ADVOCATING FOR COMPREHENSIVE POST-RESUSCITATION CARE. Heather Harrington RN, BScN, CCNC(c)
|
|
|
- Garey Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ADVOCATING FOR COMPREHENSIVE POST-RESUSCITATION CARE Heather Harrington RN, BScN, CCNC(c)
2 Objectives Define Post-Resuscitation Syndrome Discuss the American Heart Association (AHA) 2010 Guidelines: i. Optimize cardiopulmonary function and vital organ perfusion ii. Try to identify and treat the precipitating causes of the arrest and prevent recurrent arrest iii. Identifying and treating acute coronary syndromes iv. Controlling body temperature to optimize survival and neurological recovery v. Optimizing mechanical ventilation to minimize lung injury vi. Reducing the risk of multi-organ injury and supporting organ function vii. Assessing prognosis for recovery Encourage development of protocols, algorithms & checklists
3
4
5
6 After the CPR stops Post-Resuscitation Syndrome: The pathological state with associated organ failure that can occur post cardiac arrest.
7 Post Cardiac Arrest Syndrome Consists of four main clinical considerations: 1. Brain Injury Initial hyperemic blood flow (lasts minutes), followed by a more prolonged period of low blood flow Disruption on both a micro- & macro- circulatory levels often results in hyperemia and ischemia Related to: o Hypoxia during the arrest o Inflammation associated with reperfusion after the arrest Reperfusion Injury
8 2. Myocardial dysfunction Heart initially becomes hyperkinetic Circulating catecholamines Global hypokinesis often follows 3. Systemic Ischemia/Reperfusion Response Response similar to septic shock Activation of the immune system Release of inflammatory cytokines Range of cellular responses 4. Persistent precipitating pathology The cause of the arrest may continue to impact physiological parameters
9 AHA 2010 Guidelines A comprehensive, structured, multidisciplinary system of care should be implemented in a consistent manner for the treatment of post cardiac arrest patients. Programs should include as part of structured interventions: therapeutic hypothermia, optimization of hemodynamics and gas exchange, immediate coronary reperfusion when indicated for restoration of coronary blood flow with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), glycemic control and neurological diagnosis, management, and prognostication.
10
11 Why Advocate? 5-year study (5,958 patients) published in 2012 PCI was performed in 384 of 1,001 (38.4%) TH was performed in 241 of 941 (25.6%) eligible patients 2013 study (538 hospitals & 67,498 patients) showed: Post in-hospital cardiac arrest, therapeutic hypothermia was used rarely (12%) Once initiated, the target temperature was commonly not achieved (44.3%) Frequency of use increased over time but remained low ( % over 6 years) Factors associated with therapeutic hypothermia use included patient age (young), time (weekday) & location of occurrence (non-icu), and type of hospital (teaching) Two year study of post arrest care (PACT)
12
13 Care Phases Immediate: First 20 minutes after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). Early: 20 minutes to 6-12 hours: early intervention is most effective. Intermediate: 6-12 hours to 72 hours: injury pathways still active; aggressive treatment recommended. Recovery: Beyond 72 hours: recovery phase; outcomes more predictable. Rehabilitation
14 Cardiopulmonary Function & Vital Organ Perfusion Verify/establish IV access CVP IV fluids using the CVP as a guide Large amounts of volume often required Global hypokinesis & myocardial dysfunction Vasoactive drugs Recommended: MAP 65 mmhg & ScvO 2 70
15 Ensure adequate airway & support breathing (intubation may be required) Avoid using ties that pass around the patient s neck, potentially obstructing venous return from the brain Waveform capnography monitoring To monitor the correct placement of an advanced airway Continuous pulse oximetry Elevate the head of the bed 30, if tolerated Reduces the incidence of cerebral edema, aspiration and ventilatory-associated pneumonia
16 Identify & Prevent Identify and treat the precipitating causes & prevent recurrence Maintain airway o CXR - Causes/complications of arrest - Tension pneumothorax, pneumo/hemothorax, rib fracture Continuous ECG and vital sign monitoring Recurrent cardiac dysrhythmias (reperfusion/ischemic) Maintain SBP 90mmHg/MAP 65mmHg Fluid boluses (cold fluid if TH selected) Vasoactive drugs (dopamine, norepinephrine or epinephrine)
17 Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) Identify and treat ACS Most common cause of cardiac arrest is cardiovascular disease & coronary ischemia A 12-lead ECG obtained ASAP To detect ST elevation or new left bundle branch block Assess QTI
18 Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) High suspicion of AMI? Protocols for treatment of AMI and coronary reperfusion should be activated (PCI, thrombolysis, anticoagulants) Concurrent PCI and hypothermia are considered safe Good outcomes have been reported for comatose patients post cardiac arrest who undergo PCI Medical or interventional treatments may be considered for treatment of ACS and should not be deferred because of the presence of coma or if hypothermia is indicated.
19 2013 study showed STEMI patients who suffered a cardiac arrest which resulted in cardiogenic shock had a significantly higher in-hospital mortality rate than those without (62% vs. 30%) IABP or VAD therapy should be considered Pulmonary Embolism treatment Studies indicate that CPR itself does not appear to pose an unacceptable risk of bleeding for post cardiac arrest patients In post cardiac arrest patients with arrest due to presumed or known pulmonary embolism, fibrinolytics may be considered
20 Antiarrhythmic drugs such as amiodarone are often administered during initial resuscitation There is no evidence to support or refute continued or prophylactic administration of these medications Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator A meta-analysis demonstrated that patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction < 35% derived significant benefit from ICD therapy
21 Targeted Temperature Management 2009 International consensus conference sponsored by American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society, European Society of Intensive Care Medicine, Society of Critical Care Medicine & Societé de Réanimation de Langue Français issued a statement: recommends strongly for TTM to a target of 32-34⁰C as preferred treatment (versus unstructured temperature management) of out-of-hospital adult cardiac arrest victims with a first registered rhythm of VF or pulseless VT and still unconscious after [Return of Spontaneous Circulation] ROSC.
22 Targeted Temperature Management 2010 AHA Guidelines: Brain injury and cardiovascular instability are the major determinants of survival after cardiac arrest. Because therapeutic hypothermia (TH) is the only intervention demonstrated to improve neurological recovery, it should be considered for any patient who is unable to follow verbal commands after ROSC. If TH contraindicated, hyperthermia (T>37.6⁰C), common during the first 24 hours after cardiac arrest, must be avoided 3 phases of TH: induction, maintenance & rewarming
23
24
25 Induction Begin ASAP Cool the patient rapidly to C Recommendation: achieve C within 4-6 hours of ROSC Recommendation: achieve C within 1-3 hours of starting to cool TIME is BRAIN!
