Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai , China 2
|
|
|
- Prosper Garrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biomedicine and Biotechnology Volume 22, Article ID 65296, 7 pages doi:.55/22/65296 Research Article Transfer of Bone-Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Influences Vascular Remodeling and Calcification after Balloon in Hyperlipidemic Rats Jianquan Liao, Xiaochun Chen, 2 Yongdong Li, 2 Zhiping Ge, 2 Hongyu Duan, 2 Yunzeng Zou, and Junbo Ge Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 232, China 2 Department of Cardiology, The Third Affiliated Hospital, Inner Mongolia Medical College, BaoTou, Inner Mongolia 4, China Correspondence should be addressed to Xiaochun Chen, chen43@yahoo.com.cn and Junbo Ge, ge.junbo2@zs-hospital.sh.cn Received 9 December 2; Revised 27 February 22; Accepted 29 February 22 Academic Editor: Monica Fedele Copyright 22 Jianquan Liao et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-) were found to markedly increase atherosclerotic lesion size. The aim of this paper was to investigate whether BM- contribute to vascular remodeling and calcification after balloon injury in hyperlipidemic rats. Labeled BM- were found in the lesion of hyperlipidemic rats after balloon injury. Comparing injury, transferred BM- significantly triggered vascular negative remodeling, characterized by the changes of remodeling index (.628±.293 versus.544±.27), neointimal area (.78±.5 mm 2 versus.98±.9 mm 2 ), PCNA index (23.9± 6.59% versus 43. ± 5.3%), and percentage of stenosis (8.2 ±.9% versus 3.58 ±.2%). Apparent vascular calcification was detected in medial layers at 6 weeks after balloon angioplasty, which may be associated with upregulation of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2). Our data indicated that unselected BM- transfer may induce vascular remodeling and calcification after balloon injury in hyperlipidemic rats.. Introduction Cellular therapy has been an area of intense research over few decades, which is widely used for treatment of cardiovascular disease. Bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM- ) were isolated from adult bone marrow, along with the ability for self-renewal and multilineage differentiation into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, endothelium, osteoblasts, and chondroblasts [, 2]. Accumulating evidence from a growing body of animal studies demonstrated the extensive capacity of to engraft, differentiate and produce substantial functional recovery [3]. Transplantation has been considered as a potential clinical strategy for the treatment of ischemic heart diseases and heart failure. Although a growing body of evidence from animal experiments and clinical trials indicated the beneficial therapeutic potential of in cardiovascular diseases, the safety of transplantation is a critical problem that should be kept in mind. The findings that transplantation could result in tumor formation and alteration of electrophysiologic properties caused wide concerns [4, 5]. Furthermore, unexpected severe intramyocardial calcification was elicited by direct transplantation of unselected bone marrow cells into acutely infarcted myocardium [6]. It has been demonstrated that transfer of bone marrow and endothelial progenitor cells accelerated atherosclerosis and influenced the plaque stability [7]. Increasing evidence indicates a link between therapy and pathogenesis of atherosclerosis [8, 9]. Our previous studies demonstrated that oxidized LDL synergistically promoted osteodifferentiation of bone-marrow-derived in response to osteogenic inductor. In this study, we investigated the effects of transfer of unselected BM- on vascular remodeling and calcification in the hyperlipidemic rat.
2 2 Biomedicine and Biotechnology 2. Method 2.. Preparation of BM-. Unselected BM- were extracted from male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (5 2 g) femurs by flushing the bone marrow cavities with Dulbecco s modified Eagle s medium-low glucose (DMEM) and cultured in DMEM supplemented with % fetal bovine serum (FBS). After 24 h, the medium was discarded to remove hematopoietic stem cells and nonadherent cells. Medium was changed every 2 days. Cells became almost confluent after 8 days and were trypsinized with.25% trypsin containing mm EDTA for 3min at 37 C. All experiments were performed on cells cultured for up to 3 5 passages. BM- were identified as CD9-positive and CD34-negative by flow cytometry Animals. All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Fudan University according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, published by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH publication no , revised 996). Animals were fed with high cholesterol diet containing % fat, 5% cholesterol,.5% sodium cholate, and.2% propylthiouracil and received vitamin D 3 (6, U/kg body weight) for week before balloon denudation. Female SD rats were randomly allocated to three s: () rats without denudation were fed with high cholesterol diet (, n = 8); (2) rats were subjected to balloon denudation and fed with high cholesterol diet (, n = 8); (3) rats were subjected to balloon denudation and BM- transplantation plus with high cholesterol diet (MSC, n = 8). Rats were anesthetized with ketamine (5 mg/kg body weight IP) and heparinized with U/kg heparin sodium before procedures. A well-established rat model of aortic artery balloon injury was used in this study. The abdominal aorta was isolated and stripped of adventitia. A 6 F balloon catheter was introduced through incision under the renal artery bifurcation about cm and advanced into the thoracic aorta. The balloon was inflated with saline and pulled back to the abdominal aorta. After balloon denudation was performed for 3 times, saline or B labeled by DAPI were injected before removal of the catheter. After balloon denudation, rats were fed with high cholesterol diet containing % fat, 5% cholesterol,.5% sodium cholate, and.2% propylthiouracil for 6 weeks after balloon denudation. In