Sudden Cardiac Death due to Coronary Fibromuscular Dysplasia: Case Report and Literature Review
|
|
|
- Juliet Long
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Korean J Leg Med 2018;42:26-32 Case Report Sudden Cardiac Death due to Coronary Fibromuscular Dysplasia: Case Report and Literature Review Moon-Young Kim 1, Inho Kang 2, Minsung Choi 3, Sohyung Park 3, Soong Deok Lee 1,4 1 Department of Forensic Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, 2 Dongguk University Medical School, Gyeongju, Korea, 3 Medical Examiner's Office, National Forensic Service, Wonju, Korea, 4 Institute of Forensic Science, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea *Inho Kang is a senior student from Dongguk University Medical School. Received: February 2, 2018 Revised: February 19, 2018 Accepted: February 26, 2018 Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) of the coronary artery is a rare cause of sudden cardiac death; however, its prevalence and fatality may have been overlooked so far. A 47-year-old man complained of pain in his back and shoulder and became unconscious. Despite resuscitation, he died 3 hours after symptom onset. The heart weight was in the normal range; however, all three major coronary arteries showed intimal thickening without atherosclerosis or inflammatory cell infiltration. Fragmentations and duplications of the internal elastic lamina which are histologic features of intimal fibroplasia, a focal-type FMD, were observed. The prevalence of coronary FMD remains unknown, although it may be related to spontaneous coronary artery dissection and sudden death. The histopathologic confirmation of coronary FMD and exclusion of other possible coronary diseases through autopsy are essential to reveal the nature of the disease and therefore apply the information in dealing with legal problems after death. Key Words: Fibromuscular dysplasia; Coronary vessels; Tunica intima; Cause of death; Sudden cardiac death Correspondence to Soong Deok Lee Department of Forensic Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 103 Daehak-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03080, Korea Tel: Fax: sdlee@snu.ac.kr Introduction According to the 2015 annual report on legal autopsies in Korea, 51.5% of natural deaths were diagnosed as being of cardiac origin. Among them, ischemic heart disease was the cause of death in 67.3% of people [1]. In general, most cases of ischemic heart disease are known to result from coronary atherosclerosis. However, there are several nonatherosclerotic conditions with different pathophysiologic mechanisms, causes, and risk factors. These conditions include vasospasm due to smoking, drug or alcohol use; emboli associated with atrial fibrillation or infective endocarditis; vascular diseases such as vasculitis, amyloidosis, or dissection; and systemic diseases such as shock. In this study, we report a case of sudden cardiac death due to fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) of the coronary artery, diagnosed by pathologic findings and 26 ccopyright 2018 by the Korean Society for Legal Medicine This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. pissn eissn
2 Coronary Fibromuscular Dysplasia Moon-Young Kim, et al. 27 clinical symptoms. FMD is a nonatherosclerotic and noninflammatory vascular disease which can occur in any body part but most commonly in the renal and carotid areas. Coronary FMD is a rare example of a nonatherosclerotic cause of ischemic heart disease; however, its prevalence and fatality may have been overlooked so far. By sharing the experience of this case, recent advances in coronary FMD and potential legal issues will be reviewed. Case Report A 47-year-old man complained of sudden pain in his back and shoulder while resting at home with his family. Shortly thereafter, he started to vomit, and his fingers became pale and cold. On his way to the hospital, he lost consciousness and went into cardiac arrest. The emergency medical service personnel administered cardiopulmonary resuscitation; however, he died 3 hours after the onset of the symptoms. The bereaved family reported that he had presented with similar symptoms 3 days prior and had no previously known disease. His father died from aortic valve stenosis. An autopsy was performed the following day. The victim s height and weight were 163 cm and 69 kg, respectively, with a body mass index of 26.0 kg/m 2. His heart weight was 366 g, which was within the normal range for adult males. The vascular walls of all three major coronary branches were thickened circumferentially, and their lumens were narrowed by up to 85%, especially in the proximal segment. Atherosclerotic changes, such as yellowish discoloration, plaques, or calcification, were not found. The cardiac chambers did not show any morphologic changes such as hypertrophy, dilatation, fibrosis, or congenital defects (Fig. 1). Upon the microscopic examination of the major coronary branches, thickening of the coronary wall was predominantly observed in the intimal layers, without lipid deposits or inflammatory cell infiltration. The elastin stain revealed multifocal fragmentations and duplications of the internal elastic lamina (Fig. 2). According to these findings, the coronary arteries were diagnosed with focal-type FMD. In detail, the histopathologic subtype was intimal fibroplasia. Both early ischemic changes in the myocardium, such as contraction band necrosis and interstitial inflammatory cell infiltration, and typical chest pain during the perimortem period suggest that the victim died from ischemic heart damage subsequent to the coronary FMD. Discussion FMD is a unique vascular disease not associated with atherosclerosis or inflammation. Its pathogenesis and causative genetic alterations have not been revealed yet, although mutational variants of transforming growth factor beta receptor 1 (TGFβR1) and phosphatase and actin regulator 1 (PHACTR1) genes have been suggested as related gene alterations [2]. FMD can occur in arteries throughout the body, and its clinical features vary according to the involved location, the degree of stenosis or accompanying complications such as dissection, or aneurysms [3]. Several studies on FMD cohorts have reported that FMD occurred most commonly in renal arteries and that the prevalence of renal FMD was approximately 3%-4%. However, referral bias should be considered in these reports since their cohorts usually consisted of renal transplantation donors [2]. As proof of these results, the United States Registry for Fibromuscular Dysplasia (U.S. FMD Registry), established in 2008, found that extracranial carotid FMD occurred as frequently as renal disease [4]. Regrettably, this registry is insufficient to determine the prevalence of FMD in multiple vascular territories since most imaging studies focused on the head or abdominal areas. Some characteristics of FMD make it difficult to determine its prevalence. Many patients with FMD have only mild or nonspecific symptoms and therefore do not visit a hospital before vascular stenosis progresses significantly. The diagnosis of FMD requires expensive and complicated techniques such as arteriography or high-resolution imaging, or even invasive methods such as vascular resection through surgery or autopsy. Unfortunately, without sufficient indications to arise suspicion, an autopsy is not a solution for diagnosis as medium- or small-sized arteries are not usually explored thoroughly during a routine autopsy. In the current case, renal and carotid arteries were not
3 28 Korean Journal of Legal Medicine 2018;42:26-32 A B C D E Fig. 1. Gross findings of the heart and the coronary arteries of the deceased. (A,B) The heart was of normal weight without any abnormal features. (C-E) In the cross-sections of the major coronary arteries, the lumens were narrowed by wall thickening and there were no atherosclerotic changes (C, right coronary artery; D, anterior descending branch of the left coronary artery; E, circumflex branch of the left coronary artery).
