Case Report Glanzmann s thrombasthenia: report of a case and review of the literature
|
|
|
- Isabel Clarke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2010;3(4): /IJCEP Case Report Glanzmann s thrombasthenia: report of a case and review of the literature Christopher Sebastiano, Michael Bromberg, Karen Breen, Matthew T. Hurford Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Temple University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA, USA Received November 15, 2009, accepted March 25, 2010, available online: April 25, 2010 Abstract: Glanzmann s thrombasthenia is a rare congenital bleeding disorder. Patients usually present with mucocutaneous bleeding and excessive bleeding associated with trauma and/or surgery. Patients have an increased bleeding time and a normal platelet count with abnormal platelet function assays. Genetically, Glanzmann s thrombasthenia is associated with mutations in the genes which encode for glycoproteins, GPIIb or GPIIIa. Defects in these genes lead to a lack of or highly reduced expression of the glycoprotein complex (GPIIb/GPIIIa), resulting in platelet dysfunction. Bleeding is managed by platelet transfusions. Bone marrow transplants have been used successfully in rare cases. With proper supportive care Glanzmann s thrombasthenia has a very good prognosis. Keywords: Glanzmann s thrombasthenia, glycoprotein complex, GPIIb/GPIIIa, platelet dysfunction, literature review Introduction Glanzmann s thrombasthenia was first documented in 1918 by Dr. Eduard Glanzmann, who described a novel platelet abnormality with defective clot retraction and abnormal appearance on stained film [1]. It has since been more specifically described as an autosomal recessive genetic disorder in which the platelet count is normal or subnormal, the bleeding time is prolonged, and platelet aggregation is deficient or absent [2-4]. Due to this deficiency of platelet function it manifests as a bleeding disorder characterized by mucocutaneous hemorrhage of varying severity. Globally, it is extremely rare but it has a relatively high incidence in consanguineous populations where intermarriage is common [5]. Despite its rarity, it has gained attention since the discovery of its pathophysiology, due to the consequent development of antiplatelet agents now commonly used during percutaneous coronary interventions [6]. In this report, we describe a case of Glanzmann s thrombasthenia and review the current literature. Patient history The patient was a Puerto Rican female who presented with fever, shortness of breath, fatigue, and chest pain. She had a long clinical history of easy and spontaneous bruising, excessive bleeding with tooth extractions, severe epistaxis as a child, and heavy menstrual bleeding. There was no family history of easy bruising or excessive bleeding. During hospitalization the patient became hypotensive but responded successfully to treatment. However, the fever was persistent and no origin was found. The patient subsequently developed hypoxia with no response to therapy and expired. At autopsy, the patient s anatomic cause of death was found to be acute hemorrhagic fibrinous pericarditis. The autopsy also revealed petechial hemorrhages on numerous skin sites as well as foci of hemorrhage in the lungs. Additionally, intramucosal petechial hemorrhages were present in the stomach and duodenum. Clinical features Patients with Glanzmann s thrombasthenia typically present in infancy or early childhood with purpura, epistaxis, gingival bleeding, and prolonged bleeding from trauma [5]. The bleeding which is universal to the disorder is typically not spontaneous, but rather an exaggeration of bleeding which occurs in normal patients [5].
2 Cutaneous purpura usually arise as a result of pressure or minor trauma, and truly spontaneous purpura are rare [5]. As in normal patients epistaxis is common in childhood and usually subsides by adulthood, but it is more severe and the most common cause for bleeding of clinical significance [5]. Gingival bleeding is also common, though it is more often found in those with poor dental hygiene [5]. Menorrhagia occurs in most female patients at the time of menarche and presents a considerable hemorrhagic concern, usually requiring transfusion [2, 5, 7]. Gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hematuria, and hemarthroses have been observed in a small number of patients but are potentially quite severe [5, 7]. Complications from Glanzmann s thrombasthenia may arise during child birth, tooth extraction, or any surgical procedure. Pathology Discoveries in the pathophysiology of Glanzmann s thrombasthenia have greatly increased our understanding of the mechanisms underlying platelet aggregation. The disorder is caused by deficiency or abnormality of the platelet glycoprotein IIb and/or IIIa [8-11]. A single platelet membrane is covered with approximately 50,000 copies of the GPIIb/IIIa integrin complex [1, 12]. Platelet activation confers a conformational change in the complex allowing it to bind to fibrinogen on both subunits [7, 13, 14]. Von Willebrand Factor, fibronectin, and vitronectin also bind the complex though with lower affinity than fibrinogen [1, 4]. The binding of fibrinogen to this complex allows it to bridge two platelets in the presence of calcium to initiate primary and secondary platelet aggregation. Platelet aggregation is deficient when any component of the complex is mutated or the complex is present in subnormal amounts. Thus, patients with thrombasthenia have a normal platelet count but these platelets cannot bind fibrinogen after stimulation and thus cannot aggregate properly. Genetics Glanzmann s thrombasthenia has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. Heterozygotes appear asymptomatic and have essentially normal platelet function tests [5, 7]. Although it is extremely rare worldwide it is found with relatively high frequency within populations that have a prevalence of consanguineous marriages, where its frequency may rival that of much more common disorders such as Von Willebrand s Disease [5]. The four populations (all of which have a high frequency of intermarriage) in which it is most commonly seen are French Gypsies, Iraqi Jews, Jordanian Arabs, and South Indians [7, 15-18]. The genes encoding for GPIIb and GPIIIa both localize to chromosome 17q and several mutations found in these genes lead to lack of or highly reduced expression of the glycoprotein complex, resulting in the platelet dysfunction described above [1,9]. The disorder has been divided into three classifications, which were initially based on fibrinogen content and degree of clot retraction, before the GPIIb/IIIa complex was understood [5]. These classifications have since been adapted to the more recent molecular understanding of the disease. Type I and Type II result from mutations of GPIIb or GPIIIa that cause lack of (i.e., less than 5% of normal) or reduced expression (i.e., 10-20% of normal), respectively, of the IIb/ IIIa complex on the platelet surface [5, 19]. By contrast, asymptomatic heterozygotes express 50-60% of the complex [5, 7]. Additionally, rare mutations may result in a dysfunctional complex that is expressed at a normal or subnormal amount resulting in the Type III, or variant form [5, 19]. These classifications allow for a better comparison of molecular abnormalities to clinical disease, but unfortunately for the most part the two do not correlate [5]. Laboratory diagnosis Glanzmann s thrombasthenia is characterized by normal platelet morphology and normal platelet count, prolonged bleeding time, absent or decreased clot retraction, and normal platelet aggregation in the presence of ristocetin (Figure 1). Platelet aggregation is absent in the presence of epinephrine (Figure 2), collagen (Figure 3), Arachidonic Acid (Figure 4), ADP (Figure 5), due to the dependence of these factors on fibrinogen attachment to the platelet for aggregation [4, 20, 21]. Platelet aggregation occurs normally in response to ristocetin due to its independence from fibrinogen. Flow cytometry can also be used to detect the presence of the GPIIb-IIIa complex, GPIIb (CD41), GPIIIa, (CD61) and fibrinogen by using monoclonal antibodies [22]. This method can also be used to rapidly predict the carrier status of family 444 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2010;3(4):
