Diagnostic Value of NT-pro BNP Biomarker and Echocardiography in Cardiac Involvements in Beta-thalassemia Patients
|
|
|
- Joel Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: ) Diagnostic Value of NT-pro BNP Biomarker and Echocardiography in Cardiac Involvements in Beta-thalassemia Patients Noor Mohammad Noori 1, *Alireza Teimouri 1, Maryam Nakhaey Moghaddam 11 1 Children and Adolescent Health Research Center, Zahedan University of Medical Sciences, Zahedan, Iran. Abstract Background N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) is a marker to evaluate the cardiac involvement in thalassemia. We aimed to evaluate conventional and tissue Doppler echocardiography findings and its relation to plasma NT-pro BNP, Ferritin and Iron levels in beta-thalassemia patients. Materials and Methods This study performed on 164 participants equal of major beta- thalassemia patients (n=82), and controls (82 healthy children with normal cardiovascular status). The patients collected from outpatients after applied exclusion criteria. Blood samples were taken from participants in fasting to measure NT- pro BNP, Ferritin and Iron serum. Participants were under echocardiography by Pediatric cardiologist. The level of error considered as 0.05 for data analysis by SPSS version Results NT- pro BNP, Iron, Ferritin, left S', left A', right A', EF, FS, left and right A/A'; right and left MPI were significantly different in patients group (P<0.05). FS and EF were higher in younger s and left and right MPI were lower. In higher level of NT-pro BNP right S' had converse trends compared with the Iron, its level was higher in patients > 10 years, and FS had different values significantly in lower levels. In lower level of left E/E' resulted that FS was significantly higher in the age group < 10 years. Right peak E velocity was significantly higher in younger s in higher level of left E/E'. Right E/E' was significantly higher in elders in lower level of left E/E' (P<0.05). Conclusion The study confirmed that NT-pro BNP increases in thalassemia and association with age and LV diastolic dysfunction. NT-pro BNP with E/E' and S' were shown diastolic and systolic dysfunction in thalassemia. Therefore, an increased level of ferritin and NT-pro BNP can be used as a marker for the intensification of iron chelation therapy, which reverses iron-induced cardiomyopathy. Key Words: Children, Cardiac involvement, Echocardiography, NT-pro BNP, Beta-thalassemia. *Please cite this article as: Noori NM, Teimouri A, Nakhaey Moghaddam M. Diagnostic Value of NT-pro BNP Biomarker and Echocardiography in Cardiac Involvements in Beta-thalassemia Patients. Int J Pediatr 2017; 5(11): DOI: /ijp Corresponding Author: Dr. Alireza Teimouri, Assistant Professor, Children and Adolescents Health Research Center, Zahedan University of Medical Sciences, Zahedan, Iran. alirezateimouri260@ gmail.com Received date: Jul.27, 2017; Accepted date: Aug. 22, 2017 Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
2 NT-pro BNP and Involvement in Thalassemia Patients 1- INTRODUCTION Thalassemia is an autosomal recessive hemoglobinopathy characterized by chronic hemolytic anemia with the frequency of 60,000 to 100,000 in newborns around the world (1). It is endemic in Mediterranean and in several Asian countries, migration has spread it throughout the world and in Iran, Sistan and Baluchestan province is one of the provinces with high prevalence of thalassemia (1, 2). In patient with thalassemia, regular blood transfusion programs and chelation treatment have considerably improved the patients survival (3). However, a consequence of chronic transfusion therapy is secondary iron overload, which adversely effect on heart functions, liver and other organs, the cardiac complications are still the primary leading cause of death in beta thalassemia for young adults (4). Cardiac dysfunctions have traditionally been attributed to ironoverload related to repeated transfusions in thalassemia and increased intestinal absorption rate combined with a sustained state of increased cardiac output (5). The most common causes of death in thalassemia patients are congestive heart failure, secondary to iron overload and high-output state (2). Since early diagnosis of beta thalassemia may lead to intensive chelating treatment and consequently allow a better life and recently several conventional echocardiography parameters have been investigated to assess cardiac functions in asymptomatic thalassemia patients (6). Heart failure onset remains poorly predictable, because echocardiography markers remain normal until heart failure is clinically manifest. It has been demonstrated that, unlike Ejection fraction (EF), long axis function is relatively independent from chronic volume overload and could be a sensitive marker of early myocardial dysfunction (7). In comparison, N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) is more stable and has a longer half-life about 2 hours in compared to Brain Natriuretic Peptide (8). Increasing levels of NT-pro BNP in thalassemia patients with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction is directly related to age and it is a good biomarker for early diagnosis of left ventricular dysfunction. In the early phases of the cardiac involvement the level of NT-pro BNP increases before an increase in diastolic pressure and there is a strong relationship between plasma levels of NTpro BNP and iron overload (9). A significant relationship between NT-pro BNP and some diastolic dysfunctions has been observed (10). It is approved that an increase level of NT-pro BNP can be used as a tool for primary detection of cardiac hemosiderosis, and is confirmed iron chelation therapy which may reverse ironinduced cardiomyopathy. Patients with major beta- thalassemia faced to an increase in the level of NT- pro BNP, when diastolic left ventricular dysfunction increased. High serum of NT- pro BNP is related to levels of E / E' in Doppler tissue imaging (DTI) in these patients (8-10). Tissue Doppler Imaging (TDI) is a relatively new Doppler ultrasound modality that records regional systolic and diastolic velocities within the myocardium. It allows quantitative measurement of both systolic and diastolic velocities directly from the ventricular myocardium with the determination of the extent of mitral annular displacement in systole and diastole (11). This new technique can show additional information compared with other echocardiography techniques, detecting even minor changes before the occurrence of abnormal indices of global ventricular dysfunction (2). Recent studies have revealed a significant relationship between elevated NT-pro BNP levels and diastolic dysfunction in these patients with preserved systolic function (2, 3). Thalassemia patients may remain Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
3 Noori et al. asymptomatic and global left ventricular (LV) function may be preserved until late in the disease process. Therefore, early detection of myocardial dysfunction may be useful in the management plans. In order to clarify these issues, the present study was performed to evaluate conventional and tissue Doppler echocardiography findings and its relation to plasma NT-pro BNP, Ferritin and Iron levels in thalassemia patients in two pediatric centers of cardiac and specific diseases in Ali Asghar hospital, Zahedan city, Sistan and Baluchestan province, Iran, from August 2015 to June MATERIALS AND METHODS 2-1. Study Design and Population This case-control study was performed on 82 patients with major betathalassemia aged 5 to 18 years were diagnosed based on hemoglobin electrophoresis and enrolled for the study. Patients were selected from those attending outpatient clinics and inpatient wards in Ali Ibn Abi Talib hospital's pediatric clinics in Zahedan city, Sistan and baluchestan province, Iran. The control group included of 82 matched in age and gender healthy individuals with normal cardiovascular status from those who attended to the hospital for routine checkup. Sample size was based on the cost, ethical limitation especially for controls and age consideration. The following formula applied to calculate sample size. 2 r 1 ( Z Z ) n ( ) r ( difference) 2 /2 2 Where: n= Sample size, r = ratio of controls to cases = 1, Standard deviation of the outcome variable=1.6, effect size (the difference in means) = 0.7, Zβ= Represents the desired power =typically.84 for 80% power and Z α/2 = Represents the desired level of statistical significance = typically = 1.96 for 95% of confidence interval (14) Inclusion and exclusion criteria Patients who included to the study were diagnosed based on hemoglobin electrophoresis and selected randomly from clinical outpatients and inpatients. The control group included of matched in age and gender healthy individuals attended to the hospital for routine checkup. Exclusion criteria were rheumatic heart disease, history of smoking, hypertension, present or past history of overt heart failure also excluded from the study with other causes of heart failure, other than iron overload such as primary hemosiderosis, hypercalcemia, thyrotoxicosis, obvious valvar disease, rhythm abnormality, structural, active infection, other systemic inflammatory diseases, and renal insufficiency Measures NT-pro BNP, ferritin and iron Measurements Three milliliters (ml) of blood was taken from all patients at 8.00 AM after an overnight fasting. The sample was centrifuged at 3,000 rpm/min for 10 minutes at 5 C. Separated serum of NTpro BNP, ferritin and iron were kept in - 70cc refrigerator until measuring. The samples transferred to the biochemistry library of Zahedan University of Medical Sciences with considering the cold chain circumstances and then 250 microns isolated serum samples selected for measuring the levels of NT-pro BNP by ELISA kit, and same serum samples selected for measuring the levels of ferritin and iron levels by using ELISA kit (USA) Echocardiography findings Major proceedings were performed on both patients and controls such as medical history, physical examination; chest X-ray and electrocardiogram (ECG) participants without breath holding and view was taken Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
