Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
|
|
|
- Ellen Barber
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 12: Ambulatory Monitoring 1
2 Learning Outcomes 12.1 Identify the types of ambulatory monitors and their functions Explain why ambulatory monitoring is used in addition to the 12-lead ECG Summarize the common uses and variations of ambulatory monitoring Educate the patient about ambulatory monitoring. 2
3 Learning Outcomes (Cont.) 12.5 Prepare a patient for application of an ambulatory monitor Describe the procedure for applying an ambulatory monitor correctly Describe the procedure for removing the ambulatory monitor and reporting the results. 3
4 12.1 What Is Ambulatory Monitoring? Key Terms Ambulating Holter monitor
5 12.1 Ambulatory Monitoring Process of recording an ECG tracing while patient performs daily activities Typical ambulatory monitor is a small box strapped to waist or shoulder Box contains recording device Most are digital 5
6 12.1 Ambulatory Monitoring (Cont.) Holter is one type of ambulatory monitor. Requires 3 to 5 leads Patient keeps diary: Activities Symptoms Abnormal sensations Computer is used to view, print, and analyze tracing. The term Holter is often used to mean any type of ambulatory monitor. 6
7 12.1 Your Responsibilities You may be responsible for: Applying and removing the monitor Providing patient education Ensuring that results are placed in patient s chart Transferring content from the digital device Distinguishing artifact from cardiac dysrhythmias 7
8 12.1 Apply Your Knowledge How long does an ambulatory monitor typically remain on a patient? ANSWER: 24 to 48 hours 8
9 Antidysrhythmic Palpitations Stress ECG Syncope 12.2 How Is Ambulatory Monitoring Used? Key Terms
10 12.2 How Is Ambulatory Monitoring Used? To capture abnormal heart rhythms when symptoms do not occur during 12-lead or stress ECGs To monitor effectiveness of antidysrhythmic drug therapy To evaluate pacemaker function To evaluate the heart after a myocardial infarction 10
11 12.2 Reasons for Ordering Ambulatory Monitoring To determine the cause of possible cardiac symptoms: Chest pain Light-headedness Syncope Dizziness Palpitations 11
12 12.2 Apply Your Knowledge For what patient symptoms might a physician order ambulatory monitoring? ANSWER: Chest pain, light-headedness, syncope, dizziness, palpitations 12
13 12.3 Variations of Ambulatory Monitoring Continuous monitoring Intermittent monitoring Telemetry Transtelephonic monitoring 13
14 12.3 Continuous Monitoring Complete tracing from time unit is applied until removal Patient can activate event marker: Marks the exact time symptoms occur Clock in unit correlates tracings with diary entries. 14
15 12.3 Intermittent Monitoring Patient-activated Patient records only when symptoms occur Button or voice activated Only shows ECG tracing during the symptom Can be evaluated more quickly than continuous 15
16 12.3 Telemetry Monitoring Real-time monitoring Performed inside medical facility Uses 3 or 5 electrodes on chest Transmits to a central location where multiple patients may be monitored Patient diary not required 16
17 12.3 Transtelephonic Monitoring Primarily used to evaluate pacemaker function Can be used to monitor patients for 30 days or more 17
18 12.3 Transtelephonic Monitoring (Cont.) Information stored in the monitor Methods of transmission Telephone land line Cell phone tower Wi-Fi Types Postsymptom event monitor Loop memory monitor 18
19 12.3 Postsymptom Event Monitor Used when patient is experiencing symptoms Handheld type Placed against chest when experiencing symptoms Wristwatch type Worn at all times Records bipolar lead I tracing Documents dysrhythmias that last more than a few seconds 19
20 12.3 Loop-Memory Monitor Attached to chest for 30 days or more Memory on monitor can hold up to 5 minutes Provides physician with recording before, during, and after event 20
21 12.3 Wireless 12-Lead ECG 10-cable device Attached like a traditional 12-lead ECG Patient can activate anywhere, at any time Sends data to physician s office or monitoring facility Can be interpreted immediately 21
22 12.3 Troubleshooting Loose or disconnected electrodes Instruct patient to press in center to reapply Patient must return to facility if electrode falls off and cannot be reapplied 22
23 12.3 Apply Your Knowledge Which ambulatory monitor can hold up to 5 minutes of tracing data and can be used to record and preserve the tracing before the patient activates the device? ANSWER: Loop-memory monitor 23
24 12.3 Apply Your Knowledge Which ambulatory monitor is often used to evaluate pacemaker function? ANSWER: Transtelephonic monitor 24
25 12.4 Educating the Patient Ensure that patient understands: Monitoring procedure Why procedure is being done What the patient must do 25
26 12.4 Patient Diary Explain purpose of diary. Record of events and symptoms that occur while monitor is in place Used in conjunction with ECG tracing Have patient repeat diary instructions. Remind patient of any medication changes. 26
27 12.4 Diary What Is Recorded All usual and unusual activities: Urinating, bowel movements Sexual activity Walking Emotional upset Eating Sleeping 27
28 12.4 Law and Ethics Refer patient question about medication indications, side effects, and precautions to the licensed practitioner. Answering these questions is outside your scope of practice. 28
29 12.4 What the Patient Should Know during Ambulatory Monitoring Wear loose fitting clothing: For comfort To reduce artifact Sponge baths are allowed. No showers or tub baths When sleeping, make sure tension is not applied to leads. 29
30 12.4 What the Patient Should Know During Ambulatory Monitoring (Cont.) Avoid magnets, metal detectors, high-voltage areas, and electric blankets Check monitoring equipment for proper functioning Document patient education in the patient s chart. 30
31 12.4 Patient Education and Communication Have patients tell you what they already know about ambulatory monitoring. Explain what they don t know. Ask patients to repeat information back to you to ensure understanding. 31