3 Glanzmann s thrombasthenia Figure 1. Platelet aggregation tracings for Ristocetin. Blue No platelet aggregation (normal) with 0.50ug/ ml Ristocetin. Black Normal platelet aggregation with 1.2ug/ml Ristocetin. Figure 3. Platelet aggregation and secretion tracings for collagen. Blue No platelet aggregation with 1.0 µg/ml collagen. Black No ATP secretion with 1.0 µg/ml collagen. Red No platelet aggregation with 5.0 µg/ml collagen. Green No ATP secretion with 5.0 µg/ml collagen. Figure 2. Platelet aggregation and secretion tracings for Epinephrine. Blue No platelet aggregation with 7.5 µm Epinephrine. Black No ATP secretion with 7.5 µm Epinephrine. Red No platelet aggregation with 10.0 µm Epinephrine. Green No ATP secretion with 10.0 µm Epinephrine. Figure 4. Platelet aggregation and secretion tracings for Arachidonic Acid. Blue No platelet aggregation with 50 µg/ml Arachidonic Acid. Black No ATP secretion with 50µg/ml Arachidonic Acid. 445 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2010;3(4):
4 care. Drugs that affect platelet function, such as NSAIDS or aspirin, should be avoided. Immunizations for hepatitis B should be given due to the infectious risks of frequent transfusion. Oral contraceptives may be taken to treat menorrhagia [5]. Regular dental visits are encouraged to avoid gingivitis and gingival bleeding, and supplements are suggested during early childhood and adolescence to avoid iron deficiency anemia which is commonly caused by such bleeding [5]. Desmopressin (ddavp) has been attempted as therapy but has not shown any proven clinical usefulness [26]. Bone marrow transplants have been used successfully in rare cases, though this remains a drastic treatment [27, 28]. Figure 5. Platelet aggregation and secretion tracings for ADP and thrombin. Blue markedly decreased secretion with 1 unit of thrombin. Black No platelet aggregation with 2.5 µm ADP. Red No ATP secretion with 2.5 µm ADP. members of patients with the disorder [23]. DNA analysis is the most accurate in carrier detection but only when the defect is known, limiting its clinical utility. GPIIb-IIIa quantification by monoclonal antibodies and platelet antigen detection may be used for prenatal diagnosis of type I Glanzmann s thrombasthenia and heterozygous state [24, 25]. Therapy and prognosis There is no known cure for Glanzmann s thrombasthenia. The overall morbidity and mortality have been difficult to estimate due to its rarity, but in most studies the prognosis has proven to be very good [5, 7]. Hemorrhage is naturally the main clinical concern and supportive care is critical. Platelet transfusion is necessary before any invasive procedure or heavy bleeding episode [5]. Platelet alloimmunization against HLA group and/or GPIIb/IIIa glycoproteins is a genuine concern, but the risk is no greater than for any transfused patient and it is not a contraindication to this therapy [5, 19]. Other than transfusion, management is primarily preventive In summary, Glanzmann s thrombasthenia is a rare inherited bleeding disorder. It is primarily found in a limited number of populations in which consanguineous marriage is common. Patients usually present with easy bruising and bleeding from epistaxis and dental extractions. Patients have a normal platelet count but increased bleeding time and abnormal platelet function assays. Genetically, Glanzmann s thrombasthenia has an autosomal recessive pattern and may arise from a number of mutations that affect GPIIb, GPIIIa, and/or the GPIIb/ IIIa complex. The classification of type I and type II Glanzmann s thrombasthenia is based upon the amount of GPIIb/IIIa complex present on the platelet surface, whereas the variant form is classified by an abnormal GPIIb/IIIa complex present at normal or subnormal amounts. Supportive treatment is the best means for care, and bleeding is managed by platelet transfusions. Bone marrow transplants have been used successfully in rare cases. With proper supportive care Glanzmann s thrombasthenia has a very good prognosis. Please address correspondence to: Mathew T. Hurford, M.D., Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Temple University Hospital, 3401 North Broad Street Philadelphia, PA Tel: ; Fax: ; matthewh@temple.edu References [1] Glanzmann E. Hereditaire Hamorrhagische thrombasthenic. Ein Beitrag Zur Pathologie der Blutplattchen. Jahrbuch Kinderheilkde. 1918; 88: [2] Hardisty RM, Dormandy KM, Hutton RA. Thrombasthenia: studies on three cases. Br J Haema- 446 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2010;3(4):
5 tol. 1964; 10: [3] Pittman MA Jr., Graham JB. Glanzmann s thrombopathy: an autosomal recessive trait in one family. Am J Med Sci.1964; 247: [4] Larrieu MJ, Caen JP, Meyer DO, Vainer H, Sultan Y, Bernard J. Congenital bleeding disorders with long bleeding time and normal platelet count. II. Von Willebrand's disease (report of thirty-seven patients). Am J Med Sep;45(3): [5] George JN, Caen JP, Nurden AT. Glanzmann s thrombasthenia: the spectrum of clinical disease. Blood. 1990; 75: [6] Seligsohn U. Glanzmann thrombasthenia: a model disease which paved the way to powerful therapeutic agents. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb. 2002; 32: [7] Caen JP. Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1989; 2: [8] Nurden AT, Caen JP. An abnormal platelet glycoprotein pattern in three cases of Glanzmann s thrombasthenia. Br J Haematol. 1974; 28: [9] Phillips DR, Jenkins CSP, Luscher EF, Larrieu M- J. Molecular differences of exposed surface proteins on thrombasthenic platelet plasma membranes. Nature. 1975; 257: [10] French DL. The molecular genetics of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Platelets[1].998; 9: [11] Nurden AT. Inherited abnormalities of platelets. Thromb. Haemost. 1999; 82: [12] Coller BS, Cheresh DA, Asch E and Seligsohn U. Platelet vitronectin receptor expression differentiates Iraqi-Jewish from Arab patients with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia in Israel. Blood. 1991; 77: [13] Van Willigen G, Hers I, Gorter G and Akkerman JW. Exposure of ligand-binding sites on platelet integrin alpha IIb/beta 3 by phosphorylation of the beta 3 subunit. Biochem J. 1996; 314: [14] Kieffer N and Phillips DR. Platelet membrane glycoproteins: functions in cellular interactions. Ann Rev Cell Biol. 1990; 6: [15] Caen JP. Glanzmann s thrombasthenia. Clin Haematol. 1972; 1: [16] Khanduri U, Pulimood R, Sudarsanam A, Carman RH, Jadhav M, Pereira S, Pulimood BM. A review and report of 42 cases from South India. Thromb Haemost. 1981; 46: [17] Seligsohn U, Rososhansky S. A Glanzmann s thrombasthenia cluster among Iraqi Jews in Israel. Thromb Haemost. 1984; 52: [18] Awidi AS. Increased incidence of Glanzmann s thrombasthenia in Jordan compared with Scandinavia. Scand J Haematol. 1983; 30: [19] Bellucci S, Caen JP. Molecular basis of Glanzmann s Thrombasthenia and current strategies in treatment. Blood Reviews. 2002; 16: [20] Zucker MB, Pert JH, Hilgartner MW. Platelet function in a patient with thrombasthenia. Blood. 