Fibrillation. Living. withatrial. Further information
|
|
|
- Letitia Casey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy. For more information or to receive a copy of our magazine Anticoagulation UK please , send a request from our website or write to the address below. Anticoagulation UK PO Box 405, Bromley, Kent. BR2 9WP Telephone: info@anticoagulationuk.org Web: Follow us on Living withatrial Fibrillation ACUK is a registered charity and relies on membership, donations and sponsorship to continue its work. To make a donation please send a cheque or postal order to the address above, or you can donate online at our website. Registered charity number: August 2017
2 What is atrial fibrillation? If you are healthy and your heart is working normally you are likely to have a regular resting heart rate of around 60 to 90 beats per minute. 1 AORTA PULMONIC VALVE RIGHT ATRIUM TRICUSPID VALVE RIGHT VENTRICLE LEFT ATRIUM AORTIC VALVE MITRAL VALVE LEFT VENTRICLE If you are experiencing atrial fibrillation, however, you may notice your heartbeat becoming irregular and speeding up for no apparent reason. These feelings or palpitations may occur constantly or only from time to time. They are unpleasant and worrying and they should not be ignored as they may mean that something is seriously wrong with your heart. Atrial fibrillation (AF) happens when the electrical control of your heartbeat becomes disrupted. Normally your heartbeat is controlled by electrical signals from its own natural pacemaker, called the sino-atrial node. These signals cause the upper chambers of your heart (the atria) to squeeze blood into the lower chambers (the ventricles) which then squeeze blood out into your blood vessels. The regular boom-boom of a healthy heart is the sound of the contracting atria quickly followed by the contracting ventricles. In atrial fibrillation, however, the electrical signals become erratic causing the atria and ventricles to contract out of rythm. Instead of beating normally the upper chambers, the atria, start making repetitive twitching movements known as fibrillations. This hampers the movement of blood from the atria into the ventricles. The ventricles respond by beating faster and more irregularly. It is this irregular ventricular beat you feel when you have a palpitation. 2
3 How common is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is the most common cause of irregular heartbeat, affecting around one in every 100 people. Although the condition is relatively rare in people under the age of 40, the risk of developing it increases significantly as you get older. By the age of 80 around 10 people in every 100 will have suffered the condition. Overall it is estimated that over a million people in the UK have atrial fibrillation. People with AF experience a five-fold increased risk of stroke compared to those with a normal heartbeat. What are the symptoms? Some people with atrial fibrillation have no symptoms at all. In these cases the condition is likely only to be discovered during a chance medical examination or when they develop another medical condition. For most people, however, atrial fibrillation is all too obvious, causing an unpleasant feeling of an irregular or racing heartbeat. Some people describe this feeling as a thumping in their chest. It is also common to feel faint or light-headed when their heart is racing. 3 You may find that you become short of breath more often than usual, feel tired a lot of the time and that your ankles start to become swollen. What causes atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation can be caused by anything that damages the heart. This includes medical conditions such as: a heart attack high blood pressure heart failure rheumatic heart disease an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) diabetes pneumonia heart surgery Or lifestyles factors such as drinking too much alcohol on a regular basis. However, in around 30 per cent of people with AF it is not possible to identify the precise cause. These cases are sometimes referred to as lone atrial fibrillation. 4
4 How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed? If your GP suspects you have atrial fibrillation, he or she will probably refer you to a heart specialist for further tests. These are likely to include an electrocardiogram (ECG) in which electrodes are placed on your chest to test for any irregularity in the electrical activity of your heart. If your palpitations are occurring only occasionally the specialist may ask you to wear a portable ECG machine for a period of 24 hours. The specialist will also want to perform some tests for possible causes of your irregular heartbeat. These will include a blood test to look for high levels of the thyroid hormone thyroxine. Images of your chest, taken with a chest X-ray and an ultrasound machine (an echocardiogram), may also be used to try to identify any abnormality in your heart that could be causing the problem. What will happen to me? If you have been diagnosed with atrial fibrillation, or are concerned that you may have the condition, the good news is that there are a number of effective treatments that can both help bring your heartbeat back under control and reduce the risk of more serious medical consequences. However, it is important to take the problem seriously. Atrial fibrillation can be the first sign of potentially life-threatening conditions such as heart failure, coronary artery disease, heart valve disease and high blood pressure. It is also a significant cause of illness in its own right. It has been estimated that untreated atrial fibrillation raises the risk of premature death. One of the most serious consequences of atrial fibrillation is due to the development of blood clots. This can happen when blood that should be being pumped out of the heart, instead collects in the atria where it begins to form clots. These clots usually remain in the atria where they do little harm. However, occasionally a clot will break away and travel through the blood to other parts of the body. If the blood clot travels to the brain then it can lodge in one of the smaller blood vessels and block the blood supply. This, in turn, may cause a stroke. 5 6
