Immune response in obstructive male infertility. Prof. A.K.Sarda Department of Surgery Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi
|
|
|
- Juniper Reeves
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Immune response in obstructive male infertility Prof. A.K.Sarda Department of Surgery Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi
2 Sperm transport from the testicle Seminiferous tubule contractions of the myoid cells (hormone dependent) Fluid build up and pressure Testicular capsule contractions
3 Epididymis Responsible for sperm maturation and motility. Usually two-thirds of the epididymis is needed for sperm transport in the human for normal sperm fertilization capacity. Potential markers of epididymal function include carnitine and glycerol phosphocholine. Sperm take approximately two weeks to get through the epididymis. Sperm are stored near the tail portion and in the vas deferens until they are ejaculated
4 Stereological analysis of the human testis after vasectomy indicates impairment of spermatogenic efficiency with increasing obstructive interval "Vasal obstruction results in significant reductions in germ cells in the later stages of spermatogenesis and increases in testicular fibrosis, both worsening with an increasing obstructive interval. Testicular damage after vasectomy might impact upon the prospects for reversal." Fertil Steril Jun;81(6):
5 Some gross observations of the epididymides following vasectomy In 114 vasectomized men, 220 epididymides were grossly examined during vasovasostomy. Fullness, distention, turgidity, thickening, induration, and other gross changes of the epididymides, including the formation of cystic spermatic granuloma, or spermatocele, indicated inadequate removal of spermatozoa and testicular fluid from the sequestrated proximal seminal ducts and the epididymis. Fertil Steril Mar;27(3):267-70
6 Vasectomy review: sequelae in the human epididymis and ductus deferens Following vasectomy, spermatogenesis continues, the human epididymis and ductus deferens may distend and leak, and the extravasated spermatozoa stimulate formation of a sperm granuloma. Granulomas may occur at 60% of vasectomy sites and are usually asymptomatic and relieve intraluminal pressure. About 3-5% of patients experience pain. Intraluminal phagocytosis may explain why some reproductive tracts become depleted of spermatozoa. Most episodes of painful epididymitis and granulomas resolve with conservative treatment, but < 1% require vasectomy reversal or, if this is ineffective, excision of the epididymis and obstructed ductus deferens. Clin Anat. 1996;9(5):
7 Cellular responses to vasectomy Following vasectomy, epididymal distension and sperm granuloma formation result from raised intraluminal pressure. The sperm granuloma is a dynamic structure and a site of much spermatozoal phagocytosis by its macrophage population. In many species, spermatozoa in the obstructed ducts are destroyed by intraluminal macrophages, and degradation products, rather than whole sperm, are absorbed by the epididymal epithelium. In laboratory animals, there is evidence that pressure-mediated damage to the seminiferous epithelium can follow sperm granuloma formation and obstruction in the epididymal head. Int Rev Cytol. 2000;199:
8 The response of the male reproductive tract to vasectomy Inflammation of the interstitial tissue of the epididymis in Lewis rats at intervals following bilateral vasectomy, vasectomy followed 1 month later by vasovasostomy, or sham operations. In areas of interstitial reaction, numerous macrophages, monocytes, lymphocytes, neutrophils, and plasma cells occupied the connective tissue. Macrophages, containing many lysosomes and vesicles, aggregated and assumed the appearance of epithelioid cells. Many plasma cells with distended rough endoplasmic reticulum appeared in the interstitium. The majority of animals in the vasectomy and vasovasostomy groups exhibited epididymal interstitial changes by 2-3 months; the cauda epididymidis was the region most often affected. The ultrastructural features were indicative of chronic granulomatous inflammation and were consistent with an immune response. The nearly complete absence of sperm or recognizable parts thereof in the interstitial tissue in the areas of the reactions suggests that these lesions formed in response to soluble antigens leaking from the duct. Vasovasostomy was not effective in reversing or retarding epididymal inflammation at the intervals studied. Anat Rec Jan;235(1):61-73
9 Vasectomy-related changes on sonographic examination of the scrotum A retrospective study of 30 patients with a history of vasectomy and 30 patients without who were referred for scrotal sonography for various indications over a 1-year period. The following findings had a statistically higher incidence in the vasectomy group than in the controls: thickened epididymides (53% versus 17%, p < 0.05); epididymal tubular ectasia (43% versus 7%, p < 0.001); and both of the previous 2 findings simultaneously (37% versus 7%, p < 0.01). sperm granulomas were found in 3 patients in the vasectomy group, and none was seen in the control group. other findings (eg, epididymal cysts) showed no statistical difference in incidence. J Clin Ultrasound Oct;32(8):394-8.
10 Vasovasostomy Study Group This largest multicenter group to assess vasovasostomy efficacy has found that if the interval was less than 3 years from the vasectomy, patency was 97% and pregnancy was 76%. In men more than 15 years from their vasectomies, patency and pregnancy rates fell to 71% and 30%, respectively.
11 Patency and pregnancy rates after vasovasostomy at different intervals between vasectomy and reversal. Eur Urol 2001;40/4 (Curric Urol 1 10)
12 Failure following vasovasostomy Epididymal obstruction Autoantibodies Oxidation Other lower fertility factors Protein P34H Sperms with abnormal heads
13 Abnormalities of sperm morphology in cases of persistent infertility after vasectomy reversal Persistent infertility after vasectomy reversal by vasovasostomy may be due to irreversible changes in epididymal physiology, producing morphologic abnormalities of the sperm tail. The epididymal environment is required for the final maturation of spermatazoa and the acquisition of normal motility and fertilizing ability. The study results suggest that these epididymal functions may be impaired in some men after vasectomy due to a disturbance of epididymal physiology. Fertil Steril Jul;38(1):112-4.
