DROGAS PARA HIPERTENSION ARTERIAL JONATHAN POVEDA FERNANDEZ HSJD / 2013 FACC/FSCAI/FESC
|
|
|
- Sheila Glenn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DROGAS PARA HIPERTENSION ARTERIAL JONATHAN POVEDA FERNANDEZ HSJD / 2013 FACC/FSCAI/FESC
2 Pharmacotherapy of HTN Rationale for reducing arterial pressure Reduce cardiac output Reduce heart rate Reduce stroke volume Reduce system vascular Resistance Dilate systemic vasculature
3 Major Categories - Drugs Four major drug categories Sympathetic nervous system suppressors: α1 and β1 antagonists α2 agonists Direct vasodilators: Calcium channel antagonists Potassium channel agonists Renin-angiotensin system targeting drugs: ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor antagonists Diuretics: Thiazides Loop diuretics K+ - sparing diuretics
4 Classification of Drugs Used in Hypertension Diuretics Osmotic Thiazide Loop K + sparing Cardioinhibitory drugs β-blockers Ca ++ channel blockers Centrally Acting Sympatholytics Vasodilators α-blockers ACEi ARB Ca ++ channel blockers Direct acting arterial dilators Ganglionic blockers Nitrodilators K + channel openers
5 Diuretics
6 Thiazides freely filtered and secreted in proximal tubule Bind to the electroneutral NaCl cotransporter Thiazides impair Na + and Cl - reabsorption in the early distal tubule: low ceiling
7 Diuretics Thiazide chlorthalidone, hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), indapamide, metolazone Loop bumetanide, furosemide, torsemide Potassium-sparing amiloride, triamterene Aldosterone antagonists eplerenone, spironolactone 7
8 Thiazide Diuretics Dose in morning to avoid nocturnal diuresis Adverse effects: hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypercalcemia, hyperuricemia, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, sexual dysfunction lithium toxicity with concurrent administration More effective antihypertensives than loop diuretics unless CrCl < 30 ml/min Chlorthalidone 1.5 to 2 times as potent as HCTZ 8 8
9 Loop Diuretics Dose in AM or afternoon to avoid nocturnal diuresis Higher doses may be needed for patients with severely decreased glomerular filtration rate or heart failure Adverse effects: hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hyperuricemia, hyperuricemia 9
10 Potassium-sparing Diuretics Dose in AM or afternoon to avoid nocturnal diuresis Generally reserved for diuretic-induced hypokalemia patients Weak diuretics, generally used in combination with thiazide diuretics to minimize hypokalemia Adverse effects: may cause hyperkalemia especially in combination with an ACE inhibitor, angiotensin-receptor blocker or potassium supplements avoid in patients with CKD or diabetes 10
11 Aldosterone antagonists Dose in AM or afternoon to avoid nocturnal diuresis Due to increased risk of hyperkalemia, eplerenone contraindicated in CrCl < 50 ml/min & patients with type 2 diabetes & proteinuria Adverse effects: may cause hyperkalemia especially in combination with ACE inhibitor, angiotensin-receptor blocker or potassium supplements avoid in CKD or DM patients Gynecomastia: up to 10% of patients taking spironolactone 11
12 Figure 22.2 Major locations of ion and water exchange in the nephron, showing sites of action of the diuretic drugs. 12
13 13
14 β-blockers Inhibit renin release weak association with antihypertensive effect Negative chronotropic & inotropic cardiac effects reduce CO β-blockers with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) do not reduce CO lower BP decrease peripheral resistance 14
15
16 β-blockers Adverse effects: bradycardia atrioventricular conduction abnormalities acute heart failure abrupt discontinuation may cause rebound hypertension or unstable angina, myocardial infarction, & death in patients with high coronary disease risk bronchospastic pulmonary disease exacerbation may aggravate intermittent claudication, Raynaud s phenomenon 16
17 β-receptors Distributed throughout the body concentrate differently in certain organs & tissues β1 receptors: heart, kidney stimulation increases HR, contractility, renin release β2 receptors: lungs, liver, pancreas, arteriolar smooth muscle stimulation causes bronchodilation & vasodilation mediate insulin secretion & glycogenolysis 17
18 Cardioselective β-blockers Greater affinity for β1 than β2 receptors inhibit β1 receptors at low to moderate dose higher doses block β2 receptors Safer in patients with bronchospastic disease, peripheral arterial disease, diabetes may exacerbate bronchospastic disease when selectivity lost at high doses dose where selectivity lost varies from patient to patient Generally preferred β-blockers for HTN 18
19 β-blockers Cardioselective atenolol, betaxolol, bisoprolol, metoprolol, nebivolol Nonselective nadolol, propranolol, timolol Intrinsic sympathomimetic activity acebutolol, carteolol, penbutolol, pindolol Mixed α- and β-blockers carvedilol, labetolol 19
20 Nonselective β-blockers Inhibit β1 & β2 receptors at all doses Can exacerbate bronchospastic disease Additional benefits in: essential tremor migraine headache thyrotoxicosis 20
21 Intrinsic sympathomimetic activity Partial β-receptor agonists do not reduce resting HR, CO, peripheral blood flow No clear advantage except patients with bradycardia who must receive a β-blocker Contraindicated post-myocardial infarction & for patients at high risk for coronary disease May not be as cardioprotective as other β- blockers Rarely used 21
22
23
24 Side effects Bronchospasm Cold extremities Worsening of claudication Bradycardia, heart blocks Insomnia Depession Erectile dysfunction (11-26%) Metabolic side effects
25 Beta blockers without ISA LDL, TC no change Triglycerides increase by 20% HDL reduce by 10-20% In Diabetics Increase BSL by 1 to 1.5 mmol/dl Mask symptoms of hypoglyceamia Increase the risk of new DM use carvedilol or nebivolol.
