Sacral nerve stimulation lead implantation using the o-arm
|
|
|
- Gwenda Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hellström et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:48 TECHNICAL ADVANCE Open Access Sacral nerve stimulation lead implantation using the o-arm Pekka A Hellström, Jani Katisko, Pertti Finnilä and Markku H Vaarala * Abstract Background: Sacral neuromodulation operations have usually been performed based on 2D fluoro images. However, sacral nerve stimulation lead implantation may be challenging when the normal anatomy is confused by obesity or congenital anomalies. Thus the surgical navigation and intraoperative imaging methods could be helpful as those same methods have proven to be feasible methods for guiding other surgical operations. Our recent knowledge about the O-arm in trauma pelvic operations encouraged us to evaluate the usefulness of O-arm guided navigation in sacral neuromodulation. Similar navigation would be useful for complex sacral nerve stimulation lead implantations. Methods: In this preliminary article we report our experience of utilizing the orthopedically optimized O-arm to implant the S3 stimulation electrode in a patient. The 3D O-arm imaging was performed intraoperatively under surgical navigation control. General anesthesia was used. The obtained 3D image dataset was registered automatically into the patient s anatomy. The stimulation needle was guided and the tined lead electrode was implanted using navigation. Results: The bony sacral structures were clearly visualized. Due to automatic registration, the navigation was practicable instantly after the O-arm scanning and operation could be performed successfully under navigation control. Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the first published tined lead implantation which was guided based on the surgical navigation and intraoperative O-arm images. In this case, the applied method was useful and helped the surgeon to demarcate the region of surgical interest. The method is slightly more invasive than the formal technique but could be an option in anatomically challenging cases and reoperations. However, further evaluation with larger patient series is required before definitive recommendations can be made. Keywords: Transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation, Prostheses and implants, Bladder, Colon, Image-guided surgery, Intraoperative imaging Background Sacral nerve stimulation (neuromodulation) has become a widely accepted method to treat various urological and gastrointestinal problems [1]. The technique is based on the stimulation of sacral nerves, usually S3, through the sacral foramina. Usually, the localization of the nerves is easy for an experienced surgeon. In some cases, however, problems can arise, especially with anomalous sacral anatomy or morbid obesity. Recently, complications associated with sacral neuromodulation for bowel problems were * Correspondence: markku.vaarala@oulu.fi Division of Operative Care and Medical Research Center, Oulu University Hospital, P.O. Box 20, Oulu, FIN OYS, Finland reported [2]. In a literature review, thirty-five incidences of problems associated with the implanted lead were detected, including 31 lead displacements/dislodgements/ dislocations/migrations and 4 lead fractures [2]. Earlier, Siegel and colleagues [3] reported complications among the 914 test stimulation procedures done on the 581 patients, where 181 adverse events occurred in 166 of these procedures (18.2% of the 914 procedures). The vast majority of complications were related to lead migration (108 events, 11.8% of procedures) [3]. Technical advances, such as the introduction of the tined lead and the two-staged procedure, appear to have positively affected the adverse event and reoperation rates [4] Hellström et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Hellström et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:48 Page 2 of 5 In neurosurgery, navigation has been used for about 20 years and the benefits are also obvious in some orthopedic operations [5]. An earlier publication describes the use of computed tomography for needle implantation guidance [6]. To evaluate the usefulness of surgical navigation in sacral neuromodulation, the O-arm was used for the implantation of a tined lead electrode in a patient already needing their third revision. Methods Patient The patient is a 51 year-old female with multiple sclerosis. She has a neurogenic overactive bladder and severe constipation. In 2003 the patient underwent peripheral nerve evaluation (PNE). She saw no improvement in bladder symptoms but a clear alleviation of constipation, and underwent implantation using InterStim R. The tined lead technique and the left S3 were used, and the patient was satisfied with the operation. Overactive bladder symptoms were successfully treated with repeated botulinum toxin injections; the battery was changed in January The patient, however, did not have any feeling of stimulation and a revision was performed in December The left lying electrode was partially cut and a new tined lead electrode was placed on the right S3. During the following years, the patient was satisfied with stimulation but a high amount of current was needed. In winter 2011, the battery again was empty. Following X-ray it was noted that the electrode had moved outwards; therefore, a new electrode was placed on the right S4 in the second revision operation. The patient improved again. In autumn 2012, the patient again reported feeling no further stimulation and the measured impedances were over 4000 ohms. Because the patient was satisfied with the neuromodulation she wanted to have a revision. Due to the complicated history, already necessitating the third revision, the O-arm system was considered for the localization of foramina; the patient accepted the proposal and the operation was performed in January General anesthesia was used. Consent to publish her case was obtained from the patient. The treatment was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki. The O-arm The O-arm (Medtronic Inc., Louisville, CO, USA) is a mobile 2D/3D X-ray imaging system optimized for bony structures in spinal and orthopedic surgery. Scanning is based on a flat panel detector and cone-beam technology producing 192 slices in 13 seconds in the standard mode. Pixel size is mm within a slice thickness of mm. The size of the scanned cylindrical 3D volume was 16 cm 21 cm (length diameter), which fulfilled the requirements for obtaining a full scan of the sacrum (Figure 1A). Surgical table The patient lay prone on four-point cushions and on a carbon fiber operating table (Mizuho OSI, Modular Table System, Union City, CA, USA). The patient s head was placed on the soft mask, and slid into the socket of the C-Flex Polar Head Positioner System (Allen Medical Systems, Acton, MA, USA), which was fixed to the carbon fiber rails (Figure 1B). Imaging For the scanning, the patient and the O-arm s gantry were positioned so that the sacrum was in the O-arm s isocenter; this was verified using lateral and vertical 2D fluoroimages. The 3D data set were obtained utilizing the standard mode for the pelvic region with scanning values for M-size patient. Images were imported automatically to the surgical navigation system. Surgical navigation The applied surgical navigation system was StealthStation S7 (Medtronic Inc., Louisville, CO, USA), which utilizes the optical localization method. The navigation software was spine software, which enables automated registration between the scanned images and patient anatomy. Automated registration requires a line of sight from the optical camera to the active O-arm tracker and the passive patient tracker when scanned. The patient tracker was fixed to the patient s left posterior sacral crest using a percutaneous pin (Figure 1C). Procedure After fixing the pin, the earlier placed and partially cut left S3 and right S4 electrodes were removed. It had been previously decided that right S3 was to be used. A foramen needle was fixed to the patient tracker (Figure 1D). Using the monitor made it very easy for the urologist to introduce the needle inside the right S3 (Figure 1E and F). During testing an anal contraction was confirmed and a tined lead was introduced into the foramen. During the operation, the O-arm did not prevent the surgeon from working in any way (Figure 1G). With a connection cable, the electrode was attached to the old InterStim R pulse generator. The wounds were closed in layers and dressed. The recovery of the patient was uneventful and she was satisfied with the stimulation. Radiation exposure During 2D and 3D scanning, the patient was exposed to ionizing radiation. The 2D fluoroimages were used to center the O-arm in the optimal position for 3D-scanning and verifying the final location of the implanted electrode. The 3D scan was required for the navigation. In the 2D mode, total exposure time was sec and the radiation dose was comparable to those when using conventional