14 Male reproductive immunology Immunologically the testis is a privileged site with the blood-testis barrier morphologically and humorally separating the germ cell population from the interstitial tissue. The epididymis is considered to be the most likely source of antibody secretion. It is densely populated with lymphocytes and macrophages. Infertil Reprod Med Clin North Am 1999; 10:
15 Sperm degradation products In case of obstructive azoospermia, spermatozoal degradation occurs proximal to the site of obstruction in the epididymis. It is currently believed that soluble spermatozoal fragments are either absorbed or they leak from the basal lamina and the ductuli efferentis for absorption in the interstitium. Fertil Steril 1979; 32:
16 Changes following vasectomy Gross anatomical changes cystic swelling at the site of operation development of spermatic granuloma. In experimental auto-immune orchitis varying degree of vacuolization of the Sertoli cells; premature exfoliation of immature germ cells; coalescence of cellular units of the germ cell clones from multinucleate giant cells; distortion of spermatid nucleus and acrosome; and retention and degeneration of late spermatids within the epithelium. Due to phagocytosis of the spermatozoa the soluble antigens of the sperm leak into the circulation and produce autoantibodies. Sperm agglutinating antibodies in sera have been detected as soon as the 3rd or 4th day after vasectomy, but they appear in the sera more commonly between 6 weeks to 6 months. Circulating sperm immobilizing antibodies are found in 1%-3% of the nonvasectomized individuals. Within 6 months post operation, about 31% of men develop these antibodies. Swollen sperm head antibodies are found in less than 2% of nonvasectomized male populations and in 28%-33% of vasectomized males within a year following the operation. Arch Androl Sep;7(2):193-9.
17 Histologic changes in the mouse testis after bilateral vasectomy The seminiferous epithelium in the tubules was only 2-3 layers thick and showed much depletion of germ cells; in severe cases, the epithelium consisted of only a thin layer of Sertoli cells, spermatogonia and a few spermatocytes. Exfoliation of germ cells, occurrence of multinucleated giant cells and vacuolated appearance of the epithelium were of common features in the tubules. Furthermore, lumen of the retetestis was greatly dilated and showed accumulation of spermatozoa with immature germ cells; in mice vasectomized for 6-12 months, several macrophages ingesting spermatozoa were often observed in the lumen of the rete testis. Spermatic granuloma was also sometimes noticed in corpus or in cauda regions of the epididymis in mice vasectomized for 6-12 months. Asian J Androl 2000 Jun; 2:
18 Immune orchitis Clinical and pathologic evidences of immune orchitis in men exhibiting natural autoimmunity to sperm has never been provided. Frontiers in Bioscience ; e9-25
19 Antisperm antibodies Following vasectomy the prevalence of ASA is 34% to 74% and they persist in 38% to 60% following successful vasovasostomy. Frontiers in Bioscience ; e9-25. Production of ASA after obstruction of the epididymis has also been reported in experimental animals. J Androl 1998; 19: Fertil Steril 2000; 73:
20 Production of ASA The degradation spermatozoal products may also leak at the breached epididymal sites Fertil Steril 1979; 32: or may be produced in larger quantities than to be overcome by the immunological suppressor barrier Int Rev Cytol 2000; 199: ; Infertil Reprod Med Clin North Am 1999; 10: ; Br J Urol 1985; 57:
21 Antisperm antibodies & infertility Clinically antisperm antibodies are found in the serum in 3% to 12% of men who undergo evaluation for infertility as compared to 2% in the normal fertile population. Br J Urol 1977; 49: Among men from couples with unexplained infertility significant titres have been recorded in the serum in 10%-16%. J Reprod Immunol 1985; 8:
22 Antisperm antibodies May result in the serum, seminal fluid or on sperm surface either as a result of transport of spermatozoal degradation products by the macrophages to the regional lymph nodes, breakdown of the blood-testis / bloodepididymis barrier due to trauma or infection with escape of sperm antigens directly into the microcirculation, or, by production of antibodies against infective agents like Chlamydia which cross react with spermatozoa. Front Biosci 1999: 4: e9-25.
23 ASA following vasectomy Antisperm antibodies are found in approximately 50% 70% of men after vasectomy and in every mammalian species studied. Percentages of men with antibodies detected after vasectomy vary between 52% and 68% at 6 months, and 52% 60% after 1 year, and antibodies have been found to persist in the circulation for several years. Fertil Steril 2000; 73(5):
24 ASA & congenital vas obstruction The association of ASA with obstructive azoospermia due to congenital causes is not yet well established with conflicting data being reported in literature. Frontiers in Bioscience ; e9-25.