4 Coronary Fibromuscular Dysplasia Moon-Young Kim, et al. 29 A B C D Fig. 2. Histologic findings of coronary arteries. (A) The cross-section of the coronary artery shows circumferential thickening of the vascular wall (H&E stain, 4). (B) The intimal layer which showed neither noticeable inflammation nor lipid accumulation contributed mainly to the thickening (H&E, 40). (C, D) Elastin stain highlighted the internal elastic lamina and both fragmentations and duplications of the internal elastic lamina were found (C, elastin stain, 100; D, elastin stain, 200). These findings were consistent in all three major coronary branches. explored during the autopsy because coronary FMD was only diagnosed after the histologic examination. The prevalence of coronary FMD is even more controversial. More than one hundred cases of coronary FMD have been reported since 1976 [5]; however, most of them were located in small coronary branches, implying that they may be nonspecific findings of aging [6]. Only approximately 20 cases of coronary FMD involving major coronary arteries or occurring in young people are currently regarded as true coronary FMD [7]. Recent studies on FMD cohorts also appear unable to adequately cover or detect coronary FMDs, as pointed out by Olin et al. [8] in their review article. The possibility that coronary FMD may be more common and fatal than previously thought is supported by several reports. First, a few cases of sudden death by coronary FMD [5] or accompanying coronary artery dissection [9] have been reported. In addition, 60 of 303 (19.8%) patients in the U.S. FMD Registry reported a family history of sudden death [4] and 19 of 32
5 30 Korean Journal of Legal Medicine 2018;42:26-32 (59.4%) patients in another case series of coronary FMD presented with myocardial infarction [8]. Moreover, the relationship between spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) and FMD has recently captured the attention of many researchers. SCAD causes acute coronary syndrome and most frequently affects young or healthy women. It has been revealed that many SCAD victims had concomitant coronary or extracoronary FMD at the time of diagnosis [3,7,10]. These findings suggest that fatal presentations, such as myocardial infarction or sudden death, may be the first indicator of coronary FMD, resulting in an underestimation of the disease. The histopathologic classification of FMD established in the mid-1990s by Harrison and McCormack classifies the disease to three categories according to the involved layer of the arterial wall and its pathologic features. However, simplified two-tier angiographic classification has recently been suggested by several working groups. In angiographic classification, as suggested by the American Heart Association, multifocal-type FMD is indicated by a lesion with the classic string of beads pattern produced by medial fibroplasia, while focaltype demonstrates a limited length of stenosis, mostly generated by intimal fibroplasia. Focal-type disease also includes some cases of medial hyperplasia and adventitial-type fibromuscular dysplasia [8]. As mentioned above, the dominant histologic subtype of coronary FMD is uncertain. While the most common subtype of extracoronary FMD is known as medial-type, only few cases of coronary FMD appear to have the string of beads appearance characteristic of medial fibroplasia [7]. Intimal fibroplasia, a rare subtype of FMD usually found in children, may occur reasonably often in adult coronary FMD [5,7,9], as seen in the present study. The dominant subtype and histopathologic features of coronary FMD should be determined for an accurate diagnosis since intimal thickening not associated with atherosclerosis or inflammation may also be induced by traumatic endothelial injury due to hypertension, vasculitis, drug (especially cocaine) use, smoking, or congenital anomalies [5]. However, pathologic studies of coronary FMD is limited in clinical practice, considering that surgical therapy, including coronary resection, is the last choice of treatment for coronary FMD and is usually indicated for patients with multivessel involvement. In these aspects, the role of forensic pathologists who perform the autopsy on victims of internal death is critical. Unlike angiography or optical coherence tomography used for clinical diagnosis of coronary FMD, autopsy procedures directly provide clear gross findings of coronary arteries without being disturbed by ambiguous findings of other diseases. In addition, when coronary FMD is suspected, the vascular area frequently affected by FMD may be thoroughly observed and harvested for pathologic study. Some findings that are detectable during routine gross inspections of the heart suggest coronary FMD. First, the walls of coronary arteries show obvious thickening. The range of the thickened region may be focal or diffuse in length or circumference. Second, no definite atherosclerotic coronary changes are present, including yellowish discoloration, plaques, or calcification. Third, the size, weight, and anatomy of the heart of the deceased are in the normal range for his/her population group. Histopathologic confirmation, including special staining methods for the suspected coronary arteries, would be mandatory for these people. An inspection of the frequently affected regions such as the renal and carotid areas can provide additional information. The clinical symptoms of the deceased will not differ from symptoms that are present during other cases of sudden cardiac death; however, patients may have none or mild, if present, cardiovascular risk factors and a related medical history. Information accumulated during these investigations will provide valuable assistance in revealing the pathogenesis of coronary FMD and patient demographics in the future. Forensic pathologists also play a crucial role after diagnosis. Not only the manner of death but also the cause of death may affect several legal or administrative issues faced by the bereaved family. These situations are not restricted to unnatural deaths like accidents or homicides. For cases of natural death, the specific diagnostic entity that resulted in death can have different effects on insurance, compensation, or liability. Cardiovascular diseases, including coronary FMD, or cerebrovascular diseases are classic examples of diseases that can impact on legal or administrative issues. Some insurance policies contain special conditions
