown etiology: a retrospective study of 215 patients Bao-An Gao 1, Gang
Learning Curve of a Young Surgeon s Video-assisted Thoracic Surgery Lobectomy during His First Year Experience in Newly Established Institution
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2012;45:166-170 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2012.45.3.166 Learning Curve of a Young Surgeon s Video-assisted
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2012;45:166-170 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2012.45.3.166 Learning Curve of a Young Surgeon s Video-assisted
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Rahman NM, Pepperell J, Rehal S, et al. Effect of opioids vs NSAIDs and larger vs smaller chest tube size on pain control and pleurodesis efficacy among patients with malignant
Supplementary Online Content Rahman NM, Pepperell J, Rehal S, et al. Effect of opioids vs NSAIDs and larger vs smaller chest tube size on pain control and pleurodesis efficacy among patients with malignant
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 4, Issue 20,
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 4, Issue 20, 521-525 Empyema thoracis Original Article Singh DR 1, Joshi MR 2, Thapa P 2, Nath S 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Lecturer, 3 Professor,
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 4, Issue 20, 521-525 Empyema thoracis Original Article Singh DR 1, Joshi MR 2, Thapa P 2, Nath S 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Lecturer, 3 Professor,
Medical Thoracoscopy: Rigid thoracoscopy or flexi-rigid pleuroscopy?
 Medical Thoracoscopy: Rigid thoracoscopy or flexi-rigid pleuroscopy? Authors: Kim Hoong YAP 1,2 MBBS MRCP FAMS FCCP Martin J PHILLIPS 1 MBBS FRACP Y C Gary LEE 1,3 MBChB PhD FRACP FRCP FCCP kim_hoong_yap@ttsh.com.sg
Medical Thoracoscopy: Rigid thoracoscopy or flexi-rigid pleuroscopy? Authors: Kim Hoong YAP 1,2 MBBS MRCP FAMS FCCP Martin J PHILLIPS 1 MBBS FRACP Y C Gary LEE 1,3 MBChB PhD FRACP FRCP FCCP kim_hoong_yap@ttsh.com.sg
WHAT WE NEED FOR THORACOSCOPY
 WHAT WE NEED FOR THORACOSCOPY Medical School Marios Froudarakis, MD Department of Pneumonology University Hospital of Alexandroupolis mfroud@med.duth.gr Democritus University of Thrace Dedicated Course
WHAT WE NEED FOR THORACOSCOPY Medical School Marios Froudarakis, MD Department of Pneumonology University Hospital of Alexandroupolis mfroud@med.duth.gr Democritus University of Thrace Dedicated Course
Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided. CNB) versus mammograph-guided biopsy for suspicious microcalcifications. without definite breast mass
 Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
The Role of Fiberoptic bronchoscopy in Evaluating The causes of Undiagnosed Pleural Effusion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-083, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. VI (January. 2017), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org The Role of Fiberoptic bronchoscopy
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-083, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. VI (January. 2017), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org The Role of Fiberoptic bronchoscopy
Case Study #2. Case Study #1 cont 9/28/2011. CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C. LH is 78 yowf with PMHx of metz breast CA presents
 Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Advanced Interventions
 Advanced Interventions Dr. Coenraad Frederik Nicolaas Koegelenberg Stellenbosch University 7602 Cape Town SOUTH AFRICA coeniefn@sun.ac.za AIMS Optimisation of patient positioning prior to and safety during
Advanced Interventions Dr. Coenraad Frederik Nicolaas Koegelenberg Stellenbosch University 7602 Cape Town SOUTH AFRICA coeniefn@sun.ac.za AIMS Optimisation of patient positioning prior to and safety during
Clinical Features of Patients on Home Oxygen Therapy Due to Chronic Respiratory Failure at One University Hospital
 original article korean j intern med 2012;27:311-316 pissn 1226-3303 eissn 2005-6648 Clinical Features of Patients on Home Oxygen Therapy Due to Chronic Respiratory Failure at One University Hospital Kyoung