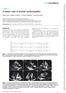
4 NT-pro BNP and Involvement in Thalassemia Patients in the mitral valve surface in parasternal position. The whole study population went under conventional echocardiography and Doppler tissue echocardiography, using My Lab 60 instrument with 3-8-MHz transducers (made in Italy). Parameters namely ejection fraction (EF), fractional shortening (FS), the velocity of the blood flow through the heart valves, as well as peak A velocity (A), peak E velocity (E), and myocardial performance index (MPI) were measured by M mode. The sample volume was positioned at the tips of the tricuspid and mitral valve leaflets in the apical four-chamber view to enable the measurement of (a): which is the time of interval between the end and the start of trans-mitral and trans-tricuspid flow. The sample volume was thereafter relocated to the left ventricular outflow tract just below the aortic valve (apical five-chamber view) so as to measure (b): which is the left ventricular ejection time. The right ventricular outflow velocity pattern was also recorded from the parasternal short-axis view with the Doppler sample volume positioned just distal to the pulmonary valve for the measurement of (b). MPI calculated as: a-b/b = IRT + ICT/ET (12-14) (Figure.1). Doppler tissue echocardiography (DTE) was another method that was performed from the apical four-chamber view, and 3mm pulsed ultrasound Doppler samples before echocardiography. Echocardiography was performed hours after packed red blood cell transfusion on patients (13), by same with using of my lab 60 with transducer 3-8 made in Italy. But for the control group only echocardiography was performed. For having high precision echocardiography repeated 3 cycles in 2D, M-Mode, Doppler and tissue Doppler imaging methods and the average was considered. Echocardiogram applied in volume was placed at the level of lateral mitral annulus. Myocardial velocity profiles of the lateral tricuspid annulus and lateral mitral annulus were obtained by placing the sample volume at the junction of the tricuspid annulus and the right ventricle (RV) free wall and at the junction of the mitral annulus and LV posterior wall, respectively. With this modality, the recorded values were the early (E) and late (A) diastolic mitral and tricuspid annular velocities, and the ratio of E/A (13-15). Fig1: Diagram of Doppler Tissue Echocardiography waves: S', systolic wave; E', early diastolic wave; A', late diastolic wave (14) Ethical considerations This study is a part of a thesis. The study was approved as a thesis for the degree of pediatric specialty by the Ethics Committee of Zahedan University of Medical Sciences, Zahedan, Iran (ID number: 6798). The written informed consent was obtained from all participants Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
5 Noori et al Data analysis All statistical procedures were performed using SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) Windows version 18.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA). Data were summarized by mean ± standard deviation (SD). Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was performed for normality. Statistically significant differences of continuous variables were determined by using the independent samples t-test and Mann- Whitney U test based on normality distribution. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. 3- RESULTS This case-control study was performed to evaluate conventional and tissue Doppler echocardiography findings and its relation to plasma NTpro BNP, Ferritin and Iron levels in thalassemia patients. The participants were collected from those who referred to Ali Ibn Abi Talib hospital's pediatric clinics in Zahedan city, Sistan and baluchestan province, Iran, assessed. From 164 participants, 82 were patients with major betathalassemia aged 5 to 18 years and same number were control which they matched in age (11.85±3.36 in control and 10.84±3.41 in patients) (p=0.099). Test of normality showed that almost all the variables had non normal distribution in the case of case and control participants. But some of variables such as height, weight, age, left A', EF, peak E in left, peak A in right, MPI left, and right had normal distribution in the case of only patients consideration (Table.1). Non-parametric test of Mann Whitney showed that variables of NT- pro BNP (MW=443, p<0.001), Iron (MW=79.5, p<0.001), Ferritin (MW=101, p<0.001), left S' (MW=2715, p=0.033), left A' (MW=2635, p=0.017), right A' (MW=2594.5, p=0.012), EF(MW=1971, p<0.001), FS(MW=1479, p<0.001), left A/A' (MW=2350, p<0.001), right A/A' (MW=2714, p=0.033), right MPI (MW=2097.5, p<0.001), and left MPI (MW=1663, p<0.001), were significantly different between case and controls. Amongst the variables in the study, the others were nonsignificant (p > 0.005) (Table.2). In the Table.3 patients comparison based on parametric and Nonparametric test for two groups of age < 10 years and patients belong to age group of years. The table showed that Mann Whitney test revealed the level of significant (MW=305, p<0.001) for the variable of FS. Next segment of the table based on the t-test showed that height (t=11.73, p<0.001), weight (t=10.72, p<0.001), age (t=8.5, p<0.001), EF (t=5.13 p<0.001), MPI left (t=4.23, p<0.001), and right (t=5.67, p<0.001), were significantly different. Amongst the variables in the study, Iron, right S' and FS were different in age groups categorization, so that Iron were different significantly (MW=208.5, p=0.026) in the case of patients who had lower level of for NT- pro BNP regarding to patients who had higher level. Right S' had convers trends compared with Iron so that its level were higher in patients who aged > 10 years regarding to the higher level of NT- pro BNP (MW=52.5, p=0.023). FS had different values significantly in lower levels of NT- pro BNP (MW= 126, p<0.001), and higher level (MW=39, p=0.004) regarding age groups. For the normal distributed variables, anthropometric variables of height, weight and age were significantly different in patients with two levels of NT- pro BNP regarding age groups. Three echocardiography Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
6 NT-pro BNP and Involvement in Thalassemia Patients findings of EF (for NT- pro BNP <847.5: (t=3.87, p<0.001), and for NT- pro BNP > 847.5: (t=3.2, p=0.004), right MPI (for NT- pro BNP < 847.5: (t=-2.87, p=0.006), and for NT- pro BNP > 847.5: (t=-3.28, p=0.003), and left MPI (for NT- pro BNP <847.5: (t=-4, p<0.001), and for NT- pro BNP > 847.5: (t=4.15, p<0.001), had different levels in two age groups (Table.4). Table.5 showed the results for variables values comparison between age groups in both left E/E' levels regarding the cutoff point 9.0. Results of the first part of the table revealed that variables of FS (MW=152.50, p<0.001) were significantly higher in the age group < 10 years for the levels of left E/E' lower than cutoff point. Right peak E velocity (MW=8.00, p=0.017) were significantly higher in the age group < 10 years for the levels of left E/E' more than cutoff point; and right E/E' (MW=351.50, p<0.022) were significantly higher in the age group > 10 years for the levels of left E/E' lower than cutoff point. Part two of the table showed the results due to independent t-test so that height, weight and age were significantly different between age groups. EF (for E/E' < 9: T=5.36, p<0.001), right MPI (for E/E '< 9: T=-4.95, p<0.001), and left MPI (for E/E' < 9: T=-5.92, p<0.001), had different values in age group <10 years compared to > 10 years aged. Part one of the Table.6 showed the results due to Mann Whitney test so that Iron and FS were significantly different between age groups. Iron (for S'<8: MW=46, p<0.028, higher in age group > 10 years), FS (for S'<8: MW=44, p=0.022, lower level in age group > 10 years, and for S'>8: MW=108.5, p<0.001, lower level in age group > 10 years). Part two of the Table.6 showed that height, weight and age were different in age groups in both levels of left S'. Same trends observed for EF, Right MPI and left MPI. EF had significantly lower value in age group of > 10 years (for left S' < 8: t=2.64, p=0.013 and for left S' > 8: t=4.12, p<0.001). Right MPI had significantly higher value in age group of > 10 years (only for left S' > 8: t= -4.64, p<0.001) and left MPI had same trends (only for left S' > 8: t= -6.96, p<0.001). Table-1: Test of normality for clinical and laboratory findings of β-thalassemia major patients and control group Variables All participant Patients Mean SD K.S P-value Mean SD K.S P-value NT- pro BNP Iron Ferritin Height Weight Age Left S' Left E' Left A' Right S' Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
