Ah S%#T!!! Deadly Overdoses That Die En Route. Jamie Syrett, MD Office of Prehospital Care Rochester General Health System
|
|
|
- Trevor Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3 Ah S%#T!!! Deadly Overdoses That Die En Route Jamie Syrett, MD Office of Prehospital Care Rochester General Health System
4 Case 1 (and 2) Male - mid 30s, pulled from a burning building by a fire-fighter without SCBA
5 Case 1 Male 30s Unconscious HR30, BP 70/50, Sats 82% (to 100% with BVM) RR - shallow/ineffective No cyanosis Had a seizure
6 Case 2 Firefighter/Smoker Dizzy, weak, headache, vomits HR160, RR40, BP120/80, Sats100% Gave the patient mouth to mouth in the building
7 Case 3 Male - 50yo Spilled something on arm, no local pain or burn Tingling/twitching/screaming in pain HR130, BP160/100,Sat100%,RR20 Wide complex tachycardia on monitor
8 Case 3
9 Case 4 Farmer found at the roadside Unconscious Covered in vomit and drooling at the mouth, pupils are pinpoint, wheezing HR130, BP140/90, RR30, Sats 94%
10 Case 5 34F unresponsive Suicide note that the antidepressants are not working HR130, SBP90, RR20, Sats 100% Wide complex on the monitor Then seizes in the ambulance
11 Case 6 6YO-M Temp 40ºC, P155, RR50(deep), sat100% Got into the pill box
12 Case 7 6YO-M twin P20, SBP60, RR20, Sat100% Got into the prescriptions
13 Plan Cyanide Hydrofluoric Acid Sarin, tabin and Organophosphates TCA Aspirin Beta Blockers/Ca channel blockers Bath Salts
14 Cyanide A few years ago smoke had a different composition Today with plastics and other synthetics smoke generates a more toxic mix of chemicals
15 Cyanide In a typical structure fire Oxides of nitrogen Hydrogen sulphide Carbon dioxide and monoxide Hydrogen cyanide
16 Cyanide The King of Smoke Toxins 30 time deadlier than CO Generated from the combustion of natural and synthetic materials Anytime Hydrogen, Carbon and Nitrogen are involved in combustion cyanide is generated
17 Cyanide Burning computers, TVs, carpets, cushions, insulation, foams, laminates It doesn t take much to kill you! Zyklon B in Nazi Germany
18 Cyanide Time to die (min) 30 min 30min 20 min 10 min 1min 0 min 135ppm 3400ppm
19 Cyanide 2006 NFPA study - fire fatalities 86% of victims had toxic cyanide levels Smoke kills them a long time before the fire does Bitter Almonds - often undetectable till 600ppm 40% can t smell it at all
20 Rapid breathing Restlessness Dizziness Weakness Headache Nausea and vomiting Rapid heart rate Cyanide
21 Cyanide Convulsions Low blood pressure Slow heart rate Loss of consciousness Lung injury Respiratory failure leading to death
22 Cyanide Questionable risk/benefit of mouth to mouth Decontaminate and ventilate
23 Cyanide Binds to the Cytochrome System Inactivates it - can t generate ATP Chemical asphyxiant
24 Cyanide Lilly Kits - Amyl Nitrite, Sodium Nitrite, Sodium Thiosulphate Nitrite - Induces methemaglobin Problem with fire victims
25 Cyanide Nitrite creates methemaglobin - high affinity for cyanide Enzyme in the liver (rhodanase) then metabolizes cyanide with sulphate (extra supplied by thiosulphate) But fire victims have - Hb, Hb-CO
26 Hydrofluoric Acid Really Bad News for EMS Classified as a corrosive Unique in its degree of action and toxicity
27 Hydrofluoric Acid Found in High Octane Fuel Production Etching Glass Semiconductors Dyes/Plastics Fireproofing
28 Hydrofluoric Acid Rapidly Penetrates Skin Dissociates to release fluoride ions Under 20% do not cause initial pain Fluoride binds to everything - calcium, magnesium and potassium Sudden rapid drop in calcium
29 Hydrofluoric Acid 20% exposure to a 5 inch by 5 inch area of skin is painless and rapidly fatal Pain occurs when the calcium-fluoric salt precipitates in the tissues
30 Hydrofluoric Acid Management Decontamination with copious irrigation Local - Calcium gluconate gel Local - Injection of calcium gluconate into the tissues Systemic - Infusions of calcium and magnesium
31 EMS Calcium Gluconate gel - 1 amp of calcium and a tube of surgilube (!) Can also nebulize calcium solutions
32 EMS Systemic management should be started with any cardiac changes on the ECG Look at the Q-T and QRS intervals and if they increase then initiate IV
33 Last Word It takes 10cc of 100% HF to bind all the calcium in a 70kg male HF can painlessly enter thru a pin hole in a glove
34 Organophosphates Nerve agents (Tabin, sarin) Organophosphates Carbamates
35 Utilization of Nerve Agents Iraq Japan in 1990s
36 Organophosphates 25m incidents of organophosphate poisoning worldwide each year in agriculture workers Jeyaratnam J; Acute pesticide poisoning: a major global health problem. World Health Stat Q. 1990;43(3): Litchfield MH; Estimates of acute pesticide poisoning in agricultural workers in less developed countries. Toxicol Rev. 2005;24(4):271-8.
37 Organophosphates Small or pinpoint pupils. Painful, blurred vision. Runny nose and eyes. Excess saliva. Eyes look 'glassy'. Nausea. Mild muscle weakness. Localised muscle twitching. Mild agitation. Headache.
