Response to cryptorchidism of the testis and epididymis
|
|
|
- Daisy Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Response to cryptorchidism of the testis and epididymis of the opossum (Didelphis virginiana) Jane N. Scott, H. Ira Fritz and F. Nagy Departments ofanatomy and Biological Chemistry, Wright State University School of Medicine, Dayton, Ohio 45435, U.SA. Summary. Adult male opossums, Didelphis virginiana, were rendered hemicryptorchid for 35 days. The cryptorchid testis exhibited a significant reduction in weight, while the contralateral testis had a compensatory weight gain compared with testes of untreated animals. Histological changes in the cryptorchid testis included fibrosis of the tunica propria, involution of the seminiferous tubules and an apparent increase in the interstitial tissue. Many seminiferous tubules were empty and germinal cells were absent. Some Sertoli cells persisted, but the cytoplasm was vacuolated. Cryptorchid testes were characterized by mononuclear leucocytic invasion around the tubules, and some eosinophils were observed. Cryptorchidism in the opossum may induce a reaction similar to experimental orchitis. Introduction There is little information regarding the male reproductive system of the opossum, Didelphis virginiana. The testes and epididymides are exteriorized in a prepenile scrotum suggesting that spermatogenesis in the testis and sperm maturation in the epididymis require an optimum temperature lower than deep body temperature. Compared with eutherian mammals, the opossum has a low body temperature and cannot efficiently regulate body temperature in response to wide-ranging environmental temperatures (Reynolds, 1952). Biggers (1966) suggested that the regulation of scrotal temperature may be augmented by the heavily pigmented layer of the tunica vaginalis which may act as a black body radiator. The present experiment was undertaken to provide information regarding the effects of prolonged exposure to elevated temperature on the opossum testis and epididymis. Materials and Methods Five adult male opossums were anaesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of Equi-thesin (active agents 9-7 mg pentobarbital/ml and 42-5 mg chloral hydrate/ml: Jensen-Salsbery Laboratories, Kansas City, U.S.A.) in a dose of 2-2 ml/kg body weight. The scrotal sac, the lower abdominal area and the inguinal areas were shaved and washed with an antiseptic solution. Sterile technique was used throughout the operation. Unilateral cryptorchidism was produced by a two-step surgical procedure. First, a scrotal incision was made and the testis, tunica vaginalis and spermatic cord were freed by blunt dissection. A second incision approximately 4-6 cm long was made lateral to the isopubic bar of the pubic bone into the abdominal cavity. Beneath the skin a tunnel was made to connect the two incisions and to auow passage of the testis into the abdominal cavity. To avoid injury to the spermatic cord, the abdominal incision was distal to the natural entry of the cord into the abdominal cavity. This meant that the cord was looped above
2 the abdominal musculature before returning into the abdominal cavity. The abdominal incision was sutured and the skin closed with surgical clips. The scrotal incision was left open to facilitate drainage of the tunnel and the scrotum. One side of the scrotal sac was left intact as a control. The side of the scrotum chosen for control or experimental treatment was selected randomly. Testes and epididymides were obtained from 5 untreated animals to control for possible effects of hemicryptorchidism on the contralateral testis. The animals were gonadectomized 35 days after surgery. Testes and epididymides were excised, weighed, and fixed in Carnoy's or HeUy's fluid. The tissues were processed for paraffinwax embedding, sectioned at 7 urn and stained with haematoxylin and eosin, Mallory's aniline blue or periodic acid-schiff reagent. Student's t test was used to analyse the data, using < 0-05 as the level of significance. Results Weights ofthe testes and epididymides As shown in Table 1 the testes which were placed in the abdomen weighed 54% less than the contralateral scrotal testes, and testes from the untreated animals weighed 23% less than the scrotal testes of the hemicryptorchid animals. Abdominal epididymides were lighter than those associated with the contralateral scrotal testis. Table 1. The effects of experimental unilateral cryptorchidism on the weights (mean ± s.e.m.) of the testis and epididymis of opossums No. of Testis wt Epididymis wt animals (g) (g) Experimental animals 5 Scrotal side 1-60 ± Cryptorchid side 0-73 ± 0-14* 0-55 ± 0-02* Control animals (untreated) ±0-05* 0-58 ± 0-02 * Significantly different from the scrotal tissues, <0-05. t Significantly different from the control tissues, < Histological changes Before the testes were placed in the abdominal cavity, the tunica vaginalis was heavily pigmented (PI. 1, Fig. 1). However, after 35 days in the abdominal cavity the pigmentation was greatly reduced (PI. 1, Fig. 2) and there were increased amounts of fibrous tissue. Pigmentation from the tunicae was sometimes observed extending into the tissue surrounding the spermatic cord. In one animal the tunica had adhered to the abdominal wall and pigmentation was present in the associated musculature. The scrotal testes of the experimental and control animals were generally histologicauy simuar although there was some cytoplasmic vacuolation in the Leydig cells of the experimental animals. Striking changes were evident in the cryptorchid testes. The tunicae albugineae were greatly thickened, apparently due to an increase in couagenous fibres, and there was a decrease in the linear organization of the fibres and ceus. OccasionaUy foci of leucocytic invasion were seen in the innermost layer of the tunic in the cryptorchid testes. Compared to the contralateral scrotal testes (PI. 1, Fig. 3), the cryptorchid gonads (PI. 1, Fig. 4; PI. 2, Fig. 5) showed a significant reduction in the diameter of the seminiferous tubules.
