Transcatheter closure of ventricular septal defects with nitinol wire occluders of type patent ductus arteriosus
|
|
|
- Cassandra Kelley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pediatric cardiology Transcatheter closure of ventricular septal defects with nitinol wire occluders of type patent ductus arteriosus Arkadiusz Wierzyk 1, Małgorzata Szkutnik 1, Roland Fiszer 1, Paweł Banaszak 1, Szymon Pawlak 2, Jacek Białkowski 1 1 Clinical Ward of Congenital Heart Diseases and Pediatric Cardiology in Zabrze, Silesian Medical University, Silesian Centre for Heart Diseases, Zabrze, Poland 2 Chair and Clinical Department of Cardiac Surgery and Transplantology in Zabrze, Silesian Medical University, Silesian Centre for Heart Diseases, Zabrze, Poland Postep Kardiol Inter 2014; 10, 1 (35): DOI: /pwki Abstract Ventricular septal defects closure (VSD) depending on the anatomy and clinical setting can be performed surgically or by a hybrid and transcatheter approach. Two cases of children with VSD will be presented. Patients defects were closed with various types of occluders made of nitinol wire mesh occluder, patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) type. The first case was a 2.5-year-old boy after cardiosurgical correction of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF). After the procedure, a significant haemodynamic residual VSD was observed, which was not successfully closed during the subsequent reoperation. Despite pharmacological treatment, symptoms of heart failure were observed in this patient. In echocardiographic images the residual VSD was presented as a tunnel-like dissection of the ventricular septum (length 6 mm and diameter 3.4 mm). The defect was closed via arterial access with an Amplatzer Duct Occluder II (ADO II). The procedure was successfully performed without any medical complications. In this child, a significant shunt reduction and a noticeable improvement in the patient s clinical status and diminished symptoms of heart failure were noticed. The second patient was a 4-year-old girl suffering from a multi-perforated perimembranous VSD accompanied by a ventricular septal defect with aneurysm. The defect was closed by a venous approach with a PDA Cardio-O-Fix occluder (very similar to ADO I). No short-term or long-term complications were visible during or after the procedure. Only a mild residual shunt through the VSD was observed 6 months afterwards. Transcatheter VSD closure with a proper morphology, with occluders of type Amplatzer Duct Occluder ADO I or ADO II, constitutes a safe and effective therapeutic alternative. Key words: transcatheter closure, ventricular septal defect, congenital heart defect. Introduction Hemodynamically significant ventricular septal defects closure (VSD), isolated as well as being an integral part of complex congenital heart defects, are closed surgically in the majority of cases. Notwithstanding, there is a group of patients in whom a transcatheter closure brings potentially greater benefits to patients than surgery (the less invasive the method of the procedure, the lower the risk of adverse reactions). It pertains to defects with specific morphology such as muscular ventricular septal defects (mvsd) and residual ventricular septal defects (re-vsd) occurring after previous surgical treatment [1, 2]. Implants, which are generally applied for that reason, are special VSD devices. We present here two examples of VSD transcatheter closure one residual postsurgery ventricular septal defect (re-vsd) and the second native perimembranous VSD (pmvsd) accompanied by intraventricular septal (IVS) aneurysm. Both of them were closed with different types of occluders made of nitinol wire mesh, which were originally designed for closure of large patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). Case reports Case 1 A 2.5-year-old boy underwent two cardiosurgical corrections of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) at the age of 2 and was reoperated on 5 months afterwards due to re-vsd. Corresponding author: Arkadiusz Wierzyk MD, Clinical Ward of Congenital Heart Diseases and Pediatric Cardiology in Zabrze, Silesian Medical University, Silesian Centre for Heart Diseases, 9 M. Curie-Skłodowskiej St, Zabrze, Poland, phone: , awierzyk@mp.pl Received: , accepted:
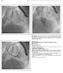
2 Just after the second procedure, transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) showed total closure of the re-vsd. However, during the following transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), conducted after moving the patient from an intensive care unit, the defect in the place of a patch size 4 5 mm reappeared. Pharmacological treatment was applied, namely captopril, furosemide, spironolactone as well as digoxin. During ambulatory observation incremental signs and symptoms of heart failure (HF) were diagnosed and the boy was admitted to the hospital again. Symptoms of poor growth were sustained (body mass 13 kg 25 th centile), tachypnea breaths. A clinical examination showed: precordial thrill, systolic murmur at left sternal side 4/6 according to Levin, hepatomegaly approximately 2 cm below the right rib cage. Saturation was 92 94%. Thorax radiography showed significantly increased vascularity of the lungs. Electrocardiography (ECG) indicated characteristics of right bundle branch block (RBBB) and left anterior hemiblock (LAH). In UCG enlarged right ventricle (RV) and left atrium were seen. The residual VSD was presented as a tunnel- like dissection of the ventricular septum, length 6 mm and diameter 3.4 mm. The patient s parents did not agree to further surgical intervention. Considering that fact, the decision A B C D Figure 1. Residual ventricular septal defect closure with ADO II. LAO 30 projection. A Left ventriculography before the closure, visible tunnel-like VSD. B Occluder still connected to the delivery system (arrow). C Left ventriculography showing the position of the occluder waist of ADO II fills in canal type VSD (arrow). D Occluder released from the delivery system (fluoroscopy magnification) 22
3 of an attempt at transcatheter closure of the re-vsd was made. Re-VSD closure was done under general anesthesia, with antibiotic protection (cefazolin 100 mg/kg body weight, administered intravenously) and under TEE control. Before the procedure, one dose of heparin 50 U/kg body weight was administered intravenously. The right artery and femoral vein were cannulated. Thereafter, 4 Fr sheaths and diagnostic catheters were implemented. Invasive measurement of blood pressure was performed. Findings were as follows: in RA 30/22/26, in RV 70/0/22, in PA 48/23/35, in LV 125/0/22 and in Ao 113/68/92 mm Hg. The size of shunt was measured (Qp : Qs 1.5 : 1) as well as resistance (PVR 5 Wood units, SVR 21.4 units). Left ventriculography showing re-vsd was carried out (Figure 1 A). Thereafter, a JR 5 Fr cathe- Figure 2. Amplatzer Duct Occluder type II (ADO II) A B C D Figure 3. Perimembranous VSD closure with aneurysm with occluder type COF PDA. Left ventriculography. LAO 30 projection. A VSD before closure. B Occluder in the diameter of the aneurysm, still connected to the delivery system. C After closure of the defect. D Cardi-O-Fix PDA Occluder 23
