Enteral Nutrition (Continuing Care)
|
|
|
- Charleen Marsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Approved by: Enteral Nutrition (Continuing Care) Senior Operating Officer, Addiction & Mental Health and Continuing Care, Edmonton; and Senior Operating Officer, Rural Services Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: VII-C-100 Date Approved March 12, 2018 Date Effective Next Review (3 years from Effective Date) April 2021 NOTE: The first appearance of terms in bold in the body of this document (except titles) are defined terms please refer to the Definitions section. Purpose To provide best practice guidelines for management of residents receiving enteral nutrition. To reduce the risk of adverse events/complications and to improve safety for the resident receiving enteral nutrition. Policy Statement Prior to administration of enteral nutrition, the health care team will consult with the resident/alternate decision maker to confirm that the intervention aligns with the resident's wishes. Inclusive in this discussion is consideration of the resident's/alternate decision maker (ADM) Advanced Care Plan: Goals of Care Designation and other care options. When administering enteral nutrition, health care professionals at Covenant Health Continuing Care facilities and programs shall adhere to criteria identified in the A.S.P.E.N Enteral Nutrition Handbook and identified Infection Control standards. Enteral nutrition requires an order from an authorized prescriber and shall have an accompanying order for dealing with a blockage of the enteral nutrition access device. Applicability This policy and procedure applies to all Covenant Health continuing care facilities, staff, medical staff, students and any other persons acting on behalf of Covenant Health. Principles Adherence to the A.S.P.E.N Enteral Nutrition Handbook guidelines and process will promote optimal nutritional support and reduce the risk of adverse events while improving resident safety. Enteral nutrition is indicated: 1. For residents with a functional GI tract who are unable to meet nutritional requirements orally whose condition is stable. 2. Those with severe dysphagia or damage to the esophagus, stomach, or intestines who can receive long-term feeding via stomach or intestines. 3. Enteral nutrition is contraindicated when aggressive therapy is not warranted or not in line with the resident s Goals of Care; e.g.in terminal phases of illness such as end-stage dementia or cancer Residents may be transferred to a Continuing Care facility with stable enteral nutrition.
2 VII-C-100 Page 2 of 10 Procedure 1. The Registered Dietitian (RD)/Authorized Prescriber Ordering of Enteral Nutrition 1.1 The RD/authorized prescriber will confirm all enteral nutrition orders on residents admitted to a continuing care facility or program. 1.2 Nursing will follow all orders received upon resident transfer to the facility. 1.3 Upon completion of their assessment, the RD/authorized prescriber will document the following: the type of enteral formula schedule of enteral nutrition all flushes required to meet fluid requirements 2. Nursing Administration of Enteral Nutrition 2.1 Review medical chart for any transfer orders for residents transferred to the facility or for changes to current enteral nutrition regime. 2.2 Contact the RD/authorized prescriber for further assessment and follow up on the transferred or changed enteral nutrition orders. 2.3 Before initiation of the enteral nutrition, review the rationale and feeding process with the resident/alternate decision-maker. 2.4 Follow Infection Control Guidelines in regard to Point of Care Risk Assessment, Hand Hygiene, etc. 2.5 Intermittent feeds should be administered using the recommended closed system and a pump where available. Open system feeds can be administered using either a pump or gravity. 2.6 The head of bed must be elevated at least 30 degrees during intermittent feedings and for at least 60 minutes following the end of the feeding. If this is not possible, position the resident on his/her right side (unless contraindicated) to lessen the risk of aspiration. 2.7 Collect the appropriate supplies; e.g. administration set, formula, personal protective equipment (PPE). 2.8 Visually inspect the plastic bag or Tetra Pak container, for external damage and altered formula characteristics with the plastic bag. 2.9 Compare the formula name to the physician s order to ensure the correct formula is being administered and check the expiry date on the formula bag/ Tetra Pak.
