HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
|
|
|
- Maude Reeves
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
2 Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research, influencing public policy, advice and information and support in the community. The information contained in this booklet is based on current guidelines and is correct at time of printing. The content has undergone peer, patient and expert review. If you have any comments about this booklet please or tel:
3 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Introduction 2 How do the electrical signals work? 3 What happens in atrial fibrillation (AF)? 4 Different types of AF 5 What are the symptoms of AF? 6 What causes AF? 7 What triggers AF? 8 What are the risks of AF? 8 What tests might be needed? 9 What is the treatment for AF? 11 Prevention of blood clots and stroke 13 Useful addresses and websites 15 Image on cover used with kind permission of NHS Scotland Crown Copyright 2009 Image on p10 used with kind permission of A-Fib.com Understanding Atrial Fibrillation 1
4 INTRODUCTION The function of your heart is to pump blood round your whole body. To do this the four chambers of your heart (2 atria and 2 ventricles) have to pump regularly and in sequence. The muscular pumping action of your heart is triggered by electrical signals which are sent through your heart muscle telling it when to contract (squeeze) and relax. If the electrical signals within your heart are disturbed this is called an arrhythmia. Your heart can beat too quickly (tachycardia), too slowly (bradycardia) and / or in an irregular way. A normal heartbeat should be between 60 and 100 beats at rest. If you have Atrial Fibrillation (AF) your heartbeat will be irregular and may be as high as 200 beats per minute at rest. AF is the most common type of heart arrhythmia. AF can affect adults of any age but it is more common in men than women and becomes more common with age. It affects approximately 2% of the general population, increasing to over 6% in people aged over Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
5 HOW DO THE ELECTRICAL SIGNALS WORK? Normally the electrical signal starts in the right atrium (see Figure 1) where the heart s natural pacemaker, the sino-atrial node, is situated. This signal crosses the atria, making them contract. Blood is then pumped through the valves into the ventricles. Figure 1. Diagram of electrical pathway Sino-atrial node: the heart s natural pacemaker Atrio-ventricular node: the heart s junction box Conducting system Where the atria meet the ventricles there is an area of special cells called the atrio-ventricular node. These cells act as a junction box and pass the electrical signals throughout the heart muscle by a system of electrical pathways known as the conducting system. This makes the ventricles contract. Blood is then pumped through the pulmonary and aortic valves into the main arteries. The pacemaker produces another electrical signal and the pumping cycle starts again. Understanding Atrial Fibrillation 3
6 WHAT HAPPENS IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION? In AF the electrical signals in the atria become chaotic and disorganised making the atria contract very rapidly and in an irregular way. This is known as fibrillation. The atrio-ventricular node can not pass on all of these signals to the ventricles but it still results in fast and irregular contraction of the ventricles. This fast, irregular rhythm prevents the heart from pumping effectively and the circulation of blood can be impaired. ECG tracing of a normal heart rhythm In atrial fibrillation, the tracing shows tiny irregular fibrillation waves between heartbeats. The rhythm is irregular and erratic. 4 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
7 DIFFERENT TYPES OF AF There are different types of AF and different degrees of severity. Each situation will be treated differently depending on how it affects the individual person. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation comes and goes and usually stops within 48 hours without any treatment. Persistent atrial fibrillation lasts for longer than 7 days and can be treated with drugs or by cardioversion to help the heart return to beating normally (see section on treatments later in this booklet). Permanent or chronic atrial fibrillation lasts for a long time (usually longer than a year). Cardioversion is rarely used in this case and is not usually successful. Drug treatment can be used to help control the heart rate. Acute-onset atrial fibrillation is an episode of AF that either starts suddenly (for the first time) or when existing AF becomes suddenly worse. This kind of AF can cause potentially dangerous symptoms (e.g. very fast heart rate) which may need to be treated in hospital. Understanding Atrial Fibrillation 5
8 WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF AF? There are varying symptoms with AF depending on the effect it has. Some people have no symptoms and AF is only discovered when a nurse or doctor feels your pulse and finds it to be fast and irregular (no pattern to the beats). However, when the heart beats fast and in an irregular way it can not work efficiently and the following symptoms may occur: dizziness tiredness chest pain shortness of breath palpitations (increased awareness of your heartbeat) If you notice a sudden change in your heartbeat and have chest pain you should always seek urgent medical advice. 6 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