6 Coronary Fibromuscular Dysplasia Moon-Young Kim, et al. 31 which guarantee increased death benefits should the insured person die from one of the designated diseases. If the death certificate or autopsy report includes the exact diagnostic term as it appears on these lists and medical records show relevant descriptions, there will rarely be a problem in receiving the disbursement. However, in many cases, different terms may be selected as the final cause of death in these documents for several reasons, although they imply similar course of the diseases to those on the list. The current case with a sequence of coronary FMD, ischemic myocardial damage, and sudden death may be used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the impact of the use of varying terminology. The pathologist may select coronary FMD as the only cause of death without mention of ischemic heart disease or acute myocardial infarction because (1) coronary FMD was the most important cause of death and ischemic damage was an incidental or subsequent event, (2) ischemic heart damage was described sufficiently in the pathology section of the report, (3) despite a strong suspicion of ischemic changes of the myocardium, the gross and microscopic findings were not definite. These decisions are acceptable and comprehensible to the other medical experts; however, the agents of the insurance company and the contractors who lack a medical background may have problems understanding the details. They may spend additional time and effort in consulting external medical experts or even reject the insurance claim due to a misunderstanding. Without appropriate interventions, these conflicts could lead to lawsuits and a repeated waste of time and resources. The roles of specific risk factors may also be controversial in the decision of compensation. When the risk factors are thought to be related to the victim s working conditions, his death may be the subject of a judgment for industrial death, and his employer or government-related organization may be held responsible for the management of the working environment. In the case of coronary FMD, there may be an attempt to assign a greater weight to the genetic predisposition for coronary FMD than to atherosclerosis and reduce the liability for the death. If coronary FMD and atherosclerotic coronary disease are considered to have different characteristics, legal or administrative decisions regarding related cases may be affected. Although an autosomal dominant pattern with variable penetrance has been suggested for FMD in early pedigree studies, the proportion of reported familial FMD has been substantially lower in recent studies than what was previously accepted [2]. Moreover, these studies included only a few subjects with coronary FMD. Among environmental factors, the evidence is accumulating of the association between smoking and FMD; however, to date, this has not been proven [2]. Forensic pathologists should expect and prepare for possible controversy surrounding these cases. It would be beneficial if all relevant information is included in the autopsy report from the beginning, but they should be prepared to provide suitable answers if conflict arises. Considering that coronary FMD is usually only diagnosed after the manifestation of critical symptoms or the discovery of extracoronary disease, it is exceedingly possible that the prevalence and clinical significance of coronary FMD have been underestimated. More research is required to reveal the pathogenesis, risk factors, disease course, and mortality of coronary FMD. There should also be a consideration for reducing confusion for the person who deals with the legal or administrative issues related to these types of internal death. The role of forensic pathologists is critical in both factors. To reduce the ambiguity of diagnosis, not only the histologic confirmation of coronary FMD and subsequent myocardial damage but also the exclusion of other possible causes of sudden cardiac death, such as atherosclerotic or hypertensive cardiac disease, should be performed through comprehensive pathologic inspection and medical record review. Conflicts of Interest No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported. References 1. Park JH, Na JY, Lee BW, et al. A statistical analysis on forensic autopsies performed in Korea in Korean J Leg Med 2016;40: Shivapour DM, Erwin P, Kim E. Epidemiology of fibromuscular
7 32 Korean Journal of Legal Medicine 2018;42:26-32 dysplasia: a review of the literature. Vasc Med 2016;21: Kadian-Dodov D, Gornik HL, Gu X, et al. Dissection and aneurysm in patients with fibromuscular dysplasia: findings from the U.S. Registry for FMD. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016;68: Olin JW, Froehlich J, Gu X, et al. The United States Registry for Fibromuscular Dysplasia: results in the first 447 patients. Circulation 2012;125: Garcia RA, deroux SJ, Axiotis CA. Isolated fibromuscular dysplasia of the coronary ostium: a rare cause of sudden death: case report and review of the literature. Cardiovasc Pathol 2015;24: Zack F, Kutter G, Blaas V, et al. Fibromuscular dysplasia of cardiac conduction system arteries in traumatic and nonnatural sudden death victims aged 0 to 40 years: a histological analysis of 100 cases. Cardiovasc Pathol 2014;23: Saw J, Bezerra H, Gornik HL, et al. Angiographic and intracoronary manifestations of coronary fibromuscular dysplasia. Circulation 2016;133: Olin JW, Gornik HL, Bacharach JM, et al. Fibromuscular dysplasia: state of the science and critical unanswered questions: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2014;129: Makino Y, Inokuchi G, Yokota H, et al. Sudden death due to coronary artery dissection associated with fibromuscular dysplasia revealed by postmortem selective computed tomography coronary angiography: A case report. Forensic Sci Int 2015;253:e Prasad M, Tweet MS, Hayes SN, et al. Prevalence of extracoronary vascular abnormalities and fibromuscular dysplasia in patients with spontaneous coronary artery dissection. Am J Cardiol 2015;115:
Coronary Artery Manifestations of Fibromuscular Dysplasia: Infrequent and Easily Missed
 Coronary Artery Manifestations of Fibromuscular Dysplasia: Infrequent and Easily Missed Jeffrey W Olin, D.O., F.A.C.C., F.A.H.A. Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) Director of Vascular Medicine & Vascular
Coronary Artery Manifestations of Fibromuscular Dysplasia: Infrequent and Easily Missed Jeffrey W Olin, D.O., F.A.C.C., F.A.H.A. Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) Director of Vascular Medicine & Vascular
The European Consensus on Fibromuscular Dysplasia
 The European Consensus on Fibromuscular Dysplasia Alexandre Persu, M.D.-PhD Cardiology Department Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc Catholic University of Louvain Brussels, Belgium Eur J Clin Invest.