38 Organophosphates Pinpoint pupils, conjunctival injection. Dizziness, disorientation. Coughing, wheezing, sneezing. Drooling, excess phlegm, bronchorrhea, bronchospasm. Breathing difficulty. Marked muscle twitching or tremors. Muscle weakness, fatigue. Vomiting, diarrhea, urination.
39 Organophosphates Pinpoint pupils. Confusion and agitation. Convulsions. Copious excess secretions. Cardiac arrhythmias. Collapse, respiratory depression or respiratory arrest. Coma. Death.
40 Organophosphates SLUDGE Salivation Lacrimation Urination Defecation Gastric Upset Emesis
41 Toxidrome Narcotic/opiate Sympathomimetic Cholinergic - SLUDGE Anticholinergic - Mad as a hatter
42 Health Protection Agency (UK) 1. Could this be cyanide? 2. Could this be a nerve agent or organophosphate?
43 Garlic Smells
44 Management Decontaminate there and then Charcoal for ingestion Atropine (20mcg/kg in children) IV 2-PAM (Pralidoxime) IV MARK1 NAAK replaced with ATNAA
45 Gulf War Syndrome? Neuropsychiatric symptoms are known to occur - both in Gulf War and Tokyo Victims
46 The Old Favorite What drug still strikes fear into the experienced paramedic?
47 Case 5 34F unresponsive Suicide note that the antidepressants are not working HR130, SBP90, RR20, Sats 100% Wide complex on the monitor Then seizes in the ambulance What information is important to determine in this case?
48 Case Vital Signs Level of Consciousness Time and amount of ingestion QRS duration
49 Tricyclics Increasingly being used in medicine after being out of favor due to risks Depression/OCD Chronic pain/migraine Bed wetting Child behavior
50 Clinical Presentation CNS effects - Altered level of consciousness, seizures (bad) Cardiac effects - Tachycardia, widening QRS Respiratory - Tachypnea due to acidosis
51 Actions Non-selective agents with multiple sites of action. Inhibit amine uptake (nor-epi, serotonin) Block sodium channels Antagonize potassium channels Antagonize GABA/Cl channels. Anticholinergic actions (only muscurinic) Inhibit adrenergic receptors (alpha 1 and 2)
52 Actions TCAs are Sodium Channel Blockers Class 1 medications Competitive type action Causes the cardiac issues
53 Toxicity in 2500 cases Tachycardia (51%) Coma (35%) Widening QRS (21%) *** Hypotension (14%) *** Seizures (8%) *** Arrhythmias (6%) ***
54 Management Symptomatic management - but NOT lidocaine Early benzodiazepines and proactive management Bicarb
55 Bicarb Indications for bicarb are if the patient has evidence of a widened QRS Prior management was if the QRS was wider than 0.2s (1 big square on ECG) Now management is if QRS is bigger than 0.12s (3 small squares) Aggressive management change
56 Bicarb Unknown actions Probably NOT due to correcting the ph Probably due to being a massive sodium donator
57 Bicarb Dose is unknown and guided by the QRS and the ph of the patient
58
59
60 Other Management Early intubation Delayed washout of stomach Charcoal does not work
61 Other Management Patients receiving early benzodiazepines did better than those that did not
62 Aspirin Many actions Anti-pyretic/analgesic/anti-platelet Cleared by liver, excreted by kidney Can cause GI irritation, nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, metabolic acidosis
63 In Overdose Patients exhibit Fever (?) Diaphoresis Confusion Hyperventilation
64 Fever Fever is caused by the aspirin causing metabolism to be uncoupled creating heat rather than ATP (energy)
65 Respiration Rate Metabolic Acidosis - Causes increased RR Central stimulation of respiratory center also causes increased RR Fever causes increased RR Hypoxia may hint at pulmonary edema
66 Clinically CNS signs may be varied irritability, confusion, delirium, vertigo, seizures (hint at brain edema)
67 Causes of Overdose Pepto-bismol Oral - Deliberate or Accidental Dermal Oil of Wintergreen (1tsp=7g)
68 Management Charcoal (One of the few that charcoal works for - may use repeat charcoal) Lavage (Due to concretions) Alkaline Diuresis (Bicarbonate therapy)
69 Alkaline Diuresis Aspirin is a weak acid In presence of strong acid it will be associated (no charge) - can cross a membrane In presence of alkaline is will dissociate (splits to H+ and Base-) and cannot cross membrane
70 Given Bicarb Bicarb is excreted in the urine making the urine alkaline When aspirin gets in to the urine it dissociates and stays there (alkaline trapping)
71 Actions? Beta-Blockers
72 Beta-Blockers Beta 1,2 and 3 receptors exist Beta 1 - More in the heart Beta 2 - More in the lungs (smooth muscle) Beta 3 - Fat tissue
73 Beta Stimulation Beta 1 stimulation Increases force and rate of heart contraction. Increases AV conduction velocity. Increases renin release. Beta 2 stimulation Relaxes smooth muscle in blood vessels, bronchial tree and GI system. Induces gluconeogenesis.
74 Beta-Blockers Frequently prescribed for Hypertension. Ischemic heart disease. Cardiac arrhythmias. Migraine. Glaucoma.
75 Common Beta-Blockers Propranolol (1 and 2) - Inderal Atenolol (selective 1) - Tenormin Metoprolol (selective 1) - Lopressor
76 Clinically Absorbed rapidly from the stomach. Signs of overdose in 20 minutes. Bradycardia and hypotension. Jeopardizes cardiac circulation - leads to more negative inotropy. Mental status changes are common. Range from delirium to coma, can seize.