9 WHAT CAUSES AF? Sometimes AF develops along with other medical conditions such as: heart conditions such as: high blood pressure, coronary heart disease (especially after a heart attack or heart surgery), heart valve disease, congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathy lung conditions such as: pulmonary embolism, asthma, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia and lung cancer an overactive thyroid gland diabetes imbalances in the blood, e.g. potassium and calcium Sometimes the cause of AF is unknown. Understanding Atrial Fibrillation 7
10 WHAT TRIGGERS AF? There are a variety of situations that can trigger an episode of, or contribute to, AF: drinking excessive amounts of alcohol, particularly binge drinking being overweight drinking a lot of caffeine, e.g. coffee, tea and energy drinks taking illegal drugs, particularly those that stimulate the heart, e.g. amphetamines ( speed ) or cocaine smoking Learning to recognise your individual trigger factors and reducing, or avoiding, them can sometimes help to minimise the symptoms of AF. WHAT ARE THE RISKS OF AF? Stroke The main risk of AF is causing a stroke. When the atria are not pumping effectively they do not always empty completely leaving a pool of blood in the chamber. This blood can become sludgy and may clot. If a blood clot enters the blood stream it may travel to the brain and lead to a stroke. Heart failure Over time AF can weaken the heart. When the heart muscle can not meet the body s demands for blood and oxygen the body develops a range of different symptoms. When this happens it is referred to as heart failure because of the failure of the heart to work efficiently. 8 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
11 WHAT TESTS MIGHT BE NEEDED? Your doctor may decide to do some tests to diagnose AF and identify any possible underlying causes. ECG ECG stands for electrocardiogram, which gives a recording of the electrical activity of the heart in the form of a graph. Electrodes attached to sticky patches, are positioned on your chest, wrists and ankles and a recording is made. Each lead gives a view of the electrical activity of the heart from a particular angle across the body. The ECG reflects what is happening in different areas of the heart and helps to show up any abnormality in conduction. An ECG is painless and the procedure usually takes about 5-10 minutes. An ECG can confirm the diagnosis of AF and can also help to rule out other types of arrhythmia. Variations of ECG include: 24-hour ECG: (also known as 24-hour tape, holter monitor or ambulatory ECG) This records the activity of your heart over a 24 hour period as you go about your normal daily activities and can identify if you are having even just short periods of AF. Exercise ECG ( stress test or treadmill test ): this records the activity of your heart as you make it work harder, i.e. by walking on a treadmill. You Understanding Atrial Fibrillation 9
12 will be closely monitored by medical staff during this test. It will be used to identify any underlying problems with the heart which have led to AF. Not everyone is able or fit enough to have this test or needs it. Echocardiogram ( echo ) This is an ultrasound scan of the heart. It can help to identify any other heart problems and assess the structure and function of the heart and valves. Chest x-ray This will help to rule out any lung problems that might cause AF. Blood tests These are taken to rule out any imbalances in your blood that might cause AF or need to be corrected, e.g. thyroid function, electrolytes. 10 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
13 WHAT IS THE TREATMENT FOR AF? Factors that your doctor should consider when deciding what treatment, if any, is best for your individual circumstances include: what type of AF you have what symptoms you have treatment of any underlying causes you have your age your overall health Depending on what treatment you receive you may have to attend regular follow up appointments to help assess how the treatment is working for you. These may be with your GP or with a specialist heart doctor (cardiologist) or nurse. Treatment for AF involves the following: controlling the heart rate (i.e. how fast it beats) controlling the heart rhythm (i.e. how regularly it beats) prevention of blood clots and stroke Drug treatment It is important that you take any prescribed drugs regularly and discuss any troublesome side effects, as well as any new symptoms, with your doctor. Sometimes you may have to try several different treatments until you find the right one for you. The following groups of drugs can be used to treat AF: beta-blockers calcium-channel blockers anti-arrhythmics Understanding Atrial Fibrillation 11
14 See the CHSS booklet Understanding heart disease for more information about commonly used heart drugs. Cardioversion Sometimes a treatment called cardioversion may be used, either on its own or in addition to drug treatment. Only some people with AF will be benefit from cardioversion treatment. Your heart specialist will carefully consider whether this is a possible treatment option for you. Cardioversion uses a controlled electric shock to the heart, from a machine called a defibrillator, to restore the normal heart rhythm. Cardioversion allows the conduction system of the heart to reset. It can be performed under a general anaesthetic or with sedation. Cardioversion can be repeated if necessary. Other treatments that are used to treat AF: Catheter ablation Catheter ablation is a surgical procedure where any areas producing electrical signals which interfere with the natural pacemaker, are destroyed using a laser. Insertion of an artificial pacemaker device A pacemaker is a device that sends electrical pulses to your heart to keep it beating regularly. Some people with atrial fibrillation have a slower pulse rate than normal. In this case a pacemaker may be recommended. 12 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