26 Cooling Methods Multiple methods for inducing TH (no single method has been demonstrated to be optimal) o Feedback-controlled endovascular catheters o Surface cooling devices o Cooling blankets and frequent application of ice bags - require more labor and closer monitoring o Iced (4⁰C) isotonic fluid can be infused to initiate core cooling - must be combined with a follow-up method for maintenance of hypothermia
27
28 Maintenance Optimal duration of TH is at least 12 hours and may be 24 hours (from start of cooling) Continuous monitoring of the patient s core temperature Esophageal thermometer Bladder catheter (in nonanuric patients) Pulmonary artery catheter (if one is placed for other indications)
29 Analgesia & Sedation should be routinely administered during TH Neuromuscular Blocking Agents (NMBA) PRN/infused to PNS/TOF monitoring
30 Re-warming Recommendation: 8-12 hours Active/passive not yet studied
31 Coagulopathy Potential Complications Lines/catheters (optimally inserted prior to initiating TH) Control any ongoing bleeding Arrhythmias Bradycardia Hyperglycemia Electrolyte disturbances Hypokalemia/Hyperkalemia Prolonged hypothermia impacts immune function Pneumonia and sepsis
32 Hyperthermia & Normathermia Hyperthermia can impair brain recovery Studies suggest that there is an association between poor survival outcomes and fever > 37.6 C May be related to activation of inflammatory cytokines similar to that seen in sepsis Hyperthermia after rewarming can also occur Identify & treat
33 Optimizing Ventilation Hyperventilation should be avoided because of potential adverse hemodynamic effects. Increases intrathoracic pressure & inversely lowers cardiac output Decreases PaCO 2 which can decrease cerebral blood flow o Start at 10 to 12 breaths/minute o Titrate to achieve a PETCO 2 of mmhg or a PaCO 2 of mmhg ( Normocapnia should be considered the standard ) Arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation (SaO 2 ) of 100% may correspond to a PaO 2 of mmhg FiO 2 should be titrated to the lowest level required to achieve an SaO 2 94%, to avoid hyperoxia
34 Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) and titrated FiO 2 are strategies that can improve pulmonary function and PaO 2 Essential diagnostic tests in intubated patients: o ABGs o CXR ETT positioning Pulmonary infiltrates/edema, VAP Routinely check PaO 2 /FiO 2 ratio o Acute Lung Injury (ALI) <300 o Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) < 200 Terminate ventilation & extubate ASAP If there are no cardiac, pulmonary or other complications
35 Pain/agitation Intermittent or continuous sedation and/or analgesia can be used to achieve specific clinical goals Daily sedation interruption protocols are recommended
36 Reduce Organ Injury & Improve Perfusion Recommended MAP 65 mmhg & ScvO 2 70 Vasoactive drugs: Limited data about vasoactive drugs Base therapy on established protocols/orders for ICU Drug actions & interactions with previously and concurrently administered drugs Hypotension (recommendations) norepinephrine, dobutamine, dopamine & epinephrine Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP) Hypertension (recommendations) nitroglycerin Consider diuretics if evidenced heart failure Transfuse red blood cells to maintain targeted ScvO 2
37 Blood Glucose Hyper/hypoglycemia should be avoided Studies have shown increased mortality among postcardiac arrest patients with hyperglycemia A target of moderate glycemic control 8-10 mmol/l may be considered
38 Acid-Base Balance, Electrolytes Acidosis & hyperkalemia are adverse prognostic factors in the post resuscitation phase Prevent severe acidosis, hyper/hypokalemia Hypomagnesemia is associated with adverse outcome in critically ill patients Although there is no RCT evaluating magnesium in post resuscitation care, it seems reasonable to avoid Standard ICU Care GI & DVT prophylaxis
39 Corticosteroids Role in the physiological response to severe stress Maintenance of vascular tone & capillary permeability. Several studies report a relative adrenal insufficiency (associated with higher rates of mortality in critically ill) No human studies have confirmed the value of routine use of these agents post cardiac arrest CRRT/Hemofiltration Treatment for AKI Proposed as a method to modify the inflammation that occurs with post cardiac arrest syndrome No studies showing improved outcomes yet Future investigations are required
40 Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain injury is a common cause of morbidity and mortality in post cardiac arrest patients. Brain injury is the cause of death in 68% of patients after out-ofhospital cardiac arrest and in 23% after in-hospital cardiac arrest. The pathophysiology of post cardiac arrest brain injury involves a complex cascade of molecular events that are triggered by ischemia and reperfusion and then executed over hours to days after ROSC. Clinical manifestations of post cardiac arrest brain injury include: Coma, seizures, myoclonus, various degrees of neurocognitive dysfunction (ranging from memory deficits to persistent vegetative state) and brain death
41 Seizure Management An EEG for the diagnosis of seizure should be performed with prompt interpretation as soon as possible and should be monitored frequently or continuously in comatose patients after ROSC. Routine prophylactic administration of neuroprotective agents has not been well studied If seizures develop, the same anticonvulsant regimens used for status epilepticus caused by other etiologies may be used
42 Prognosis The goal of post cardiac arrest management is to return patients to their pre-arrest functional level. However, many patients will die, remain permanently unresponsive, or remain permanently unable to perform independent activities. Early prognostication of neurological outcome is an essential component of post cardiac arrest care.
43 Prognostication Algorithm
44 24 hours post-cardiac arrest; routine neurological exam, routine/continuous EEG, Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SSEPs), are the best predictors in the absence of confounders (such as hypotension, seizures, sedatives, or neuromuscular blockers) No reliable studies yet on using these tests with TH Recommended that TH should be completed before prognostication CT & MRI can also be of benefit When to withdraw? No recommendations, however studies have used both 72 & 96 hours