77 Clinically Bronchospasm is NOT common in overdose. Congestive Cardiac Failure and Pulmonary edema are far more likely. Can induce a hypoglycemic event in unstable diabetics.
78 Management Charcoal is indicated Remember rapid absorption
79 Specific Treatment Aimed at countering the beta blockade. Atropine Catecholamines Dobutamine - beta 1 Dopamine - both beta 1 and 2 Glucagon - now considered drug of choice. Pace
80 Glucagon Beta blockers cause decrease in camp Glucagon increases cgmp Boluses of 3-10mg have been used with success. Dose has not been determined. Problem - In 1995 a survey found glucagon in 0% of ED and 26% of hospitals.
81 EMS Management Glucagon - Will make the patient vomit when given IV and pushed Symptomatic management may require IV dopamine and continuous epi
82 EMS Management Plan Fluid Boluses to Fill Up the Tank Give Glucagon IV Start dopamine drip as needed Use IV epi - 1mg in 1000cc at 1cc/min then increase
83 Calcium Channel Blockers Introduced in increased prescibing has led to increased toxicity issues 3 most common are Verapamil (calan), diltiazem (cardizem), nifedipine (adalat, procardia)
84 Calcium Channel Blockers Extensively 1st pass metabolized which is protective for oral ingestions Largely protein bound Spread out throughout the whole body
85 Clinically Toxicity is an extension of the therapeutic effect Decreased calcium into the myocardium and vascular smooth muscle cells Decreased AV conduction and sinus discharge Decreased heart contractility Vasodilation and hypotension
86 Clinically Bradycardia and conduction delay (1AVB, 2AVB, asystole) Hypotension - Some blockers cause more hypotension and may cause a reflex tachycardia (Nifedipine) Lethargy, slurred speech, N/V, coma
87 EMS Management Symptomatic management Specific antidotes In an unknown overdose you may want to give glucagon since calcium channel and beta-blocker overdose appear the same
88 ?Give Calcium? In general giving calcium is anecdotally not described as working but should still be considered Another anecdote says give calcium prior to giving cardizem in a hypotensive patient in rapid atrial fibrillation
89 Management Similar to beta-blockers Fluid bolus Glucagon Calcium Dopamine and Epi drips
90 Bath Salts
91 Case 1 (and 2) Male - mid 30s, pulled from a burning building by a fire-fighter without SCBA
92 Case 1 Male 30s Unconscious HR30, BP 70/50, Sats 82% (to 100% with BVM) RR - shallow/ineffective No cyanosis Had a seizure
93 Case 2 Firefighter/Smoker Dizzy, weak, headache, vomits HR160, RR40, BP120/80, Sats100% Gave the patient mouth to mouth in the building
94 Case 3 Male - 50yo Spilled something on arm, no local pain or burn Tingling/twitching/screaming in pain HR130, BP160/100,Sat100%,RR20 Wide complex tachycardia on monitor
95 Case 3
96 Case 4 Farmer found at the roadside Unconscious Covered in vomit and drooling at the mouth, pupils are pinpoint, wheezing HR130, BP140/90, RR30, Sats 94%
97 Case 5 34F unresponsive Suicide note that the antidepressants are not working HR130, SBP90, RR20, Sats 100% Wide complex on the monitor Then seizes in the ambulance
98 Case 6 6YO-M Temp 40ºC, P155, RR50(deep), sat100% Got into the pill box
99 Case 7 6YO-M twin P20, SBP60, RR20, Sat100% Got into the prescriptions
100
Poison (Toxicant): any substance or agent capable of producing a deleterious response in a biological system or living organism.
 Poison (Toxicant): any substance or agent capable of producing a deleterious response in a biological system or living organism. Poisoning= overdose toxicity intoxication= toxicity due to foreign substance
Poison (Toxicant): any substance or agent capable of producing a deleterious response in a biological system or living organism. Poisoning= overdose toxicity intoxication= toxicity due to foreign substance
Chapter 13. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications
 Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
By Dr. Magdy M. Awny. (nerve agent)
 By Dr. Magdy M. Awny (nerve agent) Pesticides Is any chemical substance or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, repelling, or mitigating any pest are a group of insecticides or Organophosphorous
By Dr. Magdy M. Awny (nerve agent) Pesticides Is any chemical substance or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, repelling, or mitigating any pest are a group of insecticides or Organophosphorous
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes
 Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control 1-800-876-4766 Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes these agents, found in virtually every household, common
Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control 1-800-876-4766 Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes these agents, found in virtually every household, common
WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA
 CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
State of Illinois NERVE GAS AUTO-INJECTOR GUIDELINES March 18, 2003
 State of Illinois NERVE GAS AUTO-INJECTOR GUIDELINES March 18, 2003 Purpose: To provide Illinois EMS agencies with guidelines on the appropriate use of Mark I kits. The Mark I kit contains antidotes to
State of Illinois NERVE GAS AUTO-INJECTOR GUIDELINES March 18, 2003 Purpose: To provide Illinois EMS agencies with guidelines on the appropriate use of Mark I kits. The Mark I kit contains antidotes to
EM Cases Course 2017 Toxicology Module
 EM Cases Course 2017 Toxicology Module quick IV access and diazepam is administered. The seizure stops. The first set of vitals show: HR 30bpm, BP 70/40. His ECG is shown below. Margaret Thompson & JP
EM Cases Course 2017 Toxicology Module quick IV access and diazepam is administered. The seizure stops. The first set of vitals show: HR 30bpm, BP 70/40. His ECG is shown below. Margaret Thompson & JP
DUODOTE AUTO-INJECTOR