addition, rats without denudation were fed with a normal diet to compare with those with a high cholesterol diet Analyses of Plasma Lipid. After feeding, the rats were fasted overnight and the samples were collected and centrifuged at 3 rpm for 5 min. The plasma lipid profile was determined by measuring the contents of total cholesterol (TC) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) by standard enzymatic procedures using reagent kits Histology. Paraffin sections of vascular tissue were stained with hematoxylin-eosin for morphometric analysis as previously described []. Histomorphometric parameters, including luminal area (LA), internal elastic lamina area (IELA), external elastic lamina area (EELA), and neointimal area were defined and determined using the software of Leica QWin Plus as previously described []. The chronic variation of the area surrounded by the external elastic lamina was evaluated by remodeling index compared with a reference normal segment upstream from the lesion site, which was calculated as a percentage as follows: EELA(lesion)/EELA (reference). The percentage of stenosis was calculated as (IELA LA/IELA) Von Kossa Stain. Von Kossa stain (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) was performed to evaluate abnormal deposits of calcium within vascular wall. Paraffin-fixed tissue sections were incubated with silver nitrate solution under a strong light. The calcium was replaced with silver deposit, visualized as metallic silver. Procedural details are described elsewhere [6] Immunohistochemistry. Proliferative activity was determined in vascular tissue using analysis of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) expression defined immunohistochemically. In brief, tissue sections were quenched for endogenous peroxidase and antigen-retrieved in. M citrate buffer (ph 6.) for 5 min in a microwave oven at C. The sections were blocked with normal goat serum and then incubated with mouse anti-pcna antibody (Boster Company, China) overnight in a humid chamber at 4 C. After incubation with biotinylated goat anti-mouse IgG, sections were visualized by using avidin-biotin horseradish peroxidase visualization system. Sections were then counterstained with haematoxylin. Images were recorded using Leica Qwin Plus Immunofluorescence Staining. Immunofluorescence staining was performed according to standard procedures. Briefly, vascular tissue sections were deparaffinized and hydrated. After preincubation with normal goat serum, sections were incubated with rabbit anti-bmp-2 antibody (Boster Company, China) overnight in humid chamber at 4 C followed by incubation with appropriate FITC-linked secondary antibody. Images were captured by using Leica Qwin Plus Statistical Analysis. Data were presented as means ± SEM. Comparison was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey test for post hoc analysis to determine the difference among s. P<.5 was considered statistically significant. 3. Result 3.. Identification of BM- Prepared for Transplantation. For transplantation, unselected BM- were isolated from bone marrow according to standard technique. A few small, bright, round cells were present in the primary culture, which gradually disappeared by the second generation or later (Figure (a)).bm-werecharacterizedas
3 Biomedicine and Biotechnology 3 (a) (b) 3 2 TC (mmol/l) LDL-C (mmol/l) 5 5 Normal diet High cholesterol diet Normal diet High cholesterol diet (c) (d) Figure : Identification of BM- and the profile of lipid level in cholesterol-rich fed rats. Phase contrast microscopy depicted that a few small, bright, round cells were present in the primary culture (a). Phase contrast microscopy revealed that BM- were characterized as a fibroblast-like spindle-shaped morphology (b). Baseline of serum lipid content before received cholesterol-rich diet did not significantly differ among three s. Cholesterol-rich diet significantly increased total serum cholesterol (c), and LDL (d) levels after angioplasty in rats. The data were expressed as means ± SEM. n = 8per. P<.5 versus normal diet. a fibroblast-like spindle-shaped morphology (Figure (b)). More than 95.69% of cells isolated from bone marrow were positive for CD9, and negative for the early hematopoietic marker CD34, indicating specific phenotype of BM- markers The Profile of Lipid Level in Rats with Cholesterol-Rich Diet. Baseline of serum lipid content before received cholesterol-rich diet did not significantly differ among three s. The addition of cholesterol to the diet significantly increased total serum cholesterol, and LDL levels. Procedures of balloon angioplasty and BM- transplantation did not affect plasma lipid levels in this study (Figures (c) and (d)) Effect of BM- on Vascular Remodeling after Balloon Angioplasty. To address vascular remodeling in vivo, histological analysis of vascular wall was assessed at 6 weeks after balloon angioplasty. Ruptured internal elastic lamina was present at the site of lesion, whereas splitting of the intima was replaced with significant neointimal formation after balloon angioplasty in injury and MSC. Data from histomorphometric parameters depicted that LA, IELA, EELA, and remodeling index significantly decreased after balloon angioplasty (LA:.632 ±.43 mm 2 versus.335 ±.56 mm 2 versus.33 ±.74 mm 2 ; IELA:.632 mm 2 ±.43 mm 2 versus.44 mm 2 ±.73 mm 2 versus.85 mm 2 ±.86 mm 2 ; EELA: 2.43 mm 2 ±.67 mm 2 versus.59 ±.58 mm 2 versus.38 ±.44; remodeling index: versus.628±.293 versus.544 ±.27; control versus injury versus MSC, resp., P <.5), whereas significant neointimal area and percentage of stenosis were increased, compared with control (neointimal area: versus.78 ±.5 mm 2 versus.98 ±.9 mm 2, P <.5; percentage of stenosis: versus 8.2 ±.9% versus 3.58 ±.2%; control versus injury versus MSC, resp., P <.5). BM- transplantation significantly aggravated vascular negative remodeling when compared with injury, characterized by the decrease of LA, IELA, EELA, and remodeling index and increased neointimal area and percentage of stenosis (Figure 2).