5 How great is the risk of stroke? If you have atrial fibrillation then, without treatment, you have a 5 per cent risk of having a stroke within a year. This risk will be even higher if you have other risk factors such as high blood pressure or other heart disease. It also rises as you get older. Overall, people with atrial fibrillation have five times the normal risk of suffering a stroke. What is more, having a stroke appears to be more serious for people with atrial fibrillation than in those without. Your chances of having a second stroke, suffering severe disability or of dying are all significantly increased if you have an abnormal heart rhythm. If all this sounds rather alarming then please be reassured there is plenty you can do to reduce these risks and protect yourself from the more serious consequences of atrial fibrillation. What treatments will I be offered? Treatment of atrial fibrillation has been shown to offer significant benefits in both reducing immediate symptoms and in offering protection against serious long-term consequences. If you have been diagnosed with atrial fibrillation your doctor may recommend a number of different treatments. The aim of these therapies is: to restore the natural rhythm of your heart to relieve any symptoms you may have of heart failure, high blood pressure or angina that may be linked to your atrial fi brillation to improve the overall performance of your heart to reduce your breathlessness when you exercise to reduce your risk of suffering blood clots and stroke 7 8
6 Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation WHAT TREATMENTS ARE AVAILABLE? Treatments for atrial fibrillation can be loosely divided into three categories: those intended to restore the natural rhythm of the heart those intended to treat the underlying cause of the atrial fi brillation those intended to reduce the risk of blood clotting and thereby offer protection against stroke How will my heart s normal rhythm be restored? Success in restoring the heart s normal rhythm will depend on how seriously your heart s rhythm is disrupted and on whether or not the doctor discovers any signs of an underlying medical condition. If your heart appears to be healthy, then drugs may be used to bring your speeding heart rate back under control. This will then allow your heart to correct its own rhythm, a process known as spontaneous conversion. In more serious cases or where the above approach does not work, the doctor may decide to restore the heart s rhythm directly. This is known as cardioversion and can be achieved using either drugs or by applying an electrical current to your chest. Pacemaker Electrical cardioversion is carried out under general anaesthetic and usually involves the patient being given a small electric shock to the chest to restores the normal heartbeat. Some people may need to have a pacemaker fitted that will help to regulate your heart rhythm after the procedure. 9 10
7 How will the doctor treat my underlying disease? This obviously depends on whatever underlying disease the doctor has identified. Common conditions associated with atrial fibrillation that your doctor may treat with medication are listed below: high blood pressure Lifestyle changes such as increased exercise, a low-salt diet, quitting smoking and reducing drinking can also help to reduce your blood pressure heart failure an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) diabetes How can I help to reduce my risk of a stroke? Although everybody with atrial fibrillation has an above average risk of suffering a stroke, the danger is much higher in some than others. Your doctor will discuss your level of risk with you. Regardless of your risk status there are a number of things you can do to reduce your risk of stroke. These include: Stop smoking Lose any excess weight Take regular exercise Eat fewer fatty and processed food food Eat more fruit and vegetables, fresh, frozen or canned Reduce the salt in your diet Don t drink alcohol to excess For some people lifestyle changes alone are unlikely to be enough to significantly reduce your risk of stroke and you should be given anticoagulant therapy to reduce your risk
8 What is anticoagulant therapy? Anticoagulants are medicines that prevent the blood from clotting as quickly as normal. Some people call anticoagulants blood thinners. The blood is not actually made any thinner - it just takes longer to clot whilst you are taking anticoagulants This reduces the chances of a blood clot forming in the heart and travelling to the brain, thereby cutting the risk of stroke. If you have atrial fibrillation, then taking an anticoagulant will help to reduce your risk of suffering a stroke by around 60 per cent. Anticoagulants also protect those who have already suffered one stroke from having another. It appears to be particularly useful in preventing the more serious and debilitating strokes. 13 What anticoagulant therapy will I be prescribed? Your doctor will discuss with you the benefits and risks of the different anticoagulants that are available. Oral anticoagulants include Apixaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban, Rivaroxaban and Warfarin. Dabigatran now has a reversal agent called Praxbind (Idarucizumab). This can be used to reverse the effects of Dabigatran in cases of emergency surgery/urgent procedures or uncontrolled bleeding. Apixaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban and Rivaroxaban are Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACS). They work on a different part of your clotting system to warfarin and do not need to be monitored by regular blood tests. You will, however, need a blood test at least once a year to monitor how your kidneys are working. This may be referred to as monitoring your renal function. Apixaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban and Rivaroxaban have been approved for use in the prevention of stroke for people with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. (That is AF not caused by a heart valve problem) by The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) and accepted by the Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC). See page