32 12.4 Apply Your Knowledge True or False: Patients should be instructed to cover the monitor and electrodes with plastic before showering. ANSWER: False. The patient should not shower or take a tub bath while the monitor is attached. Only sponge baths are allowed. 32
33 12.5 Preparing the Patient Emotional preparation: Take time to explain each step of procedure Tell patient some fear is normal Allow patient to ask questions Physical preparation: Electrode placement Patient should maintain all normal activities 33
34 12.5 Pediatric Patients Consider the child s age. Use terms the child can understand. Allow the child to touch the equipment prior to applying it. Instruct both child and parent. 34
35 12.5 Apply Your Knowledge What is the first step in reducing a patient s fears about the ambulatory monitoring procedure? ANSWER: The first step is to help the patient understand the procedure. 35
36 12.6 Gather Equipment Monitor and holder New batteries and digital disk Electrodes Lead wires Alcohol and gauze Patient diary Skin prep materials Shaving equipment Tape Checklist for patient education Manufacturer s instructions for monitor Pen 36
37 12.6 Prepare the Monitor Make sure monitor is adequately charged. Insert new batteries. Insert new blank digital disk, if required. 37
38 12.6 Place the Electrodes Have patient remove clothing from waist up. Provide drape. Have patient sit or lie down and relax. Prepare electrode sites: Dry shave electrode sites, if necessary (clip hair for telemetry monitoring). Abrade skin. Place electrodes at proper sites. 38
39 12.6 Elderly Patients Apply less pressure when abrading skin. Avoid abrasive cleansers. Use caution when applying and removing electrodes. 39
40 12.6 Apply the Monitor (Cont.) Attach lead wires to electrodes. Example of 5-Lead Electrode Placement 40
41 12.6 Apply the Monitor (Cont.) Arrange lead wires comfortably on patient. Tape each electrode in place. Attach cable to electrocardiograph. Run baseline ECG. 41
42 12.6 Apply the Monitor (Cont.) Have patient dress, then attach cable to monitor. Check lead wires and electrodes. Start monitor. Have patient make first diary entry. Review all patient instructions. Set date and time for patient return. 42
43 12.6 Apply Your Knowledge What should you do if you are unfamiliar with the ambulatory monitor assigned to the patient? ANSWER: First check the manufacturer s instructions. If you cannot locate them or do not understand them, consult your supervisor. 43
44 12.7 Removing the Ambulatory Monitor Review patient s diary. Turn off monitor and detach lead wires. Detach lead wires and cable from patient. Remove tape and electrodes. Clean skin. Record removal procedure on patient s chart. 44
45 12.7 Reporting Results Follow manufacturer s instructions to prepare recording for evaluation. Machine or computer may provide initial analysis. Final interpretation: Physician within facility Sent to outside laboratory 45
46 12.7 Reporting Results (Cont.) Factors affecting accuracy of tracing results: Improper lead attachment Incomplete patient diary Failure of patient to maintain normal routine If results are sent to an outside lab, report can take seven to ten days. 46
47 12.7 Abnormal Results Abnormal results may indicate: Electrical-conduction defects in heart s rate and rhythmcontrolling system. Rhythm abnormalities. Premature atrial or ventricular contractions. 47
48 12.7 Abnormal Results (Cont.) Additional testing that may be required: Echocardiogram Coronary angiogram CT (computerized tomography) scan MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) PET (position emission tomography) scan 48
49 12.7 Apply Your Knowledge What factors can affect the results of ambulatory monitoring? ANSWER: Improper lead attachment, incomplete patient diary, patient failure to maintain a normal routine 49
50 Chapter Summary Ambulatory monitoring is the process of recording an ECG tracing for an extended period of time while the patient performs normal daily activities. Ambulatory monitoring documents electrical activity in the heart and identifies abnormal heart behaviors that may not have occurred during 12-lead ECG or stress tests. Types of ambulatory monitoring include continuous, intermittent, telemetry, and transtelephonic monitoring. 50
51 Chapter Summary (Cont.) Patients must be thoroughly instructed on proper use of the ambulatory monitor, including the need for diary entries and behavior during the monitoring period. Patients should be prepared both emotionally and physically before the monitor is applied. Applying an ambulatory monitor includes preparing the electrode sites, placing the electrodes, connecting the monitor, running a baseline ECG to confirm proper operation, and making the first diary entry. 51
52 Chapter Summary (Cont.) After the monitoring period, review the patient diary before removing the monitor. After removing the monitor, make sure the results are evaluated and a report is placed in the patient s medical record. 52
12.1 Apply Your Knowledge How long does an ambulatory monitor typically remain on a patient?
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Learning Outcomes (Cont d) 12.4 Educate the patient about ambulatory monitoring. 12.5 Prepare a patient for application of an ambulatory monitor. 12.6 Describe the procedure for applying
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Learning Outcomes (Cont d) 12.4 Educate the patient about ambulatory monitoring. 12.5 Prepare a patient for application of an ambulatory monitor. 12.6 Describe the procedure for applying
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 4: Performing an ECG Learning Outcomes 4.1 Carry out preparation of the patient, room, and equipment for an ECG.
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 4: Performing an ECG Learning Outcomes 4.1 Carry out preparation of the patient, room, and equipment for an ECG.
Lesson 1: Types of ECG s
 Electrocardiography Lesson 1: Types of ECG s Objectives: Distinguish between a single-channel ECG machine and a multi-channel machine. Distinguish between a manual ECG machine and an automatic ECG machine.