25 Antibody interference with fertility There is little evidence that suggests a cause/effect relationship between ASA and abnormality of principal semen parameters (sperm count, motility and morphology) while the impairment of sperm penetration through the cervical mucus represents the best known and established mechanism. Analysis of human IVF results also indicate that sperm bound antibodies impair the fertilization process, which, to some extent, is related with the degree of sperm autoimmunization. Frontiers in Bioscience ; e9-25
26 ASA & conception following vasectomy reversal Studies of the immunologic consequences of vasectomy indicate that the sperm antibodies when they appear in the ejaculate following vasovasostomy, are likely to affect the sperm function, suggesting that they are clinically important. Linnet et al. documented a conception rate in the partners of men who had undergone sterilization reversal, with no evidence of antisperm antibodies in their seminal plasma, of 85% versus 14% for the partners of men whose semen contained antibodies. Lancet 1981; I: Parslow et al. confirmed this finding but also documented that fertility is impaired only when high titers of ASA are present in the seminal fluid. Fertil Steril 1985; 43: Meinhertz et al. studied the ejaculates of 216 men following sterilization reversal. The conception rate was 85% in the partners of a subgroup of men with a pure IgG response, while only 43% of men who had lga on their sperm fathered children. The conception rate was reduced even further when 100% of sperm were coated with lga (21.7%). The combination of IgA on all sperm and a high serum titer (more than 1:250) detected by agglutination test was associated with a zero conception rate. Fertil Steril 1990; 54:
27 Interference with the fertilization process The fertilization rate with in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer (IVF-ET) was significantly lower in the presence of spermbound antibodies than in the case of other indications, the likelihood of fertilization is higher with intracytoplasmatic sperm injection (ICSI), where the reported fertilization rates are similar to those in other indications. Frontiers in Bioscience ; e9-25
28 Qualitative differences in the effects of ASA in the fertility impairment Different immunoglobulin isotypes of antibodies occurring on sperm surface can produce different biological effects (i.e., cytotoxic effects due to complement activation can be produced by IgG but not IgA sperm bound antibodies). Due to their polyclonal nature, ASA are directed against more than one sperm antigen, which may differ among patients and may be more o less relevant to fertility. Frontiers in Bioscience ; e9-25
29 ICSI in obstructive azoospermia In patients of obstructive azoospermia, the pregnancy rate with ICSI using sperms aspirated from the epididymis in terms of pregnancies per cycle has been reported to be 41% - 47%. Hum. Reprod. 10: Fertil. Steril 1995; 61: In 49% of failed cycles of ICSI, fertilization failure was related to a sperm factor like the absence of motile spermatozoa for injection, or the injection of morphologically abnormal spermatozoa. Human Reprod 1995;. 10:
30 Analysis of spermatozoa from the proximal vas deferens of vasectomized men Sperm concentration in the proximal vas from vasectomized men was significantly higher than that of fertile men and was maintained at a constant level independent of the duration of vas obstruction. The means of sperm motility, sperm viability (and hypo-osmotic swelling test were statistically lower than the respective values for normal fertile men. There was no significant correlation between the duration of vas obstruction and the above semen parameters. In 46.4% of vas fluids all spermatozoa were immotile and this condition was more common after 3 years of vasectomy. Immotile spermatozoa in the proximal vas fluids at the time of vasectomy reversal may be an important factor for predicting semen quality and fertilizing ability after vasovasostomy. There were not, however, significant differences in the results of sperm-cervical mucus penetration test between spermatozoa from vasectomized and fertile men. It is noted that the presence of antisperm bodies on the spermatozoa from the vas of vasectomized men, as determined by the immunobead test, may partially explain the lower pregnancy rate after vasovasostomy, with spermatozoa parameters potentially closely reflecting those in the cauda epididymis after vasectomy. Int J Androl Aug;17(4):181-5
31 Following vaso-epididymostomy By fistula method patency rate 43.7 % and pregnancy rate 16.8% Urol Clin North Am 1987; 14: By microsurgical technique patency rate 75.3% and pregnancy rate 29% Fertil Steril 1982; 34:
32 HYPOTHESIS Normally, epididymal epithelial lining prevents the extravasation of sperms or their degradation fragments into the interstitium, thus blocking a direct interaction between antibody producing cells and sperm proteins. A breach in the epididymal epithelium would lead to a direct contact between sperm antigens and immune effector cells.
33 Post vasectomy epididymal changes Following vasectomy, dilatation of epididymal ducts with sperm extravasation due to obstruction has also been reported. J Reprod Fertil 1964; 7:1-12. Inflammatory cell infiltrate with lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages, perivasculitis and fibrosis in epididymal histology have been demonstrated following vasectomy similar to the findings in our study. Br J Urol 1982; 54: ; Fertil Steril 1979; 32: Histologic changes in the epididymis to be due to a local immune response resulting from contact of sperm proteins with local immune competent cells secondary to obstruction to sperm egress. Br J Urol 1982; 54:
34 Local immune response It is also possible that in obstructive infertility breach in the epithelium causes extravasation of sperms into the interstitium and brings them in contact with the immunocompetent cells in insufficient amounts to induce detectable ASA. However, repeated exposure to the antigenic sperms may induce a local cell mediated immune response which may be responsible for the histological changes reported in the epididymis. J Reprod Fertil 1964: 7: Br J Urol 1982: 54:
35 FSH (U/L) and Spermatogenesis < >20 Gr. I Gr. II Gr. III Gr. IV 0 2 1
36 Operative Criteria for Prognosticating Outcome Vas patency Absent Not patent Patent Epididymal distension Not distended (15) Mildly distended (4) Obviously distended (31) Epididymal discharge + (13) ++ (17) +++ (11) - (9)
37 Seminal fluid antibody levels (n=30)
38 Features in epididymal histology DUE TO OBSTRUCTION OF SPERM EGRESS * Epithelial flattening with loss of cilia 25 (50%) * Pigment in epithelial cells 20 (40%) * Ductal dilatation 31 (62%) * Ductal sperms 33 (66%) * Ductal macrophages ** Vacoulation ** Sperm ingestion ** Pigment 29 (58%) [25 (86.2%)] [18 (62.1%)] [09 (31.0%)] * Epithelial breach with sperm extravasation 20 (40%) DUE TO SPERM EXTRAVASATION IN THE INTERSTITIUM * Interstitial macrophages 11 (22%) * Interstitial lymphocytes, plasma cells, etc 31 (62%)
39 Epididymis showing normal epididymal ducts with orderly layering of nuclei and cilia on the luminal surface (H&E x100)
40 Epididymis showing markedly dilated ducts containing sperms and macrophages (H&E x60)
41 Epididymis showing dilated ducts with focal flattening of the epithelium (H&E x400)
42 Epididymis of a patient showing sperm extravasation with epithelial breach (H&E x250)
43 Epididymis showing epithelial flattening and breach, and extravasation of sperms (H&E x400)
44 Epididymis showing sperm extravasation with interstitial inflammatory cell infiltration (H&E x400)
45 Dilated epididymal ducts contents showing macrophages with phagocytosed sperms and desquamated lining cells (H&E x400)
46 Epididymis showing interstitial collection of macrophages with a dilated epididymal duct to the left (H&E x400)
47 Epididymis showing peritubular fibrosis (H&E x600)
48 Interstitial epididymal fibrosis with mild chronic inflammation (H&E x400)
49 Drawbacks of the study Direct correlation between seminal fluid antibodies and local immune response Estimation of sperm bound antibodies and their correlation with seminal fluid antibodies Reversal of seminal fluid and sperm bound antibodies following reversal Effect of local immune response on failure of vasoepididymostomy results Similar studies in vasectomized and vasectomy reversal subjects
50 Differences in immune response in primary & secondary obstruction Levels of antisperm antibody production Extent of local autoimmune response Effect on sperm (count & morphology) proximal to obstruction
51 Conclusion Systemic and local immune response may be an important factor in failure of fertility following successful recanalisation and in assisted reproductive techniques.
