constant dose of frusemide for at least two months; one patient in the first study and one in the second
|
|
|
- Moses Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1985) 61, A study of two diuretic/potassium combinations in heart failure M. Hussain, K. Walton, C. Davidson and D.B. Morgan Birch Hill Hospital, Rochdale OL12 9QB and Department ofchemical Pathology, Leeds, UK. Summary: The effect of potassium supplements was studied in 28 patients taking long term frusemide (40-80 mg daily). Plasma potassium fell when supplements were stopped, and rose towards prior values on the potassium/frusemide combination, Diumide K. In a crossover study in 14 of these patients comparing equivalent doses of frusemide, Diumide K (frusemide 40 mg, potassium 8 mmol), bumetanide, and Burinex K (bumetanide 0.5 mg, potassium 7.7 mmol) plasma potassium was lower on frusemide than on bumetanide. On Diumide K and Burinex K plasma potassium rose significantly but did not reach the levels on prior therapy. Small doses of potassium in combined formulations seem to be effective in countering the mild hypokalaemia caused by loop diuretics. Introduction Loop diuretics are the most effective and commonly prescribed drugs in heart failure, and are usually given with potassium supplements because of the risk of hypokalaemia. However a review of the literature suggested that, contrary to general opinion, the fall in serum potassium, and thus the frequency of hypokalaemia, was much less with the loop diuretics than with the thiazides (Morgan & Davidson, 1980). Nevertheless, a number of preparations have been developed where a loop diuretic is combined with either a potassium supplement or a potassium sparing duretic. We have compared the effect of two diuretics and diuretic/potassium combinations on plasma and red cell electrolytes in patients with stable heart failure. Frusemide and bumetanide were given without supplements and as combination therapy, Diumide K (frusemide 40 mg, potassium 8 mmol) and Burinex K (bumetanide 0.5 mg, potassium 7.7 mmol) per tablet in an open crossover study. Patients and methods Twenty-eight patients (14 male, 14 female) agreed to take part in the study. Eighteen patients had ischaemic heart disease, and ten patients valvular disease; their mean age was 62.5 y (range 39-75). All had been on a M. Hussain, M.B.; K. Walton, M.B., M.R.C.P.; C. Davidson, M.B., M.R.C.P.; D. B. Morgan, M.D., M.R.C.Path. Correspondence: C. Davidson, Bateman Centre for Postgraduate Medical Studies, Birch Hill Hospital, Rochdale OL12 9QB. Accepted: 30 May 1984 constant dose of frusemide for at least two months; one patient in the first study and one in the second were taking 80mg/d and the rest were on 40mg/d. Twenty-seven patients were on potassium supplements (8-32 mmol/d, average 13 mmol/d) and one on spironolactone. Seventeen patients were taking digoxin for atrial fibrillation. After initial measurements, potassium supplements or spironolactone were stopped and the patients were allocated to their treatment groups. They were seen at two weekly intervals at the same time in the morning. At each visit their cardiac state was assessed, side effects were noted and an electrocardiogram (ECG) and a 30 second rhythm strip were taken. Blood was taken without venous occlusion or muscle pumping and separated within an hour. The plasma potassium was measured with an auto-analyser, and the erythrocyte potassium was measured by a technique described elsewhere (Morgan et al., 1980). Design of study The study was in two parts: (a) Crossover comparison of frusemide and Diumide K: the first 14 patients (7 female) took frusemide or Diumide K in random order for periods of one month each; (b) Crossover comparison of 4 preparations: the second 14 patients (7 female) were randomly allocated to frusemide or bumetanide and in order to avoid prolonged periods without supplements continued as follows: bumetanide, 1 mg - Burinex K (2 tablets) - QThe Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1985
2 30 M. HUSSAIN et al. frusemide, 40 mg - Diumide K (I tablet); OR frusemide, 40 mg- Diumide K (1 tablet) - bumetanide, 1 mg - Burinex K (2 tablets). One patient was on 80 mg frusemide and 2 mg bumetanide and the equivalent doses of the combined preparations (see Ramsey et al., 1978). The treatment periods were one month each, the total duration of the study being 16 weeks. Two patients were withdrawn after completing bumetanide - Burinex K only leaving 12 for comparison of all 4 preparations. Criteria for withdrawal from the study included; clinical deterioration necessitating an increased dose of diuretic, digoxin toxicity, significant hypokalaemia (less than 3.0 mmol/l ) and side effects from the drugs. Statistical analysis was by two way analysis of variance and where appropriate, the paired 't' test. Results Clinical All patients completed the first part of the study but in the second 2 patients were withdrawn, both because of increasing heart failure. None of the patients developed clinical evidence of digoxin toxicity, and none had to be withdrawn because of hypokalaemia. There were no significant side effects from any of the preparations. Two patients died some months later, one after cardiac surgery and one from myocardial infarction. Electrocardiogram None of the patients developed any of the ECG features of hypokalaemia or digoxin toxicity. In 16 patients, 9 on digoxin, no ventricular ectopics were observed at any stage. In 5 patients, all on digoxin, ectopics occurred on only one occasion. Ventricular ectopics occurred on more than one occasion in 6 patients, 3 of whom were on digoxin. The occurrence of ectopics bore no relation to changes in plasma potassium or clinical state. Plasma and erythrocyte composition Comparison offrusemide alone and Diumide K Comparative data were available from 14 patients from the first study and 12 from the second. There were no significant differences between these two groups and their results have been combined (Table I). There were no significant changes in weight or plasma and red cell electrolytes apart from potassium. Plasma potassium fell by 0.3 mmol/l when supplements were withdrawn and the patients continued on frusemide alone but rose on Diumide K towards the level on prior therapy (P <0.001). Comparison ofbumetanide alone and Burinex K (Table II) There were no significant changes in weight or plasma and red cell electrolytes apart from plasma potassium. On bumetanide alone plasma potassium was on average 0.23 mmol/l less than on prior therapy, and rose on Burinex K (P <0.05). Comparison offour drugs Twelve patients (6 male, 6 female) completed a crossover comparison of all four drugs. There were again no significant changes in weight or plasma electrolytes apart from plasma potassium. The results (mean + s.d.) for plasma potassium were: prior therapy 3.82 (0.32), frusemide 3.43 (0.31), Diumide K 3.67 (0.23), bumetanide 3.71 (0.31), Burinex K 3.75 (0.28) mmol/l. The plasma potassium on frusemide was significantly less than all other treatment periods (P <0.01). In individual patients there was no significant correlation between the falls in plasma potassium on frusemide, and the smaller falls on bumetanide. Table I Plasma and red cell electrolytes (mean ± s.d.) in 26 patients completing a crossover comparison of frusemide alone and Diumide K. The plasma potassium was significantly lower on frusemide than on prior therapy or Diumide K (***P<0.001). Plasma Erythrocyte Weight mmol/l mmol/l (washed) (kg) Na + K+ Urea Na + (w) K+ (w) Prior therapy (16.72) (1.7) (0.32) (1.7) (1.04) (1.2) Frusemide *** (17.04) (2.6) (0.36) (1.57) (1.41) (1.4) Diumide-K (16.77) (1.7) (0.36) (2.26) (1.17) (2.1)