Electrocardiography Lesson 1: Types of ECG s Objectives: Distinguish between a single-channel ECG machine and a multi-channel machine. Distinguish between a manual ECG machine and an automatic ECG machine.
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Learning Outcomes Learning Outcomes (Cont d) 11.1 What Is Exercise Electrocardiography?
 1 2 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 11: Exercise Electrocardiography Learning Outcomes 11.1 Describe exercise electrocardiography, and identify it s other names. 11.2 Identify
1 2 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 11: Exercise Electrocardiography Learning Outcomes 11.1 Describe exercise electrocardiography, and identify it s other names. 11.2 Identify
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
10. Which of these ECGs is done in a doctor's office? A. Treadmill stress testing B. Holter monitor C. 12-lead ECG D. All of the above 11.
 1 Student: 1. What is the number one cause of death in the United States? A. Cancer B. Diabetes C. Cardiovascular disease D. Accidents 2. The abbreviation CAD stands for: A. Cold appendage disorder B.
1 Student: 1. What is the number one cause of death in the United States? A. Cancer B. Diabetes C. Cardiovascular disease D. Accidents 2. The abbreviation CAD stands for: A. Cold appendage disorder B.
Ambulatory ECG Monitoring. Gill Bouncir Blackpool Victoria Hospital
 Ambulatory ECG Monitoring Gill Bouncir Blackpool Victoria Hospital History Developed in late 1950 s as a result of research of Dr Norman Holter TYPES Holter - continuous recording. Event recorder- patient
Ambulatory ECG Monitoring Gill Bouncir Blackpool Victoria Hospital History Developed in late 1950 s as a result of research of Dr Norman Holter TYPES Holter - continuous recording. Event recorder- patient
There are different types of ICDs:
 Guidelines for Patients with Implantable Devices o Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Your ICD is approximately the size of a pager and includes the following parts: The ICD: A battery powered
Guidelines for Patients with Implantable Devices o Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Your ICD is approximately the size of a pager and includes the following parts: The ICD: A battery powered
12 Lead EKG. Brigham and Women's Hospital
 12 Lead EKG What is the heart? The heart is the organ that is responsible for pumping blood rich in oxygen to all parts of the body It is located in the center of the chest and is approximately the size
12 Lead EKG What is the heart? The heart is the organ that is responsible for pumping blood rich in oxygen to all parts of the body It is located in the center of the chest and is approximately the size
Ambulatory EEG Monitoring
 Patient and Family Education Ambulatory EEG Monitoring What to Expect from EEG Monitoring at Home An ambulatory EEG is a painless test of your child s electrical brain activity for 24 to 48 hours while
Patient and Family Education Ambulatory EEG Monitoring What to Expect from EEG Monitoring at Home An ambulatory EEG is a painless test of your child s electrical brain activity for 24 to 48 hours while
Holter monitor ECG (AR4 Plus) Patient instructions and diary
 Collection centre Phone number For further advice until 10pm, please call 9287 7700. Holter monitor ECG (AR4 Plus) Patient instructions and diary You are to be fitted with an ECG Holter monitor which has
Collection centre Phone number For further advice until 10pm, please call 9287 7700. Holter monitor ECG (AR4 Plus) Patient instructions and diary You are to be fitted with an ECG Holter monitor which has
Cardiology Services Bon Secours Hospital. Mary Buckley Staff Nurse Cardiology
 Cardiology Services Bon Secours Hospital Mary Buckley Staff Nurse Cardiology Overview Philosophy Cardiology Team Referral Criteria Electrocardiograph (ECG) 24/48 Hour Holter Monitor Event Monitors 24 Hour
Cardiology Services Bon Secours Hospital Mary Buckley Staff Nurse Cardiology Overview Philosophy Cardiology Team Referral Criteria Electrocardiograph (ECG) 24/48 Hour Holter Monitor Event Monitors 24 Hour
Holter monitor ECG. Patient instructions and diary. Collection centre Phone number
 Collection centre Phone number For further advice until 10pm, please call 9287 7700. Holter monitor ECG Patient instructions and diary Please hand to your doctor at next appointment. You are to be fitted
Collection centre Phone number For further advice until 10pm, please call 9287 7700. Holter monitor ECG Patient instructions and diary Please hand to your doctor at next appointment. You are to be fitted
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
You and your pacemaker
 You and your pacemaker You and your pacemaker Why do I need a pacemaker? A pacemaker will help improve your heart s rate. It is used to help your heart beat at a normal rate. What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker
You and your pacemaker You and your pacemaker Why do I need a pacemaker? A pacemaker will help improve your heart s rate. It is used to help your heart beat at a normal rate. What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker
A SIMPLE SOLUTION FOR CARDIAC MONITORING
 A SIMPLE SOLUTION FOR CARDIAC MONITORING SEEQ Mobile Cardiac Telemetry System Actual size. NOW THERE S AN EXTERNAL HEART MONITOR THAT S AS SIMPLE TO WEAR AS A BANDAGE It s called the SEEQ Mobile Cardiac
A SIMPLE SOLUTION FOR CARDIAC MONITORING SEEQ Mobile Cardiac Telemetry System Actual size. NOW THERE S AN EXTERNAL HEART MONITOR THAT S AS SIMPLE TO WEAR AS A BANDAGE It s called the SEEQ Mobile Cardiac
AWAY Model # RTLAGF-900 REV
 AWAY Model # RTLAGF-900 REV2.4.9.15 Contents User manual English 2 General Description 2 Intended Use 3 Included in this Package 4 Instructions for Use 7 Application Duration 7 Electrode Placement 8 Tips