4 ter was implemented with a hydrophilic guidewire from the left ventricle, through the re-vsd, to the right ventricle. The JR catheter was exchanged for a 5 Fr sheath introducer and a size 6/6 mm Amplatzer Duct Occluder type II ADO II (AGA Med. Corp., USA Figure 2) was implemented through that sheath. The aim was to open a distal disk in the RV and a proximal disk in the left ventricle. In order to achieve that, it was necessary to conduct a twofold reposition of the occluder (Figures 1 B D). The total duration of the procedure was 2 h, including 16.8 min of fluoroscopy. After the procedure, left ventriculography was carried out. A mild residual shunt without hemodynamic significance was visible. In TEE the correct position of the ADO II was confirmed. Trivial aortic valve regurgitation was diagnosed. The boy was rehospitalized 3 months after the procedure. Significantly diminished symptoms of HF were observed in this patient. The TTE showed a mild shunt in the occluder area, hemodynamically insignificant. The patient s body mass was then 15.7 kg (25 th 50 th centile). During the period of hospitalization, cardiac rhythm abnormalities (which had been diagnosed previously) were noticed a supraventricular tachycardia and one episode of bradycardia with decrease in heart rate to 38 beats per minute (bpm) in Holter ECG. Because of the resistance of supraventricular tachycardia to pharmacological treatment (no response to adenosine) the attack was interrupted by cardioversion. Thereafter, ablation RF with a satisfactory result was conducted. At preset, one year after the procedure, the patient feels well and he is under ambulatory care. Case 2 A 4-year-old girl with congenital heart defect native perimembranous VSD partially covered by IVS aneurysm was admitted to hospital in order to carry out a VSD transcatheter closure. Congenital heart defect was diagnosed just after the delivery. From that time, the girl was under the Pediatric Cardiac Department s care. Pharmacological treatment was not applied to the patient. After admission to the hospital a clinical examination was carried out. The examination included the following aspects: holosystolic murmur at left sternal side 3 4/6 of Levin scale and a mild parasternal thrill. The patient s body mass was 13 kg (25 th centile). Thorax radiography showed slightly increased vascularity as well as enlarged heart. The TTE examination showed at least 2 defects approximately 2 mm each in the perimembranous IVS with aneurysm size 8 mm, left-to-right shunt, gradient about 90 mm Hg. Cardiac catheterization was done under general anesthesia and with antibiotic protection; 50 U/kg body weight of heparin was administered. The right artery and femoral vein were cannulated. The measurement of blood pressure was checked; findings were as follows: RA 11/9/9, RV 38/0/11, PA 34/16/24, LV 110/0/20 and Ao 100/61/81 mm Hg. Qp/Qs was 1.6. During the left ventriculography, the aneurysm (diameter approximately 8 mm) in the perimembranous IVS with at least 2 defects (2 mm each) was revealed (Figure 3 A). After the removal of diagnostic catheters, a catheter type JR 5 Fr was implemented from the LV through the VSD, to the RV. Thereafter, a guidewire (0.035 cm 260 cm) was inserted into the left pulmonary artery and a 15 mm Andrasnare was introduced from the femoral vein to the left pulmonary artery and an arterio-venous loop was created. A transseptal sheath (180 st. 7 Fr) was implemented through the vein using the kissing method. After placing the sheath into an ascending aorta, the dilator was removed. A Cardi-O-Fix PDA Occluder (COF PDA Starway Medical Technology Inc., China Figure 3 D) size 8/6 mm was inserted. Having released the retentional ventricular disk, the whole delivery system was withdrawn to the IVS aneurysm. Thereafter, a proximal part of the device was opened (Figures 3 B and 3 C). Occluder implantation was monitored by TEE and fluoroscopy as well. The total duration of the procedure was 2.5 h, including 23.4 min of fluoroscopy. During the examination, carried out 6 months after the implantation of the occluder, TTE diagnosed residual shunt in the lower and upper pole of the occluder. The patient felt well and pharmacological treatment was not applied. The patient s weight was 20 kg (90 th centile), height 113 cm (90 th centile). During the clinical examination a mild murmur in the left sternal side was heard without other symptoms. No heart rhythm or conduction disorders were diagnosed (also in Holter EKG). Discussion The cases presented here indicate the utility of applied PDA nitinol occluders in transcatheter closure of selected types of VSD. The frequency of residual, post-surgical VSD constitutes 5 25%. Residual VSD may be the consequence of an unstitched patch or leak closure. A small re-vsd (diameter < 2 mm) is usually closed spontaneously [1 4]. Bigger re-vsd frequently cause significant hemodynamic consequences and the necessity of more complicated reoperation. Transcatheter closure of this defect is an alternative for patients. Based on the literature, asymmetric and symmetric Amplatzer Ventricular Septal Occluders [5, 6] or modified Chinese occluders [7] were successfully used for percutaneous closure of re-vsd. After insertion, the most severe complications were intravenous hemolysis (after implantation) or cardiac rhythm abnormalities diagnosed during or after the procedure [5 7]. In a case similar to that presented here (re-vsd after TOF correction) also a different device, a mushroom-shaped Amplatzer Duct Occluder type I (ADO I), was used successfully (Figure 3 D) [8]. There are not many articles in the literature describing the usage of Amplatzer Duct Occluder type II (ADO II) for VSD closure. It mainly concerns native VSD. In 2012 Koneti et al. [9] described transcatheter closure of perimembra- 24