3 TWO DIURETIC/POTASSIUM COMBINATIONS 31 Table II Plasma and red cell electrolytes (mean + s.d.) in 14 patients completing a crossover comparison of bumetanide and Burinex K. The plasma potassium was significantly lower on bumetanide than on prior therapy (* P <0.05) or Burinex K (*P <0.05). Plasma Erythrocyte Weight mmol/l mmol/l (washed) kg Na+ K+ Urea Na+ (w) K+ (w) Prior therapy (17.70) (2.7) (0.29) (1.57) (1.17) (2.12) Bumetanide * (17.87) (2.75) (0.33) (1.26) (1.55) (1.49) Burinex K (17.95) (3.8) (0.30) (1.45) (1.40) (1.88) Factors affecting plasma potassium during treatment: In most patients it was possible to compare the plasma potassium at the second and fourth week of each treatment period. There were no significant differences between the average values on the two visits but in individual patients there was considerable variation between the two values: mean difference mmol/l, s.d mmol/l, n = 69. Despite this variation there did seem to be a significant difference between men and women, the fall in plasma potassium being greater in women (Table III). Indeed in men there were no significant differences between any of the treatments. Discussion This study suggests that potassium supplements can at least partly correct the fall in plasma potassium caused by frusemide and bumetanide. This finding is surprising considering the low doses of potassium used (7-14 mmol/d) when compared with the normal dietary intake of potassium ( mmol/d). Nevertheless, the fall in plasma potassium when previous supplements were stopped ( mmol/l) and the rise when potassium was given again ( mmol/l), suggest that this is not a spurious result. Table III Plasma potassium (mean ± s.d.) during diuretic therapy: differences between the sexes (* P < 0.05) n Prior therapy Frusemide Diumide-K Male (0.25) 3.71(0.29) 4.01(0.36) Female (0.32) 3.50 (0.36)* 3.67 (0.29)* n Prior therapy Bumetanide Burinex K Male (0.37) 3.74(0.21) 3.91(0.32) Female (0.16) 3.60(0.40)* 3.69(0.21) Although loop diuretics have been widely used for more than twenty years, there is remarkably little information on their effect on serum (or plasma) potassium with or without potassium supplements. In early studies where frusemide was given without supplements serum potassium fell on average by 0.3 mmol/l, compared to a fall of 0.6 mmol/l on thiazides (Morgan & Davidson, 1980). Similar data for bumetanide were not available until recently, since most studies with this drug have included routine potassium supplements. Two groups have reported the effect of bumetanide alone and compared it with frusemide. In a welldesigned crossover study Gabriel & Baylor (1981) found that plasma potassium fell by 0. I mmol/l on bumetanide compared to 0.24 mmol/l on frusemide. Yajnik et al. (1981) found more striking differences in a short parallel group study, the fall on bumetanide being 0.12 mmol/i and frusemide 0.81 mmol/l. In our study there were small differences which again favoured bumetanide in the doses used. Short term balance studies have shown less urinary potassium loss after bumetanide than frusemide (Ramsay et al., 1978), and larger studies seem indicated to clarify the issue. To our knowledge there are no previous studies of the effect of potassium supplements on the hypokalaemia caused by loop diuretics in short or long term therapy. Several reports (Singh & Watt, 1976; Kubik et al., 1977; Murchison et al., 1975) with Burinex K and one (Lewis, 1979) with Diumide K show that plasma potassium is maintained over periods of up to six months, and by inference suggest that the dose of potassium included in the tablet is effective in long term treatment. This is supported by the findings of the present short term study. Although hypokalaemia was not entirely prevented, the number of patients with a plasma potassium less than 3.5 mmol/1 was reduced from 30% to 12% by the change from frusemide to Diumide K. A similar but smaller effect was seen with bumetanide and Burinex K.
4 32 M. HUSSAIN et al. These findings conflict with the generally held view that potassium supplements are relatively ineffective. Evidence for this view comes from studies with thiazides rather than loop diuretics. In a community study (Krakauer & Lauritzen, 1978) there was no significant difference in serum potassium between those taking and those not taking supplements; and in a small study Schwartz & Schatz (1974) were unable to correct the serum potassium in some patients even with 96 mmol potassium/d. In our review of the literature we found an increase in serum potassium of 0.32 mmol/l on supplements (mean dose 36 mmol/d) which was less than the rise observed with potassium sparing diuretics (Morgan & Davidson, 1980). The apparent difference in the efficacy of potassium supplements during treatment with the thiazides and the loop diuretics cannot readily be explained. Jackson et al. (1982) have shown that there is a flat dose response curve, which implies that small doses of potassium are relatively more effective than high doses. As the fall in plasma potassium on loop diuretics is less than the thiazides the relatively small effect of supplements ( mmol/l) may be sufficient to counter the hypokalaemia with loop diuretics where it cannot with thiazides. An alternative explanation is that in the combined preparations, Diumide K and Burinex K, the diuretic component is incompletely absorbed and, therefore, has a smaller effect on plasma potassium. There was however no significant change in weight or other biochemical measurement to suggest this was the case. There is still considerable debate about the clinical importance of mild hypokalaemia. One third of our patients on frusemide alone, and a smaller proportion on bumetanide, had a plasma potassium of mmol/l, but there were no clinical or ECG changes in these patients, even those taking digoxin. However, there are reports of increased ectopic References GABRIEL, R & BAYLOR, P. (1981). Comparison of the chronic effects of bendrofluazide, bumetanide, and frusemide on plasma biochemical variables. Postgraduate Medical Journal, 57, 71. HOLLAND, O.B., NIXON, J.V. & KUHNERT, L. (1981). Diuretic induced ventricular ectopic activity. American Journal of Medicine, 70, 762. HOLLIFIELD, J.W. & SLATON, P.E. (1981). Thiazide diuretics, hypokalaemia and cardiac arrhythmias. Acda Medica Scandinavica. Suppl., 647, 67. JACKSON, P.R., RAMSAY, L.E. & WAKEFIELD, V. (1982). Relative potency of spironolactone, triamterene and potassium chloride in thiazide-induced hypokalaemia. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 14, 257. KRAKAUER, R. & LAURITZEN, M. (1978). Diuretic therapy and hypokalaemia in geriatric out-patients. Danish Medical Bulletin, 25, 126. activity during continuous ECG monitoring with plasma potassium levels in this range (Steiness & Olesen, 1976; Hollifield & Slaton, 1981; Holland et al., 1981), and our observations were clearly limited in this respect. One further point of interest lies in the greater fall in plasma potassium in women than in men when supplements were stopped. There is increasing evidence that women are more susceptible to hypokalaema from any cause (Lawson et al., 1979; Morgan & Young, 1982). In a large community study Krakauer & Lauritzen (1978) found that the serum potassium during diuretic therapy was 4.1 mmol/l in men and 3.9 mmol/l in women, and in the recent report from the MRC study in mild to moderate hypertension (1983) 12 of the 16 patients who developed severe hypokalaemia on diuretics were women. The mechanism of this difference is unknown, but it is sufficiently great to question the need for supplementation at all in men, at least in the doses used in this study. This study, taken with data from longer studies using Burinex K and Diumide K, suggests that small doses of potassium can be effective in reducing the hypokalaemia caused by loop diuretics. However, the fall in plasma potassium after loop diuretics is relatively small, and the need to correct it is still disputed. If potassium supplements are indicated, the advantage of such combined diuretic/potassium formulations in terms of compliance must be set against the additional cost of these drugs. Acknowledgements We are grateful to Napp Laboratories for financial support, Mrs J. Makin for red cell measurements, Mrs L. Long for secretarial help and Mr H. Williams for statistical advice. KUBIK, M.M., BOWERS, E. & UNDERWOOD, P.N. (1977). Comparison of separate versus simultaneous administration of potassium supplement with the diuretic bumetanide. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 5, 273. LAWSON, D., HENRY, D., LOWE, J., GRAY, J. & MORGAN, H.B. (1979). Severe hypokalaemia in hospital patients. Archives of Internal Medicine, 139, 978. LEWIS, J.G. (1979). The effect on plasma potassium of a combined preparation of frusemide and slow-release potassium chloride (Diumide K Continus tablets). Journal of International Medical Research, 7, 354. MRC Working Party on Mild to Moderate Hypertension (1983). Ventricular extrasystoles during thiazide treatment: substudy of MRC mild hypertension trial. British Medical Journal, 2, MORGAN, D.B., CUMBERBATCH, M., COHN, S., SCOTT, D., GUNASUNTHARAM, T., DAVIDSON, C. & CHAPMAN, C.