3 Hellström et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:48 Page 3 of 5 Figure 1 Intraoperative figures of sacral nerve stimulator lead implantation. The O-arm is a transportable CT-like scanner. With automated positioning, it can be easily placed around the patient on the radiolucent table to obtain 2D fluoroscopic images and 3D scanning in desired directions, and repeated when necessary (A). The patient s position can be adjusted optimally to achieve a surgically and anesthetically comfortable situation (B). Patient tracker fixed to the bone (C). The multipurpose SureTrack instrument tracker was fixed to the needle and used for navigation (D). Needle inside S3, 3D image (E). The sacral structures are clearly visible in the O-arm images; it was possible to guide the instruments used in the correct direction and to the right depths. Inserts with 2D and a 3D images (F). Lead implantation; the O-arm has been moved in the cranial direction allowing free access to the operation area (G). C-arms. In the 3D mode, the CTDI (computed tomography dose index) was calculated as mgy and the DLP (dose length product) was 225 mgycm. The Finnish Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority (Säteilyturvakeskus, STUK) has not yet published the dose limits for the pelvic CTs. However, radiation doses are quite low compared to the acceptable dose limits in some other countries in Europe (CTDI: mgy and DLP: mgycm) [7]. Ionizing radiation doses should be adjusted using the collimation and limiting 2D area and by shortening the length of the 3D volume. Results The use of the O-arm was fluent. This was possible with the automated positioning system which did not cover region of the surgical area. The sacrum and the foramina
4 Hellström et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:48 Page 4 of 5 were clearly visualized. To achieve clear demarcation, the values of brightness and contrast had to be adjusted. Due to automatic registration, the navigation was practicable instantly after the O-arm scanning. The locations of the skin incision and the trajectory of the needle could be determined based on the navigation data as the foramina were well demarcated. During the operation, the surgeon was able to control the movements of the needle and to find the correct depth for both the needle and the implanted electrode. The treatment was successful with ongoing very good treatment response to constipation in September Discussion The technical advances of sacral nerve stimulation testing phase, namely the use of a tined lead and two phase testing, have improved the results during the last decade [4]. However, the complex anatomical situations may obliterate these advances and can result in increased complication rates and impaired testing phase results. In the search for safe techniques and to overcome challenging situations, the use of navigation for lead implantation during sacral nerve stimulation was evaluated and found to be successful. Navigation utilizing the O-arm has been shown to be useful in spinal trauma surgery, especially in pedicle screw positioning [8]. To our knowledge, this is the first report of surgery when navigation has been used in the implantation of the sacral nerve stimulation lead. In our clinic, we have performed neuromodulations since 1996, when the first test was performed; the first implantation was in September The Finnish urological patient material was published in 2011 [9]. One of the authors (PH) also has some experience of the treatment of fecal incontinence with neuromodulation and has performed implants in some myelomeningocele patients. Using anatomical landmarks and fluoroscopy makes it less difficult to find the foramina [10]. The technique of sacral nerve stimulation has evolved during recent decades. At first, peripheral nerve evaluation (PNE) was performed using a very thin temporary electrode [11,12]; later, the use of a tined lead electrode became routine [13]. Sometimes, however, difficulties can arise in the localization of the foramina, especially if there are anatomical variations, like in myelomeningocele patients. We think that navigation using an O-arm could be beneficial in these cases. Lansen-Koch and associates [14] performed peripheral nerve evaluation for 10 patients with spina bifida: in two, PNE was not possible, 3/10 patients had more than 50% improvement and proceeded to a permanent implant, while in one patient it was not possible to perform the implantation. The authors performed an open operation to prevent damage to the nerves. However, using navigation, open surgery could probably be avoided. Of course, the use of the tracker makes the procedure slightly more invasive. The implantation of the percutaneous pin, however, takes on only a few minutes and can be performed under local anesthesia. In overweight or obese people, however, it is often difficult to find the appropriate foramen. Our patient was relatively thin, so we cannot discuss how the technique would work in obese patients. However, as the bony structures are the landmarks for navigation, this technique should also be applicable with obese patients. Bending of the foramen needle will cause problems in navigation, meaning that a stiffer needle may be necessary. Conclusions As far we know, this is the first published tined lead implantation which was guided based on the surgical navigation and intraoperative O-arm images. The method is slightly more invasive than the formal technique and much trickier and expensive than fluoroscopy. However, it could be an option in anatomically challenging cases and reoperations. Overall, there is a place for this technique, but further studies are needed. Consent Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this Case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor of this journal. Competing interests Pekka Hellström. Consultant: Glaxo Smith Kline, SCA Hygiene Products, PhotoCure, Pfizer, Allergan. Speaker Honorarium: Medtronic, Photocure, Allergan, Abbott, Pfizer. Trial participation: Glaxo Smith Kline, Amgen, Orexo, Novartis. Travel grants: Lilly, SCA Hygiene Products, PhotoCure, Allergan, Pfizer, Glaxo Smith Kline. Jani Katisko. Consultant: Medtronic. Pertti Finnilä. Equity interests: Medtronic. Other, employee: Medtronic. Markku Vaarala. Consultant: Amgen, Astellas, Janssen. Speaker Honorarium: Amgen, Astellas, Novartis. Trial participation: Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Orexo, Millenium Pharmaceuticals, Janssen. Authors contributions PAH, JK and PF participated in the design of the study. PAH performed the operation described. JK and PF coordinated the operation including the use of the O-arm and helped to draft the manuscript. PAH and MHV drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Received: 12 August 2013 Accepted: 14 October 2013 Published: 16 October 2013 References 1. Fulton M, Peters KM: Neuromodulation for voiding dysfunction and fecal incontinence: A urology perspective. Urol Clin North Am 2012, 39: Maeda Y, Matzel K, Lundby L, Buntzen S, Laurberg S: Postoperative issues of sacral nerve stimulation for fecal incontinence and constipation: A systematic literature review and treatment guideline. Dis Colon Rectum 2011, 54: Siegel SW, Catanzaro F, Dijkema HE, Elhilali MM, Fowler CJ, Gajewski JB, Hassouna MM, Janknegt RA, Jonas U, Van Kerrebroeck PE, Nijeholt AA L a, Oleson KA, Schmidt RA: Long-term results of a multicenter study on sacral nerve stimulation for treatment of urinary urge incontinence, urgency-frequency, and retention. Urology 2000, 56:87 91.