3 Fig. 1. Normal appearance of the pigmented tunica vaginaüs. Fig. 2. Appearance of the same tunica vaginalis after 35 days in the abdominal cavity. Note the diminished coloration. Fig. 3. Section of a scrotal testis showing normal H& E, bar spermatogenesis and numerous Leydig cells. 50 µ. Fig. 4. Section of a cryptorchid testis showing the apparent increase of Leydig cells. Only Sertoli cells with vacuolated cytoplasm are present in the seminiferous tubules. Leucocytic invasion is associated with the tubule at the left. & E, bar 50pm.
4 Fig. 5. Section of a cryptorchid testis demonstrating empty seminiferous tubules. Tubules at lower right and left are surrounded by leucocytes. Sertoli ceus are absent from all tubules. H & E, bar 50 pm. Fig. 6. Section of a cryptorchid testis showing a seminiferous tubule surrounded by mononuclear leucocytes and filled with similar cells. Note the large vacuoles (arrows) suggestive of lipid deposition. H & E, bar 10 pm. Fig. 7. Section of a cryptorchid testis showing an eosinophil (arrow) within the tunica propria of a seminiferous tubule. The lumen (upper right) is empty. H&E, bar 10 pm.
5 There was an apparent increase in the amount of interstitial tissue, especiauy in the number of Leydig cells. The cytoplasm of the Leydig ceus in the cryptorchid testes stained more intensely and the nuclei were more basophilic than those of the contralateral scrotal testes. The seminiferous tubule changes in the cryptorchid testes consistently included an apparent absence of germinal cells and thickened tunicae propriae. The tunica propria of seminiferous tubules in control testes was quite thin and appeared to consist of one layer of ceus and a small amount of fibrous tissue, possibly couagen. In the cryptorchid testes the tunica propria consisted of 3 or 4 layers of cells, and there was an apparent increase in collagen (PI. 2, Fig. 5). In several cryptorchid testes the only ceus present in the seminiferous tubules were Sertoli cells with irregular and displaced nuclei (PI. 1, Fig. 4) and often cytoplasmic vacuolation. Occasionally the lumina of the tubules were empty and a PAS-positive deposit lined the luminal surface. In other tubules the Sertoli cells appeared to be replaced by mononuclear leucocytes. Numerous large vacuoles suggestive of lipid deposition were observed in the lumina (PI. 2, Fig. 5). Mononuclear leucocytic invasion frequently occurred around seminiferous tubules and appeared to disrupt the limiting membrane (PI. 2, Fig. 6). Eosinophüs were seen in the tissue surrounding the seminiferous tubules and also within or traversing the tunica propria (PI. 2, Fig. 7). Epididymides which were retained in the abdomen were devoid of spermatozoa and had a narrower lumen than control epididymides, but no other morphological changes were noted. Discussion There has been some interest in the functional relationship between testicular temperature regulation in New World marsupials and the melanized tunica vaginalis (Biggers, 1966). Scott & Fritz (1979) observed normal spermatogenesis in the testes and sperm-pairing in the epididymides of opossums in which the testes were surrounded by a non-pigmented tunica. The present study presents the first report of the effects of increased temperature on the testis and epididymis of a marsupial. In the present experiment, the surgical technique used to make the opossum hemicryptorchid left the pigmented tunica vaginaus around the testis and epididymidis. Increased fibrous tissue in the tunica may have contributed to the apparent loss of pigmentation but movement of pigment out of the tunica also seemed to have occurred because pigment was observed in nearby tissues. The elevated temperature may have stimulated migration of the melanocytes, or macrophages containing phagocytosed pigment after cell death may have migrated to the surrounding tissues. Unilateral cryptorchidism results in a compensatory increase in the size of the scrotal testis of men (Laron & Zilka, 1969), rams (Blackshaw & Samisoni, 1967) and rats (Clegg, 1961). This was also demonstrated for the opossums in the present study, even after only 35 days. In hemicryptorchid rats, Clegg (1965) attributed the compensatory increase to hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the Leydig ceus. However, van Straaten & Wensing (1977) found hypertrophy of all testicular elements in the scrotal testis of hemicryptorchid pigs. In our study, the absence of changes in the germinal epithelium and apparent increased size due to vacuolation in Leydig ceus suggest that hypertrophy of these cells caused the weight increase of the scrotal testes. The absence of a significant difference between the mean weight of the scrotal epididymides and that of the control epididymides suggests that androgen production was maintained at a normal level in the hemicryptorchid animals. The lower weight of the abdominal epididymides was partly due to the complete absence of spermatozoa. The involution of seminiferous tubules, fibrosis of the surrounding tunica propria and apparent increase of interstitial tissue seen in the opossum cryptorchid testis are commonly noted in cryptorchid testes of other species, including rat and man (Nelson, 1951 ; Leeson, 1966; Leeson & Leeson, 1970). However, these effects probably do not represent a maximal response