5 (1980). The erythrocyte sodium and potassium in patients treated with digoxin. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 10, 127. MORGAN, D.B. & DAVIDSON, C. (1980). Hypokalaemia and diuretics: an analysis of publications. British Medical Journal, 1, 905. MORGAN, D.B. & YOUNG, R.M. (1982). Acute transient hypokalaemia: new interpretation of a common event. Lancet, ii, 751. MURCHISON, L.E., BEWSHER, P.D. & SEYMOUR, R. (1975). Lack ofeffect of bumetanide on body potassium content in hypertension. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2, 87. RAMSAY, L.E., MINNES, G.T., HETTIARACHCHI, J., SHEL- TON, J. & SCOTT, P. (1978). Bumetanide and frusemide: A comparison of dose-response curves in healthy men. TWO DIURETIC/POTASSIUM COMBINATIONS 33 British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 5, 243. SCHWARTZ, A.B. & SCHATZ, C.D. (1974). Dosage of potassium elixirs to correct thiazide induced hypokalaemia. Journal of the American Medical Association, 203, 702. SINGH, B.B. & WATT, D.A.L. (1976). Patient tolerance of a long term diuretic/potassium supplement therapy. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 4, 117. STEINESS, E. & OLESEN, K.H. (1976). Cardiac arrhythmias induced by hypokalaemia and potassium loss during maintenance digoxin therapy. British Heart Journal, 38, 167. YAJNIK, V.H., KALAWADIA, S.V., PAREKH, B.H., KARELIA, L.S., PUROHIT, G.L., DOSHI, K.J. & SAXENA, K. (1981). Bumetanide versus frusemide as a diuretic. Current Therapeutic Research, 29, 584. Postgrad Med J: first published as /pgmj on 1 January Downloaded from on 29 March 2019 by guest. Protected by
potassium ratio and response to diuretics in
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (March 1977) 53, 117-121. Nineteen patients The urinary sodium : potassium ratio and response to diuretics in resistant oedema WILLIAM D. ALEXANDER* D. F. LEVINE R. A. BRANCHt
Postgraduate Medical Journal (March 1977) 53, 117-121. Nineteen patients The urinary sodium : potassium ratio and response to diuretics in resistant oedema WILLIAM D. ALEXANDER* D. F. LEVINE R. A. BRANCHt
Combination diuretic treatment in severe heart failure: a randomised controlled trial
 146 Department of Cardiology, Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Sheffield K S Channer K A McLean P Lawson-Matthew Department of Geriatrics, South Tyneside General Hospital, Southshields, Tyne and Wear M Richardson
146 Department of Cardiology, Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Sheffield K S Channer K A McLean P Lawson-Matthew Department of Geriatrics, South Tyneside General Hospital, Southshields, Tyne and Wear M Richardson
Radioimmunoassay of serum digoxin in relation to digoxin intoxication
 British Heart journal, I975, 37, 6I9-623. Radioimmunoassay of serum digoxin in relation to digoxin intoxication R. B. Singh, A. N. Rai, K. P. Dube, D. K. Srivastav, P. N. Somani, and B. C. Katiyar From
British Heart journal, I975, 37, 6I9-623. Radioimmunoassay of serum digoxin in relation to digoxin intoxication R. B. Singh, A. N. Rai, K. P. Dube, D. K. Srivastav, P. N. Somani, and B. C. Katiyar From
1. Despite the plethora of new ACE-inhibitors they offer little advantage over the earlier products captopril and enalapril.
 SUMMARY 1. Despite the plethora of new ACE-inhibitors they offer little advantage over the earlier products captopril and enalapril. 2. While diuretics and beta-blockers remain first-line antihypertensive
SUMMARY 1. Despite the plethora of new ACE-inhibitors they offer little advantage over the earlier products captopril and enalapril. 2. While diuretics and beta-blockers remain first-line antihypertensive
Younger adults with a family history of premature artherosclerotic disease should have their cardiovascular risk factors measured.
 Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Use of Signal Averaged ECG and Spectral Analysis of Heart Rate Variability in Antiarrhythmic Therapy of Patients with Ventricular Tachycardia
 October 1999 513 Use of Signal Averaged ECG and Spectral Analysis of Heart Rate Variability in Antiarrhythmic Therapy of Patients with Ventricular Tachycardia G.M. KAMALOV, A.S. GALYAVICH, N.R. KHASSANOV,
October 1999 513 Use of Signal Averaged ECG and Spectral Analysis of Heart Rate Variability in Antiarrhythmic Therapy of Patients with Ventricular Tachycardia G.M. KAMALOV, A.S. GALYAVICH, N.R. KHASSANOV,
keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests Why do we monitor patients taking diuretics and what do we monitor? Monitoring a person on
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests Why do we monitor patients taking diuretics and what do we monitor? Monitoring a person on
An Overview of the Management of Congestive Heart Failure in Malta
 Original Article An Overview of the Management of Congestive Heart Failure in Malta Stuart Schembri, David Sammut, Nicola Camilleri Abstract Background: In July 2003 the National Institute of Clinical
Original Article An Overview of the Management of Congestive Heart Failure in Malta Stuart Schembri, David Sammut, Nicola Camilleri Abstract Background: In July 2003 the National Institute of Clinical
C. DAVIDSON M.A., M.B., M.R.C.P. and John, 1972). For the subsequent, more detailed. et al., 1950; Aikawa et al., 1952; Deane and Smith,
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (February 1978) 54, 72-79. Potassium depletion in heart failure and its relation to long-term treatment with diuretics: a review of the literature D. B. MORGAN M.D., M.R.C.Path.
Postgraduate Medical Journal (February 1978) 54, 72-79. Potassium depletion in heart failure and its relation to long-term treatment with diuretics: a review of the literature D. B. MORGAN M.D., M.R.C.Path.
The use of digoxin in 55 residential homes for elderly people
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (988) 6, 9-96 Medicine in the Elderly The use of digoxin in 55 residential homes for elderly people P.B. Weedle, J.W. Poston and P.A. Parish Medicines Research Unit, Division
Postgraduate Medical Journal (988) 6, 9-96 Medicine in the Elderly The use of digoxin in 55 residential homes for elderly people P.B. Weedle, J.W. Poston and P.A. Parish Medicines Research Unit, Division
HEART FAILURE SUMMARY. and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. the cornerstone of heart failure treatment.