4 4 Biomedicine and Biotechnology LA (mm 2 ) Neointimal area (mm 2 ) Remodeling index IELA (mm 2 ) (a) (b) EELA (mm 2 ) Stenosis (%) Figure 2: Effect of BM- on vascular remodeling after balloon angioplasty. Vascular tissues were stained with hematoxylin-eosin for morphometric analysis. (a) Ruptured internal elastic lamina was present at the site of lesion, whereas splitting of the intima was replaced with significant neointimal formation after balloon angioplasty. (b) Histomorphometric parameters including LA, IELA, EELA, remodeling index, neointimal area, and percentage of stenosis indicated vascular negative remodeling. The scale bar indicated 5 µm (top row, 4x) and µm (bottom row, 4x), respectively. The data were expressed as means ± SEM. n = 8per. P<.5 versus control, P<.5 versus injury Effect of BM- on Neointimal Formation after Balloon Angioplasty. To investigate the neointimal formation in vivo, the PCNA index was evaluated. PCNA-stained nuclei were detected in the neointimal and medial layers of vascular wall at 6 weeks after vascular denudation (Figure 3). Data demonstrated that BM- resulted in a significant increase in the neointimal area (.78 ±.5 mm 2 versus.98 ±.9 mm 2, P<.5), PCNA index (23.9 ± 6.59% versus 43. ± 5.3%, P<.5), and percentage of stenosis (8.2 ±.9% versus 3.58 ±.2%, P<.5) compared with injury Effect of BM- on Vascular Calcification after Balloon Angioplasty. To further characterize vascular calcification in
5 Biomedicine and Biotechnology 5 4x 4x 4x 6 (a) 5 PCNA index (%) (b) Figure 3: Effect of BM- on neointimal formation after balloon angioplasty. (a) The PCNA expression was evaluated immunohistochemically to investigate proliferative activity in vascular tissue. PCNA-stained nuclei were detected in the neointimal and medial layers of vascular wall at 6 weeks after vascular denudation. (b) PCNA index was significantly increased after BM- transplantation compared with injury. The data were expressed as means ± SEM. n = 8per. P<.5 versus control, P<.5 versus injury. lesions, von Kossa staining was performed. Typical of calcification, revealing black metallic deposit, was obviously visualized in medial layers in MSC, compared control and injury (Figure 4(a)). In view of association between bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and vascular calcification, the expression of BMP-2 was determined by Immunofluorescence staining. Results indicated that BMP-2 was strongly expressed in the neointimal and medial layers of vascular wall (Figure 4(b)). These results indicated that BM- -induced vascular calcification might be associated with upregulation of BMP-2. To track the fate of BM-, BM- were prelabeled by DAPI. Labeled BM- were homing in the intimal layers at 6 weeks after angioplasty, indicating a role of BM- in the pathological changes of vascular remodeling and calcification (Figure 4(c)). 4. Discussion The salient findings from our current study indicated that BM- transplantation triggered vascular remodeling and calcification after balloon angioplasty in hyperlipidemic rats. These results highlighted the potential importance of complication caused by BM- which should keep in mind in the therapeutic application. Up to now, clinical trials for the treatment of ischemic heart diseases and heart failure using bone marrow cells were rapidly increased. Cell therapy has been regarded as a potential clinical strategy for cardiovascular diseases. However, intensive concerns about deleterious effectsreceived significant attention, such as tumorigenicity, arrhythmia, and unregulated differentiation. Studies from Losordo reported for the first time that severe intramyocardial calcification was detected after transplantation of unselected BM cells in acute myocardial infarction [6]. The vascular remodeling and calcification were observed after balloon injury in hyperlipidemic rats. It is plausible that unselected BM- therapy could lead to unexpected complication in coronary heart disease patients with hyperlipidemia. Actually, patients with coronary heart diseases complicated by hyperlipidemia were clinically prevalent. Particularly, intracoronary delivery of BM- was performed after successful percutaneous coronary intervention in most of clinical trials. Thus, the gross adverse effect observed in the study could be clinically significant. Increasing evidence indicated a link between bonemarrow-derived cells and the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circulating myeloid calcifying cells were identified and found to contribute to ectopic vascular calcification in type 2
6 6 Biomedicine and Biotechnology 4x 4x 4x 4x 4x 4x (a) 4x (b) (c) Figure 4: Effect of BM- on vascular calcification after balloon angioplasty and the fate of transferred BM-. (a) Von Kossa staining was performed to detect vascular calcification in lesions black metallic deposit was obviously visualized in medial layers in MSC, compared control and injury. (b) Immunofluorescence staining was performed to determine the expression of BMP-2. Results indicated that upregulated BMP-2 was strongly expressed in the neointimal and medial layers of vascular wall in MSC, compared and s. (c) Labeled BM- were homing in the intimal layers at 6 weeks after angioplasty. n = 8per. diabetes [2]. Previous studies demonstrated that transferred BM- were homing to the vascular lesion and markedly increased atherosclerotic lesion size [7]. In this study, the fate of transferred BM- were traced and found to present at a low density in the vascular sections. However, the homing BM- may be underestimated, as quenching of the DAPI cannot be completely excluded at 6 weeks after balloon injury. It was indicated that BM- were potentially involved in atherosclerotic calcification. The mechanisms by which transferred BM- modulate vascular calcification remain unclear. Compelling evidence suggested that vascular calcification was regulated by bone calcification regulatory factors locally expressed in blood vessels [3 5]. Paracrine BMP-2 caused the induction of osteoblast-like cells in intima and accelerated the atherosclerotic calcification in vivo [6]. BMP-2 was found to promote vascular calcification via increased phosphate uptake and induction of osteogenic phenotype modulation in smooth muscle cells [7]. Our observation that strongly expression of BMP-2 was detected in the neointimal and medial layers indicated a potential role of BMP-2 in the BM- -induced calcification. Our data demonstrated that ox-ldl was synergistically promoted osteodifferentiation of BM- co-cultured with vascular smooth muscle cells in the presence of osteogenic inductor (unpublished data). It was suggested that BM- together with balloon injury and hyperlipidemia contribute to the formation of vascular calcification.