AWAY Model # RTLAGF-900 REV2.4.9.15 Contents User manual English 2 General Description 2 Intended Use 3 Included in this Package 4 Instructions for Use 7 Application Duration 7 Electrode Placement 8 Tips
PREPARING FOR REFLUX TESTING. Bravo Reflux Testing System. A simple way to evaluate your gastroesophageal reflux symptoms
 PREPARING FOR REFLUX TESTING Bravo Reflux Testing System A simple way to evaluate your gastroesophageal reflux symptoms HOW IT WORKS The test involves a miniature ph capsule, which is approximately the
PREPARING FOR REFLUX TESTING Bravo Reflux Testing System A simple way to evaluate your gastroesophageal reflux symptoms HOW IT WORKS The test involves a miniature ph capsule, which is approximately the
CORONARY ARTERIES HEART
 CARDIAC/ECG MODULE THE HEART CORONARY ARTERIES FIBRILLATING HEART CORONARY ARTERIES HEART PRACTICE RHYTHMS PRACTICE RHYTHMS ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SA Node (60 100) Primary pacemaker AV Node (40 60) ***Creates
CARDIAC/ECG MODULE THE HEART CORONARY ARTERIES FIBRILLATING HEART CORONARY ARTERIES HEART PRACTICE RHYTHMS PRACTICE RHYTHMS ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SA Node (60 100) Primary pacemaker AV Node (40 60) ***Creates
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL TITLE: NURSING PROCEDURE PACEMAKERS AND DETERMINING PACEMAKER DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 10/99 11/18 1 of 7 PS1094 ISSUED FOR: Nursing RESPONSIBILITY: *Qualified RN PURPOSE: To establish
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL TITLE: NURSING PROCEDURE PACEMAKERS AND DETERMINING PACEMAKER DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 10/99 11/18 1 of 7 PS1094 ISSUED FOR: Nursing RESPONSIBILITY: *Qualified RN PURPOSE: To establish
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 10: Pacemaker Rhythms and Bundle Branch Block Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the various pacemaker rhythms. 10.2
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 10: Pacemaker Rhythms and Bundle Branch Block Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the various pacemaker rhythms. 10.2
NHA Certified EKG Technician (CET) Test Plan for the CET Exam
 NHA Certified EKG Technician (CET) Test Plan for the CET Exam 100 scored items Exam Time: 2 hours *Based on the results of a job analysis completed in 2017 This document provides both a summary and detailed
NHA Certified EKG Technician (CET) Test Plan for the CET Exam 100 scored items Exam Time: 2 hours *Based on the results of a job analysis completed in 2017 This document provides both a summary and detailed
Ambulatory Cardiac Monitors and Outpatient Telemetry Corporate Medical Policy
 Ambulatory Cardiac Monitors and Outpatient Telemetry Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry File Code: UM.SPSVC.13 Origination: 10/2015 Last
Ambulatory Cardiac Monitors and Outpatient Telemetry Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Ambulatory Event Monitors and Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry File Code: UM.SPSVC.13 Origination: 10/2015 Last
CP lead resting electrocardiograph
 CP 150 12-lead resting electrocardiograph Quick reference guide 2013 Welch Allyn, Inc. To support the intended use of the product described in this publication, the purchaser of the product is permitted
CP 150 12-lead resting electrocardiograph Quick reference guide 2013 Welch Allyn, Inc. To support the intended use of the product described in this publication, the purchaser of the product is permitted
OBJECTIVE. 1. Define defibrillation. 2. Describe Need and history of defibrillation. 3. Describe the principle and mechanism of defibrillation.
 Defibrillators OBJECTIVE 1. Define defibrillation. 2. Describe Need and history of defibrillation. 3. Describe the principle and mechanism of defibrillation. 4. Types and classes of defibrillator 5. Describe
Defibrillators OBJECTIVE 1. Define defibrillation. 2. Describe Need and history of defibrillation. 3. Describe the principle and mechanism of defibrillation. 4. Types and classes of defibrillator 5. Describe
2011 to 2017 CET Test Plan Crosswalk
 2011 to 2017 CET Test Plan Crosswalk Crosswalk Section: The following bridges tasks on the 2011 CET test plan with task statements on the 2017 CET test plan. 2011 NHA Test Plan TASK DESCRIPTION 2017 NHA
2011 to 2017 CET Test Plan Crosswalk Crosswalk Section: The following bridges tasks on the 2011 CET test plan with task statements on the 2017 CET test plan. 2011 NHA Test Plan TASK DESCRIPTION 2017 NHA
ECG UPDATE COURSE DESCRIPTION
 ECG UPDATE COURSE DESCRIPTION This CE course discusses techniques to improve ECG quality, interpretation of normal and abnormal ECG tracings, and troubleshooting ECG tracings. Note: An internet connection
ECG UPDATE COURSE DESCRIPTION This CE course discusses techniques to improve ECG quality, interpretation of normal and abnormal ECG tracings, and troubleshooting ECG tracings. Note: An internet connection
MEDICAL POLICY Cardiac Event Monitors/ Cardiac Event Detection
 POLICY: PG0039 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 10/01/11 LAST REVIEW: 12/12/17 MEDICAL POLICY Cardiac Event Monitors/ Cardiac Event Detection GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization of benefits,
POLICY: PG0039 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 10/01/11 LAST REVIEW: 12/12/17 MEDICAL POLICY Cardiac Event Monitors/ Cardiac Event Detection GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization of benefits,
WHY AM I FAINTING? Finding answers about unexplained fainting
 WHY AM I FAINTING? Finding answers about unexplained fainting PERSONAL STORIES For about 15 years, Lloyd s friends and family thought he was clumsy. Each spring, he seemed to have an unusual accident.
