THE INFLUENCE OF SEX HORMONES ON CARDIAC AND SKELETAL MUSCLE FUNCTION IN THE MDX MOUSE MODEL OF DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY
|
|
|
- Debra Adams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE INFLUENCE OF SEX HORMONES ON CARDIAC AND SKELETAL MUSCLE FUNCTION IN THE MDX MOUSE MODEL OF DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY BY CONNIE BOOKLESS BSc (with Distinction) PGDipAppSci PhD Submitted for the completion of the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY At The Department of Biological and Physical Sciences Faculty of Sciences University of Southern Queensland 2006
2 ABSTRACT Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a fatal recessive genetic human disease affecting one in 3500 live male births. DMD is progressive, there is no cure, and patients typically die of respiratory or cardiac failure in their second decade of life. Clinical disease symptoms are exacerbated at the onset of puberty and the physiological basis of this is unknown. The mdx mouse is the preferred experimental animal model of DMD, although aspects of the model remain poorly understood. This dissertation characterises physiological and histological features of the dystrophic mdx mouse in response to manipulations of hormonal status including testosterone treatment, surgical castration, and oestrogen treatment. Sex-specific differences in the mdx were also examined. Furthermore, physiological and histological features of the dystrophic mdx mouse model throughout the mdx lifespan were evaluated. Cardiac muscle contractility, left atrial response to exogenous calcium, and the contractile properties of both fast-twitch (EDL) and slow-twitch (SOL) skeletal muscles were examined in male mdx mice ranging from 14 to 330 days of age. Testosterone treatment produced a nonsignificant trend towards a dose-dependent decrease in both basal and maximal left atrial contractility in the mdx. Surgical castration produced no significant cardiac effects within mouse strains. The mdx castrates had a 45% lower maximum atrial force of contraction than control castrates (p<0.05). Conversely, oestrogen treatment significantly improved cardiac contractility in the mdx. An increase in basal left atrial contractility was evident at doses of 0.08 mg/kg/day (p<0.05) and 0.16 mg/kg/day (p<0.01) and in maximum left atrial contractility at a dose of 0.16 mg/kg/day (p<0.01). Gender studies showed cardiac forces in mdx were not different between males and females at any age tested and that both sexes in mdx had a dampened cardiac responsiveness to exogenous calcium. Skeletal muscle function studies showed that castration produced a 25% increase in mdx EDL specific force generation (p<0.01) and no increase in SOL forces. Oestrogen treatment produced a non-significant trend towards increased EDL forces and a 29% increase in SOL specific force at a dose of 0.16 mg/kg/day (p<0.05). Gender studies revealed no differences between male and female mdx in terms of skeletal muscle force production. Further to the hormonal investigations, lifespan characterisation studies revealed that the mdx mouse showed reduced basal and maximal left atrial contractility specifically at ages 14 and 90 days (p<0.05). Skeletal muscle studies showed that specific tetanic force production was significantly lower than controls at 19 (p<0.05), 21, 23, 27, and 330 days of age (p<0.01) for EDL muscles and at 19, 21, and 23 days of age in SOL muscles (p<0.01). These studies further improve our understanding of the mdx mouse as an experimental model of DMD and emphasises that the model is most appropriate a specific ages for specific muscles. These studies further illustrate that testosterone does not improve cardiac contractility in the mdx mouse but that oestrogen improves both cardiac and skeletal muscle function. Further research is warranted into the potential of oestrogen as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of both cardiac and skeletal muscle manifestations of DMD. i
3 CERTIFICATION OF DISSERTATION This thesis is my own work, except where otherwise acknowledged, and the work is original and has not been previously submitted for any other award at any other University or Institution of Tertiary Education. Signature of Candidate Date ENDORSEMENT Signature of Principal Supervisor Date ii
4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This was a very personal and challenging journey and I wish to acknowledge and thank wholeheartedly the following people for their generosity in time and spirit that made the completion of this important work and subsequent dissertation possible. Firstly, to my supervisor Professor Andrew Hoey who has continued to inspire me from my earliest undergraduate studies with his passion for learning, his inspirational lecturing style, and ethical approach to research. To my husband Dr Gregory Bookless and our children, I love you and thank you. My friend and colleague Dr Christel van Erp, never change. To Dr Renee Cornford-Nairn and the members of the Muscle Research Laboratory USQ who always encouraged perserverance even in the toughest times. Special thanks go to Christine Bartlett (USQ Office of Research and High Degrees) who was just wonderful in her tireless encouragement, to Julie Murphy and Sandra Sharp whose professionalism and dedication in the USQ Animal House breeding facility ensured that my experimental animals were always cared for with the utmost concern for their welfare. In addition, the technical expertise and knowledge imparted by the following people greatly enhanced my skills and facilitated the completion of this project; Ilona Iberle (USQ Librarian), Paul Addison (UQ Histologist), Dr Peter Dunn (USQ Statistician), Oliver Kinder (USQ Technician), Maggie Fryer, Anne Woodroffe and Julie Pember (USQ IT Services), Debbie and Steven White (USQ Administrators), Chris de Byl, Phil Hallas, and Sammy Quatromani (USQ IT Services). I wish to make special mention of Mrs Debbie Robbins and Mrs Pat Furlong whose tireless work for the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Parent Project is an inspiration to us all. It is an honour to have known you and your courage and dedication moves mountains. Finally, and most importantly my love goes to every boy with DMD. You are the reason I strove for excellence and I hope that my work, in some small way, might just contribute to a better understanding of this devastating disease and may help to make your lives a little better. Motion is life.. Guillaume Benjamin Amand Duchenne de Boulogne iii
5 GLOSSARY OF ABBREVIATIONS AAV ACE AO AR BW C57 Ca 2+ [Ca 2+ ] i CHF CK CNF CO 2 CRC CSA CV cxmd DFZ DGC DHT DMD DNA ECG EDL enos EOM ER EtOH FOC FSH FXMD g GH adeno-associated virus angiotensin converting enzyme antisense oligonucleotide androgen receptor body weight C57BL/10ScSn mouse calcium intracellular calcium concentration congestive heart failure creatine kinase centronucleated fibre carbon dioxide concentration response curve cross-sectional area cardiovascular canine X-linked muscular dystrophy deflazacort dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex dihydrotestosterone Duchenne muscular dystrophy deoxyribonucleic acid electrocardiogram extensor digitorum longus muscle endothelial nitric oxide synthase extraocular muscles oestrogen receptor ethanol force of contraction follicle stimulating hormone feline X-linked muscular dystrophy gram growth hormone iv
