Original Article. Abstract. Introduction. Patients and Methods. evaluate the outcome of the operative intervention performed.
|
|
|
- Rudolf Greer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Ureterovaginal fistula - etiological factors and outcome Badar Murtaza, 1 Arshad Mahmood, 2 Waqar Azim Niaz, 3 Muhammad Akmal, 4 Hussain Ahmad, 5 Saira Saeed 6 Department of Urology, Armed Forces Institute of Urology, 1-5 Department of Gynaecology, Military Hospital, 6 Rawalpindi. Corresponding Author: Badar Murtaza. badar_murtaza@yahoo.com Abstract Objective: To assess the etiological factors and the outcome of ureterovaginal fistula in an urban setting. Methods: The observational study was conducted at the Armed Forces Institute of Urology, Military Hospital, Rawalpindi, from January 2009 to January All the patients of uretero-vaginal fistula at the centre were included on the basis of non-probability purposive sampling. The etiology, clinical presentation and the investigative procedures were recorded. The operative modality contemplated was noted and post-operative results were evaluated. The data was entered in a structured proforma and analysed for descriptive statistics using SPSS version Results: Seventeen cases of ureterovaginal fistula were recorded. Amongst these 10 (58.8%) were posthysterectomy, while 7 (41.1%) cases post-caesarean section. The emergency procedures performed by the residents/junior registrars contributed 12 (70.2%) of the cases. All these patients were treated surgically; 14 (82.3%) were managed with ureteroneocystostomy, 2 (11.7%) required Boari Flap reconstruction, and in psoas hitch was performed in 1 (5.8%) case. The time of intervention was 4-12 weeks (9.76 ± 2.223). Post-operatively, only 1 (5.8%) case had superficial wound infection and 1 (5.8%) urinary tract infection. All the patients remained dry with a follow-up period of 3-24 months (mean ± 6.879). Conclusion: Ureterovaginal fistula is one of the complications of emergency procedures, especially in the hands of inexperienced surgeons. Prompt diagnosis and surgical intervention produce excellent results. Intervention can be done safely as early as 4 weeks after the initiation of the condition. Keywords: Ureteric injury, Incontinence, Ureteroneocystostomy. (JPMA 62: 999; 2012) Introduction Urinary leakage following gynaecological or obstetric surgery is a dreaded complication due to the formation of urogenital fistula. It has significant morbidity, with social and psychological aspects aggravating the clinical situation. The commonest urogenital is the vesicovaginal fistula. Ureteral fistulas to the genital tract in the female may connect with the vagina or much less commonly with the fallopian tube or the uterus. 1 The incidence of iatrogenic ureteral injury during major gynaecological surgery is around 0.5% to 2.5%. 2,3 Risk factors for the development of ureteral fistulas also include endometriosis, obesity, pelvic inflammatory disease, radiation therapy and pelvic malignant disease. 4 As far as urogenital fistulas are concerned, significant amount of work has been done on vesicovaginal fistula, locally as well as internationally. However, local studies available on ureterovaginal fistula are limited, reflected by the extent of literature available on it. This study was conducted to assess the etiological factors of ureterovaginal fistula and to evaluate the outcome of the operative intervention performed. Patients and Methods The descriptive case series (observational) study was conducted at the Armed Forces Institute of Urology (AFIU), Military Hospital, Rawalpindi, from January 2009 to January Permission from the hospital's Ethical Committee was obtained prior to the study, and informed written consent was obtained from the patients before their enrollment in the study. The patients were selected by non-probability purposive sampling. All the patients with ureterovaginal fistula diagnosed and treated at the AFIU were included. Other cases of urogenital fistulas were excluded. Their clinical presentation and the investigative modalities were recorded. The operative procedure contemplated was noted and the post-operative results were evaluated. The diagnosis was made on the basis of the history of surgical intervention followed by urinary incontinence. The classical history of continuous urinary incontinence along with the normal act of micturition 999 J Pak Med Assoc
2 was seen in all the cases. The surgical procedure performed was evaluated in detail, considering it to be the main etiological factor behind fistula formation. Preliminary baseline investigations, including complete blood count, urinalysis, blood sugar random, serum urea/creatinine/electrolytes, electrocardiograph and chest radiograph, were carried out in all the cases. For diagnostic purposes, kidney, ureter, bladder (KUB) ultrasound and intravenous urography were performed. The ultrasonographic findings of hydronephrosis accompanied by the intravenous findings of hydronephroureter upto the lower end of the ureter were suggestive of the diagnosis. This was followed by vaginal speculum examination with cystoscopy. The vagina was examined to localise any leaking point, as easily seen in the vesicovaginal fistula. Cystoscopically the bladder was evaluated for evidence of vesicovaginal fistula or other bladder pathology. The cystoscopy was accompanied by ureteric catheterisation, to confirm the ureteric blockade and assess its level, as seen in the ureterovaginal fistula. Under the same general anaesthesia, the patients diagnosed with ureterovaginal fistula were placed in a supine position and exploration was conducted through the lower oblique (Gibson's incision/muscle cutting incision) approach. The 17 cases considered in our study showed an indurated/fibrotic area in the lower part of the ureter. The ureter proximal to it was separated and ureteroneocystostomy alone or with Boari flap/psoas hitch was performed over a double J stent. The stent was placed for 6 weeks in all the cases and subsequently removed under local anaesthesia. The patients were reviewed 2 weeks after surgery. Later, the followup was maintained with an interval of 3 and 6 months. The data was entered in a structured proforma. It was analysed on using SPSS All data were expressed as mean, standard deviation, frequency and percentages. Frequency and percentage were calculated for categorical variables like side predilection, causative factors and treatment modalities. Mean and standard deviations were calculated for quantitative data like age of the patient, level of obstruction, time of intervention and followup. Results The age of the 17 cases ranged from years (mean ). Ureterovaginal fistula was noted on the left side in 15 (88.2%) cases, while only two (11.7%) cases were found involving the right ureter. The majority of the cases (n=12; 70.2%) were noted after emergency procedures, performed by the residents/junior registrars. Besides, 10 (58.8%) cases Table: Etiological factors of ureterovaginal fistulas. S/No Causative Factors n 17 (%) 1 Post-hysterectomy 10 (58.8%) i. Abdominal hysterectomy for fibroids 3 ii. Abdominal hysterectomy for malignancy 2 iii. Cesarean hysterectomy 4 iv. Rupture uterus with SVD 1 2 Post-cesarean Section 7 (41.1%) SVD: Spontaneous vaginal delivery. were seen after emergency hysterectomy, and 7 (41.1%) were post-emergency caesarean section (Table). All were subjected to preliminary cystoscopy with ureteric catheterisation/assessment followed by definitive procedure. On ureteric catheterisation the level of blockade was seen 3-6 cm (3.82 ± 0.951) from the ureterovesical junction. In terms of treatment, 14 (82.3%) cases were managed with