1966; 28: [21] Weiss HJ, Kochwa S. Studies of platelet function and proteins in three patients with Glanzmann s thrombasthenia. J Lab Clin Med. 1968; 71: [22] Warkentin TE, Powling MJ, Hardisty RM. Measurement of fibrinogen binding to platelets in whole blood by flow cytometry: a micromethod for the detection of platelet activation. Br J Hematol. 1990; 76: [23] Sharp WJ, Khanduri UD, Christie BS. Rapid heterozygote detection in Glanzmann s thrombasthenia. Br J Haematol. 1998; 101: [24] Seligsohn U, Mibashan RS, Rodeck CH, Nicolaides KH, Millar DS, Coller BS. Prenatal diagnosis of Glanzmann s thrombasthenia. Lancet 1985; 2: [25] Kaplan C, Patereau C, Reznikoff-Etievant MN, Muller JY, Dumez Y, Kesseler A.Antenatal PLA1 typing and detection of GP IIb-IIIa complex.br J Haematol Jul;60(3): [26] Lethagen S and Nilson IM. DDAVP-induced enhancement of platelet retention: Its dependence on platelet-von Willebrand Factor and the platelet receptor GPIIb/IIIa. Eur J Haematol. 1992; 42: [27] Bellucci S, Devergie A, Gluckman E, Tobelem G, Lethielleux P, Benbunan M, Schaison G, Boiron M.Complete correction of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia by allogeneic bone-marrow transplantation.br J Haematol Apr;59(4): [28] Bellucci S, Damaj G, Boval B, Rocha V, Devergie A, Yacoub-Agha I, Garderet L, Ribaud P, Traineau R, Socié G, Gluckman E. Bone marrow transplantation in severe Glanzmann's thrombasthenia with antiplatelet alloimmunization. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000; 25: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2010;3(4):
GLANZMANN S THROMBASTHENIA. Stacey Shiovitz January 13, 2012
 GLANZMANN S THROMBASTHENIA Stacey Shiovitz January 13, 2012 HELP!! MY PATIENTHASGT DO YOU EVEN KNOW WHAT THAT IS? CASE 27yo woman presented tdto gynecology clinic i for menorrhagia x 10 days Bleeding started
GLANZMANN S THROMBASTHENIA Stacey Shiovitz January 13, 2012 HELP!! MY PATIENTHASGT DO YOU EVEN KNOW WHAT THAT IS? CASE 27yo woman presented tdto gynecology clinic i for menorrhagia x 10 days Bleeding started
Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN
 Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN The student should be able:» To identify the mechanism of homeostasis and the role of vessels, platelets
Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN The student should be able:» To identify the mechanism of homeostasis and the role of vessels, platelets
Demographic Data about Glanzmann's Thrombasthenia and Bernard Soulier in Wassit, Iraq
 Demographic Data about Glanzmann's Thrombasthenia and Bernard Soulier in Wassit, Iraq Abstract Dr Ahmed Hatem Sabhan 1 Dr, Safaa A Faraj * Dr. Jassam Kareem Al Lami 3 1 MD Pediatrics, Welfare Children
Demographic Data about Glanzmann's Thrombasthenia and Bernard Soulier in Wassit, Iraq Abstract Dr Ahmed Hatem Sabhan 1 Dr, Safaa A Faraj * Dr. Jassam Kareem Al Lami 3 1 MD Pediatrics, Welfare Children
Platelet Disorders. By : Saja Al-Oran
 Platelet Disorders By : Saja Al-Oran Introduction The platelet arise from the fragmentation of the cytoplasm of megakaryocyte in the bone marrow. circulate in the blood as disc-shaped anucleate particles
Platelet Disorders By : Saja Al-Oran Introduction The platelet arise from the fragmentation of the cytoplasm of megakaryocyte in the bone marrow. circulate in the blood as disc-shaped anucleate particles
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn
Congenital bleeding disorders
 Congenital bleeding disorders Overview Factor VIII von Willebrand Factor Complex factor VIII von Willebrand factor (vwf) complex circulate as a complex + factor IX intrinsic pathway Platelets bind via
Congenital bleeding disorders Overview Factor VIII von Willebrand Factor Complex factor VIII von Willebrand factor (vwf) complex circulate as a complex + factor IX intrinsic pathway Platelets bind via
Catherine P. M. Hayward, MD PhD FRCPC Professor, Pathology & Molecular Medicine, & Medicine, McMaster University Head, Coagulation, Hamilton Regional
 Catherine P. M. Hayward, MD PhD FRCPC Professor, Pathology & Molecular Medicine, & Medicine, McMaster University Head, Coagulation, Hamilton Regional Laboratory Medicine Program No relevant disclosures
Catherine P. M. Hayward, MD PhD FRCPC Professor, Pathology & Molecular Medicine, & Medicine, McMaster University Head, Coagulation, Hamilton Regional Laboratory Medicine Program No relevant disclosures
BLEEDING (PLATELET) DISORDER. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BLEEDING (PLATELET) DISORDER 1 APPROACH The initial set of questions should establish the following: (1) the most common site and type of bleeding (e.g., mucocutaneous versus articular or deep muscle),
BLEEDING (PLATELET) DISORDER 1 APPROACH The initial set of questions should establish the following: (1) the most common site and type of bleeding (e.g., mucocutaneous versus articular or deep muscle),
Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College
 Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College AN APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS NORMAL HEMOSTASIS After injury, 3 processes halt bleeding Vasoconstriction
Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College AN APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS NORMAL HEMOSTASIS After injury, 3 processes halt bleeding Vasoconstriction
Coagulation Disorders. Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU
 Coagulation Disorders Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU 1 Introduction Local Vs. General Hematoma & Joint bleed Coagulation Skin/Mucosal Petechiae & Purpura PLT wound / surgical bleeding Immediate
Coagulation Disorders Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU 1 Introduction Local Vs. General Hematoma & Joint bleed Coagulation Skin/Mucosal Petechiae & Purpura PLT wound / surgical bleeding Immediate
Hemostatic System - general information
 PLATELET DISORDERS Hemostatic System - general information Normal hemostatic system vessel wall circulating blood platelets blood coagulation and fibrynolysis Bleeding Diathesis inherited or acquired defects
PLATELET DISORDERS Hemostatic System - general information Normal hemostatic system vessel wall circulating blood platelets blood coagulation and fibrynolysis Bleeding Diathesis inherited or acquired defects
Y. Helen Zhang, MD Andy Nguyen, MD 10/28/2012
 Y. Helen Zhang, MD Andy Nguyen, MD 10/28/2012 Clinical History Patient: 23-year-old female Clinical course: status-post cholecystectomy, complicated by retained common bile duct stones. Following three
Y. Helen Zhang, MD Andy Nguyen, MD 10/28/2012 Clinical History Patient: 23-year-old female Clinical course: status-post cholecystectomy, complicated by retained common bile duct stones. Following three
What are InherIted platelet FunCtIon disorders?
 What are InherIted platelet FunCtIon disorders? Published by the World Federation of Hemophilia (WFH) World Federation of Hemophilia, 2010 This publication was developed by the WFH and reviewed by Dr.
What are InherIted platelet FunCtIon disorders? Published by the World Federation of Hemophilia (WFH) World Federation of Hemophilia, 2010 This publication was developed by the WFH and reviewed by Dr.
Bleeding Disorders. Dr. Mazen Fawzi Done by Saja M. Al-Neaumy Noor A Mohammad Noor A Joseph Joseph
 Bleeding Disorders Dr. Mazen Fawzi Done by Saja M. Al-Neaumy Noor A Mohammad Noor A Joseph Joseph Normal hemostasis The normal hemostatic response involves interactions among: The blood vessel wall (endothelium)
Bleeding Disorders Dr. Mazen Fawzi Done by Saja M. Al-Neaumy Noor A Mohammad Noor A Joseph Joseph Normal hemostasis The normal hemostatic response involves interactions among: The blood vessel wall (endothelium)
Bleeding disorders. Hemostatic failure: Inappropriate and excessive bleeding either spontaneous or in response to injury.