6 GI gastrointestinal GnRH gonadotrophin releasing hormone GRMD Golden Retriever muscular dystrophy H&E haematoxylin and eosin HFMD hypertrophic feline muscular dystrophy HR heart rate HW heart weight HW% heart weight as a percentage of body weight Hz Hertz IGF-1 insulin-like growth factor 1 inos inducible nitric oxide synthase IP intraperitoneal IQ intelligence quota K + kb kda KPSS LA Lf LH LIF Lo LV LV+S M MDSC mdx mg min ml mm mn msec potassium ion kilobase(s) kilo Dalton(s) Krebs physiological salt solution left atria/left atrium absolute muscle length leutinising hormone leukaemia inhibitory factor muscle length left ventricle/ventricular left ventricle and septum molar muscle-derived stem cell muscular dystrophy X-linked milligram minute(s) millilitre millimolar millinewton millisecond(s) µm micromolar v
7 µm micrometre n number of animals in experimental group Na + sodium ion NOS nitric oxide synthase nnos neuronal nitric oxide synthase NMJ neuromuscular junction O 2 PCR oxygen polymerase chain reaction % percent PK pyruvate kinase Po tetanic force Pt twitch force Po:Pt tetanus to twitch ratio RA right atria/right atrium REM rapid eye movement rpm revolutions per minute RV right ventricular free wall RyR ryanodine receptor SC subcutaneous SEM standard error of the mean SERCA sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium-atpase SHR spontaneously hypertensive rat SOL soleus muscle spo tetanic force normalised for cross-sectional area spt twitch force normalised for cross-sectional area SR sarcoplasmic reticulum TGF transforming growth factor TPSS Tyrode physiological salt solution U/L units of active enzyme per litre of serum USQ University of Southern Queensland VC vital capacity vs versus vi
8 CONTENTS ABSTRACT... I CERTIFICATION OF DISSERTATION... II ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS... III GLOSSARY OF ABBREVIATIONS... IV CONTENTS... IX LIST OF TABLES... XV LIST OF FIGURES... XVII 1 LITERATURE REVIEW History of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) Genetics and inheritance Detection, diagnosis and clinical disease features Genetic testing Serum creatine kinase (CK) and pyruvate kinase (PK) levels Muscle biopsy Disease onset Initial clinical signs Skeletal muscle involvement Biomechanics of movement in DMD Gowers manoeuvre Cardiac muscle involvement Skeletal system involvement Respiratory muscle involvement Smooth muscle involvement Intellectual and behavioural impairment Muscle and system sparing Female DMD carriers Serum CK and PK levels in female DMD carriers...19 vii
9 1.5.2 Female DMD carrier cardiac and skeletal muscle involvement Life expectancy and mortality Physical therapies Prolongation of ambulation Orthopaedic management of scoliosis Prevention of pulmonary mortality Prevention of cardiac mortality Dystrophin and the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex (DGC) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide synthase Animal models of DMD The X-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) mouse Alternative mouse models Feline disease models Canine disease models Zebrafish model The Caenhorhabiditis elegans worm Pathology and histology of DMD Calcium homeostasis Centronucleated fibres Therapeutic agents and strategies in DMD treatment and research Dampening the inflammatory response Corticosteroids Natural remedies Tumour necrosis factor-α Nitric oxide based therapeutics L-arginine Utrophin upregulation Improving protein synthesis Anabolic steroids Growth factors...49 viii
10 1.14 Decreasing proteolysis through reducing calpain activity β 2 -adrenergic agonists Increasing proliferation and regeneration of muscle cells Myostatin inhibition Leukaemia inhibitory factor Gene based therapies Aminoglycoside antibiotic therapy Antisense oligonucleotides Sex hormones and DMD Testosterone Oestrogens Aims of study METHODOLOGY Ethical considerations Experimental animals Treatment of animals - allometric scaling Individual trial methodologies Testosterone trial Sex (gender) trial Castration trial Oestrogen trial Influence of age trial Euthanasia Dissection of tissues Organ bath (functional) experiments Skeletal muscle experiments Cardiac muscle experiments Histology protocol Histological analysis Data analysis...76 ix
11 3 TESTOSTERONE TRIAL Influence of testosterone on body weight Influence of testosterone on testes weight Influence of testosterone on cardiac characteristics Cardiac morphometry Cardiac function Influence of testosterone on skeletal muscle morphometry Discussion SEX (GENDER) TRIAL Influence of sex on body weight and heart weight Influence of sex on cardiac characteristics Cardiac morphometry Cardiac function Influence of sex on EDL characteristics EDL morphometry EDL function EDL histology Influence of sex on SOL characteristics SOL morphometry SOL function SOL histology Discussion CASTRATION TRIAL Influence of castration on body weight Influence of castration on cardiac characteristics Cardiac morphometry Cardiac function Influence of castration on skeletal muscle morphometry Influence of castration on EDL characteristics x
12 5.4.1 EDL function EDL histology Influence of castration on SOL characteristics SOL function SOL histology Discussion OESTROGEN TRIAL Influence of oestrogen on body weight Influence on oestrogen on testes weight Influence of oestrogen on cardiac characteristics Cardiac morphometry Cardiac function Influence of oestrogen on skeletal muscle morphometry Influence of oestrogen on EDL characteristics EDL function EDL histology Influence of oestrogen on SOL characteristics SOL function SOL histology Discussion INFLUENCE OF AGE TRIAL Influence of age on body weight Influence of age on testes weights Influence of age on cardiac characteristics Cardiac morphometry Cardiac function Influence of age on skeletal muscle morphometry Influence of age on EDL characteristics EDL function xi
13 7.5.2 EDL histology Influence of age on SOL characteristics SOL function SOL histology Discussion CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS REFERENCES APPENDIX I Krebs physiological salt solution (KPSS) recipe Tyrode s physiological salt solution (TPSS) recipe Haematoxylin stain (Mayer s Haematoxylin) recipe Eosin stain recipe Scott s solution recipe xii
14 LIST OF TABLES Table 1-1 Landmarks in the history of DMD... 2 Table 1-2 Reported manifestations in female DMD carriers...22 Table 1-3 Currently understood roles of the DGC...28 Table 1-4 Disease features of the GRMD canine model of DMD...37 Table 1-5 Therapeutic benefits and theoretical mechanism(s) of action of... corticosteroids in the treatment of DMD Table 1-6 Therapeutics agents in DMD treatment and research...53 Table 1-7 Known physiological effects of oestrogen(s) in non-dystrophic animals and humans...65 Table 2-1 Definitions and mathematical formulae used in skeletal muscle results calculations...74 Table 3-1 Weight of SOL and EDL muscles in male C57 and mdx mice at varying testosterone doses Table 4-1 EDL muscle function in 90 day old mice Table 4-2 EDL muscle function in 180 day old mice...98 Table 4-3 EDL muscle function in 330 day old mice...99 Table 4-4 SOL muscle function in 90 day old male and female mice Table 4-5 SOL muscle function in 180 day old male and female mice Table 4-6 SOL muscle function in 330 day old male and female mice Table 5-1 Body and cardiac weights in entire and castrated mice Table 5-2 Cardiac function of entire and castrated mice Table 5-3 Skeletal muscle morphometry of entire and castrated mice Table 5-4 EDL skeletal muscle function of entire and castrated mice Table 5-5 SOL muscle function in entire and castrated mice Table 6-1 Body and cardiac weights at varying oestrogen doses Table 6-2 EDL and SOL muscle morphometry at varying oestrogen doses Table 6-3 EDL muscle function at varying oestrogen doses Table 6-4 SOL muscle function at varying oestrogen doses Table 7-1 Body and cardiac weights of 14 day old male mice Table 7-2 Body and cardiac weights of 19 day old male mice Table 7-3 Body and cardiac weights of 21 day old male mice Table 7-4 Body and cardiac weights of 23 day old male mice Table 7-5 Body and cardiac weights of 27 day old male mice xiii
