Dermacyn Irrigation in Reducing Infection of a Median Sternotomy Wound
|
|
|
- Donald Charles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 13 (4), 2010 [Epub August 2010] doi: /HSF Online address: Dermacyn Irrigation in Reducing Infection of a Median Sternotomy Wound Abdul Ramzisham Rahman Mohd, MS, Mohd Khairulasri Ghani, MD, Raflis Ruzairee Awang, MBChB, Joanna Ooi Su Min, MMed, Mohd Zamrin Dimon, MS Heart and Lung Centre, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Dr. Ramzisham ABSTRACT Background: Sternal wound infection is an infrequent yet potentially devastating complication following sternotomy. Among the standard practices used as preventive measures are the use of prophylactic antibiotics and povidone-iodine as an irrigation agent. A new antiseptic agent, Dermacyn superoxidized water (Oculus Innovative Sciences), has recently been used as a wound-irrigation agent before the closure of sternotomy wounds. Methods: This prospective, randomized clinical trial was conducted to compare the effectiveness of Dermacyn and povidone-iodine in reducing sternotomy wound infection in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Upon chest closure and after insertion of sternal wires, wounds were soaked for 15 minutes with either Dermacyn or povidone-iodine. Subcutaneous tissue and skin were then closed routinely. Patients were followed up, and any wound infection was analyzed. Results: Of the 178 patients, 88 patients were in the Dermacyn group, and 90 were in the povidone-iodine group. The mean (±SD) age of the patients was 61.1 ± 7.6 years. The incidence of sternotomy wound infection was 19 cases (10.7%). Five (5.7%) of these cases were from the Dermacyn group, and 14 (15.6%) were from the povidone-iodine group (P =.033). No Dermacyn-related complication was identified. Conclusion: We found Dermacyn to be safe and more effective as a wound-irrigation agent than povidone-iodine for preventing sternotomy wound infection. INTRODUCTION Patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery are exposed to possible sternal wound Received October 13, 2009; received in revised form November 8, 2009; accepted November 24, Correspondence: Associate Professor Dr. Mohd Ramzisham Abdul Rahman, Senior Lecturer/Consultant Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Heart and Lung Centre, Department of Surgery, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre, Jalan Yaacob Latif, Cheras, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia; /2; fax: ( ramzisham@hotmail.com). infection despite the procedure being categorized as clean surgery. Infections range from superficial infection to deeper infection of soft tissue, sternal osteomyelitis, and mediastinitis. The incidence of such infections ranges from 0.9% to 20% of cases [Loop 1990; Ulicny 1991], and the incidence of mediastinitis reported in most studies is 1% to 2% [El Oakley 1996; Bitkover 1998]. Although deep sternal wound infections, including mediastinitis, are infrequent complications, such infections are associated with significant morbidity and mortality (between 9.8% and 14% [Loop 1990; Ulicny 1991; El Oakley 1996]), prolonged hospitalization, and an increased financial burden on the health care system [Vegas 1993]. Therefore, it is vital to prevent infection of the sternotomy wound following surgery. Among the standard practices for prevention are the prophylactic use of antibiotics and placement of the pericardial drains to facilitate drainage of blood and serous fluid. These practices have been shown to lower the rate of deep sternal infection [Blanchard 1995]. Agents that irrigate the dermal wound have also been used to facilitate removal of debris before wound closure. One common practice is the use of saline and antiseptics such as povidoneiodine as wound-irrigation agents. Dermacyn (Oculus Innovative Sciences, Petaluma, CA, USA), a superoxidized aqueous solution, is a new antiseptic agent cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that has recently been used in our center as an irrigation agent during closure of sternotomy wounds. The initial experience has been good with no adverse effects. Dermacyn is produced by means of a proprietary electrolysis process that uses a sophisticated, unique multichamber system. The solution is manufactured from purified water and sodium chloride. The electrolysis process separates and captures the ions to produce a sterile, ph-neutral solution consisting of a stable controlled formula of reactive oxygen and chlorine species [Oculus Innovative Sciences 2006]. The active compounds in Dermacyn are 99.9% water, hypochlorous acid, and sodium hypochlorite, and the inactive compounds are sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, hydrogen peroxide, chlorine dioxide, and ozone. Dermacyn wound-irrigation agent is applied to chemically debride, flush, and cleanse the wound surface. The reactive oxygen species assist in promoting the body s own healing process by reducing the microbial load and via the agent s E228
2 Dermacyn Irrigation in Reducing Infection Ramzisham et al moistening properties [Bongiovanni 2006]. Several studies have found Dermacyn to be safe and to exhibit a wide antimicrobial spectrum [Landa-Solis 2005]. Paola et al [2006] proved the effectiveness of Dermacyn over povidone-iodine and Dermacyn s safety in treating the infected diabetic foot. A study of another series by Ohno et al [2000] showed that superoxidized water had no adverse effect on hemodynamics and was safe when used as a mediastinal irrigation solution during open heart surgery. Dermacyn has also been subjected to a series of biocompatibility tests. These tests were performed in accordance with the requirements set forth by International Standards Organization and FDA guidelines. The product has also been tested in animal models to satisfy FDA requirements and to ensure its safety and efficacy [Oculus Innovative Sciences 2006]. Several studies, however, have identified various factors that contribute to wound infection that always need to be considered [Zacharias 1996]. We therefore conducted this study to compare the effectiveness of Dermacyn irrigation and povidone-iodine with respect to reducing the incidence of sternotomy wound infection following CABG. We also evaluated our study population to identify the potential risk factors for sternotomy wound infection following CABG. MATERIALS AND METHODS This prospective randomized clinical trial took place between June 2007 and December All patients scheduled for elective CABG were included in this trial. Exclusion criteria included emergency cases, patients who underwent other surgical procedures in addition to CABG, patients allergic to Dermacyn, and those who had infective or other skin lesions over anterior chest wall area. Informed consent was obtained, and patients were consecutively randomized into 2 groups. Group A patients used Dermacyn as a woundirrigation agent, and group B patients used povidone-iodine. All patients received intravenous prophylaxis with 1.2 g Augmentin (amoxicillin and clavulanate) at induction. Before the surgery, the skin was cleaned with 10% povidone-iodine solution and covered with polyurethane drapes. CABG was performed through a standard median sternotomy by 3 cardiothoracic surgeons. Upon closure, bone wax and diathermy were used sparingly for hemostasis. Two drains were normally left in the mediastinal cavity. The sternum was closed primarily with no. 6 steel wires in a figure-of-eight manner. In both groups, the wounds were then soaked for 15 minutes after insertion of the sternal wires. The subcutaneous tissue was closed in 2 layers with polyglactin 1-0 suture, and the skin was closed subcuticularly with Vicryl 3-0 suture. Diagnosis and Follow-up The sternotomy wounds were inspected on postoperative day 2 and daily until discharge. Patients were then followed up at 2, 4, and 6 weeks postoperatively to assess for the presence of wound infection and Dermacyn side effects. The primary outcome was the presence of sternotomy wound infection, which was defined according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in their National Nosocomial Infections Table 1. Clinical Characteristics of the 178 Patients Involved in the Trial* Age, y 61.1 ± 7.6 Male-female ratio 3.24:1 COPD, n 66 (37.1%) Diabetes mellitus, n 79 (44.4%) ESRF, n 32 (18.0%) Obesity (BMI >30 kg/m 2 ), n 20 (11.2%) Smoking, n 66 (37.1%) On-pump/off-pump surgery, n 153 (86%)/25 (14%) Bypass time, min 99.0 ± 7.4 IMA harvested, n 171 (96.1%) chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ESRF, end-stage renal failure; BMI, body mass index; IMA, internal mammary artery. System [Horan 1992]. Wound infections were graded according to Horan et al [1992] as superficial (involving the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the incision), deep (involving fascia, muscle layers, and sternum), or deep organ space. The nature of discharge from the wounds was documented, and samples of the discharge were sent for culture and sensitivity analyses. The risk factors for wound infections were identified and analyzed. Ethical Considerations This trial involved no financial gain and was approved by the research and ethics committee of the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre (code no. FF ). Statistical Analysis Data were stored and analyzed with SPSS software (version 12.0; SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Continuous and categorical variables were analyzed with the independent Student t test and the chi-square test, respectively. With the use of 95% confidence intervals, a P value <.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS We recruited 190 patients for this trial, 95 patients in each group. Twelve patients, however, dropped out owing to postoperative mortality (4 cases, 2 deaths due to poor left ventricular function of <20% and 2 deaths due to cerebrovascular accident) and chest reopened for bleeding (8 cases), leaving 178 patients remaining in the study. Eighty-eight patients were in group A, and 90 were in group B. The mean (±SD) age of the patients was 61.1 ± 7.6 years. The male-female ratio was 3:1. Diabetes mellitus and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) were the most common comorbidities (44.4% and 37.1%, respectively). End-stage renal failure (ESRF) and obesity were documented in 18% and 11.2% of cases, respectively. On-pump CABG surgery was performed in 86% of the patients with a mean cardiopulmonary bypass 2010 Forum Multimedia Publishing, LLC E229