7 Noori et al. Right E' Right A' EF FS Left E Left A Right E Right A Left E/ E' Right E/E' Left A/A' Right A/A' Left MPI Right MPI NT-proBNP = N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide, E' = early diastolic velocity; A' = late diastolic velocity; S' = systolic peak velocity, EF = ejection fraction, FS = fractional shortening, E = early diastolic pulsed-wave Doppler, A = late diastolic wave, E/E' = early diastolic pulsed-wave Doppler / early diastolic velocity, A/A' = late diastolic wave / late diastolic velocity MPI = myocardial performance index, SD= standard deviation, K.S= Kolmogorov Smirnov test. Table-2: Clinical and laboratory findings of β-thalassemia major patients and control group Variables Groups Number Mean SD NT-pro BNP Iron Ferritin Height Weight Age Left S' Left E' Left A' Right S' Mean Rank Sum of Mean Rank Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Mann- Whitney U P-value 443 < < < Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
8 NT-pro BNP and Involvement in Thalassemia Patients Right E' Right A' EF FS Peak E ( Left) Peak (Left) Peak E ( Right) Peak A (Right) Left E/E' A Right E/E' Left A/A Right A/A Right MPI Left MPI Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case Control Case < < < <0.001 NT-proBNP=N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide, E' = early diastolic velocity; A'= late diastolic velocity; S' =systolic peak velocity, EF= ejection fraction, FS = fractional shortening, E = early diastolic pulsedwave Doppler, A = late diastolic wave, MPI: myocardial performance index, E/E'= early diastolic pulsed-wave Doppler /early diastolic velocity, A/A'= late diastolic wave/ late diastolic velocity, Peak E= early mitral and tricuspid valve flow velocity, PeakA= late mitral and tricuspid valve flow velocity, SD= standard deviation. Table-3: Age comparison of clinical and laboratory findings of β-thalassemia major patients Variables NT-pro BNP Iron Ferritin Left S Age, year Number Mean SD < < < < Mann- Whitney U P-value Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
9 Noori et al. Left E Right S Right E Right A FS Peak A (left) Peak E (right) Left E/E Right E/E Left A/A Right A/A < < < < < < < < < < < < Variables Age Number Mean SD t-test P-value Height < < Weight < < Left A EF Peak E (left) Peak A (right) Right MPI < < < < < < <0.001 < Left MPI < NT-proBNP=N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide, E' = early diastolic velocity; A'= late diastolic velocity; S' =systolic peak velocity, EF= ejection fraction, FS = fractional shortening, E = early diastolic pulsedwave Doppler, A = late diastolic wave, E/E'= early diastolic pulsed-wave Doppler /early diastolic velocity, A/A'= late diastolic wave/ late diastolic velocity, MPI= myocardial performance index, Peak E= early mitral and tricuspid valve flow velocity, PeakA= late mitral and tricuspid valve flow velocity, SD= standard deviation. Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
10 NT-pro BNP and Involvement in Thalassemia Patients Table-4: Age comparison of clinical and laboratory findings of β-thalassemia major patients for Ntpro BNP <847.5 and Nt- pro BNP >=847.5 Variables Iron Ferritin Left S Left E Right S Right E Right A FS Peak A ( left) Peak E (right) Left E/E Right E/E Left A/A Right A/A Age, year Mean < Nt- pro BNP <847.5 Nt- pro BNP >=847.5 Mann- Mann- SD P-value Mean SD P-value Whitney U Whitney U < < < < < < < < < < < < < Variables Age Mean SD t-test P-value Mean SD t-test P-value Height Weight Age Left A EF Peak E (left) < < < < < < Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
11 Noori et al. Peak A (right) Right MPI < < < Left MPI NT-proBNP=N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide, E' = early diastolic velocity; A'= late diastolic velocity; S' =systolic peak velocity, EF= ejection fraction, FS = fractional shortening, E = early diastolic pulsedwave Doppler, A = late diastolic wave, E/E'= early diastolic pulsed-wave Doppler /early diastolic velocity, A/A'= late diastolic wave/ late diastolic velocity, MPI= myocardial performance index, Peak E= early mitral and tricuspid valve flow velocity, PeakA= late mitral and tricuspid valve flow velocity, SD= standard deviation. Table-5: Age comparison of clinical and laboratory findings of β-thalassemia patients for E/E' < 9 and E/E' > = 9 Variables Nt- pro BNP Iron Ferritin Left S Left E Right S Right E Right A FS Peak A (left) Peak E (Right) Right E/E Left A/A Right A/A Age, year Mean SD E/E'< 9 E/E'> = 9 Mann- Whitney U P- value Mean < < < SD Mann- Whitney U P- value < < < < < < < < < < < Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
12 NT-pro BNP and Involvement in Thalassemia Patients Variables Height Weight Age Left A EF Peak E (left) Peak A (Right) Right MPI Left MPI Age, P- P- Mean SD t-test Mean SD t-test year value value < < < < < < < < < NT-proBNP=N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide, E' = early diastolic velocity; A'= late diastolic velocity; S' =systolic peak velocity, EF= ejection fraction, FS = fractional shortening, E = early diastolic pulsedwave Doppler, A = late diastolic wave, E/E'= early diastolic pulsed-wave Doppler /early diastolic velocity, A/A'= late diastolic wave/ late diastolic velocity, MPI=myocardial performance index, Peak E= early mitral and tricuspid valve flow velocity, PeakA=late mitral and tricuspid valve flow velocity, SD= standard deviation. Table-6: Age comparison of clinical and laboratory findings of β-thalassemia major patients for left S < 8 and S > = 8 Variables NT-pro BNP(pg/ml) Iron Ferritin Left E Right S Right E Right A Age, year Mean Systolic peak velocity (S ) < 8 Systolic peak velocity (S ) > = 8 SD Mann- Whitney U P- value Mean < < < < < < < SD Mann- Whitney U P- value Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
13 Noori et al. FS Peak A (left) Peak E (right) Left E/E Right E/E Left A/A < < < < < < < Right A/A P- P- Variables Age(year) Mean SD t-test Mean SD t-test value value < Height Weight Age Left A EF Peak E (left) Peak A (right) Right MPI Left MPI < < < < < < < < < <0.001 NT-proBNP=N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide, E' = early diastolic velocity; A'= late diastolic velocity; S' =systolic peak velocity, EF= ejection fraction, FS = fractional shortening, E = early diastolic pulsedwave Doppler, A = late diastolic wave, E/E'= early diastolic pulsed-wave Doppler /early diastolic velocity, A/A'= late diastolic wave/ late diastolic velocity, MPI=myocardial performance index, Peak E=early mitral and tricuspid valve flow velocity, PeakA=late mitral and tricuspid valve flow velocity, SD= standard deviation. 4- DISCUSSION One of the most important organs that impressed by iron overload is heart especially in thalassemia patients. The main causes of thalassemia cardiomyopathy are increasing intestinal absorption hemolysis and lifelong blood transfusions determine myocardial iron overload (16). Ibrahim et al. (17) conducted a study on pediatric thalassemia compared with control and concluded that ferritin was significantly varied between groups, but EF and FS were same. For the right and left DTE, they observed a Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