52
Local Cell Mediated Immune Reaction in Primary Obstructive Male Infertility
 Surgical Science, 2011, 2, 31-37 doi:10.4236/ss.2011.21008 Published Online January 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ss) Local Cell Mediated Immune Reaction in Primary Obstructive Male Infertility Abstract
Surgical Science, 2011, 2, 31-37 doi:10.4236/ss.2011.21008 Published Online January 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ss) Local Cell Mediated Immune Reaction in Primary Obstructive Male Infertility Abstract
Role of Local Immune Reaction in Primary Obstructive Male Infertility
 AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (20 1 2 )5 (1 ):5 3-6 2 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE Role of Local Immune Reaction in Primary
AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (20 1 2 )5 (1 ):5 3-6 2 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE Role of Local Immune Reaction in Primary
THE INCIDENCE OF ANTISPERM ANTmODIES IN PATIENTS WITH SEMINAL TRACT OBSTRUCTIONS
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 59. 25-29,1996 THE INCIDENCE OF ANTISPERM ANTmODIES IN PATIENTS WITH SEMINAL TRACT OBSTRUCTIONS MASANORI YAMAMOTO, HATSUKI HIBI, and KOJI MIYAKE Department of Urology, Nagoya University
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 59. 25-29,1996 THE INCIDENCE OF ANTISPERM ANTmODIES IN PATIENTS WITH SEMINAL TRACT OBSTRUCTIONS MASANORI YAMAMOTO, HATSUKI HIBI, and KOJI MIYAKE Department of Urology, Nagoya University
Effect Of Obstruction To Sperm Egress On The Male Testis And Epididymis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 8 Number 1 Effect Of Obstruction To Sperm Egress On The Male Testis And Epididymis A Sarda, D Pandey, S Bhalla, S Gupta, N Khurana Citation A Sarda, D Pandey,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 8 Number 1 Effect Of Obstruction To Sperm Egress On The Male Testis And Epididymis A Sarda, D Pandey, S Bhalla, S Gupta, N Khurana Citation A Sarda, D Pandey,
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT
 ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT Reproduct ion Physiology Section, Department of Zoology, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur-302004 Summary: Rats and mice were vasectomized
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT Reproduct ion Physiology Section, Department of Zoology, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur-302004 Summary: Rats and mice were vasectomized
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1)
 Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Chapter 9. Summary & conclusion
 Chapter 9 Summary & conclusion 133 Chapter 1 Objective: To give an overview of the different vasectomy techniques utilized and try to explore from the literature what method of vasectomy could give the
Chapter 9 Summary & conclusion 133 Chapter 1 Objective: To give an overview of the different vasectomy techniques utilized and try to explore from the literature what method of vasectomy could give the
THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS
 Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
Postgraduate Training in Reproductive Health
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY Georges A. de Boccard, M.D. Consultant Urologist F.M.H., F.E.B.U. Postgraduate Training in Reproductive Health Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY Georges A. de Boccard, M.D. Consultant Urologist F.M.H., F.E.B.U. Postgraduate Training in Reproductive Health Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Male Reproductive Physiology
 Male Reproductive Physiology Overview Anatomy Function Endocrine and spermatogenesis Testis epididymus,vas deferens,seminal vesicles and prostate Hypothalamic pituitary testicular axis Hormones of the
Male Reproductive Physiology Overview Anatomy Function Endocrine and spermatogenesis Testis epididymus,vas deferens,seminal vesicles and prostate Hypothalamic pituitary testicular axis Hormones of the
Transport of Sperm. Endocrinology of the Epididymis and Sperm Maturation. Vas Efferentia. John Parrish Department of Animal Sciences
 Endocrinology of the Epididymis and Sperm Maturation John Parrish Department of Animal Sciences References: he Physiology of Reproduction, Knobil and Neill, 2006; Chapter on the Epididymis by Robaire ransport
Endocrinology of the Epididymis and Sperm Maturation John Parrish Department of Animal Sciences References: he Physiology of Reproduction, Knobil and Neill, 2006; Chapter on the Epididymis by Robaire ransport
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Reproductive System Purpose General Structures Male Structures Functions Female Anatomy Structures Functions Clinical Applications
 The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
What You Need to Know
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
HISTOLOGIC CHANGES IN THE SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES AFTER VASECTOMY
 FERTILItY AND STI!RILITY Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society Vol. 25, No.8, August 1974 PTillted in U.S.AI HISTOLOGIC CHANGES IN THE SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES AFTER VASECTOMY FLETCHER C. DERRICK,
