Medical thoracoscopy for exudative pleural effusion: an eight-year experience from a country with a young population
|
|
|
- Jody Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thomas et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017) 17:151 DOI /s y RESEARCH ARTICLE Medical thoracoscopy for exudative pleural effusion: an eight-year experience from a country with a young population Open Access Merlin Thomas 1*, Wanis H. Ibrahim 1, Tasleem Raza 1, Kamran Mushtaq 2, Adeel Arshad 2, Mushtaq Ahmed 2, Salma Taha 2, Saber Al Sarafandi 2, Hanfa Karim 2 and Hisham A. Abdul-sattar 1 Abstract Background: With the exception of areas with high prevalence of tuberculosis, medical thoracoscopy is becoming the diagnostic modality of choice for exudative pleural effusions. The aims of this study were to determine the diagnostic yield and safety of medical thoracoscopy for exudative pleural effusions and ascertain the etiology of such effusions in Qatar. Methods: This is a retrospective-descriptive study of 407 patients who underwent diagnostic medical thoracoscopy for exudative pleural effusions from January, 2008 till December, 2015 at the only tertiary referral center performing this procedure in Qatar. Results: Tuberculosis was the most common etiology of exudative pleural effusions in Qatar accounting for 84.5% of all causes. Around 85% of patients were young males (mean age of 33 ± 12.1 years). The diagnostic yield of medical thoracoscopy for tuberculous pleural effusion was 91.4%. Malignant pleural effusions accounted for 5.2% of cases. Minor bleeding occurred in 1.2% of cases with no procedure-related mortality observed. Conclusion: Medical thoracoscopy is a very safe procedure. Tuberculous pleuritis is by far the most common etiology of exudative pleural effusions in Qatar. Closed needle biopsy is a worth consideration as an initial safe, easy and low-cost diagnostic modality for exudative pleural effusions in this country. Keywords: Medical thoracoscopy, Pleural effusion, Tuberculosis, Malignancy Background The first thoracoscopy (also termed pleuroscopy) was introduced by Hans-Christian JacÖbaeus in 1910 for replacement of pleural fluid with air as a treatment of tuberculous pleural effusion [1, 2]. In the 1990s videoassisted surgical thoracoscopy (VATS), which is performed under general anesthesia, was introduced. Medical thoracoscopy (MT) (a less invasive and less expensive procedure with a single port of entry) can be performed under local anesthesia and conscious sedation, usually by pulmonologists. MT is primarily a diagnostic procedure but can also be applied for therapeutic purposes such as pleurodesis and removal of pleural adhesions [2]. Qatar is an oil * Correspondence: mmts1983@gmail.com 1 Pulmonary Division, Department of Medicine, Hamad General Hospital, P.O.BOX 3050 Doha, Qatar Full list of author information is available at the end of the article and gas-rich nation with a total population of 2,437,790 (2015 estimate). People below the age of 45 years constitute around 85% of the population of Qatar [3] and the country relies heavily on this labor force for its economic and industrial projects. The country is currently witnessing comprehensive reforms in its health care system aiming at achieving a world-class, patient-centered health care system by Hospitals in Qatar are of high standards and all accredited by the Joint Commission International. Exudative pleural effusions of unclear etiology generally require pleural biopsy for definite diagnosis. The etiology varies across different parts of the world. While pneumonia, malignancy, and thromboembolism account for most exudative effusions in the United States [4], tuberculosis (TB) is the most frequently encountered etiology in other developed as well as developing countries [5]. The objectives of the current study were to determine The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Thomas et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017) 17:151 Page 2 of 5 the yield and safety of MT as a diagnostic tool for exudative pleural effusions as well as ascertain the etiology of this type of effusion in a country with a predominantly young population. Methods This was a retrospective-descriptive study of all patients who underwent MT to confirm the etiology of undiagnosed exudative pleural effusions and in whom initial hematological, microbiological, and cytological analyses were inconclusive. The diagnosis of exudative pleural effusion in the current study was based on Light s criteria [4]. The study was conducted at Hamad general Hospital (the only tertiary referral center performing MT in the State of Qatar) during the period from January, 2008 to December, The study protocol was approved by the Medical Research Centre at Hamad Medical Corporation. Thoracoscopic procedure MT at Hamad General Hospital is performed in the bronchoscopy suite by pulmonologists under local anesthesia and conscious sedation. A rigid thoracoscope (Karl Storz Endoskope; Karl Storz; Tuttlingen, Germany) is used for such procedure. The patient usually lies on the healthy side in a lateral decubitus position with the involved side up. An anterolateral thoracic approach in the 5th or 6th intercostal space is predominantly used with ultrasound guidance. Following a 1-2 cm incision, blunt dissection is done with an artery forceps and a trocar with an inner diameter of 8 mm is inserted through a cannula followed by insertion of thoracoscope. The pleural cavity is thoroughly inspected and around 2-4 biopsies are taken from the abnormal lesions on parietal pleura by a lateral lift and peel technique. Multiple biopsies are taken if no gross abnormalities are noted and the samples are sent for histopathology and culture for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. After thoracoscopy, a 24-French chest tube connected to an underwater sealed drain is routinely inserted for drainage of iatrogenic pneumothorax and the tube is removed once pneumothorax has resolved. Data collection A structured data sheet in view of research study design and objectives was designed and created to collect all required data such as demographic details, pleural fluid characteristics, site of effusion, visual appearances on thoracoscopy, complications from the procedure, length of stay as well as pathological and microbiological diagnostic details. For quality assurance, all investigators who were involved in data collection received prior training on how to collect the data and complete the study data sheet. Statistical analysis Categorical and continuous values were expressed as frequency (percentage) and mean ± SD or median. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize demographic and all other clinical characteristics of the study subjects. The primary outcome variable was to evaluate and assess the outcome and complications rate secondary to medical thoracoscopy and enlist causes of exudative effusions. Associations between two or more qualitative variables were assessed using the chi-square test or Fisher Exact test as appropriate. Relationship between two quantitative variables was examined using Pearson s correlation coefficients. A 2-sided P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 19.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, Illinois). Results The diagnostic accuracy of MT for tuberculous pleural effusion (TPE) was 91.4% with a sensitivity of 90% and specificity of 100%. The demonstration of one or more of following abnormalities in pleural biopsy specimen in a patient with high pretest clinical probability for TB was considered diagnostic of TPE: (I) presence of acidfast bacilli on stain or culture; (II) caseating granulomas; (III) epithelioid cell granuloma with no evidence of other granulomatous diseases. Table 1 presents the demographic characteristics of the study subjects. Over a period of 8 years, a total of 407 patients underwent diagnostic MT for exudative pleural effusions. More than 85% of the patients were males with a mean age of 33 ± 12.1 years. There was a significant difference in the mean age group of patients with TPE (30.8 ± 9.5 years) Table 1 Demographic characteristics of the study subjects Characteristic n (%) Mean age 33.3 ± 12.1 Gender (n = 407) Male 357 (87.7) Female 50 (12.3) Ethnicity (n = 407) Indian Sub-continent 295 (72.5) Philippines 29 (7.1) Middle east 35 (8.6) African 36 (8.8) Others a 12 (3) Occupation (n = 325) Unskilled 197 (48) Semiskilled 76 (19) Skilled 31 (8) Others b 21 (5) a Others - Iran, Thailand, Europe, Unknown b Others - Housewife, retired, student