3 Table 2. Comparison of Comorbidities and Intraoperative Details for the 2 Randomized Groups* Group A Group B P Age, y ± ± COPD, n 35 (39.8%) 31 (34.4%).462 Diabetes mellitus, n 39 (44.3%) 40 (44.4%).986 ESRF, n 8 (9.1%) 24 (26.7%).002 Obesity (BMI >30 kg/m 2 ), n 7 (8.0 %) 13 (14.4%).170 Smoking, n 35 (39.8%) 31 (34.4%).462 On-pump surgery, n 73 (83%) 80 (88.9%).255 Bypass time, min ± ± IMA harvested, n 84 (95.5%) 87 (96.7%).677 chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ESRF, end-stage renal failure; BMI, body mass index; IMA, internal mammary artery. time of 99 ± 7.4 minutes. A single internal mammary artery (IMA) was harvested in 171 patients (96.1%). Table 1 summarizes the patients clinical characteristics. The 2 groups were well matched with respect to demographic, comorbidity, and intraoperative variables. The only exception was ESRF, which was more prevalent in group B (26.7%) than in group A (9.1%). Table 2 summarizes the comparison of comorbidities and intraoperative details of the 2 groups. Sternal wound infections occurred in 19 patients (10.7%). Group B had a significantly higher incidence of infections (14 patients, 15.6%) than group A (5 patients, 5.7%) (P =.033, Table 3). All 5 patients who developed sternotomy wound infections in group A had superficial infections. Of the 14 patients in group B who developed infections, 10 had superficial infections, and the remaining 4 patients had deep sternal wound infections that led to sternal dehiscence requiring surgical debridement and repair (Table 4). Bacteriology Swabs for microbiology analyses were obtained from infected wounds. Of the 19 patients with infections, 11 patients had significant microbial growth. Six patients had Staphylococcus aureus infection, and Acinobacter sp was cultured in 2 patients. Pseudomonas aeroginosa, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and coagulase-negative Staphylococcus were isolated from 1 patient each. Risk Factors Risk factors were divided into preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative factors. A univariate analysis of all preoperative variables revealed that COPD, diabetes mellitus, ESRF, obesity (body mass index >30 kg/m 2 ), and smoking were associated with an increased risk of sternal wound infection at a P level of <.05. In this study, however, age was not significantly associated with sternal wound infection. Intraoperatively, we studied 3 variables: the CABG technique, the use of an IMA, and bypass time. Bypass time was significantly associated with Table 3. Incidence of Sternal Wound Infection in the 2 Groups* the risk of infection (P <.001). Patients who had an IMA harvested, however, were not associated with an increased risk of infection. The duration of mechanical ventilation and the length of intensive care unit (ICU) stay, which were studied as postoperative risk factors of sternotomy wound infection in this trial, were significantly associated with an increased risk of wound infection (Table 5). DISCUSSION Sternal Wound Infected Not Infected Total Group A, n 5 (5.7%) 83 (94.3%) 88 Group B, n 14 (15.6%) 76 (84.4%) 90 *P =.033. Table 4. Type of Infection Type of Infection Superfi cial Deep Total Group A, n 5 (100%) 0 (0%) 5 Group B, n 10 (71.4%) 4 (28.6%) 14 It is imperative to reduce the risk of sternotomy wound infection, and many standard practices have been described, including meticulous scrubbing, skin preparation, use of disposable prefabricated drapes, use of prophylactic antibiotics, and placement of the pericardial drains to facilitate the drainage of blood and serous fluid. The standard practice of irrigating the wound before closure with either normal saline or povidone-iodine has long been used in most centers. The efficacy of Dermacyn for antiseptic wound irrigation during closure of the sternotomy wound following open heart surgery has yet to be proven, however. As an antiseptic solution, it exerts a wide range of antimicrobial activities [Landa-Solis 2005; Oculus Innovative Sciences 2006]. It can also be applied when chemically debriding and cleansing wound surfaces. The mechanism of action in eradicating various microorganisms is well documented [Landa-Solis 2005]. The active agents in Dermacyn consist of both chlorine and reactive oxygen ions. It is believed that the bactericidal action exhibited by Dermacyn is due to the combined effect of these species. The reactive oxygen species is also beneficial in the wound-healing process. Both ions are often referred to as free radicals. A number of different types of free radicals are also produced naturally by the body. Many free radicals provide significant health benefits, whereas free radicals produced by radiation can be destructive in nature. Conversely, Dermacyn ions and free radicals are biological and are not produced by radiation. Dermacyn technology has been tested in accordance with FDA requirements to ensure that such free radicals do not cause any harm. E230
4 Dermacyn Irrigation in Reducing Infection Ramzisham et al Table 5. Univariate Analysis of Preoperative Risk Factors for Sternal Infection* Infected (n = 19) Not Infected (n = 159) P Age, y 63.0 ± ± COPD, n 11 (57.9%) 55 (34.6%).047 Diabetes mellitus, n 13 (68.7%) 66 (41.5%).026 ESRF, n 11 (57.9%) 21 (13.2%).000 Obesity, n 16 (84.2%) 4 (5.2%).000 Smoking, n 11 (57.9%) 55 (34.6%).047 Bypass time, min ± ± IMA harvest, n 17 (89.5%) 154 (96.9%).118 Ventilation duration, h ± ± Length of ICU stay, d 2.63 ± ± chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ESRF, end-stage renal failure; IMA, internal mammary artery; ICU, intensive care unit. In this study, the 5 patients from the Dermacyn group with infected wounds had only superficial infections, and they required only a course of antibiotics and wound dressings to treat the infection and to promote wound healing. Four patients from the povidone-iodine group with wound infection, however, had associated deep wound infection and sternal dehiscence. These patients required surgical debridement and sternal rewiring. The remaining 10 patients had superficial infections and were successfully treated with antibiotics and wound dressings. Obviously, these findings indicate that the Dermacyn group not only had a lower infection rate but also had less severe infections than the povidone-iodine group. Many studies have demonstrated that the development of sternotomy wound infection following CABG is multifactorial. Most authors have classified the risk factors into 3 groups: preoperative factors pertaining to the patient, such as advanced age and comorbidities; intraoperative factors, such as a prolonged duration of operation and the need for reoperation; and postoperative factors, such as the use of an intra-aortic balloon pump, massive blood transfusion, and prolonged mechanical ventilation [Oschner 1972]. In the present study, we assessed 11 variables as potential risk factors for sternotomy wound infection. A univariate analysis was performed to determine the associations between these risk factors and wound infection (Table 5). In contrast to the results of other studies, we found that age was not significantly associated with sternotomy wound infection (P =.257). This result was probably because most of our patients were younger than 65 years, whereas several studies have shown that older patients are at high risk of developing wound infection. Our analysis revealed that patients who had diabetes mellitus and were obese were more likely to develop sternotomy wound infection, a result that is concordant with other studies [Moulton 1996]. Cigarette smoking and COPD were also identified as significant risk factors for Table 6. Infected Cases among ESRF and non-esrf Patients* Infected ESRF Non-ESRF Total Group A, n 3 (60%) 2 (40%) 5 Group B, n 8 (57.1%) 6 (42.9%) 14 *Odds ratio, 1.1. sternal wound infection following CABG. More than 60% of our patients with infection were smokers and had COPD. The latter is frequently associated with an increased risk of postoperative mediastinitis, probably because of frequent coughing, which may contribute to wound dehiscence and thereby facilitate bacterial migration into the mediastinum. Patients with COPD also experience respiratory infections more frequently and prolonged weaning from mechanical ventilation [Grossi 1991]. The details of the pathophysiology causing the infection in these patients are beyond the scope of this report. In this trial, we were unable to match the 2 groups with respect to the number of ESRF patients. ESRF was more prevalent in group B. The overall incidence of sternal wound infection in ESRF patients was statistically significant (P <.001). Further analysis, however, revealed that 3 (60%) of the 5 patients in group A and 8 (57.1%) of the 14 patients in group B who developed infection had ESRF. The calculated odds ratio between these 2 groups was 1.1, implying that sternotomy wound infection is equally likely to occur in