9 Warfarin is a drug that works by interfering with the chemical process that is involved in forming blood clots. You need to have your blood monitored regularly when you take warfarin to make sure your therapy is protecting you adequately. It will be monitored using a measurement called the INR, the International Normalised Ratio. This is a measurement of the time your blood takes to clot compared to normal. People not taking an anticoagulant have a INR of around 1.0. You will be given a target INR range and your dose of warfarin will be adjusted to help you achieve this target. Other drugs and over the counter medicines can interact with warfarin. If you decide to take warfarin send for our booklet Living with Warfarin. See page 20. When you first begin warfarin therapy your response to the drug may fluctuate a little. For this reason the blood tests will initially be taken every few days. With time, however, your response is likely to stabilise, and monitoring may be reduced to every few weeks depending on your response. If you decide to take warfarin you may want to talk to your healthcare professional about self-monitoring your INR level at home. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued guidance for self-monitoring for people with atrial fibrillation, see page What are the side effects of anti-coagulant therapy? The main risk with all anticoagulants is that they increase the risk of bleeding. This bleeding can be minor you may find you are more susceptible to bruising or nose bleeds or that it takes longer to stop the bleeding from a simple cut. However, more serious bleeds can include bleeding in the brain (haemorrhages) or in the stomach (an ulcer). The most serious bleeds can be fatal. It is therefore important that in patients who are considered at high risk of bleeding the benefits of antiocoagulation therapy are weighed against the potential dangers. Common risk factors for bleeding include: Age over 75 History of uncontrolled high blood pressure Excessive drinking of alcohol Liver disease Poor compliance with drug therapy Stomach ulcers Recent surgery Recent cerebral haemorrhage 16
10 Aspirin Aspirin is not an anticoagulant it is an anti-platelet. You should not be given aspirin to reduce your risk of a stroke as it is not as effective as taking anticoagulants, and can also cause serious bleeding. In 2014 The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) revised its guidance on atrial fibrillation. Part of that revision was to say that aspirin should not be given on its own to reduce the risk of stroke in people with atrial fibrillation. In July 2015 NICE published a Quality Standard on atrial fibrillation which repeated and reinforced that advice. See page 20. Questions you may want to ask your doctor What is causing my atrial fi brillation do I have an underlying disease? I have other symptoms (if you have other symptoms). Are these related to atrial fi brillation? Do I need anticoagulant therapy? What tests do I need? What do these tests involve? Am I likely to have a heart attack? What drugs can I take to restore my heart s rhythm? What treatments can I have to restore my heart s rythm? Do they have side effects? What do I do if I experience side effects? Will I need to be on treatment for the rest of my life? Should I alter my lifestyle? Should I alter my diet? Can I still play sport? Can I still have sex? Is it safe for me to drive? Is it safe for me to fl y? If my atrial fi brillation goes, how likely is it to come back? Am I likely to have a stroke? What can I do to reduce my risk of stroke? 17 18
11 If you need anticoagulant therapy Does my anticoagulant therapy need monitoring? How will you monitor my anticoagulant therapy? If I am taking Apixaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban or Rivaroxaban will I need to have regular check ups or blood test during the year Can I monitor my own treatment? (This only applies to warfarin) See page 20 Who can I ring for advice? To help you discuss with your doctor the benefits and risks of the anticoagulants that are available you may want to send for our fact sheets on each anticoagulant. Please send three second class stamps and your name and address to the address on the back page. READ OR DOWNLOAD LIVING WITH WARFARIN AT: For hard copy send name and address with three second class stamps to the address on the back page NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guidance on self-monitoring For Atrial fibrillation and heart valve disease: MANAGEMENT OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (REVISED GUIDANCE) QUALITY STANDARD FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Apixaban for preventing stroke and systemic embolism in people with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: Dabigatran etexilate for preventing stroke and systemic embolism in people with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: Edoxaban for preventing stroke and systemic embolism in people with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: Rivaroxaban for preventing stroke and systemic embolism in people with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: 19 Scottish Medicine Consortium advice relating to Apixaban, Dabigatran and Rivaroxaban and their indications can be found in the SMC Advice Directory: 20
12 Notes Anticoagulation UK... Publishes Anticoagulation UK, a magazine with up-to-date information, helpful articles and advice, patient stories, the latest clinical evidence and much more. Has a comprehensive website Provides information booklets For a full list please write or to the address on the back page of this booklet. Leaflets can also be read or downloaded on line. Membership is per year, you can join or renew on line or by sending a cheque made payable to Anticoagulation UK to the address on the back page. ACUK is a registered charity ( ) and relies on membership, sponsorship and donations to continue our work. You can donate on line or by sending a cheque or postal order made payable to Anticoagulation UK. You can also donate from your mobile phone. Text ACED44 3 to Shop on line and raise funds at no cost to you by going to and then follow instructions. You may need to type Anticoagulation UK as your charity to support. 21
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary
 X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide
 Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy
 Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy This leaflet offers more information about atrial fibrillation for patients who have been advised that they need anticoagulation therapy. If you have any
Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy This leaflet offers more information about atrial fibrillation for patients who have been advised that they need anticoagulation therapy. If you have any
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants
 Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: York Anticoagulant Clinic Tel: 01904