simple ureteroneocystostomy, using the extravesical Modified Lich-Gregoir technique, while 2 (11.7%) cases required Boari Flap reconstruction, and in one (5.8%) case psoas hitch was added to the ureteroneocystostomy. A double J stent was retained in all the cases. It was removed after 6 weeks under local anaesthesia. The time of intervention ranged from 4-12 weeks (mean 9.76 ± 2.223) after the primary surgery. Post operatively, all the patients remained dry, with no urinary incontinence. One (5.8%) case had superficial wound infection, which was treated by local wound management with antibiotics. One (5.8%) case had urinary tract infection, which responded to antibiotics. The patients were followed up regularly over a period of 3-24 months (mean ± 6.879). Discussion Ureterovaginal fistula predominantly occurs as a result of ureteral injury during gynaecological/obstetric surgery like abdominal/vaginal/radical hysterectomy, caesarean section or anterior colporrhaphy and other pelvic surgical procedures like vascular surgery, urological surgery, including retropubic bladder neck suspensions or colon surgery. This fistula can also result from locally advanced malignant disease, radiation therapy, pelvic trauma or chronic inflammatory diseases like actinomycosis. 4 Laparoscopically-assisted vaginal hysterectomy 5 and rarely transvaginal oocyte retrieval 6 have also been considered in the etiology. In cases of iatrogenic post-operative ureterovaginal fistula, ureteral injury usually occurs in the form of laceration, transaction, crushing, avulsion, suture ligation (partial/complete) or ischaemia due to the devitalisation of the ureteral blood supply. Pelvic adhesions due to Vol. 62, No. 10, October
3 repeated caesarean section, markedly enlarged uterus at the time of hysterectomy and massive bleeding obscuring the operative field could be considered as the main causes of ureteral injury The lower third of the ureter is usually affected, resulting in a fistulous communication with the vagina. The damage to the ureter occurs unintentionally, in an attempt by the operating surgeon to control active bleeding or in the process of clamping large segments of the tissues. The vulnerable sites of injury to the lower third of the ureter include the lateral edge of the uterosacral ligament, ventral to the uterine artery and then just lateral to the cervix and fornix of the vagina. Injury to the ureter can result in extravasation of urine, formation of a urinoma, followed by extension along the non-anatomic planes and eventual drainage through the vaginal incision or an ischaemic area of the vaginal cuff. 4 Although gynaecological surgery is considered to be the commonest cause of ureterovaginal fistula in the developed countries, the situation in the developing countries is quite different. The obstetric causes are usually considered to be the predominant ones. 7,9,10 A Nigerian study 9 reported caesarean sections (38%) and caesarean hysterectomies (25%) as the leading cause of ureterovaginal fistula, collectively reaching upto 63%, which was similar to our study where we had 70.5% cases due to the caesarean section/caesarean hysterectomies/spontanous vaginal delivery(svd) induced uterine rupture followed by hysterectomy. Interestingly, the cases in our study had been performed by the residents and the junior registrars as emergency cases in odd hours, where inadvertent injury occurred due to various manoeuvres conducted in controlling the haemorrhage during the surgery. An earlier study 11 reported 26 cases of ureterovaginal fistula, which were mainly due to unrecognized ureteral injuries during gynaecological procedures. The main presentation of the ureterovaginal fistula is urinary incontinence despite the normal act of micturition. The incontinence is usually constant developing 1 to 4 weeks after surgery. 12 Initially, the patient may experience flank pain, fever and nausea probably due to the urinoma or obstructed kidney, followed by incontinence. 4 A study 12 considered intravenous urography, retrograde pyelography and cystography essential for the diagnosis of ureterovaginal fistula. Another study 7 diagnosed UVF on the basis of simple procedures like ultrasonography with three swab test. In our study, the role of detailed history and examination followed by ultrasonography, intravenous urography and ureteric catheterisation were emphasised. We did not perform three swab test or retrograde pyelography. Evidence of hydronephroureter with obstructed lower ureter on intravenous urography and the presence of constant urinary incontinence along with the normal act of micturition strongly suggested the ureterovaginal fistula. The presence of periureteral flare due to the urinary extravasation may be seen occasionally on intravenous urography as well. However, the debate lies in the probability of upper tract appearing normal on intravenous urography in cases of large-sized fistulas, but in such cases the urine could be seen spilling into the vagina on the lateral films, before the post-void image. The retrograde pyelogram may be useful to localise the level of obstruction and the fistula as well. A study 1 considered the retrograde pyelography as the single best test for diagnosis of the ureteral injury. Anotehr study 13 emphasised on the role of vaginogram in the detection of ureterovaginal fistula. However, we performed simple ureteric catheterisation, to assess the level of obstruction followed by the exploration during the same anaesthesia. The cystogram may be useful to exclude a coexistent vesicovaginal fistula. Computed tomography urography also has a definitive role in the diagnosis of ureterovaginal fistula. Differentiating a ureterovaginal fistula from a ureterouterine fistula may become difficult occasionally. The history of paradoxical incontinence seen in the latter condition along with the findings of computed tomography intravenous urography, 14 may prove helpful in reaching a diagnosis. However, the rarity of ureterouterine fistula poses a diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma. 15 Intra-operatively, the ureteric involvement was confirmed by noting extensive fibrous adhesions surrounding the distal portion of the ureter and extending into the perivesicular space as well. In our study we noted left ureteral fistula in 88.2% as compared to 11.7% on the right side. An earlier study 16 also reported left-sided predominance. This is probably due to the fact that the operating gynaecologist usually stands on the right side of the patient; the left-sided bleeding is controlled by the clamps under obscured vision. The main aim of the treatment of ureterovaginal fistula is the resolution of the urinary leakage, prevention of urosepsis and preservation of renal function. In our study, we performed extravesical Modified Lich-Gregoir ureteroneocystostomy in majority of cases (82.3%). However, a few required adjuvant procedures (17.6%) like psoas hitch or Boari flap. The procedure was performed as early as 4 weeks. There was no recurrence in any of the cases. In fact, 1001 J Pak Med Assoc