original article korean j intern med 2012;27:311-316 pissn 1226-3303 eissn 2005-6648 Clinical Features of Patients on Home Oxygen Therapy Due to Chronic Respiratory Failure at One University Hospital Kyoung
Indwelling Pleural Catheters in Malignant and Non-Malignant Disease
 Indwelling Catheters in Malignant and Non-Malignant Disease 20th Hellenic Conference November 2011 Najib Rahman Clinical Lecturer Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine University of Oxford, UK Najib.rahman@ndm.ox.ac.uk
Indwelling Catheters in Malignant and Non-Malignant Disease 20th Hellenic Conference November 2011 Najib Rahman Clinical Lecturer Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine University of Oxford, UK Najib.rahman@ndm.ox.ac.uk
Table 2: Outcomes measured. Table 1: Intrapleural alteplase instillation therapy protocol
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Intrapleural F brinolytic Therapy with Alteplase in Empyema Thoracis in Children conducted in the Department of Pediatric critical care and Pulmonology unit at our institution
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Intrapleural F brinolytic Therapy with Alteplase in Empyema Thoracis in Children conducted in the Department of Pediatric critical care and Pulmonology unit at our institution
Introduction to transthoracic ultrasound for the pulmonologist
 Review Introduction to transthoracic ultrasound for the pulmonologist Clementine Bostantzoglou 1, Charalampos Moschos 2 1 7 th Pulmonary Department, Sotiria Hospital for Chest Diseases, Athens, Greece
Review Introduction to transthoracic ultrasound for the pulmonologist Clementine Bostantzoglou 1, Charalampos Moschos 2 1 7 th Pulmonary Department, Sotiria Hospital for Chest Diseases, Athens, Greece
Four Cases of Malignant Pleural Effusion in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
 Endocrinol Metab 26(4):330-334, December 2011 CASE REPORT Four Cases of Malignant Pleural Effusion in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Min Ji Jeon, Ji Hye Yim, Eui Young Kim, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong
Endocrinol Metab 26(4):330-334, December 2011 CASE REPORT Four Cases of Malignant Pleural Effusion in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Min Ji Jeon, Ji Hye Yim, Eui Young Kim, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy)
 Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL
 The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL Conflict of Interest This presentation is supported by AstraZeneca Two main steps before
The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL Conflict of Interest This presentation is supported by AstraZeneca Two main steps before
Lung Investigation Service Patient Information Leaflet
 Thoracoscopy Lung Investigation Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The purpose of this leaflet is to answer any questions you may have about having a thoracoscopy. If you are unsure of anything,
Thoracoscopy Lung Investigation Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The purpose of this leaflet is to answer any questions you may have about having a thoracoscopy. If you are unsure of anything,
Well-differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Pleura Diagnosed by Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgical Pleural Biopsy : A Case Report
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 25 1, 67 72, March 2013 Case Report Well-differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Pleura Diagnosed by Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgical Pleural Biopsy : A Case Report Yuri TOMITA
Showa Univ J Med Sci 25 1, 67 72, March 2013 Case Report Well-differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Pleura Diagnosed by Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgical Pleural Biopsy : A Case Report Yuri TOMITA
Korean Journal of Medicine
 Vol. 57, Suppl. II October, 1999 ISSN 1226-329X Korean Journal of Medicine 51th Meeting The Korean Association of Internal Medicine Fall Meeting Oral Presentation and Poster Section October 22-23, 1999
Vol. 57, Suppl. II October, 1999 ISSN 1226-329X Korean Journal of Medicine 51th Meeting The Korean Association of Internal Medicine Fall Meeting Oral Presentation and Poster Section October 22-23, 1999
Min Hur, Eun-Hee Kim, In-Kyung Song, Ji-Hyun Lee, Hee-Soo Kim, and Jin Tae Kim INTRODUCTION. Clinical Research
 Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Thoracic Surgery; An Overview
 Thoracic Surgery What we see Thoracic Surgery; An Overview James P. Locher, Jr, MD Methodist Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery Lung cancer Mets Fungus and TB Lung abcess and empyema Pleural based disease
Thoracic Surgery What we see Thoracic Surgery; An Overview James P. Locher, Jr, MD Methodist Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery Lung cancer Mets Fungus and TB Lung abcess and empyema Pleural based disease
Non-intubated thoracoscopic surgery: initial experience at a single center
 Original Article Non-intubated thoracoscopic surgery: initial experience at a single center Youngkyu Moon 1, Zeead M. AlGhamdi 1,2, Joonpyo Jeon 3, Wonjung Hwang 3, Yunho Kim 1, Sook Whan Sung 1 1 Department
Original Article Non-intubated thoracoscopic surgery: initial experience at a single center Youngkyu Moon 1, Zeead M. AlGhamdi 1,2, Joonpyo Jeon 3, Wonjung Hwang 3, Yunho Kim 1, Sook Whan Sung 1 1 Department
A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean university hospital pediatric dental clinic
 Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(3):203-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.203 A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean
Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(3):203-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.203 A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean
A comparison between two types of indwelling pleural catheters for management of malignant pleural effusions
 Original Article A comparison between two types of indwelling pleural catheters for management of malignant pleural effusions Sushilkumar Satish Gupta 1, Charalampos S. Floudas 2, Abhinav B. Chandra 3
Original Article A comparison between two types of indwelling pleural catheters for management of malignant pleural effusions Sushilkumar Satish Gupta 1, Charalampos S. Floudas 2, Abhinav B. Chandra 3
Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report
 303) Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report Mizuno Y., Iwata H., Shirahashi K., Matsui M., Takemura H. Department of General and Cardiothoracic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine,
303) Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report Mizuno Y., Iwata H., Shirahashi K., Matsui M., Takemura H. Department of General and Cardiothoracic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine,
Navigational bronchoscopy-guided dye marking to assist resection of a small lung nodule
 Case Report on Aerodigestive Endoscopy Navigational bronchoscopy-guided dye marking to assist resection of a small lung nodule Jennifer L. Sullivan 1, Michael G. Martin 2, Benny Weksler 1 1 Division of
Case Report on Aerodigestive Endoscopy Navigational bronchoscopy-guided dye marking to assist resection of a small lung nodule Jennifer L. Sullivan 1, Michael G. Martin 2, Benny Weksler 1 1 Division of
Malignant Effusions. Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital
 Malignant Effusions Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital Malignant Effusions Definition: Presence of malignant cells in the pleural space 75% are caused by
Malignant Effusions Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital Malignant Effusions Definition: Presence of malignant cells in the pleural space 75% are caused by
Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis)
 Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis) Sevda Sener Cömert, MD, FCCP. SBU, Kartal Dr.Lütfi Kırdar Training and Research Hospital Department of Pulmonary
Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis) Sevda Sener Cömert, MD, FCCP. SBU, Kartal Dr.Lütfi Kırdar Training and Research Hospital Department of Pulmonary
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Oncology & Hematology INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Oncology & Hematology http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.4.550 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 550-554 Clinical Implication of Microscopic Anthracotic Pigment in Mediastinal Staging of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Oncology & Hematology http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.4.550 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 550-554 Clinical Implication of Microscopic Anthracotic Pigment in Mediastinal Staging of