the 2 groups, regardless of the type of irrigation used (Table 6). We observed that 14 patients (82.4%) who developed wound infection had bypass times >110 minutes. This finding was supported by the statistical analysis, which showed bypass time to be significantly associated with the risk of sternal infection. This finding is similar to findings from most other studies, which showed a higher incidence of sepsis with longer bypass times [Loop 1990]. Many studies have linked the use of IMA grafts to a higher incidence of sternal infections [Hirotani 2002]. Of the 19 patients who developed sternotomy wound infection in the present study, 17 (89.5%) had a single IMA harvested. This incidence showed that this variable did not make a significant contribution to the risk of sternal infection. Decreased sternal perfusion has been hypothesized as a cause for an increased incidence of sternal infections following use of an IMA [Carrier 1992]. Sofer et al [1999] showed that after bilateral IMA dissection, sternal perfusion was reduced by a mean of 24% ± 6%. Four weeks postoperatively, sternal blood flow was still reduced by a mean of 2% ± 2%. This low sternal perfusion may lead to tissue necrosis, and hence to an impaired wound-healing process. We tried to avoid bilateral IMA use unless it was absolutely necessary. Our results also confirmed that prolonged mechanical ventilation and a longer ICU stay were significantly associated with wound infection. All of our patients were ventilated and observed postoperatively in the cardiac beds in the general ICU rather than in a dedicated cardiac ICU. The risk of infection is generally greater in the 2010 Forum Multimedia Publishing, LLC E231
5 general ICU. These patients not only are exposed to endogenous infection (ie, normal commensals) but also are prone to contract infections from exogenous sources, such as the staff, other patients, and visitors. This trial had certain limitations. The number of participants in this study was relatively small because our center is not the main center for cardiothoracic surgery in this region; thus, the logistics allowed for only a limited number of operations. In addition, the variables for risk factors for sternotomy wound infections were limited to 11. Although all patients underwent their operations with the same cardiothoracic surgical teams, we were not able to appoint a dedicated surgeon for closure of sternotomy wounds. Some nonobjective factors that might also have influenced this study include the number of staff and medical students entering and exiting the theater during surgery. This trial, however, suggests that the use of Dermacyn as a wound-irrigation agent at closure of sternotomy following CABG reduced the incidence of wound infection, compared with povidone-iodine. There were no adverse side effects associated with the use of Dermacyn. Therefore, it can be used without hesitancy in view of its effectiveness and safety as a wound-irrigation agent. REFERENCES Bitkover CY, Gårdlund B Mediastinitis after cardiovascular operations: a case-control study of risk factors. Ann Thorac Surg 65: Blanchard A, Hurni M, Ruchat P, Stumpe F, Fischer A, Sadeghi H Incidence of deep and superficial sternal infection after open heart surgery. A ten years retrospective study from 1981 to Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 9: Bongiovanni CM Superoxidized water improves wound care outcomes in diabetic patients. Diabet Microvasc Complications Today May/ June:11-4. Carrier M, Grégoire J, Tronc F, Cartier R, Leclerc Y, Pelletier LC Effect of internal mammary artery dissection on sternal vascularization. Ann Thorac Surg 53: El Oakley RM, Wright JE Postoperative mediastinitis: classification and management. Ann Thorac Surg 61: Grossi EA, Esposito R, Harris LJ, et al Sternal wound infections and use of internal mammary artery grafts. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 102: Hirotani T, Shirota S, Cho Y, Takeuchi S Feasibility and suitability of the routine use of bilateral internal thoracic arteries. Ann Thorac Surg 73: Horan FC, Gaynes RP, Martone WJ, Jarvis WR, Emori TG CDC definitions of nosocomial surgical site infections, 1992: a modification of CDC definitions of surgical wound infections. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 13: Landa-Solis C, González-Espinosa D, Guzmán-Soriano B, et al Microcyn: a novel super-oxidized water with neutral ph and disinfectant activity. J Hosp Infect 61: Loop FD, Lytle BW, Cosgrove DM, et al J. Maxwell Chamberlain memorial paper. Sternal wound complications after isolated coronary artery bypass grafting: early and late mortality, morbidity, and cost of care. Ann Thorac Surg 49: Moulton MJ, Creswell LL, Mackey ME, Cox JL, Rosenbloom M Obesity is not a risk factor for significant adverse outcomes after cardiac surgery. Circulation 94(suppl):II Oculus Innovative Sciences Technical description of DERMA- CYN. Microcyn Technology, Inc. Petaluma, Calif.: Oculus Innovative Sciences. Ohno H, Higashidate M, Yokosuka T Mediastinal irrigation with superoxidized water in open-heart surgery: the safety and pitfalls of cardiovascular surgical application. Surg Today 30: Oschner JL, Mills NL, Woolverton WC Disruption and infection of median sternotomy incision. J Cardiovasc Surg 13: Paola LD, Brocco E, Senesiet A, et al Super-oxidized solution (SOS) therapy for infected diabetic foot ulcers. Wounds 18: Sofer D, Gurevitch J, Shapira I, et al Sternal wound infections in patients after coronary artery bypass grafting using bilateral skeletonized internal mammary arteries. Ann Surg 229: Ulicny KS Jr, Hiratzka LF The risk factors of median sternotomy infection: a current review. J Card Surg 6: Vegas AA, Jodra VM, García ML Nosocomial infection in surgery wards: a controlled study of increased duration of hospital stays and directs cost of hospitalization. Eur J Epidemiol 9: Zacharias A, Habib RH Factors predisposing to median sternotomy complications. Deep vs superficial infection. Chest 110: E232
Factors Predisposing to Median Sternotomy Complications*
 Factors Predisposing to Median Sternotomy Complications* Deep vs Superficial Infection Anoar Zacharias, MD; and Robert H. Habib, PhD Study objectives: Median sternotomy infections are a serious complication
Factors Predisposing to Median Sternotomy Complications* Deep vs Superficial Infection Anoar Zacharias, MD; and Robert H. Habib, PhD Study objectives: Median sternotomy infections are a serious complication
Deep Sternal Wound Infection: Risk Factors and Outcomes
 Deep Sternal Wound Infection: Risk Factors and Outcomes Michael A. Borger, MD, Vivek Rao, MD, Richard D. Weisel, MD, Joan Ivanov, MSc, Gideon Cohen, MD, Hugh E. Scully, MD, and Tirone E. David, MD Division
Deep Sternal Wound Infection: Risk Factors and Outcomes Michael A. Borger, MD, Vivek Rao, MD, Richard D. Weisel, MD, Joan Ivanov, MSc, Gideon Cohen, MD, Hugh E. Scully, MD, and Tirone E. David, MD Division
Does Using a Laparoscopic Approach to Cholecystectomy Decrease the Risk of Surgical Site Infection?
 ANNALS OF SURGERY Vol. 237, No. 3, 358 362 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Does Using a Laparoscopic Approach to Cholecystectomy Decrease the Risk of Surgical Site Infection? Chesley Richards,
ANNALS OF SURGERY Vol. 237, No. 3, 358 362 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Does Using a Laparoscopic Approach to Cholecystectomy Decrease the Risk of Surgical Site Infection? Chesley Richards,
Surgery for Acquired Cardiovascular Disease. Vacuum-assisted closure as a treatment modality for infections after cardiac surgery
 Vacuum-assisted closure as a treatment modality for infections after cardiac surgery Heyman Luckraz, FRCS a Fiona Murphy, RGN a Steve Bryant, SA a Susan C. Charman, MSc b Andrew J. Ritchie, FRCS a Objective:
Vacuum-assisted closure as a treatment modality for infections after cardiac surgery Heyman Luckraz, FRCS a Fiona Murphy, RGN a Steve Bryant, SA a Susan C. Charman, MSc b Andrew J. Ritchie, FRCS a Objective:
Marc Albert, Adrian Ursulescu, Ulrich FW Franke Department of Cardiovascular Surgery Robert-Bosch-Hospital, Stuttgart, Germany
 The total arterial myocardial revascularization using bilateral IMA and the role of post-operative sternal stabilization to reduce wound infections in a large cohort study. Marc Albert, Adrian Ursulescu,
The total arterial myocardial revascularization using bilateral IMA and the role of post-operative sternal stabilization to reduce wound infections in a large cohort study. Marc Albert, Adrian Ursulescu,
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW
 CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2015 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: 2015 PQRS MEASURES IN CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP: #43 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG):
CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2015 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: 2015 PQRS MEASURES IN CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP: #43 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG):
Sternal wound infection following open heart surgery: appraisal of incidence, risk factors, changing bacteriologic pattern and treatment outcome
 Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg (Jan March 2011) 27:28 32 DOI 10.1007/s12055-011-0081-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sternal wound infection following open heart surgery: appraisal of incidence, risk factors, changing
Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg (Jan March 2011) 27:28 32 DOI 10.1007/s12055-011-0081-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sternal wound infection following open heart surgery: appraisal of incidence, risk factors, changing