14 NT-pro BNP and Involvement in Thalassemia Patients significant difference. Barbero et al. (18) applied DTE to evaluate MPI in thalassemia and resulted approximately all right heart functions were same in patients and controls; but some of predominant left hear functions such as MPI and S' were dissimilar significantly. The current study mostly found same results especially in DTE findings with these studies. Gupta et al. applied DTE and found comparable results with the current results in the case of left heart functions by DTE (S', E', A' and E'/A') that revealed similarity except E' (19). Garadah et al. (4) assessed systolic and diastolic functions of the left ventricle and found that diastolic indices of LV in patients showed higher early diastolic filling of LV, and E/A ratio suggesting restrictive diastolic pattern and stiff myocardial wall in patients. Similarly, Yaprak et al. (20) demonstrated that patients had significantly higher E wave, E/A ratio, and lower A wave velocity that suggesting a restrictive pattern but with no correlation with hemoglobin level. Spirit et al. (21) demonstrated a restrictive pattern in patients with no heart failure. This was in agreement with a previous report that high E/A ratio was the most common finding. Kremastinos et al. (3) observed lower systolic and diastolic velocity waves and E/E' in the patients group while FS and EF were same in groups. They also demonstrated that NTpro BNP was increased significantly in the third decade of life in patients, whereas E/E ratio increased in the fourth decade. Maximal left atrial and right ventricular diameters were also increased in the patients group and mitral E-wave velocity while no statistical difference was seen in A wave and E/A ratio. In the study E wave deceleration time was decreased in patients and finally they introduced NT-pro BNP as an earlier biomarker of LV diastolic dysfunction (2). Many studies implicated to this fact that NT-pro BNP is a sensitive biomarker to detect asymptomatic LV dysfunction especially with an important role in diagnostic and prognostic thalassemia implications (2, 3, 14). In these studies, NT-pro BNP levels were correlated with the presence of diastolic LV dysfunction in thalassemia patients. Kremastinos et al. (2) proposed an increase of NT-pro BNP in thalassemia patients and reported that this increase correlated with age and LV diastolic dysfunction but Balkan et al. (5) did not find a significant correlation. Current study revealed that some of heart dysfunctions values changed with the level of NT-pro BNP variation, this variation was more affected by age changes in every level of NT-pro BNP. These heart dysfunctions would be introduced as: Left and right MPI as diastolic and systolic dysfunctions, right S' as systolic dysfunction as well as FS and EF. As observed, in the present study the number of heart dysfunctions that changed with the NT-pro BNP variation was very low that could be similar with Balkan study. The probable reason for the lack of correlation in Balkan study may be was due to mean age of their patients that was lower and the range of age was narrow. The results of the current study demonstrated that NT-pro BNP, Iron, Ferritin were higher in thalassemia patients and variables of left S', left and right A', EF, FS were lower in patients and left and right A/A', left and right MPI were higher. In regards to the lower level of NT- pro BNP than cutoff point, older patients had higher levels of MPI in both left and right and Iron level as well when EF and FS were lower. Left systolic peak velocity (S') was more valuable compared to the right S' to detect systolic dysfunction. FS and EF were lower in old patients in both levels of NT- pro BNP and right and left MPI levels were higher. The most important finding of these above studies was an increase of NT-pro BNP levels in patients with no signs or symptoms of HF compared to the healthy controls similar to the previous Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
15 Noori et al. studies (2, 3). Aessopos et al. have found high levels of BNP only in patients with overt heart failure, independently of severity of cardiac insufficiency (6, 16). The patient was divided into two groups according to E/E' ratio: E/E' < 9 and E/E' 9. Patients with an E/E' ratio < 9 were considered as having normal diastolic dysfunction, whereas patients with an E/E' ratio 9 were considered as patients with suspected diastolic dysfunction. Kremastinos et al. (2) divided the study patients in three groups based on 8 and 15 cutoff points of left E/E'. In these three groups of patients, they detected that hemoglobin levels were similar between groups, while age and total transfused blood units showed an increase in the groups with a higher E/E ratio. Between patients' groups they found A' and DT were same and E, E/A, NT pro BNP and ferritin had different values so that NT-pro BNP was higher significantly in patients with higher level of E/E. For more evidences on effect of aging on NT-pro BNP levels and diastolic dysfunction Kremastino divided the patient population into the first five decades. Both NT-pro BNP levels and E/E ratio showed a statistically significant increase throughout patients' life. NT-pro BNP levels appear to increase earlier, in the third decade of life, being significantly higher than levels in the 1st or 2nd decades. On the other hand, E/E ratio seems to increase later in life, being significantly higher only in the 4th decade. They expressed that although NT-pro BNP levels were increased in patients with higher E/E ratio this increase only became statistically significant in the 3rd decade of life, while E/E ratio increased in the 4th decade. We also detected that NT- pro BNP increased by age similar with the Kremastinos et al. study (2). The current study detected that the left and right S', A' and A/A' had significant different values in all age groups except those were lower than 10 years. The levels of Left and right E' were different significantly in all age groups. Left and right A' levels were different. Patients had different levels of right E/E' significantly in all age groups except the age group of higher than 20 years. In another study, Kremastinos also found that an increase of NT-pro BNP levels in patients with beta thalassemia major was related to age and diastolic dysfunction (E/E' ratio >15) and the highest decade in the study (3). Therefore the results of the studies by Kremastinos et al. showed the similar pattern that E/E' ratio and NT- pro BNP were increased by age. From the Balkan et al. (5) study resulted that NT-pro BNP levels were higher in patients with E/E < 9 compared to controls. They also concluded that NTpro BNP levels were higher in patients with E/E' 9 compared to those with E/E'< 9, but this increase was not statistically significant. Same trends resulted for E, left ventricular end systolic diameter, left ventricular end diastolic diameter, LA diameter by Echocardiographic evaluation. In the present study, despite of difference between types of echocardiography variables, the results in general were similar with Balkan's study. These results deal to this fact that an increase in the ratio of left E/E' causes diastolic dysfunction in the patients aged < 20 years especially when the level of E/E' is more than suspected level. Balkan et al. (5) reported that NT-pro BNP levels were significantly higher in patients with E/E' ratio < 9 in comparison to healthy controls. Echocardiographic evaluation revealed that E, LVES, LVED, LA diameter, LAVI, and LVMI values were significantly higher in E/E' ratio 9 than E/E' ratio < 9. Our results revealed that according to the cutoff point 9 for left E/E', EF and FS were lower in older patients when E/E' had lower level. Right and left MPI had positive association with age when E/E' < 9. Few Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
16 NT-pro BNP and Involvement in Thalassemia Patients studies only included E and A velocities and E/A ratio as a surrogate markers of diastolic functions (5) whereas some studies included that tissue Doppler imaging (TDI), and strain imaging methods for the estimation of diastolic filling pressures (22). On the hypothesis that longitudinal ventricular functions may give early information about impending cardiac dysfunction, the current study used TDI to evaluate systolic (left S') and diastolic velocity ( left E', left A' and left E/E' ratio), and observed that Iron had higher concentration in old patients when left S' < 8. In both levels of left S' (S' > 8 cm/s and S' < 8 cm/s), EF had lower level in older patients. Right and left MPI were higher in patients aged more than 10 years in both categorization of left S'. Marcello Marc et al. (23) performed a study on patients with thalassemia to detect early cardiac dysfunction by DTE and resulted that patients with reduced systolic peak velocity (left S' < 8 cm/s) had a mild abnormality of early diastolic velocity (left E') in comparison to patients with normal systolic velocity (left S' > 8 cm/s). With similar classification of left S', the current study resulted that left E' was similar in both groups of patients even for the considered age groups. Same pattern observed for L.A. diameter, left ventricular dimensions, E and A peak velocities/a ratio, Am, and E/E' ratio in the two groups. In compare with our results, would be observed that the results are similar and in same line with our results related to EF Marcello Marc detected lower level for EF in the second group, although values were within the normal range in both groups. Same results observed from the study conducted by Kremastinos et al. (24) who found diastolic abnormalities only after onset of cardiac failure. The results of these two studies are consisted with the current study results especially for those with systolic peak velocity less than 8 cm/s. In the present study peak systolic velocity (S') was significantly reduced in patients. Also, mentioned that a peak systolic velocity < 8 cm/s allows identifying a group of patients at higher risk of cardiac adverse events. It is of interest that EF was not significantly reduced in all age groups of patients with Sm < 8 cm/s, dissimilar with Marcello Marc findings. These findings also are dissimilar with Akpinar et al. (25). Many studies demonstrated impairment of peak systolic velocity (S'), despite a normal EF. Furthermore our results corroborate findings of other recent researches which have demonstrated a pivotal role of TDI in detecting early myocardial damage in such patients. Recently Marcí et al. and Hamdy et al. have reported early impairment of longitudinal systolic function, detected by TDI, in thalassemia patients without heart failure (10, 11, 23) Limitations of the study The study limitation was lack of Proper Corporation by participants especially controls. 