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings
 Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
The Relationship of Pleural Pressure to Symptom Development During Therapeutic Thoracentesis*
 Original Research INTERVENTIONAL PULMONOLOGY The Relationship of Pleural Pressure to Symptom Development During Therapeutic Thoracentesis* David Feller-Kopman, MD, FCCP; Allan Walkey, MD; David Berkowitz,
Original Research INTERVENTIONAL PULMONOLOGY The Relationship of Pleural Pressure to Symptom Development During Therapeutic Thoracentesis* David Feller-Kopman, MD, FCCP; Allan Walkey, MD; David Berkowitz,
Advances in the Management of Empyema
 Advances in the Management of Empyema RCP Update in Respiratory Medicine 26 th January 2017 Najib M Rahman Associate Professor of Respiratory Medicine University of Oxford najib.rahman@ndm.ox.ac.uk Financial
Advances in the Management of Empyema RCP Update in Respiratory Medicine 26 th January 2017 Najib M Rahman Associate Professor of Respiratory Medicine University of Oxford najib.rahman@ndm.ox.ac.uk Financial
Long term results of pleurodesis in malignant pleural effusions: Doxycycline vs Bleomycin
 Original Article Long term results of pleurodesis in malignant pleural effusions: Doxycycline vs Bleomycin Rahmatollah Rafiei, Behnam Yazdani, Sayed Milad Ranjbar, Zahra Torabi, Sedigheh Asgary 1, Somayeh
Original Article Long term results of pleurodesis in malignant pleural effusions: Doxycycline vs Bleomycin Rahmatollah Rafiei, Behnam Yazdani, Sayed Milad Ranjbar, Zahra Torabi, Sedigheh Asgary 1, Somayeh
Tunneled pleural catheters for management of malignant pleural effusions: a 2-year review of outcomes at a high-volume center
 Original Article Page 1 of 8 Tunneled pleural catheters for management of malignant pleural effusions: a 2-year review of outcomes at a high-volume center Amit K. Mahajan 1,2, Devon T. Collins 1, Christiana
Original Article Page 1 of 8 Tunneled pleural catheters for management of malignant pleural effusions: a 2-year review of outcomes at a high-volume center Amit K. Mahajan 1,2, Devon T. Collins 1, Christiana
UAMS MEDICAL CENTER TRAUMA SERVICES MANUAL. REVIEWED: New PAGE: 1 of 7. RECOMMENDATION(S): Dr. Michael Sutherland APPROVAL: 04/28/2016
 REVIEWED: New PAGE: 1 of 7 PURPOSE: To provide guidelines for the evaluation and management of patients with traumatic chest wall injury including rib fractures, sternal fractures, hemothorax and retained
REVIEWED: New PAGE: 1 of 7 PURPOSE: To provide guidelines for the evaluation and management of patients with traumatic chest wall injury including rib fractures, sternal fractures, hemothorax and retained
(SKILLS/HANDS-ON) Chest Tubes. Rebecca Carman, MSN, ACNP-BC. Amanda Shumway, PA-C. Thomas W. White, MD, FACS, CNSC
 (SKILLS/HANDS-ON) Chest Tubes Rebecca Carman, MSN, ACNP-BC Nurse Practitioner, Trauma Services, Intermountain Medical Center, Intermountain Healthcare Amanda Shumway, PA-C APC Trauma and Critical Care
(SKILLS/HANDS-ON) Chest Tubes Rebecca Carman, MSN, ACNP-BC Nurse Practitioner, Trauma Services, Intermountain Medical Center, Intermountain Healthcare Amanda Shumway, PA-C APC Trauma and Critical Care
Interruption of the thoracic sympathetic chain is associated
 Thoracoscopic Sympathicotomy King F. Kwong and Mark J. Krasna Interruption of the thoracic sympathetic chain is associated with alleviation of symptoms for a variety of maladies. Until fairly recently,
Thoracoscopic Sympathicotomy King F. Kwong and Mark J. Krasna Interruption of the thoracic sympathetic chain is associated with alleviation of symptoms for a variety of maladies. Until fairly recently,
Endobronchial Metastasis of Epithelioid Sarcoma
 DOI: 10.4046/trd.2011.70.5.423 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2011;70:423-427 CopyrightC2011. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights reserved.
DOI: 10.4046/trd.2011.70.5.423 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2011;70:423-427 CopyrightC2011. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights reserved.