3 Thomas et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017) 17:151 Page 3 of 5 and the Non TPE patients (46.8 ± 15.8 years) (P < ). Majority of patients who underwent diagnostic MT during the study period were young expatriates from Indian subcontinents and they constituted 77% of the TPE cases. Table 2 shows the etiology of pleural effusions in the study subjects. By far, tuberculous pleuritis was the most common etiology of exudative pleural effusions during the study period accounting for 84.5% of all causes. Sputum culture grew Mycobacterium tuberculosis in 65 (19%) patients with TPE. Most of the exudative pleural effusions in the current study were unilateral with right-sided effusions being more commonthanleft-sidedeffusions(55and40%respectively). Bilateral effusions were seen in only 5% of patients. Forty five percent of effusions were moderate in size (between one-third and two-thirds of hemithorax), 22% were mild (less than one-third of hemithorax) and 19% were massive (more than two-third of hemithorax or causing midline shift). Parenchymal infiltrates were noted in 111 patients of whom 90 patients had TPE (Missing data in more than 50% of patients). Interestingly, malignant pleural effusions accounted for only 5.2% of the cases with metastatic pulmonary adenocarcinoma being the most commonly encountered neoplasm. The most common findings on gross thoracoscopic appearance of the pleura were hyperemia, sago-likenodulesandmultiplethinadhesions(around 51% of patients) (Table 3). Granulomatous inflammation was the most commonly encountered histologic finding (in around 75% of cases) followed by nonspecific fibrinous pleuritis (17%) (Table 4). Table 5 presents the complications and post-operative care findings of MT. The median length of stay for patients who underwent MT was 3 days. Minor bleeding occurred in 1.2% of cases with no procedure-related mortality observed. Table 2 Etiology of exudative effusions (n = 401) Etiology n (%) Tuberculous pleural effusions 344 (84.5) Para-pneumonic effusions 22 (5.4) Malignant Effusions 21 (5.2) Metastatic Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma 8 (38) Metastatic Breast carcinoma 4 (19) Lymphoma 4 (19) Malignant mesothelioma 3 (14) Malignant epithelial neoplasm 1 (5) Squamous cell carcinoma Lung 1 (5) Idiopathic 12 (2.9) Others a 3 (0.7) 6 patients were lost to follow up a Others Inflammatory (2) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (1) Table 3 Gross thoarcoscopic findings (n = 390) Findings n (%) Inflammation + sago like nodules ± adhesions 205 (51.2) Inflammation +/ adhesions a 128 (32.4) Inflammation with nodules/masses/plaques a 33 (8.3) Normal 27 (6.9) a Inflammation defined as edematous, deep and pink pleura Discussion Among the most common respiratory illnesses encountered in day-to-day clinical practice are undiagnosed exudative pleural effusions. Thoracentesis is usually the first diagnostic procedure performed to identify the etiology of these effusions. Although etiologies vary from country to country, malignant diseases, tuberculosis and empyema remain the most commonly encountered causes for exudative pleural effusions. Unfortunately, 40% of patients with malignant pleural effusions remain undiagnosed after a routine cytological examination of the pleural fluid and TB culture is positive in only 20% of TPE [6, 7]. Blind pleural biopsy using Abrams needle is easy to perform, safe, and inexpensive. Although the value of closed needle biopsy in malignant pleural effusions is still a matter of controversy, it has a high yield (up to 80%) in TPE particularly when combined with pleural fluid TB culture. This has been attributed to the diffuse pattern in which TB affects the pleura. Hence, closed needle biopsy remains an important diagnostic tool in countries where the pre-test probability of TB is high and has been recommended as the initial diagnostic modality in these areas [8 12]. Despite being more expensive than blind pleural biopsy, MT is becoming the standard diagnostic modality for undiagnosed exudative pleural effusions in developed and some developing countries as it enables direct visualization of the pleural space. Different studies from many countries have confirmed the high yield of MT in diagnosing exudative pleural effusions that exceeds 70% and can reach as high as 95% in malignant effusions and 99% in TPE [9, 13 16]. Taking into consideration the high prevalence of TPE in the study subjects, the diagnostic yield of MT in the current study is lower than what was anticipated. One explanation for the relatively lower yield in Qatar is Table 4 Histological and microbiological findings (n = 407) Pathology n (%) Granulomatous inflammation 304 (74.7%) Fibrinous pleuritis 69 (17) Malignant 13 (3.2) Normal pleura 9 (2.2) Others a 12 (2.9) a Others Inadequate sample-11(2.7) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (1)
4 Thomas et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017) 17:151 Page 4 of 5 Table 5 Post thoracoscopy care and complications (n = 407) Characteristic Value Length of Stay Median 3 (IQR a 5) Duration of chest tube Days Median 1 (IQR- 0) Complications n (%) Minor Bleeding 5 (1.2) Persistent Air leak >3 days 15 (3.7) a IQR Interquartile range the low threshold of performing MT for cases with extensive pleural adhesions (due to non-visualization) which has resulted in the finding of non-specific fibrinous pleuritis in as high as 17% of cases (Table 4). Furthermore, the number of thoracoscopic biopsies (2-4 biopsies) performed at Hamad General Hospital per case is lower than the international recommendation and may be a contributor to the low diagnostic yield [12, 17]. Two striking findings have been observed in the current study. The first was the very high percentage of TPE (as compared to malignant effusions) diagnosed by MT in Qatar (84.5% vs. 5.4%). This finding has not been observed in previous studies from other countries including those with high TB prevalence [16, 18]. The other striking finding was the young age of patients with undiagnosed exudative pleural effusions who underwent MT. There are 3 plausible reasons for these findings; firstly, people below the age of 45 years constituted 85% of the total population in Qatar. Labor force from countries with high TB prevalence constitutes a significant proportion of such young population as well as 97% of TB cases encountered in this country [19]. In contrast to pleural TB in developed countries, Ibrahim, et al. in a previous study of pleural TB in Qatar found that younger age groups were the most commonly affected by the disease (84% are below the age of 45 years, with mean age of 31.5). Furthermore, the pleural involvement in most of the cases resulted from primary infection rather than reactivation of an old pulmonary TB [7]. Secondly, in contrast to other developing countries where closed needle biopsy is the initial diagnostic consideration in suspected pleural TB, this procedure is very rarely performed nowadays in Qatar and has largely been replaced by MT. Moreover, owing to the highly effective and strict National TB Control Program in Qatar, there is usually emphasis on tissue or microbiologic diagnosis of TB in the country. The median length of stay (LOS) and duration of chest tube in the current study were 3 days and 1 day respectively. These findings are in agreement with international figures [12]. Nevertheless, we believe that other factors (unrelated to the procedure) such as waiting for confirmatory histologic reports and the process of incorporating patient s data in TB registry prior to discharge are important contributors to the LOS following MT in Qatar. Recently, it has become feasible in a number of countries to perform the procedure as a day-case [10]. The current study was the first to document the experience with MT in this country with a young population. The results of this study can be generalized to the whole country as Hamad General Hospital is the only tertiary referral center performing MT in Qatar and receives referrals from other health care facilities in the country. Nevertheless, in addition to the limitations inherent in a retrospective study, an important limitation of this study is the lack of comparison between MT and closed needle biopsy with regard to diagnostic yield, safety and cost effectiveness particularly in cases with suspected TPE from this