WHY AM I FAINTING? Finding answers about unexplained fainting PERSONAL STORIES For about 15 years, Lloyd s friends and family thought he was clumsy. Each spring, he seemed to have an unusual accident.
Pacemaker Therapy (PPM)
 Patient information Pacemaker Therapy (PPM) i Important information for all patients requiring pacemaker therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Patient information Pacemaker Therapy (PPM) i Important information for all patients requiring pacemaker therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulator (TENS)
 Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulator (TENS) How does TENS work? A TENS unit sends electrical pulses through the skin to start your body s own pain killers. The electrical pulses can release endorphins
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulator (TENS) How does TENS work? A TENS unit sends electrical pulses through the skin to start your body s own pain killers. The electrical pulses can release endorphins
Cardiology. Ambulatory ECG
 Cardiology Ambulatory ECG Cardiology services are provided in the Specialist Outpatient Clinic, Emergency Department, Intensive Care Unit and as an inpatient service. A full spectrum of care is provided
Cardiology Ambulatory ECG Cardiology services are provided in the Specialist Outpatient Clinic, Emergency Department, Intensive Care Unit and as an inpatient service. A full spectrum of care is provided
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D)
 Patient information Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D) i Important information for all patients requiring resynchronisation therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street
Patient information Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D) i Important information for all patients requiring resynchronisation therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street
Diagnostic tests for syncope
 Diagnostic tests for syncope Working together with individuals, families and medical professionals to offer support and information on syncope and reflex anoxic seizures www.stars.org.uk Registered Charity
Diagnostic tests for syncope Working together with individuals, families and medical professionals to offer support and information on syncope and reflex anoxic seizures www.stars.org.uk Registered Charity
Cardiology Testing. What is an echocardiogram ( echo )?
 Cardiology Testing What is an echocardiogram ( echo )? An echo is an ultrasound test used to evaluate the heart s anatomy/blood vessels, blood flow, heart muscle function and pressures within the heart.
Cardiology Testing What is an echocardiogram ( echo )? An echo is an ultrasound test used to evaluate the heart s anatomy/blood vessels, blood flow, heart muscle function and pressures within the heart.
Thank you very much for agreeing to participate in the Ontario Sleep Health Study
 Thank you very much for agreeing to participate in the Ontario Sleep Health Study By participating in this study, you are playing a key role in helping us better understand the impact of our genes on our
Thank you very much for agreeing to participate in the Ontario Sleep Health Study By participating in this study, you are playing a key role in helping us better understand the impact of our genes on our
WHAT CAN I DO ABOUT ATRIAL FIBRILLATION? Finding answers about atrial fibrillation
 WHAT CAN I DO ABOUT ATRIAL FIBRILLATION? Finding answers about atrial fibrillation DEBBIE S STORY With a full schedule of entertaining friends, dancing, working as a nurse and babysitting her granddog,
WHAT CAN I DO ABOUT ATRIAL FIBRILLATION? Finding answers about atrial fibrillation DEBBIE S STORY With a full schedule of entertaining friends, dancing, working as a nurse and babysitting her granddog,
Which ECG is Right for You?
 Which ECG is Right for You? Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary
Which ECG is Right for You? Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
2009 CPT Codes for Cardiac Device Monitoring
 2009 CPT Codes for Cardiac Device Monitoring December 2008 Notices Current Procedural Terminology (CPT ) is copyright 2008 American Medical Association. All Rights reserved. No fee schedules, basic units,
2009 CPT Codes for Cardiac Device Monitoring December 2008 Notices Current Procedural Terminology (CPT ) is copyright 2008 American Medical Association. All Rights reserved. No fee schedules, basic units,
Physicians and research nurses trained in the method are responsible for recording electrocardiograms from all subjects.
 Electrocardiogram (ECG) No: 004D 1. Introduction The electrocardiogram provides a baseline reading which shows the electrical alterations within the intracellular potential of myocardial cells. This facilitates
Electrocardiogram (ECG) No: 004D 1. Introduction The electrocardiogram provides a baseline reading which shows the electrical alterations within the intracellular potential of myocardial cells. This facilitates
Medtronic MiniMed Insulin Infusion Pumps
 Medtronic MiniMed Insulin Infusion Pumps Patients should always discuss potential risks and benefits with a physician. Please review the product manual prior to use for detailed instructions and disclosure.
Medtronic MiniMed Insulin Infusion Pumps Patients should always discuss potential risks and benefits with a physician. Please review the product manual prior to use for detailed instructions and disclosure.