The European Consensus on Fibromuscular Dysplasia Alexandre Persu, M.D.-PhD Cardiology Department Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc Catholic University of Louvain Brussels, Belgium Eur J Clin Invest.
Fibromuscular Dysplasia. Miranda Forrest Baker College
 Fibromuscular Dysplasia Miranda Forrest Baker College Overview Case Study Patient Information Exam Images Findings FMD Types Signs and Symptoms Treatment Case Study Patient Information Female 57 years
Fibromuscular Dysplasia Miranda Forrest Baker College Overview Case Study Patient Information Exam Images Findings FMD Types Signs and Symptoms Treatment Case Study Patient Information Female 57 years
Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) of the renal arteries Angiographic features and therapeutic options
 Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) of the renal arteries Angiographic features and therapeutic options Poster No.: C-0630 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. I. Ringe, B. Meyer, F. Wacker,
Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) of the renal arteries Angiographic features and therapeutic options Poster No.: C-0630 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. I. Ringe, B. Meyer, F. Wacker,
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
Pregnancy in Patients with a History of Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD)
 Pregnancy in Patients with a History of Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD) Marysia Tweet, MD The 4 th International Congress on Cardiac Problems in Pregnancy February 29 th, 2016 2015 MFMER
Pregnancy in Patients with a History of Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD) Marysia Tweet, MD The 4 th International Congress on Cardiac Problems in Pregnancy February 29 th, 2016 2015 MFMER
Endoscopic Examination in Postmortem Examination
 Korean J Leg Med 2017;41:94-99 Original Article Endoscopic Examination in Postmortem Examination Joo-Young Na 1, Ji Hye Park 2 1 Biomedical Research Institute, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju,
Korean J Leg Med 2017;41:94-99 Original Article Endoscopic Examination in Postmortem Examination Joo-Young Na 1, Ji Hye Park 2 1 Biomedical Research Institute, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju,
Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for Renal Artery FMD
 Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for Renal Artery FMD FMDSA Meeting 2016 Alan H. Matsumoto, M.D., FSIR, FACR, FAHA Professor and Chair Department of Radiology & Medical Imaging University of Virginia
Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for Renal Artery FMD FMDSA Meeting 2016 Alan H. Matsumoto, M.D., FSIR, FACR, FAHA Professor and Chair Department of Radiology & Medical Imaging University of Virginia
Ischemic heart disease
 Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
A histopathological analysis of prevalence of various heart diseases: an autopsy study
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Garg S et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2018 Apr;6(4):1414-1418 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20181306
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Garg S et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2018 Apr;6(4):1414-1418 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20181306
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD)
 700716VMJ0010.1177/1358863X17700716Vascular MedicineKhoury and Gornik research-article2017 Vascular Disease Patient Information Page Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) Marianne H Khoury and Heather L Gornik
700716VMJ0010.1177/1358863X17700716Vascular MedicineKhoury and Gornik research-article2017 Vascular Disease Patient Information Page Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) Marianne H Khoury and Heather L Gornik
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism
 Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
FMD 101. Esther S.H. Kim, MD, MPH, FACC, FSVM FMDSA Annual Meeting 18 May 2013
 FMD 101 Esther S.H. Kim, MD, MPH, FACC, FSVM FMDSA Annual Meeting 18 May 2013 Back to basics Blood Bodily fluid that transports necessary substances (oxygen, nutrients, antibodies, hormones, etc) and waste
FMD 101 Esther S.H. Kim, MD, MPH, FACC, FSVM FMDSA Annual Meeting 18 May 2013 Back to basics Blood Bodily fluid that transports necessary substances (oxygen, nutrients, antibodies, hormones, etc) and waste
THROMBOSIS. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan
 THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
Case Report Death by aortoesophageal fistula due to disseminated tuberculosis: a case study
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4):4253-4257 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0006731 Case Report Death by aortoesophageal fistula due to disseminated tuberculosis: a case study Joo-Young Na 1, Youn-Shin
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4):4253-4257 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0006731 Case Report Death by aortoesophageal fistula due to disseminated tuberculosis: a case study Joo-Young Na 1, Youn-Shin
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
Multimodality Imaging in Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection in the Peripartum Period
 Multimodality Imaging in Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection in the Peripartum Period Marysia Tweet, MD NASCI Annual Meeting October 18 th, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 DISCLOSURE No relevant financial relationship(s)
Multimodality Imaging in Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection in the Peripartum Period Marysia Tweet, MD NASCI Annual Meeting October 18 th, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 DISCLOSURE No relevant financial relationship(s)
Disclosures: Acute Aortic Syndrome. A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO
 Acute Aortic Syndrome Disclosures: A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO No financial relationships to disclose 1 Acute Aortic
Acute Aortic Syndrome Disclosures: A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO No financial relationships to disclose 1 Acute Aortic
Non Atheromatous Lesions Fibromuscular Dysplasia. Rod Samuelson, MD Babak Jahromi,, MD Elad Levy, MD Adnan Siddiqui,, PhD, MD Nick Hopkins, MD
 Non Atheromatous Lesions Fibromuscular Dysplasia Rod Samuelson, MD Babak Jahromi,, MD Elad Levy, MD Adnan Siddiqui,, PhD, MD Nick Hopkins, MD Presenter Disclosure Information L. Nelson Hopkins MD FINANCIAL
Non Atheromatous Lesions Fibromuscular Dysplasia Rod Samuelson, MD Babak Jahromi,, MD Elad Levy, MD Adnan Siddiqui,, PhD, MD Nick Hopkins, MD Presenter Disclosure Information L. Nelson Hopkins MD FINANCIAL
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE
 HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
Case Report. A Surgical Case of Venous Aneurysm of the Cephalic Vein. with Unique Clinicopathological Findings for Venous Dissection
 Case Report A Surgical Case of Venous Aneurysm of the Cephalic Vein with Unique Clinicopathological Findings for Venous Dissection Takashi Kobata, 1 Sohsuke Yamada, 2,3* Ken-ichi Mizutani, 2 Nozomu Kurose,
Case Report A Surgical Case of Venous Aneurysm of the Cephalic Vein with Unique Clinicopathological Findings for Venous Dissection Takashi Kobata, 1 Sohsuke Yamada, 2,3* Ken-ichi Mizutani, 2 Nozomu Kurose,
What is Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD) & Why is Cardiac Rehabilitation Important?