5 nous VSD with ADO II in 57 children (aged years old). Size of the defect was mm (average 5 mm). The effectiveness of the procedure was 94% (permanent closure of the defect) and remote consequences were estimated as promising. In the case of one patient, embolization of the occluder occurred. The described study case indicates beneficial and highly effective usage of ADO II in a child suffering from recurrent, post-surgical re-vsd after previous correction of entire TOF. Our experience with percutaneous closure of native perimembranous VSD with IVS aneurysm by Duct Occluder I is consistent with a report published recently by El Said et al. [10]. The authors of that article described a group of 21 patients (age 15 months to 30 years) with a similar VSD morphology treated with ADO I. In their study before the procedure, TTE showed a defect diameter in the range mm (average 5 mm) and aneurysm mm (average 11 mm). The procedure was carried out on 19 patients; 2 patients were withdrawn from the procedure. In 1 patient, while inserting the catheter through the defect, symptoms of total atrioventricular block (TAVB) appeared. Ventricular tachycardia occurred in the second patient. As far as our case is concerned, no complications were observed during and after the procedure. After the implantation residual shunt (hemodynamically insignificant) was observed, which also occurred in 7 out of 19 patients described in the publication written by El Said et al. [10]. This may suggest that more precise selection of patients who require such interventions is required. The usage of two overlapping ADO II can be an interesting alternative for VSD with multiperforated aneurysm of the intraventricular septum [11]. In transcatheter VSD closure, ADO I and ADO II are used in order to eliminate the risk of total atrioventricular block (TAVB) observed in follow-up with the use of the Amplatzer Perimembranous Ventricular Septal Occluder [12, 13]. Application of this device in children below 3 years old can lead to that complication in up to 18% of patients [14]. Theoretically, lower risk of TAVB is connected with a gentle construction of ADO II, namely thinner structure of the nitinol wire and lack of patches inside the occluder. In the case of ADO I there is a lack of a right retentional disk. In follow-up the appearance of TAVB, after the use of ADO I or ADO II for VSD closure, has not been described in any available literature (similarly to our study cases). An additional interesting aspect of this article is showing that Chinese PDA devices (very similar to ADO I) are as effective as original occluders. We documented that fact also in cases of transcatheter closure of ruptured sinus of Valsalva aneurysm [15] and coronary fistulas [16, 17]. Conclusions Transcatheter VSD closure with a proper morphology, with occluders of type Amplatzer Duct Occluder, constitutes a safe and effective therapeutic alternative in selected patients. References 1. Hassan MK, Hasan KA, Rahim AMA, et al. Residual ventricular septal defect after surgical repair of TOF a case report. Cardiovasc J 2011; 3: Erdem S, Ozbarlas N, Küçükosmanoglu O, et al. Long term follow-up of 799 children with isolated ventricular septal defects. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars 2012; 40: Miyake T, Shinohara T, Nakamura Y, et al. Spontaneous closure of ventricular septal defects followed up from <3 months of age. Pediatr Int 2004; 46: Dodge-Khatami A, Knirsch W, Tomaske M, et al. Spontaneous closure of small residual ventricular septal defects after surgical repair. Ann Thorac Surg 2007; 83: Walsh MA, Coleman DM, Oslizlok P, et al. Percutaneous closure of postoperative ventricular septal defects with the Amplatzer device. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2006; 67: Dua JS, Carminati M, Lucente M, et al. Transcatheter closure of postsurgical residual ventricular septal defects: early and midterm results. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2010; 75: Gu MB, Bai Y, Zhao XX, et al. Transcatheter closure of postoperative residual perimembranous ventricular septal defects. Ann Thorac Surg 2009; 88: Vaidyanathan B, Kannan BR, Kumar RK. Device closure of residual ventricular septal defect after repair of tetralogy of Fallot using the amplatzer duct occluder. Indian Heart J 2005; 57: Koneti NR, Sreeram N, Penumatsa RR, et al. Transcatheter retrograde closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects in children with the Amplatzer duct occluder II device. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012; 60: El Said HG, Bratincsak A, Gordon BM, et al. Closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects with aneurysmal tissue using the Amplazter Duct Occluder I: lessons learned and medium term follow up. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2012; 80: Devendran V, Koneti NR, Jesudian V. Transcatheter closure of multiple perimembranous ventricular septal defects with septal aneurysm using two overlapping Amplatzerr Duct Occluders II. Pediatr Cardiol 2013; 34: Walsh MA, Bialkowski J, Szkutnik M, et al. Atrioventricular block after transcatheter closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects. Heart 2006; 92: Zhou T, Shen XQ, Zhou SH, et al. Atrioventricular block: a serious complication in and after transcatheter closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects. Clin Cardiol 2008; 31: Predescu D, Chaturvedi RR, Friedberg MK, et al. Complete heart block associated with device closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2008; 136: Bialkowski J, Akdeniz C, Celebi A. Transcatheter closure in two rare cases of left-to-right shunt with Cardio-O-Fix occluders. Cardiol Young 2012; 22: Białkowski J, Szkutnik M, Fiszer R, Zembala M. Transcatheter occlusion of a large coronary artery fistula using a patent ductus arteriosus occluder. Kardiol Pol 2011; 69: Białkowski J, Szkutnik M, Zhang G, Jiang S. Large coronary artery fistula and patent ductus arteriosus: transcatheter closure with three PDA nitinol wire mesh occluders. Postep Kardiol Inter 2013; 9:
Type Size AP/PS RP/RS Qp/Qs. Ia Resistive <0.3 < Ib Resistive <0.3 < IIa Resistive <0.5 >2
 Transcatheter closure of VSD using Duct Occluder device Nguyen Lan Hieu, MD, PhD Hanoi Medical University Vietnam Heart Institute Anatomy of VSD 1. Perimembranous VSD: Aneurysm septal membranous(tv or
Transcatheter closure of VSD using Duct Occluder device Nguyen Lan Hieu, MD, PhD Hanoi Medical University Vietnam Heart Institute Anatomy of VSD 1. Perimembranous VSD: Aneurysm septal membranous(tv or
Percutaneous VSD closure
 Percutaneous VSD closure Gianfranco Butera San Donato Milanese - Italy Patients selection Pts having hemodynamically significant VSD Left ventricular enlargement (left ventricular overload),defined as
Percutaneous VSD closure Gianfranco Butera San Donato Milanese - Italy Patients selection Pts having hemodynamically significant VSD Left ventricular enlargement (left ventricular overload),defined as
Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children
 Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children Basil Thanopoulos, MD, PhD, a Nikolaos Eleftherakis, MD, a Konstantinos
Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children Basil Thanopoulos, MD, PhD, a Nikolaos Eleftherakis, MD, a Konstantinos
Case submission for CSI Asia-Pacific Case 2
 Case submission for CSI Asia-Pacific 2018- Case 2 Title Page Case category: Coarctation and ducts, valves Title: Simultaneous balloon aortic valvuloplasty with transcatheter closure of large hypertensive
Case submission for CSI Asia-Pacific 2018- Case 2 Title Page Case category: Coarctation and ducts, valves Title: Simultaneous balloon aortic valvuloplasty with transcatheter closure of large hypertensive
CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS IN ADULTS
 CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS IN ADULTS THE ROLE OF CATHETER INTERVENTIONS Mario Carminati CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS IN ADULTS CHD in natural history CHD with post-surgical sequelae PULMONARY VALVE STENOSIS
CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS IN ADULTS THE ROLE OF CATHETER INTERVENTIONS Mario Carminati CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS IN ADULTS CHD in natural history CHD with post-surgical sequelae PULMONARY VALVE STENOSIS
Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale using the internal jugular venous approach
 New methods in diagnosis and therapy Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale using the internal jugular venous approach Przemysław Węglarz 1,2, Ewa Konarska-Kuszewska 2, Tadeusz Zębik 2, Piotr Kuszewski
New methods in diagnosis and therapy Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale using the internal jugular venous approach Przemysław Węglarz 1,2, Ewa Konarska-Kuszewska 2, Tadeusz Zębik 2, Piotr Kuszewski
Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children
 Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children Shakeel A Qureshi, on behalf of: John P. Cheatham, MD George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Director Cardiac Catheterization &
Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children Shakeel A Qureshi, on behalf of: John P. Cheatham, MD George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Director Cardiac Catheterization &
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E42-E44 Percutaneous Closure of Iatrogenic Ventricular Septal Defect Following Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Using Two Different Approaches Takashi Matsumoto,
Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E42-E44 Percutaneous Closure of Iatrogenic Ventricular Septal Defect Following Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Using Two Different Approaches Takashi Matsumoto,
Index. cardiology.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
IMAGES. in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY. Abstract
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2008 Apr-Jun; 10(2): 11 17. PMCID: PMC3232589 Transcatheter closure of symptomatic aortopulmonary window in an infant F Pillekamp, 1 T Hannes, 1
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2008 Apr-Jun; 10(2): 11 17. PMCID: PMC3232589 Transcatheter closure of symptomatic aortopulmonary window in an infant F Pillekamp, 1 T Hannes, 1
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Uptofate Study Summary
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
Risk Factors and Outcomes of Post-Procedure Heart Blocks After Transcatheter Device Closure of Perimembranous Ventricular Septal Defect
 JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS VOL. 5, NO. 4, 2012 2012 BY THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY FOUNDATION ISSN 1936-8798/$36.00 PUBLISHED BY ELSEVIER INC. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcin.2012.01.015 Risk Factors
JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS VOL. 5, NO. 4, 2012 2012 BY THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY FOUNDATION ISSN 1936-8798/$36.00 PUBLISHED BY ELSEVIER INC. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcin.2012.01.015 Risk Factors
Percutaneous VSD closure: Problems in the mid- and long-term
 Percutaneous VSD closure: Problems in the mid- and long-term Lee Benson MD Professor Pediatrics (Cardiology) Director, Cardiac Diagnostic & Interventional Unit The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada
Percutaneous VSD closure: Problems in the mid- and long-term Lee Benson MD Professor Pediatrics (Cardiology) Director, Cardiac Diagnostic & Interventional Unit The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada
TCTAP C-217 Bilateral Pulmonary Arterio Venus Fistula Managed by Vascular Plugs and Coil Manotosh Panja 1 1 BelleVue Clinic, India
 S450 JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY, VOL. 65, NO. 17, SUPPL S, 2015 Case Summary. Aneurysm at LVOT is a rare complication after Bentall operation and the aneurysm may increase in size. In
S450 JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY, VOL. 65, NO. 17, SUPPL S, 2015 Case Summary. Aneurysm at LVOT is a rare complication after Bentall operation and the aneurysm may increase in size. In
Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle
 Case Report Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle Abstract Coronary artery fistula (CAF) is an uncommon anomaly usually congenital but can be acquired. Although,
Case Report Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle Abstract Coronary artery fistula (CAF) is an uncommon anomaly usually congenital but can be acquired. Although,
Congenital heart disease. By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics
 Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Perimembranous ventricular septal defects (pmvsds) are
 Transcatheter Closure of Congenital Perimembranous Ventricular Septal Defect in Children Using Symmetric Occluders: An 8-Year Multiinstitutional Experience Lei Wang, MD, PhD,* Sancheng Cao, MD, Jun Li,
Transcatheter Closure of Congenital Perimembranous Ventricular Septal Defect in Children Using Symmetric Occluders: An 8-Year Multiinstitutional Experience Lei Wang, MD, PhD,* Sancheng Cao, MD, Jun Li,
Patient guide: pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system. Catheter occlusion of. Patent Ductus Arteriosus. with the
 Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE. Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India
 INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India Why talk about it? What is the big deal? Are we not stating the obvious?
INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India Why talk about it? What is the big deal? Are we not stating the obvious?
Perimembranous VSD: When Do We Ask For A Surgical Closure? LI Xin. Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong
 Perimembranous VSD: When Do We Ask For A Surgical Closure? LI Xin Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong Classification (by Kirklin) I. Subarterial (10%) Outlet, conal, supracristal,
Perimembranous VSD: When Do We Ask For A Surgical Closure? LI Xin Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong Classification (by Kirklin) I. Subarterial (10%) Outlet, conal, supracristal,
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
IMAGES. in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2005 Jan-Mar; 7(1): 12 17. PMCID: PMC3232568 Stent implantation for coarctation facilitated by the anterograde trans-septal approach N Sreeram and
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2005 Jan-Mar; 7(1): 12 17. PMCID: PMC3232568 Stent implantation for coarctation facilitated by the anterograde trans-septal approach N Sreeram and
Efficacy and Safety of Using Amplatzer Ductal Occluder for Transcatheter Closure of Perimembranous Ventricular Septal Defect in Pediatrics