FERTILItY AND STI!RILITY Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society Vol. 25, No.8, August 1974 PTillted in U.S.AI HISTOLOGIC CHANGES IN THE SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES AFTER VASECTOMY FLETCHER C. DERRICK,
DEFINITION HX & PH/EX
 DEFINITION HX & PH/EX Because of the success of the assisted reproductive techniques (ART), the evaluation of the man is often ignored. The physician should not forget the fact that many causes of male
DEFINITION HX & PH/EX Because of the success of the assisted reproductive techniques (ART), the evaluation of the man is often ignored. The physician should not forget the fact that many causes of male
Information Sheet. Male Infertility
 Infertility National Public Awareness Campaign Information Sheet Male Infertility In approximately half of couples complaining of infertility part of the problem lies with the male. Male infertility has
Infertility National Public Awareness Campaign Information Sheet Male Infertility In approximately half of couples complaining of infertility part of the problem lies with the male. Male infertility has
Basic histology 5/4/2015
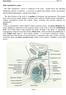 Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
MALE INFERTILITY & SEMEN ANALYSIS
 MALE INFERTILITY & SEMEN ANALYSIS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
MALE INFERTILITY & SEMEN ANALYSIS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
Microsurgical vasectomy reversal : results and predictors of success
 9 REVUE Andrologie 2005, 15, N~ 167-171 Microsurgical vasectomy reversal : results and predictors of success Gert R. DOHLE, Marij SMIT Andrology unit, Department of Urology, Erasmus University Medical
9 REVUE Andrologie 2005, 15, N~ 167-171 Microsurgical vasectomy reversal : results and predictors of success Gert R. DOHLE, Marij SMIT Andrology unit, Department of Urology, Erasmus University Medical
Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System. VIBS 289 lab
 Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University OBJECTIVE To conduct a histologic examination of the testis (which produce spermatozoa), excretory
Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University OBJECTIVE To conduct a histologic examination of the testis (which produce spermatozoa), excretory
VASOVASOSTOMY FOR OBSTRUCTIVE AZOOSPERMIA DUE TO HERNIORRHAPHY IN CHILDHOOD
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 49. 53-59, 1987 VASOVASOSTOMY FOR OBSTRUCTIVE AZOOSPERMIA DUE TO HERNIORRHAPHY IN CHILDHOOD KOJI MIYAKE, MASANORI YAMAMOTO and HIDEO MITSUYA Department of Urology, Nagoya University
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 49. 53-59, 1987 VASOVASOSTOMY FOR OBSTRUCTIVE AZOOSPERMIA DUE TO HERNIORRHAPHY IN CHILDHOOD KOJI MIYAKE, MASANORI YAMAMOTO and HIDEO MITSUYA Department of Urology, Nagoya University
Efferent Ducts and Epididymis
 increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
Microsurgical Repair of the Male Genital Tract: Refinements and Predictors of Success
 Curriculum in Urology Microsurgical Repair of the Male Genital Tract: Refinements and Predictors of Success G.R. Dohle, R.F.A. Weber Andrology Unit, Department of Urology, Erasmus University Medical Centre,
Curriculum in Urology Microsurgical Repair of the Male Genital Tract: Refinements and Predictors of Success G.R. Dohle, R.F.A. Weber Andrology Unit, Department of Urology, Erasmus University Medical Centre,
Male reproduction. Cross section of Human Testis ผศ.ดร.พญ.ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 1. Aims
 Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system Testes Genital ducts Accessory sex glands: seminal vesicles prostate bulbourethral glands External genitalia: penis Structure of the Testis Tunica
The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system Testes Genital ducts Accessory sex glands: seminal vesicles prostate bulbourethral glands External genitalia: penis Structure of the Testis Tunica
Proceedings of the Society for Theriogenology 2012 Annual Conference
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Society for Theriogenology 2012 Annual Conference Aug. 20-25, 2012 Baltimore, MD, USA www.therio.org/ Next Meeting: Aug. 7-10, 2013 Louisville, KY, USA Reprinted in the
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Society for Theriogenology 2012 Annual Conference Aug. 20-25, 2012 Baltimore, MD, USA www.therio.org/ Next Meeting: Aug. 7-10, 2013 Louisville, KY, USA Reprinted in the
Detection of Antisperm Antibodies in Sera of Iraqi Males and Females and Their Role in Fertilizing Capacity
 Detection of Antisperm Antibodies in Sera of Iraqi Males Females Their Role in Fertilizing Capacity Muhammad-Baqir M-R. Fakhrildin Phd, Sundus Fadhil Hantoosh EL-Nahi MSc Abstract Background: Antisperm
Detection of Antisperm Antibodies in Sera of Iraqi Males Females Their Role in Fertilizing Capacity Muhammad-Baqir M-R. Fakhrildin Phd, Sundus Fadhil Hantoosh EL-Nahi MSc Abstract Background: Antisperm
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 09 Page September 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i9.180 Meteroic Determination of Immunological
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i9.180 Meteroic Determination of Immunological
I would be happy to discuss all of these options for fertility after vasectomy with you at the time of our consultation or over the phone.