region. Furthermore the finding of a high percentage of nonspecific fibrinous pleuritis due to extensive adhesions has limited the yield of MT in the current study. Conclusion This study has confirmed the safety and value of MT as a diagnostic modality for undiagnosed exudative pleural effusions. In contrast to studies conducted in other parts of the world (including those with high TB prevalence), the current study confirmed that tuberculous pleuritis is by far the most common cause of undiagnosed exudative pleural effusion in Qatar. Furthermore, there is a very low threshold of using MT (rather than closed needle biopsy) for cases with suspected pleural TB. Owing to the high prevalence of TPE as compared to malignant effusions in Qatar and the previously reported high yield of closed needle biopsy, we recommend that closed needle biopsy rather than MT to be the initial safe, easy and low-cost diagnostic modality when TPE effusion is suspected. Abbreviations LOS: Length of stay; MT: Medical thoracoscopy; TB: Tuberculosis; TPE: Tuberculous pleural effusion Acknowledgements We are immensely grateful to Dr. Prem Chandra at Medical Research Centre, Hamad Medical Corporation for his assistance with the statistical analysis. Funding The approved research is funded by the Medical Research Centre at Hamad Medical Corporation for conference presentation and journal publication. Availability of data and materials The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Authors contributions MT has been involved in conceptualization, designing, data analysis, manuscript writing and review. WI, TR and HS has participated in Manuscript writing and review. KM, AA, MA, ST and SS has participated in data collection, data entry and data analysis. HK has participated in data analysis, manuscript writing and review. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
5 Thomas et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017) 17:151 Page 5 of 5 Ethics approval and consent to participate The research protocol #14422/14 has been approved by the Medical Research Centre at Hamad Medical Corporation and is classified as exempt. A waiver of informed consent has been approved for this retrospective study. Consent for publication Not applicable. 18. Sodhi R, Sindhwani G, Nadia S, Kumar S, Jethani V, Khanduri S. A three-year experience of medical Thoracoscopy at a tertiary care center of Himalayan region. J Cardiothorac Med. 2016;4(1): Khattab MA, Khan FY, Al Maslamani M, Al-Khal AL, El Gendy A, Al Soub H, et al. Pulmonary and extra pulmonary tuberculosis in Qatar: a first retrospective population-based study. Adv Infect Dis. 2015;5: Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Author details 1 Pulmonary Division, Department of Medicine, Hamad General Hospital, P.O.BOX 3050 Doha, Qatar. 2 Department of Medicine, Hamad General Hospital, P.O.BOX 3050 Doha, Qatar. Received: 21 May 2017 Accepted: 14 November 2017 References 1. JacÖbaeus HC. Ueber Moglichkeit; die Zystoskopie bei Untersuching seroser Hohlungen anzuwednde. Munch med Wschr. 1910;57: Loddenkemper R, Mathur PN, Lee P, Noppen M. History and clinical use of thoracoscopy/pleuroscopy in respiratory medicine. Breathe. 2011;8(2): Ministry of Development, Planning and Statistics/Qatar. gov.qa/en/statistics1/statisticssite/pages/default.aspx. Accessed 22 Dec Light RW. Clinical practice. Pleural effusion. N Engl J Med. 2002;346: Valdés L, Alvarez D, Valle J, Pose A, José E. The etiology of pleural effusions in an area with high incidence of tuberculosis. Chest. 1996;109(1): Brock MV, Hooker CM, Yung R, Guo M, Han Y, Ames SE, et al. Can we improve the cytologic examination of malignant pleural effusions using molecular analysis? Ann Thorac Surg. Oct. 2005;80(4): Ibrahim WH, Ghadban W, Khinji A, Yasin R, Soub H, Al-Khal AL, et al. Does pleural tuberculosis disease pattern differ among developed and developing countries? Respir Med. Aug. 2005;99(8): Solooki M, Miri M. Approach to undiagnosed exudative pleural effusion: the diagnostic yield of blind pleural biopsy. Caspian J Intern Med. 2013;4(2): Loddenkemper R, Grosser H, Gabler A, Mai J, Presseuler H, Brandt HJ. Prospective evaluation of biopsy methods in diagnosis of malignant pleural effusions: intrapatient comparison between pleural fluid cytology, blind needle biopsy and thoracoscopy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983;127(Suppl 4): Dixon G, de Fonseka D, Maskell N. Pleural controversies: image guided biopsy vs. thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusions? J Thorac Dis. 2015;7(6): Diacon AH, Van de Wal BW, Wyser C, Smedema JP, Bezuidenhout J, Bolliger CT, et al. Diagnostic tools in tuberculous pleurisy: a direct comparative study. Eur Respir J. 2003;22: Rahman NM, Ali NJ, Brown G, Chapman SJ, Davies RJ, Downer NJ, et al. Local anesthetic thoracoscopy: British Thoracic Society pleural disease guideline Thorax. 2010;65(Suppl 2):ii Tscheikuna J, Silairatana S, Sangkeaw S, Nana A. Outcome of medical thoracoscopy. J Med Assoc Thail. 2009;92(Suppl 2):S Valsecchi A, Arondi S, Marchetti G. Medical thoracoscopy: analysis on diagnostic yield through 30 years of experience. Ann Thorac Med Jul- Sep;11(3): Hansen M, Faurschou P, Clementsen P. Medical thoracoscopy, results and complications in 146 patients: a retrospective study. Respir Med. 1998;92(2): Mootha VK, Agarwal R, Singh N, Aggarwal AN, Gupta D, Jindal SK. Indian J medical thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusions: experience from a tertiary care hospital in north India. Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2011;53(1): Loddenkemper R, Lee P, Noppen M, Mathur PN. Medical thoracoscopy/ pleuroscopy: step by step. Breathe. 2011;8(2): Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and we will help you at every step: We accept pre-submission inquiries Our selector tool helps you to find the most relevant journal We provide round the clock customer support Convenient online submission Thorough peer review Inclusion in PubMed and all major indexing services Maximum visibility for your research Submit your manuscript at
The Portsmouth thoracoscopy experience, an evaluation of service by retrospective case note analysis
 Respiratory Medicine (2007) 101, 1021 1025 The Portsmouth thoracoscopy experience, an evaluation of service by retrospective case note analysis Sophie V. Fletcher,1, Robin J. Clark Respiratory Centre,
Respiratory Medicine (2007) 101, 1021 1025 The Portsmouth thoracoscopy experience, an evaluation of service by retrospective case note analysis Sophie V. Fletcher,1, Robin J. Clark Respiratory Centre,
A Repeat Case of Idiopathic Spontaneous Hemothorax
 Case Report A Repeat Case of Idiopathic Spontaneous Hemothorax Felix R. Gaw, MD Jack H. Bloch, MD, PhD, FACS Nolan J. Anderson, MD, FACS Spontaneous hemothorax, a collection of blood in the pleural cavity
Case Report A Repeat Case of Idiopathic Spontaneous Hemothorax Felix R. Gaw, MD Jack H. Bloch, MD, PhD, FACS Nolan J. Anderson, MD, FACS Spontaneous hemothorax, a collection of blood in the pleural cavity
Diagnostic Utility of Indigenous Technique of Pleuroscopy in Undiagnosed Cases of Exudative Pleural Effusions
 Journal of Health Science 6 (2018) 304-309 doi: 10.17265/2328-7136/2018.04.009 D DAVID PUBLISHING Diagnostic Utility of Indigenous Technique of Pleuroscopy in Undiagnosed Cases of Exudative Pleural Effusions
Journal of Health Science 6 (2018) 304-309 doi: 10.17265/2328-7136/2018.04.009 D DAVID PUBLISHING Diagnostic Utility of Indigenous Technique of Pleuroscopy in Undiagnosed Cases of Exudative Pleural Effusions
The Role of Fiberoptic bronchoscopy in Evaluating The causes of Undiagnosed Pleural Effusion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-083, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. VI (January. 2017), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org The Role of Fiberoptic bronchoscopy
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-083, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. VI (January. 2017), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org The Role of Fiberoptic bronchoscopy
Medical Thoracoscopy: Experiences in Siriraj Hospital
 Medical Thoracoscopy: Experiences in Siriraj Hospital Jamsak Tscheikuna MD* * Division of Respiratory Disease and Tuberculosis, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University
Medical Thoracoscopy: Experiences in Siriraj Hospital Jamsak Tscheikuna MD* * Division of Respiratory Disease and Tuberculosis, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University