 Iran J Pediatr. 2015 April; 25(2):e386. Published online 2015 April 18. DOI: 10.5812/ijp.386 Research Article Efficacy and Safety of Using Amplatzer Ductal Occluder for Transcatheter Closure of Perimembranous
Iran J Pediatr. 2015 April; 25(2):e386. Published online 2015 April 18. DOI: 10.5812/ijp.386 Research Article Efficacy and Safety of Using Amplatzer Ductal Occluder for Transcatheter Closure of Perimembranous
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 5, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /99/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 5, 1999 1999 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00011-X Transcatheter
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 5, 1999 1999 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00011-X Transcatheter
Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD
 Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD John P. Cheatham, MD, MSCAI George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Co-Director, The Heart Center, Nationwide Children s Hospital Professor, Pediatrics
Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD John P. Cheatham, MD, MSCAI George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Co-Director, The Heart Center, Nationwide Children s Hospital Professor, Pediatrics
Index. interventional.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alagille syndrome, pulmonary artery stenosis in, 143 145, 148 149 Amplatz devices for atrial septal defect closure, 42 46 for coronary
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alagille syndrome, pulmonary artery stenosis in, 143 145, 148 149 Amplatz devices for atrial septal defect closure, 42 46 for coronary
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Treatment of Inter-MitraClip Regurgitation Due to Posterior Leaflet Cleft by Use of The Amplatzer Vascular Plug II device
 Volume 1, Issue 3 Case Report ISSN: 2572-9292 Treatment of Inter-MitraClip Regurgitation Due to Posterior Leaflet Cleft by Use of The Amplatzer Vascular Plug II device Neha M. Mantri, Gagan D. Singh, Thomas
Volume 1, Issue 3 Case Report ISSN: 2572-9292 Treatment of Inter-MitraClip Regurgitation Due to Posterior Leaflet Cleft by Use of The Amplatzer Vascular Plug II device Neha M. Mantri, Gagan D. Singh, Thomas
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
Delayed Infective Endocarditis with Mycotic Aneurysm Rupture below the Mechanical Valved Conduit after the Bentall Procedure
 Case Report Acta Cardiol Sin 2014;30:341 345 Delayed Infective Endocarditis with Mycotic Aneurysm Rupture below the Mechanical Valved Conduit after the Bentall Procedure Mei-Ling Chen, 1,3 Michael Y. Chen,
Case Report Acta Cardiol Sin 2014;30:341 345 Delayed Infective Endocarditis with Mycotic Aneurysm Rupture below the Mechanical Valved Conduit after the Bentall Procedure Mei-Ling Chen, 1,3 Michael Y. Chen,
Notes by Sandra Dankwa 2009 HF- Heart Failure DS- Down Syndrome IE- Infective Endocarditis ET- Exercise Tolerance. Small VSD Symptoms -asymptomatic
 Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Implantation of Cardioverter Defibrillator After Percutaneous Closure of Atrial Septal Defect
 The Ochsner Journal 10:27 31, 2010 f Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Implantation of Cardioverter Defibrillator After Percutaneous Closure of Atrial Septal Defect Anas Bitar, MD, Maria Malaya
The Ochsner Journal 10:27 31, 2010 f Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Implantation of Cardioverter Defibrillator After Percutaneous Closure of Atrial Septal Defect Anas Bitar, MD, Maria Malaya
Atrial Septal Defect Closure. Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs
 Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 Case Report With Brief Review J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E78-E80 Percutaneous Transjugular Device Closure of Postoperative Residual Atrial Septal Defect Saktheeswaran Mahesh Kumar, MD, DM, Sasidharan
Case Report With Brief Review J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E78-E80 Percutaneous Transjugular Device Closure of Postoperative Residual Atrial Septal Defect Saktheeswaran Mahesh Kumar, MD, DM, Sasidharan
Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder.
 Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder. First case with a novel delivery system. Werner Budts, Md, PhD, FESC Congenital and Structural Cardiology University
Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder. First case with a novel delivery system. Werner Budts, Md, PhD, FESC Congenital and Structural Cardiology University
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do?
 Leading Article Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do? Duminda Samarasinghe 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2010; 39: 39-43 (Key words: Congenital heart disease) Congenital heart disease
Leading Article Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do? Duminda Samarasinghe 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2010; 39: 39-43 (Key words: Congenital heart disease) Congenital heart disease
Congenital Heart Disease
 Congenital Heart Disease Mohammed Alghamdi, MD, FRCPC, FAAP, FACC Associate Professor and Consultant Pediatric Cardiology, Cardiac Science King Fahad Cardiac Centre King Saud University INTRODUCTION CHD
Congenital Heart Disease Mohammed Alghamdi, MD, FRCPC, FAAP, FACC Associate Professor and Consultant Pediatric Cardiology, Cardiac Science King Fahad Cardiac Centre King Saud University INTRODUCTION CHD
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Διαδερμική θεραπεία των παραβαλβιδικών διαφυγών Σ.Ράμμος
 ΔΜΙΝΑΡΙΟ ΔΠΙΣΗΜΟΝΙΚΩΝ ΔΝΩΔΩΝ ΔΛΛΗΝΙΚΟΤ ΚΟΛΛΔΓΙΟΤ ΚΑΡ ΙΟΛΟΓΙΑ 2-4.10.2015 Δπιζηημονική Ένωζη Δπεμβαηικής Καρδιολογίας Βαλβιδοπάθειες, Γιαδερμικές παρεμβάζεις Διαδερμική θεραπεία των παραβαλβιδικών διαφυγών
ΔΜΙΝΑΡΙΟ ΔΠΙΣΗΜΟΝΙΚΩΝ ΔΝΩΔΩΝ ΔΛΛΗΝΙΚΟΤ ΚΟΛΛΔΓΙΟΤ ΚΑΡ ΙΟΛΟΓΙΑ 2-4.10.2015 Δπιζηημονική Ένωζη Δπεμβαηικής Καρδιολογίας Βαλβιδοπάθειες, Γιαδερμικές παρεμβάζεις Διαδερμική θεραπεία των παραβαλβιδικών διαφυγών
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso
 2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia
 Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Transcatheter Closure Versus Repeat Surgery for the Treatment of Postoperative Left-to-Right Shunts: A Single Center 15-Year Experience
 Original Article Cardiol Res. 2017;8(6):286-292 Transcatheter Closure Versus Repeat Surgery for the Treatment of Postoperative Left-to-Right Shunts: A Single Center 15-Year Experience Xinghua Gu a, Qiuwang
Original Article Cardiol Res. 2017;8(6):286-292 Transcatheter Closure Versus Repeat Surgery for the Treatment of Postoperative Left-to-Right Shunts: A Single Center 15-Year Experience Xinghua Gu a, Qiuwang
ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗ ΑΣΘΕΝΩΝ ΜΕ ΜΕΣΟΚΟΛΠΙΚΗ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΑ ΖΑΧΑΡΑΚΗ ΑΓΓΕΛΙΚΗ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΗΡΑΚΛΕΙΟ - ΚΡΗΤΗ
 ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗ ΑΣΘΕΝΩΝ ΜΕ ΜΕΣΟΚΟΛΠΙΚΗ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΑ ΖΑΧΑΡΑΚΗ ΑΓΓΕΛΙΚΗ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΗΡΑΚΛΕΙΟ - ΚΡΗΤΗ European Accreditation in TTE, TEE and CHD Echocardiography NOTHING TO DECLARE ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT TYPES SECUNDUM
ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗ ΑΣΘΕΝΩΝ ΜΕ ΜΕΣΟΚΟΛΠΙΚΗ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΑ ΖΑΧΑΡΑΚΗ ΑΓΓΕΛΙΚΗ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΗΡΑΚΛΕΙΟ - ΚΡΗΤΗ European Accreditation in TTE, TEE and CHD Echocardiography NOTHING TO DECLARE ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT TYPES SECUNDUM
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao Ma 2, Chao Yang 2. Original Article
 Original Article Anatomic and surgical factors affecting the switch from minimally invasive transthoracic occlusion to open surgery during ventricular septal defect repair Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao
Original Article Anatomic and surgical factors affecting the switch from minimally invasive transthoracic occlusion to open surgery during ventricular septal defect repair Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao
ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGY
 ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE Aristides G. Panlilio, MD, FPCP, FPCC,FPSE, FASE Philippine Heart Center Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center
ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE Aristides G. Panlilio, MD, FPCP, FPCC,FPSE, FASE Philippine Heart Center Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center
Transcatheter Closure of Acute Myocardial Infarction VSD
 The 10 th Anniversary, Interventional Vascular Therapeutics ANGIOPLASTY SUMMIT 2005 TCT ASIA PACIFIC Transcatheter Closure of Acute Myocardial Infarction VSD Dr. Mullasari S Ajit Senior Consultant Cardiologist
The 10 th Anniversary, Interventional Vascular Therapeutics ANGIOPLASTY SUMMIT 2005 TCT ASIA PACIFIC Transcatheter Closure of Acute Myocardial Infarction VSD Dr. Mullasari S Ajit Senior Consultant Cardiologist
We present the case of an asymptomatic, 75-year-old
 Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Asymptomatic Rupture of the Left Ventricle Lech Paluszkiewicz, MD; Stefan Ożegowski, MD; Mohammad Amin Parsa, MD; Jan Gummert, PhD, MD We present the case of an asymptomatic,
Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Asymptomatic Rupture of the Left Ventricle Lech Paluszkiewicz, MD; Stefan Ożegowski, MD; Mohammad Amin Parsa, MD; Jan Gummert, PhD, MD We present the case of an asymptomatic,
UNMH Pediatric Cardiology Clinical Privileges. Name: Effective Dates: From To
 All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees, effective August 18, 2017: Initial Privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of Privileges (reappointment)
All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees, effective August 18, 2017: Initial Privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of Privileges (reappointment)
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology. Emma Walker 7 th May 2016
 Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects
 Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
TRANSCATHETER REPLACEMENT OF THE PULMONARY VALVE (PPVI)
 TRANSCATHETER REPLACEMENT OF THE PULMONARY VALVE (PPVI) BASIL D. THANOPOULOS MD, PhD Director Interventional Cardiology of CHD Euroclinic ATHENS - GREECE TRANSCATHETER REPLACEMENT OF THE PULMONARY VALVE
TRANSCATHETER REPLACEMENT OF THE PULMONARY VALVE (PPVI) BASIL D. THANOPOULOS MD, PhD Director Interventional Cardiology of CHD Euroclinic ATHENS - GREECE TRANSCATHETER REPLACEMENT OF THE PULMONARY VALVE
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments
 CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) In CY2015 and in an effort to help pay providers for quality, not
CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) In CY2015 and in an effort to help pay providers for quality, not
Originally Posted: November 15, 2014 BRUIT IN THE GROIN
 Originally Posted: November 15, 2014 BRUIT IN THE GROIN Resident(s): Donald ML Tse, MD Attending(s): KT Tan, MD Program/Dept(s): University Health Network/Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, ON, Canada CHIEF
Originally Posted: November 15, 2014 BRUIT IN THE GROIN Resident(s): Donald ML Tse, MD Attending(s): KT Tan, MD Program/Dept(s): University Health Network/Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, ON, Canada CHIEF
Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease
 Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Michael Vogel Kinderherz-Praxis München CHD missed in childhood Subsequent lesions after repaired CHD Follow-up of cyanotic heart disease CHD missed in
Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Michael Vogel Kinderherz-Praxis München CHD missed in childhood Subsequent lesions after repaired CHD Follow-up of cyanotic heart disease CHD missed in
Nit-Occlud. Coil System for PDA Closure IMPLANTATION POCKET GUIDE. Rx only CV / B. Braun Interventional Systems Inc.
 Refer to the Nit-Occlud PDA Instructions for Use for relevant warnings, precautions, complications and contraindications. This device has been designed for single use only. Nit-Occlud Coil System for PDA
Refer to the Nit-Occlud PDA Instructions for Use for relevant warnings, precautions, complications and contraindications. This device has been designed for single use only. Nit-Occlud Coil System for PDA
CMR for Congenital Heart Disease
 CMR for Congenital Heart Disease * Second-line tool after TTE * Strengths of CMR : tissue characterisation, comprehensive access and coverage, relatively accurate measurements of biventricular function/
CMR for Congenital Heart Disease * Second-line tool after TTE * Strengths of CMR : tissue characterisation, comprehensive access and coverage, relatively accurate measurements of biventricular function/
Percutaneous Device Closure of Congenital VSDs Current techniques and results for treating ventricular septal defects.
 Percutaneous Device Closure of Congenital VSDs Current techniques and results for treating ventricular septal defects. BY KARIM A. DIAB, MD; QI-LING CAO, MD; AND ZIYAD M. HIJAZI, MD, MPH During the past
Percutaneous Device Closure of Congenital VSDs Current techniques and results for treating ventricular septal defects. BY KARIM A. DIAB, MD; QI-LING CAO, MD; AND ZIYAD M. HIJAZI, MD, MPH During the past
Paediatrica Indonesiana
 Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 53 July NUMBER 4 Original Article Transcatheter vs. surgical closure of patent ductus arteriosus: outcomes and cost analysis Mulyadi M Djer, Mochammading, Mardjanis Said
Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 53 July NUMBER 4 Original Article Transcatheter vs. surgical closure of patent ductus arteriosus: outcomes and cost analysis Mulyadi M Djer, Mochammading, Mardjanis Said
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Follow-up after VSD closure- what to look for?