 HEART FAILURE SUMMARY + Heart Failure is a condition affecting a large number of Irish people and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. + ACE inhibitors, in combination with diuretics,
HEART FAILURE SUMMARY + Heart Failure is a condition affecting a large number of Irish people and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. + ACE inhibitors, in combination with diuretics,
NHS Grampian Staff Guidance For The Management Of Hypomagnesaemia In Adults. Consultation Group: See Page 4. Review Date: June 2021
 NHS...... Grampian NHS Grampian Staff Guidance For The Management Of Hypomagnesaemia In Adults Co-ordinators: Consultation Group: Approver:. Senior Medicines Information Pharmacist See Page 4 Medicine
NHS...... Grampian NHS Grampian Staff Guidance For The Management Of Hypomagnesaemia In Adults Co-ordinators: Consultation Group: Approver:. Senior Medicines Information Pharmacist See Page 4 Medicine
The digoxin affair T. R. D. SHAW. B.Sc., M.B., M.R.C.P. The introduction of the radioimmunoassay of
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (February 1974) 5, 9812. Summary The cardiac glycosides are potentially dangerous medicines and consistent preparations are necessary. However, presently used tablets of digoxin
Postgraduate Medical Journal (February 1974) 5, 9812. Summary The cardiac glycosides are potentially dangerous medicines and consistent preparations are necessary. However, presently used tablets of digoxin
The antihypertensive and diuretic effects of amiloride and. of its combination with hydrochlorothiazide
 The antihypertensive and diuretic effects of amiloride and of its combination with hydrochlorothiazide The hypotensive effect as well as changes in serum electrolytes and uric acid of amiloride (AM) and
The antihypertensive and diuretic effects of amiloride and of its combination with hydrochlorothiazide The hypotensive effect as well as changes in serum electrolytes and uric acid of amiloride (AM) and
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS PRODUCT SUMMARY 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Sterile Potassium Chloride Concentrate 15%. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 15% of Potassium Chloride in
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS PRODUCT SUMMARY 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Sterile Potassium Chloride Concentrate 15%. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 15% of Potassium Chloride in
NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults
 NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults Co-ordinators: Medicines Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See relevant page in guidance Approver: Medicine Guidelines
NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults Co-ordinators: Medicines Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See relevant page in guidance Approver: Medicine Guidelines
Clinical trial of a new carbenoxolone analogue (BX24), zinc sulphate, and vitamin A in the
 Clinical trial of a new carbenoxolone analogue (BX24), zinc sulphate, and vitamin A in the treatment of gastric ulcer Gut, 1972, 13, 459-463 P. M. FRASER1, RICHARD DOLL, M. J. S. LANGMAN, J. J. MISIEWICZ,
Clinical trial of a new carbenoxolone analogue (BX24), zinc sulphate, and vitamin A in the treatment of gastric ulcer Gut, 1972, 13, 459-463 P. M. FRASER1, RICHARD DOLL, M. J. S. LANGMAN, J. J. MISIEWICZ,
Comparative Study of Different Digoxin Treatment Regimens in Egyptian Hospitals. For Partial Fulfillment of Master Degree in Pharmaceutical Sciences
 Comparative Study of Different Digoxin Treatment Regimens in Egyptian Hospitals A Thesis presented by Sahar Atef Azmy Al Shabasy, BSc Teaching Assistant, Clinical Pharmacy Department, Faculty of Pharmacy,
Comparative Study of Different Digoxin Treatment Regimens in Egyptian Hospitals A Thesis presented by Sahar Atef Azmy Al Shabasy, BSc Teaching Assistant, Clinical Pharmacy Department, Faculty of Pharmacy,
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
C. R. P. GEORGE A. M. BURKE
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (January 1980) 56, 18-22 Low salt diet and frusemide in the treatment of hypertension C. R. P. GEORGE A. M. BURKE M.B. B.S., F.R.A.C.P. M.B. B.S. Department of Renal Medicine,
Postgraduate Medical Journal (January 1980) 56, 18-22 Low salt diet and frusemide in the treatment of hypertension C. R. P. GEORGE A. M. BURKE M.B. B.S., F.R.A.C.P. M.B. B.S. Department of Renal Medicine,
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
5.2 Key priorities for implementation
 5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
Hypertension. Penny Mosley MRPharmS
 Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
TRIAL OF A TRIAMTERENE-BENZTHIAZIDE COMBINATION (DYTIDE)
 POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 706. Clinical Trial TRIAL OF A TRIAMTERENE-BENZTHIAZIDE COMBINATION (DYTIDE) R. A. THOMPSON, M.B., M.R.C.P. M. F. CROWLEY, B.Sc. University College Hospital, W.C.1. Whittington
POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 706. Clinical Trial TRIAL OF A TRIAMTERENE-BENZTHIAZIDE COMBINATION (DYTIDE) R. A. THOMPSON, M.B., M.R.C.P. M. F. CROWLEY, B.Sc. University College Hospital, W.C.1. Whittington
Metoprolol -a new cardioselective 3-adrenoceptor blocking agent for treatment of tachyarrhythmias
 British Heart journal, 1977, 39, 834-838 Metoprolol -a new cardioselective 3-adrenoceptor blocking agent for treatment of tachyarrhythmias H. S. WASIR, R. K. MAHAPATRA, M. L. BHATIA, SUJOY B. ROY, AND
British Heart journal, 1977, 39, 834-838 Metoprolol -a new cardioselective 3-adrenoceptor blocking agent for treatment of tachyarrhythmias H. S. WASIR, R. K. MAHAPATRA, M. L. BHATIA, SUJOY B. ROY, AND
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system
 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
Enalapril for severe heart failure in infancy
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 219-223 Enalapril for severe heart failure in infancy M FRENNEAUX, R A H STEWART, C M H NEWMAN, AND K A HALLIDIE-SMITH Department of Cardiology, Hammersmith
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 219-223 Enalapril for severe heart failure in infancy M FRENNEAUX, R A H STEWART, C M H NEWMAN, AND K A HALLIDIE-SMITH Department of Cardiology, Hammersmith
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPOKALAEMIA
 POLICY UNDER REVIEW Please note that this policy is under review. It does, however, remain current Trust policy subject to any recent legislative changes, national policy instruction (NHS or Department
POLICY UNDER REVIEW Please note that this policy is under review. It does, however, remain current Trust policy subject to any recent legislative changes, national policy instruction (NHS or Department
Value of serum magnesium estimation in diagnosing myocardial infarction and predicting dysrhythmias after coronary artery bypass grafting
 Thorax 1983;38:946-95 Value of serum magnesium estimation in diagnosing myocardial infarction and predicting dysrhythmias after coronary artery bypass grafting RICHARD W BUNTON From the Department of Cardiothoracic
Thorax 1983;38:946-95 Value of serum magnesium estimation in diagnosing myocardial infarction and predicting dysrhythmias after coronary artery bypass grafting RICHARD W BUNTON From the Department of Cardiothoracic
PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP
 PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP Brand or Product Name [Product name] Tablet 2mg [Product name] Tablet 4mg [Product name] Syrup 2mg/5ml Name and Strength of Active Substance(s)
PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP Brand or Product Name [Product name] Tablet 2mg [Product name] Tablet 4mg [Product name] Syrup 2mg/5ml Name and Strength of Active Substance(s)