 Hazardous Material (WMD) use only Indications The DuoDote may be administered by the EMT or Paramedic who have had adequate training in the on-site recognition and treatment of nerve agent exposure. Chemical
Hazardous Material (WMD) use only Indications The DuoDote may be administered by the EMT or Paramedic who have had adequate training in the on-site recognition and treatment of nerve agent exposure. Chemical
1/29/2014. Objectives. The unstable overdose patient. Unstable overdose case #1. Outline
 Objectives The unstable overdose patient Craig Smollin MD Associate Medical Director California Poison Control Center, SF Division Discuss clinical scenarios unique to the acutely poisoned patient and
Objectives The unstable overdose patient Craig Smollin MD Associate Medical Director California Poison Control Center, SF Division Discuss clinical scenarios unique to the acutely poisoned patient and
Weapons of Mass Destruction. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012
 Weapons of Mass Destruction Lesson Goal To become familiarize with the concept of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), how these weapons might be used, and the type of treatment that would be appropriate
Weapons of Mass Destruction Lesson Goal To become familiarize with the concept of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), how these weapons might be used, and the type of treatment that would be appropriate
Sources of carbon monoxide exposure
 Carbon monoxide Sources of carbon monoxide exposure Mechanism of action Tissue hypoxia Binds to myoglobin and cytochrome oxidase Shift oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve to left Accelerate cellular death
Carbon monoxide Sources of carbon monoxide exposure Mechanism of action Tissue hypoxia Binds to myoglobin and cytochrome oxidase Shift oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve to left Accelerate cellular death
Cholinesterase-inhibiting Chemicals C 1
 BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Cholinesterase-inhibiting Chemicals C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments Patients whose vomitus, skin or clothing
BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Cholinesterase-inhibiting Chemicals C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments Patients whose vomitus, skin or clothing
POISON ANTIDOTE DOSE* COMMENTS
 Antidotes Acetaminophen N-acetylcysteine 140 mg/kg initial oral dose, followed Most effective within 16 24 hr; may by 70 mg/kg every 4 hr 17 doses be useful after chronic intoxication or intravenously
Antidotes Acetaminophen N-acetylcysteine 140 mg/kg initial oral dose, followed Most effective within 16 24 hr; may by 70 mg/kg every 4 hr 17 doses be useful after chronic intoxication or intravenously
Acid Base Balance by: Susan Mberenga RN, BSN, MSN
 Acid Base Balance by: Susan Mberenga RN, BSN, MSN Acid Base Balance Refers to hydrogen ions as measured by ph Normal range: 7.35-7.45 Acidosis/acidemia: ph is less than 7.35 Alkalosis/alkalemia: ph is
Acid Base Balance by: Susan Mberenga RN, BSN, MSN Acid Base Balance Refers to hydrogen ions as measured by ph Normal range: 7.35-7.45 Acidosis/acidemia: ph is less than 7.35 Alkalosis/alkalemia: ph is
99 Problems but hyperglycemia ain t one SHEEREENE HUSSAIN MD, MA RAPID CITY REGIONAL HOSPITAL HOSPITALIST DEPARTMENT SEPT 12, 2018
 99 Problems but hyperglycemia ain t one SHEEREENE HUSSAIN MD, MA RAPID CITY REGIONAL HOSPITAL HOSPITALIST DEPARTMENT SEPT 12, 2018 ER Admit 17 yo F reported intentional overdose handful of her mother s
99 Problems but hyperglycemia ain t one SHEEREENE HUSSAIN MD, MA RAPID CITY REGIONAL HOSPITAL HOSPITALIST DEPARTMENT SEPT 12, 2018 ER Admit 17 yo F reported intentional overdose handful of her mother s
Chemical Agents Module 1
 1 2 - Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) - Chemical Biological Conventional weapons (guns, explosives) Nuclear devices Radiation dispersal devices 3 1 - Chemical Agents - Nerve agents Poisons Vesicants
1 2 - Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) - Chemical Biological Conventional weapons (guns, explosives) Nuclear devices Radiation dispersal devices 3 1 - Chemical Agents - Nerve agents Poisons Vesicants
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology
 ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms. Introduction to the Algorithms
 Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
Mr. Eknath Kole M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali)
 M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
Nerve Agent/Organophosphate Pesticide Exposure Treatment
 Nerve Agent/Organophosphate Pesticide Exposure Treatment Purpose: This Protocol is intended for EMS personnel at all levels to assess and treat patients exposed to nerve agents and organophosphate pesticides.
Nerve Agent/Organophosphate Pesticide Exposure Treatment Purpose: This Protocol is intended for EMS personnel at all levels to assess and treat patients exposed to nerve agents and organophosphate pesticides.
A Primer on Chemical Nerve Agents. Information for Public Health and EMS Workers
 A Primer on Chemical Nerve Agents Information for Public Health and EMS Workers This information was adapted and developed from a presentation by: Area Health Education Center of Southern Nevada 2 Chemical
A Primer on Chemical Nerve Agents Information for Public Health and EMS Workers This information was adapted and developed from a presentation by: Area Health Education Center of Southern Nevada 2 Chemical
Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose
 Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose Intravenous access Oxygen Pulse oximetry n-invasive blood pressure monitoring Accu-Check ECG monitoring and ECG Chest x-ray Respiratory depression?
Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose Intravenous access Oxygen Pulse oximetry n-invasive blood pressure monitoring Accu-Check ECG monitoring and ECG Chest x-ray Respiratory depression?