4 prompt diagnosis and appropriate surgical intervention had excellent results. The intervention need not be delayed as it used to be recommended previously. More recent literature suggests that early repair is preferred and is not associated with an increase in morbidity or higher failure rates. 2 One study 16 reported open surgical repair performed safely and as early as 12 days. Another study 17 also considered modified Lich-Gregoir surgical procedure as a simple, successful and quick method of treatment with no recurrence and minimal complications. It also recommended bilateral ureteral catheterisation prior to difficult female pelvic and gynaecological surgery to prevent such a disaster. Others have recommended 10 psoas hitch as the procedure of choice in ureterovaginal fistula cure and considered prevention to be the most efficient treatment, while still others 8 considered ureteroneocystostomy alone as the most effective method. Like our study, others have reported ureterovaginal fistulas successfully treated with ureteroneocystostomy alone in majority of cases. 16 They performed adjuvant procedures in 37.5% of cases. In cases of combined fistulas of ureterovaginal and vesicovaginal fistula, the management may require bladder reconstruction. 18 Bilateral ureterovaginal fistulas have been reported as well. 19 In cases of recurrent vesicovaginal fistula with bilateral ureterovaginal fistulas at times urinary diversion is recommended. We did not encounter either of these cases in our study. Early drainage of the affected upper urinary tract is essential, 20 as the partial ureteral obstruction is almost always present. Even recommendations have been made that, provided the open surgical procedure is not being considered immediately, an attempt should be made for ureteral stenting or percutaneous nephrostomy. 21 Spontaneous resolution 22 has been seen in patients with ureteral continuity and a normal appearing ureter beyond the fistula. Endoscopic management with ureteral stenting can promote closure of the fistula in some cases which are detected early. Percutaneous antegrade double J stenting with or without balloon dilatation has also been considered useful. 23 Complications associated with ureterovaginal fistula repair include urinary extravasation and ureteral stricture formation. Persistent urinary leak can be treated with percutaneous nephrostomy drainage, ureteral stent(s), and/or Foley catheter drainage. For short ureteral strictures, minimally invasive endoscopic treatments can be used. In our study we had only one case of wound infection and one of urinary tract infection, which responded to the treatment. All the patients remained dry with no recurrence. Conclusion Ureterovaginal fistula commonly occurs in emergency procedures conducted by the residents/junior registrars, including the emergency caesarean section and emergency hysterectomies. At least 3-6 months rotation in urology should be mandatory for residents in gynaecology and obstetrics. Planned hysterectomy for benign and malignant uterine pathologies are relatively less common. Definitive surgical procedure has excellent results for ureterovaginal fistula with no recurrence and minimal complications. The operative intervention can be done safely as early as 4 weeks. In planned cases of abdominal hysterectomy for complex pelvic/ uterine-ovarian masses, pre-operative bilateral double J ureteric stenting can be useful in avoiding the ureteric injury. Acknowledgement This article is dedicated to the contributions of Dr Muhammad Ashraf Sharif in the field of medical writing. He was a consultant histopathologist, aged 34 years, who died in a road accident on May 9, 2011 near Karak, as he was travelling to Islamabad to attend the funeral of his father. References 1. Billemeyer BR, Nygaard IE, Kreder KJ. Ureterouterine and vesicoureterovaginal fistulas as a complication of cesarean section. J Urol 2001; 165: Payne C. Ureteral injuries in the female: Fistulas and obstruction. In: Raz S. Female Urology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders 1996; Gilmour DT, Dwyer PL, Carey MP. Lower urinary tract injury during gynecologic surgery and its detection by intraoperative Cystoscopy. Obstet Gynecol 1999; 94: Rovner ES. Urinary tract fistula. In: Wein JA. Campbell-Walsh Urology. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier 2007; Waihenya CG. Ureterovaginal fistula following laparoscopic assisted vaginal hysterectomy: case report. East Afr Med J 2006; 83: Von Eye Corleta H, Moretto M, D'Avila AM, Berger M. Immediate ureterovaginal fistula secondary to oocyte retrieval: a case report. Fertil Steril 2008; 90: Randawa A, Khalid L, Abbas A. Diagnosis and management of ureterovaginal fistula in a resource-constrained setting: experience at a district hospital in northern Nigeria. Libyan J Med 2009; 4: Akman RY, Sargin S, Ozdemir G, Yazicioglu A, Cetin S. Vesicovaginal and ureterovaginal fistulas: a review of 39 cases. Int Urol Nephrol 1999; 31: Ozumba BC, Attah CA. Ureteral injury in obstetric and gynecologic operations in Nigeria. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1991; 36: Bennani S, Joual A, El Mrini M, Benjelloun S. Ureterovaginal fistulas. A report of 17 cases. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1996; 25: Nawaz H, Khan M, Tareen FM, Khan S. Retrospective study of 213 cases of female urogenital fistulae at the Department of Urology & Transplantation Civil Hospital Quetta, Pakistan. J Pak Med Assoc 2010; 60: Mandal AK, Sharma SK, Vaidyanathan S, Goswani AK. Ureterovaginal fistula: Summary of 18 years experience. Br J Urol 1990; 65: Macalusco Jr JN, Appell RA, Sullivan JW. Ureterovaginal fistula detected by vaginogram. JAMA 1981; 246: Lanary KA, Hashim H, Iaconou J. Ureterouterine fistula post caesarean Vol. 62, No. 10, October
5 section: a case report. Cases Journal 2008; 1: 253doi: / Nabi G, Hemal AK, Kumar M, Ansari MS, Dorairajan LN. Diagnosis and management of post-cesarean ureterouterine fistulae. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 2000; 11: Hanif MS, Saeed K, Sheikh MA. Surgical management of genitourinary fistula. J Pak Med Assoc 2005; 55: Shaikh R, Abro H, Shaikh F, Shaikh NA, Jokhio AH. Management of ureterovaginal fistula. J Surg Pak 2006; 11: Gan E, Li MK. Repair of complex ureterovaginal and vesicovaginal fistulas with ileal cystoplasty and ureteric reimplantation into an antireflux ileal nipple valve: a case report. An Acad Med Singapore 1998; 27: Shaw MB, Tomes M, Rix DA, Dorkin DJ, Murthy LN, Pickard RS. The management of bilateral ureteric injury following radical hysterectomy. Adv Urol 2008; 52: Gerber GS, Schoenberg HW. Female urinary tract fistulas. J Urol 1993; 149: Kostakopoulos A, Deliveliotis C, Louras G. Early repair of injury to the ureter or bladder after hysterectomy. Int Urol Nephrol 1998; 30: Hernandez AP, Lumbreras PE, Zorzo OH, Garcia JG, Canada de Arriba F, Herrero FP et al. Spontaneous resolution of ureterovaginal fistula. Arch Esp Urol 2011; 64: Ustunsoz B, Ugurel S, Duru NK, Ozgok Y, Ustunsoz A. Percutaneous management of ureteral injuries that are diagnosed late after cesarean section. Korean J Radiol 2008; 9: J Pak Med Assoc
SciFed Journal of Public Health. Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature
 SciFed Journal of Public Health Case Report Open Access Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature * Yasin Idweini * Chairperson of Urology Department
SciFed Journal of Public Health Case Report Open Access Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature * Yasin Idweini * Chairperson of Urology Department
Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018
 Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018 Bladder Anatomy Ureter Anatomy Areas of Injury Bladder: Posterior bladder wall above trigone Ureter Crosses beneath uterine vessels At pelvic brim when ligating
Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018 Bladder Anatomy Ureter Anatomy Areas of Injury Bladder: Posterior bladder wall above trigone Ureter Crosses beneath uterine vessels At pelvic brim when ligating
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 19 CBULP 2011 044 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 19 CBULP 2011 044 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