MODIFIABLE RISK FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH DEEP STERNAL SITE INFECTION AFTER CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING
 MODIFIABLE RISK FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH DEEP STERNAL SITE INFECTION AFTER CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING William E. Trick, MD a William E. Scheckler, MD b Jerome I. Tokars, MD a Kevin C. Jones, DO a Mel
MODIFIABLE RISK FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH DEEP STERNAL SITE INFECTION AFTER CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING William E. Trick, MD a William E. Scheckler, MD b Jerome I. Tokars, MD a Kevin C. Jones, DO a Mel
Postoperative Surgical Site Infection after Incisional Hernia Repair: Link to Previous Surgical Site Infection? Zulfiqar Ali, AG Rehan
 Original Article Postoperative Surgical Site Infection after Incisional Hernia Repair: Link to Previous Surgical Site Infection? Zulfiqar Ali, AG Rehan ABSTRACT Objective: Aim of the study was to determine
Original Article Postoperative Surgical Site Infection after Incisional Hernia Repair: Link to Previous Surgical Site Infection? Zulfiqar Ali, AG Rehan ABSTRACT Objective: Aim of the study was to determine
Deep sternal wound infection (DSWI), or mediastinitis,
 Variables Predicting Adverse Outcome in Patients With Deep Sternal Wound Infection Marisa De Feo, MD, Attilio Renzulli, MD, Gennaro Ismeno, MD, Rosario Gregorio, MD, Alessandro Della Corte, MD, Riccardo
Variables Predicting Adverse Outcome in Patients With Deep Sternal Wound Infection Marisa De Feo, MD, Attilio Renzulli, MD, Gennaro Ismeno, MD, Rosario Gregorio, MD, Alessandro Della Corte, MD, Riccardo
Comparison Between Closed Drainage Techniques for the Treatment of Postoperative Mediastinitis
 Comparison Between Closed Drainage Techniques for the Treatment of Postoperative Mediastinitis Hans F. Berg, MD, Willem G. B. Brands, MD, Theo R. van Geldorp, MD, Marjolein F. Q. Kluytmans-VandenBergh,
Comparison Between Closed Drainage Techniques for the Treatment of Postoperative Mediastinitis Hans F. Berg, MD, Willem G. B. Brands, MD, Theo R. van Geldorp, MD, Marjolein F. Q. Kluytmans-VandenBergh,
2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Outcome
 Measure #165 (NQF 0130): Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Deep Sternal Wound Infection Rate National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
Measure #165 (NQF 0130): Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Deep Sternal Wound Infection Rate National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
University of Florida Department of Surgery. CardioThoracic Surgery VA Learning Objectives
 University of Florida Department of Surgery CardioThoracic Surgery VA Learning Objectives This service performs coronary revascularization, valve replacement and lung cancer resections. There are 2 faculty
University of Florida Department of Surgery CardioThoracic Surgery VA Learning Objectives This service performs coronary revascularization, valve replacement and lung cancer resections. There are 2 faculty
In the United States, 97 million overweight or obese
 The Risks of Moderate and Extreme Obesity for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Outcomes: A Study From The Society of Thoracic Surgeons Database Ganga Prabhakar, MD, Constance K. Haan, MD, Eric D. Peterson,
The Risks of Moderate and Extreme Obesity for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Outcomes: A Study From The Society of Thoracic Surgeons Database Ganga Prabhakar, MD, Constance K. Haan, MD, Eric D. Peterson,
Intraoperative application of Cytosorb in cardiac surgery
 Intraoperative application of Cytosorb in cardiac surgery Dr. Carolyn Weber Heart Center of the University of Cologne Dept. of Cardiothoracic Surgery Cologne, Germany SIRS & Cardiopulmonary Bypass (CPB)
Intraoperative application of Cytosorb in cardiac surgery Dr. Carolyn Weber Heart Center of the University of Cologne Dept. of Cardiothoracic Surgery Cologne, Germany SIRS & Cardiopulmonary Bypass (CPB)
Process audit for SSI. CME on Infection Prevention & Control Breach Candy Hospital Trust
 Process audit for SSI CME on Infection Prevention & Control Breach Candy Hospital Trust Introduction SSIs are the most common healthcare-associated infection, accounting for 31% of all HAIs among hospitalized
Process audit for SSI CME on Infection Prevention & Control Breach Candy Hospital Trust Introduction SSIs are the most common healthcare-associated infection, accounting for 31% of all HAIs among hospitalized
2016 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) (for patients aged 18 years and older)
 2016 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) (for patients aged 18 years and older) IMPORTANT: Any measure with a 0% performance rate (100% for inverse
2016 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) (for patients aged 18 years and older) IMPORTANT: Any measure with a 0% performance rate (100% for inverse
Preoperative Atrial Fibrillation and Elevated C-Reactive Protein Levels as Predictors of Mediastinitis After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
 ADULT CARDIAC Preoperative Atrial Fibrillation and Elevated C-Reactive Protein Levels as Predictors of Mediastinitis After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Ted W. O. Elenbaas, MD, Mohamed A. Soliman Hamad,
ADULT CARDIAC Preoperative Atrial Fibrillation and Elevated C-Reactive Protein Levels as Predictors of Mediastinitis After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Ted W. O. Elenbaas, MD, Mohamed A. Soliman Hamad,
Sternal infection after cardiac operation is a rare but
 Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci and Sternal Infections After Cardiac Operation Anders Tegnell, MD, Claes Arén, MD, and Lena Öhman, MD, PhD Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Health and Environment,
Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci and Sternal Infections After Cardiac Operation Anders Tegnell, MD, Claes Arén, MD, and Lena Öhman, MD, PhD Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Health and Environment,
Topical Antimicrobials Biocides could be useful but are toxic Poor quality of trials & small sample size SOS therapy?
 Super Oxidized Solutions (SOS) From the Basic Science to the Bedside Andrés A Gutiérrez MD PhD Oculus Innovative Sciences Petaluma, California Use of Antimicrobials in Wound Care Oral-Parenteral Antibiotics
Super Oxidized Solutions (SOS) From the Basic Science to the Bedside Andrés A Gutiérrez MD PhD Oculus Innovative Sciences Petaluma, California Use of Antimicrobials in Wound Care Oral-Parenteral Antibiotics
Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Oxum against Povidone Iodine Topical Application in the Post-caesarean Section Wound Management
 Indian Medical Gazette DECEMBER 2007 498 Comparative Evaluation Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Oxum against Povidone Iodine Topical Application in the Post-caesarean Section Wound Management
Indian Medical Gazette DECEMBER 2007 498 Comparative Evaluation Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Oxum against Povidone Iodine Topical Application in the Post-caesarean Section Wound Management
Left Internal Mammary Artery to the Left Anterior Descending Artery: Effect on Morbidity and Mortality and Reasons for Nonusage
 Left Internal Mammary Artery to the Left Anterior Descending Artery: Effect on Morbidity and Mortality and Reasons for Nonusage Shishir Karthik, FRCS, Arun K. Srinivasan, FRCS, Antony D. Grayson, BS, Mark
Left Internal Mammary Artery to the Left Anterior Descending Artery: Effect on Morbidity and Mortality and Reasons for Nonusage Shishir Karthik, FRCS, Arun K. Srinivasan, FRCS, Antony D. Grayson, BS, Mark
Sternum Instability in Clinical Practice
 in Clinical Practice Hans Jonsson M.D Ph.D. Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery and Anesthesiology Karolinska University Hospital Is that a problem in open heart surgery? Yes!! We must stabilize sternum
in Clinical Practice Hans Jonsson M.D Ph.D. Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery and Anesthesiology Karolinska University Hospital Is that a problem in open heart surgery? Yes!! We must stabilize sternum
A Comparative Study for the Role of Preoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Prevention of Surgical Site Infections
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. IV. (Apr. 2014), PP 27-31 A Comparative Study for the Role of Preoperative Antibiotic
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. IV. (Apr. 2014), PP 27-31 A Comparative Study for the Role of Preoperative Antibiotic
Evidence-Based Recommendations for Intraoperative Prevention of SSI. Intraoperative Antiseptic Skin Preparation of the Patient
 Sven Scheffler, MD PhD Sporthopaedicum Berlin, Germany Symposium: Prevention and Management of Infection in ACL Reconstruction General Considerations for Prevention of Infection Intraoperative Precautions
Sven Scheffler, MD PhD Sporthopaedicum Berlin, Germany Symposium: Prevention and Management of Infection in ACL Reconstruction General Considerations for Prevention of Infection Intraoperative Precautions
A Comparative Study of efficacy of Superoxidized solution against Povidone Iodine in the treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. VII (August. 2016), PP 10-14 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of efficacy of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. VII (August. 2016), PP 10-14 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of efficacy of
Is a minimally invasive approach for re-operative aortic valve replacement superior to standard full resternotomy?
 Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery Advance Access published May 7, 2012 Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 0 (2012) 1 5 doi:10.1093/icvts/ivr141 BEST EVIDENCE TOPIC Is a minimally
Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery Advance Access published May 7, 2012 Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 0 (2012) 1 5 doi:10.1093/icvts/ivr141 BEST EVIDENCE TOPIC Is a minimally
A Novel Score to Estimate the Risk of Pneumonia After Cardiac Surgery
 A Novel Score to Estimate the Risk of Pneumonia After Cardiac Surgery Arman Kilic, MD 1, Rika Ohkuma, MD 1, J. Trent Magruder, MD 1, Joshua C. Grimm, MD 1, Marc Sussman, MD 1, Eric B. Schneider, PhD 1,
A Novel Score to Estimate the Risk of Pneumonia After Cardiac Surgery Arman Kilic, MD 1, Rika Ohkuma, MD 1, J. Trent Magruder, MD 1, Joshua C. Grimm, MD 1, Marc Sussman, MD 1, Eric B. Schneider, PhD 1,
Impact of Obesity on Early Outcomes after Cardiac Surgery: Experience in a Saudi Arabian Center
 Original Article Impact of Obesity on Early Outcomes after Cardiac Surgery: Experience in a Saudi Arabian Center Ghassan Baslaim, MD, Jill Bashore, RN, and Khaled Alhoroub, RN Purpose: The prevalence of
Original Article Impact of Obesity on Early Outcomes after Cardiac Surgery: Experience in a Saudi Arabian Center Ghassan Baslaim, MD, Jill Bashore, RN, and Khaled Alhoroub, RN Purpose: The prevalence of
RECOGNISINGSURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS(SSIs) NOVEMBER 2017
 RECOGNISINGSURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS(SSIs) NOVEMBER 2017 Welcome to this training resource. It has been designed for all healthcare workers involved in coordinating SSI surveillance, SSI surveillance data
RECOGNISINGSURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS(SSIs) NOVEMBER 2017 Welcome to this training resource. It has been designed for all healthcare workers involved in coordinating SSI surveillance, SSI surveillance data
Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study
 The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
Predicting Short Term Morbidity following Revision Hip and Knee Arthroplasty
 Predicting Short Term Morbidity following Revision Hip and Knee Arthroplasty A Review of ACS-NSQIP 2006-2012 Arjun Sebastian, M.D., Stephanie Polites, M.D., Kristine Thomsen, B.S., Elizabeth Habermann,
Predicting Short Term Morbidity following Revision Hip and Knee Arthroplasty A Review of ACS-NSQIP 2006-2012 Arjun Sebastian, M.D., Stephanie Polites, M.D., Kristine Thomsen, B.S., Elizabeth Habermann,
ASSESSMENT OF STERNAL VASCULARITY WITH SINGLE PHOTON EMISSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY AFTER HARVESTING OF THE INTERNAL THORACIC ARTERY
 ASSESSMENT OF STERNAL VASCULARITY WITH SINGLE PHOTON EMISSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY AFTER HARVESTING OF THE INTERNAL THORACIC ARTERY Amram J. Cohen, MD a Judith Lockman, MD b Mordechai Lorberboym, MD c Othman
ASSESSMENT OF STERNAL VASCULARITY WITH SINGLE PHOTON EMISSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY AFTER HARVESTING OF THE INTERNAL THORACIC ARTERY Amram J. Cohen, MD a Judith Lockman, MD b Mordechai Lorberboym, MD c Othman
Laparoscopic omentoplasty and split skin graft for deep sternal wound infection and dehiscence patient
 Laparoscopic omentoplasty and split skin graft for deep sternal wound infection and dehiscence patient David Sladden, Francis. X. Darmanin, Benedict Axisa, Kevin Schembri, Joseph Galea Abstract Treatment
Laparoscopic omentoplasty and split skin graft for deep sternal wound infection and dehiscence patient David Sladden, Francis. X. Darmanin, Benedict Axisa, Kevin Schembri, Joseph Galea Abstract Treatment
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER
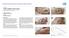 CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
Complex Thoracic and Abdominal Aortic Repair Using Hybrid Techniques
 Complex Thoracic and Abdominal Aortic Repair Using Hybrid Techniques Tariq Almerey MD, January Moore BA, Houssam Farres MD, Richard Agnew MD, W. Andrew Oldenburg MD, Albert Hakaim MD Department of Vascular
Complex Thoracic and Abdominal Aortic Repair Using Hybrid Techniques Tariq Almerey MD, January Moore BA, Houssam Farres MD, Richard Agnew MD, W. Andrew Oldenburg MD, Albert Hakaim MD Department of Vascular
Modifiable Risk Factors in Orthopaedic Infections
 Modifiable Risk Factors in Orthopaedic Infections AAOS Patient Safety Committee Burden US Surgical Site Infections (SSI) by the Numbers ~300,000 SSIs/yr (17% of all HAI; second to UTI) 2%-5% of patients
Modifiable Risk Factors in Orthopaedic Infections AAOS Patient Safety Committee Burden US Surgical Site Infections (SSI) by the Numbers ~300,000 SSIs/yr (17% of all HAI; second to UTI) 2%-5% of patients
Retrospective Study Of Redo Cardiac Surgery In A Single Centre. R Karthekeyan, K Selvaraju, L Ramanathan, M Rakesh, S Rao, M Vakamudi, K Balakrishnan
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 12 Number 2 Retrospective Study Of Redo Cardiac Surgery In A Single Centre R Karthekeyan, K Selvaraju, L Ramanathan, M Rakesh, S Rao, M Vakamudi,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 12 Number 2 Retrospective Study Of Redo Cardiac Surgery In A Single Centre R Karthekeyan, K Selvaraju, L Ramanathan, M Rakesh, S Rao, M Vakamudi,
Minimally invasive aortic valve replacement in high risk patient groups
 Review Article Minimally invasive aortic valve replacement in high risk patient groups Daniel Fudulu, Harriet Lewis, Umberto Benedetto, Massimo Caputo, Gianni Angelini, Hunaid A. Vohra Department of Cardiac
Review Article Minimally invasive aortic valve replacement in high risk patient groups Daniel Fudulu, Harriet Lewis, Umberto Benedetto, Massimo Caputo, Gianni Angelini, Hunaid A. Vohra Department of Cardiac
Interesting Case Series. Omental Flap for Thoracic Aortic Graft Infection
 Interesting Case Series Omental Flap for Thoracic Aortic Graft Infection Andrew A. Marano, BA, Adam M. Feintisch, MD, and Mark S. Granick, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Rutgers
Interesting Case Series Omental Flap for Thoracic Aortic Graft Infection Andrew A. Marano, BA, Adam M. Feintisch, MD, and Mark S. Granick, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Rutgers
Preventing Surgical Site Infections: The SSI Bundle
 Preventing Surgical Site Infections: The SSI Bundle 1 Why SSI? New York State 30,000 hospital discharges 1984 3.7% of patients experience serious adverse events related to medical management The top three
Preventing Surgical Site Infections: The SSI Bundle 1 Why SSI? New York State 30,000 hospital discharges 1984 3.7% of patients experience serious adverse events related to medical management The top three
Chapter 14 8/23/2016. Surgical Wound Care. Wound Classifications. Wound Healing. Classified According to. Phases
 Chapter 14 Surgical Wound Care All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Wound Classifications Classified According to Cause Incision
Chapter 14 Surgical Wound Care All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Wound Classifications Classified According to Cause Incision
Current Management of Postpneumonectomy Bronchopleural Fistula
 Current Management of Postpneumonectomy Bronchopleural Fistula Shaf Keshavjee MD MSc FRCSC FACS Surgeon-in-Chief, University Health Network James Wallace McCutcheon Chair in Surgery Professor, Division
Current Management of Postpneumonectomy Bronchopleural Fistula Shaf Keshavjee MD MSc FRCSC FACS Surgeon-in-Chief, University Health Network James Wallace McCutcheon Chair in Surgery Professor, Division
PREDICTORS OF PROLONGED HOSPITAL STAY
 PREDICTORS OF PROLONGED HOSPITAL STAY IN CARDIAC SURGERY Zuraida Khairudin Faculty of Science Computer and Mathematics, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Malaysia zurai405@salam.uitm.edu.my ABSTRACT quality of
PREDICTORS OF PROLONGED HOSPITAL STAY IN CARDIAC SURGERY Zuraida Khairudin Faculty of Science Computer and Mathematics, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Malaysia zurai405@salam.uitm.edu.my ABSTRACT quality of
Remodeling of the Remnant Aorta after Acute Type A Aortic Dissection Surgery
 Remodeling of the Remnant Aorta after Acute Type A Aortic Dissection Surgery Are Young Patients More Likely to Develop Adverse Aortic Remodeling of the Remnant Aorta Over Time? Suk Jung Choo¹, Jihoon Kim¹,
Remodeling of the Remnant Aorta after Acute Type A Aortic Dissection Surgery Are Young Patients More Likely to Develop Adverse Aortic Remodeling of the Remnant Aorta Over Time? Suk Jung Choo¹, Jihoon Kim¹,
Vancomycin powder to reduce surgical site infection in spine surgery
 Vancomycin powder to reduce surgical site infection in spine surgery 2014/03/25 EBM Spine Fellow 林東儀 Post-Op infection in spine surgery Wound infection: 0.7% to 11.9% Infection rates of 2.8% to 6.0% for
Vancomycin powder to reduce surgical site infection in spine surgery 2014/03/25 EBM Spine Fellow 林東儀 Post-Op infection in spine surgery Wound infection: 0.7% to 11.9% Infection rates of 2.8% to 6.0% for
Vaginal Cleansing prior to Cesarean Section and Post Operative Infectious Morbidity
 Vaginal Cleansing prior to Cesarean Section and Post Operative Infectious Morbidity Prof. Dr Syeda Batool Mazhar, Dr. Sara Asad MCH Centre, PIMS, SZABMU, Islamabad, Pakistan Vaginal Cleansing Prior to
Vaginal Cleansing prior to Cesarean Section and Post Operative Infectious Morbidity Prof. Dr Syeda Batool Mazhar, Dr. Sara Asad MCH Centre, PIMS, SZABMU, Islamabad, Pakistan Vaginal Cleansing Prior to
Helmut Mair, MD Department of Cardiac Surgery, University Hospital Grosshadern, Ludwig- Maximilians-University, Munich, Germany
 Use of PerClot, a Plant-Based Polysaccharide Hemostat, for Bleeding Control of the Sternum in High Risk Patients Helmut Mair, MD Department of Cardiac Surgery, University Hospital Grosshadern, Ludwig-
Use of PerClot, a Plant-Based Polysaccharide Hemostat, for Bleeding Control of the Sternum in High Risk Patients Helmut Mair, MD Department of Cardiac Surgery, University Hospital Grosshadern, Ludwig-
Analysis of Mortality Within the First Six Months After Coronary Reoperation
 Analysis of Mortality Within the First Six Months After Coronary Reoperation Frans M. van Eck, MD, Luc Noyez, MD, PhD, Freek W. A. Verheugt, MD, PhD, and Rene M. H. J. Brouwer, MD, PhD Departments of Thoracic
Analysis of Mortality Within the First Six Months After Coronary Reoperation Frans M. van Eck, MD, Luc Noyez, MD, PhD, Freek W. A. Verheugt, MD, PhD, and Rene M. H. J. Brouwer, MD, PhD Departments of Thoracic
IMPROVE PATIENT OUTCOMES AND SAFETY IN ADULT CARDIAC SURGERY.