5- CONCLUSION The study confirmed that NT-pro BNP increases in thalassemia patients and is related to age and LV diastolic dysfunction. NT-pro BNP with E/E' and S' were shown diastolic and systolic dysfunction in patients with major thalassemia. We presented the relation between plasma NT-pro BNP levels, iron overload, and various echocardiography indices of myocardial dysfunction in young thalassemia patients. While there was a strong correlation between plasma NT-proBNP levels and iron overload. There was no correlation between NTproBNP levels and diastolic dysfunction parameters in patients in the second decade of life. An increased level of ferritin and NT-pro BNP can be used as a marker for the intensification of iron chelation therapy, which reverses iron-induced cardiomyopathy. Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
17 Noori et al. 6- AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION Noor Mohammad Noori designed the study. Data analyzed by Alireza Teimouri as well as writing the primary manuscript and corresponding author. The critical revision supervised by Noor Mohammad Noori and Alireza Teimouri. 7- CONFLICT OF INTEREST: None. 8- ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors would like to show their warm gratitude to all parents for the participation especially control groups. The authors would like to thank to nursing staff from hospitals for data gathering. 9- REFERENCES 1. Noori NM, Mahjoubifard M, Mohammadi M, Fard AJ, Abassi A, Farzanegan B. Comparison of QT dispersion with left ventricular mass index in early diagnosis of cardiac dysfunction in patients with β-thalassemia major. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal 2014; 16(5):e Kremastinos DT, Tsiapras DP, Kostopoulou AG, Hamodraka ES, Chaidaroglou AS, Kapsali ED. NT-proBNP levels and diastolic dysfunction in β- Thalassaemia major patients. European journal of heart failure. 2007; 9(5): Kremastinos DT, Hamodraka E, Parissis J, Tsiapras D, Dima K, Maisel A. Predictive value of B-type natriuretic peptides in detecting latent left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in β-thalassemia major. American heart journal. 2010; 159(1): Garadah T, Kassab S, Mahdi N, Abu- Taleb A, Jamsheer A. Pulsed and Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Changes in Patients with Thalassemia Major. Clinical Medicine: Blood Disorders. 2010; 3: Balkan C, Tuluce SY, Basol G, Tuluce K, Ay Y, Karapinar DY, Gurgun C, Bayindir O, Kavakli K. Relation between NT probnp Levels, Iron Overload, and Early Stage of Myocardial Dysfunction in β Thalassemia Major Patients. Echocardiography. 2012; 29(3): Aessopos A, Farmakis D, Polonifi A, et al: Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide concentration in beta-thalassaemiapatients. Eur J Heart Fail 2007; 9: Tang WH, Girod JP, Lee MJ, et al: Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide levels in ambulatory patients with establishedchronic symptomatic systolic heart failure. Circulation 2003; 108: Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, et al. Plasma natriuretic peptide levels and the risk of cardiovascular events and death. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: Akpinar O, Acarturk E, Kanadasi M, et al: Tissue Doppler imaging and NT-proBNP levels show the early impairment of ventricular function in patients with betathalassemia major. Acta Cardiol 2007; 62: Hamdy AM. Use of strain and tissue velocity imaging for early detection ofregional myocardial dysfunction in patients with beta thalassemia. Eur J Echocardiography 2007; 8: Hamdy AM, Zein El-Abdin MY, Abdel-Hafey MA. Tissue Doppler has an important prognostic value in patients with beta thalassemia. Echocardiography 2008; 25: Noori N, Mohamadi M, Keshavarz K, Alavi S, Mahjoubifard M, Mirmesdagh Y. Comparison of right and left side heart functions in patients with thalassemia major, patients with thalassemia intermedia, and control group. The Journal of Tehran University Heart Center. 2015; 8(1): Noori NM, Keshavarz K, Shahriar M. Cardiac and pulmonary dysfunction in asymptomatic beta-thalassanemia major. Asian Cardiovascular and Thoracic Annals. 2012; 20(5): Noori NM, Teimouri A, Anvari N. Diagnostic Value of N Terminal Pro B Type Natriuretic Peptide (NT-pro BNP) in Cardiac Involvement in Patients with Beta- Thalassemia. International Journal of Pediatrics. 2017; 5(4): M, Totaro A, Ieva R, Brunetti ND, Di Biase M. Time intervals and myocardial Int J Pediatr, Vol.5, N.11, Serial No.47, Nov
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό
 Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
The Correlation of Ferritin and Leptin Serum Levels with Cardiac Involvement in Thalassemia Patients Compared to Controls
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 7623-7638) The Correlation of Ferritin and Leptin Serum Levels with Cardiac Involvement in Thalassemia Patients Compared to Controls Noor Mohammad Noori
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 7623-7638) The Correlation of Ferritin and Leptin Serum Levels with Cardiac Involvement in Thalassemia Patients Compared to Controls Noor Mohammad Noori
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY DATA REPORT FORM
 Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
Vevo 2100 System Cardio Measurements. Dieter Fuchs, PhD FUJIFILM VisualSonics, Inc.
 Vevo 2100 System Cardio Measurements Dieter Fuchs, PhD FUJIFILM VisualSonics, Inc. dfuchs@visualsonics.com Instructions This document is a guideline on how to assess cardiac function in rodents imaged
Vevo 2100 System Cardio Measurements Dieter Fuchs, PhD FUJIFILM VisualSonics, Inc. dfuchs@visualsonics.com Instructions This document is a guideline on how to assess cardiac function in rodents imaged
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION
 LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Evaluation of Gluten-free Diet on the Heart Functions in Children with Celiac Disease
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 8889-8905) Evaluation of Gluten-free Diet on the Heart Functions in Children with Celiac Disease 1 1 11 Noor Mohammad Noori, *Alireza Teimouri, Turan Shahraki
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 8889-8905) Evaluation of Gluten-free Diet on the Heart Functions in Children with Celiac Disease 1 1 11 Noor Mohammad Noori, *Alireza Teimouri, Turan Shahraki
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION
 RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure?
 ESC Congress Munich - 25-29 August 2012 Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction From Bench to Bedside Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure? Prof. Burkert Pieske Department of Cardiology Med.University
ESC Congress Munich - 25-29 August 2012 Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction From Bench to Bedside Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure? Prof. Burkert Pieske Department of Cardiology Med.University
British Society of Echocardiography
 British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
Effect of Average Annual Mean Serum Ferritin Levels on QTc Interval and QTc Dispersion in Beta-Thalassemia Major
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 5431-5440) Effect of Average Annual Mean Serum Ferritin Levels on QTc Interval and QTc Dispersion in Beta-Thalassemia Major Yazdan Ghandi 1, *Mehrzad Sharifi
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 5431-5440) Effect of Average Annual Mean Serum Ferritin Levels on QTc Interval and QTc Dispersion in Beta-Thalassemia Major Yazdan Ghandi 1, *Mehrzad Sharifi
Prevalence of heart failure in Turkish adult population: Results from Heart failure Prevalence and Predictors in TurkeY (HAPPY) study
 Prevalence of heart failure in Turkish adult population: Results from Heart failure Prevalence and Predictors in TurkeY (HAPPY) study M. Degertekin, Ç. Erol O. Ergene, Ö. Kozan, B. Mutlu, E. Ilkay, E.
Prevalence of heart failure in Turkish adult population: Results from Heart failure Prevalence and Predictors in TurkeY (HAPPY) study M. Degertekin, Ç. Erol O. Ergene, Ö. Kozan, B. Mutlu, E. Ilkay, E.