Ultrasound-Guided Medical Thoracoscopy in the Absence of Pleural Effusion
 [ Original Research Pulmonary Procedures ] Ultrasound-Guided Medical Thoracoscopy in the Absence of Pleural Effusion Giampietro Marchetti, MD, FCCP ; Alberto Valsecchi, MD ; Davide Indellicati, MD ; Sabrina
[ Original Research Pulmonary Procedures ] Ultrasound-Guided Medical Thoracoscopy in the Absence of Pleural Effusion Giampietro Marchetti, MD, FCCP ; Alberto Valsecchi, MD ; Davide Indellicati, MD ; Sabrina
Management of Pleural Effusion
 Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Alper Toker, MD. VATS decortication. Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery
 VATS decortication Alper Toker, MD Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery Pleural space infection is a common pathology causing morbidity and mortality. It is a collection
VATS decortication Alper Toker, MD Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery Pleural space infection is a common pathology causing morbidity and mortality. It is a collection
ROLE OF FIBREOPTIC BRONCHOSCOPY IN EVALUATION OF PLEURAL EFFUSION CASES
 ROLE OF FIBREOPTIC BRONCHOSCOPY IN EVALUATION OF PLEURAL EFFUSION CASES Somnath Dash, Sushanta Kumar Mishra, G. Srinivas, K. V. Ramana Rao, N. Durga Prasad 1. Associate Professor. Department of Pulmonary
ROLE OF FIBREOPTIC BRONCHOSCOPY IN EVALUATION OF PLEURAL EFFUSION CASES Somnath Dash, Sushanta Kumar Mishra, G. Srinivas, K. V. Ramana Rao, N. Durga Prasad 1. Associate Professor. Department of Pulmonary
Medical Thoracoscopy When to Choose Over a General Anaesthetic VATS
 Medical Thoracoscopy When to Choose Over a General Anaesthetic VATS SpR Training Day 07.07.14 Dr Alex West Consultant Chest/Pleural Physician Guy s and St Thomas Hospital Medical Thoracoscopy? No Just
Medical Thoracoscopy When to Choose Over a General Anaesthetic VATS SpR Training Day 07.07.14 Dr Alex West Consultant Chest/Pleural Physician Guy s and St Thomas Hospital Medical Thoracoscopy? No Just
Medical Thoracoscopy in Pleural Disease: Experience from a One-Center Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2017.80.2.194 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2017;80:194-200 Medical Thoracoscopy in Pleural Disease: Experience from a One-Center
ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2017.80.2.194 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2017;80:194-200 Medical Thoracoscopy in Pleural Disease: Experience from a One-Center
Chapter 8. Other Important Tests and Procedures. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis)
 Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis) Sevda Sener Cömert, MD, FCCP. SBU, Kartal Dr.Lütfi Kırdar Training and Research Hospital Department of Pulmonary
Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis) Sevda Sener Cömert, MD, FCCP. SBU, Kartal Dr.Lütfi Kırdar Training and Research Hospital Department of Pulmonary
Initial experience of medical pleuroscopy via the peel-away introducer of the indwelling pleural catheter using a thin bronchoscope
 Surgical Technique of Interventional Pulmonology Corner Initial experience of medical pleuroscopy via the peel-away introducer of the indwelling pleural catheter using a thin bronchoscope Kassem Harris
Surgical Technique of Interventional Pulmonology Corner Initial experience of medical pleuroscopy via the peel-away introducer of the indwelling pleural catheter using a thin bronchoscope Kassem Harris
Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell lymphocyte proliferative disease
 Du et al. Respiratory Research (2018) 19:247 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0941-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell
Du et al. Respiratory Research (2018) 19:247 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0941-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell
Interventional Pulmonary Case Based Discussions (ATS) Ali Imran Saeed, MD University of New Mexico
 Interventional Pulmonary Case Based Discussions (ATS) Ali Imran Saeed, MD University of New Mexico Objectives Interventional Pulmonary in New Mexico Interventional Pulmonary and Advanced Diagnostic Cases
Interventional Pulmonary Case Based Discussions (ATS) Ali Imran Saeed, MD University of New Mexico Objectives Interventional Pulmonary in New Mexico Interventional Pulmonary and Advanced Diagnostic Cases
Role of medical Thoracoscopy in the Management of Multiloculated Empyema
 Sumalani et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018) 18:179 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0745-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Role of medical Thoracoscopy in the Management of Multiloculated Empyema Kamran Khan Sumalani
Sumalani et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018) 18:179 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0745-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Role of medical Thoracoscopy in the Management of Multiloculated Empyema Kamran Khan Sumalani
Malignant Effusions. Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital
 Malignant Effusions Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital Malignant Effusions Definition: Presence of malignant cells in the pleural space 75% are caused by
Malignant Effusions Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital Malignant Effusions Definition: Presence of malignant cells in the pleural space 75% are caused by
How to do it: ultrasoundguided
 How to do it: ultrasoundguided pleural biopsy Background Malignancy is the cause of 40,000 pleural effusions in the UK and 175,000 in the USA [1], with pleural fluid cytology able to diagnose, at best,
How to do it: ultrasoundguided pleural biopsy Background Malignancy is the cause of 40,000 pleural effusions in the UK and 175,000 in the USA [1], with pleural fluid cytology able to diagnose, at best,
Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural
 Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural San José, Costa Rica Junio 29, 2017 Rodrigo Cartín Ceba, MD, MSc Consultant, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic 2010 MFMER
Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural San José, Costa Rica Junio 29, 2017 Rodrigo Cartín Ceba, MD, MSc Consultant, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic 2010 MFMER
Does serum CA125 have clinical value for follow-up monitoring of postoperative patients with epithelial ovarian cancer? Results of a 12-year study
 Guo and Peng Journal of Ovarian Research (2017) 10:14 DOI 10.1186/s13048-017-0310-y RESEARCH Does serum CA125 have clinical value for follow-up monitoring of postoperative patients with epithelial ovarian
Guo and Peng Journal of Ovarian Research (2017) 10:14 DOI 10.1186/s13048-017-0310-y RESEARCH Does serum CA125 have clinical value for follow-up monitoring of postoperative patients with epithelial ovarian
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion
 Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (IV) No (I) January-June 2015 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Rushi Patel*, Viral Shah*, Deepali Kamdar** Abstract : Aim : Normally the pleural cavities contain
Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (IV) No (I) January-June 2015 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Rushi Patel*, Viral Shah*, Deepali Kamdar** Abstract : Aim : Normally the pleural cavities contain
Modern Approaches to Empyema
 Modern Approaches to Empyema Amit Bhargava, MD Attending Thoracic Surgeon Assistant Professor Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery 1 Principles of Treatment Adequate drainage Sterilization
Modern Approaches to Empyema Amit Bhargava, MD Attending Thoracic Surgeon Assistant Professor Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery 1 Principles of Treatment Adequate drainage Sterilization
The Role of Thoracoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion of Unknown Origin
 Short Communication J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 20, Issu 8; Aug 2018. P:31-36 The Role of Thoracoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion of Unknown Origin R. Mahmodlou (MD) 1, J. Sarbazzadeh (MD) 1, S.A.
Short Communication J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 20, Issu 8; Aug 2018. P:31-36 The Role of Thoracoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion of Unknown Origin R. Mahmodlou (MD) 1, J. Sarbazzadeh (MD) 1, S.A.