 What is Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD) & Why is Cardiac Rehabilitation Important? Marysia Tweet, MD 25 th Annual MNACVPR State Conference October 3 rd, 2015 2015 MFMER slide-1 Goals: Learn
What is Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD) & Why is Cardiac Rehabilitation Important? Marysia Tweet, MD 25 th Annual MNACVPR State Conference October 3 rd, 2015 2015 MFMER slide-1 Goals: Learn
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Renal artery stenosis
 Renal artery stenosis Dr. Alexander Woywodt Consultant Renal Physician, Royal Preston Hospital Preston, 31.10.2007 Menu anatomy of the renal arteries diseases of the large renal arteries atherosclerotic
Renal artery stenosis Dr. Alexander Woywodt Consultant Renal Physician, Royal Preston Hospital Preston, 31.10.2007 Menu anatomy of the renal arteries diseases of the large renal arteries atherosclerotic
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection
 Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection Malissa J. Wood, MD FACC FAHA Co-Director MGH Heart Center Corrigan Women s Heart Health Program Massachusetts General Hospital 40 y/o female transferred from OSH
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection Malissa J. Wood, MD FACC FAHA Co-Director MGH Heart Center Corrigan Women s Heart Health Program Massachusetts General Hospital 40 y/o female transferred from OSH
Imaging Atheroma The quest for the Vulnerable Plaque
 Imaging Atheroma The quest for the Vulnerable Plaque P.J. de Feijter 1. Department of Cardiology 2. Department of Radiology Coronary Heart Disease Remains the Leading Cause of Death in the U.S, Causing
Imaging Atheroma The quest for the Vulnerable Plaque P.J. de Feijter 1. Department of Cardiology 2. Department of Radiology Coronary Heart Disease Remains the Leading Cause of Death in the U.S, Causing
Animesh Rathore, MD 4/21/17. Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of aorta
 Animesh Rathore, MD 4/21/17 Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of aorta Disclosures No financial disclosures Thank You Dr. Panneton for giving this lecture for me. I am stuck at Norfolk with an emergency
Animesh Rathore, MD 4/21/17 Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of aorta Disclosures No financial disclosures Thank You Dr. Panneton for giving this lecture for me. I am stuck at Norfolk with an emergency
Myocardial Infarction
 Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI).
 1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D.
 CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease: A Tertiary Care Hospital Based Autopsy Study
 Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Aortic CT: Intramural Hematoma. Leslie E. Quint, M.D.
 Aortic CT: Intramural Hematoma Leslie E. Quint, M.D. 43 M Mid back pain X several months What type of aortic disease? A. Aneurysm with intraluminal thrombus B. Chronic dissection with thrombosed false
Aortic CT: Intramural Hematoma Leslie E. Quint, M.D. 43 M Mid back pain X several months What type of aortic disease? A. Aneurysm with intraluminal thrombus B. Chronic dissection with thrombosed false
Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism
 1510 JACC Vol. 12, No, 6 December 1988:1510--4 Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism KEVIN J. TVETER, MD, JESSE E. EDWARDS, MD, FACC St, Paul, Minnesota This
1510 JACC Vol. 12, No, 6 December 1988:1510--4 Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism KEVIN J. TVETER, MD, JESSE E. EDWARDS, MD, FACC St, Paul, Minnesota This
Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV
 Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV Prabhakar Rajiah, MBBS, MD, FRCR Associate Professor of Radiology Associate Director, Cardiac CT and MRI University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USA
Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV Prabhakar Rajiah, MBBS, MD, FRCR Associate Professor of Radiology Associate Director, Cardiac CT and MRI University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USA
Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV. Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA
 Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA Objectives Review current terminology Identify key histopathologic
Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA Objectives Review current terminology Identify key histopathologic
Coronary Heart Disease. Angiographic and Intracoronary Manifestations of Coronary Fibromuscular Dysplasia
 Coronary Heart Disease Angiographic and Intracoronary Manifestations of Coronary Fibromuscular Dysplasia Jacqueline Saw, MD; Hiram Bezerra, MD; Heather L. Gornik, MD; Lindsay Machan, MD; G.B. John Mancini,
Coronary Heart Disease Angiographic and Intracoronary Manifestations of Coronary Fibromuscular Dysplasia Jacqueline Saw, MD; Hiram Bezerra, MD; Heather L. Gornik, MD; Lindsay Machan, MD; G.B. John Mancini,
Sudden cardiac death: Primary and secondary prevention
 Sudden cardiac death: Primary and secondary prevention By Kai Chi Chan Penultimate Year Medical Student St George s University of London at UNic Sheba Medical Centre Definition Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA)
Sudden cardiac death: Primary and secondary prevention By Kai Chi Chan Penultimate Year Medical Student St George s University of London at UNic Sheba Medical Centre Definition Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA)
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014
 Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Coronary Artery Anomalies from Birth to Adulthood; the Role of CT Coronary Angiography in Sudden Cardiac Death Screening
 Coronary Artery Anomalies from Birth to Adulthood; the Role of CT Coronary Angiography in Sudden Cardiac Death Screening E O Dwyer 1, C O Brien 1, B Loo 1, A Snow Hogan 1, O Buckley1 2, B 1. Department
Coronary Artery Anomalies from Birth to Adulthood; the Role of CT Coronary Angiography in Sudden Cardiac Death Screening E O Dwyer 1, C O Brien 1, B Loo 1, A Snow Hogan 1, O Buckley1 2, B 1. Department