Imaging in Heart Failure: A Multimodality Approach. Thomas Ryan, MD
 Imaging in Heart Failure: A Multimodality Approach Thomas Ryan, MD Heart Failure HFrEF HFpEF EF50% Lifetime risk 20% Prevalence 6M Americans Societal costs - $30B 50% 5-year survival 1 Systolic
Imaging in Heart Failure: A Multimodality Approach Thomas Ryan, MD Heart Failure HFrEF HFpEF EF50% Lifetime risk 20% Prevalence 6M Americans Societal costs - $30B 50% 5-year survival 1 Systolic
Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies
 Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ESC Congress 2010 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy To determine the differences
Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ESC Congress 2010 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy To determine the differences
Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know. Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts 2/8/2012
 Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know Pat Bailey, RDCS, FASE Technical Director Beaumont Health System Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts Practical Hints
Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know Pat Bailey, RDCS, FASE Technical Director Beaumont Health System Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts Practical Hints
Evaluation of Cardiac Complications in Patients with Thalassemia Major Using Serum Ferritin Levels
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijssJuneI/2017/016 Evaluation of Cardiac Complications in Patients with Thalassemia Major Using Serum Ferritin Levels Farideh
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijssJuneI/2017/016 Evaluation of Cardiac Complications in Patients with Thalassemia Major Using Serum Ferritin Levels Farideh
Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 5 RAAS inhibitors should be avoided if possible in patients with obstructive HCM Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Katrin Witzel,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 5 RAAS inhibitors should be avoided if possible in patients with obstructive HCM Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Katrin Witzel,
Heart Failure. Cardiac Anatomy. Functions of the Heart. Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics. Determinants of Cardiac Output. Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function
 SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
Title:Relation Between E/e' ratio and NT-proBNP Levels in Elderly Patients with Symptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:Relation Between E/e' ratio and NT-proBNP Levels in Elderly Patients with Symptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis Authors: Mihai Strachinaru (m.strachinaru@erasmusmc.nl) Bas
Author's response to reviews Title:Relation Between E/e' ratio and NT-proBNP Levels in Elderly Patients with Symptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis Authors: Mihai Strachinaru (m.strachinaru@erasmusmc.nl) Bas
The new Guidelines: Focus on Chronic Heart Failure
 The new Guidelines: Focus on Chronic Heart Failure Petros Nihoyannopoulos MD, FRCP, FESC Professor of Cardiology Imperial College London and National & Kapodistrian University of Athens 2 3 4 The principal
The new Guidelines: Focus on Chronic Heart Failure Petros Nihoyannopoulos MD, FRCP, FESC Professor of Cardiology Imperial College London and National & Kapodistrian University of Athens 2 3 4 The principal
The impacts of pericardial effusion on the heart function of infants and young children with respiratory syncytial virus infection
 The impacts of pericardial effusion on the heart function of infants and young children with respiratory syncytial virus infection Author(s): Muslim M. Al Saadi, Abdullah S. Al Jarallah Vol. 13, No. 1
The impacts of pericardial effusion on the heart function of infants and young children with respiratory syncytial virus infection Author(s): Muslim M. Al Saadi, Abdullah S. Al Jarallah Vol. 13, No. 1
A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy
 Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling. What is the pathophysiology at presentation?
 Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function
 Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice
 Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
OPTIMIZING ECHO ACQUISTION FOR STRAIN AND DIASTOLOGY
 OPTIMIZING ECHO ACQUISTION FOR STRAIN AND DIASTOLOGY October 8, 2017 Deborah Agler, ACS, RDCS, FASE Coordinator of Education and Training Cleveland Clinic General Principles Diastology Clinical Data Heart
OPTIMIZING ECHO ACQUISTION FOR STRAIN AND DIASTOLOGY October 8, 2017 Deborah Agler, ACS, RDCS, FASE Coordinator of Education and Training Cleveland Clinic General Principles Diastology Clinical Data Heart
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
B-Mode measurements protocols:
 Application Note How to Perform the Most Commonly Used Measurements from the Cardiac Measurements Package associated with Calculations of Cardiac Function using the Vevo Lab Objective The Vevo LAB offline
Application Note How to Perform the Most Commonly Used Measurements from the Cardiac Measurements Package associated with Calculations of Cardiac Function using the Vevo Lab Objective The Vevo LAB offline
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital
 LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study
 Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study Bassem A. Samad, MD, PhD, Jens M. Olson, MD, and Mahbubul Alam, MD, PhD, FESC,
Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study Bassem A. Samad, MD, PhD, Jens M. Olson, MD, and Mahbubul Alam, MD, PhD, FESC,
Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When?
 Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
Χριστίνα Χρυσοχόου Α Καρδιολογική Κλινική Πανεπιστηίου Αθηνών
 Ιωάννης Ανδρέου Χριστίνα Χρυσοχόου Α Καρδιολογική Κλινική Πανεπιστηίου Αθηνών Ιπποκράτειο Γ.Ν.Α Splenectomy at the age of 7yrs Episodes of persistent atrial fibrillation Hypothyroidism Osteoporosis Noncompliant
Ιωάννης Ανδρέου Χριστίνα Χρυσοχόου Α Καρδιολογική Κλινική Πανεπιστηίου Αθηνών Ιπποκράτειο Γ.Ν.Α Splenectomy at the age of 7yrs Episodes of persistent atrial fibrillation Hypothyroidism Osteoporosis Noncompliant
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Pediatric Echocardiographic Normal values. SIEC Firenze Febbraio 2016
 Pediatric Echocardiographic Normal values Massimiliano Cantinotti MD Fondazione Toscana G. Monasterio and Institute of Clinical Physiology (CNR) Massa and Pisa SIEC Firenze 18-20 Febbraio 2016 Background
Pediatric Echocardiographic Normal values Massimiliano Cantinotti MD Fondazione Toscana G. Monasterio and Institute of Clinical Physiology (CNR) Massa and Pisa SIEC Firenze 18-20 Febbraio 2016 Background
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease
 Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION. There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation
 PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation Better synchrony and diastolic function for septal versus apical right ventricular permanent
PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation Better synchrony and diastolic function for septal versus apical right ventricular permanent
The background of the Cardiac Sonographer Network News masthead is a diagnostic image:
 Number 5 Welcome Number 5 Welcome to the newsletter created just for you: sonographers who perform pediatric echocardiograms in primarily adult echo labs. Each issue features tips on echocardiography of
Number 5 Welcome Number 5 Welcome to the newsletter created just for you: sonographers who perform pediatric echocardiograms in primarily adult echo labs. Each issue features tips on echocardiography of
Evaluation of Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Imaging findings in children with pulmonary hypertension
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2017; 59: 244-253 DOI: 10.24953/turkjped.2017.03.003 Original Evaluation of Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Imaging findings in children with pulmonary hypertension Alper
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2017; 59: 244-253 DOI: 10.24953/turkjped.2017.03.003 Original Evaluation of Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Imaging findings in children with pulmonary hypertension Alper
NT-proBNP: Evidence-based application in primary care
 NT-proBNP: Evidence-based application in primary care Associate Professor Rob Doughty The University of Auckland, Auckland City Hospital, Auckland Heart Group NT-proBNP: Evidence in Primary Care The problem
NT-proBNP: Evidence-based application in primary care Associate Professor Rob Doughty The University of Auckland, Auckland City Hospital, Auckland Heart Group NT-proBNP: Evidence in Primary Care The problem
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on)
 Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
E/Ea is NOT an essential estimator of LV filling pressures
 Euroecho Kopenhagen Echo in Resynchronization in 2010 E/Ea is NOT an essential estimator of LV filling pressures Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD December 10, 2010 Ziekenhuis Oost Limburg Genk University Hasselt
Euroecho Kopenhagen Echo in Resynchronization in 2010 E/Ea is NOT an essential estimator of LV filling pressures Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD December 10, 2010 Ziekenhuis Oost Limburg Genk University Hasselt
Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography
 Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography Maryam Bokhamseen, RCS, RCDS, EACVI Echotechnologist ǁ, Non invasive Cardiac Laboratory King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center. Outline: Introduction. Background
Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography Maryam Bokhamseen, RCS, RCDS, EACVI Echotechnologist ǁ, Non invasive Cardiac Laboratory King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center. Outline: Introduction. Background
Heart Failure in Women: Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre
 Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Assessment of LV systolic function
 Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Københavns Universitet
 university of copenhagen Københavns Universitet Total average diastolic longitudinal displacement by colour tissue doppler imaging as an assessment of diastolic function de Knegt, Martina Chantal; Biering-Sørensen,
university of copenhagen Københavns Universitet Total average diastolic longitudinal displacement by colour tissue doppler imaging as an assessment of diastolic function de Knegt, Martina Chantal; Biering-Sørensen,
Assessment of right ventricular function by tissue Doppler in relation to plasma NT-proBNP concentration in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2007, Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 167 173 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 1507 4145 Assessment of right ventricular function by tissue Doppler in relation to plasma NT-proBNP
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2007, Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 167 173 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 1507 4145 Assessment of right ventricular function by tissue Doppler in relation to plasma NT-proBNP
Effect of Heart Rate on Tissue Doppler Measures of E/E
 Cardiology Department of Bangkok Metropolitan Administration Medical College and Vajira Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract Background: Our aim was to study the independent effect of heart rate (HR) on
Cardiology Department of Bangkok Metropolitan Administration Medical College and Vajira Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract Background: Our aim was to study the independent effect of heart rate (HR) on
Myocardial Strain Imaging in Cardiac Diseases and Cardiomyopathies.