5 Hellström et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:48 Page 5 of 5 4. Apostolidis A: Neuromodulation for intractable OAB. Neurourol Urodyn 2011, 30: Mezger U, Jendrewski C, Bartels M: Navigation in surgery. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2013, 398: Amoroso L, Pelliccioni G, Ghiselli R, Scarpino O, Saba V, Ricci S: Sacral-neuromodulation CT-guided. Radiol Med 2005, 109: European Commission: Radiation protection 118: referral guidelines for imaging. doc/118_update_en.pdf Park P, Foley KT, Cowan JA, Marca FL: Minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation utilizing O-arm fluoroscopy with computer-assisted navigation: Feasibility, technique, and preliminary results. Surg Neurol Int 2010, 1: Vaarala MH, Tammela TL, Perttila I, Luukkonen P, Hellstrom P: Sacral neuromodulation in urological indications: the Finnish experience. Scand J Urol Nephrol 2011, 45: Chai TC, Mamo GJ: Modified techniques of S3 foramen localization and lead implantation in S3 neuromodulation. Urology 2001, 58: Thon WF, Baskin LS, Jonas U, Tanagho EA, Schmidt RA: Neuromodulation of voiding dysfunction and pelvic pain. World J Urol 1991, 9: Tanagho EA: Neuromodulation in the management of voiding dysfunction in children. J Urol 1992, 148: Spinelli M, Giardiello G, Gerber M, Arduini A, van den Hombergh U, Malaguti S: New sacral neuromodulation lead for percutaneous implantation using local anesthesia: Description and first experience. J Urol 2003, 170: Lansen-Koch SM, Govaert B, Oerlemans D, Melenhorst J, Vles H, Cornips E, Weil EH, Van Heurn E, Baeten CG, Van Gemert WG: Sacral nerve modulation for defaecation and micturition disorders in patients with spina bifida. Colorectal Dis 2012, 14: doi: / Cite this article as: Hellström et al.: Sacral nerve stimulation lead implantation using the o-arm. BMC Urology :48. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Sacral neuromodulation (SNM), using permanent foramen S3 electrode, Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation Magdy M. Hassouna, MD, PhD; Mohamed S. Elkelini, MD See related article on page 111 Abstract Introduction:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation Magdy M. Hassouna, MD, PhD; Mohamed S. Elkelini, MD See related article on page 111 Abstract Introduction:
POLICIES AND PROCEDURE MANUAL
 POLICIES AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Policy: MP091 Section: Medical Benefit Policy Subject: Sacral Nerve Stimulation I. Policy: Sacral Nerve Stimulation II. Purpose/Objective: To provide a policy of coverage
POLICIES AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Policy: MP091 Section: Medical Benefit Policy Subject: Sacral Nerve Stimulation I. Policy: Sacral Nerve Stimulation II. Purpose/Objective: To provide a policy of coverage
INJINTERNATIONAL. Radiographic Position of the Electrode as a Predictor of the Outcome of InterStim Therapy. Original Article INTRODUCTION
 Official Journal of Korean Continence Society / Korean Society of Urological Research / The Korean Children s Continence and Enuresis Society / The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and
Official Journal of Korean Continence Society / Korean Society of Urological Research / The Korean Children s Continence and Enuresis Society / The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and
Sacral Neuromodulation for Dysfunctional Voiders Workshop 1 Monday, August 23, 09:00 10:30
 Sacral Neuromodulation for Dysfunctional Voiders Workshop 1 Monday, August 23, 09:00 10:30 Time Time Topic Speaker 09:00 09:05 Introduction to the aims of the workshop and the Magdy Hassouna participants
Sacral Neuromodulation for Dysfunctional Voiders Workshop 1 Monday, August 23, 09:00 10:30 Time Time Topic Speaker 09:00 09:05 Introduction to the aims of the workshop and the Magdy Hassouna participants
Sacral nerve stimulation in patients with detrusor overactivity
 Peer review Sacral nerve stimulation in patients with detrusor overactivity Abstract Detrusor overactivity, particularly with symptoms of urge incontinence, can be a debilitating and embarrassing condition.
Peer review Sacral nerve stimulation in patients with detrusor overactivity Abstract Detrusor overactivity, particularly with symptoms of urge incontinence, can be a debilitating and embarrassing condition.