26 Clinical Controversy Meta-analyses suggest β-blocker based therapy may not reduce CV events as well as other agents Atenolol t½: 6 to 7 hrs yet it is often dosed once daily IR forms of carvedilol & metoprolol tartrate have 6- to 10- & 3- to 7-hour half-lives respectively: always dosed at least BID Findings may only apply to atenolol may be a result of using atenolol daily instead of BID 26
27 Properties Of -Blockers Name -1 Selective a- blockade Lipophilic Increases ISA Other ancillary properties Atenolol Yes No No No No Acebutolol Disputed No No yes No Bisoprolol Yes No Weak No No Bucindolol No No Yes Disputed Vasodilator action Carvedilol No Yes Yes No Antioxidant, effects on endothelial function Celiprolol Yes No No -2 only No Metoprolol Yes No Yes No No Nebivolol Yes No? No Vasodilation through nitric oxide Propranolol No No Yes No Membrane stabilizing Effect Timolol No No Weak No Anti-platelet effects
28 Mixed α- & β-blockers Carvedilol reduces mortality in patients with systolic HF treated with diuretic & ACE inhibitor Adverse effects: additional blockade produces more orthostatic hypotension 28
29 Calcium Channel Blockers
30 CCBs Calcium Channel Blockers Inhibit influx of Ca 2+ across cardiac & smooth muscle cell membranes muscle contraction requires increased free intracellular Ca 2+ concentration CCBs block high-voltage (L-type) Ca 2+ channels resulting in coronary & peripheral vasodilation dihydropyridines vs non-dihydropyridines different pharmacologically similar antihypertensive efficacy 30
31 Calcium Flow pathways
32 MOA of Ca++ Channel Blockers
33 Calcium antagonists block predominantly L-type calcium channels, localized in myocardium and myocytes of blood vessels. L-type channels are connected to the plateau of the AP. Plateau phase of AP
34 CCBs Dihydropyridines: Amlodipine, felodipine, isradipine, nicardipine, nifedipine, nisoldipine, clevidipine Non-dihydropyridines: Diltiazem, verapamil Adverse effects of non-dihydropyridines: Bradycardia Atrioventricular block Systolic HF 34
35 CCBs Dihydropyridines: baroreceptor-mediated reflex tachycardia due to potent vasodilating effects do not alter conduction through atrioventricular node not effective in supraventricular tachyarrhythmias Non-dihydropyridines: decrease HR, slow atrioventricular nodal conduction may treat supraventricular tachyarrhythmias 35
36 Non-dihydropyridine CCBs ER products preferred for HTN Block cardiac SA & AV nodes: reduce HR May produce heart block Not AB rated as interchangeable/equipotent due to different release mechanisms & bioavailability Additional benefits in patients with atrial tachyarrhythmia 36
37 Dihydropyridine CCBs Avoid short-acting dihydropyridines particularly IR nifedipine, nicardipine Dihydropyridines more potent peripheral vasodilators than nondihydropyridines may cause more reflex sympathetic discharge: tachycardia, dizziness, headaches, flushing, peripheral edema Additional benefits in Raynaud s syndrome Effective in older patients with isolated systolic HTN 37
38 Classes of anti-hypertensives: CCBs Side effects of Calcium Channel Blockers Hypotension Constipation Headache Heart failure (verapamil > diltiazem) Bradycardia (non-dihydropyridines)
39 CCBs: Pharmacokinetics Agent Oral Absorption (%) Bioavail- Ability (%) Protein Bound (%) Elimination Half-Life (h) Verapamil > * Diltiazem > Nifedipine > Nicardipine > Isradipine > > Felodipine > Amlodipine >
40 Centrally Acting Sympatholytics
41
42 Sympatholytic drugs Peripheral sympatholytic drugs such as alphaadrenoceptor and beta-adrenoceptor antagonists block the influence of norepinephrine at the effector organ (heart or blood vessel) Ganglionic blockers that block impulse transmission at the sympathetic ganglia Block sympathetic activity within the brain. These are called centrally acting sympatholytic drugs clonidine guanabenz guanfacine α-methyldopa
43 ACE Inhibitors Block angiotensin I to angiotensin II conversion ACE (Angiotensin Converting Enzyme) distributed in many tissues primarily endothelial cells blood vessels: major site for angiotensin II production Block bradykinin degradation; stimulate synthesis of other vasodilating substances such as prostaglandin E 2 & prostacyclin Prevent or regress left ventricular hypertrophy by reducing angiotensin II myocardial stimulation 43
44 Classes of anti-hypertensives: ACE Inhibitors Names of ACE inhibitors Benzapril (Lotensin) Captopril (Capoten) Enalapril (Vasotec) Fosinopril (Monopril) Lisinopril (Zestril, Prinivil) Ramipril (Altace) Trandolapril (Mavik) Zofrenopril (Zofenil)
45 History ACE inhibitors 1st ACE inhibitor was teprotide, an IV nonapepetide from venom of Bothrops jararaca isolated, elucidated, and synthesized 1971 Captopril was 1st oral ACE inhibitor (1978) rapid onset of action with maximum activity in 15 to 30 minutes, but plasma T 1/2 only 2 hours. 45
46 46 46
47 Classes of anti-hypertensives: ACE Inhibitors