 Clinical Evidence Guide IMPROVE PATIENT OUTCOMES AND SAFETY IN ADULT CARDIAC SURGERY. With the INVOS cerebral/somatic oximeter An examination of controlled studies reveals that responding to cerebral desaturation
Clinical Evidence Guide IMPROVE PATIENT OUTCOMES AND SAFETY IN ADULT CARDIAC SURGERY. With the INVOS cerebral/somatic oximeter An examination of controlled studies reveals that responding to cerebral desaturation
Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection
 Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection Arglaes Controlled-Release Silver Technology Reduce bioburden with Arglaes Silver Barrier Dressings Antimicrobial Arglaes began the
Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection Arglaes Controlled-Release Silver Technology Reduce bioburden with Arglaes Silver Barrier Dressings Antimicrobial Arglaes began the
Vacuum-Assisted Closure of Perineal War Wound Related to Rectum
 Vacuum-Assisted Closure of Perineal War Wound Related to Rectum Nazım Gümüş, MD Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Department, Adana Numune Research and Training Hospital, Adana, Turkey Correspondence:
Vacuum-Assisted Closure of Perineal War Wound Related to Rectum Nazım Gümüş, MD Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Department, Adana Numune Research and Training Hospital, Adana, Turkey Correspondence:
Reexploration for Bleeding After Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: Risk Factors, Outcomes, and the Effect of Time Delay
 After Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: Risk Factors, Outcomes, and the Effect of Time Delay Shishir Karthik, FRCS, Antony D. Grayson, BS, Emer E. McCarron, FRCS, D. Mark Pullan, FRCS(C-Th), and Michael
After Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: Risk Factors, Outcomes, and the Effect of Time Delay Shishir Karthik, FRCS, Antony D. Grayson, BS, Emer E. McCarron, FRCS, D. Mark Pullan, FRCS(C-Th), and Michael
Nanogen Aktiv. Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma
 Nanogen Aktiv Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma Patient BM 75 y.o female with a history of Type 2 Diabetes, HTN, Hypercholesterolemia, Renal insufficiency, Chronic back Pain, who had undergone a L3-L4
Nanogen Aktiv Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma Patient BM 75 y.o female with a history of Type 2 Diabetes, HTN, Hypercholesterolemia, Renal insufficiency, Chronic back Pain, who had undergone a L3-L4
Cost-effectiveness of minimally invasive coronary artery bypass surgery Arom K V, Emery R W, Flavin T F, Petersen R J
 Cost-effectiveness of minimally invasive coronary artery bypass surgery Arom K V, Emery R W, Flavin T F, Petersen R J Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the
Cost-effectiveness of minimally invasive coronary artery bypass surgery Arom K V, Emery R W, Flavin T F, Petersen R J Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the
Vacuum-Assisted Wound Closure of Deep Sternal Infections in High-Risk Patients After Cardiac Surgery
 Vacuum-Assisted Wound Closure of Deep Sternal Infections in High-Risk Patients After Cardiac Surgery Kyle Northcote Cowan, MD, PhD, Laura Teague, RN, MN, Sammy C. Sue, BS, and James L. Mahoney, MD Division
Vacuum-Assisted Wound Closure of Deep Sternal Infections in High-Risk Patients After Cardiac Surgery Kyle Northcote Cowan, MD, PhD, Laura Teague, RN, MN, Sammy C. Sue, BS, and James L. Mahoney, MD Division
Respiratory Function Testing Is Safe in Patients With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms.
 Respiratory Function Testing Is Safe in Patients With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Author Zagami, Debbie, Wilson, Jessica, Bodger, Alanna, Sriram, Krishna Published 2014 Journal Title Vascular and Endovascular
Respiratory Function Testing Is Safe in Patients With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Author Zagami, Debbie, Wilson, Jessica, Bodger, Alanna, Sriram, Krishna Published 2014 Journal Title Vascular and Endovascular
A case-control study of readmission to the intensive care unit after cardiac surgery
 DOI: 0.2659/MSM.88384 Received: 202.04.24 Accepted: 203.0.25 Published: 203.02.28 A case-control study of readmission to the intensive care unit after cardiac surgery Authors Contribution: Study Design
DOI: 0.2659/MSM.88384 Received: 202.04.24 Accepted: 203.0.25 Published: 203.02.28 A case-control study of readmission to the intensive care unit after cardiac surgery Authors Contribution: Study Design
Comparison of Super-oxidized Solution versus Povidone Iodine in Management of Infected Diabetic Ulcers: Our Experience
 Original Research Article Comparison of Super-oxidized Solution versus Povidone Iodine in Management of Infected Diabetic Ulcers: Our Experience K. B. S. Prabhakar 1*, G. Purushotham 2, K. Uma 3 1 Associate
Original Research Article Comparison of Super-oxidized Solution versus Povidone Iodine in Management of Infected Diabetic Ulcers: Our Experience K. B. S. Prabhakar 1*, G. Purushotham 2, K. Uma 3 1 Associate
Sternal Wound Infection After Heart Transplantation: Incidence and Results With Aggressive Surgical Treatment
 Sternal Wound Infection After Heart Transplantation: Incidence and Results With Aggressive Surgical Treatment Michel Carrier, MD, Louis P. Perrault, MD, Michel Pellerin, MD, Richard Marchand, MD, Pierre
Sternal Wound Infection After Heart Transplantation: Incidence and Results With Aggressive Surgical Treatment Michel Carrier, MD, Louis P. Perrault, MD, Michel Pellerin, MD, Richard Marchand, MD, Pierre
Correlation of Postoperative Wound Infection with Intraoperative Culture Results and Duration of Operation
 POSTOPERATIVE THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE WOUND INFECTION MEDICAL JOURNAL Correlation of Postoperative Wound Infection with Intraoperative Culture Results and Duration of Operation INTRODUCTION: Infection is
POSTOPERATIVE THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE WOUND INFECTION MEDICAL JOURNAL Correlation of Postoperative Wound Infection with Intraoperative Culture Results and Duration of Operation INTRODUCTION: Infection is
Overview of the WHO global guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infection
 Overview of the WHO global guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infection Dr. Mohamed Abbas, MD, MS Semmelweiss CEE Conference Budapest 08.03.2017 Outline of presentation General background Burden
Overview of the WHO global guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infection Dr. Mohamed Abbas, MD, MS Semmelweiss CEE Conference Budapest 08.03.2017 Outline of presentation General background Burden
ABSTRACT. KEY WORDS antibiotics; prophylaxis; hysterectomy
 Infectious Diseases in Obstetrics and Gynecology 8:230-234 (2000) (C) 2000 Wiley-Liss, Inc. Wound Infection in Gynecologic Surgery Aparna A. Kamat,* Leo Brancazio, and Mark Gibson Department of Obstetrics
Infectious Diseases in Obstetrics and Gynecology 8:230-234 (2000) (C) 2000 Wiley-Liss, Inc. Wound Infection in Gynecologic Surgery Aparna A. Kamat,* Leo Brancazio, and Mark Gibson Department of Obstetrics
EVAR replaced standard repair in most cases. Why?