LAB 4: THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
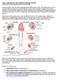 LAB 4: THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the cardiovascular system. The cardiovascular system is composed of the
LAB 4: THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the cardiovascular system. The cardiovascular system is composed of the
Case Presentation VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Vasculitis
 Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Pathophysiology of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction
 Pathophysiology of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction Cheol Woong Yu, MD, PhD Cardiology Department Division of Internal Medicine Korea University Anam Hospital. Etiologies of Chest Pain without obstructive
Pathophysiology of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction Cheol Woong Yu, MD, PhD Cardiology Department Division of Internal Medicine Korea University Anam Hospital. Etiologies of Chest Pain without obstructive
Left main coronary artery (LMCA): The proximal segment
 Anatomy and Pathology of Left main coronary artery G Nakazawa Tokai Univ. Kanagawa, Japan 1 Anatomy Difinition Left main coronary artery (LMCA): The proximal segment RCA AV LAD LM LCX of the left coronary
Anatomy and Pathology of Left main coronary artery G Nakazawa Tokai Univ. Kanagawa, Japan 1 Anatomy Difinition Left main coronary artery (LMCA): The proximal segment RCA AV LAD LM LCX of the left coronary
VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation
 VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
av ailab le at jou rn al h om epa g e:
 Journal of Cardiology Cases (2011) 4, e163 e167 av ailab le at www.sciencedirect.com jou rn al h om epa g e: www.elsevier.com/locate/jccase Case Report In vivo intravascular ultrasound imaging of fibromuscular
Journal of Cardiology Cases (2011) 4, e163 e167 av ailab le at www.sciencedirect.com jou rn al h om epa g e: www.elsevier.com/locate/jccase Case Report In vivo intravascular ultrasound imaging of fibromuscular
1 Functions of endothelial cells include all the following EXCEPT. 2 Response to vascular injury is characterised by
 airns ase Hospital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 Functions of endothelial cells include all the following XPT Formation of von-willebrand factor Formation of collagen and proteoglycans Formation of
airns ase Hospital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 Functions of endothelial cells include all the following XPT Formation of von-willebrand factor Formation of collagen and proteoglycans Formation of
This is not FMD! Fibromuscular Dysplasia Diagnosis, Treatment and Surveillance. Disclosures
 Disclosures Advisor: Innovein, inc Fibromuscular Dysplasia Diagnosis, Treatment and Surveillance Marlene Grenon, MD Department of Surgery April 2017 40 year-old woman referred for arm and leg weakness
Disclosures Advisor: Innovein, inc Fibromuscular Dysplasia Diagnosis, Treatment and Surveillance Marlene Grenon, MD Department of Surgery April 2017 40 year-old woman referred for arm and leg weakness
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion in a Young Female with Fibromuscular Dysplasia
 American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 5, 148-152 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/3/5/9 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-3-5-9 Central Retinal
American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 5, 148-152 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/3/5/9 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-3-5-9 Central Retinal
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection
 JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS VOL. 6, NO. 1, 2013 2013 BY THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY FOUNDATION ISSN 1936-8798/$36.00 PUBLISHED BY ELSEVIER INC. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2012.08.017
JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS VOL. 6, NO. 1, 2013 2013 BY THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY FOUNDATION ISSN 1936-8798/$36.00 PUBLISHED BY ELSEVIER INC. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2012.08.017
Blood Vessels. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Acute coronary syndrome. Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA
 Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings
 Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Case Report Anomalous Left Main Coronary Artery: Case Series of Different Courses and Literature Review
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 380952, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/380952 Case Report Anomalous Left Main Coronary Artery: Case Series of Different Courses and Literature
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 380952, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/380952 Case Report Anomalous Left Main Coronary Artery: Case Series of Different Courses and Literature
Quantification of Coronary Arterial Narrowing at Necropsy in Acute Transmural Myocardial Infarction
 Quantification of Coronary Arterial Narrowing at Necropsy in Acute Transmural Myocardial Infarction Analysis and Comparison of Findings in 27 Patients and 22 Controls WILLIAM C. ROBERTS, M.D., AND ANCIL
Quantification of Coronary Arterial Narrowing at Necropsy in Acute Transmural Myocardial Infarction Analysis and Comparison of Findings in 27 Patients and 22 Controls WILLIAM C. ROBERTS, M.D., AND ANCIL
11 TH ANNUAL VASCULAR NONINVASIVE TESTING SYMPOSIUM NOVEMBER 10, 2018
 11 TH ANNUAL VASCULAR NONINVASIVE TESTING SYMPOSIUM NOVEMBER 10, 2018 RENAL ARTERY DISEASE AND RENOVASCULAR HYPERTENSION 1 WHAT IS RENOVASCULAR HYPERTENSION? https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16459-renovascular-hypertension
11 TH ANNUAL VASCULAR NONINVASIVE TESTING SYMPOSIUM NOVEMBER 10, 2018 RENAL ARTERY DISEASE AND RENOVASCULAR HYPERTENSION 1 WHAT IS RENOVASCULAR HYPERTENSION? https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16459-renovascular-hypertension