7 Biomedicine and Biotechnology 7 Taken together, we demonstrated an important role of transferred BM- in vascular remodeling and calcification. These findings call for caution in potential adverse effects with respect to BM- transfer in the future clinical trials. Acknowledgments This study was supported by the Key Scientific Research Fund of Inner Mongolia Medical College (NY24ZD7) and the Natural Scientific Research Fund of Inner Mongolia (2MS3). Authors Contribution J. Liao and X. Chen contributed equally to this work. References [] H.C.Quevedo,K.E.Hatzistergos,B.N.Oskoueietal., Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells restore cardiac function in chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy via trilineage differentiating capacity, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 6, no. 33, pp , 29. [2] E.A.Jones,S.E.Kinsey,A.Englishetal., Isolationandcharacterization of bone marrow multipotential mesenchyma progenitor cells, Arthritis and Rheumatism, vol. 46, no. 2, pp , 22. [3] A. R. Williams and J. M. Hare, Mesenchymal stem cells: biology, pathophysiology, translational findings, and therapeutic implications for cardiac disease, Circulation Research, vol. 9, no. 8, pp , 2. [4] J. O. Jeong, J. W. Han, J. M. Kim et al., Malignant tumor formation after transplantation of short-term cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in experimental myocardial infarction and diabetic neuropathy, Circulation Research, vol. 8, no., pp , 2. [5] C. S. Kuo, K. Munakata, C. P. Reddy, and B. Surawicz, Characteristics and possible mechanism of ventricular arrhythmia dependent on the dispersion of action potential durations, Circulation, vol. 67, no. 6 I, pp , 983. [6]Y.S.Yoon,J.S.Park,T.Tkebuchava,C.Luedeman,andD. W. Losordo, Unexpected severe calcification after transplantation of bone marrow cells in acute myocardial infarction., Circulation, vol. 9, no. 25, pp , 24. [7] J. George, A. Afek, A. Abashidze et al., Transfer of endothelial progenitor and bone marrow cells influences atherosclerotic plaque size and composition in apolipoprotein E knockout mice, Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, vol. 25, no. 2, pp , 25. [8] A. Saiura, M. Sata, Y. Hirata, R. Nagai, and M. Makuuchi, Circulating smooth muscle progenitor cells contribute to atherosclerosis, Nature Medicine, vol. 7, no. 4, pp , 2. [9] M. Sata, A. Saiura, A. Kunisato et al., Hematopoietic stem cells differentiate into vascular cells that participate in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, Nature Medicine, vol. 8, no. 4, pp , 22. [] L. Lin, H. Gong, J. Ge et al., High density lipoprotein downregulates angiotensin II type receptor and inhibits angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, vol. 44, no., pp , 2. [] C. Brasselet, E. Durand, F. Addad et al., Collagen and elastin cross-linking: a mechanism of constrictive remodeling after arterial injury, American Physiology, vol. 289, no. 5, pp. H2228 H2233, 25. [2] G. P. Fadini, M. Albiero, L. Menegazzo et al., Widespread increase in myeloid calcifying cells contributes to ectopic vascular calcification in type 2 diabetes, Circulation Research, vol. 8, no. 9, pp. 2 2, 2. [3] K. A. Hruska, S. Mathew, and G. Saab, Bone morphogenetic proteins in vascular calcification, Circulation Research, vol. 97, no. 2, pp. 5 4, 25. [4] R. C. Johnson, J. A. Leopold, and J. Loscalzo, Vascular calcification: pathobiological mechanisms and clinical implications, Circulation Research, vol. 99, no., pp , 26. [5] M. Ketteler, G. Schlieper, and J. Floege, Calcification and cardiovascular health: new insights into an old phenomenon, Hypertension, vol. 47, no. 6, pp , 26. [6] Y. Nakagawa, K. Ikeda, Y. Akakabe et al., Paracrine osteogenic signals via bone morphogenetic protein-2 accelerate the atherosclerotic intimal calcification in vivo, Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, vol. 3, no., pp , 2. [7] X. Li, H. Y. Yang, and C. M. Giachelli, BMP-2 promotes phosphate uptake, phenotypic modulation, and calcification of human vascular smooth muscle cells, Atherosclerosis, vol. 99, no. 2, pp , 28.