A New Dimension in Vesicovaginal Fistula Management: An 8-year Experience at Ramathibodi Hospital
 Original Article A New Dimension in Vesicovaginal Fistula Management: An 8-year Experience at Ramathibodi Hospital Wachira Kochakarn and Wipaporn Pummangura, 1 Division of Urology, Department of Surgery,
Original Article A New Dimension in Vesicovaginal Fistula Management: An 8-year Experience at Ramathibodi Hospital Wachira Kochakarn and Wipaporn Pummangura, 1 Division of Urology, Department of Surgery,
Research Article Transvesicoscopic Repair of Vesicovaginal Fistula
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2010, Article ID 760348, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/760348 Research Article Transvesicoscopic Repair of Vesicovaginal Fistula R. B. Nerli and Mallikarjun Reddy
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2010, Article ID 760348, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/760348 Research Article Transvesicoscopic Repair of Vesicovaginal Fistula R. B. Nerli and Mallikarjun Reddy
Iatrogenic Ureteral Injuries in Non Urological Surgeries: An Institutional Experience
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 29-33 www.iosrjournals.org Iatrogenic Ureteral Injuries in Non Urological
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 29-33 www.iosrjournals.org Iatrogenic Ureteral Injuries in Non Urological
Interventional management of postoperative ureteric complications after pelvic surgery
 Interventional management of postoperative ureteric complications after pelvic surgery Poster No.: C-0169 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Tabashy, A. Hamed, S. El-Sebai; Cairo/EG
Interventional management of postoperative ureteric complications after pelvic surgery Poster No.: C-0169 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Tabashy, A. Hamed, S. El-Sebai; Cairo/EG
Ureteral Injury in Gynecologic Surgery: A 5-Year Review in A Community Hospital
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/./kju.22.5.2.2 Transplantation Ureteral Injury in Gynecologic Surgery: A 5-Year Review in A Community Hospital Jeong Hyun Park, Jong Wook Park, Kanghyon Song, Moon Ki
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/./kju.22.5.2.2 Transplantation Ureteral Injury in Gynecologic Surgery: A 5-Year Review in A Community Hospital Jeong Hyun Park, Jong Wook Park, Kanghyon Song, Moon Ki
THE operation of reimplantation of the ureter into the bladder has undergone
 REIMPLANTATION OF THE URETER INTO THE BLADDER J. G. WARDEN, M.D., and C. C. HIGGINS, M.D. Department of Urology THE operation of reimplantation of the ureter into the bladder has undergone a stormy course
REIMPLANTATION OF THE URETER INTO THE BLADDER J. G. WARDEN, M.D., and C. C. HIGGINS, M.D. Department of Urology THE operation of reimplantation of the ureter into the bladder has undergone a stormy course
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation
 Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
Canadian Undergraduate Urology Curriculum (CanUUC): Genitourinary Trauma. Last reviewed June 2014
 Canadian Undergraduate Urology Curriculum (CanUUC): Genitourinary Trauma Last reviewed June 2014 Session Objectives 1. Recognize hematuria as the cardinal symptom of urinary tract trauma. 1. Outline the
Canadian Undergraduate Urology Curriculum (CanUUC): Genitourinary Trauma Last reviewed June 2014 Session Objectives 1. Recognize hematuria as the cardinal symptom of urinary tract trauma. 1. Outline the
Clinical aspects in urogenital injuries
 Clinical aspects in urogenital injuries Rolf Wahlqvist Oslo Urological University Clinic Aker University Hospital Nordic Rad.2008 1 Urogenital injuries in trauma patients Renal injury Ureteral injury (infrequent/iatrogenic)
Clinical aspects in urogenital injuries Rolf Wahlqvist Oslo Urological University Clinic Aker University Hospital Nordic Rad.2008 1 Urogenital injuries in trauma patients Renal injury Ureteral injury (infrequent/iatrogenic)
Latrogenic Injuries of Renal Pelvis and Ureter Following Open Surgery for Urolithiasis
 Latrogenic Injuries of Renal Pelvis and Ureter Following Open Surgery for Urolithiasis Abstract M. Naeem,K. Anwar ( Department of Urology, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Objective:
Latrogenic Injuries of Renal Pelvis and Ureter Following Open Surgery for Urolithiasis Abstract M. Naeem,K. Anwar ( Department of Urology, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Objective:
5 DIAGNOSIS. History taking
 5 DIAGNOSIS All of the photographs in Chapter 4 were taken in theatre before operation. This chapter deals with how one can recognize the type of fistula by history taking and examination. (Note that the
5 DIAGNOSIS All of the photographs in Chapter 4 were taken in theatre before operation. This chapter deals with how one can recognize the type of fistula by history taking and examination. (Note that the
LESIONS OF THE URINARY ORGANS DURING ABDOMINAL AND VAGINAL HYSTERECTOMY
 ESTRATTO DA: UROGYNAECOLOGIA INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL 2000; 15; 2 : 19-2001 Urogynaecologia I. J. LESIONS OF THE URINARY ORGANS DURING ABDOMINAL AND VAGINAL HYSTERECTOMY F. LEANZA, G. BIANCA, G. CINQUERRUI,
ESTRATTO DA: UROGYNAECOLOGIA INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL 2000; 15; 2 : 19-2001 Urogynaecologia I. J. LESIONS OF THE URINARY ORGANS DURING ABDOMINAL AND VAGINAL HYSTERECTOMY F. LEANZA, G. BIANCA, G. CINQUERRUI,
Prevention of Surgical Injuries in Gynecology
 in Gynecology John K. Chan, M.D. Division of Gynecologic Oncology Overview Review anatomy, etiology, intraoperative, postoperative management, prevention of injuries to: 1. Urinary tract 2. Gastrointestinal
in Gynecology John K. Chan, M.D. Division of Gynecologic Oncology Overview Review anatomy, etiology, intraoperative, postoperative management, prevention of injuries to: 1. Urinary tract 2. Gastrointestinal
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series. Urological Trauma
 UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series Urological Trauma Disclaimer: This is a lot of information to cover and we are unlikely to cover it all today These slides are to be utilized for your
UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series Urological Trauma Disclaimer: This is a lot of information to cover and we are unlikely to cover it all today These slides are to be utilized for your
A Case Report Hydronephrosis and Hydrodureter due to Ureteral Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis mimic Ureteral Stricture Suryamanggala SI 1, Satria ML 2
 A Case Report Hydronephrosis and Hydrodureter due to Ureteral Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis mimic Ureteral Stricture Suryamanggala SI 1, Satria ML 2 1 Departement of Obstetric and Gynecology Faculty
A Case Report Hydronephrosis and Hydrodureter due to Ureteral Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis mimic Ureteral Stricture Suryamanggala SI 1, Satria ML 2 1 Departement of Obstetric and Gynecology Faculty
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet
 Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
West Yorkshire Major Trauma Network Clinical Guidelines 2015
 WYMTN: Pelvic fracture with urogenital trauma KEY RECOMMENDATIONS 1. During the initial exploratory survey / secondary survey, a. The external urethral meatus and the transurethral bladder catheter (if
WYMTN: Pelvic fracture with urogenital trauma KEY RECOMMENDATIONS 1. During the initial exploratory survey / secondary survey, a. The external urethral meatus and the transurethral bladder catheter (if
Pan African Urological Surgeons Association. African Journal of Urology.