45 ADVOCATE!!
46 AHA Guidelines Advocate! Develop protocols, algorithms & checklists Physician orders Optimization of hemodynamics & gas exchange Glycemic control Neurological diagnosis & management PCI Algorithm TH Algorithm Neuroprognostication Protocols WOLS guidelines/orders, organ donation guidelines/orders Structured rehabilitation plans Discharge planning, links with rehab centers, community
47 Advocate! As laypersons AHA website has info on post cardiac arrest syndrome: re/cardiacarrest/post-cardiac-arrest-syndrome- Care_UCM_307981_Article.jsp & prognosis for survivors: re/cardiacarrest/prognosis-for-cardiac-arrest- Survivors_UCM_307918_Article.jsp Canada s Heart & Stroke has similar resources:
48 Bibliography Dumas, F., White, L., Stubbs, B., Carlou, A., Rea, T. (2012). Long-term prognosis following resuscitation from out of hospital cardiac arrest: role of percutaneous coronary intervention and therapeutic hypothermia. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Vol. 60(1), p Holzer, M. [representing] The Hypothermia After Cardiac Arrest Study Group (2002). Mild therapeutic hypothermia to improve the neurologic outcome after cardiac arrest. The New England Journal of Medicine, Vol. 346 (8), p Kern, K. (2013), ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest and cardiogenic shock: an interventional triumvirate of opportunity. Journal of American College of Cardiology Interventionalists, Vol. 6 (2), p Kuiper, M., Spronk, P., Schultz, M. (2009). Use of a standardized treatment protocol for post-cardiac arrest treatment. Retrieved from: ardiac%20arrest_hayat.pdf Mikkelsen, M., Christie, J., Abella, B., Kerlin, M., Fuchs, B., Schweickert, W., Berg, Mr., Mosesso, V.,. Shofer, F., Gaieski, D. (2013.) Use of therapeutic hypothermia after in-hospital cardiac arrest. Critical Care Medicine, Vol. 41, p Nolan, J. et al. (2003). Therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest: An advisory statement by the advanced life support task force of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation. Circulation 2003, Vol.108, p Peberdy, M. et al. (2010). Post cardiac arrest care: 2010 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation 2010, Vol.122, p Sunde, K. et al. Implementation of a standardized treatment protocol for post resuscitation care after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2007, Vol.73,p.29-39
49 Thank you!
Post Cardiac Arrest Care. From : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care
 Post Cardiac Arrest Care From : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Initial Objectives of Post cardiac Arrest Care Optimize cardiopulmonary
Post Cardiac Arrest Care From : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Initial Objectives of Post cardiac Arrest Care Optimize cardiopulmonary
In-hospital Care of the Post-Cardiac Arrest Patient. David A. Pearson, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Associate Program Director Department of Emergency Medicine
 In-hospital Care of the Post-Cardiac Arrest Patient David A. Pearson, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Associate Program Director Department of Emergency Medicine Disclosures I have no financial interest, arrangement,
In-hospital Care of the Post-Cardiac Arrest Patient David A. Pearson, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Associate Program Director Department of Emergency Medicine Disclosures I have no financial interest, arrangement,
Post-Cardiac Arrest Syndrome. MICU Lecture Series
 Post-Cardiac Arrest Syndrome MICU Lecture Series Case 58 y/o female collapses at home, family attempts CPR, EMS arrives and notes VF, defibrillation x 3 with return of spontaneous circulation, brought
Post-Cardiac Arrest Syndrome MICU Lecture Series Case 58 y/o female collapses at home, family attempts CPR, EMS arrives and notes VF, defibrillation x 3 with return of spontaneous circulation, brought
Post Cardiac Arrest Care 2015 American Heart Association Guideline Update for CPR and Emergency Cardiovascular Care
 Post Cardiac Arrest Care 2015 American Heart Association Guideline Update for CPR and Emergency Cardiovascular Care รศ.ดร.พญ.ต นหยง พ พานเมฆาภรณ ภาคว ชาว ส ญญ ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม System
Post Cardiac Arrest Care 2015 American Heart Association Guideline Update for CPR and Emergency Cardiovascular Care รศ.ดร.พญ.ต นหยง พ พานเมฆาภรณ ภาคว ชาว ส ญญ ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม System
THERAPEUTIC HYPOTHERMIA POST CARDIAC ARREST
 THERAPEUTIC HYPOTHERMIA POST CARDIAC ARREST Heather Harrington RN, BScN, CNCC(c) Clinical Nurse Educator Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre Objectives Define Therapeutic Hypothermia (TH) Describe current
THERAPEUTIC HYPOTHERMIA POST CARDIAC ARREST Heather Harrington RN, BScN, CNCC(c) Clinical Nurse Educator Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre Objectives Define Therapeutic Hypothermia (TH) Describe current
SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC
 SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC The following is a summary of the key issues and changes in the AHA 2010 Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiac
SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC The following is a summary of the key issues and changes in the AHA 2010 Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiac
RACE CARS: Hospital Response. David A. Pearson, MD Department of Emergency Medicine Carolinas Medical Center February 23, 2012
 L MODULE 9 RACE CARS: Hospital Response David A. Pearson, MD Department of Emergency Medicine Carolinas Medical Center February 23, 2012 2 Objectives: Post-cardiac arrest syndrome Therapeutic hypothermia
L MODULE 9 RACE CARS: Hospital Response David A. Pearson, MD Department of Emergency Medicine Carolinas Medical Center February 23, 2012 2 Objectives: Post-cardiac arrest syndrome Therapeutic hypothermia
Post-resuscitation care for adults. Jerry Nolan Royal United Hospital Bath
 Post-resuscitation care for adults Jerry Nolan Royal United Hospital Bath Post-resuscitation care for adults Titration of inspired oxygen concentration after ROSC Urgent coronary catheterisation and percutaneous
Post-resuscitation care for adults Jerry Nolan Royal United Hospital Bath Post-resuscitation care for adults Titration of inspired oxygen concentration after ROSC Urgent coronary catheterisation and percutaneous
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation
 Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Post-Arrest Care: Beyond Hypothermia
 Post-Arrest Care: Beyond Hypothermia Damon Scales MD PhD Department of Critical Care Medicine Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre University of Toronto Disclosures CIHR Physicians Services Incorporated Main
Post-Arrest Care: Beyond Hypothermia Damon Scales MD PhD Department of Critical Care Medicine Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre University of Toronto Disclosures CIHR Physicians Services Incorporated Main
Targeted Temperature Management: An Evolving Therapy for Cardiac Arrest
 Targeted Temperature Management: An Evolving Therapy for Cardiac Arrest By Meagan Dunn, BScN, MSc,, RN, CNE NP Forum April 8, 2016 Objectives To understand: What Therapeutic Temperature Management (TTM)