 The 3rd Congress of Congenital heart disease Ventricular Septal Defect from A-Z January 9-11. 2013, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam Follow-up after VSD closure- what to look for? Nina Wunderlich University Hospital
The 3rd Congress of Congenital heart disease Ventricular Septal Defect from A-Z January 9-11. 2013, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam Follow-up after VSD closure- what to look for? Nina Wunderlich University Hospital
Percutaneous closure of large VSD using a home-made fenestrated atrial septal occluder in 18-year-old with pulmonary hypertension
 Kamali et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 2014, 14:74 CASE REPORT Percutaneous closure of large VSD using a home-made fenestrated atrial septal occluder in 18-year-old with pulmonary hypertension Hacer
Kamali et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 2014, 14:74 CASE REPORT Percutaneous closure of large VSD using a home-made fenestrated atrial septal occluder in 18-year-old with pulmonary hypertension Hacer
Device closure of congenital ventricular septal defects with Amplatzer devices: first experiences in Turkey
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2008; 50: 106-113 Original Device closure of congenital ventricular septal defects with Amplatzer devices: first experiences in Turkey Alpay Çeliker, Süheyla Özkutlu,
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2008; 50: 106-113 Original Device closure of congenital ventricular septal defects with Amplatzer devices: first experiences in Turkey Alpay Çeliker, Süheyla Özkutlu,
Interventions in Adult Congenital Heart Disease: Role of CV Imaging. Associate Professor. ACHD mortality. Pillutla. Am Heart J 2009;158:874-9
 Interventions in Adult Congenital Heart Disease: Role of CV Imaging Sangeeta Shah MD, FACC, FASE Associate Professor ACHD mortality Pillutla. Am Heart J 2009;158:874-9 Adult Congenital Heart Disease Heterogenity
Interventions in Adult Congenital Heart Disease: Role of CV Imaging Sangeeta Shah MD, FACC, FASE Associate Professor ACHD mortality Pillutla. Am Heart J 2009;158:874-9 Adult Congenital Heart Disease Heterogenity
Journal of Rare Cardiovascular Diseases 2017; 3 (2):
 Journal of Rare Cardiovascular Diseases 2017; 3 (2): 59 64 www.jrcd.eu CSE REPORT Rare congenital cardiovascular diseases Transcatheter closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defect with muscular
Journal of Rare Cardiovascular Diseases 2017; 3 (2): 59 64 www.jrcd.eu CSE REPORT Rare congenital cardiovascular diseases Transcatheter closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defect with muscular
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease
 5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Transcatheter Atrial Septal Defect Closure with Right Aortic Arch Is it really difficult? M Tokue, H Hara, K Sugi, M Nakamura
 5th Asia Pacific Congenital & Structural Heart Intervention Symposium 2014 10 12 October 2014, Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre Organizer: Hong Kong Society of Congenital & Structural Heart Disease
5th Asia Pacific Congenital & Structural Heart Intervention Symposium 2014 10 12 October 2014, Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre Organizer: Hong Kong Society of Congenital & Structural Heart Disease
Research Article A New Coated Nitinol Occluder for Transcatheter Closure of Ventricular Septal Defects in a Canine Model
 BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 507919, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/507919 Research Article A New Coated Nitinol Occluder for Transcatheter Closure of Ventricular Septal
BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 507919, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/507919 Research Article A New Coated Nitinol Occluder for Transcatheter Closure of Ventricular Septal
Journal of Pediatric Sciences
 Journal of Pediatric Sciences Rupture of sinus of valsalva aneurysm: earliest presentation in association with ventricular septal defect and aortic regurgitation Binoy Shankar, Sanjay Kumar, Dinesh Kumar
Journal of Pediatric Sciences Rupture of sinus of valsalva aneurysm: earliest presentation in association with ventricular septal defect and aortic regurgitation Binoy Shankar, Sanjay Kumar, Dinesh Kumar
Arrhythmias and congenital heart disease
 Arrhythmias and congenital heart disease Jolien Roos-Hesselink ErasmusMC Rotterdam Netherlands Patient W, born in 1969 Tetralogy of Fallot 1975 at the age of 6 years surgical correction 2002 Patient W:
Arrhythmias and congenital heart disease Jolien Roos-Hesselink ErasmusMC Rotterdam Netherlands Patient W, born in 1969 Tetralogy of Fallot 1975 at the age of 6 years surgical correction 2002 Patient W:
Initial Human Experience. Objectives: To evaluate the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of the Occlutech VR
 Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 00:00 00 (2015) Original Studies The New Occlutech V R PDA Occluder: Initial Human Experience M. A. Elbashier Abdelbasit, 1 * MBBS, MD, Mazeni Alwi, 1 MBBS,
Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 00:00 00 (2015) Original Studies The New Occlutech V R PDA Occluder: Initial Human Experience M. A. Elbashier Abdelbasit, 1 * MBBS, MD, Mazeni Alwi, 1 MBBS,
A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia
 A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia syndrome. Dr Anvesha Singh, Dr James Ogle, Dr Derek
A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia syndrome. Dr Anvesha Singh, Dr James Ogle, Dr Derek
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 12-00415 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E69-E71 A Concert in the Heart. Bilateral Melody Valve Implantation in the Branch Pulmonary Arteries Nicola Maschietto, MD, PhD and Ornella Milanesi,
12-00415 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E69-E71 A Concert in the Heart. Bilateral Melody Valve Implantation in the Branch Pulmonary Arteries Nicola Maschietto, MD, PhD and Ornella Milanesi,
Echocardiographic assessment in Adult Patients with Congenital Heart Diseases
 Echocardiographic assessment in Adult Patients with Congenital Heart Diseases Athanasios Koutsakis Cardiologist, Cl. Research Fellow George Giannakoulas Ass. Professor in Cardiology 1st Cardiology Department,
Echocardiographic assessment in Adult Patients with Congenital Heart Diseases Athanasios Koutsakis Cardiologist, Cl. Research Fellow George Giannakoulas Ass. Professor in Cardiology 1st Cardiology Department,
Late presentation of anomalous origin of the left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (ALCAPA) was confused with coronary artery fistula.
 Case Report http://www.alliedacademies.org/annals-of-cardiovascular-and-thoracic-surgery/ Late presentation of anomalous origin of the left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (ALCAPA) was confused
Case Report http://www.alliedacademies.org/annals-of-cardiovascular-and-thoracic-surgery/ Late presentation of anomalous origin of the left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (ALCAPA) was confused
TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react
 TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react Folkert Meijboom, MD, PhD, FES Dept ardiology University Medical entre Utrecht The Netherlands TGA + atrial switch: Follow-up
TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react Folkert Meijboom, MD, PhD, FES Dept ardiology University Medical entre Utrecht The Netherlands TGA + atrial switch: Follow-up
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience
 Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience Ximing Wang, M.D., Zhaoping Cheng, M.D., Dawei Wu, M.D., Lebin
Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience Ximing Wang, M.D., Zhaoping Cheng, M.D., Dawei Wu, M.D., Lebin
Case Report International Journal of Basic and Clinical Studies (IJBCS) 2013;1(1): Elbey MA et al.