 EVAR replaced standard repair in most cases. Why? Initial major steps in endograft evolution Papazoglou O. Konstantinos M.D. The story of a major breakthrough in vascular surgery 1991 Parodi introduces
EVAR replaced standard repair in most cases. Why? Initial major steps in endograft evolution Papazoglou O. Konstantinos M.D. The story of a major breakthrough in vascular surgery 1991 Parodi introduces
A Prospective Randomized Study of Sternal Closure: Comparison of Mersilene Tape versus Standard Wire Closure
 Original Article A Prospective Randomized Study of Sternal Closure: Comparison of Mersilene Tape versus Standard Wire Closure Hiroshi Imagawa, MD, 1 Susumu Nakano, MD, 2 Kanji Kawachi, MD, 1 Shinji Takano,
Original Article A Prospective Randomized Study of Sternal Closure: Comparison of Mersilene Tape versus Standard Wire Closure Hiroshi Imagawa, MD, 1 Susumu Nakano, MD, 2 Kanji Kawachi, MD, 1 Shinji Takano,
The operative mortality rate after redo valvular operations
 Clinical Outcomes of Redo Valvular Operations: A 20-Year Experience Naoto Fukunaga, MD, Yukikatsu Okada, MD, Yasunobu Konishi, MD, Takashi Murashita, MD, Mitsuru Yuzaki, MD, Yu Shomura, MD, Hiroshi Fujiwara,
Clinical Outcomes of Redo Valvular Operations: A 20-Year Experience Naoto Fukunaga, MD, Yukikatsu Okada, MD, Yasunobu Konishi, MD, Takashi Murashita, MD, Mitsuru Yuzaki, MD, Yu Shomura, MD, Hiroshi Fujiwara,
Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Repair: Indications and Approach
 Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Repair: Indications and Approach Juan P. Umaña, M.D. Chief Medical Officer Director, Cardiovascular Medicine FCI - Institute of Cardiology Bogota Colombia 1 Mitral Valve
Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Repair: Indications and Approach Juan P. Umaña, M.D. Chief Medical Officer Director, Cardiovascular Medicine FCI - Institute of Cardiology Bogota Colombia 1 Mitral Valve
Electromicyn WHO Essential Medicines List
 Electromicyn WHO Essential Medicines List Lance Gravatt PhD Founder Te Arai BioFarma Ltd Finding a Global Partner Oculus Innovative Sciences, Petaluma, CA Launched Microdacyn at NZWCS Conference, Blenheim
Electromicyn WHO Essential Medicines List Lance Gravatt PhD Founder Te Arai BioFarma Ltd Finding a Global Partner Oculus Innovative Sciences, Petaluma, CA Launched Microdacyn at NZWCS Conference, Blenheim
Surgical Wounds & Incisions
 Surgical Wounds & Incisions A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist www.woundcarenurses.org 1
Surgical Wounds & Incisions A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist www.woundcarenurses.org 1
VACUUM ASSISTED CLOSURE (V.A.C.) THERAPY: Mr. Ismazizi Zaharudin Jabatan pembedahan Am Hospital Kuala Lumpur
 VACUUM ASSISTED CLOSURE (V.A.C.) THERAPY: Mr. Ismazizi Zaharudin Jabatan pembedahan Am Hospital Kuala Lumpur Learning Objectives Define Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) Discuss guidelines for the
VACUUM ASSISTED CLOSURE (V.A.C.) THERAPY: Mr. Ismazizi Zaharudin Jabatan pembedahan Am Hospital Kuala Lumpur Learning Objectives Define Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) Discuss guidelines for the
Cardiothoracic Fellow Expectations Division of Cardiac Anesthesia, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
 The fellowship in Cardiothoracic Anesthesia at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center is intended to provide the foundation for a career as either an academic cardiothoracic anesthesiologist or clinical
The fellowship in Cardiothoracic Anesthesia at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center is intended to provide the foundation for a career as either an academic cardiothoracic anesthesiologist or clinical
Abdominal Wound Dehiscence. Presenter: T Mohammed Moderator: Dr H Pienaar
 Abdominal Wound Dehiscence Presenter: T Mohammed Moderator: Dr H Pienaar Introduction Wound Dehiscence is the premature "bursting" open of a wound along surgical suture. It is a surgical complication that
Abdominal Wound Dehiscence Presenter: T Mohammed Moderator: Dr H Pienaar Introduction Wound Dehiscence is the premature "bursting" open of a wound along surgical suture. It is a surgical complication that
Case Discussion: Post-implant infections & explant decision making
 Author Information Full Names: Sailesh Arulkumar, MD David Provenzano, MD Affiliation: Sailesh Arulkumar MD: Attending Pain Physician, The Orthopaedic Center, Tulsa OK David Provenzano, MD: Attending Pain
Author Information Full Names: Sailesh Arulkumar, MD David Provenzano, MD Affiliation: Sailesh Arulkumar MD: Attending Pain Physician, The Orthopaedic Center, Tulsa OK David Provenzano, MD: Attending Pain
I internal mammary artery (IMA) is widely accepted as
 Routine Use of the Left Internal Mammary Artery Graft in the Elderly Timothy J. Gardner, MD, Peter S. Greene, MD, Mary F. Rykiel, RN, William A. Baumgartner, MD, Duke E. Cameron, MD, Alfred S. Casale,
Routine Use of the Left Internal Mammary Artery Graft in the Elderly Timothy J. Gardner, MD, Peter S. Greene, MD, Mary F. Rykiel, RN, William A. Baumgartner, MD, Duke E. Cameron, MD, Alfred S. Casale,
Surgical Site Infection Prevention: International Consensus on Process
 Surgical Site Infection Prevention: International Consensus on Process Joseph S. Solomkin, M.D. Professor of Surgery (Emeritus) University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Executive Director, OASIS
Surgical Site Infection Prevention: International Consensus on Process Joseph S. Solomkin, M.D. Professor of Surgery (Emeritus) University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Executive Director, OASIS
Complex Thoracoscopic Resections for Locally Advanced Lung Cancer
 Complex Thoracoscopic Resections for Locally Advanced Lung Cancer Duke Thoracoscopic Lobectomy Workshop March 21, 2018 Thomas A. D Amico MD Gary Hock Professor of Surgery Section Chief, Thoracic Surgery,
Complex Thoracoscopic Resections for Locally Advanced Lung Cancer Duke Thoracoscopic Lobectomy Workshop March 21, 2018 Thomas A. D Amico MD Gary Hock Professor of Surgery Section Chief, Thoracic Surgery,
Colorectal procedure guide
 Colorectal procedure guide Illustrations by Lisa Clark Biodesign ADVANCED TISSUE REPAIR cookmedical.com 2 INDEX Anal fistula repair Using the Biodesign plug with no button.... 4 Anal fistula repair Using
Colorectal procedure guide Illustrations by Lisa Clark Biodesign ADVANCED TISSUE REPAIR cookmedical.com 2 INDEX Anal fistula repair Using the Biodesign plug with no button.... 4 Anal fistula repair Using
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Best evidence topic - Cardiac general
 doi:10.1510/icvts.2005.118935 Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 4 (2005) 577 582 www.icvts.org Best evidence topic - Cardiac general Is skeletonised internal mammary harvest better than pedicled
doi:10.1510/icvts.2005.118935 Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 4 (2005) 577 582 www.icvts.org Best evidence topic - Cardiac general Is skeletonised internal mammary harvest better than pedicled
Measure #167 (NQF 0114): Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Postoperative Renal Failure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #167 (NQF 0114): Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Postoperative Renal Failure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE
Measure #167 (NQF 0114): Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Postoperative Renal Failure National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE
Surgical site infections (SSIs) in cardiovascular surgery
 Prolonged Antibiotic Prophylaxis After Cardiovascular Surgery and Its Effect on Surgical Site Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance Stephan Harbarth, MD, MS; Matthew H. Samore, MD; Debi Lichtenberg,
Prolonged Antibiotic Prophylaxis After Cardiovascular Surgery and Its Effect on Surgical Site Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance Stephan Harbarth, MD, MS; Matthew H. Samore, MD; Debi Lichtenberg,
It is estimated that 2% to 20% of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
 Surgery for Acquired Cardiovascular Disease Olsen et al Risk factors for leg harvest surgical site infections after coronary artery bypass graft surgery Margaret A. Olsen, MPH, PhD a Thoralf M. Sundt,
Surgery for Acquired Cardiovascular Disease Olsen et al Risk factors for leg harvest surgical site infections after coronary artery bypass graft surgery Margaret A. Olsen, MPH, PhD a Thoralf M. Sundt,
Modern management of CABG patients emphasizes early return to
 Below -Knee Vein Harvesting Versus Above Knee Vein Harvesting Wound Healing In CABG Patients Using ASEPSIS Score Osama AbouelKasem, M.D*, Tarek Salah, M.D*, and Ibrahim Kasb, M.D**. Background: Lower limb
Below -Knee Vein Harvesting Versus Above Knee Vein Harvesting Wound Healing In CABG Patients Using ASEPSIS Score Osama AbouelKasem, M.D*, Tarek Salah, M.D*, and Ibrahim Kasb, M.D**. Background: Lower limb
More than 150 consecutive open umbilical hernia repairs in a major Veterans Administration Medical Center
 The American Journal of Surgery (2008) 196, 647 651 The Association of VA Surgeons More than 150 consecutive open umbilical hernia repairs in a major Veterans Administration Medical Center Buckminster
The American Journal of Surgery (2008) 196, 647 651 The Association of VA Surgeons More than 150 consecutive open umbilical hernia repairs in a major Veterans Administration Medical Center Buckminster
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in Diabetics: All Arterial or Hybrid?
 Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in Diabetics: All Arterial or Hybrid? Dr. Daniel Navia M.D. Chief Cardiac Surgery Department ICBA, Buenos Aires Argentina, 2018 No disclosures 2 Current evidence The FREEDOM
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in Diabetics: All Arterial or Hybrid? Dr. Daniel Navia M.D. Chief Cardiac Surgery Department ICBA, Buenos Aires Argentina, 2018 No disclosures 2 Current evidence The FREEDOM
Skin Closure in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty at The Northern Hospital. Dr Sam Bewsher Mr Raphael Hau
 Skin Closure in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty at The Northern Hospital Dr Sam Bewsher Mr Raphael Hau Disclosure Neither of the Authors have any disclosures Aims To investigate the outcomes of Staples
Skin Closure in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty at The Northern Hospital Dr Sam Bewsher Mr Raphael Hau Disclosure Neither of the Authors have any disclosures Aims To investigate the outcomes of Staples
STAPHYLOCOCCAL MEDIASTINITIS A RARE COMPLICATION FOLLOWING CARDIAC SURGERY A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 STAPHYLOCOCCAL MEDIASTINITIS A RARE COMPLICATION FOLLOWING CARDIAC SURGERY A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Doina Butcovan 1, Gr. Tinică 2, L. Stoica 2, R. Dănilă 3, Lidia Ionescu 3 1 Department
STAPHYLOCOCCAL MEDIASTINITIS A RARE COMPLICATION FOLLOWING CARDIAC SURGERY A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Doina Butcovan 1, Gr. Tinică 2, L. Stoica 2, R. Dănilă 3, Lidia Ionescu 3 1 Department
Cardiac surgery in Victorian public hospitals, Public report
 Cardiac surgery in Victorian public hospitals, 2009 10 Public report Cardiac surgery in Victorian public hospitals, 2009 10 Public report Authors: DT Dinh, L Tran, V Chand, A Newcomb, G Shardey, B Billah
Cardiac surgery in Victorian public hospitals, 2009 10 Public report Cardiac surgery in Victorian public hospitals, 2009 10 Public report Authors: DT Dinh, L Tran, V Chand, A Newcomb, G Shardey, B Billah
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO
 POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MD (ANAESTHESIOLOGY) FINAL EXAMINATION AUGUST 2013 Date : 2 nd August 2013 Time : 1.00 p.m. 4.00 p.m. Answer any three questions. Answer each question
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MD (ANAESTHESIOLOGY) FINAL EXAMINATION AUGUST 2013 Date : 2 nd August 2013 Time : 1.00 p.m. 4.00 p.m. Answer any three questions. Answer each question
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander.
 Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
RN Cathy Hammond. Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch
 RN Cathy Hammond Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #141: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know 15:05-16:00 WS #153: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know
RN Cathy Hammond Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #141: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know 15:05-16:00 WS #153: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know
VQI literature review
 VQI literature review Jaime Benarroch-Gampel, MD, MS Assistant Professor Emory University School of Medicine SEVSG Spring Meeting 04/28/2017 Article #1 J Vasc Surg 2017. epub ahead of print INTRODUCTION
VQI literature review Jaime Benarroch-Gampel, MD, MS Assistant Professor Emory University School of Medicine SEVSG Spring Meeting 04/28/2017 Article #1 J Vasc Surg 2017. epub ahead of print INTRODUCTION
Boonlawat Homvises MD* * Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University, Pathumthani, Thailand
 A Randomized Trial between Different Suture Materials (Polydioxanone vs. Poliglecaprone 25) and Different Suturing Techniques (Running Subcuticular Suture Alone vs. with Running Horizontal Mattress) in
A Randomized Trial between Different Suture Materials (Polydioxanone vs. Poliglecaprone 25) and Different Suturing Techniques (Running Subcuticular Suture Alone vs. with Running Horizontal Mattress) in
Alfa Ferry FRCS Cardiac Surgeon OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT IN CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
 Alfa Ferry FRCS Cardiac Surgeon OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT IN CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Management in CHD Medical (medikamentosa) Intervensi 1. Percutaneous ( PTCA & stenting ) 2. Surgical ( CABG, CABG & mitral
Alfa Ferry FRCS Cardiac Surgeon OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT IN CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Management in CHD Medical (medikamentosa) Intervensi 1. Percutaneous ( PTCA & stenting ) 2. Surgical ( CABG, CABG & mitral
Kamaruddin MY.,Anwar S., Zainabe SA and Mohd Yassim MY Faculty of Medicine University of Malaya Kuala Lumpur MALAYSIA
 Kamaruddin MY.,Anwar S., Zainabe SA and Mohd Yassim MY Faculty of Medicine University of Malaya Kuala Lumpur MALAYSIA ANTIBACTERIAL SYSTEM IN HONEY THE ANTIBACTERIAL SYSTEM 1993 HIGH SUGAR CONCENTRATION
Kamaruddin MY.,Anwar S., Zainabe SA and Mohd Yassim MY Faculty of Medicine University of Malaya Kuala Lumpur MALAYSIA ANTIBACTERIAL SYSTEM IN HONEY THE ANTIBACTERIAL SYSTEM 1993 HIGH SUGAR CONCENTRATION
Association between post-sternotomy tracheostomy and deep sternal wound infection: a retrospective analysis
 Original Article Association between post-sternotomy tracheostomy and deep sternal wound infection: a retrospective analysis Yi-Chin Tsai 1 *, Kevin Phan 2 *, Andrie Stroebel 3, Livia Williams 1, Lisa
Original Article Association between post-sternotomy tracheostomy and deep sternal wound infection: a retrospective analysis Yi-Chin Tsai 1 *, Kevin Phan 2 *, Andrie Stroebel 3, Livia Williams 1, Lisa
DISTAL PULMONARY THROMBOENDARTERECTOMY: IS IT WORTH IT?
 DISTAL PULMONARY THROMBOENDARTERECTOMY: IS IT WORTH IT? Bob Moraca, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Surgical Director of The CTEPH Program Director of Thoracic Aortic and Arrhythmia Surgery Allegheny
DISTAL PULMONARY THROMBOENDARTERECTOMY: IS IT WORTH IT? Bob Moraca, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Surgical Director of The CTEPH Program Director of Thoracic Aortic and Arrhythmia Surgery Allegheny
EACTS Adult Cardiac Database
 EACTS Adult Cardiac Database Quality Improvement Programme List of changes to Version 2.0, 13 th Dec 2018, compared to version 1.0, 1 st May 2014. INTRODUCTORY NOTES This document s purpose is to list
EACTS Adult Cardiac Database Quality Improvement Programme List of changes to Version 2.0, 13 th Dec 2018, compared to version 1.0, 1 st May 2014. INTRODUCTORY NOTES This document s purpose is to list
The Efficacy of NPWT on Primary Closed Incisions
 The Efficacy of NPWT on Primary Closed Incisions Pieter Zwanenburg Researcher / PhD Candidate Marja Boermeester Professor of Surgery, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam Incisional Negative Pressure Wound
The Efficacy of NPWT on Primary Closed Incisions Pieter Zwanenburg Researcher / PhD Candidate Marja Boermeester Professor of Surgery, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam Incisional Negative Pressure Wound
Standard AVR. Full Sternotomy CPB
 16.03.2013 by Dr. M. D. Dixit MS (Gen. Surg.), DNB (CVTS), PhD Professor & HOD, CVTS Director, KLES Heart Foundation, KLES Dr. Prabhakar Kore Hospital & MRC, Belgaum Standard AVR Full Sternotomy CPB
16.03.2013 by Dr. M. D. Dixit MS (Gen. Surg.), DNB (CVTS), PhD Professor & HOD, CVTS Director, KLES Heart Foundation, KLES Dr. Prabhakar Kore Hospital & MRC, Belgaum Standard AVR Full Sternotomy CPB