15 PREVENTION OF BLOOD CLOTS AND STROKE If you have AF then you may have an increased risk of blood clots and stroke (a stroke happens when a blood clot blocks an artery in the brain). Your doctor may prescribe a medicine to reduce the risk of blood clotting and therefore reduce the risk of a stroke. This medicine is called an anticoagulant. Warfarin is the most commonly used anticoagulant in people with AF but the use of the newer direct oral anticoagulants (dabigatran etexilate, rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban) is increasing. If you are prescribed warfarin you will need regular blood tests and your treatment will be closely monitored by your doctor and / or nurse. Your doctor will decide which type of drug is best for you and for how long you should take it. As well as benefit of risk reduction, there are risks associated with anticoagulants such as a risk of bleeding more than usual if you are cut or injured. Except in an emergency, your doctor should discuss these benefits and risks with you before you decide whether to go ahead with treatment. Understanding Atrial Fibrillation 13
16 Warfarin Warfarin is the anticoagulant most commonly used in AF. If you are prescribed warfarin you will need regular blood tests and your treatment will be closely monitored by your doctor and / or nurse. How is my warfarin monitored? The effect of warfarin is monitored by regular blood tests, that measure how long it takes your blood to clot, called the PT (Prothrombin Time) or INR (International Normalised Ratio of Prothrombin Time). Based on this blood result your doctor will be able to prescribe the appropriate dose of warfarin that will help to keep your warfarin levels within the desired range for you. See the CHSS factsheet Warfarin for more information. Direct oral anticoagulant drugs (DOACs) Direct oral anticoagulant drugs inhibit (prevent) clots from forming in the blood. Direct oral anticoagulant drugs currently in use in the UK are: Dabigatran (Pradaxa ) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) Apixaban (Eliquis ) Edoxaban (Lixiana ) These drugs may be more suitable for some people with atrial fibrillation. Your doctor will be able to discuss this with you. 14 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
17 USEFUL ADDRESSES AND WEBSITES AntiCoagulation Europe PO Box 405, Bromley, Kent BR2 9WP Tel: Website: Arrhythmia Alliance PO Box 3697, Stratford-Upon-Avon Warwickshire CV37 8YL 24-hour helpline: Website: Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland Rosebery House, 9 Haymarket Terrace, Edinburgh EH12 5EZ Tel: Fax: Advice Line nurses: adviceline@chss.org.uk Website: Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research, influencing public policy, advice and information and support in the community. Understanding Atrial Fibrillation 15
18 Stroke nformation Do you have any questions about chest heart or stroke illness? ASK THE NURSE nformation information FREEPHONE For confidential help, support and advice, call our specialist nurses or visit Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland (CHSS) is a wholly Scottish charity Scottish Charity Number SC Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
19 HEART PUBLICATIONS Booklets Factsheets Free H1 Living with Angina F1 Stopping Smoking H2 Reducing the Risk of Heart Disease F2 Salt H4 Living with High Blood Pressure F3 Cholesterol H5 Living with Heart Failure F4 Warfarin H7 Heart Attack: A Guide to your Recovery F6 Holiday information H9 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation F7 Travel and motor insurance F13 Air travel F17 Diabetes: links with heart disease and stroke F18 Coping with tiredness F22 How to make the most of a visit to your doctor F23 Living with stress and anxiety F24 Healthy eating F30 Just move! F37 Coping with low mood/depression F39 Understanding the need for change after a heart attack F40 Losing weight F41 Financial support for people affected by chest heart or stroke illness A full publication list is available from Head Office. Rosebery House, 9 Haymarket Terrace, Edinburgh EH12 5EZ Tel: Please send me the following: ORDER FORM TITLE No. of copies Up to 100 booklets free, up to 100 factsheets free If you wish to order more than 100 booklets or factsheets please contact the Health Information team at the address above. Name: Address: Postcode: Tel:
20 Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland is a wholly independent Scottish charity. We receive no core funding from Government or any public body or private agency. We need your help to achieve our aim of improving the lives of those in Scotland with chest, heart and stroke illness. See insert for more information. CONTACT US Head Office Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland Rosebery House 9 Haymarket Terrace Edinburgh EH12 5EZ Tel: Open Mon Fri West Office: Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland West of Scotland Regional Office The Hub, 70 Pacific Quay Glasgow G51 1DZ Tel: westoffice@chss.org.uk Open Mon Fri North Office: Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland North of Scotland Regional Office 5 Mealmarket Close Inverness IV1 1HS Tel: northoffice@chss.org.uk Open Mon Fri Registered with and regulated by the Office of the Scottish Charity Regulator (no SC018761), Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland is a wholly Scottish charity. It also operates as CHSS and is registered in Scotland as a company limited by guarantee, no SC October 2013 (revised December 2016) Designed by Creative Link, North Berwick
Fibrillation. Living. withatrial. Further information
 Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
Atrial fibrillation. Understanding NICE guidance
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Atrial fibrillation NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Atrial fibrillation NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke
 Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat. It means that your heart may not be pumping
Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat. It means that your heart may not be pumping
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias)
 Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
Special health. guide. Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding. Atrial Fibrillation WITH
 Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary
 X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
Arrhythmias. Pulmonary Artery
 Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion
 Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
Atrial Fibrillation. Damage to your heart caused by a heart attack or rheumatic heart disease
 Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Management strategies for atrial fibrillation Thursday, 20 October :27
 ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease
 Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Catheter Ablation. Patient Education
 Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy
 Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy This leaflet offers more information about atrial fibrillation for patients who have been advised that they need anticoagulation therapy. If you have any
Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy This leaflet offers more information about atrial fibrillation for patients who have been advised that they need anticoagulation therapy. If you have any
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants
 Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: York Anticoagulant Clinic Tel: 01904
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: York Anticoagulant Clinic Tel: 01904
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias
 Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 www.irishheart.ie AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Registered charity number CHY 5507 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation This booklet is one of the publications
www.irishheart.ie AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Registered charity number CHY 5507 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation This booklet is one of the publications
Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I (888)
 Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I was exhausted doing simple tasks because of my AFib. I couldn t walk from the store to my car in the parking lot. Then, I had a MAZE procedure. It was a very
Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I was exhausted doing simple tasks because of my AFib. I couldn t walk from the store to my car in the parking lot. Then, I had a MAZE procedure. It was a very
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide
 Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Information for patients, parents and guardians. Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation.
 Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE. Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation TABLE OF CONTENTS IMPORTANT Please Note: Information provided by Boston Scientific Corporation
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation TABLE OF CONTENTS IMPORTANT Please Note: Information provided by Boston Scientific Corporation
Understanding. Atrial Fibrillation. For more information, visit. CardioSmart.org/AFib
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation For more information, visit CardioSmart.org/AFib Understanding Atrial Fibrillation What is ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AFib)? When it s operating normally, your heart pumps to
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation For more information, visit CardioSmart.org/AFib Understanding Atrial Fibrillation What is ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AFib)? When it s operating normally, your heart pumps to
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
INFORMATION. Atrial Fibrillation. Summary. Information from the
 1. Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Atrial Fibrillation INFORMATION Summary What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is
1. Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Atrial Fibrillation INFORMATION Summary What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, shortened to COPD, is an umbrella term for a group of conditions which cause long-term damage to the airways.