15 Table 7-6 Body and cardiac weights of 34 day old male mice Table 7-7 Body and cardiac weights of 40 day old male mice Table 7-8 Body and cardiac weights of 90 day old male mice Table 7-9 Body and cardiac weights of 180 day old male mice Table 7-10 Body and cardiac weights of 330 day old male mice Table 7-11 Skeletal muscle morphometry of 14 day old male mice Table 7-12 Skeletal muscle morphometry of 19 day old male mice Table 7-13 Skeletal muscle morphometry of 21 day old male mice Table 7-14 Skeletal muscle morphometry of 23 day old male mice Table 7-15 Skeletal muscle morphometry of 27 day old male mice Table 7-16 Skeletal muscle morphometry of 34 day old male mice Table 7-17 Skeletal muscle morphometry of 40 day old male mice Table 7-18 Skeletal muscle morphometry of 90 day old male mice Table 7-19 Skeletal muscle morphometry of 180 day old male mice Table 7-20 Skeletal muscle morphometry of 330 day old male mice xiv
16 LIST OF FIGURES Figure 1-1 Guillaume Benjamin Amand Duchenne de Boulogne and the first observed case of DMD... 2 Figure 1-2 Pathways of X-linked recessive inheritance in DMD... 4 Figure 1-3 Schematic diagram of the dystrophin gene Figure 1-4 Pseudohypertrophy of the calf muscles in DMD... 9 Figure 1-5 Classical Gowers manoeuvre (sign)...11 Figure 1-6 ECG pattern in a nine year old boy with DMD...12 Figure 1-7 Progressive body posture changes in DMD...13 Figure 1-8 Severe scoliosis of the spine in a boy with DMD...14 Figure 1-9 Dystrophin and the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex (DGC)...28 Figure 1-10 Vicious cycle of muscle degeneration in DMD...30 Figure 1-11 C57BL/10ScSn (C57) and X-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) mice...32 Figure 1-12 Human skeletal muscle biopsies of unaffected and DMD affected individuals Figure 1-13 H&E stained sections of DMD affected human skeletal muscles Figure 1-14 H&E stained SOL muscles in a C57 and an mdx mouse Figure 1-15 Vector based therapeutic strategies in DMD...58 Figure 1-16 Oestrogen activation of enos Figure 3-1 Body weights of C57 and mdx mice at varying testosterone doses Figure 3-2 Testes weights of C57 and mdx mice at varying testosterone doses Figure 3-3 Left atrial weights of C57 and mdx mice at varying testosterone doses Figure 3-4 Basal force of contraction of left atria at varying testosterone doses Figure 3-5 Concentration response curves to calcium at varying testosterone doses Figure 3-6 Maximum force of contraction of the LA at varying testosterone doses Figure 4-1 Influence of sex on body weight and heart weight between strains and sexes Figure 4-2 Effects of age on cardiac tissue weights between strains and sexes Figure 4-3 Basal FOC of LA (normalised for LA weight) in mdx and C57 males and females across ages Figure 4-4 Concentration response curves to calcium comparing male and female 90 day old mice Figure 4-5 Concentration response curves to calcium comparing male and female 180 day old mice Figure 4-6 Concentration response curves to calcium comparing male and female mice 330 day old Figure 4-7 Maximum FOC of LA (normalised for LA weight) in male and female mice across ages xv
17 Figure 4-8 EDL skeletal muscle morphometry comparing mouse strains and sexes Figure 4-9 Percentage of CNFs and maximum tetanic forces in EDL muscles at varying ages and between sexes Figure 4-10 EDL cell diameters and maximum tetanic forces at varying ages and between sexes Figure 4-11 SOL skeletal muscle morphometry comparing mouse strains and sexes Figure 4-12 Percentage of CNFs and spo in SOL muscles at varying ages and sexes. 105 Figure 4-13 Cell diameters and spo in SOL muscles at varying ages and between sexes Figure 5-1 Influence of castration on body weight in C57 and mdx mice Figure 5-2 Concentration response curves to calcium in entire and castrated mice Figure 5-3 EDL percentage CNFs and spo for entire and castrated mice Figure 5-4 EDL cell diameter and spo between strains and for entire and castrated mice Figure 5-5 SOL percentage CNFs and spo between strains and for entire and castrated mice Figure 5-6 SOL cell diameters and spo between strains and for entire and castrated mice Figure 6-1 Body weights at varying oestrogen doses Figure 6-2 Testes weights at varying oestrogen doses Figure 6-3 Basal FOC of the LA (normalised for LA weight) at varying oestrogen doses Figure 6-4 Ca 2+ CRCs at varying doses of oestrogen Figure 6-5 Maximum FOC of the LA (normalised for LA weight) at varying oestrogen doses Figure 6-6 EDL percentage of CNFs at varying oestrogen doses Figure 6-7 EDL cell diameter at varying oestrogen doses Figure 6-8 SOL percentage of CNFs at varying oestrogen doses Figure 6-9 SOL cell diameter at varying oestrogen doses Figure 6-10 Pathways of testosterone action and the conversion to oestradiol Figure 7-1 Body weight comparison between C57 and mdx mice at varying ages Figure 7-2 Influence of age on testes weights across varying ages Figure 7-3 Basal FOC of the LA across ages Figure 7-4 Concentration response curves to calcium across varying ages Figure 7-5 Maximum FOC of the LA across ages Figure 7-6 SOL weight between strains across varying ages Figure 7-7 SOL CSA between strains across varying ages xvi
18 Figure 7-8 EDL weight between strains across varying ages Figure 7-9 EDL CSAs between strains across varying ages Figure 7-10 EDL spt across varying ages Figure 7-11 EDL spo across varying ages Figure 7-12 EDL percentage of CNFs and spo across varying ages in male C57 and mdx mice Figure 7-13 EDL cell diameters across varying ages Figure 7-14 SOL spt across varying ages Figure 7-15 SOL spo across varying ages Figure 7-16 SOL percentage of CNFs and spo across varying ages Figure 7-17 SOL cell diameters across varying ages Figure 7-18 Periods of peak skeletal muscle necrosis in the mdx mouse xvii
MODIFICATION OF THE MYOSTATIN AND NITRIC OXIDE SIGNALLING PATHWAYS AS TREATMENTS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND MODIFICATION OF THE MYOSTATIN AND NITRIC OXIDE SIGNALLING PATHWAYS AS TREATMENTS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY A dissertation submitted by Garth Marrett BSc (Hons) For
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND MODIFICATION OF THE MYOSTATIN AND NITRIC OXIDE SIGNALLING PATHWAYS AS TREATMENTS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY A dissertation submitted by Garth Marrett BSc (Hons) For