3 VII-C-100 Page 3 of Label the bag with the resident name, date and time the bag was administered Closed System Procedure Shake the bag well Close the roller clamp on the administration (spike) set Place the bag on a flat surface and remove the purple cap from the formula bag Ensure that the feeding tube is secured to the access site and its patency has been maintained. Report any leakage around the tube to the RN/LPN Using clean aseptic technique, remove the spike cover from the administration set and insert the spike into the port of the formula bag. Turn it clockwise until tight and give it an additional ½ turn to secure the fit Before connecting the administration set to the enteral access site, flush the enteral tube to maintain site integrity. See point 5.0 Maintaining Enteral Nutrition Before connecting the formula bag and the administration set to the resident, expel all air from the administration set line When using the infinity pump system, it is not necessary to hang the formula bag from a pole. Gravity feeding is not possible with the closed system. (Hang the bag on the IV pole if using the Kangaroo pump.) Do not interrupt feeding administration for routine care unless specifically ordered. If the feeding must be interrupted, flush the tube to reduce the residue in the tube and decrease the potential for clogging Do not re-spike a bag, even with new tubing, if it has already been spiked. See manufacturer s guidelines for administration set changes along with formula hang time based on source of preparation Open System Shake the formula Tetra Pak well Sanitize the top and rim of the Tetra Pak with an alcohol swab
4 VII-C-100 Page 4 of Pour formula into the feeding bag, without touching the inside of the bag or formula. Partially-used formula Tetra Pak must be dated, refrigerated and used within 24 hours. Visually inspect the formula for any altered formula characteristic changes Before connecting the administration set to the enteral access site, flush the enteral tube to maintain site integrity. See point 5.0 maintaining enteral nutrition Hang feed for appropriate amount of time (see manufacturer s guidelines for hang time). Hang the feeding bag on an IV pole if using the Kangaroo pump Do not interrupt feeding administration for routine care unless specifically ordered. If the feeding must be interrupted, flush the tube to reduce the residue in the tube and decrease the potential for clogging. 3. Assessing Tolerance 3.1 Monitor for signs of enteral intolerance such as emesis, abdominal distention, constipation, diarrhea and complaints of uncomfortable fullness, abdominal pain or nausea if resident is awake and alert. 3.2 If aspiration is suspected, observe for clinical signs and symptoms such as an unexplained fever, rapid breathing, shortness of breath or wheezing. Follow-up with an appropriate assessment and notify prescriber. 4. Increasing Feeding Rate 4.1 Increase the feeding rate according to the prescriber s order and in consultation with the dietitian. 4.2 Residents with diarrhea will likely require a more gradual increase. 4.3 As enteral nutrition increases, other fluid inputs such as hypodermoclysis may need to be reassessed to achieve optimal fluid balance. 5. Maintaining Enteral Nutrition 5.1 Record enteral nutrition information on the relevant forms, such as the Resident Flow Sheet/Daily Assessment/Fluid Balance Record. If there are unusual circumstances, record these in the progress notes.
5 VII-C-100 Page 5 of 10 Feeding bags, tubing, and other equipment used to flush the feedings should be changed in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions and as per site specific process. 5.2 Flush with a minimum of 10 ml water every four hours if enteral nutrition is held. Water used to flush feeding tube should not be added to feeding bag. 5.3 Separate 60 ml syringes should be used for flushes and for medications. These should be labelled and dated. 5.4 Syringes should be cleaned after use with warm soapy water and rinsed. Syringes can be kept for up to 72 hours and should be disposed of sooner if necessary. 5.5 If enteral nutrition device becomes blocked, instill ml warm water. Let sit for 15 minutes and attempt to flush with water. Cola, cranberry juice or other acidic substances are NOT recommended due to their low ph and potential for coagulation of proteins in the formulas. 5.6 If tube remains clogged: implement prescriber s order for one capsule of pancrealipase (eg. Cotazym) and one 325 mg tablet of sodium bicarbonate crush the sodium bicarbonate and open the Cotazym capsule and mix these with ml of water instill the mixture into the feeding tube clamp for five minutes flush with water until clear repeat twice if needed If tube remains obstructed, check for mechanical obstruction (tube may need replacing) If tubes remain plugged, consider using ClogZapper packages (Reference #20-000) 5.7 For residents on intermittent feeds or when feed is off, use the same cap from the spike set to cover the tip of the feeding tube. When the tip is connected, tape the cap to the pump for future use. 5.8 The tube and skin around the stoma site should be checked at the time of each feed. If leaking is noted, the RN/RPN should check the position of the tube and/or the balloon for inflation. A 2x2 gauze pad under the tube will help to determine if there is further drainage at the site. If there is further drainage, change the balloon type tube or consult the attending physician regarding leakage and a non-balloon type tube.