Satisfaction with facial laceration repair by provider specialty in the emergency department
 Clin Exp Emerg Med 15;2(3):179-183 http://dx.doi.org/.15441/ceem.15.5 Satisfaction with facial laceration repair by provider specialty in the emergency department eissn: 2383-4625 Original Article Sang-Jae
Clin Exp Emerg Med 15;2(3):179-183 http://dx.doi.org/.15441/ceem.15.5 Satisfaction with facial laceration repair by provider specialty in the emergency department eissn: 2383-4625 Original Article Sang-Jae
58 th Tri-State Consecutive Case Conference on Lung Disease
 58 th Tri-State Consecutive Case Conference on Lung Disease Presented by the Southeast Thoracic Association VIJAY S. PATEL, M.D. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY SECTION OF CARDIOTHORACIC
58 th Tri-State Consecutive Case Conference on Lung Disease Presented by the Southeast Thoracic Association VIJAY S. PATEL, M.D. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY SECTION OF CARDIOTHORACIC
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10): /ISSN: /IJCEM
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):18945-18953 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0011800 Original Article Efficacy of medical thoracoscopic talc pleurodesis in malignant pleural effusion caused by different
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):18945-18953 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0011800 Original Article Efficacy of medical thoracoscopic talc pleurodesis in malignant pleural effusion caused by different
Pleural Fluid Analysis: Back to Basics
 Pleural Fluid Analysis: Back to Basics Tonya L. Page, MSN, RN, ACNP-BC Patrick A. Laird, DNP, RN, ACNP-BC 70 y/o female with complaints of shortness of breath and orthopnea for 1 month. Symptoms have worsened
Pleural Fluid Analysis: Back to Basics Tonya L. Page, MSN, RN, ACNP-BC Patrick A. Laird, DNP, RN, ACNP-BC 70 y/o female with complaints of shortness of breath and orthopnea for 1 month. Symptoms have worsened
Pleuroscopy offers physicians a unique opportunity for the
 STATE OF THE ART: CONCISE REVIEW State of the Art: Pleuroscopy Pyng Lee, MD,* and Henri G. Colt, MD, FCCP The terms pleuroscopy, thoracoscopy, medical thoracoscopy, and video-assisted thoracic surgery
STATE OF THE ART: CONCISE REVIEW State of the Art: Pleuroscopy Pyng Lee, MD,* and Henri G. Colt, MD, FCCP The terms pleuroscopy, thoracoscopy, medical thoracoscopy, and video-assisted thoracic surgery
ISSN: (Print)/ (Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;77:
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.77.4.188 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;77:188-192 New-Onset Malignant Pleural Effusion after Abscess Formation of a Subcarinal
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.77.4.188 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;77:188-192 New-Onset Malignant Pleural Effusion after Abscess Formation of a Subcarinal
Prognostic value of visceral pleura invasion in non-small cell lung cancer q
 European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 23 (2003) 865 869 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Prognostic value of visceral pleura invasion in non-small cell lung cancer q Jeong-Han Kang, Kil Dong Kim, Kyung
European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 23 (2003) 865 869 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Prognostic value of visceral pleura invasion in non-small cell lung cancer q Jeong-Han Kang, Kil Dong Kim, Kyung
minimally invasive techniques Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery Using Single-Lumen Endotracheal Tube Anesthesia*
 minimally invasive techniques Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery Using Single-Lumen Endotracheal Tube Anesthesia* Robert James Cerfolio, MD, FCCP; Ayesha S. Bryant, MSPH; Todd M. Sheils, MD; Cynthia
minimally invasive techniques Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery Using Single-Lumen Endotracheal Tube Anesthesia* Robert James Cerfolio, MD, FCCP; Ayesha S. Bryant, MSPH; Todd M. Sheils, MD; Cynthia
Outcomes & Clinical Trials Update: Empyema & NEC
 Outcomes & Clinical Trials Update: Empyema & NEC American Pediatric Surgical Association Outcomes & Clinical Trials Committee Fizan Abdullah, Chair Saleem Islam, Vice Chair Gudrun Aspelund Catherine C.