6 in the opossum because of the subcutaneous loop of the spermatic artery and vein which could have resulted in some cooling of the blood supply to the testis. The absence of germinal cells and loss of Sertoli cells in many seminiferous tubules after 35 days exposure to elevated temperature suggests that the opossum testis is more temperaturesensitive than testes of other species. Germinal ceus and Sertoli ceus have been observed in cryptorchid testes of adult men (Sohval, 1954; Leeson, 1966) and germinal ceus have been seen in rat testes after 100 days of cryptorchidism (Nelson, 1951). Seminiferous tubules showing complete aspermatogenesis in the present study were frequently surrounded by mononuclear leucocytes and often contained some of these cells. Eosinophüs characterized the leucocytic invasion and were noted crossing the tunica propria. These observations are simüar to those made after induction of experimental autoimnune allergic orchitis in the guinea-pigs by immunization with testicular extracts (Waksman, 1959; Johnson, 1970a). Induction of experimental autoimmune orchitis is thought to result from breakdown of the blood-testis barrier (Johnson, 1970b). The SertoU cells are responsible for the blood-testis barrier which normauy isolates the contents of the seminiferous tubules (SetcheU, 1977); however, effects of temperature on the blood-testis barrier have not been conclusively demonstrated. Main & Waites (1977) noted that in rats the barrier was not altered by exposure to increased temperatures for 1 h. In the present study of the opossum, the longer exposure to elevated temperature caused degeneration and loss of SertoU cells which may have disrupted the blood-testis barrier, thus allowing contents of the tubules to leak into surrounding tissue. Proteins released from degenerating germinal ceus could have induced a reaction similar to that of experimental orchitis. We thank Robert Scott for help with the photography and Donald and Janet Gum for help in obtaining animals. Financial support was provided in part by a Biomedicai Research Grant from Wright State University School of Medicine. References Biggers, J.D. (1966) Reproduction in male marsupials. Symp. zool. Soc. Lond. 15, Blackshaw, A.W. & Samisoni, J.I. (1967) The testes of the cryptorchid ram. Res. vet. Sci. 8, Clegg, EJ. (1961) Further studies on artificial cryp torchidism: quantitative changes in the interstitial cells of the rat testis. J. Endocr. 21, Clegg, EJ. (1965) Studies on artificial cryptorchidism: the histological appearances of unilateral and bilateral abdominal testes in the rat. J. Endocr. 33, Johnson, M.H. (1970a) Changes in the blood-testis barrier of the guinea-pig in relation to histological damage following iso-immunization with testis. J. Reprod. Fert. 22, Johnson, M.H. (1970b) An immunologie barrier in the guinea-pig testis. /. Path. 101, Laron, Z. & Zilka, E. (1969) Compensatory hypertro phy of testicle in unilateral cryptorchidism. /. clin. Endocr. Metab. 29, Leeson, C.R. (1966) An electron microscopic study of cryptorchid and scrotal human testes, with special reference to pubertal maturation. Invest. Urol. 3, Leeson, T. S. & Leeson, C.R. (1970) Experimental cryptorchidism in the rat. A light and electron mic roscope study. Invest. Urol. 8, Main, SJ. & Waites, G.M.H. (1977) The blood-testis barrier and temperature damage to the testis of the rat. J. Reprod. Fert. 51,439^50. Nelson, W.O. (1951) Mammalian spermatogenesis: effect of experimental cryptorchidism in the rat and non-descent of the testis in man. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 6, Reynolds, H.C. (1952) Studies on reproduction in the opossum (Dtdelphls vlrginiana). Univ. Calif. Pubis Zool. 52, Scott, J.N. & Fritz, H.I. (1979) Nonpigmented tunica vaginalis testis in the opossum. Ohio J. Sci. 79, Setchell, B.P. (1977) The blood-testis barrier. In Frontiers in Reproduction and Fertility Control, vol. 2, pp Eds R. O. Greep & M. A. Koblinsky. MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts. Sohval, A.R. (1954) Histopathology of cryptorchidism. Am. J. Med. 16, van Straaten, H.W.M. & Wensing, CJ.G. (1977) Histomorphometric aspects of testicular morpho genesis in the naturally unilateral cryptorchid pig. Biol. Reprod. 17, Waksman, B.H. (1959) A histologie study of the autoallergic testis lesion in the guinea pig. J. exp. Med. 109, Received 26 January 1979
THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS
 Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
Spermatogenesis Following Experimental Testicular Ischemia
 Spermatogenesis Following Experimental Testicular Ischemia Frank Hinman, Jr, MD, and Gilbert I Smith, MD REGENERATION of the spermatogenic elements of the testis after depression by testosterone and by
Spermatogenesis Following Experimental Testicular Ischemia Frank Hinman, Jr, MD, and Gilbert I Smith, MD REGENERATION of the spermatogenic elements of the testis after depression by testosterone and by
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1)
 Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT
 ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT Reproduct ion Physiology Section, Department of Zoology, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur-302004 Summary: Rats and mice were vasectomized
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT Reproduct ion Physiology Section, Department of Zoology, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur-302004 Summary: Rats and mice were vasectomized
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE
 ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF GERM CELL KINETICS IN THE TESTES OF CHILDREN WITH UNILATERAL CRYPTORCHIDISM: A PRELIMINARY REPORT*
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1970 by the Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 21, No. 11, November 1970 Printed in U.S.A. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF GERM CELL KINETICS IN THE TESTES OF CHILDREN WITH UNILATERAL
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1970 by the Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 21, No. 11, November 1970 Printed in U.S.A. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF GERM CELL KINETICS IN THE TESTES OF CHILDREN WITH UNILATERAL
Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed
 Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
ANDROGEN BIOSYNTHESIS IN EXPERIMENTAL CRYPTORCHIDISM*
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright ~ 1975 The American Fertility Society Vol. 26, No.7, July 1975 Printed in U.S A. ANDROGEN BIOSYNTHESIS IN EXPERIMENTAL CRYPTORCHIDISM* JUAN CARLOS HOSCHOIAN, PH.D., AND
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright ~ 1975 The American Fertility Society Vol. 26, No.7, July 1975 Printed in U.S A. ANDROGEN BIOSYNTHESIS IN EXPERIMENTAL CRYPTORCHIDISM* JUAN CARLOS HOSCHOIAN, PH.D., AND
M. Al-Mohtaseb. Tala Saleh. Faisal Nimri
 4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for testicular cancer
 Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Inguinal Canal. It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. Present in both sexes
 Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
Male Anatomy. testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics
 Male Anatomy Male Anatomy Primary Organ testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics 1) Secondary Organs internal
Male Anatomy Male Anatomy Primary Organ testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics 1) Secondary Organs internal
HISTOLOGIC CHANGES IN THE SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES AFTER VASECTOMY
 FERTILItY AND STI!RILITY Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society Vol. 25, No.8, August 1974 PTillted in U.S.AI HISTOLOGIC CHANGES IN THE SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES AFTER VASECTOMY FLETCHER C. DERRICK,
FERTILItY AND STI!RILITY Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society Vol. 25, No.8, August 1974 PTillted in U.S.AI HISTOLOGIC CHANGES IN THE SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES AFTER VASECTOMY FLETCHER C. DERRICK,
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
preceded by pyogenic epididymoorchitis
 J. clin. Path., 1970, 23, 668-675 Infected infarcts of the testis: A study of 18 cases preceded by pyogenic epididymoorchitis D. O'B. HOURIHANE From the Central Histopathology Laboratory of the Federated
J. clin. Path., 1970, 23, 668-675 Infected infarcts of the testis: A study of 18 cases preceded by pyogenic epididymoorchitis D. O'B. HOURIHANE From the Central Histopathology Laboratory of the Federated
DISORDERS OF MALE GENITALS
 Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER)
 THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER) ROBERT P. McCOURT Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State University,
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER) ROBERT P. McCOURT Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State University,
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
The Repr duct ve System. Function: producing offspring
 The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL CASTRATION ON THE REMAINING TESTIS OF THE MOUSE
 402 THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL CASTRATION ON THE REMAINING TESTIS OF THE MOUSE BY I. W. ROWLANDS. (From the Department of Zoology, University College of North Wales, Bangor.) (Received 14th April, 1934.)
402 THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL CASTRATION ON THE REMAINING TESTIS OF THE MOUSE BY I. W. ROWLANDS. (From the Department of Zoology, University College of North Wales, Bangor.) (Received 14th April, 1934.)
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
IN normal male fowls, four developmental stages of spermatogenetic activity
 Development of the Testis Tubule in the Fowl By GAMAL A. R. KAMAR (From the Animal Production Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt) With three plates (figs. 1-3) SUMMARY Three
Development of the Testis Tubule in the Fowl By GAMAL A. R. KAMAR (From the Animal Production Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt) With three plates (figs. 1-3) SUMMARY Three
حسام أبو عوض. -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib. 1 P a g e
 5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
Immune response in obstructive male infertility. Prof. A.K.Sarda Department of Surgery Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi
 Immune response in obstructive male infertility Prof. A.K.Sarda Department of Surgery Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi Sperm transport from the testicle Seminiferous tubule contractions of the myoid
Immune response in obstructive male infertility Prof. A.K.Sarda Department of Surgery Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi Sperm transport from the testicle Seminiferous tubule contractions of the myoid
Title. Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): Issue Date
 Title A CASE OF CANINE TESTICULAR SERTOLI CELL TUMOR Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): 11-1 Issue Date 1965-03 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.13.1.11
Title A CASE OF CANINE TESTICULAR SERTOLI CELL TUMOR Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): 11-1 Issue Date 1965-03 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.13.1.11
The Use of Rabbits in Male Reproductive Toxicology
 Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 77, pp. 5-9, 1988 The Use of Rabbits in Male Reproductive Toxicology by Daniel Morton* The rabbit is the smallest and least expensive laboratory animal in which serial
Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 77, pp. 5-9, 1988 The Use of Rabbits in Male Reproductive Toxicology by Daniel Morton* The rabbit is the smallest and least expensive laboratory animal in which serial
Effects of Ablation of the Submaxillary Gland in Guinea Pigs IV. Cause of deterioration of the tubules in the testes
 1961 475 Effects of Ablation of the Submaxillary Gland in Guinea Pigs IV. Cause of deterioration of the tubules in the testes Kazuo Suzuki Received August 1, 1960 Shakujii Institute, Tokyo Medical College,
1961 475 Effects of Ablation of the Submaxillary Gland in Guinea Pigs IV. Cause of deterioration of the tubules in the testes Kazuo Suzuki Received August 1, 1960 Shakujii Institute, Tokyo Medical College,
PRENATAL HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FETAL TESTIS
 PRENATAL HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FETAL TESTIS *Mantraratnam Pramila Padmini and Bhattam Narasinga Rao Department of Anatomy Maharajahs Institute of Medical Sciences Vizianagaram Nellimarla *Author for Correspondence
PRENATAL HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FETAL TESTIS *Mantraratnam Pramila Padmini and Bhattam Narasinga Rao Department of Anatomy Maharajahs Institute of Medical Sciences Vizianagaram Nellimarla *Author for Correspondence
Intratubular Germ Cell Neoplasia of the Testis
 Intratubular Germ Cell Neoplasia of the Testis KS Ngoo Department of Urology Hospital Selayang Advanced Urology Course 15 Aug 2014 MUA Office Clinical scenario A 33 years old man has bilateral testicular