Targeted Temperature Management: An Evolving Therapy for Cardiac Arrest By Meagan Dunn, BScN, MSc,, RN, CNE NP Forum April 8, 2016 Objectives To understand: What Therapeutic Temperature Management (TTM)
Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
There is increasing recognition that systematic post cardiac
 Part 9: Post Cardiac Arrest Care 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Mary Ann Peberdy, Co-Chair*; Clifton W. Callaway, Co-Chair*;
Part 9: Post Cardiac Arrest Care 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Mary Ann Peberdy, Co-Chair*; Clifton W. Callaway, Co-Chair*;
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults
 Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults Fatma Özdemir, MD Emergency Deparment of Uludag University Faculty of Medicine OVERVIEW Introduction Pathophysiology BLS algorithm ALS algorithm Post resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults Fatma Özdemir, MD Emergency Deparment of Uludag University Faculty of Medicine OVERVIEW Introduction Pathophysiology BLS algorithm ALS algorithm Post resuscitation
INDUCED HYPOTHERMIA A Hot Topic. R. Darrell Nelson, MD, FACEP Emergency Medicine Wake Forest University Health Sciences
 INDUCED HYPOTHERMIA A Hot Topic R. Darrell Nelson, MD, FACEP Emergency Medicine Wake Forest University Health Sciences Conflicts of Interest Sadly, we have no financial or industrial conflicts of interest
INDUCED HYPOTHERMIA A Hot Topic R. Darrell Nelson, MD, FACEP Emergency Medicine Wake Forest University Health Sciences Conflicts of Interest Sadly, we have no financial or industrial conflicts of interest
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation
 Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Hypothermia: The Science and Recommendations (In-hospital and Out)
 Hypothermia: The Science and Recommendations (In-hospital and Out) L. Kristin Newby, MD, MHS Professor of Medicine Duke University Medical Center Chair, Council on Clinical Cardiology, AHA President, Society
Hypothermia: The Science and Recommendations (In-hospital and Out) L. Kristin Newby, MD, MHS Professor of Medicine Duke University Medical Center Chair, Council on Clinical Cardiology, AHA President, Society
POST-CARDIAC ARREST CARE: WHAT HAPPENS AFTER ROSC MATTERS! Emergency Nurses Association
 POST-CARDIAC ARREST CARE: WHAT HAPPENS AFTER ROSC MATTERS! Emergency Nurses Association - 2016 Nicole Kupchik MN, RN, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CMC Objectives Discuss the 2015 AHA Guideline Updates for Post- Arrest
POST-CARDIAC ARREST CARE: WHAT HAPPENS AFTER ROSC MATTERS! Emergency Nurses Association - 2016 Nicole Kupchik MN, RN, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CMC Objectives Discuss the 2015 AHA Guideline Updates for Post- Arrest
The ALS Algorithm and Post Resuscitation Care
 The ALS Algorithm and Post Resuscitation Care CET - Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st July 2018 to 30 th June 2020 2 Defibrillation Produces simultaneous mass depolarisation of myocardial cells
The ALS Algorithm and Post Resuscitation Care CET - Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st July 2018 to 30 th June 2020 2 Defibrillation Produces simultaneous mass depolarisation of myocardial cells
Case Presentation. Cooling. Case Presentation. New Developments in Cardiopulmonary Arrest: Therapeutic Hypothermia in Resuscitation
 New Developments in Cardiopulmonary Arrest: Therapeutic Hypothermia in Resuscitation Michael Sayre, MD Emergency Medicine and LeRoy Essig, MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Medicine Case Presentation 3:40 (+
New Developments in Cardiopulmonary Arrest: Therapeutic Hypothermia in Resuscitation Michael Sayre, MD Emergency Medicine and LeRoy Essig, MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Medicine Case Presentation 3:40 (+
INDUCED HYPOTHERMIA. F. Ben Housel, M.D.
 INDUCED HYPOTHERMIA F. Ben Housel, M.D. Historical Use of Induced Hypothermia 1950 s - Moderate hypothermia (30-32º C) in open heart surgery to protect brain against global ischemia 1960-1980 s - Use of
INDUCED HYPOTHERMIA F. Ben Housel, M.D. Historical Use of Induced Hypothermia 1950 s - Moderate hypothermia (30-32º C) in open heart surgery to protect brain against global ischemia 1960-1980 s - Use of
Post Resuscitation (ROSC) Care
 Standard Operating Procedure 2.10 Post Resuscitation (ROSC) Care Position Responsible: Medical Director Approved: Clinical Governance Committee Related Documents: This document is the intellectual property
Standard Operating Procedure 2.10 Post Resuscitation (ROSC) Care Position Responsible: Medical Director Approved: Clinical Governance Committee Related Documents: This document is the intellectual property
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines
 Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
SHOCK. Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital
 SHOCK Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Definition Shock is an acute, complex state of circulatory dysfunction
SHOCK Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Definition Shock is an acute, complex state of circulatory dysfunction
Post-Resuscitation Care. Prof. Wilhelm Behringer Center of Emergency Medicine University of Jena
 Post-Resuscitation Care Prof. Wilhelm Behringer Center of Emergency Medicine University of Jena Conflict of interest Emcools Shareholder and founder, honoraria Zoll: honoraria Bard: honoraria, nephew works
Post-Resuscitation Care Prof. Wilhelm Behringer Center of Emergency Medicine University of Jena Conflict of interest Emcools Shareholder and founder, honoraria Zoll: honoraria Bard: honoraria, nephew works
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
Post-resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support. ARC and NZRC Guideline 2010
 Emergency Medicine Australasia (2011) 23, 292 296 doi: 10.1111/j.1742-6723.2011.01422_15.x POST-RESUSCITATION THERAPY Post-resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support. ARC and NZRC Guideline 2010
Emergency Medicine Australasia (2011) 23, 292 296 doi: 10.1111/j.1742-6723.2011.01422_15.x POST-RESUSCITATION THERAPY Post-resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support. ARC and NZRC Guideline 2010
Prehospital Post Arrest Care AHA Strive to Revive 2017 November 3, 2017
 Prehospital Post Arrest Care AHA Strive to Revive 2017 November 3, 2017 Jon Rittenberger, MD, MS Department of University of Pittsburgh Employers: Disclosures - Rittenberger University of Pittsburgh UPMC
Prehospital Post Arrest Care AHA Strive to Revive 2017 November 3, 2017 Jon Rittenberger, MD, MS Department of University of Pittsburgh Employers: Disclosures - Rittenberger University of Pittsburgh UPMC
Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest. Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
 Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Conflict of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose regarding this presentation.
Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Conflict of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose regarding this presentation.
ACLS Review. Pulse Oximetry to be between 94 99% to avoid hyperoxia (high oxygen tension can lead to tissue death
 ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
Objectives. Trends in Resuscitation POST-CARDIAC ARREST CARE: WHAT S THE EVIDENCE?