8 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Volume 24 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 24 Diabetes Research Volume 24 Volume 24 Volume 24 International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Volume 24 Volume 24 Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Volume 24 Volume 24 Obesity Ophthalmology Volume 24 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Volume 24 Volume 24 Oncology Volume 24 Volume 24 Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume 24 AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Volume 24 Volume 24 Volume 24 Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity Volume 24
Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
 ISRN Cardiology, Article ID 825461, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/825461 Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
ISRN Cardiology, Article ID 825461, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/825461 Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
Review Article Comparison of 12-Month Outcomes with Zotarolimus- and Paclitaxel-Eluting Stents: A Meta-Analysis
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Cardiology Volume 2011, Article ID 675638, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2011/675638 Review Article Comparison of 12-Month Outcomes with Zotarolimus- and Paclitaxel-Eluting
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Cardiology Volume 2011, Article ID 675638, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2011/675638 Review Article Comparison of 12-Month Outcomes with Zotarolimus- and Paclitaxel-Eluting
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Repair Vascular Damage after Chemotherapy: Past, Present and Future
 Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Repair Vascular Damage after Chemotherapy: Past, Present and Future Cell Therapy 2014 Las Vegas, NV, USA Sulaiman Al-Hashmi, PhD Sultan Qaboos University Oman What are MSCs? Stem
Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Repair Vascular Damage after Chemotherapy: Past, Present and Future Cell Therapy 2014 Las Vegas, NV, USA Sulaiman Al-Hashmi, PhD Sultan Qaboos University Oman What are MSCs? Stem
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Case Report Coronary Artery Perforation and Regrowth of a Side Branch Occluded by a Polytetrafluoroethylene-Covered Stent Implantation
 International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2011, Article ID 212851, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/212851 Case Report Coronary Artery Perforation and Regrowth of a Side Branch Occluded by a Polytetrafluoroethylene-Covered
International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2011, Article ID 212851, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/212851 Case Report Coronary Artery Perforation and Regrowth of a Side Branch Occluded by a Polytetrafluoroethylene-Covered
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy
 Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions. Body and Disease 2011
 Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions Body and Disease 2011 Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis Intervention Goals: Acute Coronary Syndromes: Treat plaque rupture and thrombosis Significant Disease: Prevent
Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions Body and Disease 2011 Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis Intervention Goals: Acute Coronary Syndromes: Treat plaque rupture and thrombosis Significant Disease: Prevent
Invited Review. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Blood Vessels. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis with Comorbid Conditions
 Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2, Article ID 13326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/2/13326 Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis
Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2, Article ID 13326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/2/13326 Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis
Department of Internal Medicine, Saitama Citizens Medical Center, Saitama , Japan
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8790347, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8790347 Case Report GuideLiner Catheter Use for Percutaneous Intervention Involving Anomalous Origin of
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8790347, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8790347 Case Report GuideLiner Catheter Use for Percutaneous Intervention Involving Anomalous Origin of
Calcification of Porcine Aortic Valvular Interstitial Cells
 Calcification of Porcine Aortic Valvular Interstitial Cells Liwen Gu 1,2* Supervisor: Craig A. Simmons 1 Department of Engineering Science, 2 Institute of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering, University
Calcification of Porcine Aortic Valvular Interstitial Cells Liwen Gu 1,2* Supervisor: Craig A. Simmons 1 Department of Engineering Science, 2 Institute of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering, University
Conference Paper Oncothermia Basic Research at In Vivo Level: The First Results in Japan
 Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 197328, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.11/13/197328 Conference Paper Oncothermia Basic Research at In Vivo Level: The First Results in Japan G. Andocs, 1 Y. Okamoto,
Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 197328, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.11/13/197328 Conference Paper Oncothermia Basic Research at In Vivo Level: The First Results in Japan G. Andocs, 1 Y. Okamoto,
Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 2028402, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2028402 Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 2028402, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2028402 Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Case Report Successful Implantation of a Coronary Stent Graft in a Peripheral Vessel
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 725168, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/725168 Case Report Successful Implantation of a Coronary Stent Graft in a Peripheral Vessel Alexander
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 725168, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/725168 Case Report Successful Implantation of a Coronary Stent Graft in a Peripheral Vessel Alexander
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease. Why Animal Models of Disease? Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison
 In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease: A Tertiary Care Hospital Based Autopsy Study
 Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors
 Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2016, Article ID 3036476, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3036476 Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of
Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2016, Article ID 3036476, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3036476 Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of
THROMBOSIS. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan
 THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
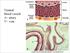 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs
 151 Technical note Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs Lukas Günther a, and Peter Hufnagl b a Department of Surgery, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg,
151 Technical note Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs Lukas Günther a, and Peter Hufnagl b a Department of Surgery, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized Medicine
 Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 719, pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/13/719 Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized
Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 719, pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/13/719 Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized
Case Report Multimodality Imaging of Chronic Ischemia
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Volume 2011, Article ID 739702, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/739702 Case Report Multimodality Imaging of Chronic Ischemia Kiyotake Ishikawa, Dennis Ladage, Kleopatra Rapti,
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Volume 2011, Article ID 739702, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/739702 Case Report Multimodality Imaging of Chronic Ischemia Kiyotake Ishikawa, Dennis Ladage, Kleopatra Rapti,
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
10/8/2018. Lecture 9. Cardiovascular Health. Lecture Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor
 Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
The changes of serum BDNF, blood lipid and PCI in the elderly patients with coronary heart disease complicated with diabetes mellitus
 184 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(16): 184-188 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.hnykdxxb.com/ The changes of serum BDNF, blood lipid and PCI in the elderly patients with
184 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(16): 184-188 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.hnykdxxb.com/ The changes of serum BDNF, blood lipid and PCI in the elderly patients with
Case Report PET/CT Imaging in Oncology: Exceptions That Prove the Rule
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 865032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/865032 Case Report PET/CT Imaging in Oncology: Exceptions That Prove the Rule M. Casali, 1 A.
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 865032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/865032 Case Report PET/CT Imaging in Oncology: Exceptions That Prove the Rule M. Casali, 1 A.
Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 129632, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/129632 Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 129632, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/129632 Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice.
