Acute heart failure: new diagnostic perspectives for the emergency physician
|
|
|
- Rebecca McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intern Emerg Med (2008) 3:37 41 DOI /s EM - REVIEW Acute heart failure: new diagnostic perspectives for the emergency physician Gino Soldati Æ Luna Gargani Æ Fernando R. Silva Received: 2 June 2007 / Accepted: 1 November 2007 / Published online: 9 February 2008 Ó SIMI 2008 Abstract The topic of heart failure (HF) in the emergency department is today relevant, since there are new serum markers and imaging techniques that may help in the diagnosis of this disease. Natriuretic peptides have now entered the flowchart for etiologic diagnosis in patients with acute dyspnea, when technical facilities are available. Recently, chest ultrasonography has been shown to be useful for the noninvasive assessment of extravascular lung water. Starting from this practical standpoint, we propose that simple chest ultrasonogrpahic signs can provide a totally noninvasive characterization of pulmonary congestion in patients with HF. Keywords Chest sonography B-lines Ultrasound lung comets Heart failure Lung ultrasound Introduction The emergency physician often makes the diagnosis and manages many acute heart failure (HF) patients. Rapid G. Soldati Emergency Department, ASL 2, Ospedale di Castelnuovo Garfagnana, Lucca, Italy L. Gargani Institute of Clinical Physiology, National Research Council, Pisa, Italy F. R. Silva Department of Emergency Medicine, New York Hospital Queens, Flushing, NY, USA G. Soldati (&) Valle del Serchio General Hospital, Via Nazionale, 106, Pieve Fosciana Lucca, Italy g.soldati@usl2.toscana.it diagnosis of decompensated HF is important for prompt, appropriate therapy, but it is often difficult to detect [1]. The topic of decompensated HF diagnosis in the emergency department (ED) is today relevant, since plasma levels of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and its aminoterminal fragment N-terminal probnp (NT-proBNP) have been proposed, in addition to clinical judgement, to facilitate this diagnosis [2 4]. BNP and NT-proBNP have a very high negative predictive value in excluding HF, thus the diagnosis of acute HF with normal values of natriuretic peptides is very unlikely. On the contrary, in many circumstances they may be elevated in absence of HF, i.e. in patients with renal failure [5]. In these cases and in the presence of slightly abnormal values, the gray zone of natriuretic peptides, diagnosis and management of patients with dyspnea should be integrated with other parameters. Recently, chest ultrasonography imaged as Ultrasound Lung Comets (ULCs or B-lines) has been proposed as a very simple method [6] for assessment of pulmonary congestion in HF patients [7]. ULCs have been found to be related to New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class [8], to radiographic signs of pulmonary congestion on chest X-ray [9], to invasive measurement of extravascular lung water (EVLW) [10], and to systolic and diastolic dysfunction [8]. The aim of this discussion is to underline the potential usefulness of chest ultrasonography in the diagnosis of acute HF in the ED. The clinical entity Among all cardiovascular diseases, HF is the only one increasing in prevalence, incidence, hospitalization rate, total burden of mortality, and costs. It is estimated that the
2 38 Intern Emerg Med (2008) 3:37 41 USA has more than 5 million cases, with 500,000 new cases diagnosed each year. At least 20 million people are asymptomatic patients with HF that will become symptomatic within 1 5 years [11, 12]. After the initial symptoms the mortality rate at 6 years is very high (80% in men, 65% in women), and 1 year after the first pulmonary edema only half the patients are alive [13]. Acute HF is a highly recurrent disease: only 21% of the cases in the ED are actually the first event [14]. Physiopathology Regardless of its many different causes, HF results from a dysfunction of the systolic or diastolic phase of cardiac function. Independent of the primary cause of HF, there are two fundamental consequences: an increase in left ventricular filling pressure, leading to pulmonary congestion and edema, causing the respiratory symptoms, and the induction of a pathological neuroendocrine activation, leading to the production of numerous substances, including cathecolamines, angiotensin II, aldosterone, endothelin, cytokines, and alpha-tnf [15]. This activation leads to many pathological consequences, including left ventricular remodeling with fibrosis, apoptosis, contraction and geometry changes, and peripheral vascular modifications. In this context, natriuretic peptides positively affect the body fluid and sodium homeostasis, through an inhibitory action on the neurohormonal and immunological systems, especially the renin angiotensin aldosterone system, with diuresis and natriuresis [16]. They also exert a fundamental role in regulating the vascular tone and remodeling, by decreasing shear stress, modulating coagulation and fibrinolysis pathways, and inhibiting platelet activation [17]. In HF patients, BNP and NT-proBNP serum levels increase after myocardial stretch, following pressure or volume overload; they correlate with the severity of ventricular dysfunction and with the NYHA class of dyspnea [18, 19]. Diagnosis The absence of standardization for the diagnosis of acute decompensated HF makes this diagnosis a challenge for clinicians. In the ED setting, diagnosis of acute HF has usually been based on clinical examination. Unfortunately, signs and symptoms of acute HF are non-specific. Dyspnea, for example, characterizes a wide range of diseases that includes bronchial and pulmonary diseases, acute coronary syndromes, pulmonary embolism, dysrhythmias, obesity, psychiatric disorders, and physical deconditioning [1]. Even the chest X-ray study is often not very helpful in the diagnosis: it fails to demonstrate at least 20% of cardiomegalies further diagnosed by ultrasound and 50% of pleural effusions, especially if small; in chronic HF, sensitivity and specificity of radiological signs in predicting increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) is low [20, 21]. The echocardiographic estimation of ejection fraction (EF) has been considered the most important measure in heart failure [22], but there is not a clear correlation between symptoms and EF values [11]. In cases of preserved systolic function, the echocardiographic assessment of diastolic function would require more expertise. Finally, echocardiography is not widely available in the ED. According to previous registries, it is estimated that over one-third of acute HF diagnoses are mistaken; about half are COPD [23]. BNP in the reality of emergency medicine Given this clinical challenge, the blood-based measurement of BNP and NT-proBNP has emerged as part of the diagnostic tools available for the diagnosis of patients presenting with acute onset of dyspnea in the ED. Many studies have compared BNP and NT-proBNP accuracy to the clinical judgment of physicians [2 4, 24 27]. Measurement of either BNP or NT-proBNP outperformed the clinician who integrated the history, physical examination, and other diagnostic test findings (i.e. chest X-ray). Thus, in the 2005 update of the ACC/AHA guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of HF, it is stated that measurement of BNP is considered useful in the evaluation of patients presenting in the urgent care setting in whom the clinical diagnosis of HF is uncertain, although it should not be used in isolation to confirm or exclude the presence of HF [11]. The multicenter breathing not properly trial established an optimal cut-off value for BNP of 100 pg/ ml for the diagnosis of decompensated HF [2], while The International Collaborative of NT-proBNP (ICON) study established optimal age-based cut-offs for NT-proBNP to rule in acute decompensated HF, and a single cut-off to rule out HF [28]. In case of very high BNP or NTproBNP values, even more than ten times below these cut-offs, diagnosis of HF is almost certain, as well as values beyond them, almost always exclude HF, unless a flash pulmonary edema is present (when we may hypothize that there is no time for the polypeptide synthesis). On the contrary, it is challenging to interpretate values that fall between the lower rule-out and higher rule-in values found in HF patients. This range is often referred to as the gray zone. In this range, integration with clinical and other diagnostic tools is mandatory, especially because BNP can be elevated in many other circumstances [29], as listed on Table 1. It is especially