Respiratory Interactive Session. Elaine Borg
 Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Clinical Study Safety and Complications of Medical Thoracoscopy
 Advances in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3794791, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3794791 Clinical Study Safety and Complications of Medical Thoracoscopy Shimaa Nour Moursi Ahmed, 1,2 Hideo
Advances in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3794791, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3794791 Clinical Study Safety and Complications of Medical Thoracoscopy Shimaa Nour Moursi Ahmed, 1,2 Hideo
Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore Catheter in the Patients with Iatrogenic Pneumothorax
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 20;44:48-422 ISSN: 2233-60X (Print) ISSN: 2093-656 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/0.5090/kjtcs.20.44.6.48 Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 20;44:48-422 ISSN: 2233-60X (Print) ISSN: 2093-656 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/0.5090/kjtcs.20.44.6.48 Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore
A randomized trial comparing the diagnostic yield of rigid and semirigid thoracoscopy in undiagnosed pleural effusions
 0 0 0 A randomized trial comparing the diagnostic yield of rigid and semirigid thoracoscopy in undiagnosed pleural effusions [Running title: RISE trial] Sahajal Dhooria Navneet Singh Ashutosh N Aggarwal
0 0 0 A randomized trial comparing the diagnostic yield of rigid and semirigid thoracoscopy in undiagnosed pleural effusions [Running title: RISE trial] Sahajal Dhooria Navneet Singh Ashutosh N Aggarwal
Thoracoscopy in the diagnosis of pleural effusion
 Thorax, 1977, 32, 550-554 Thoracoscopy in the diagnosis of pleural effusion A. CANTO, E. BLASCO, M. CASILLAS, A. G. ZARZA. J. PADILLA, J. PASTOR, V. TARAZONA, AND F. PARfS From the Thoracic Surgery Service,
Thorax, 1977, 32, 550-554 Thoracoscopy in the diagnosis of pleural effusion A. CANTO, E. BLASCO, M. CASILLAS, A. G. ZARZA. J. PADILLA, J. PASTOR, V. TARAZONA, AND F. PARfS From the Thoracic Surgery Service,
Diagnostic value of medical thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusions
 4590 Diagnostic value of medical thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusions RUI LIN CHEN, YONG QING ZHANG, JUN WANG, HUA WU and SHU MEI YANG Department of Respiratory Medicine, Shaanxi Provincial People's
4590 Diagnostic value of medical thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusions RUI LIN CHEN, YONG QING ZHANG, JUN WANG, HUA WU and SHU MEI YANG Department of Respiratory Medicine, Shaanxi Provincial People's
امعة زهر قسم ا مراض الصدریة
 Al- Azhar University Faculty of Medicine Department of Chest diseases امعة زهر كلیة الطب (بنين) قسم ا مراض الصدریة مقرر الصدریة ا مراض الدبلوم لطلبة COURSE of Chest diseases For Diploma Degree 2013-2014
Al- Azhar University Faculty of Medicine Department of Chest diseases امعة زهر كلیة الطب (بنين) قسم ا مراض الصدریة مقرر الصدریة ا مراض الدبلوم لطلبة COURSE of Chest diseases For Diploma Degree 2013-2014
Ultrasound-guided pleural cutting needle biopsy: accuracy and factors influencing diagnostic yield
 Original Article Ultrasound-guided pleural cutting needle biopsy: accuracy and factors influencing diagnostic yield Yuxin Zhang 1#, Jiaxin Tang 2#, Xinghua Zhou 1, Dazhi Zhou 1, Jinlin Wang 2, Qing Tang
Original Article Ultrasound-guided pleural cutting needle biopsy: accuracy and factors influencing diagnostic yield Yuxin Zhang 1#, Jiaxin Tang 2#, Xinghua Zhou 1, Dazhi Zhou 1, Jinlin Wang 2, Qing Tang
Etiology and clinical profile of pleural effusion in a teaching hospital of south India : A descriptive study.
 Original Article Etiology and clinical profile of pleural effusion in a teaching hospital of south India : A descriptive study. Manu Mohan K*, Ravindran C** *Associate Professor, Department of Pulmonary
Original Article Etiology and clinical profile of pleural effusion in a teaching hospital of south India : A descriptive study. Manu Mohan K*, Ravindran C** *Associate Professor, Department of Pulmonary
A Randomized Trial Comparing the Diagnostic Yield of Rigid and Semirigid Thoracoscopy in Undiagnosed Pleural Effusions
 A Randomized Trial Comparing the Diagnostic Yield of Rigid and Semirigid Thoracoscopy in Undiagnosed Pleural Effusions Sahajal Dhooria MD DM, Navneet Singh MD DM, Ashutosh N Aggarwal MD DM, Dheeraj Gupta
A Randomized Trial Comparing the Diagnostic Yield of Rigid and Semirigid Thoracoscopy in Undiagnosed Pleural Effusions Sahajal Dhooria MD DM, Navneet Singh MD DM, Ashutosh N Aggarwal MD DM, Dheeraj Gupta
Pneumothorax Post CT-guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy for Lung Nodules: Our Experience in King Hussein Medical Center
 Pneumothorax Post CT-guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy for Lung Nodules: Our Experience in King Hussein Medical Center Ala Qayet MD*, Laith Obaidat MD**, Mazin Al-Omari MD*, Ashraf Al-Tamimi MD^, Ahmad
Pneumothorax Post CT-guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy for Lung Nodules: Our Experience in King Hussein Medical Center Ala Qayet MD*, Laith Obaidat MD**, Mazin Al-Omari MD*, Ashraf Al-Tamimi MD^, Ahmad
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 4, Issue 20,
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 4, Issue 20, 521-525 Empyema thoracis Original Article Singh DR 1, Joshi MR 2, Thapa P 2, Nath S 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Lecturer, 3 Professor,
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 4, Issue 20, 521-525 Empyema thoracis Original Article Singh DR 1, Joshi MR 2, Thapa P 2, Nath S 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Lecturer, 3 Professor,
Atypical Pleural Fluid Profiles in Tuberculous Pleural Effusion: Sequential Changes Compared with Parapneumonic and Malignant Pleural Effusions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Atypical Pleural Fluid Profiles in Tuberculous Pleural Effusion: Sequential Changes Compared with Parapneumonic and Malignant Pleural Effusions Chang Ho Kim, So Yeon Lee, Yong Dae Lee,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Atypical Pleural Fluid Profiles in Tuberculous Pleural Effusion: Sequential Changes Compared with Parapneumonic and Malignant Pleural Effusions Chang Ho Kim, So Yeon Lee, Yong Dae Lee,
Tunn Ren Tay * and Augustine Tee
 Tay and Tee BMC Infectious Diseases 2013, 13:546 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Factors affecting pleural fluid adenosine deaminase level and the implication on the diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion:
Tay and Tee BMC Infectious Diseases 2013, 13:546 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Factors affecting pleural fluid adenosine deaminase level and the implication on the diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion:
Thoracoscopic Management of Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions in Young Children. Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 31, No. 4, December 2009 Thoracoscopic Management of Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions in Young Children Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Objective: To evaluate the role
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 31, No. 4, December 2009 Thoracoscopic Management of Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions in Young Children Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Objective: To evaluate the role
Role of gene Xpert MTB/ RIF assay in diagnosis of Tubercular Pleural Effusion
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 5-2017 Role of gene Xpert
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 5-2017 Role of gene Xpert
Direct comparison of the diagnostic yield of ultrasound-assisted Abrams and Tru-Cut needle biopsies for pleural tuberculosis
 Thorax Online First, published on June 27, 2010 as 10.1136/thx.2009.125146 Tuberculosis 1 Division of Pulmonology, Department of Medicine, University of Stellenbosch and Tygerberg Academic Hospital, Cape
Thorax Online First, published on June 27, 2010 as 10.1136/thx.2009.125146 Tuberculosis 1 Division of Pulmonology, Department of Medicine, University of Stellenbosch and Tygerberg Academic Hospital, Cape
Thoracoscopy for the Diagnosis of Pleural Disease Richard Menzies, MD, MSc; and Marc Charbonneau, MD
 Thoracoscopy for the Diagnosis of Pleural Disease Richard Menzies, MD, MSc; and Marc Charbonneau, MD Objective: To assess the accuracy and safety of thoracoscopy for the evaluation of pleural disease.