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: York Anticoagulant Clinic Tel: 01904
Arrhythmias. Pulmonary Artery
 Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias
 Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research,
HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research,
Introduction. What atrial fibrillation (AF) is Warning signs & symptoms, and risk factors for developing AFrelated
 Got FIB? Introduction FAST, IRREGULAR heartbeats = FIB FIB is short for fibrillation fibrillation, or quivering of the top two chambers of the heart (the atria) Important that you understand: What atrial
Got FIB? Introduction FAST, IRREGULAR heartbeats = FIB FIB is short for fibrillation fibrillation, or quivering of the top two chambers of the heart (the atria) Important that you understand: What atrial
INFORMATION. Atrial Fibrillation. Summary. Information from the
 1. Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Atrial Fibrillation INFORMATION Summary What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is
1. Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Atrial Fibrillation INFORMATION Summary What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding. Atrial Fibrillation. For more information, visit. CardioSmart.org/AFib
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation For more information, visit CardioSmart.org/AFib Understanding Atrial Fibrillation What is ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AFib)? When it s operating normally, your heart pumps to
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation For more information, visit CardioSmart.org/AFib Understanding Atrial Fibrillation What is ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AFib)? When it s operating normally, your heart pumps to
Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion
 Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke
 Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat. It means that your heart may not be pumping
Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat. It means that your heart may not be pumping
Atrial fibrillation. Understanding NICE guidance
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Atrial fibrillation NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Atrial fibrillation NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Information for patients, parents and guardians. Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation.
 Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
BIOTRONIK Clinical Studies IMPACT Clinical Study Patient Information. IMPACT Clinical Study: Patient Information Guide
 BIOTRONIK Clinical Studies IMPACT Clinical Study Patient Information IMPACT Clinical Study: Patient Information Guide Introduction and Objectives IMPACT is a clinical research study. Approximately 2,700
BIOTRONIK Clinical Studies IMPACT Clinical Study Patient Information IMPACT Clinical Study: Patient Information Guide Introduction and Objectives IMPACT is a clinical research study. Approximately 2,700
I know my value. Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring
 I know my value Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring INR* self-monitoring needs only a drop of blood, is easy, fast and decreases the possibility Be involved in your
I know my value Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring INR* self-monitoring needs only a drop of blood, is easy, fast and decreases the possibility Be involved in your
Atrial Fibrillation. Damage to your heart caused by a heart attack or rheumatic heart disease
 Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Catheter Ablation for Atrial Flutter
 Additional Notes Our mission Providing the excellent care we would expect for our own families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Additional Notes Our mission Providing the excellent care we would expect for our own families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Atrial Fibrillation. Why It s Important. Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23. Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com. Page 1
 Atrial Fibrillation Why It s Important Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23 Page 1 CONTENT ORIGINAL PRESENTATION P3 ~ P13 UPDATED ASH ABSTRACT SUBMISSION INFORMATION INTERESTING LINK
Atrial Fibrillation Why It s Important Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23 Page 1 CONTENT ORIGINAL PRESENTATION P3 ~ P13 UPDATED ASH ABSTRACT SUBMISSION INFORMATION INTERESTING LINK
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Helping to prevent stroke caused by non-valvular atrial fibrillation Information booklet
 Helping to prevent stroke caused by non-valvular atrial fibrillation Information booklet IF FOUND, PLEASE RETURN TO: Name Address Phone number Contents ALERT CARD...2 BOOKLET INFORMATION...3 What is atrial
Helping to prevent stroke caused by non-valvular atrial fibrillation Information booklet IF FOUND, PLEASE RETURN TO: Name Address Phone number Contents ALERT CARD...2 BOOKLET INFORMATION...3 What is atrial
Understanding your child s heart. Complete and partial atrioventricular septal defect
 Understanding your child s heart Complete and partial atrioventricular septal defect 7 About this book If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have lots of questions
Understanding your child s heart Complete and partial atrioventricular septal defect 7 About this book If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have lots of questions
Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery
 Issue date: May 2005 Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the
Issue date: May 2005 Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the
Blood-thinning medication after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are often prescribed
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are often prescribed
Catheter Ablation. Patient Education
 Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Atrial Flutter Patient Information
 AF A Atrial Flutter Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
AF A Atrial Flutter Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
Medicines for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. Choosing the right one for you
 Medicines for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Choosing the right one for you Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a condition that affects the heart, causing it to beat irregularly and too fast. When this