complicating myocardial infarction
 British Heart Journal, I970, 32, 21. Bretylium tosylate in treatment of refractory ventricular arrhythmias complicating myocardial infarction G. Terry,1 C. W. Vellani, M. R. Higgins, and A. Doig From the
British Heart Journal, I970, 32, 21. Bretylium tosylate in treatment of refractory ventricular arrhythmias complicating myocardial infarction G. Terry,1 C. W. Vellani, M. R. Higgins, and A. Doig From the
INDIVIDUAL STUDY TABLE REFERRING TO PART OF THE DOSSIER Volume: Page:
 SYNOPSIS Protocol No.: TOPMAT-MIG-303 EudraCT No.: 2005-000321-29 Title of Study: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, multicentre study to investigate the efficacy and tolerability of in prolonged
SYNOPSIS Protocol No.: TOPMAT-MIG-303 EudraCT No.: 2005-000321-29 Title of Study: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, multicentre study to investigate the efficacy and tolerability of in prolonged
Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults)
 Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults) It is vital for safe and appropriate patient care that there is a clear understanding of where clinical and prescribing responsibility
Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults) It is vital for safe and appropriate patient care that there is a clear understanding of where clinical and prescribing responsibility
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Irbesartan (Aprovel) for heart failure with preserved systolic function. August 2008
 Irbesartan (Aprovel) for heart failure with preserved systolic function August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It
Irbesartan (Aprovel) for heart failure with preserved systolic function August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It
NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT
 NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT CONTENTS PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH HEART FAILURE...4 Demographics... 4 Trends in Symptoms... 4 Causes and Comorbidities
NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT CONTENTS PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH HEART FAILURE...4 Demographics... 4 Trends in Symptoms... 4 Causes and Comorbidities
Potassium status of patients with cirrhosis
 Gut, 1976, 17, 152-157 Potassium status of patients with cirrhosis N. G. SOLER1, S. JAIN, H. JAMES, AND A. PATON From the Dudley Road Hospital, Birmingham, and the Department of Experimental Pathology,
Gut, 1976, 17, 152-157 Potassium status of patients with cirrhosis N. G. SOLER1, S. JAIN, H. JAMES, AND A. PATON From the Dudley Road Hospital, Birmingham, and the Department of Experimental Pathology,
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts. Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF
 Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts. Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF. Pre diagnosis. Refer to the Heart Failure Clinic at VHK for
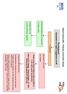 Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Active substance: enoximone
 PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Perfan Injection 100 mg/20 ml Concentrate for Solution for Injection Active substance: enoximone Read all of this leaflet carefully before you
PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Perfan Injection 100 mg/20 ml Concentrate for Solution for Injection Active substance: enoximone Read all of this leaflet carefully before you
Practolol and bendrofluazide in treatment of hypertension
 British Heart Journal, I974, 36, 867-87I. Practolol and bendrofluazide in treatment of hypertension D. B. Galloway, A. G. Beattie, and J. C. Petrie From Department of Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology,
British Heart Journal, I974, 36, 867-87I. Practolol and bendrofluazide in treatment of hypertension D. B. Galloway, A. G. Beattie, and J. C. Petrie From Department of Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology,
Appraisal of mulfifocal atrial tachycardia
 British Heart Journal, 197I, 33, 500-504. Appraisal of mulfifocal atrial tachycardia Edward K. Chung From Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, West Virginia Uuiversity School of Medicine, Morgantown,
British Heart Journal, 197I, 33, 500-504. Appraisal of mulfifocal atrial tachycardia Edward K. Chung From Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, West Virginia Uuiversity School of Medicine, Morgantown,
T wave changes and postinfarction angina pectoris
 Br Heart Y 1981; 45: 512-16 T wave changes and postinfarction angina pectoris predictive of recurrent myocardial infarction RURIK LOFMARK* From the Department of Medicine, Karolinska Institute at Huddinge
Br Heart Y 1981; 45: 512-16 T wave changes and postinfarction angina pectoris predictive of recurrent myocardial infarction RURIK LOFMARK* From the Department of Medicine, Karolinska Institute at Huddinge
Chronic heart failure: management of chronic heart failure in adults in primary and secondary care (partial update)
 Chronic heart failure: management of chronic heart failure in adults in primary and secondary care (partial update) NICE guideline Apendix C The algorithms Draft for consultation, January 2010 Chronic
Chronic heart failure: management of chronic heart failure in adults in primary and secondary care (partial update) NICE guideline Apendix C The algorithms Draft for consultation, January 2010 Chronic
MICHAEL PRITCHARD. most of the high figures for psychiatric morbidity. assuming that a diagnosis of psychiatric disorder has
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (November 1972) 48, 645-651. Who sees a psychiatrist? A study of factors related to psychiatric referral in the general hospital Summary A retrospective study was made of all
Postgraduate Medical Journal (November 1972) 48, 645-651. Who sees a psychiatrist? A study of factors related to psychiatric referral in the general hospital Summary A retrospective study was made of all
Relative potency of prorenoate potassium and spironolactone in
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1984), 18, 169-174 Relative potency of prorenoate potassium and spironolactone in attenuating diuretic induced hypokalaemia G. T. McINNES*, I. R. HARRISON, J. R. SHELTON, R. M. PERKINS
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1984), 18, 169-174 Relative potency of prorenoate potassium and spironolactone in attenuating diuretic induced hypokalaemia G. T. McINNES*, I. R. HARRISON, J. R. SHELTON, R. M. PERKINS
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Lancaster Avenue, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. to every frequency distribution has never been. as bimodal if there were two or more distinct cycle
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (February 1978) 54, 86-91. Differentiation of irregular rhythms by frequency distribution analysis S. TALBOT M.B., M.R.C.P. L. S. DREIFUS* M.D. Department of Cardiology, Hammersmith
Postgraduate Medical Journal (February 1978) 54, 86-91. Differentiation of irregular rhythms by frequency distribution analysis S. TALBOT M.B., M.R.C.P. L. S. DREIFUS* M.D. Department of Cardiology, Hammersmith
NHS Grampian Staff Guidance For The Management Of Hypomagnesaemia In Adults
 NHS Grampian Staff Guidance For The Management Of Hypomagnesaemia In Adults Co-ordinators: Sarah Gethings Medicine Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See Page 4 Approver: Medicine Guidelines and
NHS Grampian Staff Guidance For The Management Of Hypomagnesaemia In Adults Co-ordinators: Sarah Gethings Medicine Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See Page 4 Approver: Medicine Guidelines and
Aldosterone Antagonism in Heart Failure: Now for all Patients?