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
EMT. Chapter 19 Review
 EMT Chapter 19 Review Review 1. Which of the following questions is of LEAST pertinence for the EMT to ask a patient who intentionally overdosed on a medication? A. How much do you weigh? B. How much did
EMT Chapter 19 Review Review 1. Which of the following questions is of LEAST pertinence for the EMT to ask a patient who intentionally overdosed on a medication? A. How much do you weigh? B. How much did
Arrhythmias. 1. beat too slowly (sinus bradycardia). Like in heart block
 Arrhythmias It is a simple-dysfunction caused by abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. The heart is designed in such a way that allows it to generate from the SA node electrical
Arrhythmias It is a simple-dysfunction caused by abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. The heart is designed in such a way that allows it to generate from the SA node electrical
SALICYLATES. Anthony F. Pizon, M.D. Associate Professor Division Medical Toxicology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
 SALICYLATES Anthony F. Pizon, M.D. Associate Professor Division Medical Toxicology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Overview: Salicylates Found in Willow bark (Salix alba vulgaris) Widely used
SALICYLATES Anthony F. Pizon, M.D. Associate Professor Division Medical Toxicology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Overview: Salicylates Found in Willow bark (Salix alba vulgaris) Widely used
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS
 ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
Arrhythmias. Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium.
 Arrhythmias Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. However, in clinic it present as a complex family of disorders that show variety of symptoms, for
Arrhythmias Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. However, in clinic it present as a complex family of disorders that show variety of symptoms, for
Acid/Base Balance. the concentrations of these two ions affect the acidity or alkalinity of body fluids
 Acid/Base Balance some of most critical ions in body fluids are H + (hydrogen) and OH - (hydroxyl) ions the concentrations of these two ions affect the acidity or alkalinity of body fluids acidity/alkalinity
Acid/Base Balance some of most critical ions in body fluids are H + (hydrogen) and OH - (hydroxyl) ions the concentrations of these two ions affect the acidity or alkalinity of body fluids acidity/alkalinity
2/1/2013. Anti dos and don ts: Pearls and pitfalls in the use of antidotes. The first rule of surfing... The ABC s of the poisoned patient
 According to the American Academy of Poison Control Centers, what is the most common intervention performed in the management of acutely poisoned patients? Anti dos and don ts: Pearls and pitfalls in the
According to the American Academy of Poison Control Centers, what is the most common intervention performed in the management of acutely poisoned patients? Anti dos and don ts: Pearls and pitfalls in the
You. Let s Talk Hazmat. Clues to Hazmat
 Me You Let s Talk Hazmat Clues to Hazmat Location and Occupancy Container Shapes and Sizes Placards and Labels Markings and Colors Shipping Papers Senses CDC NIOSH Guide 1 The purpose of chemical protective
Me You Let s Talk Hazmat Clues to Hazmat Location and Occupancy Container Shapes and Sizes Placards and Labels Markings and Colors Shipping Papers Senses CDC NIOSH Guide 1 The purpose of chemical protective
Jeffrey N. Bernstein MD. *Simple asphyxiants *Systemic asyphyxiants *Chemical irritants
 Jeffrey N. Bernstein MD Simple asphyxiants Systemic asyphyxiants Chemical irritants 1746 (est) people killed overnight 3000 Cattle Countless wild animals There was no evidence of bleeding, physical
Jeffrey N. Bernstein MD Simple asphyxiants Systemic asyphyxiants Chemical irritants 1746 (est) people killed overnight 3000 Cattle Countless wild animals There was no evidence of bleeding, physical
The Hypotensive Poisoned Patient. Robert S. Hoffman, MD Director, NYC PCC
 The Hypotensive Poisoned Patient Robert S. Hoffman, MD Director, NYC PCC Some Definitions Hypotension = Low blood pressure Failure of macrocirculation Shock = Poor tissue perfusion Failure of microcirculation
The Hypotensive Poisoned Patient Robert S. Hoffman, MD Director, NYC PCC Some Definitions Hypotension = Low blood pressure Failure of macrocirculation Shock = Poor tissue perfusion Failure of microcirculation
Chapter 19 Toxicology Introduction Definitions Consider Poisoning In Patients With: Identifying the Patient and the Poison
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 19 Toxicology Introduction Each day, we come into contact with things that are potentially poisonous. Acute poisoning affects 5 million people each year. Chronic is much more common.
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 19 Toxicology Introduction Each day, we come into contact with things that are potentially poisonous. Acute poisoning affects 5 million people each year. Chronic is much more common.
Titrating Critical Care Medications
 Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
DYSRHYTHMIAS. D. Assess whether or not it is the arrhythmia that is making the patient unstable or symptomatic
 DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
Small Doses, Big Problems: Deadly Pediatric Poisons
 Small Doses, Big Problems: Deadly Pediatric Poisons Adam Algren, MD Departments of Pediatrics and Emergency Medicine Children s Mercy Hospital and Truman Medical Center Medical Director University of Kansas
Small Doses, Big Problems: Deadly Pediatric Poisons Adam Algren, MD Departments of Pediatrics and Emergency Medicine Children s Mercy Hospital and Truman Medical Center Medical Director University of Kansas
Substance Abuse and Poisonings. Chapter 17
 Substance Abuse and Poisonings Chapter 17 Identifying the Patient and the Poison Poison- any substance who s chemical reaction can damage body structures or impair body functions Poisons act by changing
Substance Abuse and Poisonings Chapter 17 Identifying the Patient and the Poison Poison- any substance who s chemical reaction can damage body structures or impair body functions Poisons act by changing
Salicylates commonly cause tinnitus, deafness, nausea and vomiting (salicylism). Hyperventilation results from stimulation of respiratory centre.