Medicines for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Choosing the right one for you Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a condition that affects the heart, causing it to beat irregularly and too fast. When this
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE. Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation TABLE OF CONTENTS IMPORTANT Please Note: Information provided by Boston Scientific Corporation
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation TABLE OF CONTENTS IMPORTANT Please Note: Information provided by Boston Scientific Corporation
Healthy Blood Pressure Healthy Heart Beat. Initiated by the World Hypertension League
 Healthy Blood Pressure Healthy Heart Beat Initiated by the World Hypertension League MAY 17, 2013 What is Hypertension? Hypertension Is A Global Epidemic! Hypertension is most commonly known as High Blood
Healthy Blood Pressure Healthy Heart Beat Initiated by the World Hypertension League MAY 17, 2013 What is Hypertension? Hypertension Is A Global Epidemic! Hypertension is most commonly known as High Blood
Atrial Fibrillation and Options to Reduce Your Risk of Blood Clots and Stroke
 YOUR VALUES YOUR PREFERENCES YOUR CHOICE Atrial Fibrillation and Options to Reduce Your Risk of Blood Clots and Stroke Anticoagulant Medicine and Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Device Understanding Your
YOUR VALUES YOUR PREFERENCES YOUR CHOICE Atrial Fibrillation and Options to Reduce Your Risk of Blood Clots and Stroke Anticoagulant Medicine and Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Device Understanding Your
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Patient Information
 Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org www.afa-international.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org www.afa-international.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Warfarin. Living. with. Further information
 Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 AF A Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
AF A Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
Heart Failure Overview
 Heart Failure Overview Help us make this guide better! Please fill out the brief survey at the back of the book or complete it online at heartandstroke.ca/feedback I Understanding Heart Failure The Basics
Heart Failure Overview Help us make this guide better! Please fill out the brief survey at the back of the book or complete it online at heartandstroke.ca/feedback I Understanding Heart Failure The Basics
A DECISION AID FOR AFIB STROKE PREVENTION FOR PATIENTS WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 A DECISION AID FOR AFIB STROKE PREVENTION FOR PATIENTS WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION For Patients with VERY HIGH RISK You have atrial fibrillation, also known as AFib, which means you have an irregular heart
A DECISION AID FOR AFIB STROKE PREVENTION FOR PATIENTS WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION For Patients with VERY HIGH RISK You have atrial fibrillation, also known as AFib, which means you have an irregular heart
A DECISION AID FOR AFIB STROKE PREVENTION FOR PATIENTS WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 A DECISION AID FOR AFIB STROKE PREVENTION FOR PATIENTS WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION For Patients with HIGH RISK You have atrial fibrillation, also known as AFib, which means you have an irregular heart beat.
A DECISION AID FOR AFIB STROKE PREVENTION FOR PATIENTS WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION For Patients with HIGH RISK You have atrial fibrillation, also known as AFib, which means you have an irregular heart beat.
Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients
 be informed about... Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an abnormal heart rhythm. This pamphlet answers some questions you may have about AF, and gives an overview
be informed about... Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an abnormal heart rhythm. This pamphlet answers some questions you may have about AF, and gives an overview
Special health. guide. Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding. Atrial Fibrillation WITH
 Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 www.irishheart.ie AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Registered charity number CHY 5507 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation This booklet is one of the publications
www.irishheart.ie AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Registered charity number CHY 5507 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation This booklet is one of the publications
Management strategies for atrial fibrillation Thursday, 20 October :27
 ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
What are the risk factors for AF?
 Susan Mayor was paid in her capacity as a medical writer for her time to research and write this article for Boehringer Ingelheim. This article has been reviewed by Boehringer Ingelheim to ensure compliance
Susan Mayor was paid in her capacity as a medical writer for her time to research and write this article for Boehringer Ingelheim. This article has been reviewed by Boehringer Ingelheim to ensure compliance
Preventing blood clots while you are in hospital and after you leave. Information for patients Pharmacy
 Preventing blood clots while you are in hospital and after you leave Information for patients Pharmacy Why does blood clot? When we cut ourselves, we bleed. To stop us from bleeding too much, chemicals
Preventing blood clots while you are in hospital and after you leave Information for patients Pharmacy Why does blood clot? When we cut ourselves, we bleed. To stop us from bleeding too much, chemicals
stroke.org.uk Atrial Fibrillation Reducing your risk of stroke
 stroke.org.uk Atrial Fibrillation Reducing your risk of stroke What is AF? Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat. Over 1 million people in the UK are living with the condition,
stroke.org.uk Atrial Fibrillation Reducing your risk of stroke What is AF? Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat. Over 1 million people in the UK are living with the condition,
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Atrial Fibrillation (Afib) Patient Guide. Guide contents: 2 What Is Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)? 3 What Happens During Afib?
