Clinical features of Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) Panayiotis G. Vlachoyiannopoulos MD Medical School National University of Athens 2005
|
|
|
- Jerome Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical features of Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) Panayiotis G. Vlachoyiannopoulos MD Medical School National University of Athens 2005
2 Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Definition Recurrent arterial and/or venous thrombotic events and/or Pregnancy morbidity plus acl (β2gpi dependent) antibodies and/or Lupus Anticoagulant (LA). Definite diagnosis: 1clinical and 1 laboratory criterion Wilson et al Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:
3 APS: Definitions Detection of thrombosis: With any imaging technique With biopsy (fibrin microthrombi). Definition of pregnancy morbidity: One or more of unexplained fetal deaths (10 th week) morphologically normal fetus One or more premature childbirths (preeclampsia or placental insuficiency) Three or more abortions unexplained otherwise Wilson et al Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:
4 APS: The discovery of a new antigen serum Affinity column (CL/PS/Acrylamide) apl Mono S-HR 5/5 Anion exchange column Mc Neil HP et al, PNAS (USA) 1990;87: apl β 2 GPI
5 Anti-cardiolipin (acl) ELISA: What does a positive value mean? acl-β2gpi independent antibodies acl (β2gpi dependent) antibodies Anti-β2 ( CL independent ) antibodies
6 APS/anti-phospholipid antibodies: epidemiology acl in normal individuals: % Anti-β2GPI in normal individuals: 3 13 % SLE: positive for acl: % 1/3 of SLE acl positive will develop APS SLE: positive for LA: % Petri M.:The Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Asherson et al (Eds) Elsevier 2002; 11-20
7 APS: alone or in association with underlying conditions. Underlying condition No (%) Primary antiphospholipid syndrome 531 (53) Systemic lupus erythematosus 362 (36) Lupus-like syndrome 50 (5) Primary Sjogren s syndrome 22 (2) Rheumatoid arthritis 18 (2) Systemic sclerosis 7 (0.7) Systemic vasculitis 7 (0.7) Dermatomyositis 5 (0.5) Cervera R et al Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46:
8 Clinical features at disease onset in 1000 patients with antiphospholipid syndrome Manifestations Deep vein thrombosis Thrombocytopenia (<100,000/ μ L) Livedo reticularis Stroke Superficial thrombophlebitis Pulmonary embolism Fetal loss Transient ischemic attack Hemolytic anemia Skin ulcers Epilepsy Pseudovasculitic skin lesions Myocardial infarction Amavrosis fugax Digital gangrene No (%) 317 (32) 219 (22) 204 (20) 131 (13) 91 (9) 90 (9) 83 (8) 70 (7) 66 (7) 39 (4) 34 (3) 26 (3) 28 (3) 28 (3) 19 (2) Cervera R et al Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46:
9 APS: Differential Diagnosis Inherited: Defective inhibition of coagulation factors Factor V Leiden Antithrombin III deficiency Protein C/S deficiency Impaired clot lysis Dysfibrinogemia Plasminogen deficiency tpa deficiency PAI-1 excess Uncertain Homocystinouria Aquired: Diseases or Syndromes SLE Malignancy Myeloproliferative disorder TTP Estrogens Hyperlipidemia Diabetes mellitus Hyperviscocity Nephrotic syndrome PNH Physiologic states R.I.Handin, Harrison s
10 Clinical features of venous Deep vein thrombosis 39% Pulmonary embolism..14% Superficial vein thrombosis 12% Pulmonary hypertention..2% Budd-Chiari syndrome.1% Retinal vein thrombosis...1% Cerebral venous thrombosis...1% thrombosis (1) Cervera R et al Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46:
11 Clinical features of venous thrombosis (2) Budd- Chiari syndrome Striking hepatomegaly Abdominal pain Ascites Mild jaundice Consider also: Polycythemia roubra vera PNH Myelofibrosis Trauma, infection Other coagulopathies
12 Clinical features of venous thrombosis (3) Hemorrhage and congestion in all centrilobular areas Loss of virtually all zone3 hepatocytes Sublobular vein filled with organizing thrombotic material Budd-Chiari syndrome, Figures by F.A.Mitros MD Striking dissection of red blood cells into the space of Disse. Loss of hepatocytes
13 Clinical features of venous thrombosis (4) Cerebral venous thrombosis: Headaches Nausea Vomiting Seizures (possibly) Papilleedema Forehead skin and eyelid edema, proptosis Cranial nerve III, IV, VI compromise Focal neurologic symptoms M.R.Patel MD in e-medicine july MR venography: absent flow in the ridht transverse sinous, sigmoid sinous and internal jugular vein Hypodense left temporal lobe venous infarct
14 Clinical features of venous thrombosis (5) Pulmonary emboli
15 Clinical features of arterial thrombosis (1) Migraine..20% Stroke...19% Cardiac valve thickening/dysfunction 12% Transient ischemic attack 11% Myocardial infarction...6% Arterial thrombosis in the legs...4% Arterial thrombosis in the arms..3% Angina...3% Vegetations...3% Avascular necrosis of the bone..2% Renal artery stenosis and glomerular lesions.2% Infarcts of spleen, pangreas, adrenals,peritoneum..2% Cervera R et al Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46:
16 Clinical features of arterial Libman-Sacks endocarditis thrombosis (2) Vegetations in U/S, autopsy and histopathologic examination Linear splinter hemorrhages
17 Clinical features of arterial thrombosis (2) Brain microinfarcts Peripheral arterial thrombosis
18 APS: Arterial are followed by arterial and venous by venous thrombotic events. Results from a cohort of 85 patients (Tektonidou et al QJ Med 2000;93:523) Clinical manifestations Venous thrombosis Presenting events 18 (20.7) Subsequent events 50 (32.7) Arterial thrombosis Recurrent abortions Autoimmune hemolytic anemia Central venous system events 4 (4.6) 16 (18.4) 12 (13.8) 15 (17.3) 8 (5.3) 15 (9.8) 19 (12.4) 43 (28.1)
19 APS: Neurologic manifestations Migraine 202 (20.2) Stroke 198 (19.8) Transient ischemic attack 111 (11.1) Epilepsy 70 (7.0) Multiinfarct dementia 25 (2.5) Chorea 13 (1.3) Acute encephalopathy 11 (1.1) Transient amnesia 7 (0.7) Cerebral venous thrombosis 7 (0.7) Cerebellar ataxia 7 (0.7) Transverse myelopathy 4 (0.4) Hemiballismus 3 (0.3) Cervera R et al Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46:
20 APS: Pulmonary manifestations Pulmonary embolism 141 (14.1) Pulmonary hypertension 22 (2.2) Pulmonary microthrombosis 15 (1.5) Fibrosing alveolitis 12 (1.2) Other (adult respiratory distress syndrome, 7 (0.7) pulmonary hemorrhage, pulmonary artery thrombosis) Cervera R et al Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46:
21 APS: Cardiac manifestations Valve thickening/dysfunction 116 (11.6) Myocardial infarction 55 (5.5) Angina 27 (2.7) Myocardiopathy 29 (2.9) Vegetations 27 (2.7) Coronary bypass rethrombosis 11 (1.1) Intracardiac thrombus 4 (0.4) Cervera R et al Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46:
22 APS:Obstetric & Fetal manifestations Obstetric manifestations (n 590 pregnant women) Preeclampsia 56 (9.5) Eclampsia 26 (4.4) Abruptio placentae 12 (2.0) Postpartum cardiopulmonary syndrome 3 (0.5) Fetal manifestations (n 1,580 pregnancies) Early fetal loss (10 weeks) 560 (35.4) Late fetal loss (10 weeks) 267 (16.9) Live birth 753 (47.7) Premature birth, no. premature/no. live births 80/753 Cervera R et al Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46:
23 Livedo reticularis: a sign of APS (24% of the patients, Cervera R et al A&R, 2002;86:1019)
24 Catastrophic APS: Definition Life threatening form of APS characterized by high titers of anti-phospholipid antibodies accompanied by concurrent insufficiency of at least two major organs due to difuse thromboembolic occlusion of small vessels. Asherson RA, J Rheum 1992;19:
25 Catastrophic APS: Lessons from a case Male 36 year old in : Tibia ulcers 1994:Seizures Proteinuria, Anemia, ESR Brain MRI negative ANA 1/320 fine speckled Anti-DNA negative acl/igg 922 units (normal<100) LA positive
26 Catastrophic APS: Lessons from a 12/7/94 Kidney biopsy: case 4out of 9 glomeruli were fibrotic. Rare inflammatory infiltrates of the interstitial space Tubular atrophy Fibrous intimal hyperplasia of the vessels within the kidney Presolon. Warfarin, anti-epileptics Azathiprine Divorce, poor compliance with therapy. Vomiting with azathioprine discontinued.
27 Catastrophic APS: Lessons from a case 9/1997 Tibia ulcer Coombs positive hemolytic anemia Pulmonary edema Pulmonary hypertention Loss of vision developed suddenly High 24 hour urine protein Cyclophosphamide IV pulses, Medrol,antiepileptics, warfarin
28 Catastrophic APS: Lessons from a case 1/1998: warfarin was discontinued with the responsibility of the patient. Paresis of the left arm Brain MRI: infarct in the right internal capsule Multiple pulmonary emboli Deterioration of renal function Heart failure
29 Catastrophic APS: Lessons from a case 7/1998: Pulmonary edema Renal failure dialysis Fever New brain infarcts Liver failure ( INR=20 ) Pulmonary hypertention (>100 mmhg ) Plasmapheresis/ Corticosteroids IV/ transfusions. ICU: Ventricular fibrillation Death
30 Catastrophic APS: Lessons from a case Always high titer of acl antibodies Usually LA positive Triggering factor (for instance withdrawal of warfarin) Intensive immunotherapy does not seem to help In general the results of therapy are very poor.
31 Catastrophic APS Ischemic infarct of the occipital lobe in a patient with SLE,after the course of typhoid fever. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis followed this event. Hayem G et al Arthritis & rheum, 1999;42:
32 Catastrophic APS: multiple ischemic infarcts of the bone marrow Iscemic necrosis of the bone marrow is usually associated with the HELLP syndrome (Hemolysis Elevated liver enzymes, Low platelets ). Hayem G et al Arthritis & rheum, 1999;42:
33 Catastrophic APS: Acute pulmonary failure Transesophageal U/S indicating vegetations of the mitral valve Widermann et al, J Int Medicine 2000;247:723
34 Catastrophic APS: Acute pulmonary failure ARDS Widermann et al, J Int Medicine 2000;247:723
35 Catastrophic APS: Acute respiratory failure ARDS Widermann et al, J Int Medicine 2000;247:723
36 Catastrophic APS: Acute respiratory failure ARDS in remission after instituting plasmapheresis and cyclophosphamide therapy Widermann et al, J Int Medicine 2000;247:723
37 Preliminary criteria for the classification of Catastrophic APS 1. Evidence of involvement of three or more organ systems /tissues 2. Development of manifestations simultaneously or in less than one week. 3. Confirmation by histopathology of small vessel occlusion at least in one organ or tissue. 4. Laboratory confirmation of the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies (LA and/or acl) Definite CAPS: all four criteria Probable CAPS: involvement of 2 organs/tissues or criteria1,2,4 or 1,3,4 Asherson RA et al, Lupus 2003;12: 530-4
38 Catastrophic APS: Demographic and epidemiological characteristics Male.30% Female.70% Mean age (years), (+/- SD) 38 (14) Primary APS.48% SLE.40% Lupus like syndrome.5% Others..7% Cervera R et al, Ann Rheum Dis 2005; 64:
39 Precipitating factors of the catastrophic APS Infections 20% Surgical procedures.14% Neoplasms 9% Anticoagulation withdrawal 7% Obstetric complications..5% Lupus flaires 4% Oral contrceptives..3% Cervera R et al, Ann Rheum Dis 2005; 64:
40 Renal manifestations of APS: A diagnostic and therapeutic challenge Problems in studying APS Nephropathy: Renal involvement in primary APS (PAPS) occurs rarely Renal involvement in secondary APS can be attributed to the underlying disease, mainly SLE The clinical characteristics of APS nephropathy represent a continuum from PAPS to SLE
41 FREQUENCY OF RENAL MANIFESTATIONS OF PATIENTS WITH PRIMARY ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME (PAPS) Retrospective evaluation of 16 patients with PAPS & renal manifestations Clinical Manifestations associated with kidney pathology Systemic Hypertension.15 (93) Renal Insuficiency 14 (87) Proteinuria (0,2 to 7 g/d) 12 (75) Haematuria. 9 (56) Microangiopathic anemia.1 ( 6 ) Nephrotic Syndrome. 1 ( 6 ) D. Nochy et al, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol, 1999;10:
42 RENAL MANIFESTATIONS OF APS: THE SPECTRUM OF RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGIC LESIONS A. VASCULAR LESIONS 1. Arteriosclerosis: 75% of biopsies in PAPS Nephropathy Definition : Fibrous intimal thickening with luminal reduction in the arcuate and interlobular arteries, associated with arterial hyaline and arteriosclerosis. Cellular proliferation of the fibrous intima and irregular contours of the markedly retracted lumen. (Masson s trichrome stain) D. Nochy et al, J. Ann. Soc. Nephrol,1999;10:
43 RENAL MANIFESTATIONS OF APS: THE SPECTRUM OF RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGIC LESIONS Focal Cellular FIH (Masson s trichrome ) FIH of an interlobular artery (clastic- van Gieson stained) Concentic Cellular FIH (Silvar Methenamine stained).. Tektonidou et al A&R 2004; 50:2569 A. VASCULAR LESIONS 2. Fibrous Intimal Hyperplasia (FIH) 75% of biopsies of PAPS Nephropathy Definition: The interlobular arteries and their branches are tortuous, with their intima thickened by an intense thyofibroblastic intimal cellular proliferation D. Nochy et al, J. Ann. Soc. Nephrol,1999;10:507
44 RENAL MANIFESTATIONS OF APS: THE SPECTRUM OF RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGIC LESIONS Definition: Fibrous intimal projections or cushions bulging into the lumen. The cells of the cellular proliferation of the intima are positive for alpha- and gammasmooth muscle actin (antihuman muscleactin antibody HHF35). D. Nochy et al, J. Ann. Soc. Nephrol,1999;10:
45 RENAL MANIFESTATIONS OF APS: THE SPECTRUM OF RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGIC LESIONS A. VASCULAR LESIONS 3. Arterial and arteriolar fibrous and fibrocellular occlusions (68% of biopsies of APS nephropathy) Definition: occlusions of the interlobular arteries by fibrous material. Masson s trichrome stain Nochy et al 1999 Silver methenamine Tektonidou et al 2004
46 RENAL MANIFESTATIONS OF APS: THE SPECTRUM OF RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGIC LESIONS A. VASCULAR LESIONS 4. Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) (31% of biopsies ) Definition: Presence of fibrin thrombi in arterials and glomeruli. Co-occurs with FIH Commonly affected: preglomerular arterioles, small interlobular arteries, glomerular capillaries. Nochy et al
47 RENAL MANIFESTATIONS OF APS: THE SPECTRUM OF RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGIC LESIONS B. OTHER LESIONS: 1. Focal Cortical Atrophy (FCA) (62% of biopsies) Definition: Subcapsular lesions as foci or triangles Dense interstitial fibrosis, ischemic wrinkled glomeruli, massive tubular atrophy.
48 Renal involvement in acl positive patients with and without APS: Clinical and histopathologic characteristics PAPS APS\SLE SLE Inc.SLE Characteristics ( n=78) ( n=40) (n=82) (n-=48) p Male n,(%) 19(24) 8(20) 4(5) 7(15) NS Hypertension,n(%) 44(56) 26(64) 31(38) 0(0) <0.01 Criteria for Renal biopsy n,(%) 8(10) 24(60) 43(52) 4(8) WHO-I or-ii n,(%) 1(12) 3(12) 6(14) 2(50) NS WHO-III or-iv n, (%) 1(12) 11(46) 26(60) 2(50) NS WHO V n, (%) 2(24) 6(25) 7(16) 0(0) NS Thrombi n, (%) 1(12) 6(25) 9(21) 0(0) NS FIH n, (%) 3(37) 15(62) 11(26) 0(0) <0.01 FCA n, (%) 1(12) 4(17) 5(12) 0(0) NS Vlachoyiannopoulos et al Nephrol Dial Transplant 2001;16:56-62
49 Antiphospholipid syndrome nephropathy in patients with SLE and antiphospholipid antibodies Tektonidou et al, Arthritis & Rheum 2004;50: APS nephropathy (APSN) was arbitrarily chosen as the presence of at least one of the following: Acute 1. Thrombotic microangiopathy Chronic 2. Fibrous intimal hyperplasia 3. Organized thrombi 4. Fibrous arterial/arteriolar occlusions 5. Focal cortical atrophy
50 Antiphospholipid syndrome nephropathy in patients with SLE and antiphospholipid antibodies Tektonidou et al, Arthritis & Rheum 2004;50: SLE/APS n=18 SLE/aPL(+) / nonaps n=63 SLE/aPL(-) / nonaps n=70 APSN n=12 (67%) Non APSN n=6 APSN n=20 (32%?) Non APSN n=43 APSN n=3 (4%) Non APSN n=67
51 Clinical and laboratory associations with APS nephropathy in patients with SLE Patients without APSN n=116 (%) Patients with APSN n=35 (%) Multivariate analysis OR (95% CI) p APS 6 (5.2) 12 (34.3) Not selected NS LA 4 (3.4) 16 (45.7) ( ) <0.01 acl 51 (44) 30 (85.7) 5.7 ( ) <0.01 Livedo 29 (25) 20 (57.1) Not selected NS Hypertension 42 (36.2) 27 (77.1) 4 ( ) <0.05 Increased serum creatinine 19 (16.3) 17 (48.5) Not selected NS Tektonidou et al Arthritis & Rheum 2004;50:
52 A real case of a patient with APS and premature atherosclerosis Woman 35 y old, secretary Admitted for right hemiparesis Brain MRI: thromboembolic event of the left internal capsule Heart ultrasound negative Carotid doppler: atheroma at the bifurcation of the left carotid artery (90% stenosis) Endarterectomy: atherosclerotic lesion type 6 (atheroma + thrombus) Lipid profile normal Thrombophilia work up: MTHFR, FV Leyden, FII mutations negative acl: IgG 700 u/l, IgM (-) NR u/l aβ2gpi IgG: 1758, IgM (-) NR u/l Lupus anticoagulant positive
53 Atherosclerosis in premenopausal women with antiphospholipid syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus: a controlled study Vlachoyiannopoulos et al Rheumatology 2003;42: premenopausal women with APS Age-matched controls: SLE with/without acl, RA, healthy subjects Outcome: Ultrasonography of carotid and femoral arteries for IMT and atherosclerotic plaques APS pts had more affected vessels than RA and healthy controls but not than SLE pts No evidence that acl or aβ2gpi were associated with the presence of atherosclerotic lesions in the carotid or femoral arteries
54 APS pts had more affected vessels than RA and healthy controls but not than SLE pts
55 Predictors of atherosclerosis in the carotid or femoral arteries
56 APS: Concluding remarks Occurs in 1/3 of SLE patients positive for acl antibodies 50 % of patients have primary APS. Arterial are usually followed by arterial and venous by venous thrombotic events. Wide range of clinical features and outcomes. Precipitating factors for catastrophic APS should be always evaluated. Vascular events contribute to the pathogenesis of APS nephropathy Premature atherosclerosis may be part of the syndrome
Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria
 Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria Farjah H AlGahtani Associate professor,md,mph Leukemia,Lymphoma in adolescent,thromboembolic
Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria Farjah H AlGahtani Associate professor,md,mph Leukemia,Lymphoma in adolescent,thromboembolic
Sindrome da anticorpi antifosfolipidi: clinica e terapia. Vittorio Pengo Clinical Cardiology, Padova, Italy
 Sindrome da anticorpi antifosfolipidi: clinica e terapia Vittorio Pengo Clinical Cardiology, Padova, Italy Revised Classification Criteria for the Antiphospholipid Syndrome J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:295-306
Sindrome da anticorpi antifosfolipidi: clinica e terapia Vittorio Pengo Clinical Cardiology, Padova, Italy Revised Classification Criteria for the Antiphospholipid Syndrome J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:295-306
Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT?
 Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Thrombosis and emboli. Peter Nagy
 Thrombosis and emboli Peter Nagy A thrombus is any solid object developing from the blood in vivo within the vascular system or heart. Thrombosis is hemostasis in the wrong place. Major components, forms:
Thrombosis and emboli Peter Nagy A thrombus is any solid object developing from the blood in vivo within the vascular system or heart. Thrombosis is hemostasis in the wrong place. Major components, forms:
Some renal vascular disorders
 Some renal vascular disorders Introduction Nearly all diseases of the kidney involve the renal blood vessels secondarily We will discuss: -Hypertension (arterionephrosclerosis in benign HTN & hyperplastic
Some renal vascular disorders Introduction Nearly all diseases of the kidney involve the renal blood vessels secondarily We will discuss: -Hypertension (arterionephrosclerosis in benign HTN & hyperplastic
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook
 Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, Oier Ateka-Barrutia, and Munther A. Khamashta Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, MD, PhD Lupus Research Unit The Rayne
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, Oier Ateka-Barrutia, and Munther A. Khamashta Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, MD, PhD Lupus Research Unit The Rayne
CEREBRO VASCULAR ACCIDENTS
 CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
AMPLIADO SÍNDROME ANTIFOSFOLÍPIDO SÍNDROME DE SJÖGREN María José Cuadrado Lozano Clínica Universidad de Navarra-Madrid
 AMPLIADO SÍNDROME ANTIFOSFOLÍPIDO SÍNDROME DE SJÖGREN María José Cuadrado Lozano Clínica Universidad de Navarra-Madrid PLASMABLAST PROLIFERATION IS ASSOCIATED WITH TLR7 POLYMORPHISMS AND UPREGULATION OF
AMPLIADO SÍNDROME ANTIFOSFOLÍPIDO SÍNDROME DE SJÖGREN María José Cuadrado Lozano Clínica Universidad de Navarra-Madrid PLASMABLAST PROLIFERATION IS ASSOCIATED WITH TLR7 POLYMORPHISMS AND UPREGULATION OF
The Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 The Antiphospholipid Syndrome 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Antiphospholipid Syndrome Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (commonly called antiphospholipid syndrome or APS) is an autoimmune disease present mostly
The Antiphospholipid Syndrome 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Antiphospholipid Syndrome Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (commonly called antiphospholipid syndrome or APS) is an autoimmune disease present mostly
Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease
 Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease SØREN JACOBSEN Department Rheumatology, Rigshospitalet Søren Jacobsen Main sponsors: Gigtforeningen Novo Nordisk Fonden Rigshospitalet Disclaimer: Novo
Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease SØREN JACOBSEN Department Rheumatology, Rigshospitalet Søren Jacobsen Main sponsors: Gigtforeningen Novo Nordisk Fonden Rigshospitalet Disclaimer: Novo
Thrombophilia. Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS
 Autoimmune Thrombophilia Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS Saraf@sina.tums.ac.ir Acquired Thrombophilia HIT PNH Cyckle cell Anemia Myeloproliferative lf Diseases Thrombocytosis
Autoimmune Thrombophilia Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS Saraf@sina.tums.ac.ir Acquired Thrombophilia HIT PNH Cyckle cell Anemia Myeloproliferative lf Diseases Thrombocytosis
Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Vascular Ischemic (Occlusive) Diseases: An Overview
 Yonsei Med J 48(6):901-926, 2007 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.6.901 Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Vascular Ischemic (Occlusive) Diseases: An Overview Penka A. Atanassova Department of Neurology, Medical University,
Yonsei Med J 48(6):901-926, 2007 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.6.901 Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Vascular Ischemic (Occlusive) Diseases: An Overview Penka A. Atanassova Department of Neurology, Medical University,
Lung diseases of Vascular Origin. By: Shefaa Qa qqa
 Lung diseases of Vascular Origin By: Shefaa Qa qqa Pulmonary Hypertension Pulmonary hypertension is defined as a mean pulmonary artery pressure greater than or equal to 25 mm Hg at rest. Based on underlying
Lung diseases of Vascular Origin By: Shefaa Qa qqa Pulmonary Hypertension Pulmonary hypertension is defined as a mean pulmonary artery pressure greater than or equal to 25 mm Hg at rest. Based on underlying
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders
 HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
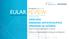
Supplemental Figures and Legends
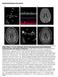 Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
Pathophysiology. Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders
 Pathophysiology Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders ILOs Recall different causes of thrombosis. Explain different types of embolism and their predisposing factors. Differentiate between hemorrhage types.