 African Journal of Urology (2012) 18, 175 179 Pan African Urological Surgeons Association African Journal of Urology www.ees.elsevier.com/afju www.sciencedirect.com Martius flap and anterior vaginal wall
African Journal of Urology (2012) 18, 175 179 Pan African Urological Surgeons Association African Journal of Urology www.ees.elsevier.com/afju www.sciencedirect.com Martius flap and anterior vaginal wall
Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux
 Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux Suzi DEMIRBAG, MD Department of Pediatric Surgery, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, TURKEY Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux Suzi DEMIRBAG, MD Department of Pediatric Surgery, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, TURKEY Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
Uroradiology For Medical Students
 Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Recent advances have improved the
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUES BY NEERAJ KOHLI, MD, MBA, and JOHN R. MIKLOS, MD Meeting the challenge of vesicovaginal fistula repair: Conservative and surgical measures A number of simple adjustments to technique
SURGICAL TECHNIQUES BY NEERAJ KOHLI, MD, MBA, and JOHN R. MIKLOS, MD Meeting the challenge of vesicovaginal fistula repair: Conservative and surgical measures A number of simple adjustments to technique
11 th Dynasty- Egyptian mummies : Queen Henhenit circa 2050 BC wife of King Mentuhotep II VVF 550 BC- Ancient Egyptian documents (papyri)
 February 2019 11 th Dynasty- Egyptian mummies : Queen Henhenit circa 2050 BC wife of King Mentuhotep II VVF 550 BC- Ancient Egyptian documents (papyri) Prescription for a woman whose urine is in an irksome
February 2019 11 th Dynasty- Egyptian mummies : Queen Henhenit circa 2050 BC wife of King Mentuhotep II VVF 550 BC- Ancient Egyptian documents (papyri) Prescription for a woman whose urine is in an irksome
Cervical Cancer 3/25/2019. Abnormal vaginal bleeding
 Cervical Cancer Abnormal vaginal bleeding Postcoital, intermenstrual or postmenopausal Vaginal discharge Pelvic pain or pressure Asymptomatic In most patients who are not sexually active due to symptoms
Cervical Cancer Abnormal vaginal bleeding Postcoital, intermenstrual or postmenopausal Vaginal discharge Pelvic pain or pressure Asymptomatic In most patients who are not sexually active due to symptoms
ENDOSCOPIC URETERECTOMY DURING NEPHROURETERECTOMY FOR UPPER URINARY TRACT TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA
 ENDOSCOPIC URETERECTOMY DURING NEPHROURETERECTOMY FOR UPPER URINARY TRACT TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA Il. Saltirov, Ts. Petkov, G. Georgiev, K.Petkova Department of Urology and Nephrology, Military Medical
ENDOSCOPIC URETERECTOMY DURING NEPHROURETERECTOMY FOR UPPER URINARY TRACT TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA Il. Saltirov, Ts. Petkov, G. Georgiev, K.Petkova Department of Urology and Nephrology, Military Medical
Morbidity Audit and Logbook Tool SNOMED Board Reporting Terms for SET and IMG Urology ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT
 ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
M-AFRAKHTEH. MD OCT.2017 SHOHADA HOSPITAL TAJRISH
 Unrestricted M-AFRAKHTEH. MD OCT.2017 SHOHADA HOSPITAL TAJRISH Patients at imminent risk of exsanguination Manual aortic compression Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta Uterine tourniquet
Unrestricted M-AFRAKHTEH. MD OCT.2017 SHOHADA HOSPITAL TAJRISH Patients at imminent risk of exsanguination Manual aortic compression Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta Uterine tourniquet
Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (61)
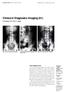 Singapore Med J 2001 Vol 42(5) : 233-237 M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (61) K B J Sheah, S K H Yip, V T Joseph Fig. 1a Control abdominal radiograph. Fig. 1b Coned oblique
Singapore Med J 2001 Vol 42(5) : 233-237 M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (61) K B J Sheah, S K H Yip, V T Joseph Fig. 1a Control abdominal radiograph. Fig. 1b Coned oblique
Avoiding and Managing Urologic Injury
 Avoiding and Managing Urologic Injury Jubilee Brown, MD Professor & Associate Director, Gynecologic Oncology Levine Cancer Institute at the Carolinas HealthCare System Charlotte, North Carolina 1 No relevant
Avoiding and Managing Urologic Injury Jubilee Brown, MD Professor & Associate Director, Gynecologic Oncology Levine Cancer Institute at the Carolinas HealthCare System Charlotte, North Carolina 1 No relevant
Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان
 4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse
 Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse Genital(utero-vaginal )prolapse is extremely common, with an estimated 11% of women undergoing at least one operation for this condition. Definition: A
Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse Genital(utero-vaginal )prolapse is extremely common, with an estimated 11% of women undergoing at least one operation for this condition. Definition: A
THE LOWER END OF THE URETER*
 Vol.7, No.2. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL 86 June, 1966. THE LOWER END OF THE URETER* By Laurence F. Tinckler, M.D., Ch. M., F.R.C.S., D.T.M. & H. (Professor of Surgery. University of Singapore) The lower
Vol.7, No.2. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL 86 June, 1966. THE LOWER END OF THE URETER* By Laurence F. Tinckler, M.D., Ch. M., F.R.C.S., D.T.M. & H. (Professor of Surgery. University of Singapore) The lower
Alimited degree of vaginal discharge is expected
 ADULT UROLOGY POSTHYSTERECTOMY VAGINAL CUFF FISTULA: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF AN UNUSUAL CAUSE OF INCONTINENCE DAVID A. GINSBERG, ERIC S. ROVNER, AND SHLOMO RAZ ABSTRACT Objectives. Connection between
ADULT UROLOGY POSTHYSTERECTOMY VAGINAL CUFF FISTULA: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF AN UNUSUAL CAUSE OF INCONTINENCE DAVID A. GINSBERG, ERIC S. ROVNER, AND SHLOMO RAZ ABSTRACT Objectives. Connection between
Original Article. Abstract. Introduction
 Original Article Surgical Management of Genitourinary Fistula Muhammad Shahbaz Hanif, Khalid Saeed, Masood Ahmed Sheikh Department of Urology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre, Karachi. Abstract Objective:
Original Article Surgical Management of Genitourinary Fistula Muhammad Shahbaz Hanif, Khalid Saeed, Masood Ahmed Sheikh Department of Urology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre, Karachi. Abstract Objective:
Female Urology. The Results of Grade IV Cystocele Repair Using Mesh. Introduction ZARGAR MA, EMAMI M*, ZARGAR K, JAMSHIDI M
 Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 1, No. 4, 263-267 Autumn 2004 Printed in IRAN Female Urology The Results of Grade IV Cystocele Repair Using Mesh ZARGAR MA, EMAMI M*, ZARGAR K, JAMSHIDI M Department of Urology,
Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 1, No. 4, 263-267 Autumn 2004 Printed in IRAN Female Urology The Results of Grade IV Cystocele Repair Using Mesh ZARGAR MA, EMAMI M*, ZARGAR K, JAMSHIDI M Department of Urology,
Unlocking the Challenges of Diagnosing Fistulas in the Pelvis
 Unlocking the Challenges of Diagnosing Fistulas in the Pelvis Lucy Chow, MD & Simin Bahrami, MD Department of Radiological Sciences David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Goals and Objectives Understand
Unlocking the Challenges of Diagnosing Fistulas in the Pelvis Lucy Chow, MD & Simin Bahrami, MD Department of Radiological Sciences David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Goals and Objectives Understand
Genitourinary. Common Clinical Scenarios Protocoling Module. Patty Ojeda & Mariam Shehata
 The following training module was developed as a quality improvement project to serve as an educational tool for junior radiology residents. The following diagnostic radiology protocoling modules were
The following training module was developed as a quality improvement project to serve as an educational tool for junior radiology residents. The following diagnostic radiology protocoling modules were
An Unexpected Cause Of Spontaneous Perinephric Urinoma: A Case Report. L Chandrasekharan, T Abdl Ghaffar, M Venkatramana, K Mammigatty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 An Unexpected Cause Of Spontaneous Perinephric Urinoma: A Case Report L Chandrasekharan, T Abdl Ghaffar, M Venkatramana, K Mammigatty Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 An Unexpected Cause Of Spontaneous Perinephric Urinoma: A Case Report L Chandrasekharan, T Abdl Ghaffar, M Venkatramana, K Mammigatty Citation
The circumferential obstetric fistula: characteristics, management and outcomes
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2007.01329.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Short communication The circumferential obstetric fistula: characteristics, management and outcomes A Browning Barhirdar Hamlin Fistula
DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2007.01329.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Short communication The circumferential obstetric fistula: characteristics, management and outcomes A Browning Barhirdar Hamlin Fistula
 1 2 Infertile women are seven to ten times more likely to have endometriosis than their fertile 3 The mechanism by which endometriosis develops is unknown Theories for the histogenesis of endometriosis
1 2 Infertile women are seven to ten times more likely to have endometriosis than their fertile 3 The mechanism by which endometriosis develops is unknown Theories for the histogenesis of endometriosis
Introduction/Learning Objectives. Incontinence: Natural History. Course Outline 10/14/2016. Urinary Incontinence: Conservative Measures
 Management of Urinary Complications after Prostatectomy Course Faculty: Introduction/Learning Objectives Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Associate Attending Urologist Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Management of Urinary Complications after Prostatectomy Course Faculty: Introduction/Learning Objectives Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Associate Attending Urologist Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Role of imaging in evaluation of genitourinary i trauma Spectrum of GU injuries Relevance of imaging findings in determining management Focus on MDCT
 Genitourinary Tract Injuries 6 th Nordic Course Scott D. Steenburg, MD Assistant Professor University of Maryland Department of Radiology Division of Trauma and Emergency Radiology R Adams Cowley Shock
Genitourinary Tract Injuries 6 th Nordic Course Scott D. Steenburg, MD Assistant Professor University of Maryland Department of Radiology Division of Trauma and Emergency Radiology R Adams Cowley Shock
FIG The inferior and posterior peritoneal reflection is easily
 PSOAS HITCH, BOARI FLAP, AND COMBINATION OF PSOAS 7 HITCH AND BOARI FLAP The psoas hitch procedure, Boari flap, and transureteroureterostomy are useful operative procedures for reestablishing continuity
PSOAS HITCH, BOARI FLAP, AND COMBINATION OF PSOAS 7 HITCH AND BOARI FLAP The psoas hitch procedure, Boari flap, and transureteroureterostomy are useful operative procedures for reestablishing continuity
Pelvic Pain. What you need to know. 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone Fax
 Pelvic Pain What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 PELVIC PAIN This is a common problem and most women experience some form
Pelvic Pain What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 PELVIC PAIN This is a common problem and most women experience some form
Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence
 Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Ureterallnjuries in an O bstetric and GynaecologyTeaching Hospital
 -- ---- ---------------------------------------------------- Ureterallnjuries in an O bstetric and GynaecologyTeaching Hospital C T Yeong, MRCOG, T t W tim, MBBS, K H Tan, MRCOG, Department of Reproductive
-- ---- ---------------------------------------------------- Ureterallnjuries in an O bstetric and GynaecologyTeaching Hospital C T Yeong, MRCOG, T t W tim, MBBS, K H Tan, MRCOG, Department of Reproductive
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Renal Trauma: Management Options
 Renal Trauma: Management Options Immediate surgical repair Nephrectomy Conservative management Alonso RC et al. Kidney in Danger: CT Findings of Blunt and Penetrating Renal Trauma. RadioGraphics 2009;
Renal Trauma: Management Options Immediate surgical repair Nephrectomy Conservative management Alonso RC et al. Kidney in Danger: CT Findings of Blunt and Penetrating Renal Trauma. RadioGraphics 2009;
Complication of long indwelling urinary catheter and stent COMPLICATION OF LONG INDWELLING URINARY CATHETER AND STENT
 151 COMPLICATION OF LONG INDWELLING URINARY CATHETER AND STENT Jain A 1 *, Srivastava R 1, Prasad A 1, Marwah K 1 1. Department of surgery, Subharti medical college, Meerut U.P. India Correspondence: Dr.
151 COMPLICATION OF LONG INDWELLING URINARY CATHETER AND STENT Jain A 1 *, Srivastava R 1, Prasad A 1, Marwah K 1 1. Department of surgery, Subharti medical college, Meerut U.P. India Correspondence: Dr.
Outcome of Obstructive Uropathy After Pelvic Irradiation in Patients with Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix
 631 Outcome of Obstructive Uropathy After Pelvic Irradiation in Patients with Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix K O Lau,*MBBS, FRCS, T N Hia,**MBBS, C Cheng,***FAMS, FRCS, M Med (Surg), S K Tay****FAMS,
631 Outcome of Obstructive Uropathy After Pelvic Irradiation in Patients with Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix K O Lau,*MBBS, FRCS, T N Hia,**MBBS, C Cheng,***FAMS, FRCS, M Med (Surg), S K Tay****FAMS,
Procedure related complications and how to prevent them
 Procedure related complications and how to prevent them Rama Jayanthi, M.D. Section of Urology Nationwide Children s Hospital The Ohio State University Retroperitoneoscopic surgery Inadvertent peritoneal
Procedure related complications and how to prevent them Rama Jayanthi, M.D. Section of Urology Nationwide Children s Hospital The Ohio State University Retroperitoneoscopic surgery Inadvertent peritoneal
GUIDELINEs ON UROLOGICAL TRAUMA
 GUIDELINEs ON UROLOGICAL TRAUMA (Text update March 2009) N. Djakovic, Th. Lynch, L. Martínez-Piñeiro, Y. Mor, E. Plas, E. Serafetinides, L. Turkeri, R.A. Santucci, M. Hohenfellner Eur Urol 2005;47(1):1-15
GUIDELINEs ON UROLOGICAL TRAUMA (Text update March 2009) N. Djakovic, Th. Lynch, L. Martínez-Piñeiro, Y. Mor, E. Plas, E. Serafetinides, L. Turkeri, R.A. Santucci, M. Hohenfellner Eur Urol 2005;47(1):1-15
Urological Complications in Gynecological Surgery and Radiotherapy
 Urological Complications in Gynecological Surgery and Radiotherapy Contributions to Gynecology and Obstetrics Vol. 11 Series Editor P. J. Keller, Zürich ]11Wξ]1 Contributions to S. Karger Basel München
Urological Complications in Gynecological Surgery and Radiotherapy Contributions to Gynecology and Obstetrics Vol. 11 Series Editor P. J. Keller, Zürich ]11Wξ]1 Contributions to S. Karger Basel München
Marietta Mahendeka, M.D. Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Bugando Medical Centre Tanzania. Tutor: Dr Luc de Bernis, WHO
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE MANAGEMENT OF VESICO AND/OR RECTO-VAGINAL FISTULAE AT BUGANDO MEDICAL CENTRE, MWANZA, TANZANIA, EAST AFRICA: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Marietta Mahendeka, M.D. Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE MANAGEMENT OF VESICO AND/OR RECTO-VAGINAL FISTULAE AT BUGANDO MEDICAL CENTRE, MWANZA, TANZANIA, EAST AFRICA: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Marietta Mahendeka, M.D. Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
Retrospective study of 213 cases of female urogenital fistulae at the Department of Urology & Transplantation Civil Hospital Quetta, Pakistan
 Original Article Retrospective study of 213 cases of female urogenital fistulae at the Department of Urology & Transplantation Civil Hospital Quetta, Pakistan Haq Nawaz, Masha Khan, Faiz Muhammed Tareen,
Original Article Retrospective study of 213 cases of female urogenital fistulae at the Department of Urology & Transplantation Civil Hospital Quetta, Pakistan Haq Nawaz, Masha Khan, Faiz Muhammed Tareen,
Retroperitoneoscopic Transureteroureterostomy with Cutaneous Ureterostomy to Salvage Failed Ileal Conduit Urinary Diversion
 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Study of the Month Retroperitoneoscopic Transureteroureterostomy with Cutaneous Ureterostomy to Salvage Failed Ileal Conduit
available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Study of the Month Retroperitoneoscopic Transureteroureterostomy with Cutaneous Ureterostomy to Salvage Failed Ileal Conduit
GUIDELINEs ON UROLOGICAL TRAUMA
 GUIDELINEs ON UROLOGICAL TRAUMA (Text update March 2009) N. Djakovic, Th. Lynch, L. Martínez-Piñeiro, Y. Mor, E. Plas, E. Serafetinides, L. Turkeri, R.A. Santucci, M. Hohenfellner Eur Urol 2005;47(1):1-15
GUIDELINEs ON UROLOGICAL TRAUMA (Text update March 2009) N. Djakovic, Th. Lynch, L. Martínez-Piñeiro, Y. Mor, E. Plas, E. Serafetinides, L. Turkeri, R.A. Santucci, M. Hohenfellner Eur Urol 2005;47(1):1-15
Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology
 Updated July 201 Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology GOAL: The primary goal of the Urogynecology rotation at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) is to train physicians to have a broad knowledge
Updated July 201 Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology GOAL: The primary goal of the Urogynecology rotation at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) is to train physicians to have a broad knowledge
URETERORENOSCOPY: INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS - A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 9 (58) No. 2-2016 URETERORENOSCOPY: INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS - A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY L. MAXIM 1,2 I.A. BĂNUŢĂ 2 I.