UNDERSTANDING PACEMAKERS
 UNDERSTANDING PACEMAKERS Living Well with a Pacemaker Why You Need a Pacemaker Your heart has an electrical system that keeps it beating at the right speed. Problems with this system can make your heart
UNDERSTANDING PACEMAKERS Living Well with a Pacemaker Why You Need a Pacemaker Your heart has an electrical system that keeps it beating at the right speed. Problems with this system can make your heart
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease
 Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY
 Policy Name: Policy Number: Responsible Department(s): CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY Single-use Ambulatory Electrocardiographic Monitors (e.g., Zio Patch) MP-076-MD-DE Medical Management Provider Notice Date:
Policy Name: Policy Number: Responsible Department(s): CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY Single-use Ambulatory Electrocardiographic Monitors (e.g., Zio Patch) MP-076-MD-DE Medical Management Provider Notice Date:
Diagnostic tests for syncope
 Diagnostic tests for syncope Working together with individuals, families and medical professionals to offer support and information on syncope and reflex anoxic seizures www.stars.org.uk Registered Charity
Diagnostic tests for syncope Working together with individuals, families and medical professionals to offer support and information on syncope and reflex anoxic seizures www.stars.org.uk Registered Charity
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery Interoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging (imri)
 1 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery Interoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging (imri) Patient Information Booklet What are the benefits and risks of this treatment for me? Am I a good candidate? What should
1 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery Interoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging (imri) Patient Information Booklet What are the benefits and risks of this treatment for me? Am I a good candidate? What should
Atrial Fibrillation. Damage to your heart caused by a heart attack or rheumatic heart disease
 Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This booklet describes cardiac catheterization. It also details how to prepare for the procedure and the care needed after it is done. Before You
Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This booklet describes cardiac catheterization. It also details how to prepare for the procedure and the care needed after it is done. Before You
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular
 Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
MRI Scan. Patient Information. MRI Department Cobalt Imaging Centre. Registered Charity No:
 MRI Scan Patient Information MRI Department Cobalt Imaging Centre www.cobalthealth.co.uk Registered Charity No: 1090790 This leaflet aims to answer questions about having an MRI scan What is an MRI scan?
MRI Scan Patient Information MRI Department Cobalt Imaging Centre www.cobalthealth.co.uk Registered Charity No: 1090790 This leaflet aims to answer questions about having an MRI scan What is an MRI scan?
Patient Resources: Syncope
 Patient Resources: Syncope Overview Syncope is the medical term for fainting or loss of consciousness. Fainting can occur for a few different reasons. The autonomic (involuntary) nervous system helps to
Patient Resources: Syncope Overview Syncope is the medical term for fainting or loss of consciousness. Fainting can occur for a few different reasons. The autonomic (involuntary) nervous system helps to
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
Your surgeon will order pre-operative testing before you have surgery.
 Tests You May Need Prior to Surgery Your surgeon will order pre-operative testing before you have surgery. These tests give your surgeon valuable information regarding your current health condition. Below
Tests You May Need Prior to Surgery Your surgeon will order pre-operative testing before you have surgery. These tests give your surgeon valuable information regarding your current health condition. Below
8/20/ Identify the functions of common ECG machines. 3.3 Explain how each ECG machine control is used. 3.4 Recognize common electrodes.
 1 2 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 3: The Electrocardiograph Learning Outcomes 3.1 Identify three types of leads, and explain how each is recorded. 3.2 Identify the functions
1 2 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 3: The Electrocardiograph Learning Outcomes 3.1 Identify three types of leads, and explain how each is recorded. 3.2 Identify the functions
After Your Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD) Generator Change
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD) Generator Change What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD) Generator Change What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic
FlexAbs EMS ABDOMINAL STIMULATOR. FlexBody. EMS Body Stimulator INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 FlexAbs TM EMS ABDOMINAL STIMULATOR FlexBody TM EMS Body Stimulator INSTRUCTION MANUAL Read entire manual before operating this product. Use only as directed. INTRODUCTION The FlexAbs TM and FlexBody TM
FlexAbs TM EMS ABDOMINAL STIMULATOR FlexBody TM EMS Body Stimulator INSTRUCTION MANUAL Read entire manual before operating this product. Use only as directed. INTRODUCTION The FlexAbs TM and FlexBody TM
Thank you very much for agreeing to participate in the Ontario Sleep and Brain Health Study
 Thank you very much for agreeing to participate in the Ontario Sleep and Brain Health Study By participating in this study, you will play a key role in helping us better understand the links between sleep
Thank you very much for agreeing to participate in the Ontario Sleep and Brain Health Study By participating in this study, you will play a key role in helping us better understand the links between sleep
Living With Your Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Living With Your Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Aussi disponible en français : Vivre avec votre défibrillateur cardioverteur implantable (DCI) (FF85-1719) www.nshealth.ca
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Living With Your Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Aussi disponible en français : Vivre avec votre défibrillateur cardioverteur implantable (DCI) (FF85-1719) www.nshealth.ca
TELEMETRY BASICS FOR NURSING STUDENTS
 TELEMETRY BASICS FOR NURSING STUDENTS Accuracy of cardiac monitoring is an important component of patient safety in hospitalized patients who meet the criteria for dysrhythmia monitoring. (AACN, 2016,
TELEMETRY BASICS FOR NURSING STUDENTS Accuracy of cardiac monitoring is an important component of patient safety in hospitalized patients who meet the criteria for dysrhythmia monitoring. (AACN, 2016,
The Biomet EBI Bone Healing System. Patient Manual
 The Biomet EBI Bone Healing System Patient Manual Contents Introduction... Page 1 Symbol Description... Page 2 Warnings... Page 3 Battery Warning... Page 5 Indications, Contraindications, Usage and Adverse
The Biomet EBI Bone Healing System Patient Manual Contents Introduction... Page 1 Symbol Description... Page 2 Warnings... Page 3 Battery Warning... Page 5 Indications, Contraindications, Usage and Adverse
PVDOMICS: ECG Training
 PVDOMICS: ECG Training Cardiovascular Physiology Core Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland OH March 16, 2018 NHLBI Pulmonary Vascular Disease Phenomics Program Funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
PVDOMICS: ECG Training Cardiovascular Physiology Core Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland OH March 16, 2018 NHLBI Pulmonary Vascular Disease Phenomics Program Funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
Caring for Your Pacemaker
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Caring for Your Pacemaker What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206.598.4300. If you have a question
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Caring for Your Pacemaker What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206.598.4300. If you have a question
EVALUATION. When is a Heart Transplanted?