Pathophysiology Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders ILOs Recall different causes of thrombosis. Explain different types of embolism and their predisposing factors. Differentiate between hemorrhage types.
ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID (HUGHES) SYNDROME
 1 ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID (HUGHES) SYNDROME INTRODUCTION In 1983, Hughes et al describe a syndrome characterized by arterial and venous thrombosis, recurrent foetal wastage, and thrombocytopenia, which were seen
1 ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID (HUGHES) SYNDROME INTRODUCTION In 1983, Hughes et al describe a syndrome characterized by arterial and venous thrombosis, recurrent foetal wastage, and thrombocytopenia, which were seen
Daniel Egan, MD April 13, 2012
 Daniel Egan, MD April 13, 2012 Aug 2006 (at age 15): Acute unprovoked DVT in left common femoral vein Factor V Leiden heterozygous Positive lupus inhibitor Lovenox BID 2 weeks later: increased clot burden,
Daniel Egan, MD April 13, 2012 Aug 2006 (at age 15): Acute unprovoked DVT in left common femoral vein Factor V Leiden heterozygous Positive lupus inhibitor Lovenox BID 2 weeks later: increased clot burden,
Mortality in the Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 8, August 2006, pp 2568 2576 DOI 10.1002/art.22018 2006, American College of Rheumatology Mortality in the Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Causes of Death and
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 8, August 2006, pp 2568 2576 DOI 10.1002/art.22018 2006, American College of Rheumatology Mortality in the Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Causes of Death and
Case report 24 th Summer School of Internal Medicine 2015
 Case report 24 th Summer School of Internal Medicine 2015 Goldmannová D., Horák P., Skácelová M. IIIrd Internal Clinic - endocrinology, diabetology, rheumatology, nephrology University hospital Olomouc,
Case report 24 th Summer School of Internal Medicine 2015 Goldmannová D., Horák P., Skácelová M. IIIrd Internal Clinic - endocrinology, diabetology, rheumatology, nephrology University hospital Olomouc,
Case Report Lower Limb Ischemia: Aortoiliac Thrombosis Related to Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 536971, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/536971 Case Report Lower Limb Ischemia: Aortoiliac Thrombosis Related to Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Case
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 536971, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/536971 Case Report Lower Limb Ischemia: Aortoiliac Thrombosis Related to Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Case
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease
 Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Blood Vessels. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Images in Cardiovascular Medicine
 Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Numerous Small Vegetations Revealing Libman-Sacks Endocarditis in Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Hideo Yamamoto, MD; Tamaki Iwade, MD; Ryuji Nakano, MD; Masahiro
Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Numerous Small Vegetations Revealing Libman-Sacks Endocarditis in Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Hideo Yamamoto, MD; Tamaki Iwade, MD; Ryuji Nakano, MD; Masahiro
Disclosures. Sneddon Syndrome: Untangling the Web. Case Presentation. MRI head w/ and w/o contrast. Further Workup. Further Workup 10/26/2017
 Sneddon Syndrome: Untangling the Web Sadhana Murali, MD, PGY-4 University of Wisconsin-Madison WNS Conference October 27-28, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with any commercial
Sneddon Syndrome: Untangling the Web Sadhana Murali, MD, PGY-4 University of Wisconsin-Madison WNS Conference October 27-28, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with any commercial
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: Management Issues for the Hematologist
 Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: Management Issues for the Hematologist Wisconsin Institute of Discovery Karen Rossi/Bristol-Myers Squibb Morey A. Blinder, MD Washington University, St. Louis, MO March
Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: Management Issues for the Hematologist Wisconsin Institute of Discovery Karen Rossi/Bristol-Myers Squibb Morey A. Blinder, MD Washington University, St. Louis, MO March
Thrombophilia: To test or not to test
 Kenneth Bauer, MD Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Professor of Medicine VA Boston Healthcare System Chief, Hematology Section Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA Director, Thrombosis Clinical
Kenneth Bauer, MD Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Professor of Medicine VA Boston Healthcare System Chief, Hematology Section Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA Director, Thrombosis Clinical
THROMBOSIS. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan
 THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
Histological Features of Antiphospholipid Nephropathy in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histological Features of Antiphospholipid Nephropathy in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Faisal Naseeb 1, Abdulrehman Al Arfaj 1, Afzal Hamdani 1, Hala Kfoury 2, Khalid Parvez
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histological Features of Antiphospholipid Nephropathy in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Faisal Naseeb 1, Abdulrehman Al Arfaj 1, Afzal Hamdani 1, Hala Kfoury 2, Khalid Parvez
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
Asthma J45.20 Mild, uncomplicated J45.21 Mild, with (acute) exacerbation J45.22 Mild, with status asthmaticus
 A Fib & Flutter I48.0 Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation I48.1 Persistent atrial fibrillation I48.2 Chronic atrial fibrillation I48.3 Typical atrial flutter Asthma J45.20 Mild, uncomplicated J45.21 Mild, with
A Fib & Flutter I48.0 Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation I48.1 Persistent atrial fibrillation I48.2 Chronic atrial fibrillation I48.3 Typical atrial flutter Asthma J45.20 Mild, uncomplicated J45.21 Mild, with
Epidemiologia e clinica del tromboembolismo venoso. Maria Ciccone Sezione di Ematologia e Fisiopatologia della Coagulazione
 Epidemiologia e clinica del tromboembolismo venoso Maria Ciccone Sezione di Ematologia e Fisiopatologia della Coagulazione Thrombophilia may present clinically as one or more of several thrombotic manifestations
Epidemiologia e clinica del tromboembolismo venoso Maria Ciccone Sezione di Ematologia e Fisiopatologia della Coagulazione Thrombophilia may present clinically as one or more of several thrombotic manifestations
Blood Vessel Disorders
 Blood Vessel Disorders Objectives: Hyperlipidemia Arterioschlerosis Disorders associated with arteries Disorders associated with veins Hypertension and hypotension Part 1: Diseases Associated with Arterial
Blood Vessel Disorders Objectives: Hyperlipidemia Arterioschlerosis Disorders associated with arteries Disorders associated with veins Hypertension and hypotension Part 1: Diseases Associated with Arterial
THROMBOTIC MICROANGIOPATHY. Jun-Ki Park 7/19/11
 THROMBOTIC MICROANGIOPATHY Jun-Ki Park 7/19/11 TMAs are microvascular occlusive disorders characterized by systemic or intrarenal aggregation of platelets, thrombocytopenia, and mechanical injury to erythrocytes.