6 VII-C-100 Page 6 of Medication and Enteral Nutrition: Procedure for Administering Medication 6.1 Enteral nutrition tubes should be flushed with a minimum of 30 ml of water by syringe (60 ml) before and after medications. 6.2 Do not add medications directly to the formula bag in either the open or closed enteral system. 6.3 Use a liquid preparation where possible. Medications that can be crushed must be crushed to a fine powder, and then mixed to a slurry in water before adding to feeding tube by syringe. Certain medications should not be crushed e.g. sustained-release, enteric coated or micro capsulated products (check with Pharmacy before crushing pills). 6.4 Each drug must be administered separately to avoid clogging and to prevent drug interactions (i.e. do not administer multiple drugs together) If more than one drug is to be administered: flush with 30 ml water before the first drug; flush with 5-10 ml water between each drug; flush with 30 ml water after last drug 6.5 Refer to Covenant Health policy #VII-A-75, Infusion Line and Tubing Verification. 7. Care of the Replaceable Gastrostomy Tube (i.e. Balloon) 7.1 RNs/RPNs may insert, reposition and remove the replaceable gastrostomy tube (balloon type) only. RNs/RPNs may not insert, reposition or remove other types of gastrostomy tubes. If these gastrostomy tubes are accidently removed or displaced, contact the attending physician. 7.2 If a replacement tube is not readily available, any foley catheter can be inserted to maintain the gastrostomy stoma until a replacement gastrostomy tube is available. Contact the attending physician and document if the foley catheter is to remain in situ longer than eight hours. Note: the foley catheter is temporary and shall not be utilized for any instillations. 7.3 A replaceable Gastrostomy tube should be left in situ until the stoma site is established, at least six months.
7 8. Insertion VII-C-100 Page 7 of See the manufacturer s instructions regarding the insertion of the replaceable gastrostomy tube and the balloon volume. 8.2 Inflate the balloon with sterile water or saline in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Do not use air. 8.3 Inspect the balloon. There should be no leaks and the balloon should inflate evenly. Deflate the balloon. If the balloon sticks to the tube, fill the balloon with 12 cc sterile water or saline then bend the tube while pressing on the balloon. 8.4 Cleanse the stoma area with soap and water. 8.5 Lubricate the tip of the tube with water soluble lubricant (i.e. Muko). Do not use petroleum jelly. 8.6 Gently insert the tube. Ensure the tube is advanced through the tract and into the stomach. 8.7 Hold the tube in place and inflate the balloon with half the volume of sterile water or saline in accordance with manufacturer's instructions. Gently pull the tube up and away from the abdomen until resistance is felt. The tube is now positioned against the stomach wall. Following this placement check, fill balloon to its maximum inflation. 8.8 Wipe any fluid or lubricant from the tube and stoma. 8.9 Check for wetness around the stoma. If there are signs of gastric leakage, check the tube position. Add fluid to the balloon in 1 or 2 cc increments as needed. Do not exceed manufacturer's recommendations Verify the tube is properly placed by injecting 10 cc of air in the feeding port and auscultating the stomach for a bubbling or gurgling of air Record the tube type, gauge, length and the balloon inflation volume on the resident chart. 9. Removal of the Tube Note: The balloon and tube may be a stained brown color from contact with gastric juices. This is normal and will not affect the function of the tube. When the tube becomes brittle, schedule a change. Non-balloon type tubes can be functional for one to two years.
8 VII-C-100 Page 8 of To Change/Replace the GastrostomyTube Balloon type tubes (eg. MIC, MICKEY, or BARD trifunnel) can be changed by an RN if they come out or there is drainage at the stoma site. The site will close within four to six hours. A foley catheter can be used in the interim to maintain patency of the site if equipment is not available when the tube comes out. Consult the attending physician and document same if the tube is to be replaced by a foley catheter for longer than eight hours For non-balloon type tubes (eg. Ponsky), changes are done by the gastroenterologist and need to be ordered and pre-booked through an endoscopy day unit. Should non-balloon type tubes come out unexpectedly, a foley catheter can be used to maintain patency of the site, however, the resident must be sent to an Emergency Department to have the tube replaced. Consult the attending physician if the non-balloon type tube comes out When changing a tube, ensure that the same lumen diameter and balloon size is used this is determined by the gastroenterologist Once the replacement tube has been properly inserted and placement confirmed, enteral nutrition can resume. 9.2 To Remove the Gastrostomy Tube: Attach a luer-tipped syringe to the balloon port and withdraw the fluid. Note the amount and color of the withdrawn fluid. If the amount withdrawn is less than what the balloon was inflated with suspect leakage from the balloon Gently remove the tube while bracing the stoma site with gentle pressure If resistance is noted, lubricate the tube and stoma with water soluble lubricant (Muko) and gently rotate the tube as it is pushed in one inch. Gently work the tube free. Never use force to remove a tube. If the tube still cannot be removed, consult the attending physician. Definitions Advance Care Planning means a process which encourages people to reflect and think about their values regarding clinically indicated current and future health care choices; explore medical information that is relevant to their health concerns; communicate wishes and values to those important to them, their alternate decision-maker and their health care team; and record those choices.