 F Sperm Aspiration We perform and, in fact, are pioneers in sperm aspiration here at The New York Presbyterian Hospital-Cornell Medical Center. Sperm aspiration involves extraction of sperm from either
F Sperm Aspiration We perform and, in fact, are pioneers in sperm aspiration here at The New York Presbyterian Hospital-Cornell Medical Center. Sperm aspiration involves extraction of sperm from either
THE PATIENT S GUIDE TO VASECTOMY REVERSAL
 The Basics of Vasectomy Reversal What is a Vasectomy? A vasectomy is a safe, simple, quick and effective method of contraception. As shown in Figure 1a, the testicles are continually producing sperm even
The Basics of Vasectomy Reversal What is a Vasectomy? A vasectomy is a safe, simple, quick and effective method of contraception. As shown in Figure 1a, the testicles are continually producing sperm even
Evaluation and Treatment of the Subfertile Male. Karen Baker, MD Associate Professor Duke University, Division of Urology
 Evaluation and Treatment of the Subfertile Male Karen Baker, MD Associate Professor Duke University, Division of Urology Disclosures: None Off label uses: There are no oral medications approved by the
Evaluation and Treatment of the Subfertile Male Karen Baker, MD Associate Professor Duke University, Division of Urology Disclosures: None Off label uses: There are no oral medications approved by the
Associations of Ultrasonographic Features with Scrotal Pain after Vasectomy
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2011.52.11.782 Infection/Inflammation Associations of Ultrasonographic Features with Scrotal Pain after Vasectomy Seung Hoon Cho, Seung Ki Min, Seung Tae
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2011.52.11.782 Infection/Inflammation Associations of Ultrasonographic Features with Scrotal Pain after Vasectomy Seung Hoon Cho, Seung Ki Min, Seung Tae
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE
 ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
GUIDELINES ON THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY
 GUIDELINES ON THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY G. Dohle (chairman), A. Jungwirth and W. Weidner. Eur Urol 2002;42(4):313-322 Eur Urol 2004;46(5):555-558 1. Introduction Infertility is
GUIDELINES ON THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY G. Dohle (chairman), A. Jungwirth and W. Weidner. Eur Urol 2002;42(4):313-322 Eur Urol 2004;46(5):555-558 1. Introduction Infertility is
The Use of Rabbits in Male Reproductive Toxicology
 Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 77, pp. 5-9, 1988 The Use of Rabbits in Male Reproductive Toxicology by Daniel Morton* The rabbit is the smallest and least expensive laboratory animal in which serial
Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 77, pp. 5-9, 1988 The Use of Rabbits in Male Reproductive Toxicology by Daniel Morton* The rabbit is the smallest and least expensive laboratory animal in which serial
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Getting Help for Obstructive Azoospermia A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE Getting Help for Obstructive Azoospermia A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE Getting Help for Obstructive Azoospermia A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice
Reversible Conditions Organising More Information semen analysis Male Infertility at Melbourne IVF Fertility Preservation
 Male Infertility Understanding fertility in men Conceiving a baby depends on a number of factors, including healthy sperm. After a woman s age, this can be the biggest issue. Reproduction, although simple
Male Infertility Understanding fertility in men Conceiving a baby depends on a number of factors, including healthy sperm. After a woman s age, this can be the biggest issue. Reproduction, although simple
describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it
 You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
S S GURAYA and ARBANS J KAUR Department of Zoology, College of Basic Sciences and Humanities, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana , India
 Proc. Indian Acad, Sci. (Anim. Sci.), Vol. 90, Number 5, SeptcIl1ber 1981, pp. 49S-soi. o Printed in India. Effect of castration on some hydrolytic enzymes in the rat vas deferens: A histochemical study
Proc. Indian Acad, Sci. (Anim. Sci.), Vol. 90, Number 5, SeptcIl1ber 1981, pp. 49S-soi. o Printed in India. Effect of castration on some hydrolytic enzymes in the rat vas deferens: A histochemical study
GUIDELINES FOR THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY
 GUIDELINES FOR THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY G.R. Dohle, Z. Kopa, A. Jungwirth, T.B. Hargreave. Eur Urol 2002;42(4):313-322 Eur Urol 2004;46(5):555-558 Definition Infertility is the
GUIDELINES FOR THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY G.R. Dohle, Z. Kopa, A. Jungwirth, T.B. Hargreave. Eur Urol 2002;42(4):313-322 Eur Urol 2004;46(5):555-558 Definition Infertility is the
Effects of Cryopreservation on the Ultrastructure of Human Testicular Sperm
 Journal of Reproduction & Contraception (2005) 16 (4):195-200 ORIGINAL PAPER Effects of Cryopreservation on the Ultrastructure of Human Testicular Sperm Xin-qiang LAI 1, Wei-jie ZHU 2, Jing LI 3, Fu-xing
Journal of Reproduction & Contraception (2005) 16 (4):195-200 ORIGINAL PAPER Effects of Cryopreservation on the Ultrastructure of Human Testicular Sperm Xin-qiang LAI 1, Wei-jie ZHU 2, Jing LI 3, Fu-xing
The spermatogenesis CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SPERMATOZOON 26/04/2017. Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I. Prof. Alberto Contri
 Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I The spermatogenesis Prof. Alberto Contri CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SPERMATOZOON 1) Aploid cell with high condensed DNA 2) Forward motility - flagellum 3) Enzymes for
Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I The spermatogenesis Prof. Alberto Contri CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SPERMATOZOON 1) Aploid cell with high condensed DNA 2) Forward motility - flagellum 3) Enzymes for
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Clinical evaluation of infertility
 Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Physiologic Anatomy of the Male Sexual Organs
 Reproductive and Hormonal Functions of the Male The reproductive functions of the male can be divided into three major subdivisions: (1) spermatogenesis, which means simply the formation of sperm; (2)
Reproductive and Hormonal Functions of the Male The reproductive functions of the male can be divided into three major subdivisions: (1) spermatogenesis, which means simply the formation of sperm; (2)
To General Embryology Dr: Azza Zaki
 Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male factors determining the outcome of intracytoplasmic sperm injection with epididymal and testicular spermatozoa
 andrologia 35, 220 226 (2003) Accepted: April 25, 2003 Male factors determining the outcome of intracytoplasmic sperm injection with epididymal and testicular spermatozoa J. U. Schwarzer, K. Fiedler, I.
andrologia 35, 220 226 (2003) Accepted: April 25, 2003 Male factors determining the outcome of intracytoplasmic sperm injection with epididymal and testicular spermatozoa J. U. Schwarzer, K. Fiedler, I.