 Myocardial Strain Imaging in Cardiac Diseases and Cardiomyopathies. Session: Cardiomyopathy Tarun Pandey MD, FRCR. Associate Professor University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Disclosures No relevant
Myocardial Strain Imaging in Cardiac Diseases and Cardiomyopathies. Session: Cardiomyopathy Tarun Pandey MD, FRCR. Associate Professor University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Disclosures No relevant
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto
 How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1
 A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Keerthy M. A Study of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Hypertension. Journal of
A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Keerthy M. A Study of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Hypertension. Journal of
Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function
 Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function J A F E R A L I, M D U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L S C A S E M E D I C A L C E N T E R S T A F F C A R D I O T
Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function J A F E R A L I, M D U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L S C A S E M E D I C A L C E N T E R S T A F F C A R D I O T
Jong-Won Ha*, Jeong-Ah Ahn, Jae-Yun Moon, Hye-Sun Suh, Seok-Min Kang, Se-Joong Rim, Yangsoo Jang, Namsik Chung, Won-Heum Shim, Seung-Yun Cho
 Eur J Echocardiography (2006) 7, 16e21 CLINICAL/ORIGINAL PAPERS Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: The presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic
Eur J Echocardiography (2006) 7, 16e21 CLINICAL/ORIGINAL PAPERS Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: The presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic
Objectives. Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. LV Diastolic Function: Introduction. LV Diastolic Function: Introduction
 Objectives Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Jacobo Kirsch, MD Cardiopulmonary Imaging, Section Head Division of Radiology Cleveland Clinic Florida Weston, FL To review the physiology and
Objectives Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Jacobo Kirsch, MD Cardiopulmonary Imaging, Section Head Division of Radiology Cleveland Clinic Florida Weston, FL To review the physiology and
Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION
 Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION Overview Coronary arteries Terminology to describe contractility Measuring ventricular function Systolic dysfunction Practice cases- LV
Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION Overview Coronary arteries Terminology to describe contractility Measuring ventricular function Systolic dysfunction Practice cases- LV
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) of cats is the
 J Vet Intern Med 2006;20:65 77 Pulsed Tissue Doppler Imaging in Normal Cats and Cats with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy H. Koffas, J. Dukes-McEwan, B.M. Corcoran, C.M. Moran, A. French, V. Sboros, K. Simpson,
J Vet Intern Med 2006;20:65 77 Pulsed Tissue Doppler Imaging in Normal Cats and Cats with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy H. Koffas, J. Dukes-McEwan, B.M. Corcoran, C.M. Moran, A. French, V. Sboros, K. Simpson,
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and. Diastolic Function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and Diastolic Function Mitra Niroumand Raffael Kuperstein Zion Sasson Patrick J. Hanly St. Michael s Hospital University
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and Diastolic Function Mitra Niroumand Raffael Kuperstein Zion Sasson Patrick J. Hanly St. Michael s Hospital University
Study of grading of severity of Heart Failure in patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy
 Original article: Study of grading of severity of Heart Failure in patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dr Satyajeet Shantaram Nighute *, Dr Govind S. Shiddapur, Dr Madhulika Mahashaabde, Dr Chintan K.
Original article: Study of grading of severity of Heart Failure in patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dr Satyajeet Shantaram Nighute *, Dr Govind S. Shiddapur, Dr Madhulika Mahashaabde, Dr Chintan K.
Advanced Echocardiography in the Evaluation of Chemotherapy Patients
 Advanced Echocardiography in the Evaluation of Chemotherapy Patients Juan Carlos Plana, MD, FACC, FASE Co-Director, Cardio-Oncology Center Section of Cardiovascular Imaging Department of Cardiovascular
Advanced Echocardiography in the Evaluation of Chemotherapy Patients Juan Carlos Plana, MD, FACC, FASE Co-Director, Cardio-Oncology Center Section of Cardiovascular Imaging Department of Cardiovascular
Index. K Knobology, TTE artifact, image resolution, ultrasound, 14
 A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
Squeeze, Squeeze, Squeeze: The Importance of Right Ventricular Function and PH
 Squeeze, Squeeze, Squeeze: The Importance of Right Ventricular Function and PH Javier Jimenez MD PhD FACC Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute
Squeeze, Squeeze, Squeeze: The Importance of Right Ventricular Function and PH Javier Jimenez MD PhD FACC Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi
 Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
Evaluation of the Right Ventricle and Risk Stratification for Sudden Cardiac Death
 Evaluation of the Right Ventricle and Risk Stratification for Sudden Cardiac Death Presenters: Sabrina Phillips, MD FACC FASE Director, Adult Congenital Heart Disease Services The University of Oklahoma
Evaluation of the Right Ventricle and Risk Stratification for Sudden Cardiac Death Presenters: Sabrina Phillips, MD FACC FASE Director, Adult Congenital Heart Disease Services The University of Oklahoma
i n d i a n h e a r t j o u r n a l 6 8 ( ) Available online at ScienceDirect
 i n d i a n h e a r t j o u r n a l 6 8 ( 2 0 1 6 ) 8 3 8 7 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ihj Original Article Myocardial Performance
i n d i a n h e a r t j o u r n a l 6 8 ( 2 0 1 6 ) 8 3 8 7 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ihj Original Article Myocardial Performance
Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in South Indian Essential Hypertensive Patient
 Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in South Indian Essential Hypertensive Patient Dr. Peersab.M. Pinjar 1, Dr Praveenkumar Devarbahvi 1 and Dr Vasudeva Murthy.C.R 2, Dr.S.S.Bhat 1, Dr.Jayaraj S G 1
Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in South Indian Essential Hypertensive Patient Dr. Peersab.M. Pinjar 1, Dr Praveenkumar Devarbahvi 1 and Dr Vasudeva Murthy.C.R 2, Dr.S.S.Bhat 1, Dr.Jayaraj S G 1
Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference?