Outcomes & Clinical Trials Update: Empyema & NEC American Pediatric Surgical Association Outcomes & Clinical Trials Committee Fizan Abdullah, Chair Saleem Islam, Vice Chair Gudrun Aspelund Catherine C.
The Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index in Predicting the Prognosis of Patients With Pulmonary Embolism
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2009.24.2.123 The Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index in Predicting the Prognosis of Patients With Pulmonary Embolism Won-Ho Choi 1, Sung Uk Kwon 1,2, Yoon Jung Jwa 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2009.24.2.123 The Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index in Predicting the Prognosis of Patients With Pulmonary Embolism Won-Ho Choi 1, Sung Uk Kwon 1,2, Yoon Jung Jwa 1,
Surgical decortication as the first-line treatment for pleural empyema
 Shin et al General Thoracic Surgical decortication as the first-line treatment for pleural empyema Jung Ar Shin, MD, a Yoon Soo Chang, MD, PhD, a Tae Hoon Kim, MD, PhD, b Seok Jin Haam, MD, c Hyung Jung
Shin et al General Thoracic Surgical decortication as the first-line treatment for pleural empyema Jung Ar Shin, MD, a Yoon Soo Chang, MD, PhD, a Tae Hoon Kim, MD, PhD, b Seok Jin Haam, MD, c Hyung Jung
Is the Initial Size of Tuberculous Lymphadenopathy associated with Lymph Node Enlargement during Treatment?
 Brief Communication https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2017.49.2.130 Infect Chemother 2017;49(2):130-134 ISSN 2093-2340 (Print) ISSN 2092-6448 (Online) Infection & Chemotherapy Is the Initial Size of Tuberculous
Brief Communication https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2017.49.2.130 Infect Chemother 2017;49(2):130-134 ISSN 2093-2340 (Print) ISSN 2092-6448 (Online) Infection & Chemotherapy Is the Initial Size of Tuberculous
16 year old with Disabling Chest Wall Pain after Thoracoscopic Talc Pleurodesis for Treatment of Recurrent Spontaneous Pneumothoraces
 16 year old with Disabling Chest Wall Pain after Thoracoscopic Talc Pleurodesis for Treatment of Recurrent Spontaneous Pneumothoraces Moderators: Kendra Grim, MD, Robert T. Wilder, MD, PhD Institution:
16 year old with Disabling Chest Wall Pain after Thoracoscopic Talc Pleurodesis for Treatment of Recurrent Spontaneous Pneumothoraces Moderators: Kendra Grim, MD, Robert T. Wilder, MD, PhD Institution:
Image: reproduced from Eur Respir Mon 2010; 48: with permission from the publisher.
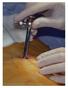 Image: reproduced from Eur Respir Mon 2010; 48: 119 132 with permission from the publisher. R. Loddenkemper 1 P. Lee 2 M. Noppen 3 P.N. Mathur 4 1 German Central Committee against Tuberculosis (DZK), Lungenklinik
Image: reproduced from Eur Respir Mon 2010; 48: 119 132 with permission from the publisher. R. Loddenkemper 1 P. Lee 2 M. Noppen 3 P.N. Mathur 4 1 German Central Committee against Tuberculosis (DZK), Lungenklinik
Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
Routine chest drainage after patent ductus arteriosis ligation is not necessary
 Original Article Brunei Int Med J. 2010; 6 (3): 126-130 Routine chest drainage after patent ductus arteriosis ligation is not necessary Amy THIEN, Samuel Kai San YAPP, Chee Fui CHONG Department of Surgery,
Original Article Brunei Int Med J. 2010; 6 (3): 126-130 Routine chest drainage after patent ductus arteriosis ligation is not necessary Amy THIEN, Samuel Kai San YAPP, Chee Fui CHONG Department of Surgery,
Study of Predictors for Successful Pleurodesis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 1, March: 11-20, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Study of Predictors for Successful Pleurodesis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion TALAT A. ARAFA,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 1, March: 11-20, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Study of Predictors for Successful Pleurodesis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion TALAT A. ARAFA,
Imaging of small amounts of pleural fluid. Part two - physiologic pleural fluid