48 ACE Pharmacology Differences: Active Moieties sulfhydryl -Captopril phosphinyl -Fosinopril carboxyl -Enalapril,lisinopril, Benzapril, Quinapril, Ramapril, Trandilopril, Moexipril Potency & Plasma half life Distribution and affinity for tissue bound ACE Cardiac affinity quniapril=benazapril>lisinopril>fosinopril>captopril Excretion- all renal (fosinopril and trandolapril also metab by liver) 48
49 ACE Inhibitors Monitor serum K + & SCr within 4 weeks of initiation or dose increase Adverse effects: cough up to 20% of patients due to increased bradykinin angioedema hyperkalemia: particularly in patients with CKD or DM neutropenia, agranulocytosis, proteinuria, glomerulonephritis, acute renal failure 49
50 ARBs Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Angiotensin II generation renin-angiotensin-aldosterone pathway alternative pathway using other enzymes such as chymases Inhibit angiotensin II from all pathways directly block angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor ACE inhibitors partially block effects of angiotensin II 50
51 ARBs Do not block bradykinin breakdown less cough than ACE Inhibitors Adverse effects: orthostatic hypotension renal insufficiency hyperkalemia 51
52 Classes of anti-hypertensives: ARBs Names of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Candesartan (Atacand) Eprosartan (Teveten) Losartan (Cozaar) Valsartan (Diovan) Irbesartan ( Aprovel) Termisartan ( Micardis) Olmesartan ( Benicar/Olmetec)
53 Classes of anti-hypertensives: ARBs Effects of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Block RAAS more completely than ACE Inhibitors NO effect on bradykinin, prostaglandins, or nitrous oxide Are not interfered with by NSAIDS Are a very good substitute for ACE Inhibitors Have the SAME side effects as ACE inhibitors, except no cough
54 54 54
55 AT II Receptor -Types AT 1 Receptor AT 2 Receptor Vasoconstriction Cell growth & Proliferation Promotes Reabsorption of Na & Water Produces Free radicals Induces growth factors, Endothelin and Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1(PAI-1) Vasodilation Anti-growth Natriuresis Produces Nitric oxide (Vasodilation)
56 Pathological role of AT II
57 Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) Block activation of angiotensin II AT1 receptors Effects include: Vasodilation Reduced secretion of vasopressin Reduced production and secretion of aldosterone Reduction in blood pressure
58 Side Effects of ARBs Usually well-tolerated Dizziness Headache Hyperkalemia Infrequent ADRs First dose orthostatic hypotension Rash Diarrhea Dyspepsia Abnormal liver function Muscle cramp, back pain Insomnia, Decreased Hb Renal impairment Pharyngitis/nasal congestion
59 ACE I / ARBs Preferred agent in Diabetic HTN Offer Reno protection AT II Increase Intra-renal Pr & Constricts Efferent Arteriole Thickening of Glomerular basement membrane : Stimulates Renal fibrosis & Stimulates TGF beta (Hypertrophy, collagen syn.) ; Stimulates MCP ( Inflammation) Endothelial dysfn ACEI / ARB Decreases Corrects Improvement in Endothelial fn
60 Safety and tolerability of ACEi and ARBs continued Concern that ARBs may increase risk of cancer A meta-analysis found a small increased risk of cancers with ARBs vs. non-arbs EMA and FDA have reviewed evidence and concluded that the evidence does not support any increased risk of cancer with ARBs Concern that olmesartan may increase CV death risk Two studies found higher rate of fatal CV events with olmesartan vs. placebo FDA have stated that benefits of olmesartan outweigh potential risks FDA Drug Safety Communication: Safety Review Update of Benicar (olmesartan) and cardiovascular events. US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) FDA Drug Safety Communication: No increase in risk of cancer with certain blood pressure drugs-- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs). US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
61 For what conditions are ACEi and ARBs used? Used for a range of conditions. Licensed indications for different ACEi and ARBs vary. All ACEi and ARBs are licensed for the treatment of hypertension. Variously indicated for the treatment of other conditions including: Heart Failure Prophylaxis of cardiovascular (CV ) events in patients at high risk Secondary prevention after myocardial infarction (MI) Diabetic nephropathy 61
62 New Antihypertensive Drugs Vasodilator beta-blockers Renin inhibitors Endothelin receptor antagonists Dual-acting angiotensin-plus endothelinreceptor antagonist Angiotensin-targeting vaccines
63 Renin Inhibitors Aliskiren Aliskiren is the first in a new class of potent, orally effective renin inhibitors. Whereas all of the other drugs act by inhibiting certain aspects of the ultimate step in the reninangiotensin system (RAS), ie, angiotensin II, aliskiren targets the first and rate-limiting step - namely, renin.