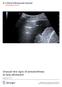
3 Intern Emerg Med (2008) 3: Table 1 Situations that can increase serum BNP levels Old age Renal failure Hypertension with LV hypertrophy Cirrhosis Pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary embolism Myocardial ischemia Sustained arrhythmias important to interpretate BNP and NT-proBNP values, always considering the renal function. Chest ultrasonography Currently, there is evidence that chest ultrasonography may be very helpful in differentiating cardiogenic dyspnea, associated with increased EVLW, from non-cardiogenic dyspnea. This distinction is based on the presence of ULCs or B-lines [7, 30], a pathological expression of enlarged pulmonary interstitium or alveolar interstitial syndrome (AIS). The ULCs or B-lines are defined as echogenic, coherent, wedge-shaped signals with a narrow origin in the near field of the image (Figs. 1, 2). They represent one of the lung ultrasound artefacts produced by normal and pathologic pleural and subpleural points of high impedance, that act as ultrasound resonators. In a normal aerated lung, we can only visualize a black screen, where at least only the normal A-lines are visible (Fig. 3); A-lines are horizontal reverberation artefacts that reproduce the Fig. 2 In this image several merging ultrasound lung comets or B-lines are visible, creating almost homogenous echogenic fields (white lung) normal pleural line (the basic physiological linear reflector). The ULCs or B-lines are focal resonance of subpleural interlobular septa thickened by water (similar to traditional Kerley B-lines) or, as EVLW increases and fill the alveolar space, they represent acoustic resonance in the alveolar spaces surrounded by water. The interstitial syndrome is characterized by separated ULCs or B-lines, while the involvement of the alveolar spaces leads to the coalescence of ULCs or B-lines, appearing as a white screen ( the white lung ). Fig. 1 Heart failure with pulmonary edema. Septal ultrasound lung comets or B-lines, arising from the pleural line and erasing the A-lines Fig. 3 An intercostal space showing a normal lung pattern, where horizontal artefacts (A-lines) are visible beyond the pleural line
4 40 Intern Emerg Med (2008) 3:37 41 Table 2 Chest sonography results showing a correlation between cardiogenic dyspnea, B-Lines (ULCs), BNP values and radiographic findings of acute heart failure ED emergency department, BNP brain natriuretic peptide, HF heart failure, ULCs ultrasound lung comets, ROC receiver operating characteristic Study 83 patients with dyspnea: chest sonography identification of pulmonary edema, correlation with clinical presentation and chest X-ray [31] 52 patients with dyspnea in ED: BNP values among subjects with final diagnosis of HF and with other diagnosis [36] 52 patients with dyspnea in ER: chest sonography edema score in subjects with and without final diagnosis of HF [36, 37] 27 patients with dyspnea in ER: ROC curve analysis of BNP levels and chest sonography edema score versus final diagnosis of HF [36] Results Sensitivity 96%, specificity 100% of ultrasound versus chest X-ray Subjects with HF: BNP 905 pg/dl Subjects without HF: 140 pg/dl (P \ 0.01) BNP values in the gray zone ( pg/dl): 40% Mean ULCs or B-Lines in subjects without HF: 8 Mean ULCs or B-Lines in subjects with HF: 55 Correlation between ultrasound score and BNP serum levels: 0.7 (P \ 0.01) BNP [118 pg/dl: sensitivity 100%, specificity 64% for diagnosis of HF Over 20 bilateral ULCs or B-lines: specificity 100%, sensitivity 84% for diagnosis of HF Cardiologists have become aware of the potential importance of the echographic pattern of the edematous lung. Several studies from the late 1990s have confirmed a good correlation of this echographic sign with the clinical and radiographic presentation of cardiogenic pulmonary edema [9, 31 33]. Picano and coworkers find a significant correlation between the number of ULCs or B-lines with a score of radiographic signs of pulmonary congestion [9], and also with EVLW volume, invasively quantified by the indicator diluition method, and with the PCWP obtained by right heart catheterization [10]. Volpicelli et al. [34] in an ED setting, find a sensitivity of 85.7% and a specificity of 97.7% for ULCs or B-Lines to detect AIS. A small pivotal study in patients with dyspnea, find a significant correlation between ULCs number and NT-proBNP values (r = 0.69, P \ ); with receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, ULCs showed an area under the curve of.893, and NT-proBNP of (P = 0.001), in predicting the cardiac origin of dyspnea [35]. Other chest sonography findings at the ED, in HF patients, also confirm these first results, and are synthesized in Table 2 [31, 36, 37]. Basing on these initial data, although on small numbers of patients, a 2- or 3-min chest ultrasonographic scanning may elucidate a doubtful clinical presentation or a grayzone BNP/NT-proBNP level. Although ULCs or B-lines with a considerable number (at least more than 5, bilaterally) can quickly identify pulmonary congestion, we must remember that they are a non-specific echographic sign of pulmonary edema, including non-cardiogenic forms as acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome [38]. Moreover, they may be also present in interstitial pneumonia and other interstitial and fibrogenic granulomatous diseases [39]. In these cases, together with clinical information and history, other chest ultrasonographic signs may be helpful, such as presence or absence of pleural effusion, and the different patterns of ultrasonographic findings (homogeneous, inhomogeneous, focal or diffuse) [37, 40]. Conclusions In the challenging task of diagnosing acute HF at the ED, especially in case of gray zone levels of BNP/NTproBNP, pulmonary congestion detected by ULCs or B- lines, could be definitive for the diagnosis of HF. Moreover, a normal lung echographic pattern (with less than 5 ULCs or B-lines on the whole thorax) in a patient with BNP [ 100 pg/dl may suggest a right-ventricle origin of the peptide (pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary embolism). References 1. Stevenson LW, Perloff JK (1989) The limited reliability of physical signs for estimating hemodynamics in chronic heart failure. JAMA 261: Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P, Omland T, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Wu AH, Clopton P, Steg PG, Westheim A, Knudsen CW, Perez A, Kazanegra R, Herrmann HC, McCullough PA (2002) Breathing not properly multinational study investigators. Rapid measurement of B-Type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med 347: Mueller C, Scholer A, Laule-Kilian K, Martina B, Schindler C, Buser P, Pfisterer M, Perruchoud AP (2004) Use of B-type natriuretic peptide in the evaluation and management of acute dyspnea. N Engl J Med 350: McCullough PA, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Herrmann HC, Steg PG, Duc P, Westheim A, Omland T, Knudsen CW, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Lamba S, Wu AH, Perez A, Clopton P, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, Maisel AS (2002) B- type natriuretic peptide and clinical judgment in emergency diagnosis of heart failure: analysis from Breathing Not Properly (BNP) Multinational Study. Circulation 106:
5 Intern Emerg Med (2008) 3: Anwaruddin S, Lloyd-Jones DM, Baggish A, Chen A, Krauser D, Tung R, Chae C, Januzzi JL Jr (2006) Renal function, congestive heart failure, and amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide measurement: results from the ProBNP Investigation of Dyspnea in the Emergency Department (PRIDE) Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 47: Bedetti G, Gargani L, Corbisiero A, Frassi F, Poggianti E, Mottola G (2006) Evaluation of ultrasound lung comets by handheld echocardiography. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 4:34 7. Picano E, Frassi F, Agricola E, Gligorova S, Gargani L, Mottola G (2006) Ultrasound lung comets: a clinically useful sign of extravascular lung water. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 19: Frassi F, Gargani L, Gligorova S, Ciampi Q, Mottola G, Picano E (2007) Clinical and echocardiographic determinants of ultrasound lung comets. Eur J Echocardiogr 8: Jambrik Z, Monti S, Coppola V, Agricola E, Mottola G, Miniati M, Picano E (2004) Usefulness of ultrasound lung comets as a nonradiologic sign of extravascular lung water. Am J Cardiol 93: Agricola E, Bove T, Oppizzi M, Marino G, Zangrillo A, Margonato A, Picano E (2005) Ultrasound comet-tail images : a marker of pulmonary edema: a comparative study with wedge pressure and extravascular lung water. Chest 127: Hunt SA (2005) ACC/AHA 2005 guideline update for the diagnosis and management of chronic heart failure in the adult: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (writing committee to update the 2001 guidelines for the evaluation and management of heart failure). J Am Coll Cardiol 46:e1 e American Heart Association (2007) Heart disease and stroke statistics 2007 update. American Heart Association, Dallas 13. Peacock WF (2004) Heart failure management in the Emergency Department Observation Unit. Progr Cardiovasc Dis 46: Aghababian R (2002) Acutely decompensated heart failure: opportunities to improve care and outcomes in the emergency department. Rev Cardiovasc Med 3(suppl 4): Braunwald E (2005) Heart disease, 7th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam 16. de Bold AJ, Ma KK, Zhang Y, de Bold ML, Bensimon M, Khoshbaten A (2001) The physiological and pathophysiological modulation of the endocrine function of the heart. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 79: Clerico A, Recchia FA, Passino C, Emdin M (2006) Cardiac endocrine function is an essential component of the homeostatic regulation network: physiological and clinical implications. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290:H17 H Panteghini M (2004) Role and importance of biochemical markers in clinical cardiology. Eur Heart J 25: Struthers AD (1994) Ten years of natriuretic peptide research: a new dawn for their diagnostic and therapeutic use? BMJ 308: Ruskin JA, Gurney JW, Thorsen MK, Goodman LR (1987) Detection of pleural effusions on supine chest radiographs. Am J Roentgenol 148: Chakko S, Woska D, Marinez H de Marchena E, Futterman L, Kessler KM, Myerberg RJ (1991) Clinical, radiographic and hemodynamic correlations in chronic congestive heart failure: conflicting results may lead to inappropriate care. Am J Med 90: Packer M, Cohn JN (1999) Consensus recommendations for the management of chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol 83:1A 38A 23. Remes J, Miettinen H, Reunanen A, Pyörälä K (1991) Validity of clinical diagnosis of heart failure in primary health care. Eur Heart J 12: Januzzi JL Jr, Camargo CA, Anwaruddin S et al (2005) The N- terminal Pro-BNP investigation of dyspnea in the emergency department (PRIDE) study. Am J Cardiol 95: Lainchbury JG, Campbell E, Frampton CM, Yandle TG, Nicholls MG, Richards AM (2003) Brain natriuretic peptide and n-terminal brain natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of heart failure in patients with acute shortness of breath. J Am Coll Cardiol 42: Zaphiriou A, Robb S, Murray-Thomas T et al (2005) The diagnostic accuracy of plasma BNP and NTproBNP in patients referred from primary care with suspected heart failure: results of the UK natriuretic peptide study. Eur J Heart Fail 7: Maisel A, Hollander JE, Gauss D et al (2004) Primary results of the rapid emergency department heart failure outpatient trial (REDHOT): a multicenter study of B-type natriuretic peptide levels, emergency decision making and outcomes in patients presenting with shortness of breath. J Am Coll Cardiol 44: Januzzi JL, van Kimmenade R, Lainchbury J et al (2006) NTproBNP testing for diagnosis and short-term prognosis in acute destabilized heart failure: an international pooled analysis of 1256 patients: the International Collaborative of NT-proBNP Study. Eur Heart J 27: Emdin M, Clerico A, Clemenza F, Galvani M, Latini R, Masson S, Mule P, Panteghini M, Valle R, Zaninotto M, Ganau A, Mariotti R, Volpe M, Aspromonte N, Cacciatore G, Cappelletti P, L Abbate A, Miglio F, Ottani F, Pagani F, Passino C, Plebani M, Sarzani R, Zucchelli G (2005) Italian Association of Hospital Cardiologists; Italian Society of Cardiology; Italian Federation of Cardiology; Italian Society of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Biology; Italian Society of Laboratory Medicine; Italian Society of Emergency Medicine. Recommendations for the clinical use of cardiac natriuretic peptides. Ital Heart J 6: Lichtenstein D, Meziere G, Biderman P, Gepner A, Barre O (1997) The comet-tail artifact. An ultrasound sign of alveolar interstitial syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156: Soldati G, Rossi M (1999) Wet and dry lungs. A useful sonographic distinction. Crit Care 3(suppl 1):P Soldati G (2001) Lung ultrasound: movement, artifact or echotexture? Giornale Italiano Ecografia 4: Lichtenstein D, Meziere G (1998) A lung ultrasound sign allowing bedside distinction between pulmonary edema and COPD: the comet tail artifact. Intensive Care Med 24: Volpicelli G, Mussa A, Garofalo G, Cardinale L, Casoli G, Perotto F, Fava C, Frascisco M (2006) Bedside lung ultrasound in the assessment of alveolar interstitial syndrome. Am J Emerg Med 24: Gargani L, Soldati G, Frassi F, Agrusta M, Tesorio P, Mottola G, Picano E (2006) Ultrasound lung comets for differential diagnosis of dyspnea: comparison with plasma cardiac peptides. Circulation (November supplement: 3589) 36. Soldati G, Bergamini C (2006) A sonographic lung score for the detection of extravascular lung water in patients with CHF. Acad Emerg Med 13: Soldati G, Bergamini C (2006) Chest sonography in the diagnosis of congestive heart failure. Acad Emerg Med 13: Soldati G, Testa A, Silva FR, Carbone L, Portale G, Silveri NG (2006) Chest ultrasonography in lung contusion. Chest 130: Reissig A, Kroegel C (2003) Transthoracic sonography of diffuse parenchymal lung disease: the role of comet tail artifacts. J Ultrasound Med 22: Soldati G, Copetti R (2006) Ecografia toracica. GCEMS Ed. Medico Scientifiche, Torino
Diagnostic value of N-terminal ProB-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Emergency Department: Analysis by subgroups
 emergency care journal Diagnostic value of N-terminal ProB-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Emergency Department: Analysis by subgroups P. Villa, A. Dolci*, R. Dominici*, M. Panteghini**, C. Fundarò, S. Guzzetti
emergency care journal Diagnostic value of N-terminal ProB-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Emergency Department: Analysis by subgroups P. Villa, A. Dolci*, R. Dominici*, M. Panteghini**, C. Fundarò, S. Guzzetti
Using Lung Ultrasound to Diagnose and Manage Acute Heart Failure
 Using Lung Ultrasound to Diagnose and Manage Acute Heart Failure Jennifer Martindale, MD Assistant Professor Department of Emergency Medicine SUNY Downstate/Kings County Hospital Brooklyn, NY What is acute
Using Lung Ultrasound to Diagnose and Manage Acute Heart Failure Jennifer Martindale, MD Assistant Professor Department of Emergency Medicine SUNY Downstate/Kings County Hospital Brooklyn, NY What is acute
Ultrasound lung comets for the differential diagnosis of acute cardiogenic dyspnoea: A comparison with natriuretic peptides
 European Journal of Heart Failure 10 (2008) 70 77 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejheart Ultrasound lung comets for the differential diagnosis of acute cardiogenic dyspnoea: A comparison with natriuretic peptides
European Journal of Heart Failure 10 (2008) 70 77 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejheart Ultrasound lung comets for the differential diagnosis of acute cardiogenic dyspnoea: A comparison with natriuretic peptides
Non Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in the ED
 Is haemodinamic monitoring useful in the ED? Non Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in the ED Roberta PETRINO Director Emergency Medicine Unit S. Andrea Hospital, Vercelli - Italy EuSEM Vice-president Helps
Is haemodinamic monitoring useful in the ED? Non Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in the ED Roberta PETRINO Director Emergency Medicine Unit S. Andrea Hospital, Vercelli - Italy EuSEM Vice-president Helps
Prognostic Value of Extravascular Lung Water Assessed With Ultrasound Lung Comets by Chest Sonography in Patients With Dyspnea and/or Chest Pain
 Journal of Cardiac Failure Vol. 13 No. 10 2007 Prognostic Value of Extravascular Lung Water Assessed With Ultrasound Lung Comets by Chest Sonography in Patients With Dyspnea and/or Chest Pain FRANCESCA
Journal of Cardiac Failure Vol. 13 No. 10 2007 Prognostic Value of Extravascular Lung Water Assessed With Ultrasound Lung Comets by Chest Sonography in Patients With Dyspnea and/or Chest Pain FRANCESCA
6/6/17. Heart Failure and Natriuretic Peptides. Learning objectives
 Heart Failure and Natriuretic Peptides Maria-Magdalena Patru, MD, PhD Director, Medical and Scientific Affairs This promotional educational activity is brought to you by Ortho-Clinical Diagnostics, Inc.