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4979182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4979182 Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4979182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4979182 Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
Antioxidants And Stem Cells For Coronary Heart Disease By Philip B Oliva
 Antioxidants And Stem Cells For Coronary Heart Disease By Philip B Oliva If you are searched for the ebook by Philip B Oliva Antioxidants and Stem Cells for Coronary Heart Disease in pdf form, in that
Antioxidants And Stem Cells For Coronary Heart Disease By Philip B Oliva If you are searched for the ebook by Philip B Oliva Antioxidants and Stem Cells for Coronary Heart Disease in pdf form, in that
Case Report Anomalous Left Main Coronary Artery: Case Series of Different Courses and Literature Review
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 380952, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/380952 Case Report Anomalous Left Main Coronary Artery: Case Series of Different Courses and Literature
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 380952, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/380952 Case Report Anomalous Left Main Coronary Artery: Case Series of Different Courses and Literature
Research Article The Effect of Elevated Triglycerides on the Onset and Progression of Coronary Artery Disease: A Retrospective Chart Review
 Cholesterol Volume 2015, Article ID 292935, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/292935 Research Article The Effect of Elevated Triglycerides on the Onset and Progression of Coronary Artery Disease:
Cholesterol Volume 2015, Article ID 292935, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/292935 Research Article The Effect of Elevated Triglycerides on the Onset and Progression of Coronary Artery Disease:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
1 Functions of endothelial cells include all the following EXCEPT. 2 Response to vascular injury is characterised by
 airns ase Hospital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 Functions of endothelial cells include all the following XPT Formation of von-willebrand factor Formation of collagen and proteoglycans Formation of
airns ase Hospital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 Functions of endothelial cells include all the following XPT Formation of von-willebrand factor Formation of collagen and proteoglycans Formation of
Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall
 Histol Histopath (1 990) 5: 161-1 67 Histology and Histopathology Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall Reinhold Kittelberger,
Histol Histopath (1 990) 5: 161-1 67 Histology and Histopathology Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall Reinhold Kittelberger,
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
DOWNLOAD PDF CARDIAC REMODELING AND CELL DEATH IN HEART FAILURE
 Chapter 1 : The fibrosis-cell death axis in heart failure Remodeling may be defined as changes in the morphology, structure, and function of the heart related to alterations in loading conditions and/or
Chapter 1 : The fibrosis-cell death axis in heart failure Remodeling may be defined as changes in the morphology, structure, and function of the heart related to alterations in loading conditions and/or
Vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypes in primary pulmonary hypertension
 Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 316 320 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 CASE STUDY Vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypes in primary
Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 316 320 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 CASE STUDY Vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypes in primary
Paracrine Mechanisms in Adult Stem Cell Signaling and Therapy
 Paracrine Mechanisms in Adult Stem Cell Signaling and Therapy Massimiliano Gnecchi, Zhiping Zhang, Aiguo Ni, Victor J. Dzau Circulation Research 2008 Nov 21;103(11):1204-19 Introduction(1) After AMI all
Paracrine Mechanisms in Adult Stem Cell Signaling and Therapy Massimiliano Gnecchi, Zhiping Zhang, Aiguo Ni, Victor J. Dzau Circulation Research 2008 Nov 21;103(11):1204-19 Introduction(1) After AMI all
International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science
 1 International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science This work has been supported by the European Community s Sixth Framework Programme under grant agreement n LSHM-CT-2005-01883 EUGeneHeart.
1 International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science This work has been supported by the European Community s Sixth Framework Programme under grant agreement n LSHM-CT-2005-01883 EUGeneHeart.
Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism
 1510 JACC Vol. 12, No, 6 December 1988:1510--4 Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism KEVIN J. TVETER, MD, JESSE E. EDWARDS, MD, FACC St, Paul, Minnesota This
1510 JACC Vol. 12, No, 6 December 1988:1510--4 Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism KEVIN J. TVETER, MD, JESSE E. EDWARDS, MD, FACC St, Paul, Minnesota This
THE BLOOD VESSELS. Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department.
 THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
Case Report Exercised-Induced Coronary Spasm in Near Normal Coronary Arteries
 International Vascular Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 207479, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/207479 Case Report Exercised-Induced Coronary Spasm in Near Normal Coronary Arteries Damian Franzen 1 and Thomas
International Vascular Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 207479, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/207479 Case Report Exercised-Induced Coronary Spasm in Near Normal Coronary Arteries Damian Franzen 1 and Thomas
Observe the effects of atherosclerosis on the coronary artery lumen
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Case Report Osteolysis of the Greater Trochanter Caused by a Foreign Body Granuloma Associated with the Ethibond Suture after Total Hip Arthroplasty
 Hindawi Volume 2017, Article ID 6082302, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6082302 Case Report Osteolysis of the Greater Trochanter Caused by a Foreign Body Granuloma Associated with the Ethibond Suture
Hindawi Volume 2017, Article ID 6082302, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6082302 Case Report Osteolysis of the Greater Trochanter Caused by a Foreign Body Granuloma Associated with the Ethibond Suture