 1 Bleeding disorders Objectives: 1. Discuss briefly the physiology of hemostasis. 2. Define the mechanisms of thrombocytopenia and the relative bleeding risk at any given platelet count. 3. Be able to
1 Bleeding disorders Objectives: 1. Discuss briefly the physiology of hemostasis. 2. Define the mechanisms of thrombocytopenia and the relative bleeding risk at any given platelet count. 3. Be able to
Case Studies: Congenital Platelet Disorders
 Case Studies: Congenital Platelet Disorders Presented to Atlanta Wednesday, November 2, 2016 Disclosures for Michele P. Lambert, MD, MTR In compliance with COI policy, ISTH requires the following disclosures
Case Studies: Congenital Platelet Disorders Presented to Atlanta Wednesday, November 2, 2016 Disclosures for Michele P. Lambert, MD, MTR In compliance with COI policy, ISTH requires the following disclosures
Easy Bleeding General Presentation
 Easy Bleeding General Presentation It is not uncommon for children to bleed and bruise after experiencing trauma. However, a child may also have an underlying coagulopathy, which results in easy and possibly
Easy Bleeding General Presentation It is not uncommon for children to bleed and bruise after experiencing trauma. However, a child may also have an underlying coagulopathy, which results in easy and possibly
Platelet Dysfunction- What a Physician
 Platelet Dysfunction- What a Physician Should Know 10 : 5 Mathew Thomas, Trivandrum Abstract Platelet functional disorders are on the increase. The basic platelet functions are a continuous process starting
Platelet Dysfunction- What a Physician Should Know 10 : 5 Mathew Thomas, Trivandrum Abstract Platelet functional disorders are on the increase. The basic platelet functions are a continuous process starting
BLEEDING DISORDERS Simple complement:
 BLEEDING DISORDERS Simple complement: 1. Select the statement that describe the thrombocytopenia definition: A. Marked decrease of the Von Willebrandt factor B. Absence of antihemophilic factor A C. Disorder
BLEEDING DISORDERS Simple complement: 1. Select the statement that describe the thrombocytopenia definition: A. Marked decrease of the Von Willebrandt factor B. Absence of antihemophilic factor A C. Disorder
, Malcolm Tait, Barry Frank Jacobson, Evashin Pillay and Susan J. Louw. Elizabeth Sarah Mayne *
 Mayne et al. Thrombosis Journal (2018) 16:30 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12959-018-0184-2 CASE REPORT Open Access Combination of acquired von Willebrand syndrome (AVWS) and Glanzmann thrombasthenia in monoclonal
Mayne et al. Thrombosis Journal (2018) 16:30 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12959-018-0184-2 CASE REPORT Open Access Combination of acquired von Willebrand syndrome (AVWS) and Glanzmann thrombasthenia in monoclonal
The Adolescent Hematology Clinic: A New Service from Nationwide Children s Hospital
 Hematology/Oncology & BMT The Adolescent Hematology Clinic: A New Service from Nationwide Children s Hospital When is a heavy period a possible sign of a bleeding disorder? Unrecognized bleeding disorders
Hematology/Oncology & BMT The Adolescent Hematology Clinic: A New Service from Nationwide Children s Hospital When is a heavy period a possible sign of a bleeding disorder? Unrecognized bleeding disorders
Platelet disorders. Information for families. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust
 Platelet disorders Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust Platelets are the cells responsible for making blood clot so platelet disorders mean that injured
Platelet disorders Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust Platelets are the cells responsible for making blood clot so platelet disorders mean that injured
GUIDELINES. for the diagnosis and management of von Willebrand disease (VWD)
 GUIDELINES for the diagnosis and management of von Willebrand disease (VWD) The Canadian Hemophilia Society (CHS) is committed to improve the health and quality of life of all people with inherited bleeding
GUIDELINES for the diagnosis and management of von Willebrand disease (VWD) The Canadian Hemophilia Society (CHS) is committed to improve the health and quality of life of all people with inherited bleeding
Factor XI deficiency. Information for families. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust
 Factor XI deficiency Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 2 Factor XI deficiency (also known as Haemophilia C, plasma thromboplastin antecedent deficiency
Factor XI deficiency Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 2 Factor XI deficiency (also known as Haemophilia C, plasma thromboplastin antecedent deficiency
Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development No
 SEED Coagulation Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development No 2 2016 An approach to the bleeding patient The purpose of this newsletter is to provide an overview of the approach to the bleeding patient
SEED Coagulation Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development No 2 2016 An approach to the bleeding patient The purpose of this newsletter is to provide an overview of the approach to the bleeding patient
Easy bruising vs Coagulopathy
 Easy bruising vs Coagulopathy Sept. 19, 2015 Lakehead Summer School Chris Hillis, MD MSc FRCPC hillis@hhsc.ca @HemeHillis Aim & Objectives Aim: To increase comfort in detecting non-pathologic bleeding
Easy bruising vs Coagulopathy Sept. 19, 2015 Lakehead Summer School Chris Hillis, MD MSc FRCPC hillis@hhsc.ca @HemeHillis Aim & Objectives Aim: To increase comfort in detecting non-pathologic bleeding
BLEEDING. Introduction. Starship Children s Health Clinical Guideline. Introduction Bleeding Questionnaire. Scoring Key References
 te: The electronic version of this guideline is the version currently in use. Any printed version can Introduction Bleeding Questionnaire Scoring Key References Introduction This bleeding questionnaire
te: The electronic version of this guideline is the version currently in use. Any printed version can Introduction Bleeding Questionnaire Scoring Key References Introduction This bleeding questionnaire
Approach to bleeding disorders &treatment. by RAJESH.N General medicine post graduate
 Approach to bleeding disorders &treatment by RAJESH.N General medicine post graduate 2 Approach to a patient of bleeding diathesis 1. Clinical evaluation: History, Clinical features 2. Laboratory approach:
Approach to bleeding disorders &treatment by RAJESH.N General medicine post graduate 2 Approach to a patient of bleeding diathesis 1. Clinical evaluation: History, Clinical features 2. Laboratory approach:
TREATMENT & MANAGEMENT OF VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE
 TREATMENT & MANAGEMENT OF VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE Dr Susan Russell Director HTC Sydney Children s Hospital, Randwick HFA Meeting 2015 What is von Willebrand Factor? VWF is a large multimeric protein Two
TREATMENT & MANAGEMENT OF VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE Dr Susan Russell Director HTC Sydney Children s Hospital, Randwick HFA Meeting 2015 What is von Willebrand Factor? VWF is a large multimeric protein Two
COAGULATIONS. Dr. Hasan Fahmawi, MRCP(UK), FRCP(Edin)
 COAGULATIONS Dr. Hasan Fahmawi, MRCP(UK), FRCP(Edin) Haemostasis-blood must be maintained in a fluid state in order to function as a transport system, but must be able to solidify to form a clot following
COAGULATIONS Dr. Hasan Fahmawi, MRCP(UK), FRCP(Edin) Haemostasis-blood must be maintained in a fluid state in order to function as a transport system, but must be able to solidify to form a clot following
Factor VII deficiency
 Factor VII deficiency Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 1 Factor VII deficiency (also known as Alexander s disease) is a type of clotting disorder.
Factor VII deficiency Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 1 Factor VII deficiency (also known as Alexander s disease) is a type of clotting disorder.