 Guide contents: 2 What Is Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)? 3 What Happens During Afib? 4 For Your Appointment 5 For Your Future 6 Symptom Tracker Form 7 Your Team at Orlando Health Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)
Guide contents: 2 What Is Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)? 3 What Happens During Afib? 4 For Your Appointment 5 For Your Future 6 Symptom Tracker Form 7 Your Team at Orlando Health Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)
Atrial Fibrillation Implementation challenges. Lesley Edgar Ross Maconachie
 Atrial Fibrillation Implementation challenges Lesley Edgar Ross Maconachie Atrial Fibrillation Most common heart rhythm disturbance Rapid and irregular electrical signals Reduced efficiency of blood flow
Atrial Fibrillation Implementation challenges Lesley Edgar Ross Maconachie Atrial Fibrillation Most common heart rhythm disturbance Rapid and irregular electrical signals Reduced efficiency of blood flow
Catheter Ablation for Supra-ventricular Tachycardia
 Additional Notes Our mission To provide the excellent care we would expect for our families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Additional Notes Our mission To provide the excellent care we would expect for our families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Blood-thinning medication after stroke
 Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are
Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are
Treating atrial fibrillation using heat energy delivered to the outside of the heart through a thin tube
 Issue date March 2009 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services NICE interventional procedures guidance advises the NHS on when and how new procedures can be used in clinical
Issue date March 2009 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services NICE interventional procedures guidance advises the NHS on when and how new procedures can be used in clinical
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS. A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology MY LIFE HAS TAKEN A TURN FOR THE BETTER. -Emie Bishop ARRHYTHMIAANSWERS.COM AF ANSWERS. A PATIENT EDUCATION HANDBOOK ON ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology MY LIFE HAS TAKEN A TURN FOR THE BETTER. -Emie Bishop ARRHYTHMIAANSWERS.COM AF ANSWERS. A PATIENT EDUCATION HANDBOOK ON ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
Understand. your risk of. blood clot
 Going into hospital? Understand how to reduce your risk of developing a blood clot Printing of this leaflet has been supported by a donation from Bayer HealthCare. Bayer HealthCare has had no editorial
Going into hospital? Understand how to reduce your risk of developing a blood clot Printing of this leaflet has been supported by a donation from Bayer HealthCare. Bayer HealthCare has had no editorial
Heart Attack Your quick guide
 Heart Attack Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Heart Attack Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Cryoablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery. Issue date: May 2005
 Issue date: May 2005 Cryoablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the public Information
Issue date: May 2005 Cryoablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the public Information
Pancreas transplants. What you need to know. Information for patients Sheffield Kidney Institute (Renal Unit)
 Pancreas transplants What you need to know Information for patients Sheffield Kidney Institute (Renal Unit) page 2 of 16 What is the pancreas and why is it transplanted? The pancreas is part of the digestive
Pancreas transplants What you need to know Information for patients Sheffield Kidney Institute (Renal Unit) page 2 of 16 What is the pancreas and why is it transplanted? The pancreas is part of the digestive
Blood thinning (anticoagulation) in atrial fibrillation (AF)
 AF A Blood thinning (anticoagulation) in atrial fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
AF A Blood thinning (anticoagulation) in atrial fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
To prevent blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This booklet contains information for those who have been prescribed ELIQUIS (apixaban)
 To prevent blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This booklet contains information for those who have been prescribed ELIQUIS (apixaban) after hip or knee replacement surgery Always read the
To prevent blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This booklet contains information for those who have been prescribed ELIQUIS (apixaban) after hip or knee replacement surgery Always read the
all about your heart...
 For a healthy heart If you smoke, stop smoking. Eat lots of fruit and vegetables and less fat. Be more active every day. Be a healthy weight. Relax take time out for yourself. Local contact: For more information
For a healthy heart If you smoke, stop smoking. Eat lots of fruit and vegetables and less fat. Be more active every day. Be a healthy weight. Relax take time out for yourself. Local contact: For more information
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast. Information for patients Pharmacy
 Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION
 Spotlight on Health 2017 HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women worldwide, accounting for over 17 million deaths per year.
Spotlight on Health 2017 HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women worldwide, accounting for over 17 million deaths per year.