 EVALUATION When is a Heart Transplanted? The heart is a pump. Its only job is to move blood into the lungs and throughout the body. This movement of blood is essential to supply the body tissue with nutrients
EVALUATION When is a Heart Transplanted? The heart is a pump. Its only job is to move blood into the lungs and throughout the body. This movement of blood is essential to supply the body tissue with nutrients
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Device GF-3 / GF-3T
 Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Device GF-3 / GF-3T Operation Manual Read Before Using GF-3-INS-LAB-RevA08 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO TENS INDICATIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Device GF-3 / GF-3T Operation Manual Read Before Using GF-3-INS-LAB-RevA08 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO TENS INDICATIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS. Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions THE DEVICE Do I need a prescription to use the device? Yes. You need a prescription from your eye care professional to use the TrueTear device. How and where can I purchase the
Frequently Asked Questions THE DEVICE Do I need a prescription to use the device? Yes. You need a prescription from your eye care professional to use the TrueTear device. How and where can I purchase the
After Your Pacemaker Generator Change
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Pacemaker Generator Change What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206.598.4300. If you have
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Pacemaker Generator Change What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206.598.4300. If you have
This leaflet is intended for patients with permanent pacemakers and their parents.
 Permanent PACEMAKER This leaflet is intended for patients with permanent pacemakers and their parents. It serves as an information tool and a guide that offers some advice in order to live safely. General
Permanent PACEMAKER This leaflet is intended for patients with permanent pacemakers and their parents. It serves as an information tool and a guide that offers some advice in order to live safely. General
Information for patients. Diagnostic Telemetry. Department of Neurophysiology
 Information for patients Diagnostic Telemetry Department of Neurophysiology We must obtain your consent for any procedure or treatment beforehand. Staff will explain all the risks, benefits and alternatives
Information for patients Diagnostic Telemetry Department of Neurophysiology We must obtain your consent for any procedure or treatment beforehand. Staff will explain all the risks, benefits and alternatives
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
What to expect when having a pacemaker implantation
 What to expect when having a pacemaker implantation Cardiology Department Patient information leaflet What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker is a small metal device which contains an electronic circuit and a
What to expect when having a pacemaker implantation Cardiology Department Patient information leaflet What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker is a small metal device which contains an electronic circuit and a
Information for patients. The Cambridge Heart Clinic. World class private patient cardiology services in partnership with Addenbrooke s Hospital
 Information for patients The Cambridge Heart Clinic World class private patient cardiology services in partnership with Addenbrooke s Hospital This information can also be provided in different languages,
Information for patients The Cambridge Heart Clinic World class private patient cardiology services in partnership with Addenbrooke s Hospital This information can also be provided in different languages,
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed after you
Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed after you
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material 1 Table S1. Codes for Patient Selection Cohort Codes Primary PM CPT: 33206 or 33207 or 33208 (without 33225) ICD-9 proc: 37.81, 37.82, 37.83 Primary ICD Replacement PM Replacement
Supplemental Material 1 Table S1. Codes for Patient Selection Cohort Codes Primary PM CPT: 33206 or 33207 or 33208 (without 33225) ICD-9 proc: 37.81, 37.82, 37.83 Primary ICD Replacement PM Replacement
Psychologists who map the brain s fissures (grooves on the brain which appear as a deep fold) and inner recesses
 Also called psychobiologists Psychologists who map the brain s fissures (grooves on the brain which appear as a deep fold) and inner recesses Methods include: 1) Recording 2) Stimulating 3) Lesioning 4)
Also called psychobiologists Psychologists who map the brain s fissures (grooves on the brain which appear as a deep fold) and inner recesses Methods include: 1) Recording 2) Stimulating 3) Lesioning 4)
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
CAUTION...2 INSTRUCTION...5 IF-4000 INTERFERENTIAL STIMUATOR CONTROLS AND FUCTIONS...7 HOW TO USE YOUR IF-4000 STIMULATOR...14 ELECTRODES CARE...
 CONTENTS CAUTION...2 INSTRUCTION...5 IF-4000 INTERFERENTIAL STIMUATOR CONTROLS AND FUCTIONS...7 HOW TO USE YOUR IF-4000 STIMULATOR...14 SKIN CARE...17 ELECTRODES CARE...18 BATTERY REPLACEMENT...20 TECHNICAL
CONTENTS CAUTION...2 INSTRUCTION...5 IF-4000 INTERFERENTIAL STIMUATOR CONTROLS AND FUCTIONS...7 HOW TO USE YOUR IF-4000 STIMULATOR...14 SKIN CARE...17 ELECTRODES CARE...18 BATTERY REPLACEMENT...20 TECHNICAL
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Pacemaker (CRT-P)
 Patient information Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Pacemaker (CRT-P) i Important information for all patients requiring resynchronisation therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank,
Patient information Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Pacemaker (CRT-P) i Important information for all patients requiring resynchronisation therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank,
Biomet SpinalPak Non-Invasive Spine Fusion Stimulator System
 Biomet SpinalPak Non-Invasive Spine Fusion Stimulator System A Patient s Guide 100 Interpace Parkway Parsippany, NJ 07054 800-526-2579 www.biomet.com BNS231003 2009 EBI, LLC. All trademarks are the property
Biomet SpinalPak Non-Invasive Spine Fusion Stimulator System A Patient s Guide 100 Interpace Parkway Parsippany, NJ 07054 800-526-2579 www.biomet.com BNS231003 2009 EBI, LLC. All trademarks are the property
Arrhythmias. Pulmonary Artery
 Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Take control of your pain therapy. Getting started with Algovita SCS.