Long Term Results of Neuromodulation by Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: A Retrospective Single Center Study
 european urology 49 (2006) 366 372 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Long Term Results of Neuromodulation by Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Lower
european urology 49 (2006) 366 372 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Long Term Results of Neuromodulation by Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Lower
Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve
 Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve Stefan De Wachter, MD, PhD, FEBU Professor of Urology University of Antwerpen, Belgium Chairman dept of Urology, UZA Disclosures Consultant speaker: Astellas, Medtronic,
Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve Stefan De Wachter, MD, PhD, FEBU Professor of Urology University of Antwerpen, Belgium Chairman dept of Urology, UZA Disclosures Consultant speaker: Astellas, Medtronic,
Sacral Neuromodulation for Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: Results of a Nationwide Registry in Switzerland
 european urology 51 (2007) 1357 1363 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Neuro-urology Sacral Neuromodulation for Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: Results
european urology 51 (2007) 1357 1363 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Neuro-urology Sacral Neuromodulation for Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: Results
Sexual response in patients treated with sacral neuromodulation for lower. van Voskuilen AC, Oerlemans DJ, Gielen N, Lansen-Koch SM, Weil EH, van
 Publicaties Dr. Ernest Weil: Sexual response in patients treated with sacral neuromodulation for lower urinary tract symptoms or fecal incontinence. van Voskuilen AC, Oerlemans DJ, Gielen N, Lansen-Koch
Publicaties Dr. Ernest Weil: Sexual response in patients treated with sacral neuromodulation for lower urinary tract symptoms or fecal incontinence. van Voskuilen AC, Oerlemans DJ, Gielen N, Lansen-Koch
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation
 Protocol Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation (70169) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/14 Next Review Date: 09/14 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 01/08, 11/08, 09/09, 09/10, 09/11, 09/12, 09/13
Protocol Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation (70169) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/14 Next Review Date: 09/14 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 01/08, 11/08, 09/09, 09/10, 09/11, 09/12, 09/13
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION
 MEDICAL POLICY 01/16/14, 01/22/15, 03/15/16 PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
MEDICAL POLICY 01/16/14, 01/22/15, 03/15/16 PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
Sacral neurostimulation for urinary retention: 10-year experience from one UK centre
 Original Articles SACRAL NEUROSTIMULATION FOR URINARY RETENTIONDATTA ET AL. Sacral neurostimulation for urinary retention: 1-year experience from one UK centre Soumendra N. Datta, Charlotte Chaliha, Anubha
Original Articles SACRAL NEUROSTIMULATION FOR URINARY RETENTIONDATTA ET AL. Sacral neurostimulation for urinary retention: 1-year experience from one UK centre Soumendra N. Datta, Charlotte Chaliha, Anubha
Applications of Neuromodulation of the Lower Urinary Tract in Female Urology
 Review Article Neuromodulation of the Lower Urinary Tract in Females International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (3): 262-272, May - June, 2006 Applications of Neuromodulation of the Lower Urinary Tract in Female
Review Article Neuromodulation of the Lower Urinary Tract in Females International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (3): 262-272, May - June, 2006 Applications of Neuromodulation of the Lower Urinary Tract in Female
New PercutaneousTechnique of Sacral Nerve Stimulation Has High Initial Success Rate: Preliminary Results
 European Urology European Urology 43 (2003) 70±74 New PercutaneousTechnique of Sacral Nerve Stimulation Has High Initial Success Rate: Preliminary Results Michele Spinelli a,*, Gianluca Giardiello b, Andrea
European Urology European Urology 43 (2003) 70±74 New PercutaneousTechnique of Sacral Nerve Stimulation Has High Initial Success Rate: Preliminary Results Michele Spinelli a,*, Gianluca Giardiello b, Andrea
OHTAC Recommendation
 OHTAC Recommendation Sacral Nerve Stimulation for the Management of Urge Incontinence, Urgency-Frequency, Urinary Retention and Fecal Incontinence March 2, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory
OHTAC Recommendation Sacral Nerve Stimulation for the Management of Urge Incontinence, Urgency-Frequency, Urinary Retention and Fecal Incontinence March 2, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory
AUAUpdateSeries. Lesson 19 Volume Treatment of Non-Neurogenic Overactive Bladder with Electrical Stimulation
 AUAUpdateSeries Lesson 19 Volume 27 2008 Treatment of Non-Neurogenic Overactive Bladder with Electrical Stimulation Learning Objective: At the conclusion of this continuing medical education activity,
AUAUpdateSeries Lesson 19 Volume 27 2008 Treatment of Non-Neurogenic Overactive Bladder with Electrical Stimulation Learning Objective: At the conclusion of this continuing medical education activity,
Contrasting the Percutaneous Nerve Evaluation Versus Staged Implantation in Sacral Neuromodulation
 Curr Urol Rep (2010) 11:310 314 DOI 10.1007/s11934-010-0128-2 Contrasting the Percutaneous Nerve Evaluation Versus Staged Implantation in Sacral Neuromodulation Chad Baxter & Ja-Hong Kim Published online:
Curr Urol Rep (2010) 11:310 314 DOI 10.1007/s11934-010-0128-2 Contrasting the Percutaneous Nerve Evaluation Versus Staged Implantation in Sacral Neuromodulation Chad Baxter & Ja-Hong Kim Published online:
Urodynamic Results of Sacral Neuromodulation Correlate with Subjective Improvement in Patients with an Overactive Bladder
 European Urology European Urology 43 (2003) 282±287 Urodynamic Results of Sacral Neuromodulation Correlate with Subjective Improvement in Patients with an Overactive Bladder W.A. Scheepens a, G.A. van
European Urology European Urology 43 (2003) 282±287 Urodynamic Results of Sacral Neuromodulation Correlate with Subjective Improvement in Patients with an Overactive Bladder W.A. Scheepens a, G.A. van
Sacral Neuromodulation Beyond Pelvic Pain!!!