Intratubular Germ Cell Neoplasia of the Testis KS Ngoo Department of Urology Hospital Selayang Advanced Urology Course 15 Aug 2014 MUA Office Clinical scenario A 33 years old man has bilateral testicular
Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1
 Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1 Professor dr Ali Hassan Altimimi Professor of Pathology& Histology MSc, PHD, MD(UK) MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The internal male genitalia consist of the testes with
Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1 Professor dr Ali Hassan Altimimi Professor of Pathology& Histology MSc, PHD, MD(UK) MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The internal male genitalia consist of the testes with
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
川北医学院讲稿. Under low power note the testis is enclosed by a strong fibrous. layer of serous epithelium. These fibrous tissue
 川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
U NDUE DELAY in the treatment of cryptorchidism will, in my opmlon,
 Delayed Treatment of Cryptorchidisnt with Subsequent Infertility L. STUART SCOTT, M.D., CH.M., F.R.C.S. (EDIN.), F.R.C.S. (GLAsc.) U NDUE DELAY in the treatment of cryptorchidism will, in my opmlon, inevitably
Delayed Treatment of Cryptorchidisnt with Subsequent Infertility L. STUART SCOTT, M.D., CH.M., F.R.C.S. (EDIN.), F.R.C.S. (GLAsc.) U NDUE DELAY in the treatment of cryptorchidism will, in my opmlon, inevitably
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
IF SEXUALLY MATURE male rats are subjected to experimental cryptorchidism,
 Cryptorchidism Its Pre- and Postpubertal Effects on the Hypophysis of the Rat JAMES R. MOREHEAD, PH.D.,* and CHARLES F. MORGAN, Pn.D:r IF SEXUALLY MATURE male rats are subjected to experimental cryptorchidism,
Cryptorchidism Its Pre- and Postpubertal Effects on the Hypophysis of the Rat JAMES R. MOREHEAD, PH.D.,* and CHARLES F. MORGAN, Pn.D:r IF SEXUALLY MATURE male rats are subjected to experimental cryptorchidism,
Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM
 Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM 1) Other Names: Scrotum None Testicles Testes (Curry Tempkin, p. 236, 2/3/2) Ductus deferens spermatic cord (Tempkin, p. 279, Anatomy
Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM 1) Other Names: Scrotum None Testicles Testes (Curry Tempkin, p. 236, 2/3/2) Ductus deferens spermatic cord (Tempkin, p. 279, Anatomy
ROLE OF SOME ANTIOXIDANTS ON MERCURY CHLORIDE INDUCED SPERMATOGENESIS IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DURING PRE PUBERTAL PHASE OF LIFE
 Indian J.Sci.Res.1(2) : 19-25, 2010 ROLE OF SOME ANTIOXIDANTS ON MERCURY CHLORIDE INDUCED SPERMATOGENESIS IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DURING PRE PUBERTAL PHASE OF LIFE a1 DUGESH NANDINI SHARMA AND LATA BHATTACHARYA
Indian J.Sci.Res.1(2) : 19-25, 2010 ROLE OF SOME ANTIOXIDANTS ON MERCURY CHLORIDE INDUCED SPERMATOGENESIS IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DURING PRE PUBERTAL PHASE OF LIFE a1 DUGESH NANDINI SHARMA AND LATA BHATTACHARYA
Male Reproductive Physiology
 Male Reproductive Physiology Overview Anatomy Function Endocrine and spermatogenesis Testis epididymus,vas deferens,seminal vesicles and prostate Hypothalamic pituitary testicular axis Hormones of the
Male Reproductive Physiology Overview Anatomy Function Endocrine and spermatogenesis Testis epididymus,vas deferens,seminal vesicles and prostate Hypothalamic pituitary testicular axis Hormones of the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Dr Bruce Sutherland General Practitioner, Warkworth
 Dr Bruce Sutherland General Practitioner, Warkworth VASECTOMY Dr Bruce Sutherland Overview Embryology Anatomy Procedure Pre Op consultation Post Op care Pitfalls EMBRYOLOGY Fetus at age 7 weeks Fig.
Dr Bruce Sutherland General Practitioner, Warkworth VASECTOMY Dr Bruce Sutherland Overview Embryology Anatomy Procedure Pre Op consultation Post Op care Pitfalls EMBRYOLOGY Fetus at age 7 weeks Fig.
Scrotal pain and Swelling
 Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Reproductive System Purpose General Structures Male Structures Functions Female Anatomy Structures Functions Clinical Applications
 The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Sweat glands of the scrotum of the bull
 s of the scrotum of the bull N. B. Blazquez, G. J. Mallard and S. R. Wedd Department of Animal Husbandry, University of Bristol, School of Veterinary Science, Langford House, Langford, Bristol BS18 7DU,
s of the scrotum of the bull N. B. Blazquez, G. J. Mallard and S. R. Wedd Department of Animal Husbandry, University of Bristol, School of Veterinary Science, Langford House, Langford, Bristol BS18 7DU,
Seminiferous Tubules
 Testes The testes are compound tubular glands that lie within a scrotal sac, suspended from the body by a spermatic cord. The testes are dual organs that act as exocrine glands producing a holocrine secretion,
Testes The testes are compound tubular glands that lie within a scrotal sac, suspended from the body by a spermatic cord. The testes are dual organs that act as exocrine glands producing a holocrine secretion,
Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology
 Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
fibroproliferation, and mononuclear cell infiltration. An autoallergic aetiology (Received 13th December 1972)
 EARLY HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN EXPERIMENTAL CONTRALATERAL EPIDIDYMO\x=req-\ ORCHITIS IN THE RABBIT E. ZAPPI and S. SHULMAN Department of Microbiology, Mew York Medical College, New York, N.Y. 10029, U.S.A.
EARLY HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN EXPERIMENTAL CONTRALATERAL EPIDIDYMO\x=req-\ ORCHITIS IN THE RABBIT E. ZAPPI and S. SHULMAN Department of Microbiology, Mew York Medical College, New York, N.Y. 10029, U.S.A.
Basic histology 5/4/2015
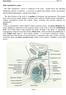 Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
Macroscopic and Microscopic Study of the Testis after Ligation Of Head And Body Of Epididymis In Adult Male Albino Rats.