Thoracoscopy for the Diagnosis of Pleural Disease Richard Menzies, MD, MSc; and Marc Charbonneau, MD Objective: To assess the accuracy and safety of thoracoscopy for the evaluation of pleural disease.
EMPYEMA. Catheter Based Treatment vs. VATS. UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds August 27 th, Jeremy Hedges, M.D.
 EMPYEMA Catheter Based Treatment vs. VATS UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds August 27 th, 2007 Jeremy Hedges, M.D. OVERVIEW Empyema Pathogenesis Treatment Catheter based treatment Fibrinolytics
EMPYEMA Catheter Based Treatment vs. VATS UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds August 27 th, 2007 Jeremy Hedges, M.D. OVERVIEW Empyema Pathogenesis Treatment Catheter based treatment Fibrinolytics
Lung. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density in the inferior lingular segment worrisome for neoplasm. Malignancy cannot be excluded.
 Lung Case Scenario 1 A 54 year white male presents with a recent abnormal CT of the chest. The patient has a history of melanoma, kidney, and prostate cancers. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density
Lung Case Scenario 1 A 54 year white male presents with a recent abnormal CT of the chest. The patient has a history of melanoma, kidney, and prostate cancers. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS. Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP
 APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
Interventional Pulmonology
 Interventional Pulmonology The Division of Thoracic Surgery Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical College p: 212-746-6275 f: 212-746-8223 https://weillcornell.org/eshostak
Interventional Pulmonology The Division of Thoracic Surgery Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical College p: 212-746-6275 f: 212-746-8223 https://weillcornell.org/eshostak
Torsion bottle, a very simple, reliable, and cheap tool for a basic scoliosis screening
 Romano and Mastrantonio Scoliosis and Spinal Disorders (2018) 13:4 DOI 10.1186/s13013-018-0150-6 RESEARCH Open Access Torsion bottle, a very simple, reliable, and cheap tool for a basic scoliosis screening
Romano and Mastrantonio Scoliosis and Spinal Disorders (2018) 13:4 DOI 10.1186/s13013-018-0150-6 RESEARCH Open Access Torsion bottle, a very simple, reliable, and cheap tool for a basic scoliosis screening
Thoracic Surgery; An Overview
 Thoracic Surgery What we see Thoracic Surgery; An Overview James P. Locher, Jr, MD Methodist Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery Lung cancer Mets Fungus and TB Lung abcess and empyema Pleural based disease
Thoracic Surgery What we see Thoracic Surgery; An Overview James P. Locher, Jr, MD Methodist Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery Lung cancer Mets Fungus and TB Lung abcess and empyema Pleural based disease
Top Tips for Pleural Disease in 2012
 Top Tips for Pleural Disease in 2012 The unilateral pleural effusion on the Post Take Ward Round Pleural Effusion on CXR Bedside ultrasound + Pleural aspirate Empyema Nil evidence infection Admit IV antibiotics
Top Tips for Pleural Disease in 2012 The unilateral pleural effusion on the Post Take Ward Round Pleural Effusion on CXR Bedside ultrasound + Pleural aspirate Empyema Nil evidence infection Admit IV antibiotics
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion
 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
Navigational bronchoscopy-guided dye marking to assist resection of a small lung nodule
 Case Report on Aerodigestive Endoscopy Navigational bronchoscopy-guided dye marking to assist resection of a small lung nodule Jennifer L. Sullivan 1, Michael G. Martin 2, Benny Weksler 1 1 Division of
Case Report on Aerodigestive Endoscopy Navigational bronchoscopy-guided dye marking to assist resection of a small lung nodule Jennifer L. Sullivan 1, Michael G. Martin 2, Benny Weksler 1 1 Division of
Pleural Effusion. Exudative pleural effusion - Involve an increase in capillary permeability and impaired pleural fluid resorption
 Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
Flex-rigid pleuroscopic biopsy with the SB knife Jr is a novel technique for diagnosis of malignant or benign fibrothorax
 Case Report Flex-rigid pleuroscopic biopsy with the SB knife Jr is a novel technique for diagnosis of malignant or benign fibrothorax Xiao-Bo Wang 1, Yan Yin 1, Yuan Miao 2, Ralf Eberhardt 3, Gang Hou
Case Report Flex-rigid pleuroscopic biopsy with the SB knife Jr is a novel technique for diagnosis of malignant or benign fibrothorax Xiao-Bo Wang 1, Yan Yin 1, Yuan Miao 2, Ralf Eberhardt 3, Gang Hou
Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Pleural effusions Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases A pleural effusion is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space resulting from excess fluid production or decreased
Pleural effusions Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases A pleural effusion is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space resulting from excess fluid production or decreased
Original article Bronchoscopic profile of various diseases in a rural care hospital
 J M e d A l l i e d S c i 2 0 1 7 ; 7 ( 2 ) : 87-91 w w w. j m a s. i n P r i n t I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 6 9 6 O n l i n e I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 7 0 X Journal of M e d i cal & Allied Sciences Original article
J M e d A l l i e d S c i 2 0 1 7 ; 7 ( 2 ) : 87-91 w w w. j m a s. i n P r i n t I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 6 9 6 O n l i n e I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 7 0 X Journal of M e d i cal & Allied Sciences Original article
The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL
 The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL Conflict of Interest This presentation is supported by AstraZeneca Two main steps before
The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL Conflict of Interest This presentation is supported by AstraZeneca Two main steps before
Image: reproduced from Eur Respir Mon 2010; 48: with permission from the publisher.