 Sacral Neuromodulation Beyond Pelvic Pain!!! Dr. Hirachand S Mutagi. Senior Consultant Pain Physician. Head -Sakra World Hospital. Director ReLeaf Pain Services. Rapid advances in neurostimulation therapy
Sacral Neuromodulation Beyond Pelvic Pain!!! Dr. Hirachand S Mutagi. Senior Consultant Pain Physician. Head -Sakra World Hospital. Director ReLeaf Pain Services. Rapid advances in neurostimulation therapy
Sacral neuromodulation for lower urinary tract dysfunction
 World J Urol (2012) 30:445 450 DOI 10.1007/s00345-011-0780-2 TOPIC PAPER Sacral neuromodulation for lower urinary tract dysfunction Philip E. V. Van Kerrebroeck Tom A. T. Marcelissen Received: 22 August
World J Urol (2012) 30:445 450 DOI 10.1007/s00345-011-0780-2 TOPIC PAPER Sacral neuromodulation for lower urinary tract dysfunction Philip E. V. Van Kerrebroeck Tom A. T. Marcelissen Received: 22 August
Coding for Sacral Neuromodulation
 301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 Coding for Sacral Neuromodulation Sacral Neuromodulation (SNS) is a widely used technique in Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery (FPMRS), with several FDA-approved
301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 Coding for Sacral Neuromodulation Sacral Neuromodulation (SNS) is a widely used technique in Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery (FPMRS), with several FDA-approved
SACRAL NEUROMODULATION: EVOLUTION OVER TIME
 SACRAL NEUROMODULATION: EVOLUTION OVER TIME Anurag K. Das, MD, FACS Director Center for Neuro-urology and Continence Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA First use of
SACRAL NEUROMODULATION: EVOLUTION OVER TIME Anurag K. Das, MD, FACS Director Center for Neuro-urology and Continence Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA First use of
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION. POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION EFFECTIVE DATE: 11/19/99 PAGE: 1 OF: 9 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION EFFECTIVE DATE: 11/19/99 PAGE: 1 OF: 9 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation
 Protocol Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation (70169) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/16 Next Review Date: 09/18 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 01/08, 11/08, 09/09, 09/10, 09/11, 09/12, 09/13,
Protocol Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation (70169) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/16 Next Review Date: 09/18 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 01/08, 11/08, 09/09, 09/10, 09/11, 09/12, 09/13,
Neuromodulation for pelvic floor dysfunctions: exploring tibial, sacral and pudendal nerve stimulation. W3, 29 August :00-12:00
 Neuromodulation for pelvic floor dysfunctions: exploring tibial, sacral and pudendal nerve stimulation. W3, 29 August 2011 09:00-12:00 Start End Topic Speakers 09:00 09:10 Introduction Stefan De Wachter
Neuromodulation for pelvic floor dysfunctions: exploring tibial, sacral and pudendal nerve stimulation. W3, 29 August 2011 09:00-12:00 Start End Topic Speakers 09:00 09:10 Introduction Stefan De Wachter
Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy: a case report
 Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation. Description
 Subject: Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Page: 1 of 16 Last Review Status/Date: June 2014 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Description Sacral nerve neuromodulation (SNM), also referred
Subject: Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Page: 1 of 16 Last Review Status/Date: June 2014 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Description Sacral nerve neuromodulation (SNM), also referred
03/13/18. A. Symptoms lasting for greater than or equal to 12 months that have resulted to significant impairment in activities of daily living; and
 Reference #: MC/I008 Page: 1 of 5 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA PreferredOne Community Health Plan
Reference #: MC/I008 Page: 1 of 5 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA PreferredOne Community Health Plan
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street. Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation (PTNS)
 University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation (PTNS) Urology Directorate If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of this document, please contact
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation (PTNS) Urology Directorate If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of this document, please contact
Satisfaction and Patient Experience With Sacral Neuromodulation: Results of a Single Center Sample Survey
 Satisfaction and Patient Experience With Sacral Neuromodulation: Results of a Single Center Sample Survey Randall K. Leong, Tom A. Marcelissen, Fred H. Nieman, Rob A. De Bie, Philip E. Van Kerrebroeck*
Satisfaction and Patient Experience With Sacral Neuromodulation: Results of a Single Center Sample Survey Randall K. Leong, Tom A. Marcelissen, Fred H. Nieman, Rob A. De Bie, Philip E. Van Kerrebroeck*
IMAGE-GUIDED SPINE SURGERY
 SPINE NAVIGATION IMAGE-GUIDED SPINE SURGERY CONFIDENCE AND ACCURACY Brainlab Spinal Navigation combines state-of-the-art touch screen based image control with best-in-class registration methods for image-guided
SPINE NAVIGATION IMAGE-GUIDED SPINE SURGERY CONFIDENCE AND ACCURACY Brainlab Spinal Navigation combines state-of-the-art touch screen based image control with best-in-class registration methods for image-guided
The Presence of Fowler s Syndrome Predicts Successful Long-Term Outcome of Sacral Nerve Stimulation in Women with Urinary Retention
 european urology 51 (2007) 229 234 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Neuro-urology Voiding Dysfunction The Presence of Fowler s Syndrome Predicts Successful Long-Term
european urology 51 (2007) 229 234 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Neuro-urology Voiding Dysfunction The Presence of Fowler s Syndrome Predicts Successful Long-Term
Second-line Treatment for OAB
 Patient Information English 35 Second-line Treatment for OAB The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Sometimes the drugs your doctor prescribed do not improve your overactive symptoms (OAB). In
Patient Information English 35 Second-line Treatment for OAB The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Sometimes the drugs your doctor prescribed do not improve your overactive symptoms (OAB). In
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation. Description
 Subject: Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Page: 1 of 17 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Description Sacral nerve neuromodulation (SNM), also referred
Subject: Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Page: 1 of 17 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Description Sacral nerve neuromodulation (SNM), also referred
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
Caudal Neuromodulation with the Transforaminal Sacral Electrode (InterStim R ): Experience in a Pain Center Regarding 12 Implants
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2016 January; Vol. 29, No. 1: 23-28 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2016.29.1.23 Caudal Neuromodulation with the Transforaminal Sacral Electrode
Original Article Korean J Pain 2016 January; Vol. 29, No. 1: 23-28 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2016.29.1.23 Caudal Neuromodulation with the Transforaminal Sacral Electrode
Neuro-urology for the Urogynaecologist and urologist W20, 15 October :00-18:00
 Neuro-urology for the Urogynaecologist and urologist W20, 15 October 2012 14:00-18:00 Start End Topic Speakers 14:00 14:05 Introduction to the Workshop Sohier Elneil 14:05 14:25 Neurology of the Bladder
Neuro-urology for the Urogynaecologist and urologist W20, 15 October 2012 14:00-18:00 Start End Topic Speakers 14:00 14:05 Introduction to the Workshop Sohier Elneil 14:05 14:25 Neurology of the Bladder
Stimulation of the Sacral Anterior Root Combined with Posterior Sacral Rhizotomy in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury. Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.58 Stimulation of the Sacral Anterior Root Combined with Posterior Sacral Rhizotomy in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Medical Policy Section Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review
MP 7.01.58 Stimulation of the Sacral Anterior Root Combined with Posterior Sacral Rhizotomy in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Medical Policy Section Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review
PERCUTANEOUS TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION
 PERCUTANEOUS TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical
PERCUTANEOUS TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction. Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield
 GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
Intraoperative case studies. Portable full body 32-slice CT scanner
 Intraoperative case studies Portable full body 32-slice CT scanner Point-of-care CT imaging Your multi-departmental imaging solution Orthopedic surgery Arthroplasty Musculoskeletal disorders Hip replacement
Intraoperative case studies Portable full body 32-slice CT scanner Point-of-care CT imaging Your multi-departmental imaging solution Orthopedic surgery Arthroplasty Musculoskeletal disorders Hip replacement
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: percutaneous_tibial_nerve_stimulation_for_voiding_dysfunction
Corporate Medical Policy Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: percutaneous_tibial_nerve_stimulation_for_voiding_dysfunction
NeuromodulationöSacral, Peripheral and Central: Current Status, Indications, Results and New Developments
 EAU Update Series EAU Update Series 2 (2004) 187 194 NeuromodulationöSacral, Peripheral and Central: Current Status, Indications, Results and New Developments Peter Martin Braun*, Christoph Seif, Christof
EAU Update Series EAU Update Series 2 (2004) 187 194 NeuromodulationöSacral, Peripheral and Central: Current Status, Indications, Results and New Developments Peter Martin Braun*, Christoph Seif, Christof
Neuromodulation for pelvic floor dysfunctions: exploring tibial, sacral and pudendal nerve stimulation. W18, 15 October :00-17:00
 Neuromodulation for pelvic floor dysfunctions: exploring tibial, sacral and pudendal nerve stimulation. W18, 15 October 2012 14:00-17:00 Start End Topic Speakers 14:00 14:10 Introduction Stefan de Wachter
Neuromodulation for pelvic floor dysfunctions: exploring tibial, sacral and pudendal nerve stimulation. W18, 15 October 2012 14:00-17:00 Start End Topic Speakers 14:00 14:10 Introduction Stefan de Wachter
SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION FOR EXPERIENCE IN CHILDREN
 SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION FOR COLORECTAL DISEASES: EXPERIENCE IN CHILDREN C. LOUIS-BORRIONE - JM. GUYS TIMONE-ENFANTS MARSEILLE SACRAL NEUROMODULATION IN CHILDREN 26 : Humphreys et al - 23 children with
SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION FOR COLORECTAL DISEASES: EXPERIENCE IN CHILDREN C. LOUIS-BORRIONE - JM. GUYS TIMONE-ENFANTS MARSEILLE SACRAL NEUROMODULATION IN CHILDREN 26 : Humphreys et al - 23 children with
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PERCUTANEOUS POSTERIOR TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION (PPTNS) POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PERCUTANEOUS POSTERIOR Clinical criteria used to make utilization review decisions are based on credible scientific evidence published in peer reviewed medical literature generally
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PERCUTANEOUS POSTERIOR Clinical criteria used to make utilization review decisions are based on credible scientific evidence published in peer reviewed medical literature generally
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation
 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.69 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 2/2001 Next Review: 2/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.69 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 2/2001 Next Review: 2/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PERCUTANEOUS POSTERIOR TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION (PPTNS)
 MEDICAL POLICY 03/19/15, 05/17/16 PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria
MEDICAL POLICY 03/19/15, 05/17/16 PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
Medical Review Criteria Implantable Neurostimulators
 Medical Review Criteria Implantable Neurostimulators Subject: Implantable Neurostimulators Effective Date: April 14, 2017 Authorization: Prior authorization is required for covered implantable stimulators
Medical Review Criteria Implantable Neurostimulators Subject: Implantable Neurostimulators Effective Date: April 14, 2017 Authorization: Prior authorization is required for covered implantable stimulators
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation for Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
 Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 134 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation for Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Next Review: December 2018 Last Review: June 2018 Effective: July 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 134 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation for Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Next Review: December 2018 Last Review: June 2018 Effective: July 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
PERCUTANEOUS TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION
 PERCUTANEOUS TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical
PERCUTANEOUS TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Content must not be changed in any way or reproduced in any format or medium without the formal permission of the copyright holder(s)
 n Lim, D., Ramsay, A., Small, D., and Conn, I. (2014) Socioeconomic demographics of patients referred to the Scottish National Service: sacral nerve stimulation for urinary dysfunction. Journal of Clinical
n Lim, D., Ramsay, A., Small, D., and Conn, I. (2014) Socioeconomic demographics of patients referred to the Scottish National Service: sacral nerve stimulation for urinary dysfunction. Journal of Clinical
Sacral, ilioinguinal, and vasal nerve stimulation for treatment of pelvic, sacral, inguinal and testicular Pain.
 Chapter 14 Sacral, ilioinguinal, and vasal nerve stimulation for treatment of pelvic, sacral, inguinal and testicular Pain. Introduction Sacral nerve root stimulation has been recognized as a treatment
Chapter 14 Sacral, ilioinguinal, and vasal nerve stimulation for treatment of pelvic, sacral, inguinal and testicular Pain. Introduction Sacral nerve root stimulation has been recognized as a treatment
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Page 1 of 23 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Professional Institutional
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Page 1 of 23 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Professional Institutional
CT SCAN PROTOCOL. Shoulder
 CT SCAN PROTOCOL Shoulder Purpose and Summary CT images made with this protocol are used to provide the orthopedic surgeon with a detailed 3D anatomical reconstruction of the patient s scapula and proximal
CT SCAN PROTOCOL Shoulder Purpose and Summary CT images made with this protocol are used to provide the orthopedic surgeon with a detailed 3D anatomical reconstruction of the patient s scapula and proximal
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
 Sacral Neuromodulation for Treatment of Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Alex Kavanagh, PGY3 Mar 30/2011 Goals 1. Define sacral neuromodulation (SNM) and review the clinical implementation 2. Provide
Sacral Neuromodulation for Treatment of Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Alex Kavanagh, PGY3 Mar 30/2011 Goals 1. Define sacral neuromodulation (SNM) and review the clinical implementation 2. Provide
The success of any Inter-
 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation (InterStim ) Part II: Review of Programming Helen Rittenmeyer The success of any Inter- Stim Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation program depends on the positioning of the chronic
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation (InterStim ) Part II: Review of Programming Helen Rittenmeyer The success of any Inter- Stim Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation program depends on the positioning of the chronic
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation for Pelvic Floor Dysfunction File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: sacral_nerve_neuromodulation_stimulation_for_pelvic_floor_dysfunction
Corporate Medical Policy Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation for Pelvic Floor Dysfunction File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: sacral_nerve_neuromodulation_stimulation_for_pelvic_floor_dysfunction
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Sacral Nerve Stimulation (SNS) System Implantation
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Sacral Nerve Stimulation (SNS) System Implantation www.nshealth.ca Sacral Nerve Stimulation (SNS) System Implantation SNS system implantation involves placing a lead ( leed,