For unclear reasons, only about 40% of patients with calcific aortic stenosis also have coronary
 Αθηροσκλήρωση και ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας. Οµοιότητες και διαφορές Ν. Μεζίλης Κλινική «Άγιος Λουκάς» Ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας: Μία ακόµα µορφή αθηρωµάτωσης; Some observations
Αθηροσκλήρωση και ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας. Οµοιότητες και διαφορές Ν. Μεζίλης Κλινική «Άγιος Λουκάς» Ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας: Μία ακόµα µορφή αθηρωµάτωσης; Some observations
Promoting Fracture Healing Through Systemic or Local Administration of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Promoting Fracture Healing Through Systemic or Local Administration of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Gang Li Dept. of Orthopaedics and Traumatology School of Biomedical Sciences, The Chinese University
Promoting Fracture Healing Through Systemic or Local Administration of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Gang Li Dept. of Orthopaedics and Traumatology School of Biomedical Sciences, The Chinese University
Case Report A Rare Case of Complete Stent Fracture, Coronary Arterial Transection, and Pseudoaneurysm Formation Induced by Repeated Stenting
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2015, Article ID 192853, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/192853 Case Report A Rare Case of Complete Stent Fracture, Coronary Arterial Transection, and Pseudoaneurysm
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2015, Article ID 192853, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/192853 Case Report A Rare Case of Complete Stent Fracture, Coronary Arterial Transection, and Pseudoaneurysm
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism
 Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
In the name of GOD. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension
 In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the
 The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
Clinical Study Age Differences in Long Term Outcomes of Coronary Patients Treated with Drug Eluting Stents at a Tertiary Medical Center
 Aging Research Volume 2013, Article ID 471026, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/471026 Clinical Study Age Differences in Long Term Outcomes of Coronary Patients Treated with Drug Eluting Stents at
Aging Research Volume 2013, Article ID 471026, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/471026 Clinical Study Age Differences in Long Term Outcomes of Coronary Patients Treated with Drug Eluting Stents at
Tom Eisele, Benedikt M. Muenz, and Grigorios Korosoglou. Department of Cardiology & Vascular Medicine, GRN Hospital Weinheim, Weinheim, Germany
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 7376457, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7376457 Case Report Successful Endovascular Repair of an Iatrogenic Perforation of the Superficial
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 7376457, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7376457 Case Report Successful Endovascular Repair of an Iatrogenic Perforation of the Superficial
FOCUS ON CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
 The Consequences of Vitamin D Deficiency: FOCUS ON CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE Vitamin D deficiency is a global health problem. With all the medical advances of the century, vitamin D deficiency is still epidemic.
The Consequences of Vitamin D Deficiency: FOCUS ON CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE Vitamin D deficiency is a global health problem. With all the medical advances of the century, vitamin D deficiency is still epidemic.
12 Lead EKG Chapter 4 Worksheet
 Match the following using the word bank. 1. A form of arteriosclerosis in which the thickening and hardening of the vessels walls are caused by an accumulation of fatty deposits in the innermost lining
Match the following using the word bank. 1. A form of arteriosclerosis in which the thickening and hardening of the vessels walls are caused by an accumulation of fatty deposits in the innermost lining
Acute coronary syndrome. Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA
 Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY
 MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
Jung Han Kim, PhD Project 1 Project 2
 Jung Han Kim, PhD Professor Joan C Edwards School of Medicine at Marshall University 1700 3 rd Ave, 435 BBSC Huntington, WV 25755 Tel: (304) 696-3873 Email: kimj@marshall.edu My long-term research interest
Jung Han Kim, PhD Professor Joan C Edwards School of Medicine at Marshall University 1700 3 rd Ave, 435 BBSC Huntington, WV 25755 Tel: (304) 696-3873 Email: kimj@marshall.edu My long-term research interest
Structural abnormalities of the heart and vascular system in CKD & Dialysis - Thick but weak
 Structural abnormalities of the heart and vascular system in CKD & Dialysis - Thick but weak Kerstin Amann Nephropathology, Dept. of Pathology, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg Krankenhausstr. 8-10 91054
Structural abnormalities of the heart and vascular system in CKD & Dialysis - Thick but weak Kerstin Amann Nephropathology, Dept. of Pathology, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg Krankenhausstr. 8-10 91054
Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Conference Paper Programmed Cell Death Induced by Modulated Electrohyperthermia
 Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 187835, 3 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187835 Conference Paper Programmed Cell Death Induced by Modulated Electrohyperthermia Meggyesházi Nóra, 1 Andócs
Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 187835, 3 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187835 Conference Paper Programmed Cell Death Induced by Modulated Electrohyperthermia Meggyesházi Nóra, 1 Andócs
Histopathology: healing
 Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmal Diameter
 International Vascular Medicine, Article ID 574762, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574762 Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum
International Vascular Medicine, Article ID 574762, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574762 Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum
Sylwia Mizia, 1 Dorota Dera-Joachimiak, 1 Malgorzata Polak, 1 Katarzyna Koscinska, 1 Mariola Sedzimirska, 1 and Andrzej Lange 1, 2. 1.