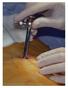 Image: reproduced from Eur Respir Mon 2010; 48: 119 132 with permission from the publisher. R. Loddenkemper 1 P. Lee 2 M. Noppen 3 P.N. Mathur 4 1 German Central Committee against Tuberculosis (DZK), Lungenklinik
Image: reproduced from Eur Respir Mon 2010; 48: 119 132 with permission from the publisher. R. Loddenkemper 1 P. Lee 2 M. Noppen 3 P.N. Mathur 4 1 German Central Committee against Tuberculosis (DZK), Lungenklinik
CT findings in patients with Cabazitaxel induced pelvic pain and haematuria: a case series
 Malalagama et al. Cancer Imaging (2017) 17:17 DOI 10.1186/s40644-017-0119-3 CASE SERIES CT findings in patients with Cabazitaxel induced pelvic pain and haematuria: a case series Geethal N. Malalagama
Malalagama et al. Cancer Imaging (2017) 17:17 DOI 10.1186/s40644-017-0119-3 CASE SERIES CT findings in patients with Cabazitaxel induced pelvic pain and haematuria: a case series Geethal N. Malalagama
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 03 Page March 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-4 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/.18535/jmscr/v6i3.63 Diagnostic Role of FOB in Radiological
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-4 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/.18535/jmscr/v6i3.63 Diagnostic Role of FOB in Radiological
Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report
 303) Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report Mizuno Y., Iwata H., Shirahashi K., Matsui M., Takemura H. Department of General and Cardiothoracic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine,
303) Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report Mizuno Y., Iwata H., Shirahashi K., Matsui M., Takemura H. Department of General and Cardiothoracic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine,
CT-Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Pleural Lesions: Evaluating Diagnostic Yield and Associated Complications
 Original Article Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.1.206 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(1):206-212 CT-Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Pleural Lesions: Evaluating
Original Article Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.1.206 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(1):206-212 CT-Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Pleural Lesions: Evaluating
Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems
 Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems Pneumothorax Definition Air accumulation in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse Sources Visceral pleura Ruptured esophagus Chest wall defect Gas-forming
Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems Pneumothorax Definition Air accumulation in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse Sources Visceral pleura Ruptured esophagus Chest wall defect Gas-forming
Thoracoscopy: medical versus surgical in the management of pleural diseases
 Review Article on Pleural Disease Thoracoscopy: medical versus surgical in the management of pleural diseases Samira Shojaee 1, Hans J. Lee 2 1 Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA 23219, USA;
Review Article on Pleural Disease Thoracoscopy: medical versus surgical in the management of pleural diseases Samira Shojaee 1, Hans J. Lee 2 1 Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA 23219, USA;
Treatment of multiloculated empyema thoracis using minimally invasive methods
 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med J 2010; 51(3) : 242 Treatment of multiloculated empyema thoracis using minimally invasive methods Metin M, Yeginsu A, Sayar A, Alzafer S, Solak O, Ozgul A, Erkorkmaz
O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med J 2010; 51(3) : 242 Treatment of multiloculated empyema thoracis using minimally invasive methods Metin M, Yeginsu A, Sayar A, Alzafer S, Solak O, Ozgul A, Erkorkmaz
To study the combined use of pleural fluid lymphocyte/ neutrophil ratio and ADA for the diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion
 and ADA for the diagnosis of tuberculous. IAIM, 2017; 4(9): 1-5. Original Research Article To study the combined use of fluid lymphocyte/ neutrophil ratio and ADA for the diagnosis of tuberculous Ramasamy
and ADA for the diagnosis of tuberculous. IAIM, 2017; 4(9): 1-5. Original Research Article To study the combined use of fluid lymphocyte/ neutrophil ratio and ADA for the diagnosis of tuberculous Ramasamy
Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit
 Page1 Original Article NJR 2011;1(1):1 7;Available online at www.nranepal.org Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit S
Page1 Original Article NJR 2011;1(1):1 7;Available online at www.nranepal.org Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit S
Preface. Date: May 1, 2003 Vol.1/MX-2/05/03
 Date: May 1, 2003 Vol.1/MX-2/05/03 Preface Tulip Group of companies believes in offering our valued customers the technical support and scientific information to keep updated with the latest international
Date: May 1, 2003 Vol.1/MX-2/05/03 Preface Tulip Group of companies believes in offering our valued customers the technical support and scientific information to keep updated with the latest international
Lung Investigation Service Patient Information Leaflet
 Thoracoscopy Lung Investigation Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The purpose of this leaflet is to answer any questions you may have about having a thoracoscopy. If you are unsure of anything,
Thoracoscopy Lung Investigation Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The purpose of this leaflet is to answer any questions you may have about having a thoracoscopy. If you are unsure of anything,
PAKISTAN JOURNAL OF CHEST MEDICINE. Volume 18, No 1, January-March REVIEW ARTICLE MEDICAL PLEUROSCOPY
 82 REVIEW ARTICLE MEDICAL PLEUROSCOPY Pyng Lee MD,* Henri G Colt,**Ali I. Musani MD*** ABSTRACT Pleuroscopy or medical thoracoscopy are terms used interchangeably to describe a minimally invasive procedure
82 REVIEW ARTICLE MEDICAL PLEUROSCOPY Pyng Lee MD,* Henri G Colt,**Ali I. Musani MD*** ABSTRACT Pleuroscopy or medical thoracoscopy are terms used interchangeably to describe a minimally invasive procedure
available at journal homepage:
 Respiratory Medicine (2010) 104, 1211e1217 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed Diagnosing tuberculous pleural effusion using clinical data and pleural fluid
Respiratory Medicine (2010) 104, 1211e1217 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed Diagnosing tuberculous pleural effusion using clinical data and pleural fluid
Bao-An Gao 1, Gang Zhou 2 *, Li Guan 1, Ling-Yun Zhang 1, Guang-Ming Xiang 1. Introduction
 Original Article Effectiveness and safety of diagnostic flexi-rigid thoracoscopy in differentiating exudative pleural effusion of unknown etiology: a retrospective study of 215 patients Bao-An Gao 1, Gang
Original Article Effectiveness and safety of diagnostic flexi-rigid thoracoscopy in differentiating exudative pleural effusion of unknown etiology: a retrospective study of 215 patients Bao-An Gao 1, Gang
Video-assisted thoracoscopic PlasmaJet ablation for malignant pleural mesothelioma
 Case Report on Thoracic Surgery Page 1 of 5 Video-assisted thoracoscopic PlasmaJet ablation for malignant pleural mesothelioma Periklis Perikleous, Nizar Asadi, Vladimir Anikin Department of Thoracic Surgery,
Case Report on Thoracic Surgery Page 1 of 5 Video-assisted thoracoscopic PlasmaJet ablation for malignant pleural mesothelioma Periklis Perikleous, Nizar Asadi, Vladimir Anikin Department of Thoracic Surgery,
Ligation of lymph vessels for the treatment of recurrent inguinal lymphoceles following lymphadenectomy
 Syddansk Universitet Ligation of lymph vessels for the treatment of recurrent inguinal lymphoceles following lymphadenectomy Toyserkani, Navid Mohamadpour; Nielsen, Henrik Toft; Bakholdt, Vivi T.; Sørensen,
Syddansk Universitet Ligation of lymph vessels for the treatment of recurrent inguinal lymphoceles following lymphadenectomy Toyserkani, Navid Mohamadpour; Nielsen, Henrik Toft; Bakholdt, Vivi T.; Sørensen,
A comparison between two types of indwelling pleural catheters for management of malignant pleural effusions
 Original Article A comparison between two types of indwelling pleural catheters for management of malignant pleural effusions Sushilkumar Satish Gupta 1, Charalampos S. Floudas 2, Abhinav B. Chandra 3
Original Article A comparison between two types of indwelling pleural catheters for management of malignant pleural effusions Sushilkumar Satish Gupta 1, Charalampos S. Floudas 2, Abhinav B. Chandra 3
Bilateral multiple choroidal granulomas and systemic vasculitis as presenting features of tuberculosis in an immunocompetent patient
 Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
Well-differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Pleura Diagnosed by Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgical Pleural Biopsy : A Case Report
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 25 1, 67 72, March 2013 Case Report Well-differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Pleura Diagnosed by Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgical Pleural Biopsy : A Case Report Yuri TOMITA
Showa Univ J Med Sci 25 1, 67 72, March 2013 Case Report Well-differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Pleura Diagnosed by Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgical Pleural Biopsy : A Case Report Yuri TOMITA
Takashi Yagisawa 1,2*, Makiko Mieno 1,3, Norio Yoshimura 1,4, Kenji Yuzawa 1,5 and Shiro Takahara 1,6
 Yagisawa et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2016) 2:68 DOI 10.1186/s41100-016-0080-9 POSITION STATEMENT Current status of kidney transplantation in Japan in 2015: the data of the Kidney Transplant Registry
Yagisawa et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2016) 2:68 DOI 10.1186/s41100-016-0080-9 POSITION STATEMENT Current status of kidney transplantation in Japan in 2015: the data of the Kidney Transplant Registry
A new approach to left sleeve pneumonectomy: complete VATS left pneumonectomy followed by right thoracotomy for carinal resection and reconstruction