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Sacral Nerve Stimulation (SNS) System Implantation www.nshealth.ca Sacral Nerve Stimulation (SNS) System Implantation SNS system implantation involves placing a lead ( leed,
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS
 NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS. A08/S/d Colorectal: Faecal Incontinence (Adult)
 A08/S/d 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR COLORECTAL: FAECAL INCONTINENCE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Lead Provider
A08/S/d 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR COLORECTAL: FAECAL INCONTINENCE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Lead Provider
The cost of the Axonics sacral neuromodulation system is 475 for the trial phase, 9,210 for a
 pat hways Axonics sacral al neuromodulation system for overactive bladder and faecal incontinence Medtech innovation briefing Published: 10 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib164 Summary The technology
pat hways Axonics sacral al neuromodulation system for overactive bladder and faecal incontinence Medtech innovation briefing Published: 10 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib164 Summary The technology
Paediatric Urotherapy Training
 Paediatric Urotherapy Training Frances Shit NS, MSc (Hons), ET, Dept. of Surgery, PWH, CUHK HKSAR Urinary Incontinence in Children Urine leakage in a child from 5 years of age Leakage occurs on a regular
Paediatric Urotherapy Training Frances Shit NS, MSc (Hons), ET, Dept. of Surgery, PWH, CUHK HKSAR Urinary Incontinence in Children Urine leakage in a child from 5 years of age Leakage occurs on a regular
Subject: Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation
 02-64000-01 Original Effective Date: 05/15/08 Reviewed: 05/24/18 Revised: 06/15/18 Subject: Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION,
02-64000-01 Original Effective Date: 05/15/08 Reviewed: 05/24/18 Revised: 06/15/18 Subject: Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION,
Go Yoshida, Tokumi Kanemura, Yoshimoto Ishikawa. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Spine Center, Konan Kosei Hospital, Konan, Japan
 194 Asian / Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 3, pp 194~198, 2012 ASJ: Vol. 6, No. 3, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.3.194 Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation of a Hangman s Fracture Using Intraoperative,
194 Asian / Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 3, pp 194~198, 2012 ASJ: Vol. 6, No. 3, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.3.194 Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation of a Hangman s Fracture Using Intraoperative,
Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage posterior surgery: a case report
 Iizuka et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:421 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage
Iizuka et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:421 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Quality of Life and Morbidity After Permanent Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Fecal Incontinence
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality of Life and Morbidity After Permanent Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Fecal Incontinence Franc H. Hetzer, MD; Dieter Hahnloser, MD; Pierre-Alain Clavien, MD, PhD; Nicolas Demartines,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality of Life and Morbidity After Permanent Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Fecal Incontinence Franc H. Hetzer, MD; Dieter Hahnloser, MD; Pierre-Alain Clavien, MD, PhD; Nicolas Demartines,
Disclosures. Sacroiliac Joint (SIJ) Pain. Modified Triplanar Fluoroscopic Approach in Percutaneous Fixation of Sacroiliac Joint 5/12/2017
 Modified Triplanar Fluoroscopic Approach in Percutaneous Fixation of Sacroiliac Joint J.E. Barrett, M.D. Atlanta Medical Center Atlanta Trauma Symposium 22 April 2017 Disclosures None Sacroiliac Joint
Modified Triplanar Fluoroscopic Approach in Percutaneous Fixation of Sacroiliac Joint J.E. Barrett, M.D. Atlanta Medical Center Atlanta Trauma Symposium 22 April 2017 Disclosures None Sacroiliac Joint
InterStim CONSULTATION INFORMATION.
 InterStim CONSULTATION INFORMATION www.urologyaustin.com The Urinary System Making An Informed Decision How Does The Urinary System Work? To understand how sacral nerve stimulation works, it is helpful
InterStim CONSULTATION INFORMATION www.urologyaustin.com The Urinary System Making An Informed Decision How Does The Urinary System Work? To understand how sacral nerve stimulation works, it is helpful
Initial experience with sacral neuromodulation for the treatment of lower urinary tract dysfunction in Brazil
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (2): 312-320, March - April, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0603 Initial experience with sacral neuromodulation for the treatment of lower urinary tract dysfunction in
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (2): 312-320, March - April, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0603 Initial experience with sacral neuromodulation for the treatment of lower urinary tract dysfunction in
Information about your operation: Sacral nerve stimulation (SNS)
 Information about your operation: Sacral nerve stimulation (SNS) Urogynaecology Unit Information for Patients i Important supplementary information What is an overactive bladder? Women with an overactive
Information about your operation: Sacral nerve stimulation (SNS) Urogynaecology Unit Information for Patients i Important supplementary information What is an overactive bladder? Women with an overactive
Urogynecology Office. Can You Hold? An Update on the Treatment of OAB. Can You Hold? Urogynecology Office
 Urogynecology Office Urogynecology Office Can You Hold? An Update on the Treatment of OAB Can You Hold? Karen Noblett, MD Professor and Chair Department of OB/GYN University of California, Riverside Disclosures
Urogynecology Office Urogynecology Office Can You Hold? An Update on the Treatment of OAB Can You Hold? Karen Noblett, MD Professor and Chair Department of OB/GYN University of California, Riverside Disclosures
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence. Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa
 Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
Since its introduction in spine surgery, pedicle screw
 SPINE Volume 37, Number 25, pp E1580 E1587 2012, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins SURGERY A Prospective Multicenter Registry on the Accuracy of Pedicle Screw Placement in the Thoracic, Lumbar, and Sacral
SPINE Volume 37, Number 25, pp E1580 E1587 2012, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins SURGERY A Prospective Multicenter Registry on the Accuracy of Pedicle Screw Placement in the Thoracic, Lumbar, and Sacral
Clinical Policy: Urinary Incontinence Devices and Treatments
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.142 Last Review Date: 03/18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications Revision Log Description
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.142 Last Review Date: 03/18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications Revision Log Description
Clinical Policy: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.133 Last Review Date: 08/18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications Revision Log Description
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.133 Last Review Date: 08/18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications Revision Log Description
CT Imaging at the Point-of-Care
 ENGLISH True Dedication The new Planmed Verity Extremity CT Scanner revolutionizes extremity CT imaging. The compact unit brings 3D imaging at emergency departments, orthopedic clinics or trauma centers
ENGLISH True Dedication The new Planmed Verity Extremity CT Scanner revolutionizes extremity CT imaging. The compact unit brings 3D imaging at emergency departments, orthopedic clinics or trauma centers
Clinical Policy: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Reference Number: CP.MP.133
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.133 Effective Date: 10/16 Last Review Date: 10/16 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.133 Effective Date: 10/16 Last Review Date: 10/16 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications
1st stage neuromodulation test
 1st stage neuromodulation test Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST page 2 of 12 This leaflet is to give you some background information
1st stage neuromodulation test Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST page 2 of 12 This leaflet is to give you some background information
Technologies and architectures" Stimulator, electrodes, system flexibility, reliability, security, etc."