Muscular Dystrophy. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Growth and DMD Endocrine aspects of care
 Growth and DMD Endocrine aspects of care Meilan Rutter, MB,BCh, FRACP Division of Endocrinology Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center July 2007 Where are we now? Inactive Reactive Proactive CCHMC
Growth and DMD Endocrine aspects of care Meilan Rutter, MB,BCh, FRACP Division of Endocrinology Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center July 2007 Where are we now? Inactive Reactive Proactive CCHMC
A dissertation by. Clare Rachel Watsford
 Young People s Expectations, Preferences and Experiences of Seeking Help from a Youth Mental Health Service and the Effects on Clinical Outcome, Service Use and Future Help-Seeking Intentions A dissertation
Young People s Expectations, Preferences and Experiences of Seeking Help from a Youth Mental Health Service and the Effects on Clinical Outcome, Service Use and Future Help-Seeking Intentions A dissertation
Edasalonexent (CAT-1004) Program
 Edasalonexent (CAT-1004) Program Oral small molecule designed to inhibit NF-κB for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy Joanne M. Donovan, MD, PhD Chief Medical Officer, Catabasis Pharmaceuticals
Edasalonexent (CAT-1004) Program Oral small molecule designed to inhibit NF-κB for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy Joanne M. Donovan, MD, PhD Chief Medical Officer, Catabasis Pharmaceuticals
Gene therapy and genome editing technologies for the study and potential treatment of :
 WORKSHOP ON GENOME EDITING Gene therapy and genome editing technologies for the study and potential treatment of : Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by Dr France Piétri-Rouxel, Institut de Myologie Centre de
WORKSHOP ON GENOME EDITING Gene therapy and genome editing technologies for the study and potential treatment of : Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by Dr France Piétri-Rouxel, Institut de Myologie Centre de
Biology 2100 Human Physiology C. Iltis SLCC March 8, Midterm Examination #2
 Biology 2100 Human Physiology Name: KEY C. Iltis SLCC March 8, 2000 Midterm Examination #2 Multiple Choice Questions (2 POINTS EACH) 1. When glucose levels are above 100 mg/dl, which of the following is
Biology 2100 Human Physiology Name: KEY C. Iltis SLCC March 8, 2000 Midterm Examination #2 Multiple Choice Questions (2 POINTS EACH) 1. When glucose levels are above 100 mg/dl, which of the following is
CARE CONSIDERATIONS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY
 IMPORTANT NEW UPDATE A Summary of the Report of the DMD Care Considerations Working Group Intended for US healthcare professionals only. CARE CONSIDERATIONS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Full article
IMPORTANT NEW UPDATE A Summary of the Report of the DMD Care Considerations Working Group Intended for US healthcare professionals only. CARE CONSIDERATIONS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Full article
ANALYSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF EEG SIGNALS. A Dissertation Submitted by. Siuly. Doctor of Philosophy
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND, AUSTRALIA ANALYSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF EEG SIGNALS A Dissertation Submitted by Siuly For the Award of Doctor of Philosophy July, 2012 Abstract Electroencephalography
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND, AUSTRALIA ANALYSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF EEG SIGNALS A Dissertation Submitted by Siuly For the Award of Doctor of Philosophy July, 2012 Abstract Electroencephalography
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_duchenne_and_becker_muscular_dystrophy
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_duchenne_and_becker_muscular_dystrophy
Leucine and exercise improve skeletal muscle function in the mdx mouse. Kevin Andrew Voelker
 Leucine and exercise improve skeletal muscle function in the mdx mouse Kevin Andrew Voelker Dissertation submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
Leucine and exercise improve skeletal muscle function in the mdx mouse Kevin Andrew Voelker Dissertation submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
Physiology sheet #2. The heart composed of 3 layers that line its lumen and cover it from out side, these layers are :
 Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SPORT AND BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES SPORT AND EXERCISE SCIENCE PATHWAY SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017
 LH14 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SPORT AND BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES SPORT AND EXERCISE SCIENCE PATHWAY SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 INTRODUCTION TO SPORT AND EXERCISE PHYSIOLOGY MODULE NO: SPS4002 Date: Thursday
LH14 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SPORT AND BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES SPORT AND EXERCISE SCIENCE PATHWAY SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 INTRODUCTION TO SPORT AND EXERCISE PHYSIOLOGY MODULE NO: SPS4002 Date: Thursday
1. Differences in function of the 3 muscle types: a) Skeletal Muscle b) Cardiac Muscle c) Smooth Muscle
 Ch 9: Muscle Physiology Objectives: 1. Review 3 muscle types and how they are regulated. 2. Review muscle anatomy. 3. Sliding filament theory of how muscles contract and relax. 4. Energetics of muscle
Ch 9: Muscle Physiology Objectives: 1. Review 3 muscle types and how they are regulated. 2. Review muscle anatomy. 3. Sliding filament theory of how muscles contract and relax. 4. Energetics of muscle
Muscular System Module 3: Contraction and Relaxation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m48498 1 Muscular System Module 3: Contraction and Relaxation * Donna Browne Based on Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
OpenStax-CNX module: m48498 1 Muscular System Module 3: Contraction and Relaxation * Donna Browne Based on Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
Sphingolipids Modulate the Inflammatory Response and Muscle Function in Mdx Mice. Jonathan Adam Doering
 Sphingolipids Modulate the Inflammatory Response and Muscle Function in Mdx Mice Jonathan Adam Doering Thesis to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
Sphingolipids Modulate the Inflammatory Response and Muscle Function in Mdx Mice Jonathan Adam Doering Thesis to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Current Research Strategies and Therapeutic Approaches in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
 Current Research Strategies and Therapeutic Approaches in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy H. Lee Sweeney, Ph.D. Department of Physiology University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine Current Research
Current Research Strategies and Therapeutic Approaches in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy H. Lee Sweeney, Ph.D. Department of Physiology University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine Current Research
Thyroidal Trophic Influence Skeletal Muscle. Myosin >>>CLICK HERE<<<
 Thyroidal Trophic Influence Skeletal Muscle Myosin Even though skeletal muscle by sheer volume alone is the ample, antibody to myosin heavy chains from red Thyroidal trophic influence on skeletal muscle.