Approach To A Bleeding Patient
 ABDUL MAJEED, RAHUL RAJEEV REVIEW ARTICLE INTRODUCTION Hemostasis is the process of forming clots in the walls of damaged blood vessels and preventing blood loss while maintaining blood in a fluid state
ABDUL MAJEED, RAHUL RAJEEV REVIEW ARTICLE INTRODUCTION Hemostasis is the process of forming clots in the walls of damaged blood vessels and preventing blood loss while maintaining blood in a fluid state
Controversies in the Diagnosis of Type 1 VWD. Paula James MD, FRCPC ISLH Honolulu, Hawaii Friday, May 5, 2017
 Controversies in the Diagnosis of Type 1 VWD Paula James MD, FRCPC ISLH Honolulu, Hawaii Friday, May 5, 2017 Disclosures for Paula James Research Support/P.I. Employee Consultant Major Stockholder Speakers
Controversies in the Diagnosis of Type 1 VWD Paula James MD, FRCPC ISLH Honolulu, Hawaii Friday, May 5, 2017 Disclosures for Paula James Research Support/P.I. Employee Consultant Major Stockholder Speakers
Guidelines for Shared Care Centres and Community Staff
 Reference: CG1410 Written by: Dr Jeanette Payne Peer reviewer Dr Jenny Welch Approved: February 2016 Approved by D&TC: 8th January 2016 Review Due: February 2019 Intended Audience This document contains
Reference: CG1410 Written by: Dr Jeanette Payne Peer reviewer Dr Jenny Welch Approved: February 2016 Approved by D&TC: 8th January 2016 Review Due: February 2019 Intended Audience This document contains
Meiqiu Lu and Xin Yang *
 Lu and Yang BMC Women's Health (2018) 18:45 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-018-0533-0 CASE REPORT Open Access Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system for treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding in adolescents
Lu and Yang BMC Women's Health (2018) 18:45 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-018-0533-0 CASE REPORT Open Access Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system for treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding in adolescents
Bleeding Disorders HOPE Maram Al-anbar
 Bleeding Disorders HOPE Maram Al-anbar 9-9 - 2014 ^^ Attention Please ^^ We ( correction team of pediatric package^hope/2010^ ) had decided to make one lecture of bleeding disorders in place of the two
Bleeding Disorders HOPE Maram Al-anbar 9-9 - 2014 ^^ Attention Please ^^ We ( correction team of pediatric package^hope/2010^ ) had decided to make one lecture of bleeding disorders in place of the two
Factor XIII deficiency
 Factor XIII deficiency Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 2 Factor XIII deficiency is a type of clotting disorder. A specific protein is missing from
Factor XIII deficiency Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 2 Factor XIII deficiency is a type of clotting disorder. A specific protein is missing from
Introduction to von Willebrand Disease Mary Lesh RN, MS, CPNP
 Introduction to von Willebrand Disease Mary Lesh RN, MS, CPNP OVERVIEW Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is the most common hereditary bleeding disorder in humans, with an estimated prevalence ranging upward
Introduction to von Willebrand Disease Mary Lesh RN, MS, CPNP OVERVIEW Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is the most common hereditary bleeding disorder in humans, with an estimated prevalence ranging upward
Rare Bleeding Disorders
 Rare Bleeding Disorders Item type Authors Publisher Other Irish Haemophilia Society (IHS) Irish Haemophilia Society (IHS) Downloaded 20-Jun-2018 06:21:18 Link to item http://hdl.handle.net/10147/575445
Rare Bleeding Disorders Item type Authors Publisher Other Irish Haemophilia Society (IHS) Irish Haemophilia Society (IHS) Downloaded 20-Jun-2018 06:21:18 Link to item http://hdl.handle.net/10147/575445
L iter diagnostico di laboratorio nelle coagulopatie congenite emorragiche
 L iter diagnostico di laboratorio nelle coagulopatie congenite emorragiche Armando Tripodi Angelo Bianchi Bonomi Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center Dept. of Clinical Sciences and Community Health University
L iter diagnostico di laboratorio nelle coagulopatie congenite emorragiche Armando Tripodi Angelo Bianchi Bonomi Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center Dept. of Clinical Sciences and Community Health University
von Willebrand Disease
 von Willebrand Disease Jeremy Robertson Paediatric Haematologist Royal Children s s Hospital & Pathology Queensland Foglo,, April 1924: the journey begins Oskar and Augusta sail to Helsinki... ...to o
von Willebrand Disease Jeremy Robertson Paediatric Haematologist Royal Children s s Hospital & Pathology Queensland Foglo,, April 1924: the journey begins Oskar and Augusta sail to Helsinki... ...to o
HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS II
 HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS II Congenital/Acquired Hemorrhagic Disorders & Their Treatment COAGULATION TESTING!Bleeding time primary screening test for platelet function!if bleeding time abnormal!platelet Aggregation
HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS II Congenital/Acquired Hemorrhagic Disorders & Their Treatment COAGULATION TESTING!Bleeding time primary screening test for platelet function!if bleeding time abnormal!platelet Aggregation
GUIDELINE: ASSESSMENT OF BRUISING & BLEEDING IN CHILDREN. All children in whom there is concern regarding bruising / bleeding
 GUIDELINE: ASSESSMENT OF BRUISING & BLEEDING IN CHILDREN Reference: Bruising / Bleeding / NAI Version No: 1 Applicable to All children in whom there is concern regarding bruising / bleeding Classification
GUIDELINE: ASSESSMENT OF BRUISING & BLEEDING IN CHILDREN Reference: Bruising / Bleeding / NAI Version No: 1 Applicable to All children in whom there is concern regarding bruising / bleeding Classification
Bleeding Disorders.2 MS Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD. FRCP.FRCPath Feras Fararjeh MD
 Bleeding Disorders.2 MS4.25.02.2019 Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD. FRCP.FRCPath Feras Fararjeh MD Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Case 6: GT 18 yr old female was admitted with pallor, abdominal pain and gum
Bleeding Disorders.2 MS4.25.02.2019 Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD. FRCP.FRCPath Feras Fararjeh MD Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Case 6: GT 18 yr old female was admitted with pallor, abdominal pain and gum
Outline. What is aplastic anemia? 9/19/2012. Aplastic Anemia Current Thinking on the Disease, Diagnosis, and Non-Transplant Treatment Options
 Aplastic Anemia Current Thinking on the Disease, Diagnosis, and Non-Transplant Treatment Options Carlos M. de Castro, MD Duke University Medical Center Outline What is Aplastic Anemia? What other diseases
Aplastic Anemia Current Thinking on the Disease, Diagnosis, and Non-Transplant Treatment Options Carlos M. de Castro, MD Duke University Medical Center Outline What is Aplastic Anemia? What other diseases
Coagulation an Overview Dr.Abdolreza Abdolr Afrasiabi Thal assem a & Heamophili hilia G ene i tic R esearc C en er Shiraz Medical Medic University
 In The Name God Coagulation an Overview Dr.Abdolreza Afrasiabi Thalassemia & Heamophilia Genetic Research hcenter Shiraz Medical University Bleeding Clotting Hemostasis Review of platelet function Platelets
In The Name God Coagulation an Overview Dr.Abdolreza Afrasiabi Thalassemia & Heamophilia Genetic Research hcenter Shiraz Medical University Bleeding Clotting Hemostasis Review of platelet function Platelets
The LaboratoryMatters
 Laboratory Medicine Newsletter for clinicians, pathologists & clinical laboratory technologists. A Initiative. HEMOSTASIS AND THE LABORATORY This issue highlights: Primary Hemostasis Screening Tests Case
Laboratory Medicine Newsletter for clinicians, pathologists & clinical laboratory technologists. A Initiative. HEMOSTASIS AND THE LABORATORY This issue highlights: Primary Hemostasis Screening Tests Case
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders
 HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
Platelet secretion defects. Komal Arora, MD
 Platelet secretion defects Komal Arora, MD COMPONENTS OF NORMAL HAEMOSTASIS Blood vessels Platelets Plasma coagulation factors Their inhibitors The fibrinolytic system Small fragments of cytoplasm derived
Platelet secretion defects Komal Arora, MD COMPONENTS OF NORMAL HAEMOSTASIS Blood vessels Platelets Plasma coagulation factors Their inhibitors The fibrinolytic system Small fragments of cytoplasm derived
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) Seminar. Ron Kopilov 4 th year Medical Student, Tel Aviv University Internal Medicine A 8.3.
 Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) Seminar Ron Kopilov 4 th year Medical Student, Tel Aviv University Internal Medicine A 8.3.2012 1 Our plan: Understand the pathophysiology Identify risk factors
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) Seminar Ron Kopilov 4 th year Medical Student, Tel Aviv University Internal Medicine A 8.3.2012 1 Our plan: Understand the pathophysiology Identify risk factors
Platelet function in diabetes
 Platelet function in diabetes Agneta Siegbahn, MD, PhD, FESC Professor Clinical Coagulation Science Department of Medical Sciences and Uppsala Clinical Research Center Uppsala University Disclosures: None
Platelet function in diabetes Agneta Siegbahn, MD, PhD, FESC Professor Clinical Coagulation Science Department of Medical Sciences and Uppsala Clinical Research Center Uppsala University Disclosures: None
 https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Majeed Syndrome Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS MAJEED 1.1 What is it? Majeed syndrome is a rare genetic disease. Affected children suffer from Chronic
https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Majeed Syndrome Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS MAJEED 1.1 What is it? Majeed syndrome is a rare genetic disease. Affected children suffer from Chronic
Symptoms and Signs in Hematology/ 2013
 Symptoms and Signs in Hematology/ 2013 Abdallah Abbadi.MD.FRCP Professor of Hematology & Oncology University of Jordan & JUH Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Diseases of Blood & Blood forming organs A- Benign
Symptoms and Signs in Hematology/ 2013 Abdallah Abbadi.MD.FRCP Professor of Hematology & Oncology University of Jordan & JUH Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Diseases of Blood & Blood forming organs A- Benign
HAEMOPHAGOCYTIC LYMPHOHISTIOCYTOSIS HLH ADULTS & Young People
 HAEMOPHAGOCYTIC LYMPHOHISTIOCYTOSIS HLH ADULTS & Young People Histiocytosis UK Introduction Despite the misery it causes, Histiocytosis is too rare a disease to have generated substantial research in medical
HAEMOPHAGOCYTIC LYMPHOHISTIOCYTOSIS HLH ADULTS & Young People Histiocytosis UK Introduction Despite the misery it causes, Histiocytosis is too rare a disease to have generated substantial research in medical
Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89
 Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89 Presented by Jennifer Kurkulonis 1 FOUR MAJOR TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS White blood cells
Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89 Presented by Jennifer Kurkulonis 1 FOUR MAJOR TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS White blood cells
Von Willebrand Disease. Alison Street Malaysia April 2010
 Von Willebrand Disease Alison Street Malaysia April 2010 Physiology of VWF OUTLINE Clinical presentation of VWD Classification of VWD with emphases on Type 1, 2B and 2N disease Testing for VWD Treatment
Von Willebrand Disease Alison Street Malaysia April 2010 Physiology of VWF OUTLINE Clinical presentation of VWD Classification of VWD with emphases on Type 1, 2B and 2N disease Testing for VWD Treatment
Customer Information Literature List Platelets
 Customer Information Literature List Platelets Date: August 2015 Subject: Literature List Platelets Issued by: Scientific Customer Services Number: 150803 Note: Whether references are given in British
Customer Information Literature List Platelets Date: August 2015 Subject: Literature List Platelets Issued by: Scientific Customer Services Number: 150803 Note: Whether references are given in British
This slide belongs to iron lecture and it is to clarify the iron cycle in the body and the effect of hypoxia on erythropoitein secretion
 This slide belongs to iron lecture and it is to clarify the iron cycle in the body and the effect of hypoxia on erythropoitein secretion Topics of today lectures: Hemostasis Meaning of hemostasis Mechanisms
This slide belongs to iron lecture and it is to clarify the iron cycle in the body and the effect of hypoxia on erythropoitein secretion Topics of today lectures: Hemostasis Meaning of hemostasis Mechanisms
2010, Metzler Helfried
 Perioperative Strategies in Patients on Dual Antiplatelet Drug Therapy: Noncardiac Surgery H. Metzler Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine Medical University of Graz, Austria What
Perioperative Strategies in Patients on Dual Antiplatelet Drug Therapy: Noncardiac Surgery H. Metzler Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine Medical University of Graz, Austria What
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35456 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Hassan, Suha Mustafa Title: Toward prevention of Hemoglobinopathies in Oman Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35456 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Hassan, Suha Mustafa Title: Toward prevention of Hemoglobinopathies in Oman Issue
Clinical profile of ITP in Children: A single center study
 Clinical profile of ITP in Children: A single center study Dr.Ramadan Allalous 1,Dr Fathia Alriani 1, Dr Amna Rayani 2. 1Tripoli ' s Medical center,medical Faculty, Tripoli University 2Tripoli Children
Clinical profile of ITP in Children: A single center study Dr.Ramadan Allalous 1,Dr Fathia Alriani 1, Dr Amna Rayani 2. 1Tripoli ' s Medical center,medical Faculty, Tripoli University 2Tripoli Children
Chapter 11. Hyper IgM Syndromes
 Chapter 11 Hyper IgM Syndromes Patients with Hyper-IgM (HIGM) syndrome are susceptible to recurrent and severe infections and in some types of HIGM syndrome opportunistic infections and an increased risk
Chapter 11 Hyper IgM Syndromes Patients with Hyper-IgM (HIGM) syndrome are susceptible to recurrent and severe infections and in some types of HIGM syndrome opportunistic infections and an increased risk
Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS)
 ALPS Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) Information for families hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this leaflet This leaflet is designed to help answer the questions families
ALPS Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) Information for families hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this leaflet This leaflet is designed to help answer the questions families
Miss. kamlah ahmed 1
 Miss. kamlah ahmed 1 Anatomy & Physiology Blood has two compartments: 1- a fluid portion called plasma. 2- a cellular portion known as the formed elements of the blood. Which are RBC (erythrocytes), WBC
Miss. kamlah ahmed 1 Anatomy & Physiology Blood has two compartments: 1- a fluid portion called plasma. 2- a cellular portion known as the formed elements of the blood. Which are RBC (erythrocytes), WBC
THALASSEMIA AND COMPREHENSIVE CARE
 1 THALASSEMIA AND COMPREHENSIVE CARE Melanie Kirby MBBS, FRCP (C), Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto Associate Professor of Paediatrics, University of Toronto. Objectives 2 By the end of this presentation,
1 THALASSEMIA AND COMPREHENSIVE CARE Melanie Kirby MBBS, FRCP (C), Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto Associate Professor of Paediatrics, University of Toronto. Objectives 2 By the end of this presentation,
Pediatric Bleeding Questionnaire (PBQ)
 Date Patient Number Patient Name Gender Male Female Age DOB (dd/mm/yy) Ethnic Background of: Father Mother Presenting complaint of bleeding or bruising today? Ever been diagnosed with a bleeding disorder?