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Chris Davies & Greg Handley
 Chris Davies & Greg Handley Contents Definition Epidemiology Aetiology Conditions for pregnancy Female Infertility Male Infertility Shared infertility Treatment Definition Failure of a couple to conceive
Chris Davies & Greg Handley Contents Definition Epidemiology Aetiology Conditions for pregnancy Female Infertility Male Infertility Shared infertility Treatment Definition Failure of a couple to conceive
Male Fertility: Your Questions Answered
 Male Fertility: Your Questions Answered Michael S. Neal Scientific Director, ONE Fertility, 3210 Harvester Rd. Burlington, Ontario www.onefertility.com mneal@onefertility.com Outline Assisted Conception
Male Fertility: Your Questions Answered Michael S. Neal Scientific Director, ONE Fertility, 3210 Harvester Rd. Burlington, Ontario www.onefertility.com mneal@onefertility.com Outline Assisted Conception
Variability in testis biopsy interpretation: implications for male infertility care in the era of intracytoplasmic sperm injection
 Variability in testis biopsy interpretation: implications for male infertility care in the era of intracytoplasmic sperm injection Matthew R. Cooperberg, M.D., a Thomas Chi, B.A., a Amir Jad, M.D., a Imok
Variability in testis biopsy interpretation: implications for male infertility care in the era of intracytoplasmic sperm injection Matthew R. Cooperberg, M.D., a Thomas Chi, B.A., a Amir Jad, M.D., a Imok
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Abnormalities of Spermatogenesis
 Abnormalities of Spermatogenesis Male Factor 40% of the cause for infertility Sperm is constantly produced by the germinal epithelium of the testicle Sperm generation time 73 days Sperm production is thermoregulated
Abnormalities of Spermatogenesis Male Factor 40% of the cause for infertility Sperm is constantly produced by the germinal epithelium of the testicle Sperm generation time 73 days Sperm production is thermoregulated
Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1
 Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1 Professor dr Ali Hassan Altimimi Professor of Pathology& Histology MSc, PHD, MD(UK) MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The internal male genitalia consist of the testes with
Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1 Professor dr Ali Hassan Altimimi Professor of Pathology& Histology MSc, PHD, MD(UK) MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The internal male genitalia consist of the testes with
CHANGES IN THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE TESTES AND EPIDIDYMIDES IN VASECTOMIZED RAMS*
 FERTLTY AND STERLTY Copyright 1978 The American Fertility Society Vol. 29, No.3, March 1978 Printed in U.SA. CHANGES N THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTON OF THE TESTES AND EPDDYMDES N VASECTOMZED RAMS* B. M. A.
FERTLTY AND STERLTY Copyright 1978 The American Fertility Society Vol. 29, No.3, March 1978 Printed in U.SA. CHANGES N THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTON OF THE TESTES AND EPDDYMDES N VASECTOMZED RAMS* B. M. A.
Immune response following vasectomy in the rat: a study of
 J. Anat. (1992) 181, pp. 471-479, with 11 figures Printed in Great Britain Immune response following vasectomy in the rat: a study of the stimulation of the regional lymph node 471 J. LEWIS AND S. W. McDONALD
J. Anat. (1992) 181, pp. 471-479, with 11 figures Printed in Great Britain Immune response following vasectomy in the rat: a study of the stimulation of the regional lymph node 471 J. LEWIS AND S. W. McDONALD
Male fertility disorders
 Male fertility disorders Etiology diagnosis therapeutic approaches Dr. Cornelia Roggenbuck September 29, 2009 Orthomol pharmazeutische Vertriebs GmbH Content Fertility Facts and figures Factors of influence
Male fertility disorders Etiology diagnosis therapeutic approaches Dr. Cornelia Roggenbuck September 29, 2009 Orthomol pharmazeutische Vertriebs GmbH Content Fertility Facts and figures Factors of influence
Histology of Male Reproductive System
 Histology of Male Reproductive System Lecture Objectives Describe the histological features of the male reproductive system Male Reproductive System The male structures of reproduction include the: testes,
Histology of Male Reproductive System Lecture Objectives Describe the histological features of the male reproductive system Male Reproductive System The male structures of reproduction include the: testes,
INTRACYTOPLASMIC SPERM INJECTION
 1 Background... 2 2 Male Factor Infertility... 2 3 ICSI... 3 4 Surgical sperm aspiration... 4 5 What is the chance of success?... 6 6 What are the risks?... 7 M Rajkhowa, October 2004 Authorised by V Kay
1 Background... 2 2 Male Factor Infertility... 2 3 ICSI... 3 4 Surgical sperm aspiration... 4 5 What is the chance of success?... 6 6 What are the risks?... 7 M Rajkhowa, October 2004 Authorised by V Kay
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Male reproductive system The physiology of sexual act
 Male reproductive system The physiology of sexual act Gabriella Kékesi 65. The development and physiology of the male reproductive system. The physiology of the sexual act Define chromosomal, gonadal and
Male reproductive system The physiology of sexual act Gabriella Kékesi 65. The development and physiology of the male reproductive system. The physiology of the sexual act Define chromosomal, gonadal and
5 15/3/2012. Malik Al-Momani
 5 15/3/2012 Malik Al-Momani بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Spermatogenesis Note : Please refer to slides so see photos. Quick Revision : - Testis is divided by septum into testicular lobules, inside the lobules