 review Imaging of small amounts of pleural fluid. Part two - physiologic pleural fluid Igor Kocijančič Department of Radiology, Institute of Oncology, Ljubljana, Slovenia Background. There are only a few
review Imaging of small amounts of pleural fluid. Part two - physiologic pleural fluid Igor Kocijančič Department of Radiology, Institute of Oncology, Ljubljana, Slovenia Background. There are only a few
Atypical Pleural Fluid Profiles in Tuberculous Pleural Effusion: Sequential Changes Compared with Parapneumonic and Malignant Pleural Effusions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Atypical Pleural Fluid Profiles in Tuberculous Pleural Effusion: Sequential Changes Compared with Parapneumonic and Malignant Pleural Effusions Chang Ho Kim, So Yeon Lee, Yong Dae Lee,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Atypical Pleural Fluid Profiles in Tuberculous Pleural Effusion: Sequential Changes Compared with Parapneumonic and Malignant Pleural Effusions Chang Ho Kim, So Yeon Lee, Yong Dae Lee,
Post-Graduate ERS Seminar on Medical Thoracoscopy. October 13-15, Alexandroupolis, Greece
 Post-Graduate ERS Seminar on Medical Thoracoscopy October 13-15, 2011 - Alexandroupolis, Greece Invited speakers Subjects Robert Loddenkemper, Berlin, Germany YC Gary Lee, Perth Australia Wolfgang Frank,
Post-Graduate ERS Seminar on Medical Thoracoscopy October 13-15, 2011 - Alexandroupolis, Greece Invited speakers Subjects Robert Loddenkemper, Berlin, Germany YC Gary Lee, Perth Australia Wolfgang Frank,
How to do it: ultrasoundguided
 How to do it: ultrasoundguided pleural biopsy Background Malignancy is the cause of 40,000 pleural effusions in the UK and 175,000 in the USA [1], with pleural fluid cytology able to diagnose, at best,
How to do it: ultrasoundguided pleural biopsy Background Malignancy is the cause of 40,000 pleural effusions in the UK and 175,000 in the USA [1], with pleural fluid cytology able to diagnose, at best,
Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems
 Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems Pneumothorax Definition Air accumulation in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse Sources Visceral pleura Ruptured esophagus Chest wall defect Gas-forming
Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems Pneumothorax Definition Air accumulation in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse Sources Visceral pleura Ruptured esophagus Chest wall defect Gas-forming
Long-term respiratory function recovery in patients with stage I lung cancer receiving video-assisted thoracic surgery versus thoracotomy
 Original Article Long-term respiratory function recovery in patients with stage I lung cancer receiving video-assisted thoracic surgery versus thoracotomy Tae Yun Park 1,2, Young Sik Park 2 1 Division
Original Article Long-term respiratory function recovery in patients with stage I lung cancer receiving video-assisted thoracic surgery versus thoracotomy Tae Yun Park 1,2, Young Sik Park 2 1 Division
A Case of Locally Advanced Well-Differentiated Fetal Adenocarcinoma of the Lung Treated with Concurrent Chemoradiation Therapy
 http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2013.74.5.226 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2013;74:226-230 CopyrightC2013. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights
http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2013.74.5.226 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2013;74:226-230 CopyrightC2013. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights
Best timing for surgical intervention of empyema. Supervisor: Intern:
 Best timing for surgical intervention of empyema Supervisor: Intern: Brief history 56 y/o male, farmer With anesthesia medication at LMD Admission 30d 7d Dry cough Progressive productive cough with yellow
Best timing for surgical intervention of empyema Supervisor: Intern: Brief history 56 y/o male, farmer With anesthesia medication at LMD Admission 30d 7d Dry cough Progressive productive cough with yellow