Beyond Stenosis Severity: Top 5 Important Duplex Characteristics to Identify in a Patient with Carotid Disease
 Beyond Stenosis Severity: Top 5 Important Duplex Characteristics to Identify in a Patient with Carotid Disease Jan M. Sloves RVT, RCS, FASE Technical Director New York Cardiovascular Associates Disclosures
Beyond Stenosis Severity: Top 5 Important Duplex Characteristics to Identify in a Patient with Carotid Disease Jan M. Sloves RVT, RCS, FASE Technical Director New York Cardiovascular Associates Disclosures
Common Codes for ICD-10
 Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
AORTIC DISSECTION. DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or CLASSIFICATION
 DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or AORTIC DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION DeBakey classified aortic dissections into types I, II, and III :- Type I dissection the tear site originates in the ascending aorta,
DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or AORTIC DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION DeBakey classified aortic dissections into types I, II, and III :- Type I dissection the tear site originates in the ascending aorta,
Cardiovascular Disorders. Heart Disorders. Diagnostic Tests for CV Function. Bio 375. Pathophysiology
 Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial
 Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial Myeong-Ki Hong, MD. PhD on behalf of the IVUS-XPL trial investigators
Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial Myeong-Ki Hong, MD. PhD on behalf of the IVUS-XPL trial investigators
Recurrent Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection in a Patient with Fibromuscular Dysplasia
 Recurrent Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection in a Patient with Fibromuscular Dysplasia Craig Basman, MD; Tannaz Shoja, MD; Aditya Mangla, DO; Jaffar Raza, MD; Suresh Jain, MD; Zoran Lasic, MD Clinical
Recurrent Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection in a Patient with Fibromuscular Dysplasia Craig Basman, MD; Tannaz Shoja, MD; Aditya Mangla, DO; Jaffar Raza, MD; Suresh Jain, MD; Zoran Lasic, MD Clinical
The ruptured dissecting aneurysm of the renal artery is a
 Case Report A Ruptured Dissecting Aneurysm of the Renal Artery into the Perinephric Region: A Case Report Abstract A case report of a ruptured dissecting aneurysm of the renal artery into the perinephric
Case Report A Ruptured Dissecting Aneurysm of the Renal Artery into the Perinephric Region: A Case Report Abstract A case report of a ruptured dissecting aneurysm of the renal artery into the perinephric
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
ARRHYTHMIAS AND DEVICE THERAPY
 Topic List A BASICS 1 History of Cardiology 2 Clinical Skills 2.1 History Taking 2.2 Physical Examination 2.3 Electrocardiography 2.99 Clinical Skills - Other B IMAGING 3 Imaging 3.1 Echocardiography 3.2
Topic List A BASICS 1 History of Cardiology 2 Clinical Skills 2.1 History Taking 2.2 Physical Examination 2.3 Electrocardiography 2.99 Clinical Skills - Other B IMAGING 3 Imaging 3.1 Echocardiography 3.2
Visceral aneurysm. Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA
 Visceral aneurysm Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA History 1953 De Bakeyand Cooley Visceral aneurysm VAAs rare, reported incidence of 0.01 to 0.2% on routine autopsies. Clinically important Potentially
Visceral aneurysm Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA History 1953 De Bakeyand Cooley Visceral aneurysm VAAs rare, reported incidence of 0.01 to 0.2% on routine autopsies. Clinically important Potentially
The MAIN-COMPARE Study
 Long-Term Outcomes of Coronary Stent Implantation versus Bypass Surgery for the Treatment of Unprotected Left Main Coronary Artery Disease Revascularization for Unprotected Left MAIN Coronary Artery Stenosis:
Long-Term Outcomes of Coronary Stent Implantation versus Bypass Surgery for the Treatment of Unprotected Left Main Coronary Artery Disease Revascularization for Unprotected Left MAIN Coronary Artery Stenosis:
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
3. Results of study. Causes of death
 3. Results of study Causes of death Towards the end of an autopsy report is the pathologist's opinion as to the cause of death, which should be presented in the standard manner prescribed by the Office
3. Results of study Causes of death Towards the end of an autopsy report is the pathologist's opinion as to the cause of death, which should be presented in the standard manner prescribed by the Office
Clinical Policy: Cardiac Biomarker Testing for Acute Myocardial Infarction Reference Number: CP.MP.156
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.156 Effective Date: 12/17 Last Review Date: 12/17 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Description The
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.156 Effective Date: 12/17 Last Review Date: 12/17 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Description The
Lung diseases of Vascular Origin. By: Shefaa Qa qqa
 Lung diseases of Vascular Origin By: Shefaa Qa qqa Pulmonary Hypertension Pulmonary hypertension is defined as a mean pulmonary artery pressure greater than or equal to 25 mm Hg at rest. Based on underlying
Lung diseases of Vascular Origin By: Shefaa Qa qqa Pulmonary Hypertension Pulmonary hypertension is defined as a mean pulmonary artery pressure greater than or equal to 25 mm Hg at rest. Based on underlying
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 7: Non traumatic brain haemorrhage
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 7: Non traumatic brain haemorrhage ILOS To list the causes of intracranial haemorrhage. To understand the pathogenesis of each cause.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 7: Non traumatic brain haemorrhage ILOS To list the causes of intracranial haemorrhage. To understand the pathogenesis of each cause.