Thyroidal Trophic Influence Skeletal Muscle Myosin Even though skeletal muscle by sheer volume alone is the ample, antibody to myosin heavy chains from red Thyroidal trophic influence on skeletal muscle.
Advancing New Treatments for DMD and C. difficile Infection
 Advancing New Treatments for DMD and C. difficile Infection Oppenheimer 25 th Annual Healthcare Conference December 2014 Legal Disclaimer No undertaking, representation, warranty or other assurance is
Advancing New Treatments for DMD and C. difficile Infection Oppenheimer 25 th Annual Healthcare Conference December 2014 Legal Disclaimer No undertaking, representation, warranty or other assurance is
Elise Cook. BForensics (Hons) Forensic Biology and Toxicology. BSc Biomedical Science and Molecular Biology
 Acute and chronic toxicity of methamphetamine exposure in cultured neuronal cells Elise Cook BForensics (Hons) Forensic Biology and Toxicology BSc Biomedical Science and Molecular Biology This thesis is
Acute and chronic toxicity of methamphetamine exposure in cultured neuronal cells Elise Cook BForensics (Hons) Forensic Biology and Toxicology BSc Biomedical Science and Molecular Biology This thesis is
(D) (E) (F) 6. The extrasystolic beat would produce (A) increased pulse pressure because contractility. is increased. increased
 Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Cardiac Care in pa+ents with Duchenne muscular dystrophy
 Cardiac Care in pa+ents with Duchenne muscular dystrophy Linda Cripe, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics The Heart Center.... Why are cardiologists interested in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy?....
Cardiac Care in pa+ents with Duchenne muscular dystrophy Linda Cripe, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics The Heart Center.... Why are cardiologists interested in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy?....
Cardiac Properties MCQ
 Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
Doctor of Philosophy
 Regulation of Gene Expression of the 25-Hydroxyvitamin D la-hydroxylase (CYP27BI) Promoter: Study of A Transgenic Mouse Model Ivanka Hendrix School of Molecular and Biomedical Science The University of
Regulation of Gene Expression of the 25-Hydroxyvitamin D la-hydroxylase (CYP27BI) Promoter: Study of A Transgenic Mouse Model Ivanka Hendrix School of Molecular and Biomedical Science The University of
BMS : An Anti-Myostatin Adnectin Targeting Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
 BMS-986089: An Anti-Myostatin Adnectin Targeting Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Leslie Jacobsen, MD Medical Lead GS Tirucherai, M Ahlijanian, F Luo, C Bechtold and the BMS Anti-Myostatin Team PPMD Connect
BMS-986089: An Anti-Myostatin Adnectin Targeting Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Leslie Jacobsen, MD Medical Lead GS Tirucherai, M Ahlijanian, F Luo, C Bechtold and the BMS Anti-Myostatin Team PPMD Connect
CHAPTER 6 2/9/2016. Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common.
 Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Experimental Models of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Relationship with Cardiovascular Disease
 The Open Cardiovascular Medicine Journal, 2010, 4, 265-277 265 Open Access Experimental Models of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Relationship with Cardiovascular Disease Venus Ameen and Lesley G. Robson
The Open Cardiovascular Medicine Journal, 2010, 4, 265-277 265 Open Access Experimental Models of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Relationship with Cardiovascular Disease Venus Ameen and Lesley G. Robson
Objectives of the lecture:
 Yesterday s lecture was an introduction for the cardiovascular system. Today we will talk about the cardiac muscle physiology because if you know how the cardiac muscle works you will know as a generalization
Yesterday s lecture was an introduction for the cardiovascular system. Today we will talk about the cardiac muscle physiology because if you know how the cardiac muscle works you will know as a generalization
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Septal Defects. How does the heart work?
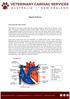 Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
NZQA Expiring unit standard version 2 Page 1 of 5. Demonstrate knowledge of exercise physiology and human anatomy
 Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate knowledge of exercise physiology and human anatomy Level 3 Credits 10 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: explain the nervous system and its functions;
Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate knowledge of exercise physiology and human anatomy Level 3 Credits 10 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: explain the nervous system and its functions;
;~ STEPHEN EDWARD ALWAY, BoSco, MoSco
 THE EFFECTS OF TRAINING ON MUSCLE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION IN ~HE ~ TRICEPS SURAE by ~ ;~ STEPHEN EDWARD ALWAY, BoSco, MoSco A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfillment of
THE EFFECTS OF TRAINING ON MUSCLE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION IN ~HE ~ TRICEPS SURAE by ~ ;~ STEPHEN EDWARD ALWAY, BoSco, MoSco A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfillment of
Chapter 9 Muscle. Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle. Striated muscle
 Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Smooth Muscle. Spindle shaped 1/10 th Skel. Musc. cell width 1/1000s Skel. Musc. cell length Some endomysium (No Peri- or Epi-) Organized into sheets
 Smooth Muscle Spindle shaped 1/10 th Skel. Musc. cell width 1/1000s Skel. Musc. cell length Some endomysium (No Peri- or Epi-) Organized into sheets Typically two outside [longi] inside [circ] Innervation
Smooth Muscle Spindle shaped 1/10 th Skel. Musc. cell width 1/1000s Skel. Musc. cell length Some endomysium (No Peri- or Epi-) Organized into sheets Typically two outside [longi] inside [circ] Innervation
Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Types and structure of muscle cells Structural basis of contraction Triggering muscle contraction Skeletal muscle consists of
Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Types and structure of muscle cells Structural basis of contraction Triggering muscle contraction Skeletal muscle consists of
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES SPORT PATHWAYS WITH FOUNDATION YEAR SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016
 LH8 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES SPORT PATHWAYS WITH FOUNDATION YEAR SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY MODULE NO: SRB3008 Date: Monday
LH8 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES SPORT PATHWAYS WITH FOUNDATION YEAR SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY MODULE NO: SRB3008 Date: Monday
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA (
 Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department
 Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
AGE-RELATED DIFFERENCES IN VERBAL, VISUAL. AND SPATIAL MEMORY: The Same or Different?
 i AGE-RELATED DIFFERENCES IN VERBAL, VISUAL AND SPATIAL MEMORY: The Same or Different? Thesis submitted by Rhonda M Shaw (B.Psych [Hons]) February 1 2007 For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy School of
i AGE-RELATED DIFFERENCES IN VERBAL, VISUAL AND SPATIAL MEMORY: The Same or Different? Thesis submitted by Rhonda M Shaw (B.Psych [Hons]) February 1 2007 For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy School of
Ch 12: Muscles sarcolemma, t-tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibrils, myofilaments, sarcomere...