 POST-CARDIAC ARREST CARE: WHAT S THE EVIDENCE? Nicole Kupchik RN, MN, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CMC Objectives Discuss the 2015 AHA Guideline Updates for Post- Arrest Care Discuss oxygenation & hemodynamic taregts
POST-CARDIAC ARREST CARE: WHAT S THE EVIDENCE? Nicole Kupchik RN, MN, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CMC Objectives Discuss the 2015 AHA Guideline Updates for Post- Arrest Care Discuss oxygenation & hemodynamic taregts
Post-Resuscitation Care: Optimizing & Improving Outcomes after Cardiac Arrest. Objectives: U.S. stats
 Post-Resuscitation Care: Optimizing & Improving Outcomes after Cardiac Arrest Nicole L. Kupchik RN, MN, CCNS CCRN-CMC Clinical Nurse Specialist Harborview Medical Center Seattle, WA Objectives: At the
Post-Resuscitation Care: Optimizing & Improving Outcomes after Cardiac Arrest Nicole L. Kupchik RN, MN, CCNS CCRN-CMC Clinical Nurse Specialist Harborview Medical Center Seattle, WA Objectives: At the
Post Resuscitation Care
 Princess Margaret Hospital f Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Post Resuscitation Care Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should
Princess Margaret Hospital f Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Post Resuscitation Care Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should
Regionalization of Post-Cardiac Arrest Care
 Regionalization of Post-Cardiac Arrest Care David A. Pearson, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Department of Emergency Medicine Disclosures I have no financial interest, arrangement, or affiliations and no commercial
Regionalization of Post-Cardiac Arrest Care David A. Pearson, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Department of Emergency Medicine Disclosures I have no financial interest, arrangement, or affiliations and no commercial
Objectives. Design: Setting &Patients: Patients. Measurements and Main Results: Common. Adverse events VS Mortality
 ADVERSE EVENTS AND THEIR RELATION TO MORTALITY IN OUT-OF-HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST PATIENTS TREATED WITH THERAPEUTIC HYPOTHERMIA Reporter R1 吳志華 Supervisor VS 王瑞芳 100.04.02 Niklas Nielsen, MD, PhD; Kjetil
ADVERSE EVENTS AND THEIR RELATION TO MORTALITY IN OUT-OF-HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST PATIENTS TREATED WITH THERAPEUTIC HYPOTHERMIA Reporter R1 吳志華 Supervisor VS 王瑞芳 100.04.02 Niklas Nielsen, MD, PhD; Kjetil
Therapeutic Hypothermia
 Objectives Overview Therapeutic Hypothermia Nerissa U. Ko, MD, MAS UCSF Department of Neurology Critical Care Medicine and Trauma June 4, 2011 Hypothermia as a neuroprotectant Proven indications: Adult
Objectives Overview Therapeutic Hypothermia Nerissa U. Ko, MD, MAS UCSF Department of Neurology Critical Care Medicine and Trauma June 4, 2011 Hypothermia as a neuroprotectant Proven indications: Adult
Mild. Moderate. Severe. 32 to to and below
 Mohamud Daya MD, MS Mild 32 to 34 Moderate 28 to 32 Severe 28 and below Jon Rittenberger Shervin Ayati Protocol Development Committee Hypothermia Working Group Lynn Wittwer Jon Jui John Stouffer Scott
Mohamud Daya MD, MS Mild 32 to 34 Moderate 28 to 32 Severe 28 and below Jon Rittenberger Shervin Ayati Protocol Development Committee Hypothermia Working Group Lynn Wittwer Jon Jui John Stouffer Scott
Outcomes of Therapeutic Hypothermia in Cardiac Arrest. Saad Mohammed Shariff, MBBS Aravind Herle, MD, FACC
 Outcomes of Therapeutic Hypothermia in Cardiac Arrest Saad Mohammed Shariff, MBBS Aravind Herle, MD, FACC https://my.americanheart.org/idc/groups/ahamah-public/@wcm/@sop/@scon/documents/downloadable/ucm_427331.pdf
Outcomes of Therapeutic Hypothermia in Cardiac Arrest Saad Mohammed Shariff, MBBS Aravind Herle, MD, FACC https://my.americanheart.org/idc/groups/ahamah-public/@wcm/@sop/@scon/documents/downloadable/ucm_427331.pdf
Emergency Cardiac Care Guidelines 2015
 Emergency Cardiac Care Guidelines 2015 VACEP 2016 William Brady, MD University of Virginia Guidelines 2015 Basic Life Support & Advanced Cardiac Life Support Acute Coronary Syndrome Pediatric Advanced
Emergency Cardiac Care Guidelines 2015 VACEP 2016 William Brady, MD University of Virginia Guidelines 2015 Basic Life Support & Advanced Cardiac Life Support Acute Coronary Syndrome Pediatric Advanced
national CPR committee Saudi Heart Association (SHA). International Liason Commission Of Resuscitation (ILCOR)
 2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
Prehospital Care Bundles
 Prehospital s The MLREMS Prehospital s have been created to provide a simple framework to help EMS providers identify the most critical elements when caring for a patient. These bundles do not replace
Prehospital s The MLREMS Prehospital s have been created to provide a simple framework to help EMS providers identify the most critical elements when caring for a patient. These bundles do not replace
Surviving Sepsis Campaign. Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock. An Overview
 Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock An Overview Mechanical Ventilation of Sepsis-Induced ALI/ARDS ARDSnet Mechanical Ventilation Protocol Results: Mortality
Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock An Overview Mechanical Ventilation of Sepsis-Induced ALI/ARDS ARDSnet Mechanical Ventilation Protocol Results: Mortality
IN HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST AND SEPSIS
 IN HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST AND SEPSIS MARGARET DISSELKAMP, MD OVERVIEW Background Epidemiology of in hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA) Use a case scenario to introduce new guidelines Review surviving sepsis
IN HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST AND SEPSIS MARGARET DISSELKAMP, MD OVERVIEW Background Epidemiology of in hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA) Use a case scenario to introduce new guidelines Review surviving sepsis
SHOCK AETIOLOGY OF SHOCK (1) Inadequate circulating blood volume ) Loss of Autonomic control of the vasculature (3) Impaired cardiac function
 SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
CrackCast Episode 8 Brain Resuscitation
 CrackCast Episode 8 Brain Resuscitation Episode Overview: 1) Describe 6 therapeutic interventions for the post-arrest brain 2) List 5 techniques for initiating therapeutic hypothermia 3) List 4 mechanisms
CrackCast Episode 8 Brain Resuscitation Episode Overview: 1) Describe 6 therapeutic interventions for the post-arrest brain 2) List 5 techniques for initiating therapeutic hypothermia 3) List 4 mechanisms
State of the art lecture: 21st Century Post resuscitation management
 State of the art lecture: 21st Century Post resuscitation management ACCA Masterclass 2017 Prof Alain CARIOU Intensive Care Unit - Cochin Hospital (APHP) Paris Descartes University INSERM U970 - France
State of the art lecture: 21st Century Post resuscitation management ACCA Masterclass 2017 Prof Alain CARIOU Intensive Care Unit - Cochin Hospital (APHP) Paris Descartes University INSERM U970 - France
Curricullum Vitae. Dr. Isman Firdaus, SpJP (K), FIHA
 Curricullum Vitae Dr. Isman Firdaus, SpJP (K), FIHA Email: ismanf@yahoo.com Qualification : o GP 2001 (FKUI) o Cardiologist 2007 (FKUI) o Cardiovascular Intensivist 2010 - present o Cardiovascular Intervensionist
Curricullum Vitae Dr. Isman Firdaus, SpJP (K), FIHA Email: ismanf@yahoo.com Qualification : o GP 2001 (FKUI) o Cardiologist 2007 (FKUI) o Cardiovascular Intensivist 2010 - present o Cardiovascular Intervensionist
2010 ACLS Guidelines. Primary goals of therapy for patients
 2010 ACLS Guidelines Part 10: Acute Coronary Syndrome Present : 內科 R1 鍾伯欣 Supervisor: F1 吳亮廷 991110 Primary goals of therapy for patients of ACS Reduce the amount of myocardial necrosis that occurs in
2010 ACLS Guidelines Part 10: Acute Coronary Syndrome Present : 內科 R1 鍾伯欣 Supervisor: F1 吳亮廷 991110 Primary goals of therapy for patients of ACS Reduce the amount of myocardial necrosis that occurs in
HigHligHts of the 2018 Focused In 2015 Updates to the American Heart Association Guidelines for CPR and ECC: Advanced Cardiovascular Life
 Highlights of the 2018 Focused Updates to the American Heart Association Guidelines for CPR and ECC: Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support and Pediatric Advanced Life Support - Heart and Stroke Foundation