 Aspirin poisoning CLINICAL FEATURES Salicylates commonly cause tinnitus, deafness, nausea and vomiting (salicylism). Hyperventilation results from stimulation of respiratory centre. Severe poisoning causes
Aspirin poisoning CLINICAL FEATURES Salicylates commonly cause tinnitus, deafness, nausea and vomiting (salicylism). Hyperventilation results from stimulation of respiratory centre. Severe poisoning causes
Chapter 26. Media Directory. Dysrhythmias. Diagnosis/Treatment of Dysrhythmias. Frequency in Population Difficult to Predict
 Chapter 26 Drugs for Dysrythmias Slide 33 Slide 35 Media Directory Propranolol Animation Amiodarone Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Dysrhythmias Abnormalities of electrical
Chapter 26 Drugs for Dysrythmias Slide 33 Slide 35 Media Directory Propranolol Animation Amiodarone Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Dysrhythmias Abnormalities of electrical
Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies)
 SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
Instruct patient and caregivers: Need for constant monitoring Potential complications of drug therapy
 Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
Contra Costa County Emergency Medical Services Drug Reference. Indication Dosing Cautions Comments
 Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE
 UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE 1 Objectives: Review the physiological mechanism responsible to regulate acid base balance in the body i.e.: Buffers (phosphate, hemoglobin, carbonate) Renal mechanism Respiratory
UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE 1 Objectives: Review the physiological mechanism responsible to regulate acid base balance in the body i.e.: Buffers (phosphate, hemoglobin, carbonate) Renal mechanism Respiratory
Objectives: This presentation will help you to:
 emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
March 2009 CE. Site code # E Carbon Monoxide, Smoke Inhalation, Cyanide Poisoning and Medical Rehab
 March 2009 CE Site code #107200-E-1209 Carbon Monoxide, Smoke Inhalation, Cyanide Poisoning and Medical Rehab Objectives and materials by: F/M Dan Ogurek Countryside Fire Protection Dist. Packet Prepared
March 2009 CE Site code #107200-E-1209 Carbon Monoxide, Smoke Inhalation, Cyanide Poisoning and Medical Rehab Objectives and materials by: F/M Dan Ogurek Countryside Fire Protection Dist. Packet Prepared
Respiratory Pharmacology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
NJSP HMRU June 10, 2004
 June 10, 2004 Chemical-Bio Agents Module 3 Overview 1 Objectives Student will: Demonstrate ability to recognize signs and symptoms of chemical agent exposure Describe how to protect oneself against chemical
June 10, 2004 Chemical-Bio Agents Module 3 Overview 1 Objectives Student will: Demonstrate ability to recognize signs and symptoms of chemical agent exposure Describe how to protect oneself against chemical
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS
 VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis IERHA Immunization Program September 2016 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever, lymphadenopathy
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis IERHA Immunization Program September 2016 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever, lymphadenopathy
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
 INTRODUCTION This SOP applies to HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF). HYDROFLUORIC ACID is one of the strongest acids. It is extremely destructive to tissue and potentially fatal. HF causes such severe burns because
INTRODUCTION This SOP applies to HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF). HYDROFLUORIC ACID is one of the strongest acids. It is extremely destructive to tissue and potentially fatal. HF causes such severe burns because
These drugs produce effects similar to the sympathetic nervous system
 Terms adrenergic Drugs mydriasis sympathetic nervous system adrenergic drugs adrenergic mechanism of action positive inotropic effect positive chronotropic effect positive dromotropic effect adrenergic
Terms adrenergic Drugs mydriasis sympathetic nervous system adrenergic drugs adrenergic mechanism of action positive inotropic effect positive chronotropic effect positive dromotropic effect adrenergic
1 Chapter 19 Toxicology 2 Introduction Each day, we come into contact with things that are potentially poisonous. Acute poisoning affects 5 million
 1 Chapter 19 Toxicology 2 Introduction Each day, we come into contact with things that are potentially poisonous. Acute poisoning affects 5 million people each year. Chronic is much more common. Caused
1 Chapter 19 Toxicology 2 Introduction Each day, we come into contact with things that are potentially poisonous. Acute poisoning affects 5 million people each year. Chronic is much more common. Caused
Cardiotoxic Medications
 Cardiotoxic Medications Dean Olsen, DO Faculty, New York City Poison Control Center Director Emergency Medicine Residency Nassau University Medical Center Assistant Professor Pharmacology, Toxicology New
Cardiotoxic Medications Dean Olsen, DO Faculty, New York City Poison Control Center Director Emergency Medicine Residency Nassau University Medical Center Assistant Professor Pharmacology, Toxicology New
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
 Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
PHARMACOLOGY OF ARRHYTHMIAS
 PHARMACOLOGY OF ARRHYTHMIAS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: November 27, 2012 Materials on: Exam #5 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 14 1 CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Abnormalities
PHARMACOLOGY OF ARRHYTHMIAS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: November 27, 2012 Materials on: Exam #5 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 14 1 CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Abnormalities
Toxic Chemical Threats
 Toxic Chemical Threats John Devlin, MD, FACEP GA Poison Center / Emory University / Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Objectives To give you tools to help recognize what chemical agent is present
Toxic Chemical Threats John Devlin, MD, FACEP GA Poison Center / Emory University / Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Objectives To give you tools to help recognize what chemical agent is present
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
Welcome Applicants! FRIDAY, OCTOBER 24
 Welcome Applicants! FRIDAY, OCTOBER 24 Friday Prep A 3-year-old girl is brought to your office for re-evaluation of a fever that began 6 days ago. Her mother tells you that her daughter s temperature has