Heart Failure and Natriuretic Peptides Maria-Magdalena Patru, MD, PhD Director, Medical and Scientific Affairs This promotional educational activity is brought to you by Ortho-Clinical Diagnostics, Inc.
Natriuretic Peptides The Cardiologists View. Christopher defilippi, MD University of Maryland Baltimore, MD, USA
 Natriuretic Peptides The Cardiologists View Christopher defilippi, MD University of Maryland Baltimore, MD, USA Disclosures Research support: Alere, BG Medicine, Critical Diagnostics, Roche Diagnostics,
Natriuretic Peptides The Cardiologists View Christopher defilippi, MD University of Maryland Baltimore, MD, USA Disclosures Research support: Alere, BG Medicine, Critical Diagnostics, Roche Diagnostics,
Abstract. ª 2009 by the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine ISSN doi: /j x PII ISSN
 Emergency Thoracic Ultrasound in the Differentiation of the Etiology of Shortness of Breath (ETUDES): Sonographic B-lines and N-terminal Pro-brain-type Natriuretic Peptide in Diagnosing Congestive Heart
Emergency Thoracic Ultrasound in the Differentiation of the Etiology of Shortness of Breath (ETUDES): Sonographic B-lines and N-terminal Pro-brain-type Natriuretic Peptide in Diagnosing Congestive Heart
ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ. ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΠΟΔΙΣΤΡΙΑΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΑΘΗΝΩΝ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ Ά ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ Διευθυντής: Καθηγητής Δημήτριος Τούσουλης ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΠΟΔΙΣΤΡΙΑΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΑΘΗΝΩΝ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ Ά ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ Διευθυντής: Καθηγητής Δημήτριος Τούσουλης ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions
 POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions Jeremy S. Boyd, MD, FACEP Asst. Professor of Emergency Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Illustrations courtesy of Robinson Ferre, MD, FACEP
POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions Jeremy S. Boyd, MD, FACEP Asst. Professor of Emergency Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Illustrations courtesy of Robinson Ferre, MD, FACEP
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Lnformation Coverage Guidance
 Lnformation Coverage Guidance Coverage Indications, Limitations, and/or Medical Necessity Abstract: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a cardiac neurohormone produced mainly in the left ventricle. It
Lnformation Coverage Guidance Coverage Indications, Limitations, and/or Medical Necessity Abstract: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a cardiac neurohormone produced mainly in the left ventricle. It
Original Article A meta analysis on diagnostic effectiveness of ultrasound in diagnosis of acute pulmonary edema in ICU
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(2):3345-3351 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0030097 Original Article A meta analysis on diagnostic effectiveness of ultrasound in diagnosis of acute pulmonary edema in ICU
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(2):3345-3351 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0030097 Original Article A meta analysis on diagnostic effectiveness of ultrasound in diagnosis of acute pulmonary edema in ICU
Heart Failure. Cardiac Anatomy. Functions of the Heart. Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics. Determinants of Cardiac Output. Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress
 A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
NT-proBNP: Evidence-based application in primary care
 NT-proBNP: Evidence-based application in primary care Associate Professor Rob Doughty The University of Auckland, Auckland City Hospital, Auckland Heart Group NT-proBNP: Evidence in Primary Care The problem
NT-proBNP: Evidence-based application in primary care Associate Professor Rob Doughty The University of Auckland, Auckland City Hospital, Auckland Heart Group NT-proBNP: Evidence in Primary Care The problem
Risk Stratification in Heart Failure: The Role of Emerging Biomarkers
 Risk Stratification in Heart Failure: The Role of Emerging Biomarkers David G. Grenache, PhD Associate Professor of Pathology, University of Utah Medical Director, ARUP Laboratories Salt Lake City, UT
Risk Stratification in Heart Failure: The Role of Emerging Biomarkers David G. Grenache, PhD Associate Professor of Pathology, University of Utah Medical Director, ARUP Laboratories Salt Lake City, UT
World Journal of Radiology
 W J R World Journal of Radiology Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.230 World J Radiol 2014 June 28; 6(6): 230-237
W J R World Journal of Radiology Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.230 World J Radiol 2014 June 28; 6(6): 230-237
To estimate the serum level of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide levels in acute coronary syndrome
 Original Research Article To estimate the serum level of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide levels in acute coronary syndrome Mohamed Yasar Arafath 1, K. Babu Raj 2* 1 First Year Post Graduate, 2
Original Research Article To estimate the serum level of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide levels in acute coronary syndrome Mohamed Yasar Arafath 1, K. Babu Raj 2* 1 First Year Post Graduate, 2
NT-proBNP A New Test for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Management of Congestive Heart Failure
 Reference Section NT-proBNP A New Test for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Management of Congestive Heart Failure a report by Drs Rahul Sakhuja and James L Januzzi Cardiology Division and Department of Medicine,
Reference Section NT-proBNP A New Test for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Management of Congestive Heart Failure a report by Drs Rahul Sakhuja and James L Januzzi Cardiology Division and Department of Medicine,
B-type Natriuretic Peptide for Diagnosis of Heart Failure in Emergency Department Patients: A Critical Appraisal
 686 Schwam d BNP FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HF B-type Natriuretic Peptide for Diagnosis of Heart Failure in Emergency Department Patients: A Critical Appraisal Abstract The diagnosis of heart failure in the outpatient
686 Schwam d BNP FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HF B-type Natriuretic Peptide for Diagnosis of Heart Failure in Emergency Department Patients: A Critical Appraisal Abstract The diagnosis of heart failure in the outpatient
*Christian M. Carlsen, 1 Mette Mouridsen, 1 Ahmad Sajadieh, 1 Lars Køber, 2 Olav W. Nielsen 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND
 USE OF N-TERMINAL NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE IN A REAL- WORLD SETTING OF PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH ACUTE DYSPNOEA AND THE IMPLICATION FOR TRIAGING PATIENTS IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT *Christian M. Carlsen, 1 Mette
USE OF N-TERMINAL NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE IN A REAL- WORLD SETTING OF PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH ACUTE DYSPNOEA AND THE IMPLICATION FOR TRIAGING PATIENTS IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT *Christian M. Carlsen, 1 Mette
Using Ultrasound Lung Comets in the Diagnosis of High Altitude Pulmonary Edema: Fact or Fiction?