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 9 (58) No. 2-2016 URETERORENOSCOPY: INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS - A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY L. MAXIM 1,2 I.A. BĂNUŢĂ 2 I.
HOW TO USE THE UROLOGY SNOMED MORBIDITY AUDIT AND LOGBOOK TOOL (MALT)
 HOW TO USE THE UROLOGY SNOMED MORBIDITY AUDIT AND LOGBOOK TOOL (MALT) OPEN MALT THROUGH SURGEONS.ORG Make sure you re using the correct logbook if you re doing a nonurology rotation in nset 1 CLICK ADD
HOW TO USE THE UROLOGY SNOMED MORBIDITY AUDIT AND LOGBOOK TOOL (MALT) OPEN MALT THROUGH SURGEONS.ORG Make sure you re using the correct logbook if you re doing a nonurology rotation in nset 1 CLICK ADD
Interposition of Omentum, Perivesical Fat, Martious Fat in Management of Lower Urinary Tract Fistula - A Comparative Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Interposition of Omentum, Perivesical Fat, Martious Fat in Management of Lower Urinary Tract Fistula - A Comparative Study KHIZAR HAYAT 1, SHAH JAHAN UR REHMAN 2, MUJAHID ALAM 3, SAJJAD
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Interposition of Omentum, Perivesical Fat, Martious Fat in Management of Lower Urinary Tract Fistula - A Comparative Study KHIZAR HAYAT 1, SHAH JAHAN UR REHMAN 2, MUJAHID ALAM 3, SAJJAD
A clinical study of surgical management of benign ureteric stricture
 Original Research Article A clinical study of surgical management of benign ureteric stricture Pallav Patel 1, Hiren Parmar 2*, Gaurang Vaghela 3 1 Assistant Professor, Surgery Department, GMERS Medical
Original Research Article A clinical study of surgical management of benign ureteric stricture Pallav Patel 1, Hiren Parmar 2*, Gaurang Vaghela 3 1 Assistant Professor, Surgery Department, GMERS Medical
Genitourinary Tract Injuries
 Genitourinary Tract Injuries Chapter 18 Genitourinary Tract Injuries Introduction Genitourinary injuries constitute approximately 5% of the total injuries encountered in combat. Their treatment adheres
Genitourinary Tract Injuries Chapter 18 Genitourinary Tract Injuries Introduction Genitourinary injuries constitute approximately 5% of the total injuries encountered in combat. Their treatment adheres
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
Management of Urethrovaginal Fistulas
 european urology 50 (2006) 1000 1005 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Management of Urethrovaginal Fistulas Dmitri Y. Pushkar *, Vladimir V.
european urology 50 (2006) 1000 1005 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Management of Urethrovaginal Fistulas Dmitri Y. Pushkar *, Vladimir V.
ENDOSCOPIC MANAGEMENT OF A URETERAL OBSTRUCTION CAUSED BY ENDOMETRIOSIS: A CASE REPORT
 ENDOSCOPIC MANAGEMENT OF A URETERAL OBSTRUCTION CAUSED BY ENDOMETRIOSIS: A CASE REPORT Hsu-Cheng Juan, 1 Hsin-Chih Yeh, 1 Hsi-Lin Hsiao, 1 Shean-Fang Yang, 2 and Wen-Jeng Wu 1,3 Departments of 1 Urology
ENDOSCOPIC MANAGEMENT OF A URETERAL OBSTRUCTION CAUSED BY ENDOMETRIOSIS: A CASE REPORT Hsu-Cheng Juan, 1 Hsin-Chih Yeh, 1 Hsi-Lin Hsiao, 1 Shean-Fang Yang, 2 and Wen-Jeng Wu 1,3 Departments of 1 Urology
Clinical Study Initial Experience with Robotic Retropubic Urethropexy Compared to Open Retropubic Urethropexy
 Obstetrics and Gynecology International Volume 2013, Article ID 315680, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/315680 Clinical Study Initial Experience with Retropubic Urethropexy Compared to Open Retropubic
Obstetrics and Gynecology International Volume 2013, Article ID 315680, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/315680 Clinical Study Initial Experience with Retropubic Urethropexy Compared to Open Retropubic
SURGICAL PROCEDURES OPERATIONS ON THE UROGENITAL SYSTEM
 KIDNEYS AND PERINEPHRUM 1. No additional claim should be made for nephroscopy when done at the time of pyelolithotomy or nephrolithotomy. 2. In a routine surgical approach to the kidney and related procedures,
KIDNEYS AND PERINEPHRUM 1. No additional claim should be made for nephroscopy when done at the time of pyelolithotomy or nephrolithotomy. 2. In a routine surgical approach to the kidney and related procedures,
Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students
 Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students Lesson 3: Cystography & Urethrography Part 1 American Urological Association Introduction Conventional radiography of the urinary tract includes several diagnostic
Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students Lesson 3: Cystography & Urethrography Part 1 American Urological Association Introduction Conventional radiography of the urinary tract includes several diagnostic
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
Amd 12 Draft 1. December 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 2016)
 Urogenital and Urinary Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PREAMBLE - KIDNEY AND UPPER URINARY TRACT 1. No additional claim should be made for nephroscopy when done at the time
Urogenital and Urinary Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PREAMBLE - KIDNEY AND UPPER URINARY TRACT 1. No additional claim should be made for nephroscopy when done at the time
Repetitive Ureteral Stenting for Management of Transplant Graft Ureteral Obstruction
 Clinical Urology Stenting for Management of Transplant Ureteral Obstruction International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (2): 142-146, March - April, 2006 Repetitive Ureteral Stenting for Management of Transplant
Clinical Urology Stenting for Management of Transplant Ureteral Obstruction International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (2): 142-146, March - April, 2006 Repetitive Ureteral Stenting for Management of Transplant
Laparoscopic Bladder-Preserving Surgery for Enterovesical Fistula Complicated with Benign Gastrointestinal Disease
 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the article
This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the article
Dr. Aso Urinary Symptoms
 Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Vesicoureteral Reflux
 What is the normal urinary tract? The kidneys filter the blood and extract waste products from the blood to make urine. Urine passes from the kidneys, down the ureters, and into the bladder for storage
What is the normal urinary tract? The kidneys filter the blood and extract waste products from the blood to make urine. Urine passes from the kidneys, down the ureters, and into the bladder for storage
By:Dr:ISHRAQ MOHAMMED
 By:Dr:ISHRAQ MOHAMMED Protrusion of an organ or structure beyond its normal confines. Prolapses are classified according to their location and the organs contained within them. 1-Anterior vaginal wall
By:Dr:ISHRAQ MOHAMMED Protrusion of an organ or structure beyond its normal confines. Prolapses are classified according to their location and the organs contained within them. 1-Anterior vaginal wall
Case Report Transplantation of Horseshoe Kidney from Living, Genetically Unrelated Donor
 Case Reports in Transplantation Volume 2015, Article ID 390381, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/390381 Case Report Transplantation of Horseshoe Kidney from Living, Genetically Unrelated Donor Kazuro
Case Reports in Transplantation Volume 2015, Article ID 390381, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/390381 Case Report Transplantation of Horseshoe Kidney from Living, Genetically Unrelated Donor Kazuro
Ureteral orifice opening into the bladder diverticulum in a boy: A case report