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive Agents
 Antihypertensive Agents Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 7, 08, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D! Usual Dose,
Antihypertensive Agents Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 7, 08, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D! Usual Dose,
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Hypertension (JNC-8)
 Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Section 3, Lecture 2
 59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics
 sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
7/7/ CHD/MI LVH and LV dysfunction Dysrrhythmias Stroke PVD Renal insufficiency and failure Retinopathy. Normal <120 Prehypertension
 Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES. Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVES Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Hypertension Hypertension is a condition in which the blood pressure is persistently higher than normal Hypertension > 140 mmhg > 90 mmhg Systolic Blood Pressure
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Hypertension Hypertension is a condition in which the blood pressure is persistently higher than normal Hypertension > 140 mmhg > 90 mmhg Systolic Blood Pressure
Hypertension is also an important risk factor in the development of chronic kidney disease and heart failure.
 Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension is defined as either a sustained systolic blood pressure of greater than 140 mm Hg or a sustained diastolic blood pressure of greater than 90 mm Hg. Hypertension
Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension is defined as either a sustained systolic blood pressure of greater than 140 mm Hg or a sustained diastolic blood pressure of greater than 90 mm Hg. Hypertension
Antihypertensives. Antihypertensive Classes. RAAS Inhibitors. Renin-Angiotensin Cascade. Angiotensin Receptors. Approaches to Hypertension Treatment
 Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS)
 DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood:
 Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
What in the World is Functional Medicine?
 What in the World is Functional Medicine? An Introduction to a Systems Based Approach of Chronic Disease Meneah R Haworth, FNP-C Disclosure v I am a student of the Institute for Functional Medicine. They
What in the World is Functional Medicine? An Introduction to a Systems Based Approach of Chronic Disease Meneah R Haworth, FNP-C Disclosure v I am a student of the Institute for Functional Medicine. They
New classification of HT Systolic Diastolic Normal <120 <80 Prehypertension Stage1HT Stage 2 HT >160 or >100
 Hypertension 1 Definition Hypertension can be defined as a condition where blood pressure is elevated to an extent that clinical benefit is obtained from blood pressure lowering. it is an important risk
Hypertension 1 Definition Hypertension can be defined as a condition where blood pressure is elevated to an extent that clinical benefit is obtained from blood pressure lowering. it is an important risk
Treatment of Essential Hypertension
 2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
Antihypertensives. Diagnostic category
 Measurement of blood pressure At first assessment, take both arms then choose the one with the higher reading. Beware of orthostatic hypotension. Measure BP in sitting position, and repeat after patient
Measurement of blood pressure At first assessment, take both arms then choose the one with the higher reading. Beware of orthostatic hypotension. Measure BP in sitting position, and repeat after patient
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP
 HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP What is normal blood pressure? Prehypertension 130-139/80-90 Compared with normal BP Double the risk for developing hypertension. Lifestyle
HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP What is normal blood pressure? Prehypertension 130-139/80-90 Compared with normal BP Double the risk for developing hypertension. Lifestyle
Treatment of Essential Hypertension
 2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
HYPERTENSION: Sustained elevation of arterial blood pressure above normal o Systolic 140 mm Hg and/or o Diastolic 90 mm Hg
 Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
ASEBP and ARTA TARP Drugs and Reference Price by Categories
 ASEBP Pantoprazole Sodium 40 mg (generic) $0.2016 ASEBP Dexlansoprazole 30 mg Dexlansoprazole 60 mg Esomeprazole 10 mg Esomeprazole 20 mg Esomeprazole 40 mg Lansoprazole 15 mg Lansoprazole 30 mg Omeprazole
ASEBP Pantoprazole Sodium 40 mg (generic) $0.2016 ASEBP Dexlansoprazole 30 mg Dexlansoprazole 60 mg Esomeprazole 10 mg Esomeprazole 20 mg Esomeprazole 40 mg Lansoprazole 15 mg Lansoprazole 30 mg Omeprazole
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park.
 Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI
 DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
New Hypertension Guidelines: How Lower Blood Pressure Targets Affect Medication Safety
 New Hypertension Guidelines: How Lower Blood Pressure Targets Affect Medication Safety Diana Isaacs, PharmD, BCPS, BC-ADM, CDE Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Cleveland Clinic Andrew Straw, PharmD, BC-ADM
New Hypertension Guidelines: How Lower Blood Pressure Targets Affect Medication Safety Diana Isaacs, PharmD, BCPS, BC-ADM, CDE Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Cleveland Clinic Andrew Straw, PharmD, BC-ADM
12.5mg, 25mg, 50mg. 25mg, 50mg. 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg. 5mg, 10mg, 20mg, 100mg. 25mg. -- $2.81 Acetazolamide (IR, 125mg, 250mg, 500mg (ER)
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 5/9/2017 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, 5/07 LOB
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 5/9/2017 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, 5/07 LOB
Therapeutics of Diuretics
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
β adrenergic blockade, a renal perspective Prof S O McLigeyo
 β adrenergic blockade, a renal perspective Prof S O McLigeyo Carvedilol Third generation β blocker (both β 1 and β 2 ) Possesses α 1 adrenergic blocking properties. β: α blocking ratio 7:1 to 3:1 Antioxidant
β adrenergic blockade, a renal perspective Prof S O McLigeyo Carvedilol Third generation β blocker (both β 1 and β 2 ) Possesses α 1 adrenergic blocking properties. β: α blocking ratio 7:1 to 3:1 Antioxidant
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 28, 2010 Materials on: Exam #3 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 11 1 1 in 3 adults HYPERTENSION 64% of
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 28, 2010 Materials on: Exam #3 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 11 1 1 in 3 adults HYPERTENSION 64% of
Cardiac Medications At A Glance
 Cardiac Medications At A Glance 1) Anticoagulants (Also known as Blood Thinners.) Dalteparin (Fragmin), Danaparoid (Orgaran) Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Heparin (various) Tinzaparin (Innohep) Warfarin (Coumadin)
Cardiac Medications At A Glance 1) Anticoagulants (Also known as Blood Thinners.) Dalteparin (Fragmin), Danaparoid (Orgaran) Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Heparin (various) Tinzaparin (Innohep) Warfarin (Coumadin)
8/20/2018. Objectives. What is hypertension? cont. What is hypertension? Epidemiology cont. Epidemiology
 Objectives Hypertension (high blood pressure): Clinical Pearls for the Pharmacy Technician Tanya Schmidt PharmD, RPh Director of Central Operations at Thrifty White Pharmacy North Dakota Board of Pharmacy
Objectives Hypertension (high blood pressure): Clinical Pearls for the Pharmacy Technician Tanya Schmidt PharmD, RPh Director of Central Operations at Thrifty White Pharmacy North Dakota Board of Pharmacy
Antihypertensive Agents
 Antihypertensive Agents Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.11.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005
Antihypertensive Agents Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.11.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005
HypertensionTreatment Guidelines. Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC
 HypertensionTreatment Guidelines Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC Objectives: Review the definition of the different stages of HTN. Review the current guidelines for treatment of HTN. Provided
HypertensionTreatment Guidelines Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC Objectives: Review the definition of the different stages of HTN. Review the current guidelines for treatment of HTN. Provided
ANTI- HYPERTENSIVE AGENTS
 CLINICAL ANTI- HYPERTENSIVE AGENTS Jacqueline van Schoor, MPharm, BSc (Hons) Amayeza Info Centre Hypertension represents a major public health concern. It affects about a billion people worldwide and is
CLINICAL ANTI- HYPERTENSIVE AGENTS Jacqueline van Schoor, MPharm, BSc (Hons) Amayeza Info Centre Hypertension represents a major public health concern. It affects about a billion people worldwide and is
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D
 University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1. Antihypertensives 2. Antianginal 3. Drugs for HF 4. Antiarrythemics 5. Drugs for Hyperlipoproteniemia
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1. Antihypertensives 2. Antianginal 3. Drugs for HF 4. Antiarrythemics 5. Drugs for Hyperlipoproteniemia
4/3/2014 OBJECTIVES BLOOD PRESSURE BASICS. Discuss the new blood pressure guidelines (JNC 8) and recognize the changes from JNC 7
 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the new blood pressure guidelines (JNC 8) and recognize the changes from JNC 7 Review mechanisms for the main drug classes used to treat hypertension Describe the dosing strategies
1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the new blood pressure guidelines (JNC 8) and recognize the changes from JNC 7 Review mechanisms for the main drug classes used to treat hypertension Describe the dosing strategies
Beta 1 Beta blockers A - Propranolol,
 Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Combining Antihypertensives in People with Diabetes
 Combining ntihypertensives in People with Diabetes The majority of people with diabetes will develop hypertension and this subsequently increases the risk of microvascular and macrovascular complications.
Combining ntihypertensives in People with Diabetes The majority of people with diabetes will develop hypertension and this subsequently increases the risk of microvascular and macrovascular complications.
Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy
 Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy Overview Mechanism of cardiovascular drugs Indications and clinical use in cardiology Renin-Angiotensin Inhibitors: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors, Angiotensin
Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy Overview Mechanism of cardiovascular drugs Indications and clinical use in cardiology Renin-Angiotensin Inhibitors: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors, Angiotensin
Difficult to Treat Hypertension
 Difficult to Treat Hypertension According to Goldilocks JNC 8 Blood Pressure Goals (2014) BP Goal 60 years old and greater*- systolic < 150 and diastolic < 90. (Grade A)** BP Goal 18-59 years old* diastolic
Difficult to Treat Hypertension According to Goldilocks JNC 8 Blood Pressure Goals (2014) BP Goal 60 years old and greater*- systolic < 150 and diastolic < 90. (Grade A)** BP Goal 18-59 years old* diastolic
By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat
 What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
Hypertension Management - Summary
 Who should have blood pressure assessed? Hypertension Management - Summary All patients over the age of 40 years, every 1-3 years in order to determine their cardiovascular risk (ie. Framingham Risk Score)
Who should have blood pressure assessed? Hypertension Management - Summary All patients over the age of 40 years, every 1-3 years in order to determine their cardiovascular risk (ie. Framingham Risk Score)
Introduction. Factors affecting blood pressure: 1-COP = HR X SV mainly affect SBP. 2-TPR = diameter of arterioles X viscosity of blood affect DBP
 Introduction Hypertension is a persistent elevation of blood pressure above 140 / 90 mmhg for more than three sitting. (0ptimal level
Introduction Hypertension is a persistent elevation of blood pressure above 140 / 90 mmhg for more than three sitting. (0ptimal level
Heart failure. Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs. CHF = congestive heart failure. increased blood volume, interstitial fluid
 Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Beta-blockers. Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol.
 Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Chapter 10 Worksheet Blood Pressure and Antithrombotic Agents
 Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
12.5mg, 25mg, 50mg. 25mg, 50mg. 250mg, 500mg, 250mg/5ml. 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg. 5mg, 10mg, 20mg, 100mg. 25mg
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 9/11/2018 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 5/17, 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, LOB
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 9/11/2018 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 5/17, 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, LOB
Antihypertensive Drugs. Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014
 Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension: A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension: A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
Antihypertensive Drugs. Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan October, 2017
 Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan October, 2017 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension? A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan October, 2017 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension? A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs. Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland
 State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland First line therapies in hypertension ACE inhibitors AT
State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland First line therapies in hypertension ACE inhibitors AT
HYPERTENSION IN CKD. LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL
 HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009
 Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009 Oklahoma HealthCare Authority April 2010 Current Prior Authorization Criteria There are 7 categories of antihypertensive medications currently included
Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009 Oklahoma HealthCare Authority April 2010 Current Prior Authorization Criteria There are 7 categories of antihypertensive medications currently included
Hypertension Update. Objectives 4/28/2015. Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015
 Hypertension Update Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015 Objectives Learn new recommendations for BP treatment goals Approach to hypertension in the office Use of hypertensive drugs, and how to tailor
Hypertension Update Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015 Objectives Learn new recommendations for BP treatment goals Approach to hypertension in the office Use of hypertensive drugs, and how to tailor
Factors Involved in Poor Control of Risk Factors
 Factors Involved in Poor Control of Risk Factors Patient compliance Clinical inertia Health Care System structure 14781 M Limitations of Formal Studies Selection of patients Recruitment and follow-up alter
Factors Involved in Poor Control of Risk Factors Patient compliance Clinical inertia Health Care System structure 14781 M Limitations of Formal Studies Selection of patients Recruitment and follow-up alter
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias
 1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
Hypertension Update. Sarah J. Payne, MS, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacotherapy UNT System College of Pharmacy
 Hypertension Update Sarah J. Payne, MS, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacotherapy UNT System College of Pharmacy Introduction 1/3 of US adults have HTN More prevalent in non-hispanic
Hypertension Update Sarah J. Payne, MS, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacotherapy UNT System College of Pharmacy Introduction 1/3 of US adults have HTN More prevalent in non-hispanic
Cardiovascular Clinical Practice Guideline Pilot Implementation
 Cardiovascular Clinical Practice Guideline Pilot Implementation Pharmacologic Management of Chronic Heart Failure Sept 15, 2004 Angela Allerman, PharmD, BCPS DoD Pharmacoeconomic Center Promoting high
Cardiovascular Clinical Practice Guideline Pilot Implementation Pharmacologic Management of Chronic Heart Failure Sept 15, 2004 Angela Allerman, PharmD, BCPS DoD Pharmacoeconomic Center Promoting high
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR.
 ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson you will be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT SUBCOURSE MD0806 LESSON 7 Therapeutics III. Antihypertensive Agents. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1--7-12. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson you will be able to: 7-1. From
LESSON ASSIGNMENT SUBCOURSE MD0806 LESSON 7 Therapeutics III. Antihypertensive Agents. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1--7-12. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson you will be able to: 7-1. From
PRINCIPLES OF DIURETIC ACTIONS:
 DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
Heart Failure. Subjective SOB (shortness of breath) Peripheral edema. Orthopnea (2-3 pillows) PND (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea)
 Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Antihypertensive drugs: I. Thiazide and other diuretics:
 Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Hypertension: Update
 Hypertension: Update Meenakshi A Bhalla MD,FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Director Preventive Cardiology Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiology University of Kentucky Faculty Disclosure
Hypertension: Update Meenakshi A Bhalla MD,FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Director Preventive Cardiology Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiology University of Kentucky Faculty Disclosure
Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017
 Insert Logo or Org Name Here Primary Care Medical Directive for Hypertension Management Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017 Title:
Insert Logo or Org Name Here Primary Care Medical Directive for Hypertension Management Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017 Title:
8/19/2016. No Conflicts. I struggled with everything cardiac in nursing school.
 Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS CC, FNP BC Assistant Professor, Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Nursing Describe and define epidemiology and pathophysiology of hypertension Differentiate JNC8
Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS CC, FNP BC Assistant Professor, Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Nursing Describe and define epidemiology and pathophysiology of hypertension Differentiate JNC8
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
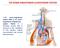 THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
Beta blockers in primary hypertension. Dr. Md. Billal Alam Associate Professor of Medicine DMC
 Beta blockers in primary hypertension Dr. Md. Billal Alam Associate Professor of Medicine DMC Development of antihypertensive drugs Beta blockers 1958 - The first beta-blocker, dichloroisoproterenol, was
Beta blockers in primary hypertension Dr. Md. Billal Alam Associate Professor of Medicine DMC Development of antihypertensive drugs Beta blockers 1958 - The first beta-blocker, dichloroisoproterenol, was
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists
 Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Chapter 23. Media Directory. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Hypertension: Classified into Three Categories
 Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes
 Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or by any
Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or by any
Angina pectoris due to coronary atherosclerosis : Atenolol is indicated for the long term management of patients with angina pectoris.
 Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Blood pressure (BP) control. Hypertension
 Blood pressure (BP) control Normal heart function Blood pressure (BP) control blood pressure (BP) cardiac output (CO) = total peripheral resistance (TPR) heart rate (HR) filling pressure arteriolar volume
Blood pressure (BP) control Normal heart function Blood pressure (BP) control blood pressure (BP) cardiac output (CO) = total peripheral resistance (TPR) heart rate (HR) filling pressure arteriolar volume
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY
 M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system
 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
Adrenergic Receptor as part of ANS
 Adrenergic Receptor as part of ANS Actions of Adrenoceptors Beta-1 adrenergic receptor Located on the myocytes of the heart Specific actions of the β1 receptor include: 0 Increase cardiac output, by 0
Adrenergic Receptor as part of ANS Actions of Adrenoceptors Beta-1 adrenergic receptor Located on the myocytes of the heart Specific actions of the β1 receptor include: 0 Increase cardiac output, by 0
Diuretics (Saluretics)
 Diuretics (Saluretics) Diuretics increase urine excretion mainly by reabsorption of salts and water from kidney tubules These agents are ion transport inhibitors that decrease the reabsorption of Na+ at
Diuretics (Saluretics) Diuretics increase urine excretion mainly by reabsorption of salts and water from kidney tubules These agents are ion transport inhibitors that decrease the reabsorption of Na+ at
Network Hypertension Algorithm
 Network Hypertension Algorithm Content Review and Approval: This document is subject to review, revision, and (re)approval by the Clinical Integration and Oversight Committee (CIOC) annually and following
Network Hypertension Algorithm Content Review and Approval: This document is subject to review, revision, and (re)approval by the Clinical Integration and Oversight Committee (CIOC) annually and following
Hypertension. Kaveh Eslami Pharm.D, board certified clinical pharmacy resident Clinical pharmacy department Tehran university of medical science
 Hypertension Kaveh Eslami Pharm.D, board certified clinical pharmacy resident Clinical pharmacy department Tehran university of medical science 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximately 31% of the population (72 million
Hypertension Kaveh Eslami Pharm.D, board certified clinical pharmacy resident Clinical pharmacy department Tehran university of medical science 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximately 31% of the population (72 million
Table 1. Diuretics. Drugs Mechanisms of Action Indications Adverse Drug Effects. Table 2. Electrolyte Modifiers.