 Iosr Journal Of Pharmacy E-Issn: 2250-3013, P-Issn: 2319-4219 Www.Iosrphr.Org Volume 3, Issue 2 (March 2013), Pp 16-23 Macroscop and Mroscop Study of the Testis after Ligation Of Head And Body Of Epididymis
Iosr Journal Of Pharmacy E-Issn: 2250-3013, P-Issn: 2319-4219 Www.Iosrphr.Org Volume 3, Issue 2 (March 2013), Pp 16-23 Macroscop and Mroscop Study of the Testis after Ligation Of Head And Body Of Epididymis
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems. Male 11/29/2015. Male reproductive system is composed of... BIO 218 Fall Gonads (testes)
 Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
Developmental Changes of Müllerian and Wolffian Ducts in Domestic Cat Fetuses
 Exp. Anim. 58(1), 41 45, 2009 Note Developmental Changes of Müllerian and Wolffian Ducts in Domestic Cat Fetuses Tomo INOMATA 1), Hiroyoshi NINOMIYA 1), Katsuyasu SAKITA 1), Naomi KASHIWAZAKI 2), Junya
Exp. Anim. 58(1), 41 45, 2009 Note Developmental Changes of Müllerian and Wolffian Ducts in Domestic Cat Fetuses Tomo INOMATA 1), Hiroyoshi NINOMIYA 1), Katsuyasu SAKITA 1), Naomi KASHIWAZAKI 2), Junya
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
Spermatogenesis after scrotal reconstruction
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 484 488 Spermatogenesis after scrotal reconstruction Dali Wang a, *, Hong Zheng b, Fei Deng b a Department of Plastic Surgery, The Affiliated Hospital
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 484 488 Spermatogenesis after scrotal reconstruction Dali Wang a, *, Hong Zheng b, Fei Deng b a Department of Plastic Surgery, The Affiliated Hospital
Pathology of Male Reproductive System 2
 Pathology of Male Reproductive System 2 Professor Dr Ali Hassan Altimimi Professor of pathology & histology MSc, PHD, MD(UK) MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The Vas deferens (or ductus deferens) The mucosa of
Pathology of Male Reproductive System 2 Professor Dr Ali Hassan Altimimi Professor of pathology & histology MSc, PHD, MD(UK) MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The Vas deferens (or ductus deferens) The mucosa of
the liver and kidney function (both vital when dealing with anaesthetic drugs) and to rule out any unsuspected illnesses.
 Orchiectomy: Castration reduces overpopulation by inhibiting male fertility and decreases male aggressiveness, roaming, and undesirable urination behaviour. It helps prevent androgenrelated diseases, including
Orchiectomy: Castration reduces overpopulation by inhibiting male fertility and decreases male aggressiveness, roaming, and undesirable urination behaviour. It helps prevent androgenrelated diseases, including
DEVELOPMENT OF THE RECTUM-TESTIS TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCE IN THE POST-NATAL RAT
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE RECTUM-TESTIS TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCE IN THE POST-NATAL RAT MARTTI KORMANO Department of Anatomy, University of Helsinki, Siltavuorenpenger, Helsinki, and Research Laboratory of the Sauna-Seura,
DEVELOPMENT OF THE RECTUM-TESTIS TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCE IN THE POST-NATAL RAT MARTTI KORMANO Department of Anatomy, University of Helsinki, Siltavuorenpenger, Helsinki, and Research Laboratory of the Sauna-Seura,
Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man
 Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man V. Nikkanen, K.-O. S\l=o"\derstr\l=o"\m and M. Parvinen Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Turku University Central
Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man V. Nikkanen, K.-O. S\l=o"\derstr\l=o"\m and M. Parvinen Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Turku University Central
straight tubules Ultrastructural evidence for phagocytosis of spermatozoa in the bovine rete testis and testicular
 Ultrastructural evidence for phagocytosis of spermatozoa in the bovine rete testis and testicular straight tubules F. Sinowatz, K.-H. Wrobel, S. Sinowatz and P. Kugler Institutfür Anatomie der Universität
Ultrastructural evidence for phagocytosis of spermatozoa in the bovine rete testis and testicular straight tubules F. Sinowatz, K.-H. Wrobel, S. Sinowatz and P. Kugler Institutfür Anatomie der Universität
Functional Importance of the Vascularization of the Testis and Epididymis for the Maintenance of Normal Spermatogenesis
 Functional Importance of the Vascularization of the Testis and Epididymis for the Maintenance of Normal Spermatogenesis R. G. Harrison, M.A., D.M., B.Ch. THE TREATMENT of male infertility is now recognized
Functional Importance of the Vascularization of the Testis and Epididymis for the Maintenance of Normal Spermatogenesis R. G. Harrison, M.A., D.M., B.Ch. THE TREATMENT of male infertility is now recognized
Ultrastructural studies on the epididymal spermatozoa in the rhesus monkey
 J. Biosci., Vol. 2, Number 3, September 1980, pp. 261-266. Printed in India. Ultrastructural studies on the epididymal spermatozoa in the rhesus monkey ASHA PRAKASH, M. R. N. PRASAD and T.C. ANAND KUMAR
J. Biosci., Vol. 2, Number 3, September 1980, pp. 261-266. Printed in India. Ultrastructural studies on the epididymal spermatozoa in the rhesus monkey ASHA PRAKASH, M. R. N. PRASAD and T.C. ANAND KUMAR
Optimum Time for Orchiopexy in Cryptorchidism
 Optimum Time for Orchiopexy in Cryptorchidism Frank Hinman, Jr., M.D. THE RESULTS of orchiopexy are disappointing. Is it that the surgical procedure is faulty, or can the defect be in the patient or in
Optimum Time for Orchiopexy in Cryptorchidism Frank Hinman, Jr., M.D. THE RESULTS of orchiopexy are disappointing. Is it that the surgical procedure is faulty, or can the defect be in the patient or in
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