 Take control of your pain therapy. Getting started with Algovita SCS. The two-step approach to spinal cord stimulation therapy. You ve talked with your doctor. You ve discussed it with your family. You
Take control of your pain therapy. Getting started with Algovita SCS. The two-step approach to spinal cord stimulation therapy. You ve talked with your doctor. You ve discussed it with your family. You
Cardiac Catheterization
 Cardiac Catheterization What is cardiac catheterization? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. During cardiac catheterization, a long thin tube called
Cardiac Catheterization What is cardiac catheterization? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. During cardiac catheterization, a long thin tube called
Having a diagnostic catheter angiogram
 Having a diagnostic catheter angiogram This information leaflet will explain what an angiogram is and why you have been sent for one. Please read this leaflet carefully. If you have any questions or concerns
Having a diagnostic catheter angiogram This information leaflet will explain what an angiogram is and why you have been sent for one. Please read this leaflet carefully. If you have any questions or concerns
The Johns Hopkins Hospital Patient Information Home Instructions After REVERSE Total Shoulder Replacement Surgery
 Shoulder Replacement Edward G. McFarland, M.D. Johns Hopkins Division of Shoulder Department of Orthopaedic 10753 Falls Road/Suite 215 Lutherville, MD 21093 The following instructions are a guide for the
Shoulder Replacement Edward G. McFarland, M.D. Johns Hopkins Division of Shoulder Department of Orthopaedic 10753 Falls Road/Suite 215 Lutherville, MD 21093 The following instructions are a guide for the
Compatible with the following products TENS. Replacement Pads. User Manual. Last revised: V Last revised: V
 Compatible with the following products TENS Replacement Pads User Manual Last revised: V11-160923 Last revised: V4-170619 Contents Introduction 2-3 Parts 3 General Warnings and Safety 4-10 Using your TENS
Compatible with the following products TENS Replacement Pads User Manual Last revised: V11-160923 Last revised: V4-170619 Contents Introduction 2-3 Parts 3 General Warnings and Safety 4-10 Using your TENS
Patient & Family Guide. Using TENS for Pain.
 Patient & Family Guide 2017 Using TENS for Pain www.nshealth.ca Using TENS for Pain TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) provides stimulation that your body responds to by making natural
Patient & Family Guide 2017 Using TENS for Pain www.nshealth.ca Using TENS for Pain TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) provides stimulation that your body responds to by making natural
PVDOMICS: ECG Training Module
 PVDOMICS: ECG Training Module Cardiovascular Physiology Core Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland OH November 7, 2016 NHLBI Pulmonary Vascular Disease Phenomics Program Funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood
PVDOMICS: ECG Training Module Cardiovascular Physiology Core Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland OH November 7, 2016 NHLBI Pulmonary Vascular Disease Phenomics Program Funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood
Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise. Background Cardiac function
 Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) Heart Failure and Electrical Problems How CRT Helps Getting a Biventricular Pacemaker or ICD
 Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) Heart Failure and Electrical Problems How CRT Helps Getting a Biventricular Pacemaker or ICD What Is CRT? When you have heart failure, your heart is weakened and
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) Heart Failure and Electrical Problems How CRT Helps Getting a Biventricular Pacemaker or ICD What Is CRT? When you have heart failure, your heart is weakened and
Intravascular Ultrasound
 Scan for mobile link. Intravascular Ultrasound Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) uses a transducer or probe to generate sound waves and produce pictures of the coronary arteries. IVUS can show the entire
Scan for mobile link. Intravascular Ultrasound Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) uses a transducer or probe to generate sound waves and produce pictures of the coronary arteries. IVUS can show the entire
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Cardiac Nuclear Medicine
 Cardiac Nuclear Medicine What is Cardiac Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
Cardiac Nuclear Medicine What is Cardiac Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
Magnetoencephalography
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetoencephalography Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a non-invasive medical test that measures the magnetic fields produced by your brain s electrical currents. It is performed
Scan for mobile link. Magnetoencephalography Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a non-invasive medical test that measures the magnetic fields produced by your brain s electrical currents. It is performed
Falls clinic tests explained
 Falls clinic tests explained Day Hospital RDaSH Doncaster Community Integrated Services Have you had one or more falls recently? It happens to more people than you think. It can be a common problem and
Falls clinic tests explained Day Hospital RDaSH Doncaster Community Integrated Services Have you had one or more falls recently? It happens to more people than you think. It can be a common problem and
Your Subcutaneous Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD)
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Your Subcutaneous Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD) What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206-598-4300.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Your Subcutaneous Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD) What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206-598-4300.
Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT)
 Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) What is Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Scanning? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare for
Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) What is Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Scanning? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare for
MRI scan. Radiology Department Patient Information Leaflet
 MRI scan Radiology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people having an MRI scan. MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging. It gives information on the scan, and the
MRI scan Radiology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people having an MRI scan. MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging. It gives information on the scan, and the
Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter
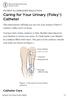 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
Neurostimulation. Spinal cord stimulators use electrodes placed in the space surrounding the spinal cord (epidural space).
 Neurostimulation.305145613.pdf 1 8/11/12 11:32 PM Neurostimulation Neurostimulation, also called electrostimulation, uses low-level electrical impulses to interfere with pain signals or block them from
Neurostimulation.305145613.pdf 1 8/11/12 11:32 PM Neurostimulation Neurostimulation, also called electrostimulation, uses low-level electrical impulses to interfere with pain signals or block them from