 Table 1. Diuretics. hydrochlorothiazide 23 furosemide 23 triamterene 23 Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the distal convoluted tubule Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the loop of Henle Competitive inhibitor
Table 1. Diuretics. hydrochlorothiazide 23 furosemide 23 triamterene 23 Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the distal convoluted tubule Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the loop of Henle Competitive inhibitor
Difficult to Control HTN: It is not all the same. Structured approach to evaluation and treatment
 Difficult to Control HTN: It is not all the same. Structured approach to evaluation and treatment Dmitri Vasin M.D. Nephrologist and ASH certified clinical hypertension specialist Bremerton, WA, USA Johnson
Difficult to Control HTN: It is not all the same. Structured approach to evaluation and treatment Dmitri Vasin M.D. Nephrologist and ASH certified clinical hypertension specialist Bremerton, WA, USA Johnson
COMPLEX HYPERTENSION. Anita Ralstin, FNP-BC Next Step Health Consultant, LLC
 COMPLEX HYPERTENSION Anita Ralstin, FNP-BC Next Step Health Consultant, LLC Incidence Of Hypertension About 70 million American adults have high blood pressure. About 33% of the population Only 52% have
COMPLEX HYPERTENSION Anita Ralstin, FNP-BC Next Step Health Consultant, LLC Incidence Of Hypertension About 70 million American adults have high blood pressure. About 33% of the population Only 52% have
Byvalson. (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow
 Byvalson (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Byvalson Generic name: Nebivolol, valsartan Pharmacological class: Beta-blocker + angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) Strength
Byvalson (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Byvalson Generic name: Nebivolol, valsartan Pharmacological class: Beta-blocker + angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) Strength
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Hypertension. Penny Mosley MRPharmS
 Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS. Lecture 5
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS Lecture 5 Hypertension Blood pressure BP = CO x PVR n Interaction between autonomic nervous system, cardiovascular system and renal system Normal: 110/70 Prehypertension
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS Lecture 5 Hypertension Blood pressure BP = CO x PVR n Interaction between autonomic nervous system, cardiovascular system and renal system Normal: 110/70 Prehypertension
1/4/18. Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update. Disclosure. Pharmacist Objectives. Pharmacy Technician Objectives. What is Heart Failure?
 Disclosure Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial sponsor with a vested interest in this presentation. Natalie Beiter,
Disclosure Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial sponsor with a vested interest in this presentation. Natalie Beiter,
Heart Failure. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Scientific conclusions and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation
 Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
Medications and Falls Part 1
 Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron Medication Safety Pharmacist Saint Francis Hospital and Medical Center
Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron Medication Safety Pharmacist Saint Francis Hospital and Medical Center
Some Facts. Medications and Falls Part 1. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Falls Statistics for Older Adults ( 65yrs) 11/27/2018
 Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron reports no real or potential conflicts of interest relevant to this
Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron reports no real or potential conflicts of interest relevant to this
2017 Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults
 DETAILED SUMMARY FROM THE 2017 Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults A REPORT OF THE American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association
DETAILED SUMMARY FROM THE 2017 Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults A REPORT OF THE American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari
![Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari](/thumbs/90/104323364.jpg) Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS ALISKIREN 150MG TABLET RASILAZ RENIN INHIBITOR
 S/N ME OF MEDICATIONS BRANDED/GENERIC DRUG CLASS * UNIT PRICE RANGE (SGD$) 1 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG CAPSULE SECTRAL BETA BLOCKERS 0.50 2 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS 0.33 3 ALISKIREN
S/N ME OF MEDICATIONS BRANDED/GENERIC DRUG CLASS * UNIT PRICE RANGE (SGD$) 1 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG CAPSULE SECTRAL BETA BLOCKERS 0.50 2 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS 0.33 3 ALISKIREN
Angina Pectoris Dr. Shariq Syed
 Angina Pectoris Dr. Syed 1 What is Angina Pectoris (AP)? Commonly known as angina is chest pain often due to ischemia of the heart muscle, Because of obstruction or spasm of the coronary arteries 2 What
Angina Pectoris Dr. Syed 1 What is Angina Pectoris (AP)? Commonly known as angina is chest pain often due to ischemia of the heart muscle, Because of obstruction or spasm of the coronary arteries 2 What
Cardiovascular drugs
 chapter 13 Cardiovascular drugs Cardiovascular drugs act on the heart or blood vessels to control the cardiovascular system. They are used to treat a variety of conditions from hypertension to chronic
chapter 13 Cardiovascular drugs Cardiovascular drugs act on the heart or blood vessels to control the cardiovascular system. They are used to treat a variety of conditions from hypertension to chronic
Antihypertensive Drugs. Nafrialdi
 Antihypertensive Drugs Nafrialdi 1 Mechanisms of Blood Pressure Regulation Blood Presure Cardiac Output Peripheral Resistance Heart Rate Stroke volume Vascular tone Vessel elasticity Myocardial contractility
Antihypertensive Drugs Nafrialdi 1 Mechanisms of Blood Pressure Regulation Blood Presure Cardiac Output Peripheral Resistance Heart Rate Stroke volume Vascular tone Vessel elasticity Myocardial contractility
Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Introduction This Clinician Guide is based on the 2018
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Introduction This Clinician Guide is based on the 2018
The JNC-7 classification includes normal BP, prehypertension, stage 1 hypertension, and stage 2 hypertension.
 Hypertension is defined as an elevated SBP ( 140 mm Hg), DBP ( 90 mm Hg), or both. - A clinical diagnosis of hypertension is based on the mean of two or more properly measured seated BP measurements taken
Hypertension is defined as an elevated SBP ( 140 mm Hg), DBP ( 90 mm Hg), or both. - A clinical diagnosis of hypertension is based on the mean of two or more properly measured seated BP measurements taken