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease
 Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Transient Ischaemic Attack (TIA) Patient Handbook
 Transient Ischaemic Attack (TIA) Patient Handbook Contents Introduction 3 About my handbook 3 My details 4 Information about transient 6 ischaemic attack (TIA) What is transient ischaemic attack (TIA)
Transient Ischaemic Attack (TIA) Patient Handbook Contents Introduction 3 About my handbook 3 My details 4 Information about transient 6 ischaemic attack (TIA) What is transient ischaemic attack (TIA)
Information about TIA
 Information about TIA Transient Ischemic Attack (mini-stroke) Did I have a TIA? Did you have stroke-like symptoms such as slurred speech or weakness in one arm that seemed to go away after a few minutes
Information about TIA Transient Ischemic Attack (mini-stroke) Did I have a TIA? Did you have stroke-like symptoms such as slurred speech or weakness in one arm that seemed to go away after a few minutes
requesting information regarding atrial fibrillation in NHS Ashford Clinical Commissioning Group
 October 2015 Our Ref: FOI.15.ASH0149 requesting information regarding atrial fibrillation in NHS Ashford Clinical Commissioning Group Original Request Survey attached. Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and
October 2015 Our Ref: FOI.15.ASH0149 requesting information regarding atrial fibrillation in NHS Ashford Clinical Commissioning Group Original Request Survey attached. Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and
Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Heart Failure. Symptoms and Treatments. FloridaHospital.com
 Heart Failure Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Understanding Heart Failure According to the American Heart Association, one in five people over age 40 will develop heart failure. Right now,
Heart Failure Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Understanding Heart Failure According to the American Heart Association, one in five people over age 40 will develop heart failure. Right now,
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
Mitral Regurgitation
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and 30 June 2015, in the area covered by your CCG:
 Atrial Fibrillation in Your Area Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and 30 June 2015, in the area covered by your CCG: a) What was the prevalence of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 6636 (as of 22/10/2015) 2.1%
Atrial Fibrillation in Your Area Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and 30 June 2015, in the area covered by your CCG: a) What was the prevalence of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 6636 (as of 22/10/2015) 2.1%
Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet. Therapy
 Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Therapy Your Heart and Blood Clots You ve been told by your healthcare provider that you have a condition that can cause blood clots. This may be due to several factors,
Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Therapy Your Heart and Blood Clots You ve been told by your healthcare provider that you have a condition that can cause blood clots. This may be due to several factors,
Get the Facts on Atrial Fibrillation
 Get the Facts on Atrial Fibrillation The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease, or to replace professional medical
Get the Facts on Atrial Fibrillation The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease, or to replace professional medical
GETTING THE MOST FROM BLOOD PRESSURE MEDICINES
 GETTING THE MOST FROM BLOOD PRESSURE MEDICINES Helping you to lower your blood pressure BLOOD PRESSURE UK About this booklet This is one of a series of booklets produced by Blood Pressure UK, to help people
GETTING THE MOST FROM BLOOD PRESSURE MEDICINES Helping you to lower your blood pressure BLOOD PRESSURE UK About this booklet This is one of a series of booklets produced by Blood Pressure UK, to help people
Patient and primary care checklist
 AF A www.afa.org.uk Patient and primary care checklist Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No.
AF A www.afa.org.uk Patient and primary care checklist Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No.
Atrial Fibrillaton. Key: RA: right atrium RV: right ventricle PA: pulmonic artery LA: left atrium LV: left ventricle AO: aorta
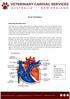 Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
This information explains heart failure, including causes and signs of heart failure, how heart failure is diagnosed, and how it s treated.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Heart Failure This information explains heart failure, including causes and signs of heart failure, how heart failure is diagnosed, and how it s treated. About Heart Failure
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Heart Failure This information explains heart failure, including causes and signs of heart failure, how heart failure is diagnosed, and how it s treated. About Heart Failure
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
pat hways Key therapeutic topic Published: 26 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ktt16
 pat hways Anticoagulants, including non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs) Key therapeutic topic Published: 26 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ktt16 Options for local implementation NICE
pat hways Anticoagulants, including non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs) Key therapeutic topic Published: 26 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ktt16 Options for local implementation NICE
INTRODUCING HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE
 INTRODUCING HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE Helping you to lower your blood pressure BLOOD PRESSURE UK About this booklet This is one of a series of booklets produced by Blood Pressure UK, to help people with high
INTRODUCING HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE Helping you to lower your blood pressure BLOOD PRESSURE UK About this booklet This is one of a series of booklets produced by Blood Pressure UK, to help people with high
Reduce Your Risk of Stroke Starting Now
 Reduce Your Risk of Stroke Starting Now Take steps against recurrent stroke by making the necessary changes in your life. Stroke prevention tips for better health Prevent stroke. Live healthy. You can
Reduce Your Risk of Stroke Starting Now Take steps against recurrent stroke by making the necessary changes in your life. Stroke prevention tips for better health Prevent stroke. Live healthy. You can
Deep Vein Thrombosis
 Deep Vein Thrombosis from NHS (UK) guidelines Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in one of the deep veins in the body. Blood clots that develop in a vein are also known as venous thrombosis.
Deep Vein Thrombosis from NHS (UK) guidelines Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in one of the deep veins in the body. Blood clots that develop in a vein are also known as venous thrombosis.