Date Patient Number Patient Name Gender Male Female Age DOB (dd/mm/yy) Ethnic Background of: Father Mother Presenting complaint of bleeding or bruising today? Ever been diagnosed with a bleeding disorder?
Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood
 Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood Guideline developed by Robert Saylors, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team. Last reviewed by Robert Saylors, MD September 22, 2016. Key Points
Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood Guideline developed by Robert Saylors, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team. Last reviewed by Robert Saylors, MD September 22, 2016. Key Points
Factor X deficiency. Information for families. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust
 Factor X deficiency Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 1 Factor X (previously known as the Stuart-Prower factor) deficiency is a type of clotting disorder.
Factor X deficiency Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust 1 Factor X (previously known as the Stuart-Prower factor) deficiency is a type of clotting disorder.
Bleeding Disorders: (Hemorrhagic Diatheses) Tests used to evaluate different aspects of hemostasis are the following:
 Bleeding Disorders: (Hemorrhagic Diatheses) Excessive bleeding can result from: 1. Increased fragility of vessels. 2. Platelet deficiency or dysfunction. 3. Derangement of coagulation. 4. Combinations
Bleeding Disorders: (Hemorrhagic Diatheses) Excessive bleeding can result from: 1. Increased fragility of vessels. 2. Platelet deficiency or dysfunction. 3. Derangement of coagulation. 4. Combinations
Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Kristine Krafts, M.D. Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Bleeding disorders von Willebrand disease Hemophilia A and B DIC TTP/HUS ITP Thrombotic disorders Factor V Leiden
Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Kristine Krafts, M.D. Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Bleeding disorders von Willebrand disease Hemophilia A and B DIC TTP/HUS ITP Thrombotic disorders Factor V Leiden
V.N. KARAZIN KHARKOV NATIONAL UNIVERSITY
 V.N. KARAZIN KHARKOV NATIONAL UNIVERSITY Kharkov Regional Centre of Cardiovascular surgery V.N. Karazin Kharkov National University Department of Internal Medicine Immune thrombocytopenic purpura Abduyeva
V.N. KARAZIN KHARKOV NATIONAL UNIVERSITY Kharkov Regional Centre of Cardiovascular surgery V.N. Karazin Kharkov National University Department of Internal Medicine Immune thrombocytopenic purpura Abduyeva
Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease Olga Olevsky, M.D. and Stephen Wong, M.D. Von Willebrand s Disease is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. Low levels of Von
CLINICAL VIGNETTE Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease Olga Olevsky, M.D. and Stephen Wong, M.D. Von Willebrand s Disease is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. Low levels of Von
In adults, the predominant Hb (HbA) molecule has four chains: two α and two β chains. In thalassemias, the synthesis of either the α or the β chains
 Thalassaemias Thalassemia Thalassemia is an inherited autosomal recessive blood disease. Associated with absence or reduction in a or b globin chains. Reduced synthesis of one of the globin chains can
Thalassaemias Thalassemia Thalassemia is an inherited autosomal recessive blood disease. Associated with absence or reduction in a or b globin chains. Reduced synthesis of one of the globin chains can
Carriers of Haemophilia Information for patients
 Carriers of Haemophilia Information for patients page 2 You have been given this leaflet to explain what being a carrier of haemophilia means and the screening tests which are available. What is haemophilia?
Carriers of Haemophilia Information for patients page 2 You have been given this leaflet to explain what being a carrier of haemophilia means and the screening tests which are available. What is haemophilia?
Δοκιμασίες λειτουργικότητας αιμοπεταλίων και PCI Εμμανουήλ Βαβουρανάκης
 Δοκιμασίες λειτουργικότητας αιμοπεταλίων και PCI Εμμανουήλ Βαβουρανάκης Αναπλ. Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας Ιπποκράτειο ΓΝΑ Haematology Research Laboratory!! Platelets Small anucleate discoid cells Involved
Δοκιμασίες λειτουργικότητας αιμοπεταλίων και PCI Εμμανουήλ Βαβουρανάκης Αναπλ. Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας Ιπποκράτειο ΓΝΑ Haematology Research Laboratory!! Platelets Small anucleate discoid cells Involved
Hematologic Disorders. Assistant professor of anesthesia
 Preoperative Evaluation Hematologic Disorders Dr M.Razavi Assistant professor of anesthesia Anemia Evaluation needs to consider the extent and type of surgery, the anticipated blood loss, and the patient's
Preoperative Evaluation Hematologic Disorders Dr M.Razavi Assistant professor of anesthesia Anemia Evaluation needs to consider the extent and type of surgery, the anticipated blood loss, and the patient's
The Child with a Hematologic Alteration
 47 The Child with a Hematologic Alteration HELPFUL HINT Review the anatomy and physiology of the hematologic system in an anatomy and physiology textbook. MATCHING KEY TERMS Match the term with the correct
47 The Child with a Hematologic Alteration HELPFUL HINT Review the anatomy and physiology of the hematologic system in an anatomy and physiology textbook. MATCHING KEY TERMS Match the term with the correct
Haemostasis & Coagulation disorders Objectives:
 Haematology Lec. 1 د.ميسم مؤيد علوش Haemostasis & Coagulation disorders Objectives: - Define haemostasis and what are the major components involved in haemostasis? - How to assess the coagulation status?
Haematology Lec. 1 د.ميسم مؤيد علوش Haemostasis & Coagulation disorders Objectives: - Define haemostasis and what are the major components involved in haemostasis? - How to assess the coagulation status?
Hemostatic derangement in Dengue infection
 Hemostatic derangement in Dengue infection By Assoc. Prof. Darintr Sosothikul, MD Pediatric Hematology-Oncology division, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University
Hemostatic derangement in Dengue infection By Assoc. Prof. Darintr Sosothikul, MD Pediatric Hematology-Oncology division, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University
Blood Components & Indications for Transfusion. Neda Kalhor
 Blood Components & Indications for Transfusion Neda Kalhor Blood products Cellular Components: Red blood cells - Leukocyte-reduced RBCs - Washed RBCs - Irradiated RBCs Platelets - Random-donor platelets
Blood Components & Indications for Transfusion Neda Kalhor Blood products Cellular Components: Red blood cells - Leukocyte-reduced RBCs - Washed RBCs - Irradiated RBCs Platelets - Random-donor platelets
Platelet Aggregation Testing in Platelet-Rich Plasma Description of Procedures With the Aim to Develop Standards in the Field
 Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / PLATELET FUNCTION TESTING Platelet Aggregation Testing in Platelet-Rich Plasma Description of Procedures With the Aim to Develop Standards in the Field Lan Zhou,
Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / PLATELET FUNCTION TESTING Platelet Aggregation Testing in Platelet-Rich Plasma Description of Procedures With the Aim to Develop Standards in the Field Lan Zhou,
Approach to bleeding
 Approach to bleeding By Assoc. Prof. Darintr Sosothikul, MD Pediatric Hematology-Oncology division, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University The mechanism of
Approach to bleeding By Assoc. Prof. Darintr Sosothikul, MD Pediatric Hematology-Oncology division, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University The mechanism of
BLEEDING DISORDERS. JC Opperman 2012
 BLEEDING DISORDERS JC Opperman 2012 Primary and Secondary Clotting Laboratory Tests Routine screening tests Prothrombin time (PT) (INR) increased in neonates (12-18 sec) Partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
BLEEDING DISORDERS JC Opperman 2012 Primary and Secondary Clotting Laboratory Tests Routine screening tests Prothrombin time (PT) (INR) increased in neonates (12-18 sec) Partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
Evaluating for Suspected Child Abuse: Conditions That Predispose to Bleeding
 FROM THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS TECHNICAL REPORT Evaluating for Suspected Child Abuse: Conditions That Predispose to Bleeding Shannon L. Carpenter, MD, MS, Thomas C. Abshire, MD, James D. Anderst,
FROM THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS TECHNICAL REPORT Evaluating for Suspected Child Abuse: Conditions That Predispose to Bleeding Shannon L. Carpenter, MD, MS, Thomas C. Abshire, MD, James D. Anderst,
Haemorrhagic Disorders. Dr. Bashar Department of Pathology Mosul Medical College
 Haemorrhagic Disorders Dr. Bashar Department of Pathology Mosul Medical College Hemorrhagic Disorders These include Disorders of platelets. Disorders of blood vessels. Disorders of coagulation & fibrinolysis.