 Ped Urol Case Rep 2014;1(5):20-25 DOI:10.14534/PUCR.201457200 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN:2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Ureteral
Ped Urol Case Rep 2014;1(5):20-25 DOI:10.14534/PUCR.201457200 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN:2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Ureteral
THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN*
 THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN* BY FRANK G. DELUCA, ORVAR SWENSONt, JOHN H. FISHER and ADEL H. LOUTFI From the Boston Floating Hospital for Infants and Children, Boston, Massachusetts
THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN* BY FRANK G. DELUCA, ORVAR SWENSONt, JOHN H. FISHER and ADEL H. LOUTFI From the Boston Floating Hospital for Infants and Children, Boston, Massachusetts
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
Appendix 1. Canadian Classification of Health Intervention Codes Used to Identify
 1 2 3 Appendix 1. Canadian Classification of Health Intervention Codes Used to Identify any Vaginal Mesh (Synthetic) Implantation Procedure(s) for Pelvic Organ Prolapse 4 Canadian Classification of health
1 2 3 Appendix 1. Canadian Classification of Health Intervention Codes Used to Identify any Vaginal Mesh (Synthetic) Implantation Procedure(s) for Pelvic Organ Prolapse 4 Canadian Classification of health
Goals & Objectives by Year in Training: U-1
 Goals & Objectives by Year in Training: U-1 U-1 (PGY-2, 3) Resident Responsibilities, Goals and Objectives In addition to the goals listed for PGY-1, the U-1 resident will add to his/her knowledge base
Goals & Objectives by Year in Training: U-1 U-1 (PGY-2, 3) Resident Responsibilities, Goals and Objectives In addition to the goals listed for PGY-1, the U-1 resident will add to his/her knowledge base
GENERAL GOALS & OBJECTIVES U-1. U-1 (PGY-2, 3) GENERAL GOALS and OBJECTIVES
 GENERAL GOALS & OBJECTIVES U-1 U-1 (PGY-2, 3) GENERAL GOALS and OBJECTIVES In addition to the goals listed for PGY-1, the U-1 resident will add to his/her knowledge base by participating actively in conferences,
GENERAL GOALS & OBJECTIVES U-1 U-1 (PGY-2, 3) GENERAL GOALS and OBJECTIVES In addition to the goals listed for PGY-1, the U-1 resident will add to his/her knowledge base by participating actively in conferences,
Facing Gynecologic Surgery?
 Facing Gynecologic Surgery? Domenico Vitobello, MD Domenico Vitobello is the medical director of the Gynecologic Unit at the Humanitas Clinical and Research Center since 2009. He has developed a comprehensive
Facing Gynecologic Surgery? Domenico Vitobello, MD Domenico Vitobello is the medical director of the Gynecologic Unit at the Humanitas Clinical and Research Center since 2009. He has developed a comprehensive
Objectives: To analyze various factors predicting success of retrograde ureteric stenting in managing patients with ureteric obstruction.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 14 Number 1 Factors Predicting Success Rate Of Retrograde Ureteric Stenting In Managing Patients With Ureteric Obstruction- Our Experiences In A South Indian
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 14 Number 1 Factors Predicting Success Rate Of Retrograde Ureteric Stenting In Managing Patients With Ureteric Obstruction- Our Experiences In A South Indian
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 301.681.3400 OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is surgery to remove the uterus. It is a very common type of surgery for women in the United States. Removing your uterus means
301.681.3400 OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is surgery to remove the uterus. It is a very common type of surgery for women in the United States. Removing your uterus means
RECTAL INJURY IN UROLOGIC SURGERY. Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences.
 RECTAL INJURY IN 27 UROLOGIC SURGERY Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences. With good mechanical bowel preparation plus antibiotic
RECTAL INJURY IN 27 UROLOGIC SURGERY Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences. With good mechanical bowel preparation plus antibiotic
ISSN East Cent. Afr. J. surg. (Online)
 87 Ureteroscopy in a Resource Limited Setting: The Tikur Anbessa General Specialized Hospital Experience in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. D. Andualem, L. Be-ede, T. Mulat, L. Samodi Addis Ababa University-School
87 Ureteroscopy in a Resource Limited Setting: The Tikur Anbessa General Specialized Hospital Experience in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. D. Andualem, L. Be-ede, T. Mulat, L. Samodi Addis Ababa University-School
Rare case of urinary bladder agenesis - Multislice CT abdomen imaging
 Rare case of urinary bladder agenesis - Multislice CT abdomen imaging Venkatraman Indiran 1*, Kabilan Chokkappan 2, Emmanuel Gunaseelan 2 1. Department of Radiodiagnosis, Sree Balaji Medical College and
Rare case of urinary bladder agenesis - Multislice CT abdomen imaging Venkatraman Indiran 1*, Kabilan Chokkappan 2, Emmanuel Gunaseelan 2 1. Department of Radiodiagnosis, Sree Balaji Medical College and
In the August 2016 issue of OBG Management,
 GYN coding changes to note for your maximized reimbursement Revised ICD-10 gynecologic diagnostic codes go into effect October 1. Here is a look at the added, expanded, and revised codes you will need
GYN coding changes to note for your maximized reimbursement Revised ICD-10 gynecologic diagnostic codes go into effect October 1. Here is a look at the added, expanded, and revised codes you will need
THE URETER AND HYSTERECTOMY
 J Obs Gyn Brit Emp 1960 V67 THE URETER AND HYSTERECTOMY Including the Effects of Certain Gynaecological Conditions on the Urinary Tract BY J. K. MORRISON, M.B., M.R.C.O.G. Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
J Obs Gyn Brit Emp 1960 V67 THE URETER AND HYSTERECTOMY Including the Effects of Certain Gynaecological Conditions on the Urinary Tract BY J. K. MORRISON, M.B., M.R.C.O.G. Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
Urogenital Injuries The role of radiology
 Urogenital Injuries The role of radiology NORDTER 7 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course Helsinki, Finland May 21-24, 2012 Johann Baptist Dormagen, MD, PhD Oslo University Hospital, Norway Kidney injuries
Urogenital Injuries The role of radiology NORDTER 7 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course Helsinki, Finland May 21-24, 2012 Johann Baptist Dormagen, MD, PhD Oslo University Hospital, Norway Kidney injuries
EAU GUIDELINES POCKET EDITION 4
 EAU GUIDELINES POCKET EDITION 4 CONTENTS: UROLOGICAL TRAUMA PAIN MANAGEMENT IN UROLOGY UROGENERIC LUTS RENAL TRANSPLANTATION 2 EAU POCKET GUIDELINES POCKET EDITION 4 Introduction 3 Introduction This is
EAU GUIDELINES POCKET EDITION 4 CONTENTS: UROLOGICAL TRAUMA PAIN MANAGEMENT IN UROLOGY UROGENERIC LUTS RENAL TRANSPLANTATION 2 EAU POCKET GUIDELINES POCKET EDITION 4 Introduction 3 Introduction This is
List of Core and Specialised Procedures for Urology
 List of Core and Specialised Procedures for Urology Appendix 5 The list below of privileges for core and specialised procedures is subject to periodic review by Farrer Park Hospital and/or Farrer Park
List of Core and Specialised Procedures for Urology Appendix 5 The list below of privileges for core and specialised procedures is subject to periodic review by Farrer Park Hospital and/or Farrer Park