Highlights of the 2018 Focused Updates to the American Heart Association Guidelines for CPR and ECC: Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support and Pediatric Advanced Life Support - Heart and Stroke Foundation
Intensive Care Paramedic
 Doc Control Ref: TEM-003 Version 2.0 (Admin use only) Version no: (Admin use only) Effective Date: (Admin use only) 1. Principle Post-return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) management is an important
Doc Control Ref: TEM-003 Version 2.0 (Admin use only) Version no: (Admin use only) Effective Date: (Admin use only) 1. Principle Post-return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) management is an important
Printed copies of this document may not be up to date, obtain the most recent version from
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Septic Shock Document Control Information Author Claire Fraser P.Ramnarayan Author Position tanp CATS Consultant Document Owner E. Polke Document
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Septic Shock Document Control Information Author Claire Fraser P.Ramnarayan Author Position tanp CATS Consultant Document Owner E. Polke Document
SYSTEM-WIDE POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL. Policy Title: Hypothermia Post Cardiac Arrest Policy Number: PC-124. President & CEO Page 1 of 9
 Approved By: President & CEO Date Page 1 of 9 POLICY: PURPOSE: To define and describe the implementation of induced hypothermia post cardiac arrest and the nursing assessment and interventions required
Approved By: President & CEO Date Page 1 of 9 POLICY: PURPOSE: To define and describe the implementation of induced hypothermia post cardiac arrest and the nursing assessment and interventions required
Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines
 Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines Bernd W. Böttiger Seite 1 To preserve human life by making high quality resuscitation available to all Outcome after CPR in Germany ROSC ( Return
Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines Bernd W. Böttiger Seite 1 To preserve human life by making high quality resuscitation available to all Outcome after CPR in Germany ROSC ( Return
Frank Sebat, MD - June 29, 2006
 Types of Shock Hypovolemic Shock Low blood volume decreasing cardiac output. AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM OF CARE FOR PATIENTS AT RISK SHOCK TEAM and RAPID RESPONSE TEAM Septic or Distributive Shock Decrease in
Types of Shock Hypovolemic Shock Low blood volume decreasing cardiac output. AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM OF CARE FOR PATIENTS AT RISK SHOCK TEAM and RAPID RESPONSE TEAM Septic or Distributive Shock Decrease in
Patient Case. Post cardiac arrest pathophysiology 10/19/2017. Disclosure. Objectives. Patient Case-TM
 Disclosure TARGETED TEMPERATURE MANAGEMENT POST CARDIAC ARREST I have nothing to disclose concerning possible financial or personal relationships with commercial entities that may have a direct or indirect
Disclosure TARGETED TEMPERATURE MANAGEMENT POST CARDIAC ARREST I have nothing to disclose concerning possible financial or personal relationships with commercial entities that may have a direct or indirect
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During. Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE
 Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Pravit Jetanachai, MD QSNICH Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation Causes of oxygen desaturation 1.
Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Pravit Jetanachai, MD QSNICH Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation Causes of oxygen desaturation 1.
Post-Cardiac Arrest Syndrome Henry L. Green, MD, FACC Clinical Professor of Medicine, Wayne State University December 11, 2016
 Post-Cardiac Arrest Syndrome Henry L. Green, MD, FACC Clinical Professor of Medicine, Wayne State University December 11, 2016 Introduction Advanced cardiac life support training focuses on restoration
Post-Cardiac Arrest Syndrome Henry L. Green, MD, FACC Clinical Professor of Medicine, Wayne State University December 11, 2016 Introduction Advanced cardiac life support training focuses on restoration
Simulation 15: 51 Year-Old Woman Undergoing Resuscitation
 Simulation 15: 51 Year-Old Woman Undergoing Resuscitation Flow Chart Flow Chart Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: DM Arrive after 5-6 min in-progress resuscitation 51 YO female; no pulse or BP, just received
Simulation 15: 51 Year-Old Woman Undergoing Resuscitation Flow Chart Flow Chart Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: DM Arrive after 5-6 min in-progress resuscitation 51 YO female; no pulse or BP, just received
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Stayin Alive: Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) Updated Guidelines
 Stayin Alive: Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) Updated Guidelines Margaret Oates, PharmD, BCPPS Pediatric Critical Care Specialist GSHP Summer Meeting July 16, 2016 Disclosures I have nothing to
Stayin Alive: Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) Updated Guidelines Margaret Oates, PharmD, BCPPS Pediatric Critical Care Specialist GSHP Summer Meeting July 16, 2016 Disclosures I have nothing to
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen, and aorta, as causes of shock, point-of-care ultrasonography in assessment of, 915 917 Abdominal compartment syndrome, trauma patient
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen, and aorta, as causes of shock, point-of-care ultrasonography in assessment of, 915 917 Abdominal compartment syndrome, trauma patient
Cardiogenic Shock in Acute MI
 Cardiogenic Shock in Acute MI Mark Sheldon, MD UNMH Interventional Cardiology Objectives Overview Treatment Definition Shock profiles Causes Medical Mechanical Illustrative case Questions? Revascularization
Cardiogenic Shock in Acute MI Mark Sheldon, MD UNMH Interventional Cardiology Objectives Overview Treatment Definition Shock profiles Causes Medical Mechanical Illustrative case Questions? Revascularization
No conflicts of interest
 Robert M. Rodriguez, MD FAAEM Clinical Professor of Medicine and Emergency Medicine, UCSF No conflicts of interest Major Points Most ICU patients start in ED Chain of critical care starting in field and
Robert M. Rodriguez, MD FAAEM Clinical Professor of Medicine and Emergency Medicine, UCSF No conflicts of interest Major Points Most ICU patients start in ED Chain of critical care starting in field and
Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket
 BLS BASICS: Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket facemask or AMBU bag) Adults call it in, start CPR, get AED Child CPR First, Phone call second
BLS BASICS: Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket facemask or AMBU bag) Adults call it in, start CPR, get AED Child CPR First, Phone call second
PALS NEW GUIDELINES 2010
 PALS NEW GUIDELINES 2010 DR WALEED ALAMRI PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY CONSULTANT FEB 24, 2011 Pediatric Basic Life Support Change in CPR Sequence (C-A-B Rather Than A-B-C) 2010 (New): Initiate CPR for infants
PALS NEW GUIDELINES 2010 DR WALEED ALAMRI PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY CONSULTANT FEB 24, 2011 Pediatric Basic Life Support Change in CPR Sequence (C-A-B Rather Than A-B-C) 2010 (New): Initiate CPR for infants
University of Wisconsin - Madison Cardiovascular Medicine Fellowship Program UW CICU Rotation Goals and Objectives
 Background: The field of critical care cardiology has evolved considerably over the past 2 decades. Contemporary critical care cardiology is increasingly focused on the management of patients with advanced
Background: The field of critical care cardiology has evolved considerably over the past 2 decades. Contemporary critical care cardiology is increasingly focused on the management of patients with advanced
PRACTICE GUIDELINE. DEFINITIONS: Mild head injury: Glasgow Coma Scale* (GCS) score Moderate head injury: GCS 9-12 Severe head injury: GCS 3-8
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
Targeted temperature management after post-anoxic brain insult: where do we stand?