DISINTEGRATION OF EPIDIDYMAL SPERMATOZOA BY APPLICATION OF ICE TO THE SCROTAL TESTIS
 [ DINTEGRATION OF EPIDIDYMAL SPERMATOZOA BY APPLICATION OF ICE TO THE SCROTAL TEST By MIN CHUEH CHANG, Ph.D. (Cantab.), School of Agriculture, Cambridge University (Received i May ) (With Four Text-figures)
[ DINTEGRATION OF EPIDIDYMAL SPERMATOZOA BY APPLICATION OF ICE TO THE SCROTAL TEST By MIN CHUEH CHANG, Ph.D. (Cantab.), School of Agriculture, Cambridge University (Received i May ) (With Four Text-figures)
SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS
 SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS GONADECTOMY: CASTRATION USING SCROTAL METHOD 1. The animal is anesthetized and placed in dorsal recumbency with the tail toward the surgeon. 2. The abdominal and scrotal
SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS GONADECTOMY: CASTRATION USING SCROTAL METHOD 1. The animal is anesthetized and placed in dorsal recumbency with the tail toward the surgeon. 2. The abdominal and scrotal
Academic Script Surgical Techniques Like Ovariectomy, Orchidectomy, Adrenalectomy, Etc
 Academic Script Surgical Techniques Like Ovariectomy, Orchidectomy, Adrenalectomy, Etc Aim: To Study the Surgical Techniques like Ovariectomy, Orchidectomy, Adrenalectomy, Tubectomy and Vasectomy in Rodents
Academic Script Surgical Techniques Like Ovariectomy, Orchidectomy, Adrenalectomy, Etc Aim: To Study the Surgical Techniques like Ovariectomy, Orchidectomy, Adrenalectomy, Tubectomy and Vasectomy in Rodents
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system Testes Genital ducts Accessory sex glands: seminal vesicles prostate bulbourethral glands External genitalia: penis Structure of the Testis Tunica
The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system Testes Genital ducts Accessory sex glands: seminal vesicles prostate bulbourethral glands External genitalia: penis Structure of the Testis Tunica
W.S. O University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA November 2-5, 2011 Hyderabad, India Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission of WEVA Organizers
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA November 2-5, 2011 Hyderabad, India Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission of WEVA Organizers
Male reproduction. Cross section of Human Testis ผศ.ดร.พญ.ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 1. Aims
 Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
STUDY ON THE VRSYA PROPERTY (TESTICULAR REGENERATIVE POTENTIAL) OF VANGA BHASMA NAGARAJU, V., JOSHI, D., AND ARYYA, N.C.
 Ancient Science of Life, Vol No. V No. 1 July 1985, STUDY ON THE VRSYA PROPERTY (TESTICULAR REGENERATIVE POTENTIAL) OF VANGA BHASMA NAGARAJU, V., JOSHI, D., AND ARYYA, N.C. Institute of Medical Sciences,
Ancient Science of Life, Vol No. V No. 1 July 1985, STUDY ON THE VRSYA PROPERTY (TESTICULAR REGENERATIVE POTENTIAL) OF VANGA BHASMA NAGARAJU, V., JOSHI, D., AND ARYYA, N.C. Institute of Medical Sciences,
Impairment of rat spermatogenesis following unilateral experimental ischemia
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1982 The American Fertility Society Vol. 38, No.4, October 1982 Printed in U.8A. Impairment of rat spermatogenesis following unilateral experimental ischemia David Iwan
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1982 The American Fertility Society Vol. 38, No.4, October 1982 Printed in U.8A. Impairment of rat spermatogenesis following unilateral experimental ischemia David Iwan
Immune response following vasectomy in the rat: a study of
 J. Anat. (1992) 181, pp. 471-479, with 11 figures Printed in Great Britain Immune response following vasectomy in the rat: a study of the stimulation of the regional lymph node 471 J. LEWIS AND S. W. McDONALD
J. Anat. (1992) 181, pp. 471-479, with 11 figures Printed in Great Britain Immune response following vasectomy in the rat: a study of the stimulation of the regional lymph node 471 J. LEWIS AND S. W. McDONALD
Male Reproductive System. Anatomy
 Male Reproductive System Medical Terminology Chapter Seven HIT # 141 Anatomy Testis or testicle = main male sex organs, paired, oval shaped, enclosed in a sac called the scrotum. Seminiferous tubules =
Male Reproductive System Medical Terminology Chapter Seven HIT # 141 Anatomy Testis or testicle = main male sex organs, paired, oval shaped, enclosed in a sac called the scrotum. Seminiferous tubules =
DAX1, testes development role 7, 8 DFFRY, spermatogenesis role 49 DMRT genes, male sex differentiation role 15
 Subject Index N-Acetylcysteine, sperm quality effects 71 Ambiguous genitalia, origins 1, 2 Anti-Müllerian hormone function 13 receptors 13 Sertoli cell secretion 10, 38 Apoptosis assays in testes 73, 74
Subject Index N-Acetylcysteine, sperm quality effects 71 Ambiguous genitalia, origins 1, 2 Anti-Müllerian hormone function 13 receptors 13 Sertoli cell secretion 10, 38 Apoptosis assays in testes 73, 74
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
*OPERATIVE PROCEDURE. Serum tumour markers within normal limits S1.04 PRINCIPAL CLINICIAN
 Neoplasia of the Testis - Orchidectomy Histopathology Reporting Proforma Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Neoplasia of the Testis - Orchidectomy Histopathology Reporting Proforma Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Efferent Ducts and Epididymis
 increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
CHANGES IN THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE TESTES AND EPIDIDYMIDES IN VASECTOMIZED RAMS*
 FERTLTY AND STERLTY Copyright 1978 The American Fertility Society Vol. 29, No.3, March 1978 Printed in U.SA. CHANGES N THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTON OF THE TESTES AND EPDDYMDES N VASECTOMZED RAMS* B. M. A.