 March 2011 Introduction" Basic principle (Depolarization, hyper polarization, etc.." Stimulation types (Magnetic and electrical)" Main stimulation parameters (Current, voltage, etc )" Characteristics (Muscular
March 2011 Introduction" Basic principle (Depolarization, hyper polarization, etc.." Stimulation types (Magnetic and electrical)" Main stimulation parameters (Current, voltage, etc )" Characteristics (Muscular
Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence
 Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital
Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital
Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder Symptoms. Patient Information Leaflet
 Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder Symptoms Patient Information Leaflet About this leaflet The information provided in this leaflet should be used as a guide. There may be some
Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder Symptoms Patient Information Leaflet About this leaflet The information provided in this leaflet should be used as a guide. There may be some
historical perspective 78 outcomes 81 rationale 78 technique 79 81
 Subject Index ALS, see Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Altius Electric Nerve Block, extremity pain management 151, 152 Amputation, see Postamputation pain Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), phrenic nerve
Subject Index ALS, see Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Altius Electric Nerve Block, extremity pain management 151, 152 Amputation, see Postamputation pain Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), phrenic nerve
A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA. Eric Michael Stetz
 A Study of the Sacral Anatomy and Its Implications on the Development of a Guide to Improve the Efficacy of Locating the S3 Foramen for Implantation of a Sacral Nerve Stimulation Lead A THESIS SUBMITTED
A Study of the Sacral Anatomy and Its Implications on the Development of a Guide to Improve the Efficacy of Locating the S3 Foramen for Implantation of a Sacral Nerve Stimulation Lead A THESIS SUBMITTED
CT Fluoroscopy-Guided vs Multislice CT Biopsy ModeGuided Lung Biopies:a preliminary experience
 CT Fluoroscopy-Guided vs Multislice CT Biopsy ModeGuided Lung Biopies:a preliminary experience Poster No.: C-0097 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Casarin, G. Rech, C. Cicero, A.
CT Fluoroscopy-Guided vs Multislice CT Biopsy ModeGuided Lung Biopies:a preliminary experience Poster No.: C-0097 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Casarin, G. Rech, C. Cicero, A.
Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (4): 739-743, July - August, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0303 Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (4): 739-743, July - August, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0303 Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in
Reduction of Radiation Exposure in Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement by Using a New Extension Instrument
 Reduction of Radiation Exposure in Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement by Using a New Extension Instrument Franquiz M. Juan, Myers J.Behnam, Thomas A. Michael, Greenhalgh J. Travis, Shoup J. Andrew Study
Reduction of Radiation Exposure in Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement by Using a New Extension Instrument Franquiz M. Juan, Myers J.Behnam, Thomas A. Michael, Greenhalgh J. Travis, Shoup J. Andrew Study
ProFx. Exceptional Orthopedic Versatility
 ProFx Exceptional Orthopedic Versatility Maximized Versatility For Optimal Results1-4 The ProFx elevates surgery to a new level for the orthopedic trauma surgeon by providing the perfect table complement
ProFx Exceptional Orthopedic Versatility Maximized Versatility For Optimal Results1-4 The ProFx elevates surgery to a new level for the orthopedic trauma surgeon by providing the perfect table complement
Vague symptoms. Unexpected flares.
 PELVIC FLOOR DYSFUNCTION We need to expand the differential diagnosis for chronic pelvic pain to include pelvic myofascial pain Amie Kawasaki, MD Dr. Kawasaki is Fellow in the Division of Female Pelvic
PELVIC FLOOR DYSFUNCTION We need to expand the differential diagnosis for chronic pelvic pain to include pelvic myofascial pain Amie Kawasaki, MD Dr. Kawasaki is Fellow in the Division of Female Pelvic
Uroplasty, Inc. Investor Update Canaccord Genuity Conference December 6, 2011
 Uroplasty, Inc. Investor Update Canaccord Genuity Conference December 6, 2011 Forward Looking Statement This presentation includes forward-looking statements, including financial projections, relating
Uroplasty, Inc. Investor Update Canaccord Genuity Conference December 6, 2011 Forward Looking Statement This presentation includes forward-looking statements, including financial projections, relating
Motility Disorders. Pelvic Floor. Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 701) January 2010 November 2011
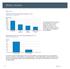 Motility Disorders Pelvic Floor Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 71) January 21 November 211 New Patients 35 3 25 2 15 1 5 Constipation Fecal Incontinence Rectal Prolapse Digestive-Genital
Motility Disorders Pelvic Floor Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 71) January 21 November 211 New Patients 35 3 25 2 15 1 5 Constipation Fecal Incontinence Rectal Prolapse Digestive-Genital
Subject: Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation
 02-61000-23 Original Effective Date: 01/01/01 Reviewed: 06/28/18 Revised: 01/01/19 Subject: Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION,
02-61000-23 Original Effective Date: 01/01/01 Reviewed: 06/28/18 Revised: 01/01/19 Subject: Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION,
A Clinical Study of Electroacupuncture on an Overactive Bladder
 2004. Vol. 25. No. 4. 220-225 Korean Journal of Oriental Medicine Original Articles A Clinical Study of Electroacupuncture on an Overactive Bladder Jong-Deog Kim, Kyung-Tai Kim, Eun-Jung Kim, Ji-Chul Jung,
2004. Vol. 25. No. 4. 220-225 Korean Journal of Oriental Medicine Original Articles A Clinical Study of Electroacupuncture on an Overactive Bladder Jong-Deog Kim, Kyung-Tai Kim, Eun-Jung Kim, Ji-Chul Jung,