 Aldosterone Antagonism in Heart Failure: Now for all Patients? Inder Anand, MD, FRCP, D Phil (Oxon.) Professor of Medicine, University of Minnesota, Director Heart Failure Program, VA Medical Center 111C
Aldosterone Antagonism in Heart Failure: Now for all Patients? Inder Anand, MD, FRCP, D Phil (Oxon.) Professor of Medicine, University of Minnesota, Director Heart Failure Program, VA Medical Center 111C
Serum potassium responses to nebulized salbutamol administered during an
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1989, 6, 22-26 Serum potassium responses to nebulized salbutamol administered during an acute asthmatic attack D. DaCRUZ & C. HOLBURN Accident and Emergency Department,
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1989, 6, 22-26 Serum potassium responses to nebulized salbutamol administered during an acute asthmatic attack D. DaCRUZ & C. HOLBURN Accident and Emergency Department,
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline Guideline for the Treatment of Hypokalaemia in Adults
 Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline Guideline for the Treatment of (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Hypokalaemia in Adults Contact Name and Job Title (author) Emily Snow, Pharmacist
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline Guideline for the Treatment of (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Hypokalaemia in Adults Contact Name and Job Title (author) Emily Snow, Pharmacist
Hypertension, Antihypertensive Treatment, and Sudden Coronary Death. The Framingham Study WILLIAM B. KANNEL, L. ADRIENNE CUPPLES, RALPH B.
 Hypertension, Antihypertensive Treatment, and Sudden Coronary Death The Framingham Study WILLIAM B. KANNEL, L. ADRIENNE CUPPLES, RALPH B. AND JOSEPH STOKES IE D'AGOSTINO, SUMMARY During 30 years of follow-up,
Hypertension, Antihypertensive Treatment, and Sudden Coronary Death The Framingham Study WILLIAM B. KANNEL, L. ADRIENNE CUPPLES, RALPH B. AND JOSEPH STOKES IE D'AGOSTINO, SUMMARY During 30 years of follow-up,
during and after the second world war
 Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1986, 40, 37-44 Diet and coronary heart disease in England and Wales during and after the second world war D J P BARKER AND C OSMOND From the MRC Environmental
Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1986, 40, 37-44 Diet and coronary heart disease in England and Wales during and after the second world war D J P BARKER AND C OSMOND From the MRC Environmental
PROPRIETARY PREPARATIONS OF LITHIUM CARBONATE (PRIADEL, PHASAL AND CAMCOLIT)
 Br J clin Pharmac (1977), 4, 479-483 SERUM CONCENTRATIONS OF LITHIUM AFTER THREE PROPRIETARY PREPARATIONS OF LITHIUM CARBONATE (PRIADEL, PHASAL AND CAMCOLIT) EH BENNIE, AKM MANZOOR & AM SCOTT Leverndale
Br J clin Pharmac (1977), 4, 479-483 SERUM CONCENTRATIONS OF LITHIUM AFTER THREE PROPRIETARY PREPARATIONS OF LITHIUM CARBONATE (PRIADEL, PHASAL AND CAMCOLIT) EH BENNIE, AKM MANZOOR & AM SCOTT Leverndale
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF AMI/ACS
 DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF AMI/ACS Diagnostic criteria are used to validate clinical diagnoses. Those used in epidemiological studies are here below reported. 1. MONICA - Monitoring trends and determinants
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF AMI/ACS Diagnostic criteria are used to validate clinical diagnoses. Those used in epidemiological studies are here below reported. 1. MONICA - Monitoring trends and determinants
insulin, lipid and lipoprotein levels in twenty-five patients suffering from peripheral arterial disease. Subjects
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1972) 48, 409-413. The effect of fenfluramine on glucose tolerance, insulin, lipid and lipoprotein levels in patients with peripheral arterial disease B. P. BLISS M.S.,
Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1972) 48, 409-413. The effect of fenfluramine on glucose tolerance, insulin, lipid and lipoprotein levels in patients with peripheral arterial disease B. P. BLISS M.S.,
Type of intervention Treatment and secondary prevention. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 Cost effectiveness in the treatment of heart failure with ramipril: a Swedish substudy of the AIRE study Erhardt L, Ball S, Andersson F, Bergentoft P, Martinez C. Record Status This is a critical abstract
Cost effectiveness in the treatment of heart failure with ramipril: a Swedish substudy of the AIRE study Erhardt L, Ball S, Andersson F, Bergentoft P, Martinez C. Record Status This is a critical abstract
Setting The setting was primary care. The economic study was carried out in the United Kingdom.
 The cost-effectiveness of lipid lowering in patients with ischaemic heart disease: an intervention and evaluation in primary care Hippisley-Cox J, Pringle M Record Status This is a critical abstract of
The cost-effectiveness of lipid lowering in patients with ischaemic heart disease: an intervention and evaluation in primary care Hippisley-Cox J, Pringle M Record Status This is a critical abstract of
Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).
![Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside). Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).](/thumbs/80/80478709.jpg) 1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
University of Wisconsin - Madison Cardiovascular Medicine Fellowship Program UW CCU Rotation Goals and Objectives Goals
 Goals Learn to coordinate a variety of data from multiple cardiovascular sub-disciplines, e.g. catheterization laboratory, hemodynamic study, non-invasive imaging, nuclear, electrophysiologic, and in combination
Goals Learn to coordinate a variety of data from multiple cardiovascular sub-disciplines, e.g. catheterization laboratory, hemodynamic study, non-invasive imaging, nuclear, electrophysiologic, and in combination
The ECG in healthy people
 The ECG in healthy people The normal cardiac rhythm 3 The heart rate 3 Extrasystoles 7 The P wave 7 The PR interval The QRS complex 3 The ST segment 29 The T wave 33 The QT interval 42 The ECG in athletes
The ECG in healthy people The normal cardiac rhythm 3 The heart rate 3 Extrasystoles 7 The P wave 7 The PR interval The QRS complex 3 The ST segment 29 The T wave 33 The QT interval 42 The ECG in athletes
PROCAINE AMIDE IN THE CONTROL OF CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS
 PROCAINE AMIDE IN THE CONTROL OF CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS BY B. G. B. LUCAS AND D. S. SHORT From the National Heart Hospital Received March 21, 1952 Recent developments in cardiac surgery and modern methods
PROCAINE AMIDE IN THE CONTROL OF CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS BY B. G. B. LUCAS AND D. S. SHORT From the National Heart Hospital Received March 21, 1952 Recent developments in cardiac surgery and modern methods
Plasma lipids can be reliably assessed within 24 hours after
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1988) 64, 352-356 Plasma lipids can be reliably assessed within 24 hours after acute myocardial infarction M. Sewdarsen, S. Vythilingum, I. Jialal* and R. Nadar Ischaemic
Postgraduate Medical Journal (1988) 64, 352-356 Plasma lipids can be reliably assessed within 24 hours after acute myocardial infarction M. Sewdarsen, S. Vythilingum, I. Jialal* and R. Nadar Ischaemic
Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic
 Thorax 1984;39:340-344 Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic asthma RICHARD F WILLEY, RONALD J FERGUSSON, DAVID J GODDEN, GRAHAM K CROMPTON,
Thorax 1984;39:340-344 Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic asthma RICHARD F WILLEY, RONALD J FERGUSSON, DAVID J GODDEN, GRAHAM K CROMPTON,