Understanding your child s heart. Tricuspid atresia
 Understanding your child s heart Tricuspid atresia 9 bout this book Contents If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news and have lots of questions running through your
Understanding your child s heart Tricuspid atresia 9 bout this book Contents If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news and have lots of questions running through your
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Helping you to lower your blood pressure. COVER.indd 1 16/07/ :29
 Helping you to lower your blood pressure COVER.indd 1 16/07/2015 16:29 intro.booklet 2014_BPA 26/03/2014 10:45 Page 2 B L O O D P R E S S U R E U K Pressure Points series Pressure Points is a series of
Helping you to lower your blood pressure COVER.indd 1 16/07/2015 16:29 intro.booklet 2014_BPA 26/03/2014 10:45 Page 2 B L O O D P R E S S U R E U K Pressure Points series Pressure Points is a series of
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias)
 Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
Heart Health C M Y K. Fotolia
 Heart Health C M Y K Fotolia PAGE 2 HEART HEALTH RECOVERY Life After Heart Attack O vercoming a heart attack may seem like an overwhelming feat. While it will be a lifelong recovery, you can still live
Heart Health C M Y K Fotolia PAGE 2 HEART HEALTH RECOVERY Life After Heart Attack O vercoming a heart attack may seem like an overwhelming feat. While it will be a lifelong recovery, you can still live
Patient Information. Preventing and treating blood clots
 Patient Information Preventing and treating blood clots 1_Clexane_Patient_Booklet_AW05.indd 1 8/04/2016 11:26 a The information provided in this document is for patients prescribed CLEXANE, and should
Patient Information Preventing and treating blood clots 1_Clexane_Patient_Booklet_AW05.indd 1 8/04/2016 11:26 a The information provided in this document is for patients prescribed CLEXANE, and should
Patient & Primary Care Checklist
 established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist Tel: +44 (0)1789 451 837 Registered Charity Number: 1122442 2011 INTRODUCTION If you have been recently
established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist Tel: +44 (0)1789 451 837 Registered Charity Number: 1122442 2011 INTRODUCTION If you have been recently
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
What is an. arrhythmia?
 What is an arrhythmia? What is an arrhythmia? Arrhythmia is an umbrella term used to describe a number of conditions where the muscle contraction of the heart is too slow, too fast or irregular because
What is an arrhythmia? What is an arrhythmia? Arrhythmia is an umbrella term used to describe a number of conditions where the muscle contraction of the heart is too slow, too fast or irregular because
Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I (888)
 Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I was exhausted doing simple tasks because of my AFib. I couldn t walk from the store to my car in the parking lot. Then, I had a MAZE procedure. It was a very
Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I was exhausted doing simple tasks because of my AFib. I couldn t walk from the store to my car in the parking lot. Then, I had a MAZE procedure. It was a very
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
PhD FRCP MESC MEAPCI. Consultant Cardiologist SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia. Coronary Arteries
 SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
Atrial Fibrillation. A guide for Southwark General Practice. Key Messages. Always work within your knowledge and competency
 Atrial Fibrillation A guide for Southwark General Practice Key Messages 1. Routinely offer pulse checks to patients at high risk of AF 2. Use the CHA 2 DS 2 VASc score to identify patients for anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation A guide for Southwark General Practice Key Messages 1. Routinely offer pulse checks to patients at high risk of AF 2. Use the CHA 2 DS 2 VASc score to identify patients for anticoagulation
Surgery for Patients on Oral Anticoagulants
 Surgery for Patients on Oral Anticoagulants (for example: warfarin, rivaroxaban, apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban) Surgery Patient Information Leaflet You have been given this leaflet because you are due
Surgery for Patients on Oral Anticoagulants (for example: warfarin, rivaroxaban, apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban) Surgery Patient Information Leaflet You have been given this leaflet because you are due
Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge
 Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge What is a venous thromboembolism (VTE)? This is a medical term that describes a blood clot that develops in a deep vein
Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge What is a venous thromboembolism (VTE)? This is a medical term that describes a blood clot that develops in a deep vein
Angioplasty Your quick guide
 Angioplasty Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Angioplasty Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
CARD 1: What is AFib and how does it relate to stroke? Talk to your patient about their condition and its connection to stroke.
 4WARD CONVERSATION CARDS OVERVIEW Please find educational materials to facilitate shared decision making between you and your atrial fibrillation (AFib) patients. More information can be found at AFib4WARD.com.
4WARD CONVERSATION CARDS OVERVIEW Please find educational materials to facilitate shared decision making between you and your atrial fibrillation (AFib) patients. More information can be found at AFib4WARD.com.
Warfarin. Information for patients taking warfarin
 Warfarin Information for patients taking warfarin Read this booklet to learn: what warfarin is and why you are taking it what blood tests you need to use warfarin safely how other medicines and diet can
Warfarin Information for patients taking warfarin Read this booklet to learn: what warfarin is and why you are taking it what blood tests you need to use warfarin safely how other medicines and diet can