 Treatment of Interrupted Aorta in Adult Patients; a Challenge Both in Surgery and Transcatheter Intervention Mehmet Ali Elbey MD 1, Ahmet Caliskan MD 2, Ferhat Isık MD 1, Faruk Ertas MD 1, Mehmet Serdar
Treatment of Interrupted Aorta in Adult Patients; a Challenge Both in Surgery and Transcatheter Intervention Mehmet Ali Elbey MD 1, Ahmet Caliskan MD 2, Ferhat Isık MD 1, Faruk Ertas MD 1, Mehmet Serdar
Stenosis of Pulmonary Veins
 Stenosis of Pulmonary Veins Report of a Patient Corrected Surgically Yasunaru Kawashima, M.D., Takeshi Ueda, M.D., Yasuaki Naito, M.D, Eiji Morikawa, M.D., and Hisao Manabe, M.D. ABSTRACT A 15-year-old
Stenosis of Pulmonary Veins Report of a Patient Corrected Surgically Yasunaru Kawashima, M.D., Takeshi Ueda, M.D., Yasuaki Naito, M.D, Eiji Morikawa, M.D., and Hisao Manabe, M.D. ABSTRACT A 15-year-old
Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum
 Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum Craig E Fleishman, MD FACC FASE The Heart Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2013 Las Vegas Disclosure Information
Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum Craig E Fleishman, MD FACC FASE The Heart Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2013 Las Vegas Disclosure Information
Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.1, March 2000 Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant F Hakim, MD* A Madani, MD* A Abu Haweleh, MD,MRCP*
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.1, March 2000 Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant F Hakim, MD* A Madani, MD* A Abu Haweleh, MD,MRCP*
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: The New Reality. Disclosures
 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: The New Reality Kathryn Rouine-Rapp, MD Professor of Anesthesia Disclosures I have nothing to disclose 1 Outline Historic perspective Our reality Common lesions Guidelines
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: The New Reality Kathryn Rouine-Rapp, MD Professor of Anesthesia Disclosures I have nothing to disclose 1 Outline Historic perspective Our reality Common lesions Guidelines
Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease
 Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease Introduction A therapeutic cardiac catheterization is a procedure performed to treat your child s heart defect. A doctor
Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease Introduction A therapeutic cardiac catheterization is a procedure performed to treat your child s heart defect. A doctor
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Fabien Praz, Andreas Wahl, Sophie Beney, Stephan Windecker, Heinrich P. Mattle*, Bernhard Meier
 Procedural Outcome after Percutaneous Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale using the Amplatzer PFO Occluder Without Intra-Procedural Echocardiography in 1,000 Patients Fabien Praz, Andreas Wahl, Sophie Beney,
Procedural Outcome after Percutaneous Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale using the Amplatzer PFO Occluder Without Intra-Procedural Echocardiography in 1,000 Patients Fabien Praz, Andreas Wahl, Sophie Beney,
A case report: Percutaneous transcatheter treatment of Lutembacher syndrome
 A case report: Percutaneous transcatheter treatment of Lutembacher syndrome Dr. Sainath Hegde* Dr. Tukaram Aute** *Registrar, Dept of Cardiology, M.G.M Hospital, Aurangabad. **Asst. Prof, Dept of Cardiology,
A case report: Percutaneous transcatheter treatment of Lutembacher syndrome Dr. Sainath Hegde* Dr. Tukaram Aute** *Registrar, Dept of Cardiology, M.G.M Hospital, Aurangabad. **Asst. Prof, Dept of Cardiology,
Nit-Occlud. Coil System for PDA Closure PATIENT EDUCATIONAL BROCHURE
 Nit-Occlud PDA Coil System for PDA Closure PATIENT EDUCATIONAL BROCHURE A Patient s Educational Brochure to Non-Surgical Closure of the Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Using the Nit-Occlud PDA Inside This
Nit-Occlud PDA Coil System for PDA Closure PATIENT EDUCATIONAL BROCHURE A Patient s Educational Brochure to Non-Surgical Closure of the Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Using the Nit-Occlud PDA Inside This
Mitral Valve Disease, When to Intervene
 Mitral Valve Disease, When to Intervene Swedish Heart and Vascular Institute Ming Zhang MD PhD Interventional Cardiology Structure Heart Disease Conflict of Interest None Current ACC/AHA guideline Stages
Mitral Valve Disease, When to Intervene Swedish Heart and Vascular Institute Ming Zhang MD PhD Interventional Cardiology Structure Heart Disease Conflict of Interest None Current ACC/AHA guideline Stages
Research Presentation June 23, Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine
 Research Presentation June 23, 2009 Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine Research Question In adult patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot, how does Echocardiography compare to MRI in evaluating
Research Presentation June 23, 2009 Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine Research Question In adult patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot, how does Echocardiography compare to MRI in evaluating
Percutaneous Intervention for totally Occluded Coarctation Of Aorta. John Jose, Vipin Kumar, Ommen K George Dept Of Cardiology
 Percutaneous Intervention for totally Occluded Coarctation Of Aorta John Jose, Vipin Kumar, Ommen K George Dept Of Cardiology Background Coarctation of aorta (CoA) forms 5-7% of congenital heart diseases
Percutaneous Intervention for totally Occluded Coarctation Of Aorta John Jose, Vipin Kumar, Ommen K George Dept Of Cardiology Background Coarctation of aorta (CoA) forms 5-7% of congenital heart diseases
Stent implantation into the patent ductus arteriosus in cyanotic congenital heart disease with duct-dependent or diminished pulmonary circulation
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2007; 49: 413-417 Original Stent implantation into the patent ductus arteriosus in cyanotic congenital heart disease with duct-dependent or diminished pulmonary circulation
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2007; 49: 413-417 Original Stent implantation into the patent ductus arteriosus in cyanotic congenital heart disease with duct-dependent or diminished pulmonary circulation
PDA Device Closure with and without Arterial Access
 Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Interventional Cardiology Journal DOI: 10.21767/2471-8157.100061 Abstract PDA Device Closure with and without Arterial Access Background: PDA device closure
Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Interventional Cardiology Journal DOI: 10.21767/2471-8157.100061 Abstract PDA Device Closure with and without Arterial Access Background: PDA device closure