5 15/3/2012 Malik Al-Momani بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Spermatogenesis Note : Please refer to slides so see photos. Quick Revision : - Testis is divided by septum into testicular lobules, inside the lobules
Seminiferous Tubules
 Testes The testes are compound tubular glands that lie within a scrotal sac, suspended from the body by a spermatic cord. The testes are dual organs that act as exocrine glands producing a holocrine secretion,
Testes The testes are compound tubular glands that lie within a scrotal sac, suspended from the body by a spermatic cord. The testes are dual organs that act as exocrine glands producing a holocrine secretion,
Mohammad Sha ban. Basheq Jehad. Hamzah Nakhleh
 11 Mohammad Sha ban Basheq Jehad Hamzah Nakhleh Physiology of the reproductive system In physiology, we are concerned with the mechanisms in which the system functions, and how the system responds to different
11 Mohammad Sha ban Basheq Jehad Hamzah Nakhleh Physiology of the reproductive system In physiology, we are concerned with the mechanisms in which the system functions, and how the system responds to different
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Male factors can be identified as the cause of infertility in 30~40% of couples and a
 Focused Issue of This Month Causes and Diagnosis of Male Infertility Nam Cheol Park, MD Department of Urology, Pusan National University College of Medicine Email : pnc@pusan.ac.kr J Korean Med Assoc 2007;
Focused Issue of This Month Causes and Diagnosis of Male Infertility Nam Cheol Park, MD Department of Urology, Pusan National University College of Medicine Email : pnc@pusan.ac.kr J Korean Med Assoc 2007;
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Male History, Clinical Examination and Testing
 Male History, Clinical Examination and Testing Dirk Vanderschueren, MD, PhD Case Jan is 29 years old and consults for 1 year primary subfertility partner 28 years old and normal gynaecological investigation
Male History, Clinical Examination and Testing Dirk Vanderschueren, MD, PhD Case Jan is 29 years old and consults for 1 year primary subfertility partner 28 years old and normal gynaecological investigation
Embryology 3. Spermatogenesis:
 Embryology 3 Spermatogenesis: The 2 testis in males are each divided into lobes and lobules by connective tissue septa forming 250 lobule and in each lobule there are 1 to 4 seminefrous tubule ( so almost
Embryology 3 Spermatogenesis: The 2 testis in males are each divided into lobes and lobules by connective tissue septa forming 250 lobule and in each lobule there are 1 to 4 seminefrous tubule ( so almost
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
a. the tail disappears b. they become spermatids c. they undergo capacitation d. they have been stored in the uterus for several days
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
Chapter1 Introduction
 Chapter1 Introduction Male subfertility is a very significant global problem. Epidemiological data show that approximately 1-in-7 couples are classed as subfertile [1]. Sperm dysfunction is the single
Chapter1 Introduction Male subfertility is a very significant global problem. Epidemiological data show that approximately 1-in-7 couples are classed as subfertile [1]. Sperm dysfunction is the single
CM-B 2008: Semen Analysis INTRODUCTION ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION Semen analysis is a laboratory test that is primarily used for evaluating fertility potential and for assessing success following a vasectomy procedure. The composition of semen, also known
INTRODUCTION Semen analysis is a laboratory test that is primarily used for evaluating fertility potential and for assessing success following a vasectomy procedure. The composition of semen, also known
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
ENZYMES IN THE SEMINAL PLASMA FROM AZOOSPERMIC MEN: CORRELATION WITH THE ORIGIN OF THEIR AZOOSPERMIA
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright C'1981 The American Fertility Society Vol. 36, No.3, September 1981 PrinU!d in UBA. ENZYMES IN THE SEMINAL PLASMA FROM AZOOSPERMIC MEN: CORRELATION WITH THE ORIGIN OF
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright C'1981 The American Fertility Society Vol. 36, No.3, September 1981 PrinU!d in UBA. ENZYMES IN THE SEMINAL PLASMA FROM AZOOSPERMIC MEN: CORRELATION WITH THE ORIGIN OF
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
AZOOSPERMIA CYTOLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS
 ý Comptes rendus de l Académie bulgare des Sciences ÌÓÑ ÆÓ ¾¼½½ BIOLOGIE Morphologie AZOOSPERMIA CYTOLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS Stefka Ivanova, Petia Tzvetkova (Submitted by Corresponding Member J. Jordanov
ý Comptes rendus de l Académie bulgare des Sciences ÌÓÑ ÆÓ ¾¼½½ BIOLOGIE Morphologie AZOOSPERMIA CYTOLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS Stefka Ivanova, Petia Tzvetkova (Submitted by Corresponding Member J. Jordanov
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
Adapted from Preg. & Part., Senger
 MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
Animal Science 434. Sperm Head. Sperm From Different Species. Sperm Structure. Epididymis, Ejaculation and Semen. Head Acrosome Neck Middle Piece
 Sperm Structure Head Acrosome Neck Middle Piece Animal Science 434 Annulus Principal Piece Epididymis, Ejaculation and Semen End Piece Sperm From Different Species Sperm Head (Equatorial Segment) Nucleus
Sperm Structure Head Acrosome Neck Middle Piece Animal Science 434 Annulus Principal Piece Epididymis, Ejaculation and Semen End Piece Sperm From Different Species Sperm Head (Equatorial Segment) Nucleus
Sperm production. Sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