Welcome Applicants! FRIDAY, OCTOBER 24 Friday Prep A 3-year-old girl is brought to your office for re-evaluation of a fever that began 6 days ago. Her mother tells you that her daughter s temperature has
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + )
 Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
Intermediate Medications. Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol
 Intermediate Medications Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol Needle Handling Precautions Minimize the tasks performed in a moving ambulance Balance the
Intermediate Medications Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol Needle Handling Precautions Minimize the tasks performed in a moving ambulance Balance the
Episode 90 Low and Slow Poisoning
 Hyperkalemia Myxedema coma Spinal cord injury Hypothermia Episode 90 Low and Slow Poisoning With Drs. Margaret Thompson & Emily Austin Prepared by Dr. Keerat Grewal, edited by Dr. Anton Helman, Jan 2017
Hyperkalemia Myxedema coma Spinal cord injury Hypothermia Episode 90 Low and Slow Poisoning With Drs. Margaret Thompson & Emily Austin Prepared by Dr. Keerat Grewal, edited by Dr. Anton Helman, Jan 2017
Facts About VX. What VX is
 Facts About VX What VX is VX is a human-made chemical warfare agent classified as a nerve agent. Nerve agents are the most toxic and rapidly acting of the known chemical warfare agents. They are similar
Facts About VX What VX is VX is a human-made chemical warfare agent classified as a nerve agent. Nerve agents are the most toxic and rapidly acting of the known chemical warfare agents. They are similar
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter
 Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 23.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 12, 16, 23, 31, 46, 55, 59 63 23.2 Describe ways in which poisons can enter the body. Slide
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 23.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 12, 16, 23, 31, 46, 55, 59 63 23.2 Describe ways in which poisons can enter the body. Slide
Getting On My Nerves!!!!!!!! Mississippi Chempack Program
 Getting On My Nerves!!!!!!!! Mississippi Chempack Program Chris Reid Emergency Response Coordinator Office of Emergency Response Mississippi State Department of Health What is the CHEMPACK Program? Developed
Getting On My Nerves!!!!!!!! Mississippi Chempack Program Chris Reid Emergency Response Coordinator Office of Emergency Response Mississippi State Department of Health What is the CHEMPACK Program? Developed
LESSON ASSIGNMENT Given the trade and/or generic name of an adrenergic blocking agent, classify that agent as either an alpha or beta blocker.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
Dysrhythmias. Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics. EKG Parameters. Dysrhythmias. Components of an ECG Wave. Dysrhythmias
 Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
7/21/2017. Learning Objectives. Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology. Epinephrine. Cardiotonic Agents. Epinephrine. Epinephrine. Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT
 Learning Objectives Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Explain the actions, effects, indications, adverse effects, & precautions for agents from the following drug categories Cardiotonic
Learning Objectives Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Explain the actions, effects, indications, adverse effects, & precautions for agents from the following drug categories Cardiotonic
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET ACUPAN TM. 3. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM White, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets (7 mm diameter) engraved APN on one face.
 1. PRODUCT NAME ACUPAN 30 mg tablets 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains nefopam hydrochloride 30 mg. For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1. 3. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM
1. PRODUCT NAME ACUPAN 30 mg tablets 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains nefopam hydrochloride 30 mg. For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1. 3. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Chapter 149 Aspirin and Nonsteroidal Agents
 Chapter 149 Aspirin and Nonsteroidal Agents Episode overview: Core questions: 1. What is the pathophysiology of ASA toxicity? 2. What is the toxic dose of ASA? 3. How is aspirin eliminated from the body?
Chapter 149 Aspirin and Nonsteroidal Agents Episode overview: Core questions: 1. What is the pathophysiology of ASA toxicity? 2. What is the toxic dose of ASA? 3. How is aspirin eliminated from the body?
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood:
 Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
CHAPTER 5 CYANOGEN AGENTS (BLOOD AGENTS) SECTION I - GENERAL
 CHAPTER 5 CYANOGEN AGENTS (BLOOD AGENTS) SECTION I - GENERAL 501. Introduction. a. Cyanogen agents produce their effects by interfering with oxygen utilisation at the cellular level. Inhalation is the
CHAPTER 5 CYANOGEN AGENTS (BLOOD AGENTS) SECTION I - GENERAL 501. Introduction. a. Cyanogen agents produce their effects by interfering with oxygen utilisation at the cellular level. Inhalation is the
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
CRACKCast Episode Hydrocarbons (Ch th )
 CRACKCast Episode Hydrocarbons (Ch. 152 9 th ) Episode Overview Key Concepts: Aspiration is the major toxic risk of hydrocarbon poisoning. Hydrocarbons may cause systemic toxicity, burns, seizures, cardiac
CRACKCast Episode Hydrocarbons (Ch. 152 9 th ) Episode Overview Key Concepts: Aspiration is the major toxic risk of hydrocarbon poisoning. Hydrocarbons may cause systemic toxicity, burns, seizures, cardiac
CLICK ON A TOPIC BELOW
 CLICK ON A TOPIC BELOW AMLS Patient Assessment Pathway Contiguous Leads Common Laboratory Values Selected Common Toxidromes AMLS Patient Assessment Pathway INITIAL OBSERVATIONS Scene/Situation Safety threats
CLICK ON A TOPIC BELOW AMLS Patient Assessment Pathway Contiguous Leads Common Laboratory Values Selected Common Toxidromes AMLS Patient Assessment Pathway INITIAL OBSERVATIONS Scene/Situation Safety threats
Beta 1 Beta blockers A - Propranolol,
 Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
2/1/2013. Poisoning pitfalls. The original pitfall
 The original pitfall Poisoning pitfalls Craig Smollin MD Associate Medical Director, California Poison Control System - SF Division Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine, UCSF What will we talk about?