Haemorrhagic Disorders Dr. Bashar Department of Pathology Mosul Medical College Hemorrhagic Disorders These include Disorders of platelets. Disorders of blood vessels. Disorders of coagulation & fibrinolysis.
Genetics of Thalassemia
 Genetics of Thalassemia Submitted by : Raya Samir Al- Hayaly Sura Zuhair Salih Saad Ghassan Al- Dulaimy Saad Farouq Kassir Sama Naal Salouha Zahraa Jasim Al- Aarajy Supervised by : Dr. Kawkab Adris Mahmod
Genetics of Thalassemia Submitted by : Raya Samir Al- Hayaly Sura Zuhair Salih Saad Ghassan Al- Dulaimy Saad Farouq Kassir Sama Naal Salouha Zahraa Jasim Al- Aarajy Supervised by : Dr. Kawkab Adris Mahmod
By: Andres Solis, Laura Ornelas, and Sandra Ornelas AP Biology 3 rd period
 By: Andres Solis, Laura Ornelas, and Sandra Ornelas AP Biology 3 rd period Rare inherited bleeding disorder where blood doesn t t clot normally People with hemophilia may bleed for a longer time than others
By: Andres Solis, Laura Ornelas, and Sandra Ornelas AP Biology 3 rd period Rare inherited bleeding disorder where blood doesn t t clot normally People with hemophilia may bleed for a longer time than others
Expanding your Choices: Recent additions to the VWF test menu
 Expanding your Choices: Recent additions to the VWF test menu Kenneth Friedman, M.D. Director, Hemostasis Reference Lab BloodCenter of Wisconsin, Milwaukee WI Disclosures for Ken Friedman, M.D. Research
Expanding your Choices: Recent additions to the VWF test menu Kenneth Friedman, M.D. Director, Hemostasis Reference Lab BloodCenter of Wisconsin, Milwaukee WI Disclosures for Ken Friedman, M.D. Research
Familial Mediterranean Fever
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS FMF 1.1 What is it? Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a genetically transmitted disease. Patients
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS FMF 1.1 What is it? Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a genetically transmitted disease. Patients
Platelet Function Disorders (PFD)
 Platelet Function Disorders (PFD) Dr Tim Brighton Haematology, SEALS POWH Randwick Platelet Function in Haemostasis Essential to primary haemostasis (platelet adhesion and plug formation Platelet activation
Platelet Function Disorders (PFD) Dr Tim Brighton Haematology, SEALS POWH Randwick Platelet Function in Haemostasis Essential to primary haemostasis (platelet adhesion and plug formation Platelet activation
PCCN Review Hematology
 PCCN Review Hematology Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Anemia Definition reduction in RBC concentration Causes iron deficiency
PCCN Review Hematology Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Anemia Definition reduction in RBC concentration Causes iron deficiency
6.1 Extended family screening
 CHAPTER 6 CONCLUSION Cost benefit analysis of thalassemia screening programs have shown that the single years treatment for a β-thalassemia major patient was much higher than a total cost per case prevented.
CHAPTER 6 CONCLUSION Cost benefit analysis of thalassemia screening programs have shown that the single years treatment for a β-thalassemia major patient was much higher than a total cost per case prevented.
Pediatrics. Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment. Definition. Epidemiology of Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency.
 Pediatrics Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment See online here Pyruvate kinase deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder characterized by a deficiency in the enzyme "pyruvate kinase"
Pediatrics Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment See online here Pyruvate kinase deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder characterized by a deficiency in the enzyme "pyruvate kinase"
Differences In Efficacy Of Antiplatelet Therapy-Is That Gender Specific?
 Differences In Efficacy Of Antiplatelet Therapy-Is That Gender Specific? DR.O.SAI SATISH PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF CARDIOLOGY NIMS Death is inevitable but Premature death is not Sir Richard Doll Topic outline
Differences In Efficacy Of Antiplatelet Therapy-Is That Gender Specific? DR.O.SAI SATISH PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF CARDIOLOGY NIMS Death is inevitable but Premature death is not Sir Richard Doll Topic outline
A s doctors who care for children, we have a
 1163 PERSONAL PRACTICE The bleeding child; is it NAI? A E Thomas... As a paediatric haematologist, the question of whether a child has been abused or whether they might have a bleeding diathesis is a question
1163 PERSONAL PRACTICE The bleeding child; is it NAI? A E Thomas... As a paediatric haematologist, the question of whether a child has been abused or whether they might have a bleeding diathesis is a question
How to Write a Life Care Plan for a Child with Hemoglobinopathy
 How to Write a Life Care Plan for a Child with Hemoglobinopathy Tamar Fleischer, BSN, MSN, CNLCP & Mona Yudkoff, RN, MPH, CRRN, CNLCP BalaCare Solutions March 2018 St. Peterburg, Florida What is Hemoglobinopathy?
How to Write a Life Care Plan for a Child with Hemoglobinopathy Tamar Fleischer, BSN, MSN, CNLCP & Mona Yudkoff, RN, MPH, CRRN, CNLCP BalaCare Solutions March 2018 St. Peterburg, Florida What is Hemoglobinopathy?
Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing. IgA & ttg IgA
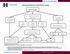 Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing IgA & ttg IgA IgA Normal ttg IgA Negative IgA >10 mg/dl, but less than age matched range IgA
Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing IgA & ttg IgA IgA Normal ttg IgA Negative IgA >10 mg/dl, but less than age matched range IgA
HAEMORRHAGIA Bleeding
 HAEMORRHAGIA Bleeding Cassification Size Location pathomechanism Hematoma: external or may be enclosed within a tissue petechiae : 1-2 mm hemorrhages into skin, mucous membranes, or serosal surfaces increased
HAEMORRHAGIA Bleeding Cassification Size Location pathomechanism Hematoma: external or may be enclosed within a tissue petechiae : 1-2 mm hemorrhages into skin, mucous membranes, or serosal surfaces increased
INHERITED COAGULOPATHY
 Disorder Etiology Pathophysiology and Presentation Lab Findings and Diagnosis Treatment INHERITED COAGULOPATHY HEMOPHILIA A and B Hemophilia A: deficiency in XIII (85%) Hemophilia B: deficiency in IX (15%)
Disorder Etiology Pathophysiology and Presentation Lab Findings and Diagnosis Treatment INHERITED COAGULOPATHY HEMOPHILIA A and B Hemophilia A: deficiency in XIII (85%) Hemophilia B: deficiency in IX (15%)