 10 Common QuESTIonS AbouT CoPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, shortened to COPD, is an umbrella term for a group of conditions which cause long-term damage to the airways. COPD includes: chronic
10 Common QuESTIonS AbouT CoPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, shortened to COPD, is an umbrella term for a group of conditions which cause long-term damage to the airways. COPD includes: chronic
Catheter Ablation for Atrial Flutter
 Additional Notes Our mission Providing the excellent care we would expect for our own families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Additional Notes Our mission Providing the excellent care we would expect for our own families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
STROKE SERIES SS3 REDUCING THE RISK OF STROKE
 STROKE SERIES SS3 REDUCING THE RISK OF STROKE Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland is determined to deliver stronger, longer lives to people in Scotland affected by chest and heart illness and by stroke, through
STROKE SERIES SS3 REDUCING THE RISK OF STROKE Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland is determined to deliver stronger, longer lives to people in Scotland affected by chest and heart illness and by stroke, through
BIOTRONIK Clinical Studies IMPACT Clinical Study Patient Information. IMPACT Clinical Study: Patient Information Guide
 BIOTRONIK Clinical Studies IMPACT Clinical Study Patient Information IMPACT Clinical Study: Patient Information Guide Introduction and Objectives IMPACT is a clinical research study. Approximately 2,700
BIOTRONIK Clinical Studies IMPACT Clinical Study Patient Information IMPACT Clinical Study: Patient Information Guide Introduction and Objectives IMPACT is a clinical research study. Approximately 2,700
Direct Current Cardioversion (DCCV)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is a This is a procedure carried out under a brief anaesthetic, which uses a
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is a This is a procedure carried out under a brief anaesthetic, which uses a
Introduction. What atrial fibrillation (AF) is Warning signs & symptoms, and risk factors for developing AFrelated
 Got FIB? Introduction FAST, IRREGULAR heartbeats = FIB FIB is short for fibrillation fibrillation, or quivering of the top two chambers of the heart (the atria) Important that you understand: What atrial
Got FIB? Introduction FAST, IRREGULAR heartbeats = FIB FIB is short for fibrillation fibrillation, or quivering of the top two chambers of the heart (the atria) Important that you understand: What atrial
Atrial fibrillation and you. Atrial fibrillation and your treatment options
 Atrial fibrillation and you Atrial fibrillation and your treatment options What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation The Normal Heart Rhythm Electrical System of the Heart The heart pumps blood to
Atrial fibrillation and you Atrial fibrillation and your treatment options What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation The Normal Heart Rhythm Electrical System of the Heart The heart pumps blood to
stroke.org.uk Atrial Fibrillation Reducing your risk of stroke
 stroke.org.uk Atrial Fibrillation Reducing your risk of stroke What is AF? Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat. Over 1 million people in the UK are living with the condition,
stroke.org.uk Atrial Fibrillation Reducing your risk of stroke What is AF? Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat. Over 1 million people in the UK are living with the condition,
How does the heart work? The heart is muscle whose main function is a pump; to push blood the rest of your body.
 1 You have a condition called atrial fibrillation. I would like you to learn more about this condition. You should read about it below, and can also watch an Internet program about it. After reading about
1 You have a condition called atrial fibrillation. I would like you to learn more about this condition. You should read about it below, and can also watch an Internet program about it. After reading about
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps
 Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS. A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology MY LIFE HAS TAKEN A TURN FOR THE BETTER. -Emie Bishop ARRHYTHMIAANSWERS.COM AF ANSWERS. A PATIENT EDUCATION HANDBOOK ON ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology MY LIFE HAS TAKEN A TURN FOR THE BETTER. -Emie Bishop ARRHYTHMIAANSWERS.COM AF ANSWERS. A PATIENT EDUCATION HANDBOOK ON ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients
 be informed about... Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an abnormal heart rhythm. This pamphlet answers some questions you may have about AF, and gives an overview
be informed about... Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an abnormal heart rhythm. This pamphlet answers some questions you may have about AF, and gives an overview
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
FACTSHEET F18 COPING WITH TIREDNESS
 COPING WITH TIREDNESS Many people with chest, heart and stroke conditions experience tiredness or fatigue. This factsheet explains some of the reasons why you might feel so tired. It also offers advice
COPING WITH TIREDNESS Many people with chest, heart and stroke conditions experience tiredness or fatigue. This factsheet explains some of the reasons why you might feel so tired. It also offers advice
Atrial Flutter Patient Information
 AF A Atrial Flutter Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
AF A Atrial Flutter Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland. Cardiac & Respiratory Support Service. Supporting those living with heart and chest conditions
 Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland Cardiac & Respiratory Support Service Supporting those living with heart and chest conditions The Cardiac & Respiratory Support Service (C&RSS) offers a variety of resources
Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland Cardiac & Respiratory Support Service Supporting those living with heart and chest conditions The Cardiac & Respiratory Support Service (C&RSS) offers a variety of resources
Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
What is an. arrhythmia?