 Ch 12: Muscles Review micro-anatomy of muscle tissue Terminology examples: sarcolemma, t-tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibrils, myofilaments, sarcomere... SLOs Differentiate levels of muscle structure:
Ch 12: Muscles Review micro-anatomy of muscle tissue Terminology examples: sarcolemma, t-tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibrils, myofilaments, sarcomere... SLOs Differentiate levels of muscle structure:
AN EXPLORATORY STUDY OF LEADER-MEMBER EXCHANGE IN CHINA, AND THE ROLE OF GUANXI IN THE LMX PROCESS
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND AN EXPLORATORY STUDY OF LEADER-MEMBER EXCHANGE IN CHINA, AND THE ROLE OF GUANXI IN THE LMX PROCESS A Dissertation submitted by Gwenda Latham, MBA For the award of Doctor
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND AN EXPLORATORY STUDY OF LEADER-MEMBER EXCHANGE IN CHINA, AND THE ROLE OF GUANXI IN THE LMX PROCESS A Dissertation submitted by Gwenda Latham, MBA For the award of Doctor
Model Answer. M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology)
 Model Answer M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination-2013 Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology) Section A 1. (i) d (ii) b (iii) b (iv) c (v) c (vi) a (vii) c (viii) a (ix) d (x) b Section B Q.2 Answer Hormonal
Model Answer M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination-2013 Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology) Section A 1. (i) d (ii) b (iii) b (iv) c (v) c (vi) a (vii) c (viii) a (ix) d (x) b Section B Q.2 Answer Hormonal
-- Edasalonexent Substantially Slowed Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Disease Progression through 36 Weeks --
 Catabasis Pharmaceuticals Reports Positive Results from Open-Label Extension of Phase 2 MoveDMD Trial Evaluating Edasalonexent in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Plans to Initiate Phase 3 Clinical Trial
Catabasis Pharmaceuticals Reports Positive Results from Open-Label Extension of Phase 2 MoveDMD Trial Evaluating Edasalonexent in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Plans to Initiate Phase 3 Clinical Trial
Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3
 Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is a one semester laboratory course, in which the structure and function of
Montgomery County Community College BIO 130 Introductory Anatomy and Physiology 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course is a one semester laboratory course, in which the structure and function of
Capricor Therapeutics. NASDAQ: CAPR October 2017
 Capricor Therapeutics NASDAQ: CAPR October 2017 Forward-Looking Statements Statements in this presentation regarding the efficacy, safety, and intended utilization of Capricor's product candidates; the
Capricor Therapeutics NASDAQ: CAPR October 2017 Forward-Looking Statements Statements in this presentation regarding the efficacy, safety, and intended utilization of Capricor's product candidates; the
A scientist studied the behaviour of winged termites. He divided these termites into three groups.
 2 Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 1 Termites are insects. Some species live in colonies in the soil. Although most termites are wingless, winged termites are sometimes produced. The winged
2 Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 1 Termites are insects. Some species live in colonies in the soil. Although most termites are wingless, winged termites are sometimes produced. The winged
Outline. Bio 105: Muscular System. Muscular System. Types of Muscles. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle 4/6/2016
 Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
BETWIXT AND IN-BETWEEN STATE AND COMMUNITY:
 BETWIXT AND IN-BETWEEN STATE AND COMMUNITY: Illness identities and the distinct expertise of a health-orientated communitybased organisation within the contemporary socio-political environment Paul Leslie
BETWIXT AND IN-BETWEEN STATE AND COMMUNITY: Illness identities and the distinct expertise of a health-orientated communitybased organisation within the contemporary socio-political environment Paul Leslie
Cardiac Health in Duchenne: What we are Learning from Cardiac MRI
 Cardiac Health in Duchenne: What we are Learning from Cardiac MRI 24 th Annual Duchenne Connect Conference Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy Scottsdale, AZ June 29, 2018 Kan N. Hor, MD Director of Cardiac
Cardiac Health in Duchenne: What we are Learning from Cardiac MRI 24 th Annual Duchenne Connect Conference Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy Scottsdale, AZ June 29, 2018 Kan N. Hor, MD Director of Cardiac
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and
 Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Edasalonexent (CAT-1004)
 Edasalonexent (CAT-1004) An NF-κB Inhibitor in Development for Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Joanne M. Donovan, MD PhD Chief Medical Officer 17 February 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements This
Edasalonexent (CAT-1004) An NF-κB Inhibitor in Development for Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Joanne M. Donovan, MD PhD Chief Medical Officer 17 February 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements This
Vascular reactivity in sepsis and platelet dysfunction in septic shock
 Vascular reactivity in sepsis and platelet dysfunction in septic shock Benjamin Reddi Discipline of Physiology School of Medical Science University of Adelaide Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor
Vascular reactivity in sepsis and platelet dysfunction in septic shock Benjamin Reddi Discipline of Physiology School of Medical Science University of Adelaide Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor
Investigating the Potential Effectiveness of Two Therapeutic Targets, Utrophin and HSP70, in the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
 Investigating the Potential Effectiveness of Two Therapeutic Targets, Utrophin and HSP70, in the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Daniel Spensieri A Thesis Proposal in The Department of Exercise
Investigating the Potential Effectiveness of Two Therapeutic Targets, Utrophin and HSP70, in the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Daniel Spensieri A Thesis Proposal in The Department of Exercise
Skeletal Muscle. Connective tissue: Binding, support and insulation. Blood vessels
 Chapter 12 Muscle Physiology Outline o Skeletal Muscle Structure o The mechanism of Force Generation in Muscle o The mechanics of Skeletal Muscle Contraction o Skeletal Muscle Metabolism o Control of Skeletal
Chapter 12 Muscle Physiology Outline o Skeletal Muscle Structure o The mechanism of Force Generation in Muscle o The mechanics of Skeletal Muscle Contraction o Skeletal Muscle Metabolism o Control of Skeletal
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Supplemental Figure I
 Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE
 HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
THE EFFECT OF THE HOMOEOPATHIC SIMILIMUM ON SIDE EFFECTS OF CHEMOTHERAPY IN BREAST CANCER PATIENTS
 THE EFFECT OF THE HOMOEOPATHIC SIMILIMUM ON SIDE EFFECTS OF CHEMOTHERAPY IN BREAST CANCER PATIENTS A Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Johannesburg, in partial fulfillment
THE EFFECT OF THE HOMOEOPATHIC SIMILIMUM ON SIDE EFFECTS OF CHEMOTHERAPY IN BREAST CANCER PATIENTS A Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Johannesburg, in partial fulfillment
DEPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH CANCER RECEIVING ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND DEPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH CANCER RECEIVING ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY A Dissertation submitted by Kathryn Beyer, Bachelor of Nursing CQU For the award of Masters of Health
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN QUEENSLAND DEPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH CANCER RECEIVING ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY A Dissertation submitted by Kathryn Beyer, Bachelor of Nursing CQU For the award of Masters of Health
A biopsychosocial model of diabetes self-management: Mediators and moderators Karen Glaister
 A biopsychosocial model of diabetes self-management: Mediators and moderators by Karen Glaister This thesis is presented for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy at Murdoch University, 2010 i Declaration
A biopsychosocial model of diabetes self-management: Mediators and moderators by Karen Glaister This thesis is presented for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy at Murdoch University, 2010 i Declaration
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *6170897587* BIOLOGY 9700/22 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions October/November 2018 1 hour 15 minutes
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *6170897587* BIOLOGY 9700/22 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions October/November 2018 1 hour 15 minutes
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. The Muscular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Developing an instrument to measure informed consent comprehension in non-cognitively impaired adults
 University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2009 Developing an instrument to measure informed consent comprehension
University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2009 Developing an instrument to measure informed consent comprehension
MUSCLE METABOLISM. Honors Anatomy & Physiology
 MUSCLE METABOLISM Honors Anatomy & Physiology ROLE OF ATP ATP binds to myosin heads and upon hydrolysis into ADP and Pi, transfers its energy to the cross bridge, energizing it. ATP is responsible for
MUSCLE METABOLISM Honors Anatomy & Physiology ROLE OF ATP ATP binds to myosin heads and upon hydrolysis into ADP and Pi, transfers its energy to the cross bridge, energizing it. ATP is responsible for
Chapter 10! Chapter 10, Part 2 Muscle. Muscle Tissue - Part 2! Pages !
 ! Chapter 10, Part 2 Muscle Chapter 10! Muscle Tissue - Part 2! Pages 308-324! SECTION 10-5! Sarcomere shortening and muscle fiber stimulation produce tension! 2! Tension Production - Muscle FIBER! All-or-none
! Chapter 10, Part 2 Muscle Chapter 10! Muscle Tissue - Part 2! Pages 308-324! SECTION 10-5! Sarcomere shortening and muscle fiber stimulation produce tension! 2! Tension Production - Muscle FIBER! All-or-none
Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM II NAME, Section (circle): am 21 October Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes.
 Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM II NAME, Section (circle): am 21 October 2003. Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes. pm True or False (write true or false ; 10 points total; 1 point each) 1. Calsequestrin
Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM II NAME, Section (circle): am 21 October 2003. Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes. pm True or False (write true or false ; 10 points total; 1 point each) 1. Calsequestrin
Index. Bacterial infection of joint, immobilization
 Index ADP (Adenosine diphosphate), 65--Q6 Ambulation, early or postoperative, 8 Anemia, pressure sore formation in, 113-114 Antagonist muscles, 72 Arteriovenous shunting, bed rest and, 27-28 ATP (Adenosine
Index ADP (Adenosine diphosphate), 65--Q6 Ambulation, early or postoperative, 8 Anemia, pressure sore formation in, 113-114 Antagonist muscles, 72 Arteriovenous shunting, bed rest and, 27-28 ATP (Adenosine
C H A R A C T E R I Z A T I O N O F T H E N O V E L D O M A I N W I T H N O N A M E G E N E I N C O L O N C A N C E R
 C H A R A C T E R I Z A T I O N O F T H E N O V E L D O M A I N W I T H N O N A M E G E N E I N C O L O N C A N C E R Charleen Rupnarain A dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Science, University of
C H A R A C T E R I Z A T I O N O F T H E N O V E L D O M A I N W I T H N O N A M E G E N E I N C O L O N C A N C E R Charleen Rupnarain A dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Science, University of
COURSE OUTLINE Pathophysiology
 Butler Community College Health, Education, and Public Services Division Denise LaKous Revised Spring 2014 Implemented Fall 2015 Textbook Update Fall 2015 COURSE OUTLINE Pathophysiology Course Description
Butler Community College Health, Education, and Public Services Division Denise LaKous Revised Spring 2014 Implemented Fall 2015 Textbook Update Fall 2015 COURSE OUTLINE Pathophysiology Course Description
How does Exercise Work at the Cellular/Molecular Level
 How does Exercise Work at the Cellular/Molecular Level Volker Adams, PhD ESC, Paris 28. Aug. 211 UNIVERSITÄT LEIPZIG H E R Z Z E N T R U M Nothing to disclose Survival Exercise Training in Patients With
How does Exercise Work at the Cellular/Molecular Level Volker Adams, PhD ESC, Paris 28. Aug. 211 UNIVERSITÄT LEIPZIG H E R Z Z E N T R U M Nothing to disclose Survival Exercise Training in Patients With
Lai et al 2008 JCI RG-Revision 2
 Lai et al 2008 JCI 36612-RG-Revision 2 Suppmentary Table 1. Epitope specific dystrophin antibodies Name Epitope Dilution Source Dys-3* Hinge 1 1:20 Novocastra Dys-1 Repeats 6-8 1:100 Novocastra Mandys8
Lai et al 2008 JCI 36612-RG-Revision 2 Suppmentary Table 1. Epitope specific dystrophin antibodies Name Epitope Dilution Source Dys-3* Hinge 1 1:20 Novocastra Dys-1 Repeats 6-8 1:100 Novocastra Mandys8
Bio Factsheet April 2000 Number 66
 April Number 66 The Physiology of Exercise This factsheet summarises the aspects of exercise physiology that relate to skeletal muscles on current syllabuses. The student should have a basic knowledge
April Number 66 The Physiology of Exercise This factsheet summarises the aspects of exercise physiology that relate to skeletal muscles on current syllabuses. The student should have a basic knowledge
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
The Efficacy of Phosphorus 6CH in treating Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
 The Efficacy of Phosphorus 6CH in treating Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder A research dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Johannesburg, as partial fulfilment
The Efficacy of Phosphorus 6CH in treating Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder A research dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Johannesburg, as partial fulfilment
Warm Up! Test review (already! ;))
 Warm Up! Test review (already! ;)) Write a question you might find on the Unit 5 test next week! (Multiple choice, matching, fill in, or short answer!) - challenge yourself and be ready to share!!! PowerPoint
Warm Up! Test review (already! ;)) Write a question you might find on the Unit 5 test next week! (Multiple choice, matching, fill in, or short answer!) - challenge yourself and be ready to share!!! PowerPoint
About This Chapter. Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Pearson Education, Inc.