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND PREPONDERANCE OF A VENTRICLE
 POTASSIUM EFFECTS ON T WAVE INVERSION IN MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND PREPONDERANCE OF A VENTRICLE BY E. P. SHARPEY-SCHAFER From the Department of Medicine, British Postgraduate Medical School, London Received
POTASSIUM EFFECTS ON T WAVE INVERSION IN MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND PREPONDERANCE OF A VENTRICLE BY E. P. SHARPEY-SCHAFER From the Department of Medicine, British Postgraduate Medical School, London Received
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Solomon SD, Uno H, Lewis EF, et al. Erythropoietic response
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Solomon SD, Uno H, Lewis EF, et al. Erythropoietic response
Essential Shared Care Agreement: Lithium
 Ref No. E042 Essential Shared Care Agreement: Lithium Please complete the following details: Patient s name, address, date of birth Treatment (indication, dose regimen, brand name) Monitoring (proposed
Ref No. E042 Essential Shared Care Agreement: Lithium Please complete the following details: Patient s name, address, date of birth Treatment (indication, dose regimen, brand name) Monitoring (proposed
R. B. VAUGHAN. M.B., B.S., Ph.D. Clinical Research Department, Pfizer Limited tion of the indanyl ester. Serum levels were also
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1972) 48, 422-426. The pharmacokinetics of an oral form of carbenicillin in patients with renal failure R. R. BAILEY* M.D.(N.Z.), M.R.A.C.P., M.R.C.P. J. B. EASTWOOD
Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1972) 48, 422-426. The pharmacokinetics of an oral form of carbenicillin in patients with renal failure R. R. BAILEY* M.D.(N.Z.), M.R.A.C.P., M.R.C.P. J. B. EASTWOOD
care unit. Myocardial infarction or ischaemia had been diagnosed on the basis of clinical history, electrocardiograms,
 British Heart Journal, I9, 36, 6-. Use of plasma levels in evaluation of procainamide dosage T. R. D. Shaw, C. R. Kumana, R. B. Royds, C. M. Padgham, and John Hamer From the Department of Cardiology and
British Heart Journal, I9, 36, 6-. Use of plasma levels in evaluation of procainamide dosage T. R. D. Shaw, C. R. Kumana, R. B. Royds, C. M. Padgham, and John Hamer From the Department of Cardiology and
The effect of a change in ambient temperature on blood pressure in normotensives
 (2001) 15, 113 117 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of a change in ambient temperature on blood pressure in normotensives
(2001) 15, 113 117 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of a change in ambient temperature on blood pressure in normotensives
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu Indicator area: Pulse rhythm assessment for AF Indicator: NM146 Date: June 2017 Introduction There is evidence
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu Indicator area: Pulse rhythm assessment for AF Indicator: NM146 Date: June 2017 Introduction There is evidence
FAILURE IN PATIENTS WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1982), 14, 187S-19lS BENEFICIAL EFFECTS OF CAPTOPRIL IN LEFT VENTRICULAR FAILURE IN PATIENTS WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION J.P. BOUNHOURE, J.G. KAYANAKIS, J.M. FAUVEL & J. PUEL Departments
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1982), 14, 187S-19lS BENEFICIAL EFFECTS OF CAPTOPRIL IN LEFT VENTRICULAR FAILURE IN PATIENTS WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION J.P. BOUNHOURE, J.G. KAYANAKIS, J.M. FAUVEL & J. PUEL Departments
a lecture series by SWESEMJR
 Electrolyte disturbances Hypokalaemia Decreased extracellular potassium increases excitability in the myocardial cells and consequently the effect of very severe hypokalaemia is ventricular arrhythmia.
Electrolyte disturbances Hypokalaemia Decreased extracellular potassium increases excitability in the myocardial cells and consequently the effect of very severe hypokalaemia is ventricular arrhythmia.
Heart failure for syndicate
 Heart failure for syndicate By M.Wafaie Aboleineen,MD,FACC ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure Part I 1 4 2 Common ECG abnormalities in HF 3 Common CXR abnormalities in HF Common
Heart failure for syndicate By M.Wafaie Aboleineen,MD,FACC ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure Part I 1 4 2 Common ECG abnormalities in HF 3 Common CXR abnormalities in HF Common
Ischaemic heart disease in the elderly
 Ischaemic heart disease in the elderly R. D. KENNEDY, G. R. ANDREWS, AND F. I. CAIRD From the University Department of Geriatric Medicine, University of Glasgow British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1121-1127
Ischaemic heart disease in the elderly R. D. KENNEDY, G. R. ANDREWS, AND F. I. CAIRD From the University Department of Geriatric Medicine, University of Glasgow British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1121-1127
The Failing Heart in Primary Care
 The Failing Heart in Primary Care Hamid Ikram How fares the Heart Failure Epidemic? 4357 patients, 57% women, mean age 74 years HFSA 2010 Practice Guideline (3.1) Heart Failure Prevention A careful and
The Failing Heart in Primary Care Hamid Ikram How fares the Heart Failure Epidemic? 4357 patients, 57% women, mean age 74 years HFSA 2010 Practice Guideline (3.1) Heart Failure Prevention A careful and
Dosing Information. The First & Only FDA-approved Spironolactone Oral Suspension P HARM A. Exclusively from
 Dosing Information The First & Only FDA-approved Spironolactone Oral Suspension Exclusively from P HARM A The Formulation That s Easy To Prescribe CAROSPIR is an antagonist of aldosterone indicated for:
Dosing Information The First & Only FDA-approved Spironolactone Oral Suspension Exclusively from P HARM A The Formulation That s Easy To Prescribe CAROSPIR is an antagonist of aldosterone indicated for:
Treatment A Placebo to match COREG CR 20 mg OD + Lisinopril 10 mg OD (Days 1-7) Placebo to match COREG CR 40 mg OD + Lisinopril 10 mg OD (Days 8-14)
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Treatment of Hypomagnesaemia in adults Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Dr Peter Sharpe, Dr Neal Morgan, Jillian Redpath Chemical Pathology/Nephrology/Pharmacy
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Treatment of Hypomagnesaemia in adults Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Dr Peter Sharpe, Dr Neal Morgan, Jillian Redpath Chemical Pathology/Nephrology/Pharmacy
Remote management of heart failure using implanted devices and formalized follow-up procedures (REM-HF)
 Remote management of heart failure using implanted devices and formalized follow-up procedures (REM-HF) Martin R Cowie Professor of Cardiology, Imperial College London (Royal Brompton Hospital) London,
Remote management of heart failure using implanted devices and formalized follow-up procedures (REM-HF) Martin R Cowie Professor of Cardiology, Imperial College London (Royal Brompton Hospital) London,
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 27 May 2009
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 27 May 2009 CARDENSIEL 1.25 mg, film-coated tablet B/30 (CIP code: 352 968-1) CARDENSIEL 2.5 mg, film-coated tablet
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 27 May 2009 CARDENSIEL 1.25 mg, film-coated tablet B/30 (CIP code: 352 968-1) CARDENSIEL 2.5 mg, film-coated tablet
EFFECT OF ACUTE SALINE LOADING ON THE ERYTH ROCYTE SODIUM TRANSPORT IN CHILDREN
 Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 36, No. 109-113, 1989 EFFECT OF ACUTE SALINE LOADING ON THE ERYTH ROCYTE SODIUM TRANSPORT IN CHILDREN M. UCHIYAMA I. SATOKATA T. AIKAWA K. SAKAI Department 0/ pediatrics,
Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 36, No. 109-113, 1989 EFFECT OF ACUTE SALINE LOADING ON THE ERYTH ROCYTE SODIUM TRANSPORT IN CHILDREN M. UCHIYAMA I. SATOKATA T. AIKAWA K. SAKAI Department 0/ pediatrics,
PHARMACOLOGY AND PHARMACOKINETICS
 DRUG GUIDELINE Insulin, human neutral (Actrapid ) Intravenous Infusion for SCOPE (Area): FOR USE IN: Critical Care Unit, Emergency Department and Operating Suite EXCLUSIONS: Paediatrics (seek Paediatrician
DRUG GUIDELINE Insulin, human neutral (Actrapid ) Intravenous Infusion for SCOPE (Area): FOR USE IN: Critical Care Unit, Emergency Department and Operating Suite EXCLUSIONS: Paediatrics (seek Paediatrician
Policy Compliance Procedure
 Policy Compliance Procedure Safe Handling of Adult Intravenous Potassium Chloride Preparations This PCP relates to NSW Health PD NSW Health Policy Directive PD2005_342 Safe Handling of Intravenous Potassium
Policy Compliance Procedure Safe Handling of Adult Intravenous Potassium Chloride Preparations This PCP relates to NSW Health PD NSW Health Policy Directive PD2005_342 Safe Handling of Intravenous Potassium
Drug Name: Lithium Clinical Indications: Treatment and prophylaxis of mania; bipolar disorder; augmentation therapy in treatment resistant depression
 SHARED CARE PROTOCOL AND INFORMATION FOR GPS Drug Name: Lithium Clinical Indications: Treatment and prophylaxis of mania; bipolar disorder; augmentation therapy in treatment resistant depression Version:
SHARED CARE PROTOCOL AND INFORMATION FOR GPS Drug Name: Lithium Clinical Indications: Treatment and prophylaxis of mania; bipolar disorder; augmentation therapy in treatment resistant depression Version:
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
BUMETANIDE IN CONGESTIVE CARDIAC FAILURE
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1979), 8, 173-178 A SINGLE DOSE COMPARISON OF PIRETANIDE AND BUMETANIDE IN CONGESTIVE CARDIAC FAILURE M. HOMEIDA & C.J.C. ROBERTS Departments of Medicine and Pharmacology, University
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1979), 8, 173-178 A SINGLE DOSE COMPARISON OF PIRETANIDE AND BUMETANIDE IN CONGESTIVE CARDIAC FAILURE M. HOMEIDA & C.J.C. ROBERTS Departments of Medicine and Pharmacology, University
Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure. Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta
 Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta Learning Objectives: 1) Become familiar with pathogenesis of congestive heart failure. 2) Discuss clinical manifestations
Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta Learning Objectives: 1) Become familiar with pathogenesis of congestive heart failure. 2) Discuss clinical manifestations
MPharmProgramme. Hypertension (HTN)
 MPharmProgramme Hypertension (HTN) Slide 1 of 30 Overview Definition Prevalence Type Causes Diagnosis Management Patients perspective Slide 2 of 30 Definition It is not a disease! So what is it? What two
MPharmProgramme Hypertension (HTN) Slide 1 of 30 Overview Definition Prevalence Type Causes Diagnosis Management Patients perspective Slide 2 of 30 Definition It is not a disease! So what is it? What two
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 1 MILRINONE-CLARIS (as lactate) 10 mg/ml concentrate for injection Milrinone-Claris (as lactate) 10 mg/10ml concentrate for injection. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Milrinone-Claris is a sterile,
1 MILRINONE-CLARIS (as lactate) 10 mg/ml concentrate for injection Milrinone-Claris (as lactate) 10 mg/10ml concentrate for injection. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Milrinone-Claris is a sterile,
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 7 January 2009
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 7 January 2009 LERCAPRESS 10 mg/10 mg, film-coated tablets Pack of 30 (CIP code: 385 953-3) Pack of 90 (CIP code:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 7 January 2009 LERCAPRESS 10 mg/10 mg, film-coated tablets Pack of 30 (CIP code: 385 953-3) Pack of 90 (CIP code:
P. TURNER M.D., F.R.C.P. (Briant, Reid and Dollery, 1973), is impaired by. treatment with tricyclic antidepressant drugs. Since
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (December 1974) 5, 729-733. Some clinical pharmacological studies with indoramin, with observations on its therapeutic usefulness C. DE B. WHITE M.R.C.P. Summary In the treatment
Postgraduate Medical Journal (December 1974) 5, 729-733. Some clinical pharmacological studies with indoramin, with observations on its therapeutic usefulness C. DE B. WHITE M.R.C.P. Summary In the treatment
Hypertension and the Challenge of Adherence. Geneva Clark Briggs, Pharm.D., BCPS
 Hypertension and the Challenge of Adherence Geneva Clark Briggs, Pharm.D., BCPS Outline Brief overview of HTN and pharmacologic therapies Role of pharmacists in collaboration with patients and physicians
Hypertension and the Challenge of Adherence Geneva Clark Briggs, Pharm.D., BCPS Outline Brief overview of HTN and pharmacologic therapies Role of pharmacists in collaboration with patients and physicians
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE
 SHARED CARE GUIDELINE Title: Lithium Treatment in Adults aged 18-65 years Scope: Pennine Care NHS Foundation Trust NHS Bury NHS Oldham NHS Heywood, Middleton and Rochdale NHS Stockport NHS Tameside & Glossop
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE Title: Lithium Treatment in Adults aged 18-65 years Scope: Pennine Care NHS Foundation Trust NHS Bury NHS Oldham NHS Heywood, Middleton and Rochdale NHS Stockport NHS Tameside & Glossop
Volume 6; Number 1 January 2012 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 127: HYPERTENSION CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF PRIMARY HYPERTENSION IN ADULTS (AUGUST 2011)
 Volume 6; Number 1 January 2012 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 127: HYPERTENSION CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF PRIMARY HYPERTENSION IN ADULTS (AUGUST 2011) What s new in hypertension? NICE has issued an updated Clinical
Volume 6; Number 1 January 2012 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 127: HYPERTENSION CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF PRIMARY HYPERTENSION IN ADULTS (AUGUST 2011) What s new in hypertension? NICE has issued an updated Clinical
INSPRA 25 & 50 mg TABLETS
 INSPRA 25 & 50 mg TABLETS SCHEDULING STATUS: Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAMES (and dosage forms): INSPRA 25 (Tablets) INSPRA 50 (Tablets) COMPOSITION: INSPRA 25: INSPRA 50: Each tablet contains 25 mg eplerenone
INSPRA 25 & 50 mg TABLETS SCHEDULING STATUS: Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAMES (and dosage forms): INSPRA 25 (Tablets) INSPRA 50 (Tablets) COMPOSITION: INSPRA 25: INSPRA 50: Each tablet contains 25 mg eplerenone
hydrochlorothiazide in the treatment of moderate arterial
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 65S-69S Determination of the optimal dosage regimen of captopril + hydrochlorothiazide in the treatment of moderate arterial hypertension D. STERU1, M. CHILDS', S. LANCRENON',
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 65S-69S Determination of the optimal dosage regimen of captopril + hydrochlorothiazide in the treatment of moderate arterial hypertension D. STERU1, M. CHILDS', S. LANCRENON',
Can spironolactone cause high potassium levels
 P ford residence southampton, ny Can spironolactone cause high potassium levels 28-4-2017 Diuretics are medications commonly used to treat high blood pressure. A side effect of some diuretics is low potassium.
P ford residence southampton, ny Can spironolactone cause high potassium levels 28-4-2017 Diuretics are medications commonly used to treat high blood pressure. A side effect of some diuretics is low potassium.