 What is an arrhythmia? What is an arrhythmia? Arrhythmia is an umbrella term used to describe a number of conditions where the muscle contraction of the heart is too slow, too fast or irregular because
What is an arrhythmia? What is an arrhythmia? Arrhythmia is an umbrella term used to describe a number of conditions where the muscle contraction of the heart is too slow, too fast or irregular because
Electrocardiogram Your quick guide
 Electrocardiogram Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Electrocardiogram Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
PhD FRCP MESC MEAPCI. Consultant Cardiologist SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia. Coronary Arteries
 SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Patient Information
 Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org www.afa-international.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org www.afa-international.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Blood-thinning medication after stroke
 Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are
Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are
I'm in control of my Atrial fibrillation (AF) Alan Weaver
 I'm in control of my Atrial fibrillation (AF) Alan Weaver ABOUT THE BRITISH HEART FOUNDATION CONTENTS As the nation s heart charity, we have been funding cutting-edge research that has made a big difference
I'm in control of my Atrial fibrillation (AF) Alan Weaver ABOUT THE BRITISH HEART FOUNDATION CONTENTS As the nation s heart charity, we have been funding cutting-edge research that has made a big difference
Atrial Fibrillation. Why It s Important. Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23. Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com. Page 1
 Atrial Fibrillation Why It s Important Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23 Page 1 CONTENT ORIGINAL PRESENTATION P3 ~ P13 UPDATED ASH ABSTRACT SUBMISSION INFORMATION INTERESTING LINK
Atrial Fibrillation Why It s Important Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23 Page 1 CONTENT ORIGINAL PRESENTATION P3 ~ P13 UPDATED ASH ABSTRACT SUBMISSION INFORMATION INTERESTING LINK
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Todd J. Florin, M.D. Table of Contents The Normal Heart...1 What is Atrial Fibrillation...3 Risks of Afib: Stroke...5 Treatment Options...7 Radiofrequency Ablation...9
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Todd J. Florin, M.D. Table of Contents The Normal Heart...1 What is Atrial Fibrillation...3 Risks of Afib: Stroke...5 Treatment Options...7 Radiofrequency Ablation...9
Blood-thinning medication after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are often prescribed
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are often prescribed
Catheter Ablation for Supra-ventricular Tachycardia
 Additional Notes Our mission To provide the excellent care we would expect for our families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Additional Notes Our mission To provide the excellent care we would expect for our families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information What is Ventricular Tachycardia? Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information What is Ventricular Tachycardia? Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart
The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph
 AF A The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary
AF A The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012
 The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 What does the heart do? 3 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The heart is a muscular organ located in the thorax. It pumps blood continuously around
The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 What does the heart do? 3 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The heart is a muscular organ located in the thorax. It pumps blood continuously around
Atrial Fibrillation. A guide for Southwark General Practice. Key Messages. Always work within your knowledge and competency
 Atrial Fibrillation A guide for Southwark General Practice Key Messages 1. Routinely offer pulse checks to patients at high risk of AF 2. Use the CHA 2 DS 2 VASc score to identify patients for anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation A guide for Southwark General Practice Key Messages 1. Routinely offer pulse checks to patients at high risk of AF 2. Use the CHA 2 DS 2 VASc score to identify patients for anticoagulation
I know my value. Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring
 I know my value Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring INR* self-monitoring needs only a drop of blood, is easy, fast and decreases the possibility Be involved in your
I know my value Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring INR* self-monitoring needs only a drop of blood, is easy, fast and decreases the possibility Be involved in your
Patient and primary care checklist
 AF A www.afa.org.uk Patient and primary care checklist Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No.
AF A www.afa.org.uk Patient and primary care checklist Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No.
Elective DC Cardioversion
 Elective DC Cardioversion Cardiology Medicine This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that you may have. Introduction
Elective DC Cardioversion Cardiology Medicine This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that you may have. Introduction
HEART SERIES H3 UNDERSTANDING HEART DISEASE
 HEART SERIES H3 UNDERSTANDING HEART DISEASE Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research, influencing
HEART SERIES H3 UNDERSTANDING HEART DISEASE Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research, influencing
Newer pacemakers also can monitor your blood temperature, breathing, and other factors and adjust your heart rate to changes in your activity.
 Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
MUGA Scan. A Patient s Guide. Copyrighted Material. HeartWise Patient Education
 MUGA Scan Copyrighted Material HeartWise Patient Education 800-747-1606 A Patient s Guide What Is a MUGA Scan? A multiple gated acquisition (or MUGA) scan is a test that uses a radioactive substance, called
MUGA Scan Copyrighted Material HeartWise Patient Education 800-747-1606 A Patient s Guide What Is a MUGA Scan? A multiple gated acquisition (or MUGA) scan is a test that uses a radioactive substance, called
Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation. Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation
 Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
Treating atrial fibrillation using heat energy delivered to the outside of the heart through a thin tube
 Issue date March 2009 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services NICE interventional procedures guidance advises the NHS on when and how new procedures can be used in clinical
Issue date March 2009 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services NICE interventional procedures guidance advises the NHS on when and how new procedures can be used in clinical
Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation
 AF A Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
AF A Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
Dysrhythmias 11/7/2017. Disclosures. 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias. None. Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics
 Dysrhythmias CYDNEY STEWART MD, FACC NOVEMBER 3, 2017 Disclosures None 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics Prevent imminent death/hemodynamic compromise
Dysrhythmias CYDNEY STEWART MD, FACC NOVEMBER 3, 2017 Disclosures None 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics Prevent imminent death/hemodynamic compromise
Patient & Primary Care Checklist
 established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist Tel: +44 (0)1789 451 837 Registered Charity Number: 1122442 2011 INTRODUCTION If you have been recently
established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist Tel: +44 (0)1789 451 837 Registered Charity Number: 1122442 2011 INTRODUCTION If you have been recently
CATHETER ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Patient Information Booklet
 CATHETER ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Patient Information Booklet Our mission is to provide advanced, safe and effective heart rhythm management. The Heart Rhythm Clinic is a team of dedicated healthcare
CATHETER ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Patient Information Booklet Our mission is to provide advanced, safe and effective heart rhythm management. The Heart Rhythm Clinic is a team of dedicated healthcare
Diseases. Cardiovascular System
 Diseases Cardiovascular System Angina Pectoris A condition marked by severe pain in the chest, often spreading to the shoulder or neck. Caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart. Cardiomyopathy Refers
Diseases Cardiovascular System Angina Pectoris A condition marked by severe pain in the chest, often spreading to the shoulder or neck. Caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart. Cardiomyopathy Refers
Pharmaceutical Care of People with Atrial Fibrillation. Course information
 Pharmaceutical Care of People with Atrial Fibrillation Course information Pharmaceutical Care of People with Atrial Fibrillation Course information page 3 Introduction 5 Teaching plan 6 Needs Assessment
Pharmaceutical Care of People with Atrial Fibrillation Course information Pharmaceutical Care of People with Atrial Fibrillation Course information page 3 Introduction 5 Teaching plan 6 Needs Assessment
The use of B-type natriuretic peptides in the investigation of patients with suspected heart failure
 Understanding our advice ~ May 2005 The use of B-type natriuretic peptides in the investigation of patients with suspected heart failure The use of B-type natriuretic peptides in the investigation of patients
Understanding our advice ~ May 2005 The use of B-type natriuretic peptides in the investigation of patients with suspected heart failure The use of B-type natriuretic peptides in the investigation of patients
Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery
 Issue date: May 2005 Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the
Issue date: May 2005 Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the
Amyloidosis and the Heart
 Amyloidosis and the Heart Martha Grogan, MD October 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Cardiac Amyloidosis Normal Heart Function How Amyloid affects the heart Symptoms Explanation of Heart Tests Treatment Options
Amyloidosis and the Heart Martha Grogan, MD October 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Cardiac Amyloidosis Normal Heart Function How Amyloid affects the heart Symptoms Explanation of Heart Tests Treatment Options
Mitral Regurgitation
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
Transient ischaemic attack (TIA)
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Transient ischaemic attack (TIA) A transient ischaemic attack or TIA is similar to a stroke, but the symptoms do not last as long. However, it should
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Transient ischaemic attack (TIA) A transient ischaemic attack or TIA is similar to a stroke, but the symptoms do not last as long. However, it should
Congestive Heart Failure
 Congestive Heart Failure GENERAL INFORMATION: What is congestive heart failure? Congestive heart failure is a life-threatening disease that occurs when your heart becomes too weak to pump blood properly.
Congestive Heart Failure GENERAL INFORMATION: What is congestive heart failure? Congestive heart failure is a life-threatening disease that occurs when your heart becomes too weak to pump blood properly.
Coronary Artery Disease
 Coronary Artery Disease This information is at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/diseases/cad/cad_all.html and is provided by the NHLBI, one of the Institutes of the National Institutes of Health. To
Coronary Artery Disease This information is at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/diseases/cad/cad_all.html and is provided by the NHLBI, one of the Institutes of the National Institutes of Health. To
Guide to Atrial Fibrillation
 Guide to Atrial Fibrillation 1 2 A. How does the normal heart work? The heart is a pump, and is part of a system which circulates blood around the body to supply oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues.
Guide to Atrial Fibrillation 1 2 A. How does the normal heart work? The heart is a pump, and is part of a system which circulates blood around the body to supply oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues.