 About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
Declaration of conflict of interest. I have nothing to disclose.
 Declaration of conflict of interest I have nothing to disclose. Left Bundle branch block in HF: DO GENETICS MATTER? Silvia Giuliana Priori Cardiovascular Genetics, Langone Medical Center, New York University
Declaration of conflict of interest I have nothing to disclose. Left Bundle branch block in HF: DO GENETICS MATTER? Silvia Giuliana Priori Cardiovascular Genetics, Langone Medical Center, New York University
Skeletal Muscle Contraction 4/11/2018 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction 4/11/2018 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Skeletal Muscle Fiber About 40 per cent of the body is skeletal muscle, and 10 per cent is smooth and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscles are composed
Skeletal Muscle Contraction 4/11/2018 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Skeletal Muscle Fiber About 40 per cent of the body is skeletal muscle, and 10 per cent is smooth and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscles are composed
QUESTIONSHEET 1. tissues. (a) Suggest two factors which could be responsible for the shift of the curve from A to B.
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 The figure shows the oxygen saturation curves for haemoglobin under different conditions. Curve A represents normal resting conditions. % oxygen saturation of haemoglobin 100 A B 0 0 tissues
QUESTIONSHEET 1 The figure shows the oxygen saturation curves for haemoglobin under different conditions. Curve A represents normal resting conditions. % oxygen saturation of haemoglobin 100 A B 0 0 tissues
Human Biology HBIO4. (JUN14HBIO401) WMP/Jun14/HBIO4/E7w. General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2014
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Human Biology Unit 4 Friday 13 June 2014 For this paper you must have: l a ruler with millimetre
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Human Biology Unit 4 Friday 13 June 2014 For this paper you must have: l a ruler with millimetre
Environmental Education In The Workplace: vehicle trips by commuters into the Perth CBD. Catherine M. Baudains BSc. Dip Ed. Hons.
 Environmental Education In The Workplace: Inducing voluntary transport behaviour change to decrease single occupant vehicle trips by commuters into the Perth CBD. Catherine M. Baudains BSc. Dip Ed. Hons.
Environmental Education In The Workplace: Inducing voluntary transport behaviour change to decrease single occupant vehicle trips by commuters into the Perth CBD. Catherine M. Baudains BSc. Dip Ed. Hons.
Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the Central Nervous System Ischemic Response. 2. Describe chemical sensitivities of arterial and cardiopulmonary chemoreceptors,
Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the Central Nervous System Ischemic Response. 2. Describe chemical sensitivities of arterial and cardiopulmonary chemoreceptors,
Muscle Tissue- 3 Types
 AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
MUSCULAR SYSTEM CHAPTER 09 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 09 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Part 2 of 2 Dr. Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy
1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 09 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Part 2 of 2 Dr. Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy
The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
AN EVALUATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR RISK IN EARLY BEREAVEMENT
 AN EVALUATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR RISK IN EARLY BEREAVEMENT THOMAS BUCKLEY, RN, BSc (Honours), MN A thesis submitted in accordance with the total requirements for admission to the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
AN EVALUATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR RISK IN EARLY BEREAVEMENT THOMAS BUCKLEY, RN, BSc (Honours), MN A thesis submitted in accordance with the total requirements for admission to the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
The Effect of a Chiropractic Adjustment on Sensorineural. Hearing Loss
 The Effect of a Chiropractic Adjustment on Sensorineural Hearing Loss A dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Johannesburg, In partial fulfilment of the requirements for
The Effect of a Chiropractic Adjustment on Sensorineural Hearing Loss A dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Johannesburg, In partial fulfilment of the requirements for
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Highly Specialised Technology Evaluation
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Highly Specialised Technology Evaluation Drisapersen for treating Duchenne muscular Draft scope (pre-referral) Draft remit/evaluation objective
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Highly Specialised Technology Evaluation Drisapersen for treating Duchenne muscular Draft scope (pre-referral) Draft remit/evaluation objective
DMD STANDARDS OF CARE
 DMD STANDARDS OF CARE PPMD 2019 END DUCHENNE TOUR Russell Butterfield MD, PhD Director, Muscular Dystrophy Clinics Associate Professor University of Utah, School of Medicine February 2, 2019 DISCLOSURES
DMD STANDARDS OF CARE PPMD 2019 END DUCHENNE TOUR Russell Butterfield MD, PhD Director, Muscular Dystrophy Clinics Associate Professor University of Utah, School of Medicine February 2, 2019 DISCLOSURES
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Honors Muscular System Notes CHAPTER 8
 Honors Muscular System Notes CHAPTER 8 I. Types of Muscle Tissue Fill in the chart with the correct information (p.162) Type of muscle Location Characteristics Control Action 1. 2. 3. II. The Muscular
Honors Muscular System Notes CHAPTER 8 I. Types of Muscle Tissue Fill in the chart with the correct information (p.162) Type of muscle Location Characteristics Control Action 1. 2. 3. II. The Muscular
In the name of GOD. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension
 In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
Projects related to nutrition and DMD Duchenne Parent Project Netherlands 2018
 Projects related to nutrition and DMD Duchenne Parent Project Netherlands 2018 1. Dominic Wells, Royal College London, UK. Dietary manipulation for the amelioration of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 90.142
Projects related to nutrition and DMD Duchenne Parent Project Netherlands 2018 1. Dominic Wells, Royal College London, UK. Dietary manipulation for the amelioration of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 90.142
Muscle Contraction and Relaxation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m60011 1 Muscle Contraction and Relaxation * Steven Telleen Based on Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the
OpenStax-CNX module: m60011 1 Muscle Contraction and Relaxation * Steven Telleen Based on Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the
BIPN 100 F15 (Kristan) Human Physiology Lecture 10. Smooth muscle p. 1
 BIPN 100 F15 (Kristan) Human Physiology Lecture 10. Smooth muscle p. 1 Terms you should understand: smooth muscle, L-type Ca ++ channels, actin, myosin, sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), myosine phosphatase,
BIPN 100 F15 (Kristan) Human Physiology Lecture 10. Smooth muscle p. 1 Terms you should understand: smooth muscle, L-type Ca ++ channels, actin, myosin, sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), myosine phosphatase,