 Bone Marrow Research Volume 2012, Article ID 873695, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/873695 Clinical Study Both Optimal Matching and Procedure Duration Influence Survival of Patients after Unrelated Donor Hematopoietic
Bone Marrow Research Volume 2012, Article ID 873695, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/873695 Clinical Study Both Optimal Matching and Procedure Duration Influence Survival of Patients after Unrelated Donor Hematopoietic
Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral Fracture: Two Case Reports of Curved Femurs
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 213614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/213614 Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 213614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/213614 Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral
Coronary Artery Calcium Score
 Coronary Artery Calcium Score August 19, 2014 by Axel F. Sigurdsson MD 174 Comments essential for living organisms. Calcium is a chemical element that is Most of the calcium within the human body is found
Coronary Artery Calcium Score August 19, 2014 by Axel F. Sigurdsson MD 174 Comments essential for living organisms. Calcium is a chemical element that is Most of the calcium within the human body is found
Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway
 Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway Jieyuan Zhang, Xiaolin Liu, Haiyan Li, Chunyuan Chen, Bin Hu, Xin Niu, Qing
Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway Jieyuan Zhang, Xiaolin Liu, Haiyan Li, Chunyuan Chen, Bin Hu, Xin Niu, Qing
Stem Cells. Keith Channon. Department of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Oxford John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford
 Stem Cells Keith Channon Department of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Oxford John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford Adult Stem Cells Unique cells that are capable of self-renewal Have the ability to differentiate
Stem Cells Keith Channon Department of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Oxford John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford Adult Stem Cells Unique cells that are capable of self-renewal Have the ability to differentiate
Regenerative Medicine for Cardiomyocytes
 Regenerative Medicine Regenerative Medicine for JMAJ 47(7): 328 332, 2004 Keiichi FUKUDA Assistant Professor, Institute for Advanced Cardiac Therapeutics, Keio University School of Medicine Abstract: Heart
Regenerative Medicine Regenerative Medicine for JMAJ 47(7): 328 332, 2004 Keiichi FUKUDA Assistant Professor, Institute for Advanced Cardiac Therapeutics, Keio University School of Medicine Abstract: Heart
Alireza Bakhshaeekia and Sina Ghiasi-hafezi. 1. Introduction. 2. Patients and Methods
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 0, Article ID 4578, 4 pages doi:0.55/0/4578 Clinical Study Comparing the Alteration of Nasal Tip Sensibility and Sensory Recovery Time following Open Rhinoplasty with
Plastic Surgery International Volume 0, Article ID 4578, 4 pages doi:0.55/0/4578 Clinical Study Comparing the Alteration of Nasal Tip Sensibility and Sensory Recovery Time following Open Rhinoplasty with
Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report of Neoadjuvant Use Enabling Complete Surgical Resection
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 496351, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/496351 Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 496351, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/496351 Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report
CCR Keywords Primary keywords
 CCR Keywords Primary keywords 1 Aboriginal health 2 Administration and health services 3 Allied health 4 Anaesthesia and intensive care 5 Biochemistry 6 Cardiology and cardiac surgery 7 Complementary medicine
CCR Keywords Primary keywords 1 Aboriginal health 2 Administration and health services 3 Allied health 4 Anaesthesia and intensive care 5 Biochemistry 6 Cardiology and cardiac surgery 7 Complementary medicine
Case Report Complete Obstruction of Endotracheal Tube in an Infant with a Retropharyngeal and Anterior Mediastinal Abscess
 Hindawi Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2017, Article ID 1848945, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1848945 Case Report Complete Obstruction of Endotracheal Tube in an Infant with a Retropharyngeal
Hindawi Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2017, Article ID 1848945, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1848945 Case Report Complete Obstruction of Endotracheal Tube in an Infant with a Retropharyngeal
Research Article Subcutaneous Single Injection Digital Block with Epinephrine
 Anesthesiology Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 487650, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/487650 Research Article Subcutaneous Single Injection Digital Block with Epinephrine Motoki Sonohata, 1 Satomi
Anesthesiology Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 487650, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/487650 Research Article Subcutaneous Single Injection Digital Block with Epinephrine Motoki Sonohata, 1 Satomi
Research Article The Impact of Warfarin on Patients with End Stage Renal Disease
 Advances in Vascular Medicine, Article ID 542034, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/542034 Research Article The Impact of Warfarin on Patients with End Stage Renal Disease Anahita Dua, 1 Sapan S.
Advances in Vascular Medicine, Article ID 542034, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/542034 Research Article The Impact of Warfarin on Patients with End Stage Renal Disease Anahita Dua, 1 Sapan S.
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Resident cardiac stem cells: how to find and use them
 Resident cardiac stem cells: how to find and use them G. Hasenfuß Cardiology and Pneumology Heart Research Center Göttingen Georg-August-University Göttingen Definition: Stem cell Selfrenewal Stem cell
Resident cardiac stem cells: how to find and use them G. Hasenfuß Cardiology and Pneumology Heart Research Center Göttingen Georg-August-University Göttingen Definition: Stem cell Selfrenewal Stem cell
Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV. Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA
 Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA Objectives Review current terminology Identify key histopathologic
Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA Objectives Review current terminology Identify key histopathologic
조현재 서울대학교병원순환기내과, 심혈관연구실,
 Molecular Mechanism of Vascular Calcification 2010. 4. 17. 조현재 서울대학교병원순환기내과, 심혈관연구실, 서울대학교병원심혈관센터 Vascular calcification : clinical hurdles Vascular calcification : clinical significance! Clinical consequences
Molecular Mechanism of Vascular Calcification 2010. 4. 17. 조현재 서울대학교병원순환기내과, 심혈관연구실, 서울대학교병원심혈관센터 Vascular calcification : clinical hurdles Vascular calcification : clinical significance! Clinical consequences
Devendra V. Kulkarni, Rahul G. Hegde, Ankit Balani, and Anagha R. Joshi. 2. Case Report. 1. Introduction
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 614647, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614647 Case Report A Rare Case of Pulmonary Atresia with Ventricular Septal Defect with a Right Sided Aortic Arch and
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 614647, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614647 Case Report A Rare Case of Pulmonary Atresia with Ventricular Septal Defect with a Right Sided Aortic Arch and
stem cell products Basement Membrane Matrix Products Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products
 stem cell products Basement Membrane Matrix Products Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products Stem Cell Qualified Extracellular Matrix Proteins Stem cell research requires the finest
stem cell products Basement Membrane Matrix Products Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products Stem Cell Qualified Extracellular Matrix Proteins Stem cell research requires the finest
Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis
 Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210972, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210972 Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis Hiroaki
Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210972, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210972 Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis Hiroaki
Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication for Repeat Metastasectomy
 Respiratory Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 570314, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/570314 Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication
Respiratory Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 570314, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/570314 Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication
Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Common Codes for ICD-10
 Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells
 Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