Atrial Fibrillation Ablation
 Patient Information Atrial Fibrillation Ablation This leaflet is designed to give you more information about atrial fibrillation and catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. It will hopefully cover any
Patient Information Atrial Fibrillation Ablation This leaflet is designed to give you more information about atrial fibrillation and catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. It will hopefully cover any
Local steroid injections to joints and soft tissues
 Local steroid injections to joints and soft tissues Pain Management Team Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet will provide you with information about what to expect when you come in for
Local steroid injections to joints and soft tissues Pain Management Team Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet will provide you with information about what to expect when you come in for
Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care
 Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care We are dedicated to provide a compassionate and an outstanding care for patients with cardiac arrhythmias. We will be utilizing the cutting edge and the most advanced
Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care We are dedicated to provide a compassionate and an outstanding care for patients with cardiac arrhythmias. We will be utilizing the cutting edge and the most advanced
ICD Implantation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm ICD Implantation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers (the right atrium
Melbourne Heart Rhythm ICD Implantation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers (the right atrium
Cardiac Arrhythmias. Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company
 Cardiac Arrhythmias Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company The Cardiovascular System Three primary functions Transport of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to
Cardiac Arrhythmias Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company The Cardiovascular System Three primary functions Transport of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to
Atrial fibrillation. Treatment Guide
 Treatment Guide Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is the most common irregular or abnormal heart rhythm disorder, affecting more than 3 million Americans today. Thankfully, more options
Treatment Guide Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is the most common irregular or abnormal heart rhythm disorder, affecting more than 3 million Americans today. Thankfully, more options
Information about TIA
 Information about TIA Transient Ischemic Attack (mini-stroke) Did I have a TIA? Did you have stroke-like symptoms such as slurred speech or weakness in one arm that seemed to go away after a few minutes
Information about TIA Transient Ischemic Attack (mini-stroke) Did I have a TIA? Did you have stroke-like symptoms such as slurred speech or weakness in one arm that seemed to go away after a few minutes
Arrhythmia 341. Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU
 Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
NHS. Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) for arrhythmias. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Issue date: January 2006
 NHS National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Issue date: January 2006 Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) for arrhythmias Understanding NICE guidance information for people with
NHS National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Issue date: January 2006 Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) for arrhythmias Understanding NICE guidance information for people with
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information Normal Heart Function The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information Normal Heart Function The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two
Atrial Fibrillation and Options to Reduce Your Risk of Blood Clots and Stroke
 YOUR VALUES YOUR PREFERENCES YOUR CHOICE Atrial Fibrillation and Options to Reduce Your Risk of Blood Clots and Stroke Anticoagulant Medicine and Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Device Understanding Your
YOUR VALUES YOUR PREFERENCES YOUR CHOICE Atrial Fibrillation and Options to Reduce Your Risk of Blood Clots and Stroke Anticoagulant Medicine and Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Device Understanding Your
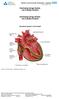
Atrial Fibrillaton. Key: RA: right atrium RV: right ventricle PA: pulmonic artery LA: left atrium LV: left ventricle AO: aorta
 Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Implantation of an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is an Implantable? Your doctor has recommended that you have an Implantable.
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is an Implantable? Your doctor has recommended that you have an Implantable.
Closing your atrial septal defect without surgery
 Patient information service Bristol Heart Institute Closing your atrial septal defect without surgery Respecting everyone Embracing change Recognising success Working together Our hospitals. What is an
Patient information service Bristol Heart Institute Closing your atrial septal defect without surgery Respecting everyone Embracing change Recognising success Working together Our hospitals. What is an
FACTSHEET CHOLESTEROL. What is cholesterol? Why is too much cholesterol harmful?
 CHOLESTEROL This factsheet explains what cholesterol is and why too much cholesterol in your blood is harmful. It also provides information regarding cholesterol testing and tips to help reduce your blood
CHOLESTEROL This factsheet explains what cholesterol is and why too much cholesterol in your blood is harmful. It also provides information regarding cholesterol testing and tips to help reduce your blood
Sample. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
requesting information regarding atrial fibrillation in NHS Ashford Clinical Commissioning Group
 October 2015 Our Ref: FOI.15.ASH0149 requesting information regarding atrial fibrillation in NHS Ashford Clinical Commissioning Group Original Request Survey attached. Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and
October 2015 Our Ref: FOI.15.ASH0149 requesting information regarding atrial fibrillation in NHS Ashford Clinical Commissioning Group Original Request Survey attached. Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and