 WILDERNESS & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE, 24, 159 164 (2013) REVIEW ARTICLE Using Ultrasound Lung Comets in the Diagnosis of High Altitude Pulmonary Edema: Fact or Fiction? Yashvi Wimalasena, BM, FCEM, DiMM;
WILDERNESS & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE, 24, 159 164 (2013) REVIEW ARTICLE Using Ultrasound Lung Comets in the Diagnosis of High Altitude Pulmonary Edema: Fact or Fiction? Yashvi Wimalasena, BM, FCEM, DiMM;
Diastolic Heart Failure. Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012
 Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure
 Original Research Article A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure Bhavik Prajapati 1*, Anirudh Kulkarni 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, SMS Multispecialty
Original Research Article A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure Bhavik Prajapati 1*, Anirudh Kulkarni 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, SMS Multispecialty
Definition of Congestive Heart Failure
 Heart Failure Definition of Congestive Heart Failure A clinical syndrome of signs & symptoms resulting from the heart s inability to supply adequate tissue perfusion. CHF Epidemiology Affects 4.7 million
Heart Failure Definition of Congestive Heart Failure A clinical syndrome of signs & symptoms resulting from the heart s inability to supply adequate tissue perfusion. CHF Epidemiology Affects 4.7 million
Lung Ultrasound in Hemodialysis: A Card to be Played?
 In-Depth Review Received: December 2, 2016 Accepted: January 23, 2017 Published online: February 23, 2017 Lung Ultrasound in Hemodialysis: A Card to be Played? Pierpaolo Di Nicolò a Giacomo Magnoni b Antonio
In-Depth Review Received: December 2, 2016 Accepted: January 23, 2017 Published online: February 23, 2017 Lung Ultrasound in Hemodialysis: A Card to be Played? Pierpaolo Di Nicolò a Giacomo Magnoni b Antonio
Introduction. Summary. Karim Gariani a, Alain Delabays b, Thomas V. Perneger c, Thomas Agoritsas a,c
 Published 9 November 2011, doi:10.4414/smw.2011.13298 Cite this as: Use of brain natriuretic peptide to detect previously unknown left ventricular dysfunction in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic
Published 9 November 2011, doi:10.4414/smw.2011.13298 Cite this as: Use of brain natriuretic peptide to detect previously unknown left ventricular dysfunction in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic
Pathophysiology: Heart Failure
 Pathophysiology: Heart Failure Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology Heart Failure: Definitions
Pathophysiology: Heart Failure Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology Heart Failure: Definitions
Chronic valvular heart disease (CVHD) is the most
 Standard Article J Vet Intern Med 2017;31:700 704 Assessment of Lung Ultrasound B-Lines in Dogs with Different Stages of Chronic Valvular Heart Disease T. Vezzosi, T. Mannucci, A. Pistoresi, F. Toma, R.
Standard Article J Vet Intern Med 2017;31:700 704 Assessment of Lung Ultrasound B-Lines in Dogs with Different Stages of Chronic Valvular Heart Disease T. Vezzosi, T. Mannucci, A. Pistoresi, F. Toma, R.
Diagnosing Acute Heart Failure in Patients With Undifferentiated Dyspnea: A Lung
 Diagnosing Acute Heart Failure in Patients With Undifferentiated Dyspnea: A Lung and Cardiac Ultrasound (LuCUS) Protocol Frances M. Russell MD, Robert R. Ehrman MD, Karen Cosby MD, Asim Ansari MD, Stephanie
Diagnosing Acute Heart Failure in Patients With Undifferentiated Dyspnea: A Lung and Cardiac Ultrasound (LuCUS) Protocol Frances M. Russell MD, Robert R. Ehrman MD, Karen Cosby MD, Asim Ansari MD, Stephanie
The clinical value of natriuretic peptide testing in heart failure
 The clinical value of natriuretic peptide testing in heart failure James L. Januzzi, Jr, MD, FACC, FESC Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Roman W. DeSanctis Endowed Clinical Scholar
The clinical value of natriuretic peptide testing in heart failure James L. Januzzi, Jr, MD, FACC, FESC Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Roman W. DeSanctis Endowed Clinical Scholar
Role of Biomarkers for the Prevention, Assessment, and Management of Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association
 Role of Biomarkers for the Prevention, Assessment, and Management of Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association We combed through both guidelines and summarized 3 recommendations
Role of Biomarkers for the Prevention, Assessment, and Management of Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association We combed through both guidelines and summarized 3 recommendations
Pitfalls in the use of biomarkers
 Pitfalls in the use of biomarkers Alan Maisel MD Professor of Medicine, University of California, San Diego Director Coronary Care Unit And Heart Failure Program San Diego Veterans Hospital Disclosure
Pitfalls in the use of biomarkers Alan Maisel MD Professor of Medicine, University of California, San Diego Director Coronary Care Unit And Heart Failure Program San Diego Veterans Hospital Disclosure
Unusual new signs of pneumothorax at lung ultrasound
 Unusual new signs of pneumothorax at lung ultrasound Volpicelli et al. Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 SHORT COMMUNICATION
Unusual new signs of pneumothorax at lung ultrasound Volpicelli et al. Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 SHORT COMMUNICATION
Review. Identification of circulating biomarkers that may provide. Natriuretic peptides in the diagnosis and management of heart failure.
 Natriuretic peptides in the diagnosis and management of heart failure G. Michael Felker, John W. Petersen, Daniel B. Mark DOI:1503/cmaj.060236 Abstract The natriuretic peptides are a family of related
Natriuretic peptides in the diagnosis and management of heart failure G. Michael Felker, John W. Petersen, Daniel B. Mark DOI:1503/cmaj.060236 Abstract The natriuretic peptides are a family of related
Why, when, and how to assess pulmonary congestion in heart failure: pathophysiological, clinical, and methodological implications
 DOI 10.1007/s10741-009-9148-8 Why, when, and how to assess pulmonary congestion in heart failure: pathophysiological, clinical, and methodological implications Eugenio Picano Æ Luna Gargani Æ Mihai Gheorghiade
DOI 10.1007/s10741-009-9148-8 Why, when, and how to assess pulmonary congestion in heart failure: pathophysiological, clinical, and methodological implications Eugenio Picano Æ Luna Gargani Æ Mihai Gheorghiade
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Clinical Uncertainty, Diagnostic Accuracy, and Outcomes in Emergency Department Patients Presenting With Dyspnea
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Clinical Uncertainty, Diagnostic Accuracy, and Outcomes in Emergency Department Patients Presenting With Dyspnea Sandy M. Green, MD; Abelardo Martinez-Rumayor, MD; Shawn A. Gregory,
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Clinical Uncertainty, Diagnostic Accuracy, and Outcomes in Emergency Department Patients Presenting With Dyspnea Sandy M. Green, MD; Abelardo Martinez-Rumayor, MD; Shawn A. Gregory,
Topic Page: congestive heart failure
 Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Prognostic Value of B-type Natriuretic Peptide for Assessment of Left Ventricular Function in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease
 Kidney Diseases Prognostic Value of B-type Natriuretic Peptide for Assessment of Left Ventricular Function in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Alireza Soleimani, 1 Omid Nasiri, 2 Hassan Nikoueinejad,
Kidney Diseases Prognostic Value of B-type Natriuretic Peptide for Assessment of Left Ventricular Function in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Alireza Soleimani, 1 Omid Nasiri, 2 Hassan Nikoueinejad,
Impact of Renal Disease on Natriuretic Peptide Testing for Diagnosing Decompensated Heart Failure and Predicting Mortality
 Clinical Chemistry 53:8 1511 1519 (2007) General Clinical Chemistry Impact of Renal Disease on Natriuretic Peptide Testing for Diagnosing Decompensated Heart Failure and Predicting Mortality Christopher
Clinical Chemistry 53:8 1511 1519 (2007) General Clinical Chemistry Impact of Renal Disease on Natriuretic Peptide Testing for Diagnosing Decompensated Heart Failure and Predicting Mortality Christopher
Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure
 Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Francesco Paneni, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Unit Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Cardiology University Hospital Zurich Switzerland francesco.paneni@gmail.com
Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Francesco Paneni, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Unit Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Cardiology University Hospital Zurich Switzerland francesco.paneni@gmail.com
Heart Failure in Women: Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre
 Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Identification of lung sliding: a basic ultrasound technique with a steep learning curve
 SIGNA VITAE 2013; 8(1): 31-35 ORIGINAL Identification of lung sliding: a basic ultrasound technique with a steep learning curve MATEJ STRNAD SABINA ZADEL ZALIKA KLEMENC-KETIS MATEJ STRNAD ( ) SABINA ZADEL
SIGNA VITAE 2013; 8(1): 31-35 ORIGINAL Identification of lung sliding: a basic ultrasound technique with a steep learning curve MATEJ STRNAD SABINA ZADEL ZALIKA KLEMENC-KETIS MATEJ STRNAD ( ) SABINA ZADEL
Objectives. Systolic Heart Failure: Definitions. Heart Failure: Historical Perspective 2/7/2009
 Objectives Diastolic Heart Failure and Indications for Echocardiography in the Asian Population Damon M. Kwan, MD UCSF Asian Heart & Vascular Symposium 02.07.09 Define diastolic heart failure and differentiate
Objectives Diastolic Heart Failure and Indications for Echocardiography in the Asian Population Damon M. Kwan, MD UCSF Asian Heart & Vascular Symposium 02.07.09 Define diastolic heart failure and differentiate
Outline. Pathophysiology: Heart Failure. Heart Failure. Heart Failure: Definitions. Etiologies. Etiologies
 Outline Pathophysiology: Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology : Definitions An inability of the
Outline Pathophysiology: Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology : Definitions An inability of the
HFpEF. April 26, 2018
 HFpEF April 26, 2018 (J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;70:2476 86) HFpEF 50% or more (40-71%) of patients with CHF have preserved LV systolic function. HFpEF is an increasingly frequent hospital discharge. Outcomes
HFpEF April 26, 2018 (J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;70:2476 86) HFpEF 50% or more (40-71%) of patients with CHF have preserved LV systolic function. HFpEF is an increasingly frequent hospital discharge. Outcomes
ASSESSMENT OF LUNG PARENCHYMAL ABNORMALITIES
 2016 by the author Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as
2016 by the author Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CARDIAC FUNCTION: BIOCHEMICAL MARKERS UPDATE
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CARDIAC FUNCTION: BIOCHEMICAL MARKERS UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CARDIAC FUNCTION: BIOCHEMICAL MARKERS UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Usefulness of lung ultrasound in diagnosing causes of exacerbation in patients with chronic dyspnea
 PRACA ORYGINALNA Review Katarzyna Rogoza 1, Wojciech Kosiak 2 1 Department of Allergology, Medical University of Gdańsk, Poland 2 Ultrasound and Biopsy Diagnostics Lab, Department of Pediatrics, Hematology
PRACA ORYGINALNA Review Katarzyna Rogoza 1, Wojciech Kosiak 2 1 Department of Allergology, Medical University of Gdańsk, Poland 2 Ultrasound and Biopsy Diagnostics Lab, Department of Pediatrics, Hematology
Overview & Update on the Utilization of the Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure
 June 28, 2016 Overview & Update on the Utilization of the Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure Linda C. Rogers, PhD, DABCC, FACB. Agenda Overview of the Natriuretic Peptides and Efficacy studies Similarities
June 28, 2016 Overview & Update on the Utilization of the Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure Linda C. Rogers, PhD, DABCC, FACB. Agenda Overview of the Natriuretic Peptides and Efficacy studies Similarities
Acute Heart Failure: Diagnosis and Risk Assessment in the Emergency Department
 Acute Heart Failure: Diagnosis and Risk Assessment in the Emergency Department J. Douglas Kirk, MD Professor and Vice Chairman, Department of Emergency Medicine Director, Chest Pain Evaluation Unit, University
Acute Heart Failure: Diagnosis and Risk Assessment in the Emergency Department J. Douglas Kirk, MD Professor and Vice Chairman, Department of Emergency Medicine Director, Chest Pain Evaluation Unit, University
Acute HF is a complex and often life-threatening clinical condition. 1 Existing
 ACUTE HEART FAILURE: WHAT IS NEW? John Parissis, MD, PhD; Vasiliki Bistola, MD Author affiliations: Heart Failure Unit, University of Athens, Athens, Greece Address for correspondence: John Parissis, Navarinou
ACUTE HEART FAILURE: WHAT IS NEW? John Parissis, MD, PhD; Vasiliki Bistola, MD Author affiliations: Heart Failure Unit, University of Athens, Athens, Greece Address for correspondence: John Parissis, Navarinou
AMINO-TERMINAL PRO-BRAIN NATRIURETIC PEPTID IN PREDICTION OF LEFT VENTRICULAR EJECTION FRACTION
 & AMINO-TERMINAL PRO-BRAIN NATRIURETIC PEPTID IN PREDICTION OF LEFT VENTRICULAR EJECTION FRACTION Mugdim Bajrić¹, Fahir Baraković¹, Zumreta Kušljugić¹, Nermin Salkić¹, Elmir Jahić¹, Mensura Aščerić³*,
& AMINO-TERMINAL PRO-BRAIN NATRIURETIC PEPTID IN PREDICTION OF LEFT VENTRICULAR EJECTION FRACTION Mugdim Bajrić¹, Fahir Baraković¹, Zumreta Kušljugić¹, Nermin Salkić¹, Elmir Jahić¹, Mensura Aščerić³*,
Circulating CD34-positive cell number is associated with brain natriuretic peptide level in type 2 diabetes patients
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online October 24, 2007 Circulating CD34-positive cell number is associated with brain natriuretic peptide level in type 2 diabetes patients Sadanori Okada,
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online October 24, 2007 Circulating CD34-positive cell number is associated with brain natriuretic peptide level in type 2 diabetes patients Sadanori Okada,
BNP. Daniel J. Fink, MD, MPH Director, Core Laboratory New York Presbyterian Hospital Columbia University Medical Center New York, New York
 Daniel J. Fink, MD, MPH Director, Core Laboratory New York Presbyterian Hospital Columbia University Medical Center New York, New York October 10, 2005 1 Outline The Biochemistry of Natriuretic Peptides
Daniel J. Fink, MD, MPH Director, Core Laboratory New York Presbyterian Hospital Columbia University Medical Center New York, New York October 10, 2005 1 Outline The Biochemistry of Natriuretic Peptides
Diagnosing Acute Heart Failure in Patients With Undifferentiated Dyspnea: A Lung and Cardiac Ultrasound (LuCUS) Protocol
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Diagnosing Acute Heart Failure in Patients With Undifferentiated Dyspnea: A Lung and Cardiac Ultrasound (LuCUS) Protocol Frances M. Russell, MD, Robert R. Ehrman, MD, Karen Cosby,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Diagnosing Acute Heart Failure in Patients With Undifferentiated Dyspnea: A Lung and Cardiac Ultrasound (LuCUS) Protocol Frances M. Russell, MD, Robert R. Ehrman, MD, Karen Cosby,
The Role of Brain Natriuretic Peptide in the Patients with Acute Dyspnea in the Emergency Department
 REVIEW Korean Circulation J 2007;37:464-469 ISSN 1738-5520 c 2007, The Korean Society of Cardiology The Role of Brain Natriuretic Peptide in the Patients with Acute Dyspnea in the Emergency Department
REVIEW Korean Circulation J 2007;37:464-469 ISSN 1738-5520 c 2007, The Korean Society of Cardiology The Role of Brain Natriuretic Peptide in the Patients with Acute Dyspnea in the Emergency Department
a Center for Emergency Medicine, Community Health Center Maribor, b Department of Family Medicine, Medical Faculty and c Department of Physiology,
 50 Original article Bedside lung ultrasound for monitoring the effectiveness of prehospital treatment with continuous positive airway pressure in acute decompensated heart failure Matej Strnad a,b, Gregor
50 Original article Bedside lung ultrasound for monitoring the effectiveness of prehospital treatment with continuous positive airway pressure in acute decompensated heart failure Matej Strnad a,b, Gregor
Lung ultrasound: Present and future
 Review Article Lung ultrasound: Present and future Ashish Saraogi Department of Anaesthesiology, National Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India ABSTRACT The scope of ultrasound
Review Article Lung ultrasound: Present and future Ashish Saraogi Department of Anaesthesiology, National Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India ABSTRACT The scope of ultrasound
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
Plasma MR-proADM is superior to NTproBNP for all-cause short term mortality prediction in acute pulmonary embolism.