The original pitfall Poisoning pitfalls Craig Smollin MD Associate Medical Director, California Poison Control System - SF Division Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine, UCSF What will we talk about?
Dancing with Death: MDMA, PMMA and other 4 letter words
 Dancing with Death: MDMA, PMMA and other 4 letter words Mark Yarema, MD FRCPC Poison and Drug Information Service Alberta Health Services AARC Community Intervention Series March 15, 2016 Objectives At
Dancing with Death: MDMA, PMMA and other 4 letter words Mark Yarema, MD FRCPC Poison and Drug Information Service Alberta Health Services AARC Community Intervention Series March 15, 2016 Objectives At
Top 200 Section 4. Cardiovascular Drugs
 Top 200 Section 4 Cardiovascular Drugs Objectives After finishing this presentation the audience should be able to: Describe conditions/disease states that would make a person a candidate for drug therapy.
Top 200 Section 4 Cardiovascular Drugs Objectives After finishing this presentation the audience should be able to: Describe conditions/disease states that would make a person a candidate for drug therapy.
Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate).
 VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
9/11/2012. Chapter 11. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Endocrine Emergencies. Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes
 Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
Methamphetamine Abuse During Pregnancy
 Methamphetamine Abuse During Pregnancy Robert Davis, MD / r.w.davismd@gmail.com ❶ Statistics ❷ Pregnancy Concerns ❸ Postpartum Concerns ❹ Basic Science ❺ Best Practice Guidelines ❻ Withdrawal ❼ Recovery
Methamphetamine Abuse During Pregnancy Robert Davis, MD / r.w.davismd@gmail.com ❶ Statistics ❷ Pregnancy Concerns ❸ Postpartum Concerns ❹ Basic Science ❺ Best Practice Guidelines ❻ Withdrawal ❼ Recovery
Adenosine. poison/drug induced. flushing, chest pain, transient asystole. Precautions: tachycardia. fibrillation, atrial flutter. Indications: or VT
 Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Nassau Regional EMS Council Basic Life Support Protocols and Supplements to State BLS Protocol Manual Table of Contents
 Nassau Regional EMS Council Basic Life Support Protocols and Supplements to State BLS Protocol Manual Table of Contents Approved/ Revised Effective BLS Adult Nerve Agent/Organophosphate Poisoning Antidote
Nassau Regional EMS Council Basic Life Support Protocols and Supplements to State BLS Protocol Manual Table of Contents Approved/ Revised Effective BLS Adult Nerve Agent/Organophosphate Poisoning Antidote
CONSIDER POISONING IN PATIENTS WITH:
 1 2 3 4 5 CHAPTER 21 Toxicology INTRODUCTION Each day, we come into contact with things that are potentially poisonous. Acute poisoning affects 2 people each year. Chronic poisoning is more common. Deaths
1 2 3 4 5 CHAPTER 21 Toxicology INTRODUCTION Each day, we come into contact with things that are potentially poisonous. Acute poisoning affects 2 people each year. Chronic poisoning is more common. Deaths
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 8
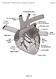 Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Skills: Recall the incidence of seizures Recall the causes of seizures Describe types of seizures List signs and symptoms of seizure patients
 Medical 1 Resuscitation Describe the morbidity and mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest List the chain of survival for sudden cardiac arrest as identified by the American Heart Association Discuss
Medical 1 Resuscitation Describe the morbidity and mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest List the chain of survival for sudden cardiac arrest as identified by the American Heart Association Discuss
INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES. When the student has finished this module, he/she will be able to:
 Care of the Poisoned Patient WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A.,
Care of the Poisoned Patient WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A.,
Winter Questions. Name: OASIS: EPCP. Professional Development: Non-prescription drug overdoses
 EPCP Professional Development: Non-prescription drug overdoses Winter 2012-13 Questions Name: OASIS: 1) The early stages of an ASA overdose is marked by: a) slow, irregular respirations b) deep rapid respirations
EPCP Professional Development: Non-prescription drug overdoses Winter 2012-13 Questions Name: OASIS: 1) The early stages of an ASA overdose is marked by: a) slow, irregular respirations b) deep rapid respirations
Antiarrhythmic Drugs. Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2017
 Antiarrhythmic Drugs Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2017 Types of Cardiac Arrhythmias Abnormalities of Impulse Formation: Rate disturbances. Triggered
Antiarrhythmic Drugs Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2017 Types of Cardiac Arrhythmias Abnormalities of Impulse Formation: Rate disturbances. Triggered
HEAVY METALS : Review
 HEAVY METALS : Review INHALED TOXINS Dr. Tawfiq Almezeiny MBBS FRCPC (CCM) Introduction Airborne toxins typically produce local noxious effects on the airways and lungs. Examples of Inhalational exposure:
HEAVY METALS : Review INHALED TOXINS Dr. Tawfiq Almezeiny MBBS FRCPC (CCM) Introduction Airborne toxins typically produce local noxious effects on the airways and lungs. Examples of Inhalational exposure:
Algorithm Focus. Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms. Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate algorithms
 Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Algorithms for the Conscious Patient Prehospital Medication Profiles Algorithm Focus Bradycardia Acute Pulmonary Edema and Shock Hypothermia
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Algorithms for the Conscious Patient Prehospital Medication Profiles Algorithm Focus Bradycardia Acute Pulmonary Edema and Shock Hypothermia
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS)
 DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