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES
 NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
Cho et al., 2009 Journal of Cardiology (2009), 54:
 Endothelial Dysfunction, Increased Carotid Artery Intima-media Thickness and Pulse Wave Velocity, and Increased Level of Inflammatory Markers are Associated with Variant Angina Cho et al., 2009 Journal
Endothelial Dysfunction, Increased Carotid Artery Intima-media Thickness and Pulse Wave Velocity, and Increased Level of Inflammatory Markers are Associated with Variant Angina Cho et al., 2009 Journal
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection
 Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection Esther S.H. Kim, MD, MPH Director, Arteriopathy Clinic Associate Professor of Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Center April 18, 2018 No Disclosures Patient
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection Esther S.H. Kim, MD, MPH Director, Arteriopathy Clinic Associate Professor of Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Center April 18, 2018 No Disclosures Patient
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION. Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta
 DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 2005 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-30, 2005
 Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 25 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-3, 25 Renu Virmani, MD CVPath, A Research Service of the International Registry of Pathology Gaithersburg, MD Plaque
Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 25 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-3, 25 Renu Virmani, MD CVPath, A Research Service of the International Registry of Pathology Gaithersburg, MD Plaque
AN UNUSUAL TORTUOUS BRACHIAL ARTERY AND ITS BRANCHES: HISTOLOGICAL BASIS AND ITS CLINICAL PERSPECTIVE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Ashwini C and Vasantha Kuberappa, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 2, April 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved AN UNUSUAL TORTUOUS
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Ashwini C and Vasantha Kuberappa, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 2, April 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved AN UNUSUAL TORTUOUS
Women and Ischemic Heart Disease Lessons Learned
 Women and Ischemic Heart Disease 2017- Lessons Learned Bina Ahmed MD Interventional Cardiology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Assistant Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine Lebanon, NH ba@hitchcock.org
Women and Ischemic Heart Disease 2017- Lessons Learned Bina Ahmed MD Interventional Cardiology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Assistant Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine Lebanon, NH ba@hitchcock.org
Functional vascular disorders
 Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist
 Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
CVS Lab exam questions - Soul Batch -
 A- Medicine, SGD, and Cases CVS Lab exam questions - Soul Batch - 1) All of the following are causes of Heart failure EXCEPT: 1- hypertension 2- anemia 3- myocarditis 4- chronic use of amiodarone 2) All
A- Medicine, SGD, and Cases CVS Lab exam questions - Soul Batch - 1) All of the following are causes of Heart failure EXCEPT: 1- hypertension 2- anemia 3- myocarditis 4- chronic use of amiodarone 2) All
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary
 1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease
 Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Jessi Smith, MD Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University Slides courtesy of Stacy Rissing, MD Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Jessi Smith, MD Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University Slides courtesy of Stacy Rissing, MD Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used
Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease. Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab. Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University
 Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University Pulmonary vascular disease Type of pulmonary circulation: Types
Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University Pulmonary vascular disease Type of pulmonary circulation: Types
ADVANCED CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING. Medical Knowledge. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Medical Knowledge Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational Know the basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including the role of the magnetic fields and gradient coil systems, generation
Medical Knowledge Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational Know the basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including the role of the magnetic fields and gradient coil systems, generation
cm 8 1 / Computed Tomography CT Fig Tel:
 12 103 107 2003 1 1 1 1 2 1 25 1.5 1.2cm 8 1 / 3 12 103 107 2003 1 2 5 25 1999 Computed Tomography CT 2000 1Tel: 03-5803-5253 2 113-8519 1-5-45 2002 8 26 2003 4 1 11 16 162.4cm 46kg 37.2 C 102 / 66mmHg72
12 103 107 2003 1 1 1 1 2 1 25 1.5 1.2cm 8 1 / 3 12 103 107 2003 1 2 5 25 1999 Computed Tomography CT 2000 1Tel: 03-5803-5253 2 113-8519 1-5-45 2002 8 26 2003 4 1 11 16 162.4cm 46kg 37.2 C 102 / 66mmHg72
Diseases of the Aorta
 Diseases of the Aorta ASE Review 2018 Susan E Wiegers, MD, FASE, FACC Professor of Medicine My great friend Dr. Roberto Lang Disclosure None related to this presentation 1 Objectives Aneurysm Dissection
Diseases of the Aorta ASE Review 2018 Susan E Wiegers, MD, FASE, FACC Professor of Medicine My great friend Dr. Roberto Lang Disclosure None related to this presentation 1 Objectives Aneurysm Dissection
Supplementary material 1. Definitions of study endpoints (extracted from the Endpoint Validation Committee Charter) 1.
 Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the SIGNIFY trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ivabradine in patients with stable coronary artery disease without clinical
Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the SIGNIFY trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ivabradine in patients with stable coronary artery disease without clinical
Pearls & Pitfalls in nuclear cardiology
 Pearls & Pitfalls in nuclear cardiology Maythinee Chantadisai, MD., NM physician Division of Nuclear Medicine, Department of radiology, KCMH Principle of myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) Radiotracer
Pearls & Pitfalls in nuclear cardiology Maythinee Chantadisai, MD., NM physician Division of Nuclear Medicine, Department of radiology, KCMH Principle of myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) Radiotracer
Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Cardiac Catheterization (L29090)
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Cardiac Catheterization (L29090) Contractor Information Contractor Name First Coast Service Options, Inc. Contractor Number 09102 Contractor Type MAC - Part B LCD
Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Cardiac Catheterization (L29090) Contractor Information Contractor Name First Coast Service Options, Inc. Contractor Number 09102 Contractor Type MAC - Part B LCD
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease
 Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Stacy Rissing, MD! Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University! Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used for each indication Pathophysiology
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Stacy Rissing, MD! Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University! Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used for each indication Pathophysiology
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Coronary Atherosclerosis In Jammu Region - A Random Postmortem Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Coronary Atherosclerosis In Jammu Region - A Random Postmortem Study Sindhu Sharma, Jagriti Singh, P. Angmo, Chavi, K.K. Kaul Abstract Atherosclerosis is a complex and common disease contributing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Coronary Atherosclerosis In Jammu Region - A Random Postmortem Study Sindhu Sharma, Jagriti Singh, P. Angmo, Chavi, K.K. Kaul Abstract Atherosclerosis is a complex and common disease contributing
Case 1. Your diagnosis
 Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