 17 th International Conference on Prenatal Diagnosis and Therapy Lisbon, June 2013 Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference? Fàtima Crispi Department of Maternal-Fetal Medicine,
17 th International Conference on Prenatal Diagnosis and Therapy Lisbon, June 2013 Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference? Fàtima Crispi Department of Maternal-Fetal Medicine,
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines - Update II
 Chamber Quantitation Guidelines - Update II Right Heart Measurements Steven A. Goldstein MD FACC FASE Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Medical Center MedStar Heart Institute Washington Hospital
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines - Update II Right Heart Measurements Steven A. Goldstein MD FACC FASE Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Medical Center MedStar Heart Institute Washington Hospital
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
 ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
Beta-thalassemia, or thalassemia major (TM), is an inherited hemoglobin
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2012; 18:208 214 Turkish Society of Radiology 2012 CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship between color M-mode echocardiography flow propagation and cardiac iron load
Diagn Interv Radiol 2012; 18:208 214 Turkish Society of Radiology 2012 CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship between color M-mode echocardiography flow propagation and cardiac iron load
Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size
 2017 KSE 2017-11-25 Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size Division of Cardiology Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center In-Cheol Kim M.D., Ph.D. LV size and function Internal linear dimensions PLX
2017 KSE 2017-11-25 Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size Division of Cardiology Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center In-Cheol Kim M.D., Ph.D. LV size and function Internal linear dimensions PLX
*Christian M. Carlsen, 1 Mette Mouridsen, 1 Ahmad Sajadieh, 1 Lars Køber, 2 Olav W. Nielsen 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND
 USE OF N-TERMINAL NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE IN A REAL- WORLD SETTING OF PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH ACUTE DYSPNOEA AND THE IMPLICATION FOR TRIAGING PATIENTS IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT *Christian M. Carlsen, 1 Mette
USE OF N-TERMINAL NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE IN A REAL- WORLD SETTING OF PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH ACUTE DYSPNOEA AND THE IMPLICATION FOR TRIAGING PATIENTS IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT *Christian M. Carlsen, 1 Mette
Little is known about the degree and time course of
 Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Clinical material and methods. Departments of 1 Cardiology and 2 Anatomy, Gaziantep University, School of Medicine, Gaziantep, Turkey
 Interatrial Block and P-Terminal Force: A Reflection of Mitral Stenosis Severity on Electrocardiography Murat Yuce 1, Vedat Davutoglu 1, Cayan Akkoyun 1, Nese Kizilkan 2, Suleyman Ercan 1, Murat Akcay
Interatrial Block and P-Terminal Force: A Reflection of Mitral Stenosis Severity on Electrocardiography Murat Yuce 1, Vedat Davutoglu 1, Cayan Akkoyun 1, Nese Kizilkan 2, Suleyman Ercan 1, Murat Akcay
Research Article Changes in Mitral Annular Ascent with Worsening Echocardiographic Parameters of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function
 Scientifica Volume 216, Article ID 633815, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/633815 Research Article Changes in Mitral Annular Ascent with Worsening Echocardiographic Parameters of Left Ventricular
Scientifica Volume 216, Article ID 633815, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/633815 Research Article Changes in Mitral Annular Ascent with Worsening Echocardiographic Parameters of Left Ventricular
The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function
 II Baltic Heart Failure Meeting and Congress of Latvian Society of Cardiology The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function Dr. Artem Kalinin Eastern Clinical University Hospital Riga 30.09.2010.
II Baltic Heart Failure Meeting and Congress of Latvian Society of Cardiology The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function Dr. Artem Kalinin Eastern Clinical University Hospital Riga 30.09.2010.
Ref 1. Ref 2. Ref 3. Ref 4. See graph
 Ref 1 Ref 2 Ref 3 1. Ages 6-23 y/o 2. Significant LVM differences by gender 3. For males 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 103 b. LVM/height = 100 4. For females 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 84 b. LVM/height
Ref 1 Ref 2 Ref 3 1. Ages 6-23 y/o 2. Significant LVM differences by gender 3. For males 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 103 b. LVM/height = 100 4. For females 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 84 b. LVM/height
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False?
 Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function
 Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right ventricular sinusoids
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
ESCBM meeting 2018, Prague Utility of Cardiac Biomarkers in Clinical Heart Failure Care. Md. Shahidul Islam, M.D., Ph.D
 ESCBM meeting 2018, Prague Utility of Cardiac Biomarkers in Clinical Heart Failure Care Md. Shahidul Islam, M.D., Ph.D shaisl@me.com 2 3 Circulating Biomarkers in Heart Failure. Berezin AE. Adv. Exp. Med.
ESCBM meeting 2018, Prague Utility of Cardiac Biomarkers in Clinical Heart Failure Care Md. Shahidul Islam, M.D., Ph.D shaisl@me.com 2 3 Circulating Biomarkers in Heart Failure. Berezin AE. Adv. Exp. Med.
An Echocardiographic Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Thalassemia Major
 \ An Echocardiographic Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Thalassemia Major Syed Najam Hyder 1, Uzma Kazmi 1, Abdul Malik 1 1 Department of Pediatric Cardiology, The Children s Hospital
\ An Echocardiographic Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Thalassemia Major Syed Najam Hyder 1, Uzma Kazmi 1, Abdul Malik 1 1 Department of Pediatric Cardiology, The Children s Hospital
AIMI-HF PROCEDURE MANUAL TECHNICAL GUIDE FOR ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY. MHI Core Laboratory E. O Meara - J.C. Tardif J. Vincent, G. Grenier, C.
 AIMI-HF PROCEDURE MANUAL TECHNICAL GUIDE FOR ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY MHI Core Laboratory E. O Meara - J.C. Tardif J. Vincent, G. Grenier, C. Roy February 2016 Montreal Heart Institute HF Research Aude Turgeon,
AIMI-HF PROCEDURE MANUAL TECHNICAL GUIDE FOR ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY MHI Core Laboratory E. O Meara - J.C. Tardif J. Vincent, G. Grenier, C. Roy February 2016 Montreal Heart Institute HF Research Aude Turgeon,
Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page:
 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Paricalcitol Capsules (ABT-358) (Zemplar ) Name of Active Ingredient: Paricalcitol Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For
Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Paricalcitol Capsules (ABT-358) (Zemplar ) Name of Active Ingredient: Paricalcitol Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
Right Heart Evaluation ASE Guidelines Review. Chris Mann RDCS, RCS, FASE Faculty, Echocardiography Pitt Community College Greenville, NC
 Right Heart Evaluation ASE Guidelines Review Chris Mann RDCS, RCS, FASE Faculty, Echocardiography Pitt Community College Greenville, NC Objectives Briefly review right atrial and right ventricular anatomy
Right Heart Evaluation ASE Guidelines Review Chris Mann RDCS, RCS, FASE Faculty, Echocardiography Pitt Community College Greenville, NC Objectives Briefly review right atrial and right ventricular anatomy
Ιπποκράτειες μέρες καρδιολογίας Θεσσαλονίκη, 9-10 Μαρτίου Φωτεινή Α. Λαζαρίδου Επιμελήτρια Α Γενικό Νοσοκομείο Αγιος Παύλος, Θεσσαλονίκη
 Ιπποκράτειες μέρες καρδιολογίας Θεσσαλονίκη, 9-10 Μαρτίου 2018 Φωτεινή Α. Λαζαρίδου Επιμελήτρια Α Γενικό Νοσοκομείο Αγιος Παύλος, Θεσσαλονίκη RV shape Triangular shape in frontal plane crescent shape in
Ιπποκράτειες μέρες καρδιολογίας Θεσσαλονίκη, 9-10 Μαρτίου 2018 Φωτεινή Α. Λαζαρίδου Επιμελήτρια Α Γενικό Νοσοκομείο Αγιος Παύλος, Θεσσαλονίκη RV shape Triangular shape in frontal plane crescent shape in
Updates in Congestive Heart Failure
 Updates in Congestive Heart Failure GREGORY YOST, DO JOHNSTOWN CARDIOVASCULAR ASSOCIATES 1/28/2018 Disclosures Edwards speaker on Sapien3 valves (TAVR) Stages A-D and NYHA Classes I-IV Stage A: High risk
Updates in Congestive Heart Failure GREGORY YOST, DO JOHNSTOWN CARDIOVASCULAR ASSOCIATES 1/28/2018 Disclosures Edwards speaker on Sapien3 valves (TAVR) Stages A-D and NYHA Classes I-IV Stage A: High risk
Left ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunction in asymptomatic, normotensive type 2 diabetes mellitus
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
Atrial dyssynchrony syndrome: An overlooked cause of heart failure with normal ejection fraction
 Atrial dyssynchrony syndrome: An overlooked cause of heart failure with normal ejection fraction JC Eicher, G Laurent, O Barthez, A Mathé, G Bertaux, JE Wolf Heart Failure Treatment Unit, Rhythmology and
Atrial dyssynchrony syndrome: An overlooked cause of heart failure with normal ejection fraction JC Eicher, G Laurent, O Barthez, A Mathé, G Bertaux, JE Wolf Heart Failure Treatment Unit, Rhythmology and
Topic Page: congestive heart failure
 Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