 Targeted temperature management after post-anoxic brain insult: where do we stand? Alain Cariou Intensive Care Unit Cochin University Hospital Paris Descartes University INSERM U970 (France) COI Disclosure
Targeted temperature management after post-anoxic brain insult: where do we stand? Alain Cariou Intensive Care Unit Cochin University Hospital Paris Descartes University INSERM U970 (France) COI Disclosure
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING DEPARTMENT POLICY
 PS1070 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: ADMISSION/DISCHARGE CRITERIA: CARDIOVASCULAR INTENSIVE Job Title of Reviewer: Director, CVICU EFFECTIVE DATE: REVIEWED/REVISED DATE: POLICY
PS1070 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: ADMISSION/DISCHARGE CRITERIA: CARDIOVASCULAR INTENSIVE Job Title of Reviewer: Director, CVICU EFFECTIVE DATE: REVIEWED/REVISED DATE: POLICY
PALS Pulseless Arrest Algorithm.
 PALS Pulseless Arrest Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Bradycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Tachycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M
PALS Pulseless Arrest Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Bradycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Tachycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M
INFORMAL COPY WHEN PRINTED
 Doc Control Ref: TEM-003 Version 2.0 (Admin use only) Version no: (Admin use only) Effective Date: (Admin use only) 1. Principle Post-return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) management is an important
Doc Control Ref: TEM-003 Version 2.0 (Admin use only) Version no: (Admin use only) Effective Date: (Admin use only) 1. Principle Post-return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) management is an important
Sepsis: Management ANUPOL PANITCHOTE, MD. Division of Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Thailand
 Sepsis: Management ANUPOL PANITCHOTE, MD. Division of Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Thailand Vital signs Symptoms LAB BT > 38.3 or < 36 ๐ C HR > 90 bpm RR > 20 /min
Sepsis: Management ANUPOL PANITCHOTE, MD. Division of Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Thailand Vital signs Symptoms LAB BT > 38.3 or < 36 ๐ C HR > 90 bpm RR > 20 /min
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Update of CPR AHA Guidelines
 Update of CPR AHA Guidelines Donald Hal Shaffner Course objective is to have an updated understanding of the American Heart Association s treatment algorithms for the management of cardiac decompensation
Update of CPR AHA Guidelines Donald Hal Shaffner Course objective is to have an updated understanding of the American Heart Association s treatment algorithms for the management of cardiac decompensation
State of Florida Systemic Supportive Care Guidelines. Michael D. Weiss, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Neonatology
 State of Florida Systemic Supportive Care Guidelines Michael D. Weiss, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Neonatology I. FEN 1. What intravenous fluids should be initiated upon admission
State of Florida Systemic Supportive Care Guidelines Michael D. Weiss, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Neonatology I. FEN 1. What intravenous fluids should be initiated upon admission
MICHIGAN. State Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
Therapeutic Hypothermia after Resuscitated Cardiac Arrest
 Therapeutic Hypothermia after Resuscitated Cardiac Arrest The purpose of this protocol is to improve the neurologic outcomes of patients who have experienced cardiac arrest and have been successfully resuscitated.
Therapeutic Hypothermia after Resuscitated Cardiac Arrest The purpose of this protocol is to improve the neurologic outcomes of patients who have experienced cardiac arrest and have been successfully resuscitated.
AllinaHealthSystem 1
 : Definition End-organ hypoperfusion secondary to cardiac failure Venoarterial ECMO: Patient Selection Michael A. Samara, MD FACC Advanced Heart Failure, Cardiac Transplant & Mechanical Circulatory Support
: Definition End-organ hypoperfusion secondary to cardiac failure Venoarterial ECMO: Patient Selection Michael A. Samara, MD FACC Advanced Heart Failure, Cardiac Transplant & Mechanical Circulatory Support
New ACLS/Post Arrest Guidelines: For Everyone? Laurie Morrison, Li Ka Shing, Knowledge Institute, St Michael s Hospital, University of Toronto
 New ACLS/Post Arrest Guidelines: For Everyone? Laurie Morrison, Li Ka Shing, Knowledge Institute, St Michael s Hospital, University of Toronto COI Declaration Industry and ROC ALS Taskforce ILCOR Author
New ACLS/Post Arrest Guidelines: For Everyone? Laurie Morrison, Li Ka Shing, Knowledge Institute, St Michael s Hospital, University of Toronto COI Declaration Industry and ROC ALS Taskforce ILCOR Author
ILCOR, ARC & NZRC PAEDIATRIC RESUSCITATION RECOMMENDATIONS 2010
 ILCOR, ARC & NZRC PAEDIATRIC RESUSCITATION RECOMMENDATIONS 2010 Jim Tibballs Officer, RCH Convenor, Paediatric Sub-Committee, (ARC) ARC Paediatric Representative International Liaison Committee on (ILCOR)
ILCOR, ARC & NZRC PAEDIATRIC RESUSCITATION RECOMMENDATIONS 2010 Jim Tibballs Officer, RCH Convenor, Paediatric Sub-Committee, (ARC) ARC Paediatric Representative International Liaison Committee on (ILCOR)
Hypothermia After Cardiac Arrest: Where Are We Now?