 J. Pedowska-Wloszek, M. Kostrubiec, A. Labyk, S. Pacho, O. Dzikowska-Diduch, P. Bienias, B. Lichodziejewska, P. Palczewski, M. Ciurzynski, P. Pruszczyk Plasma MR-proADM is superior to NTproBNP for all-cause
J. Pedowska-Wloszek, M. Kostrubiec, A. Labyk, S. Pacho, O. Dzikowska-Diduch, P. Bienias, B. Lichodziejewska, P. Palczewski, M. Ciurzynski, P. Pruszczyk Plasma MR-proADM is superior to NTproBNP for all-cause
Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management
 Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management Best Practices Juan M. Aranda Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Heart Failure/ Transplant Program University of Florida College of Medicine Disclosures:
Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management Best Practices Juan M. Aranda Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Heart Failure/ Transplant Program University of Florida College of Medicine Disclosures:
Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure?
 ESC Congress Munich - 25-29 August 2012 Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction From Bench to Bedside Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure? Prof. Burkert Pieske Department of Cardiology Med.University
ESC Congress Munich - 25-29 August 2012 Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction From Bench to Bedside Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure? Prof. Burkert Pieske Department of Cardiology Med.University
Association between B-lines detected during lung ultrasound and various factors in hemodialysis patients
 Kuzuhara et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2017) 3:17 DOI 10.1186/s41100-017-0101-3 RESEARCH Association between B-lines detected during lung ultrasound and various factors in hemodialysis patients Shinzo
Kuzuhara et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2017) 3:17 DOI 10.1186/s41100-017-0101-3 RESEARCH Association between B-lines detected during lung ultrasound and various factors in hemodialysis patients Shinzo
B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Predicts Future Cardiac Events in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Dyspnea
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Predicts Future Cardiac Events in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Dyspnea From the Division of Cardiology and General Internal Medicine
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Predicts Future Cardiac Events in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Dyspnea From the Division of Cardiology and General Internal Medicine
Ultrasound lung comets in systemic sclerosis: a chest sonography hallmark of pulmonary interstitial fibrosis
 Rheumatology Advance Access published August 28, 2009 Rheumatology 2009; 1 of 6 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep263 Ultrasound lung comets in systemic sclerosis: a chest sonography hallmark of pulmonary interstitial
Rheumatology Advance Access published August 28, 2009 Rheumatology 2009; 1 of 6 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep263 Ultrasound lung comets in systemic sclerosis: a chest sonography hallmark of pulmonary interstitial
Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the. impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood.
 Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood. As of 2013, an estimated 5.8 million people in the United
Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood. As of 2013, an estimated 5.8 million people in the United
Cor pulmonale. Dr hamid reza javadi
 1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
Heart Failure Guidelines For your Daily Practice
 Heart Failure Guidelines For your Daily Practice Juan M. Aranda, Jr., MD, FACC, FHFSA Professor of Medicine Director of Heart Failure and Cardiac Transplantation University of Florida College of Medicine
Heart Failure Guidelines For your Daily Practice Juan M. Aranda, Jr., MD, FACC, FHFSA Professor of Medicine Director of Heart Failure and Cardiac Transplantation University of Florida College of Medicine
Diagnosis of heart failure in dogs with mitral valve disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Diagnosis of heart failure in dogs with mitral valve disease Author : PHILLIP SPEER Categories : Vets Date : March 31, 2014
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Diagnosis of heart failure in dogs with mitral valve disease Author : PHILLIP SPEER Categories : Vets Date : March 31, 2014
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό
 Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
THE PROPER APPROACH TO DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE WITH PRESERVED EJECTION FRACTION
 THE PROPER APPROACH TO DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE WITH PRESERVED EJECTION FRACTION James C. Fang, MD, FACC Professor and Chief Cardiovascular Division University of Utah School of Medicine Disclosures Data
THE PROPER APPROACH TO DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE WITH PRESERVED EJECTION FRACTION James C. Fang, MD, FACC Professor and Chief Cardiovascular Division University of Utah School of Medicine Disclosures Data
Biomarkers in cardiovascular disease. Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018
 Biomarkers in cardiovascular disease Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018 Biomarkers NIH: A biomarker is a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological
Biomarkers in cardiovascular disease Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018 Biomarkers NIH: A biomarker is a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological
Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year
![Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year](/thumbs/76/74263761.jpg) PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
Οξεία καρδιακή ανεπάρκεια: Ποιες παράμετροι συμβάλλουν στη διαστρωμάτωση κινδύνου των ασθενών;
 Οξεία καρδιακή ανεπάρκεια: Ποιες παράμετροι συμβάλλουν στη διαστρωμάτωση κινδύνου των ασθενών; Γ. Φιλιππάτος, MD, FACC, FESC, FCCP Επ. Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας Πανεπ. Αθηνών Clinical Outcomes in Patients
Οξεία καρδιακή ανεπάρκεια: Ποιες παράμετροι συμβάλλουν στη διαστρωμάτωση κινδύνου των ασθενών; Γ. Φιλιππάτος, MD, FACC, FESC, FCCP Επ. Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας Πανεπ. Αθηνών Clinical Outcomes in Patients
Heart Failure Background, recognition, diagnosis and management
 Heart Failure Background, recognition, diagnosis and management Speaker bureau: Novartis At the conclusion of this activity, participants will be able to: Recognize signs and symptoms of heart failure
Heart Failure Background, recognition, diagnosis and management Speaker bureau: Novartis At the conclusion of this activity, participants will be able to: Recognize signs and symptoms of heart failure
Heart Failure A Team Approach Background, recognition, diagnosis and management
 Heart Failure A Team Approach Background, recognition, diagnosis and management Speaker bureau: Novartis At the conclusion of this activity, participants will be able to: Recognize signs and symptoms of
Heart Failure A Team Approach Background, recognition, diagnosis and management Speaker bureau: Novartis At the conclusion of this activity, participants will be able to: Recognize signs and symptoms of
THE CORRELATION BETWEEN
 THE CORRELATION BETWEEN NT Pro-BNP LEVELS AND ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS IN A PATIENT WITH ACUTE ONSET DYSPNEA. Sonal Virani, Pavan Kumar. M, Sunil Dalvi 1. Assistant Professor, Department of General Medicine,
THE CORRELATION BETWEEN NT Pro-BNP LEVELS AND ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS IN A PATIENT WITH ACUTE ONSET DYSPNEA. Sonal Virani, Pavan Kumar. M, Sunil Dalvi 1. Assistant Professor, Department of General Medicine,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy ST2 Assay for Chronic Heart Failure File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: st_assay_for_chronic_heart_failure 2/2015 4/2018 4/2019 4/2018 Description
Corporate Medical Policy ST2 Assay for Chronic Heart Failure File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: st_assay_for_chronic_heart_failure 2/2015 4/2018 4/2019 4/2018 Description
LCZ696 A First-in-Class Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor
 The Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor LCZ696 in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction The Prospective comparison of ARNI with ARB on Management Of heart failure with preserved ejection
The Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor LCZ696 in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction The Prospective comparison of ARNI with ARB on Management Of heart failure with preserved ejection
Lung Ultrasound Predicts Well Extravascular Lung Water but Is of Limited Usefulness in the Prediction of Wedge Pressure
 CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Lung Ultrasound Predicts Well Extravascular Lung Water but Is of Limited Usefulness in the Prediction of Wedge Pressure Giovanni Volpicelli, M.D.,
CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Lung Ultrasound Predicts Well Extravascular Lung Water but Is of Limited Usefulness in the Prediction of Wedge Pressure Giovanni Volpicelli, M.D.,
Chest ultrasound and hidden lung congestion in peritoneal dialysis patients
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2012) 0: 1 5 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs116 NDT Advance Access published May 9, 2012 Original Article Chest ultrasound and hidden lung congestion in peritoneal dialysis patients Vincenzo
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2012) 0: 1 5 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs116 NDT Advance Access published May 9, 2012 Original Article Chest ultrasound and hidden lung congestion in peritoneal dialysis patients Vincenzo
Chest Ultrasonography in Lung Contusion*
 CHEST Chest Ultrasonography in Lung Contusion* Gino Soldati, MD; Americo Testa, MD; Fernando R. Silva, MD; Luigi Carbone, MD, PhD; Grazia Portale, MD; and Nicolò G. Silveri, MD Original Research CHEST
CHEST Chest Ultrasonography in Lung Contusion* Gino Soldati, MD; Americo Testa, MD; Fernando R. Silva, MD; Luigi Carbone, MD, PhD; Grazia Portale, MD; and Nicolò G. Silveri, MD Original Research CHEST
Heart 101. Objectives. Types of Heart Failure How common is HF? Sign/Symptoms, when to see a doctor? Diagnostic testing
 EXAMING HEART FAILURE: HOW TO RECOGNIZE AND TREAT THE WEAK HEART What is Heart Failure? Treatment of Heart Failure End Stage Heart Failure Munir S. Janmohamed M.D. FACC Assistant Clinical Professor of
EXAMING HEART FAILURE: HOW TO RECOGNIZE AND TREAT THE WEAK HEART What is Heart Failure? Treatment of Heart Failure End Stage Heart Failure Munir S. Janmohamed M.D. FACC Assistant Clinical Professor of
DIASTOLOGY DON T BE SUCH A STIFF
 DIASTOLOGY DON T BE SUCH A STIFF Michael Mallin, MD University of Utah Director Emergency Ultrasound www.ultrasoundpodcast.com Warning: The education found within this presentation is not approved by anyone
DIASTOLOGY DON T BE SUCH A STIFF Michael Mallin, MD University of Utah Director Emergency Ultrasound www.ultrasoundpodcast.com Warning: The education found within this presentation is not approved by anyone
Assessment and Diagnosis of Heart Failure
 Assessment and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome resulting from any structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood and is characterized
Assessment and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome resulting from any structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood and is characterized
Dr Dinna Soon. Consultant Cardiologist, Department of Cardiology. GP symposium 2 April 2016
 Dr Dinna Soon Consultant Cardiologist, Department of Cardiology GP symposium 2 April 2016 Case presentation 76 years old male, chronic smoker, hypertension, previous MI 3/7 SOB and chest tightness BP
Dr Dinna Soon Consultant Cardiologist, Department of Cardiology GP symposium 2 April 2016 Case presentation 76 years old male, chronic smoker, hypertension, previous MI 3/7 SOB and chest tightness BP
Copyright 2011, 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Normal Cardiac Anatomy
 Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Lung ultrasound for severe acute dyspnea evaluation in critical care patients
 Page 950 VOJNOSANITETSKI PREGLED Vojnosanit Pregl 2016; 73(10): 950 955. PRACTICAL ADVICE FOR PHYSICIANS UDC: 616-08-039.74::616.14-073.432.19 DOI: 10.2298/VSP150609085R Lung ultrasound for severe acute
Page 950 VOJNOSANITETSKI PREGLED Vojnosanit Pregl 2016; 73(10): 950 955. PRACTICAL ADVICE FOR PHYSICIANS UDC: 616-08-039.74::616.14-073.432.19 DOI: 10.2298/VSP150609085R Lung ultrasound for severe acute
Current Utilities of Cardiac Biomarker Testing at POC. June 24, 2010 Joe Pezzuto, MT (ASCP) Carolyn Kite, RN
 Current Utilities of Cardiac Biomarker Testing at POC June 24, 2010 Joe Pezzuto, MT (ASCP) Carolyn Kite, RN 1. Discuss challenges associated with diagnosing Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS) and Heart Failure
Current Utilities of Cardiac Biomarker Testing at POC June 24, 2010 Joe Pezzuto, MT (ASCP) Carolyn Kite, RN 1. Discuss challenges associated with diagnosing Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS) and Heart Failure
Treating the patient with acute heart failure. What do we really know? Principles of acute heart failure treatment
 ESC 2012 27Aug - 3Sep, 2012, Munich, Germany Treating the patient with acute heart failure. What do we really know? Principles of acute heart failure treatment Marco Metra, MD, FESC Cardiology University
ESC 2012 27Aug - 3Sep, 2012, Munich, Germany Treating the patient with acute heart failure. What do we really know? Principles of acute heart failure treatment Marco Metra, MD, FESC Cardiology University
Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax.
 Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax. Poster No.: C-0526 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Stefanidis, K. Vintzilaios, D. D. Cokkinos, E. Antypa, S. Dimopoulos, S. Nanas,
Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax. Poster No.: C-0526 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Stefanidis, K. Vintzilaios, D. D. Cokkinos, E. Antypa, S. Dimopoulos, S. Nanas,
Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of Pneumothorax in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1 Division of Pediatric Pulmonology, Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1 Division of Pediatric Pulmonology, Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 11, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /03/$30.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 11, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00405-4
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 11, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00405-4
Type of intervention Diagnosis. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 The use of B-type natriuretic peptide in the management of patients with diabetes and acute dyspnoea Mueller C, Laule-Kilian K, Christ A, Perruchoud A P Record Status This is a critical abstract of an
The use of B-type natriuretic peptide in the management of patients with diabetes and acute dyspnoea Mueller C, Laule-Kilian K, Christ A, Perruchoud A P Record Status This is a critical abstract of an
N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in patients with acute pulmonary embolism
 Eur Respir J 23; 22: 649 653 DOI: 1.1183/931936.3.2333 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 23 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide
Eur Respir J 23; 22: 649 653 DOI: 1.1183/931936.3.2333 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 23 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide
The Treatment Targets in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
 SUCCESS WITH HEART FAILURE The Treatment Targets in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Gregg C. Fonarow, MD The Ahmanson-UCLA Cardiomyopathy Center, Division of Cardiology, UCLA School of Medicine, Los
SUCCESS WITH HEART FAILURE The Treatment Targets in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Gregg C. Fonarow, MD The Ahmanson-UCLA Cardiomyopathy Center, Division of Cardiology, UCLA School of Medicine, Los
New CHF Patient in my Office: What Should I Do?
 New CHF Patient in my Office: What Should I Do? Joseph Mishkin MD FACC Advanced Heart Failure, Transplantation and Mechanical Circulatory Support No disclosures Disclosures Clinical Presentation 38 year
New CHF Patient in my Office: What Should I Do? Joseph Mishkin MD FACC Advanced Heart Failure, Transplantation and Mechanical Circulatory Support No disclosures Disclosures Clinical Presentation 38 year
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM. General Instructions: ID NUMBER: FORM NAME: H F A DATE: 10/13/2017 VERSION: CONTACT YEAR NUMBER:
 ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