 Fujino et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:91 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0496-2 CASE REPORT A new approach to left sleeve pneumonectomy: complete VATS left pneumonectomy followed by right thoracotomy
Fujino et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:91 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0496-2 CASE REPORT A new approach to left sleeve pneumonectomy: complete VATS left pneumonectomy followed by right thoracotomy
DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF ADENOSINE DEAMINASE (ADA) IN TUBERCULAR PLEURAL EFFUSION
 Original research article International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208 DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF ADENOSINE DEAMINASE (ADA) IN TUBERCULAR PLEURAL EFFUSION Dr.Alpana
Original research article International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208 DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF ADENOSINE DEAMINASE (ADA) IN TUBERCULAR PLEURAL EFFUSION Dr.Alpana
Different characteristics of tuberculous pleural effusion according to pleural fluid cellular predominance and loculation
 Original Article Different characteristics of tuberculous pleural effusion according to pleural fluid cellular predominance and loculation Jaehee Lee 1, Jae Kwang Lim 2, Seung Soo Yoo 1, Shin Yup Lee 1,
Original Article Different characteristics of tuberculous pleural effusion according to pleural fluid cellular predominance and loculation Jaehee Lee 1, Jae Kwang Lim 2, Seung Soo Yoo 1, Shin Yup Lee 1,
Larry Tan, MD Thoracic Surgery, HSC. Community Cancer Care Educational Conference October 27, 2017
 Larry Tan, MD Thoracic Surgery, HSC Community Cancer Care Educational Conference October 27, 2017 To describe patient referral & triage for the patient with suspected lung cancer To describe the initial
Larry Tan, MD Thoracic Surgery, HSC Community Cancer Care Educational Conference October 27, 2017 To describe patient referral & triage for the patient with suspected lung cancer To describe the initial
Tuberculosis and cancer
 Tuberculosis and cancer David P. Holland, MD, MHS Chief Clinical Officer, CDPB Fulton County Department of Health and Wellness Assistant Professor, Emory University Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures
Tuberculosis and cancer David P. Holland, MD, MHS Chief Clinical Officer, CDPB Fulton County Department of Health and Wellness Assistant Professor, Emory University Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures
Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of. Pulmonary Mycetoma. Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu***
 Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of Pulmonary Mycetoma Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu*** Departments of *Respiratory Medicine, **Physiology, and ***Radiodiagnosis,
Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of Pulmonary Mycetoma Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu*** Departments of *Respiratory Medicine, **Physiology, and ***Radiodiagnosis,
Utility of PET-CT for detection of N2 or N3 nodal mestastases in the mediastinum in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
 Utility of PET-CT for detection of N2 or N3 nodal mestastases in the mediastinum in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Poster No.: C-1360 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Utility of PET-CT for detection of N2 or N3 nodal mestastases in the mediastinum in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Poster No.: C-1360 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3
 Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
minimally invasive techniques Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery Using Single-Lumen Endotracheal Tube Anesthesia*
 minimally invasive techniques Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery Using Single-Lumen Endotracheal Tube Anesthesia* Robert James Cerfolio, MD, FCCP; Ayesha S. Bryant, MSPH; Todd M. Sheils, MD; Cynthia
minimally invasive techniques Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery Using Single-Lumen Endotracheal Tube Anesthesia* Robert James Cerfolio, MD, FCCP; Ayesha S. Bryant, MSPH; Todd M. Sheils, MD; Cynthia
Study of Predictors for Successful Pleurodesis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 1, March: 11-20, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Study of Predictors for Successful Pleurodesis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion TALAT A. ARAFA,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 1, March: 11-20, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Study of Predictors for Successful Pleurodesis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion TALAT A. ARAFA,
The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax
 Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Clinical Utility of CT-Based Bronchial Aspirate TB-PCR for the Rapid Diagnosis of Pleural Tuberculosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2013.75.4.150 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2013;75:150-156 Clinical Utility of CT-Based Bronchial Aspirate TB-PCR for the Rapid
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2013.75.4.150 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2013;75:150-156 Clinical Utility of CT-Based Bronchial Aspirate TB-PCR for the Rapid
Pleural controversies: image guided biopsy vs. thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusions?
 Review Article Pleural controversies: image guided biopsy vs. thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusions? Giles Dixon 1,2, Duneesha de Fonseka 1,2, Nick Maskell 1,2 1 North Bristol NHS Trust, Bristol,
Review Article Pleural controversies: image guided biopsy vs. thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusions? Giles Dixon 1,2, Duneesha de Fonseka 1,2, Nick Maskell 1,2 1 North Bristol NHS Trust, Bristol,
BGS Autumn The wet lung - Pleural effusions. Nick Maskell. BGS Autumn Meeting November 2017
 The wet lung - Pleural effusions BGS Autumn Meeting November 2017 Nick Maskell Professor of Respiratory Medicine Bristol University, Bristol Conflicts of interest Prof Maskell has sat on advisory boards
The wet lung - Pleural effusions BGS Autumn Meeting November 2017 Nick Maskell Professor of Respiratory Medicine Bristol University, Bristol Conflicts of interest Prof Maskell has sat on advisory boards
Some clinical conditions such as congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, acute. Bleomycin in the treatment of 50 cases with malignant pleural effusion
 Original Article Bleomycin in the treatment of 5 cases with malignant pleural effusion Novin Nikbakhsh (MD) *1 Ali Pourhasan Amiri (MD) 2 Danial Hoseinzadeh (MD) 3 1- Department of Surgery, Babol University
Original Article Bleomycin in the treatment of 5 cases with malignant pleural effusion Novin Nikbakhsh (MD) *1 Ali Pourhasan Amiri (MD) 2 Danial Hoseinzadeh (MD) 3 1- Department of Surgery, Babol University
Combined efficacy of pleural fluid lymphocyte neutrophil ratio and pleural fluid adenosine deaminase for the diagnosis of tubercular pleural effusion
 Original article: Combined efficacy of pleural fluid lymphocyte neutrophil ratio and pleural fluid adenosine deaminase for the diagnosis of tubercular pleural effusion Kavita S Kore, Guruprasad Antin,
Original article: Combined efficacy of pleural fluid lymphocyte neutrophil ratio and pleural fluid adenosine deaminase for the diagnosis of tubercular pleural effusion Kavita S Kore, Guruprasad Antin,
Case Scenario 1. The patient agreed to a CT guided biopsy of the left upper lobe mass. This was performed and confirmed non-small cell carcinoma.
 Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications of Pleural Adhesions in Malignant Effusions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications of Pleural Adhesions in Malignant Effusions Silvia Bielsa, MD,* José Martín-Juan, MD, José M. Porcel, MD,* and Francisco Rodríguez-Panadero, MD Background
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications of Pleural Adhesions in Malignant Effusions Silvia Bielsa, MD,* José Martín-Juan, MD, José M. Porcel, MD,* and Francisco Rodríguez-Panadero, MD Background
Comment / Changes / Approval. Initial version for consultation
 Document Control Title Pleural Procedures Guidelines Author Respiratory Consultant Directorate Medicine Date Version Issued 0.1 Aug 2011 0.2 Sep 2011 0.3 Sep 2011 0.4 Oct 2011 1.0 Oct 2011 Status Draft
Document Control Title Pleural Procedures Guidelines Author Respiratory Consultant Directorate Medicine Date Version Issued 0.1 Aug 2011 0.2 Sep 2011 0.3 Sep 2011 0.4 Oct 2011 1.0 Oct 2011 Status Draft
Common things are common, but not always the answer
 Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Subdural hemorrhages in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: case report and literature review
 Yin et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2016) 2:25 DOI 10.1186/s41016-016-0045-4 CHINESE NEUROSURGICAL SOCIETY CASE REPORT CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION Subdural hemorrhages in acute lymphoblastic leukemia:
Yin et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2016) 2:25 DOI 10.1186/s41016-016-0045-4 CHINESE NEUROSURGICAL SOCIETY CASE REPORT CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION Subdural hemorrhages in acute lymphoblastic leukemia:
Unilateral lateral rectus muscle advancement surgery based on one-fourth of the angle of consecutive esotropia
 Kim and Lee BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:266 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0658-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Unilateral lateral rectus muscle advancement surgery based on one-fourth of the angle of consecutive
Kim and Lee BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:266 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0658-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Unilateral lateral rectus muscle advancement surgery based on one-fourth of the angle of consecutive