 Hypothermia After Cardiac Arrest: Where Are We Now? David A. Pearson, MD, MS Associate Professor Director of Cardiac Arrest Resuscitation Carolinas HealthCare System Disclosures I have no financial interest,
Hypothermia After Cardiac Arrest: Where Are We Now? David A. Pearson, MD, MS Associate Professor Director of Cardiac Arrest Resuscitation Carolinas HealthCare System Disclosures I have no financial interest,
CPR What Works, What Doesn t
 Resuscitation 2017 ECMO and ECLS April 1, 2017 Corey M. Slovis, M.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Metro Nashville Fire Department Nashville International Airport Nashville, TN Circulation 2013;128:417-35
Resuscitation 2017 ECMO and ECLS April 1, 2017 Corey M. Slovis, M.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Metro Nashville Fire Department Nashville International Airport Nashville, TN Circulation 2013;128:417-35
Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University SHOCK Definition: Shock is a syndrome = inability to provide sufficient oxygenated blood to tissues. Oxygen
Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University SHOCK Definition: Shock is a syndrome = inability to provide sufficient oxygenated blood to tissues. Oxygen
ACLS/ACS Updates 2015
 ACLS/ACS Updates 2015 Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support by: Fareed Al Nozha, JBIM, ABIM, FKFSH&RC(Cardiology) Consultant Cardiologist Faculty, National CPR Committee, ACLS Program Head, SHA Dr Abdulhalim
ACLS/ACS Updates 2015 Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support by: Fareed Al Nozha, JBIM, ABIM, FKFSH&RC(Cardiology) Consultant Cardiologist Faculty, National CPR Committee, ACLS Program Head, SHA Dr Abdulhalim
Acute heart failure: ECMO Cardiology & Vascular Medicine 2012
 Acute heart failure: ECMO Cardiology & Vascular Medicine 2012 Lucia Jewbali cardiologist-intensivist 14 beds/8 ICU beds Acute coronary syndromes Heart failure/ Cardiogenic shock Post cardiotomy Heart
Acute heart failure: ECMO Cardiology & Vascular Medicine 2012 Lucia Jewbali cardiologist-intensivist 14 beds/8 ICU beds Acute coronary syndromes Heart failure/ Cardiogenic shock Post cardiotomy Heart
THE EVIDENCED BASED 2015 CPR GUIDELINES
 SAUDI HEART ASSOCIATION NATIONAL CPR COMMITTEE THE EVIDENCED BASED 2015 CPR GUIDELINES (EXECUTIVE SUMMARY) Page 1 FORWARD Since 2000, the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) has published
SAUDI HEART ASSOCIATION NATIONAL CPR COMMITTEE THE EVIDENCED BASED 2015 CPR GUIDELINES (EXECUTIVE SUMMARY) Page 1 FORWARD Since 2000, the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) has published
ECG Changes in Patients Treated with Mild Hypothermia after Cardio-pulmonary Resuscitation for Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest
 ECG Changes in Patients Treated with Mild Hypothermia after Cardio-pulmonary Resuscitation for Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest R. Schneider, S. Zimmermann, W.G. Daniel, S. Achenbach Department of Internal
ECG Changes in Patients Treated with Mild Hypothermia after Cardio-pulmonary Resuscitation for Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest R. Schneider, S. Zimmermann, W.G. Daniel, S. Achenbach Department of Internal
Critical Care Treatment Guidelines
 Critical Care Treatment Guidelines West Virginia Office of Emergency Medical Services CCT Guidelines CCT Guidelines TABLE OF CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgments Using the Guidelines INITIAL TREATMENT / UNIVERSAL
Critical Care Treatment Guidelines West Virginia Office of Emergency Medical Services CCT Guidelines CCT Guidelines TABLE OF CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgments Using the Guidelines INITIAL TREATMENT / UNIVERSAL
Case Scenario 3: Shock and Sepsis
 Name: Molly Boyle 1. Define the term shock (Lewis textbook): Shock is a syndrome characterized by decreased perfusion and impaired metabolism. Shock can have a number of causes that result in damage to
Name: Molly Boyle 1. Define the term shock (Lewis textbook): Shock is a syndrome characterized by decreased perfusion and impaired metabolism. Shock can have a number of causes that result in damage to
Advanced Cardiac Life Support ACLS
 Essential Medical Training, LLC Providing Quality, Professional Training Advanced Cardiac Life Support ACLS Course Study Guide and Agenda 772-781-9249 office 772-382-0607 fax Email: treasurecoastcpr@gmail.com
Essential Medical Training, LLC Providing Quality, Professional Training Advanced Cardiac Life Support ACLS Course Study Guide and Agenda 772-781-9249 office 772-382-0607 fax Email: treasurecoastcpr@gmail.com
Post Arrest Ventilation/Oxygenation Management
 Post Arrest Ventilation/Oxygenation Management Richard Branson MSc RRT Professor of Surgery University of Cincinnati Editor-In-Chief Respiratory Care 0 Presenter Disclosure Information Richard Branson
Post Arrest Ventilation/Oxygenation Management Richard Branson MSc RRT Professor of Surgery University of Cincinnati Editor-In-Chief Respiratory Care 0 Presenter Disclosure Information Richard Branson
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
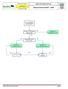 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Identifying Best Practice for Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest (OHCA) in the Hospital Setting
 Identifying Best Practice for Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest (OHCA) in the Hospital Setting Mary Ann Peberdy, MD, FACC, FAHA C. Kenneth Wright Professor of Cardiology & Professor of Emergency Medicine
Identifying Best Practice for Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest (OHCA) in the Hospital Setting Mary Ann Peberdy, MD, FACC, FAHA C. Kenneth Wright Professor of Cardiology & Professor of Emergency Medicine
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult
 Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Percutaneous Mechanical Circulatory Support Devices
 Percutaneous Mechanical Circulatory Support Devices Daniel Vazquez RN, RCIS Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES none CASE STUDY CASE STUDY 52 year old gentlemen Complaining of dyspnea
Percutaneous Mechanical Circulatory Support Devices Daniel Vazquez RN, RCIS Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES none CASE STUDY CASE STUDY 52 year old gentlemen Complaining of dyspnea
Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician
 Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician Sepsis Continuum 1 Sepsis Continuum SIRS = 2 or more clinical criteria, resulting in Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Sepsis = SIRS + proven/suspected
Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician Sepsis Continuum 1 Sepsis Continuum SIRS = 2 or more clinical criteria, resulting in Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Sepsis = SIRS + proven/suspected
The Pharmacology of Hypotension: Vasopressor Choices for HIE patients. Keliana O Mara, PharmD August 4, 2018
 The Pharmacology of Hypotension: Vasopressor Choices for HIE patients Keliana O Mara, PharmD August 4, 2018 Objectives Review the pathophysiology of hypotension in neonates Discuss the role of vasopressors
The Pharmacology of Hypotension: Vasopressor Choices for HIE patients Keliana O Mara, PharmD August 4, 2018 Objectives Review the pathophysiology of hypotension in neonates Discuss the role of vasopressors