FERTLTY AND STERLTY Copyright 1978 The American Fertility Society Vol. 29, No.3, March 1978 Printed in U.SA. CHANGES N THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTON OF THE TESTES AND EPDDYMDES N VASECTOMZED RAMS* B. M. A.
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Growth pattern of the sex ducts in foetal mouse hermaphrodites
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. 73, 59-68, 1983 59 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Growth pattern of the sex ducts in foetal mouse hermaphrodites By C. YDING ANDERSEN 1, A. G. BYSKOV
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. 73, 59-68, 1983 59 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Growth pattern of the sex ducts in foetal mouse hermaphrodites By C. YDING ANDERSEN 1, A. G. BYSKOV
What do we mean by male infertility?
 Chapter1 What do we mean by male infertility? What do we mean by male infertility? This may be a strange question to ask at the beginning of a book on male infertility but it is an important one and, as
Chapter1 What do we mean by male infertility? What do we mean by male infertility? This may be a strange question to ask at the beginning of a book on male infertility but it is an important one and, as
Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center
 Ultrasound of the Scrotum Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center Etiologies of Acute Scrotal Pain Epididymitis/Orchitis
Ultrasound of the Scrotum Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center Etiologies of Acute Scrotal Pain Epididymitis/Orchitis
Effect of Low Temperatures on Rat Spermatogenesis
 Effect of Low Temperatures on Rat Spermatogenesis Jean Macdonald, B.Sc., and R. G. Harrison, D.M. ALTHOUGH THERE HAVE BEEN several investigations of the effect of increased temperature on spermatogenesis
Effect of Low Temperatures on Rat Spermatogenesis Jean Macdonald, B.Sc., and R. G. Harrison, D.M. ALTHOUGH THERE HAVE BEEN several investigations of the effect of increased temperature on spermatogenesis
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
MICROSCOPIC AND CONVENTIONAL SUB INGUINAL VARICOCELECTOMY COMPARITIVE STUDY
 MICROSCOPIC AND CONVENTIONAL SUB INGUINAL VARICOCELECTOMY COMPARITIVE STUDY Mahmoud Abou Amraa Surgery Department, Al-Azhar University, Assiut ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MICROSCOPIC AND CONVENTIONAL SUB INGUINAL VARICOCELECTOMY COMPARITIVE STUDY Mahmoud Abou Amraa Surgery Department, Al-Azhar University, Assiut ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
REAPPRAISAL OF THE VALUE OF TESTICULAR BIOPSY IN THE INVESTIGATION OF INFERTILITY
 FERTWTY AND STEIuLlTY Copyright 1980 The American Fertility Society Vol., No.1 January 1980 Prinwl in U.S.A. REAPPRAISAL OF THE VALUE OF TESTICULAR BIOPSY IN THE INVESTIGATION OF INFERTILITY TERENCE
FERTWTY AND STEIuLlTY Copyright 1980 The American Fertility Society Vol., No.1 January 1980 Prinwl in U.S.A. REAPPRAISAL OF THE VALUE OF TESTICULAR BIOPSY IN THE INVESTIGATION OF INFERTILITY TERENCE
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
5 15/3/2012. Malik Al-Momani
 5 15/3/2012 Malik Al-Momani بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Spermatogenesis Note : Please refer to slides so see photos. Quick Revision : - Testis is divided by septum into testicular lobules, inside the lobules
5 15/3/2012 Malik Al-Momani بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Spermatogenesis Note : Please refer to slides so see photos. Quick Revision : - Testis is divided by septum into testicular lobules, inside the lobules
Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester
 Laboratory 9 Cat Dissection II Respiratory Urinary/Reproductive Systems Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester Cat dissection labs Dissection II (today) Respiratory (Ex. 57 in Hole) Human Reproductive Systems
Laboratory 9 Cat Dissection II Respiratory Urinary/Reproductive Systems Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester Cat dissection labs Dissection II (today) Respiratory (Ex. 57 in Hole) Human Reproductive Systems
STERILITY IN MALE ANIMALS INDUCED BY INJECTION OF CHEMICAL AGENTS INTO THE VAS DEFERENS*
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No. 11, November 1973 Printed in U.S.A. STERILITY IN MALE ANIMALS INDUCED BY INJECTION OF CHEMICAL AGENTS INTO THE VAS DEFERENS*
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No. 11, November 1973 Printed in U.S.A. STERILITY IN MALE ANIMALS INDUCED BY INJECTION OF CHEMICAL AGENTS INTO THE VAS DEFERENS*
Congenital mesonephric defects in male infants
 J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 725-730 Congenital mesonephric defects in male infants with mucoviscidosis J. R. OLSON AND D. K. WEAVER From the Department ofpathology, The University of Michigan Medical Center,
J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 725-730 Congenital mesonephric defects in male infants with mucoviscidosis J. R. OLSON AND D. K. WEAVER From the Department ofpathology, The University of Michigan Medical Center,
Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System. VIBS 289 lab
 Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University OBJECTIVE To conduct a histologic examination of the testis (which produce spermatozoa), excretory
Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University OBJECTIVE To conduct a histologic examination of the testis (which produce spermatozoa), excretory