THROMBOTIC MICROANGIOPATHY Jun-Ki Park 7/19/11 TMAs are microvascular occlusive disorders characterized by systemic or intrarenal aggregation of platelets, thrombocytopenia, and mechanical injury to erythrocytes.
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal radiotherapy, toxic effects of, 636 637 Acute promyelocytic leukemia, associated with acquired bleeding problems, 614 615 Acute renal
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal radiotherapy, toxic effects of, 636 637 Acute promyelocytic leukemia, associated with acquired bleeding problems, 614 615 Acute renal
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Hemolytic uremic syndrome: Investigations and management
 Hemolytic uremic syndrome: Investigations and management SAWAI Toshihiro M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Shiga University of Medical Science Otsu, JAPAN AGENDA TMA; Thrombotic micro angiopathy STEC-HUS;
Hemolytic uremic syndrome: Investigations and management SAWAI Toshihiro M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Shiga University of Medical Science Otsu, JAPAN AGENDA TMA; Thrombotic micro angiopathy STEC-HUS;
HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS
 HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS Normal fluid homeostasis requires vessel wall integrity as well as maintenance of intravascular pressure and osmolarity within certain physiologic ranges. Increases in vascular volume
HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS Normal fluid homeostasis requires vessel wall integrity as well as maintenance of intravascular pressure and osmolarity within certain physiologic ranges. Increases in vascular volume
DISCLOSURE. Presented by: Merav Sendowski, MD Oregon Health and Science University
 Thrombophilia! DISCLOSURE Presented by: Merav Sendowski, MD Oregon Health and Science University Created by: Thomas Deloughery, MD Oregon Health and Science University Current Relevant Financial Relationship(s)
Thrombophilia! DISCLOSURE Presented by: Merav Sendowski, MD Oregon Health and Science University Created by: Thomas Deloughery, MD Oregon Health and Science University Current Relevant Financial Relationship(s)
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome an overview
 Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome an overview C Sridevi, DNB (Medicine) DNB (Cardiology) MNAMS* P Krishnam Raju, MD DM (Cardiology)* INTRODUCTION Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APLAS) was first described
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome an overview C Sridevi, DNB (Medicine) DNB (Cardiology) MNAMS* P Krishnam Raju, MD DM (Cardiology)* INTRODUCTION Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APLAS) was first described
Situaciones estresantes en el lupus
 Situaciones estresantes en el lupus Munther A Khamashta MD FRCP PhD Director: Lupus Research Unit Barcelona, Noviembre 2008 What is Lupus? Lupus is a neurological disease and sometimes affects other organs
Situaciones estresantes en el lupus Munther A Khamashta MD FRCP PhD Director: Lupus Research Unit Barcelona, Noviembre 2008 What is Lupus? Lupus is a neurological disease and sometimes affects other organs
Comorbidity or medical history Existing diagnoses between 1 January 2007 and 31 December 2011 AF management care AF symptoms Tachycardia
 Supplementary Table S1 International Classification of Disease 10 (ICD-10) codes Comorbidity or medical history Existing diagnoses between 1 January 2007 and 31 December 2011 AF management care I48 AF
Supplementary Table S1 International Classification of Disease 10 (ICD-10) codes Comorbidity or medical history Existing diagnoses between 1 January 2007 and 31 December 2011 AF management care I48 AF
Disturbance of Circulation Hemodynamic Disorder
 Disturbance of Circulation Hemodynamic Disorder 2/17/2017 By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1 Thrombosis Definition: Thrombosis is the formation of solid or semisolid blood clot within
Disturbance of Circulation Hemodynamic Disorder 2/17/2017 By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1 Thrombosis Definition: Thrombosis is the formation of solid or semisolid blood clot within
APPENDIX 2 Eight New Cases of LAHS and Review of Literature: Treatment and Follow-Up
 Supplementary Digital Content 2 Mazodier Lupus Anticoagulant- Hypoprothrombinemia Syndrome: Report of 8 Cases and Review of the Literature Medicine (Baltimore). 2012;91(5). APPEIX 2 Eight New Cases of
Supplementary Digital Content 2 Mazodier Lupus Anticoagulant- Hypoprothrombinemia Syndrome: Report of 8 Cases and Review of the Literature Medicine (Baltimore). 2012;91(5). APPEIX 2 Eight New Cases of
Key words: antiphospholipid syndrome, trombosis, pathogenesis
 26. XI,. 4/2011,.,..,..,., -..,,. 2GPI. -,.,,., -,, -, -,,,,, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-10, TNF, INF-. :,, N. Stoilov, R. Rashkov and R. Stoilov. ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME HISTORICAL DATA, ETI-
26. XI,. 4/2011,.,..,..,., -..,,. 2GPI. -,.,,., -,, -, -,,,,, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-10, TNF, INF-. :,, N. Stoilov, R. Rashkov and R. Stoilov. ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME HISTORICAL DATA, ETI-
Pulmonary Vascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Pulmonary Vascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A. OLUSEGUN FAYEMI, M.D.* Department of Pathology, The Mount Sinai School of Medicine of the City University of New York, New York, New York 129
Pulmonary Vascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A. OLUSEGUN FAYEMI, M.D.* Department of Pathology, The Mount Sinai School of Medicine of the City University of New York, New York, New York 129
CLINICAL CASE PRESENTATION
 European Winter School of Internal Medicine 2015 Riga, Latvia, 26-30 January CLINICAL CASE PRESENTATION Vasiliy Chulkov South Ural State Medical University (Chelyabinsk, Russia) CHELYABINSK CLINICAL HISTORY
European Winter School of Internal Medicine 2015 Riga, Latvia, 26-30 January CLINICAL CASE PRESENTATION Vasiliy Chulkov South Ural State Medical University (Chelyabinsk, Russia) CHELYABINSK CLINICAL HISTORY
Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease. Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab. Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University
 Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University Pulmonary vascular disease Type of pulmonary circulation: Types
Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University Pulmonary vascular disease Type of pulmonary circulation: Types
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing renal failure Highlight diagnostic pitfalls. Crescentic GN: renal
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing renal failure Highlight diagnostic pitfalls. Crescentic GN: renal
AN INTERESTING CASE OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS. Dr.V.Akila Devi DNB PG Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital Chennai
 AN INTERESTING CASE OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS Dr.V.Akila Devi DNB PG Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital Chennai 11 month old female infant 1 st born to parents of NC marriage referred from Kolkatta H/O:
AN INTERESTING CASE OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS Dr.V.Akila Devi DNB PG Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital Chennai 11 month old female infant 1 st born to parents of NC marriage referred from Kolkatta H/O:
Hematologic Disorders. Assistant professor of anesthesia
 Preoperative Evaluation Hematologic Disorders Dr M.Razavi Assistant professor of anesthesia Anemia Evaluation needs to consider the extent and type of surgery, the anticipated blood loss, and the patient's
Preoperative Evaluation Hematologic Disorders Dr M.Razavi Assistant professor of anesthesia Anemia Evaluation needs to consider the extent and type of surgery, the anticipated blood loss, and the patient's
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock. Richard A. McPherson, M.D.
 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Fußzeile (Titel der Präsentation) 1. Thrombotic Microangiopathy: The German Experience 4. Conflictof interest: none
 Thrombotic Microangiopathy: The German Experience 3 Nephropathology Section, Institute of Pathology, Hamburg, Germany Agenda 1. Difficulties in the diagnosis TMA 2. Previous efforts to reach consensus
Thrombotic Microangiopathy: The German Experience 3 Nephropathology Section, Institute of Pathology, Hamburg, Germany Agenda 1. Difficulties in the diagnosis TMA 2. Previous efforts to reach consensus
Medical Complications of Pregnancy
 Medical Complications of Pregnancy Systems Cardiovascular Pulmonary Endocrine Gastrointestinal Urologic Neurologic Cardiovascular System Physiologic anemia 3:1 increase of plasma volume:rbc mass Treat
Medical Complications of Pregnancy Systems Cardiovascular Pulmonary Endocrine Gastrointestinal Urologic Neurologic Cardiovascular System Physiologic anemia 3:1 increase of plasma volume:rbc mass Treat
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service
 M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
Thrombotic Microangiopathies
 Thrombotic Microangiopathies ASH/San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium Review James N. George March 14, 2015 Thrombotic Microangiopathies (TMA): Everything you need to know from 5 patient stories Thrombotic
Thrombotic Microangiopathies ASH/San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium Review James N. George March 14, 2015 Thrombotic Microangiopathies (TMA): Everything you need to know from 5 patient stories Thrombotic
Cerebrovascular Disease
 Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
A 23 year old Caucasian male presented with shortness of breath, hypertension, bloody sputum, and a history of drug abuse (confirmed by urinalysis).
 A 23 year old Caucasian male presented with shortness of breath, hypertension, bloody sputum, and a history of drug abuse (confirmed by urinalysis). He was found to have severe kidney injury requiring
A 23 year old Caucasian male presented with shortness of breath, hypertension, bloody sputum, and a history of drug abuse (confirmed by urinalysis). He was found to have severe kidney injury requiring
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome
 Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
9/25/2013 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE)
 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE) 1 Other Types of Lupus Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Lupus Pernio --- Sarcoidosis Lupus Vulgaris --- Tuberculosis of the face Manifestations of SLE Fever Rashes Arthritis
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE) 1 Other Types of Lupus Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Lupus Pernio --- Sarcoidosis Lupus Vulgaris --- Tuberculosis of the face Manifestations of SLE Fever Rashes Arthritis
Pathology of Hypertension
 2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis
 Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis A Summary Sinus and cerebral vein clots are uncommon. They can lead to severe headaches, confusion, and stroke-like symptoms. They may lead to bleeding into the surrounding
Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis A Summary Sinus and cerebral vein clots are uncommon. They can lead to severe headaches, confusion, and stroke-like symptoms. They may lead to bleeding into the surrounding
Thrombosis (lec#1) * Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad ): Endothelial Injury Stasis Blood Hypercoagulability. stimulated Stasis:
 Thrombosis (lec#1) * Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): Endothelial Injury ( Heart, Arteries), Stasis (abnormal blood flow),blood Hypercoagulability. * Endothelial cells can be stimulated by direct
Thrombosis (lec#1) * Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): Endothelial Injury ( Heart, Arteries), Stasis (abnormal blood flow),blood Hypercoagulability. * Endothelial cells can be stimulated by direct
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS
 THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Rituximab. B Cell Inhibition in APS. Methods. B Cell Inhibition in APS. Disclosure 11/6/2011
 Rituximab in Antiphospholipid Syndrome (RITAPS) A Pilot Open-Label Phase II Prospective Trial for Non-Criteria Manifestations of Antiphospholipid Antibodies (NCT: 00537290) Disclosure Research Support:
Rituximab in Antiphospholipid Syndrome (RITAPS) A Pilot Open-Label Phase II Prospective Trial for Non-Criteria Manifestations of Antiphospholipid Antibodies (NCT: 00537290) Disclosure Research Support:
THE BLOOD VESSELS. Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department.
 THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
Thursday, February 26, :00 am. Regulation of Coagulation/Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS III
 REGULATION OF COAGULATION Introduction HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS III Regulation of Coagulation/Disseminated Coagulation necessary for maintenance of vascular integrity Enough fibrinogen to clot all vessels
REGULATION OF COAGULATION Introduction HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS III Regulation of Coagulation/Disseminated Coagulation necessary for maintenance of vascular integrity Enough fibrinogen to clot all vessels
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to
 Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Case Report Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Presenting as Bilateral Central Retinal Artery Occlusions
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 206906, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/206906 Case Report Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 206906, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/206906 Case Report Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Anticoagulants and Head Injuries. Asaad Shujaa,MD,FRCPC,FAAEM Assistant Professor,weill Corneal Medicne Senior Consultant,HMC Qatar
 Anticoagulants and Head Injuries Asaad Shujaa,MD,FRCPC,FAAEM Assistant Professor,weill Corneal Medicne Senior Consultant,HMC Qatar Common Anticoagulants and Indications Coumadin (warfarin) indicated for
Anticoagulants and Head Injuries Asaad Shujaa,MD,FRCPC,FAAEM Assistant Professor,weill Corneal Medicne Senior Consultant,HMC Qatar Common Anticoagulants and Indications Coumadin (warfarin) indicated for
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE
 HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
Alliance A Symptomatic brain radionecrosis after receiving radiosurgery for
 RANDOMIZED PHASE II STUDY: CORTICOSTEROIDS + BEVACIZUMAB VS. CORTICOSTEROIDS + PLACEBO (BEST) FOR RADIONECROSIS AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR BRAIN METASTASES Pre-registration Eligibility Criteria Required Initial
RANDOMIZED PHASE II STUDY: CORTICOSTEROIDS + BEVACIZUMAB VS. CORTICOSTEROIDS + PLACEBO (BEST) FOR RADIONECROSIS AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR BRAIN METASTASES Pre-registration Eligibility Criteria Required Initial
Neuropathology lecture series. III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease. Physiology of cerebral blood flow
 Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
THE URINARY SYSTEM. The cases we will cover are:
 THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary
 Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism or Arthritis 2. Arthritis Monoarticular Polyarticular - :- (Asymmetrical) (Symetrical) :- -Crystals, Gout - Infective acute
Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism or Arthritis 2. Arthritis Monoarticular Polyarticular - :- (Asymmetrical) (Symetrical) :- -Crystals, Gout - Infective acute
THE URINARY SYSTEM. The cases we will cover are:
 THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
Antiphospholipid antibodies
 CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE Antiphospholipid Antibodies Caron P. Misita, PharmD; Stephan Moll, MD Antiphospholipid antibodies (APLAs) are proteins that may be present in the blood and
CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE Antiphospholipid Antibodies Caron P. Misita, PharmD; Stephan Moll, MD Antiphospholipid antibodies (APLAs) are proteins that may be present in the blood and
Approach to Thrombosis
 Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute lung injury (ALI) transfusion-related, 363 372. See also Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) ALI. See Acute lung injury
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute lung injury (ALI) transfusion-related, 363 372. See also Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) ALI. See Acute lung injury
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم أوتيتم من العلم إال قليال وما
 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم أوتيتم من العلم إال قليال وما 1 2 Goals of the Lecture: What is the portal vein? How common is PVT? What conditions are associated with PVT? How does patient with PVT present? How
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم أوتيتم من العلم إال قليال وما 1 2 Goals of the Lecture: What is the portal vein? How common is PVT? What conditions are associated with PVT? How does patient with PVT present? How
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK?
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United
 Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United States, totaling about 750,000 individuals annually
Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United States, totaling about 750,000 individuals annually
Thrombophilia. Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC. GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, Disclosures. Conflicts of interest: NONE
 LA APLA 1 3 ACA Anti-ß2-GP I 2 45 Thrombophilia Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, 2017 Disclosures Conflicts of interest: NONE Off-label product use discussion:
LA APLA 1 3 ACA Anti-ß2-GP I 2 45 Thrombophilia Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, 2017 Disclosures Conflicts of interest: NONE Off-label product use discussion:
Acta Medica Okayama. Catastrophic secondary antiphospholipid syndrome with peripheral nervous system involvement: a case report.
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 58, Issue 2 2004 Article 7 APRIL 2004 Catastrophic secondary antiphospholipid syndrome with peripheral nervous system involvement: a case report. Nilgun Erten Bulent Saka M Akif
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 58, Issue 2 2004 Article 7 APRIL 2004 Catastrophic secondary antiphospholipid syndrome with peripheral nervous system involvement: a case report. Nilgun Erten Bulent Saka M Akif
Ischemic heart disease
 Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Thrombotic Microangiopathies (TMA) / TTP/HUS/αHUS Pathology & Molecular. Genetics
 Thrombotic Microangiopathies (TMA) / TTP/HUS/αHUS Pathology & Molecular Genetics Helen Liapis, M.D. Senior Consultant Arkana Labs Professor of Pathology & Immunology. retired Washington University School
Thrombotic Microangiopathies (TMA) / TTP/HUS/αHUS Pathology & Molecular Genetics Helen Liapis, M.D. Senior Consultant Arkana Labs Professor of Pathology & Immunology. retired Washington University School
A 60 year old woman with altered mental status and thrombotic microangiopathy. Josh Veatch
 A 60 year old woman with altered mental status and thrombotic microangiopathy Josh Veatch Previously healthy 60 year old woman 2 3 months of fatigue following a URI, transient episodes being out of it
A 60 year old woman with altered mental status and thrombotic microangiopathy Josh Veatch Previously healthy 60 year old woman 2 3 months of fatigue following a URI, transient episodes being out of it
Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy
 Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy Jeong-Am Ryu 1, Oh Young Bang 2, Daesang Lee 1, Jinkyeong Park 1, Jeong Hoon Yang 1, Gee Young Suh 1, Joongbum Cho 1, Chi Ryang Chung 1, Chi-Min
Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy Jeong-Am Ryu 1, Oh Young Bang 2, Daesang Lee 1, Jinkyeong Park 1, Jeong Hoon Yang 1, Gee Young Suh 1, Joongbum Cho 1, Chi Ryang Chung 1, Chi-Min
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome.
 Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Functional vascular disorders
 Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM
 REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