9 VII-C-100 Page 9 of 10 Alternate decision-maker means a person who is authorized to make decisions with or on behalf of the resident. These may include, specific decision-maker, a minor s legal representative, a guardian, a nearest relative in accordance with the Mental Health Act [Alberta], an agent in accordance with a Personal Directive, or a person designated in accordance with the Human Tissue and Organ Donation Act [Alberta]. Authorized prescriber means a health care professional who is permitted by Federal and Provincial legislation, her/his regulatory college, Covenant Health, and practice setting (where applicable) to prescribe medications. Enteral nutrition refers to the system of providing nutrition directly into the gastrointestinal tract bypassing the oral cavity. Enteral nutrition may be necessary because of decreased level of consciousness, and swallowing difficulties. Closed enteral nutrition system is a tube feeding formula that is available in sterile, ready to hang plastic bags. This is the recommended system. The benefits of a closed system include improved resident safety, decreased contamination risk, reduced tubing cost and formula wastage. The bag is spiked with an administration set, releasing the formula. Can only be used with a pump, no gravity feeds permitted. Open enteral nutrition system uses commercially sterilized cans that are poured into bags. The open system can be used with or without a pump. Family means one or more individuals identified by the resident as an important support, and who the resident wishes to be included in any encounters with the health care system, including, but not limited to, family members, legal guardians, friends and informal caregivers. Goals of Care Designation means a codified instruction that provides direction regarding general care intentions, specific health interventions, transfer decisions and locations of care, for a patient as established after consultation between the most responsible health practitioner, patient and when appropriate, alternate decision-maker. Goals of care designation order means the documented order for the Goals of Care Designation as written by the most responsible health practitioner Related Documents Covenant Health Policies Nutrition and Hydration Policy, #VII-C-105 Palliative Care Pathways, #VII-C-20 Advance Care Planning Goals of Care Designation, #VII-B-350
10 VII-C-100 Page 10 of 10 References A.S.P.E.N. (2010). Enteral Nutrition Handbook. Editors Boullata, J, Carney, L, Guenter, P. Fessler, TA. (June 2010). Fletcher, J. (2011). Nutrition: Safe Practice in Adult Enteral Tube Feeding. British Journal of Nursing 20(19): Simons, S and Remington, R. (2013). The Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Tube: A Nurse s Guide to PEG Tubes. Pages 77 to 83. Framingham State University. The A.S.P.E.N. Adult Nutrition Support Core Curriculum. (2012). Chapter 10 (Overview of Enteral Nutrition); Chapter 11 (Enteral Formulations); Chapter 12 (Enteral Access Devices); Chapter 13 (Complications of Enteral Nutrition) accessed Nov. 16, al_nutrition_toolkit/enteral_nutrition_practice_recommendations/. Perry AG, Potter PA, Ostendorf WR. (2014). Enteral Nutrition, Clinical Nursing Skills and Techniques, Chapter 31 (pages 775 to 795). Previous Version Date(s) N/A
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: ADMINISTRATION OF A FEEDING (CONTINUOUS OR INTERMITTENT) OR MEDICATION VIA A GASTROSTOMY TUBE-ADULT Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 07/82
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: ADMINISTRATION OF A FEEDING (CONTINUOUS OR INTERMITTENT) OR MEDICATION VIA A GASTROSTOMY TUBE-ADULT Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 07/82
Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the gravity method to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the gravity method to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous
Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, G Tubes, and J Tubes (TJUH) General Information, English (SaveNote version)
 The Patient was given access to the following documents on Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, G Tubes, and J Tubes (TJUH) General Information, English (SaveNote version) Before you leave the hospital,
The Patient was given access to the following documents on Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, G Tubes, and J Tubes (TJUH) General Information, English (SaveNote version) Before you leave the hospital,
Gastrostomy Tube Feeding
 Gastrostomy Tube Feeding A gastrostomy tube (g-tube) is a tube that enters through your abdomen and rests in your stomach. This tube is used for tube feeding formula, water, and medicine (instead of taking
Gastrostomy Tube Feeding A gastrostomy tube (g-tube) is a tube that enters through your abdomen and rests in your stomach. This tube is used for tube feeding formula, water, and medicine (instead of taking
Tube Feeding With a Pump
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will help teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will help teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
DEPARTMENT NAME GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT
 GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT Texas Children s Hospital Advanced Practice Provider Conference Pediatric Surgery April 4 th, 2019 Madison Fitzgerald PA-C, Celia Flores PA-C OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the
GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT Texas Children s Hospital Advanced Practice Provider Conference Pediatric Surgery April 4 th, 2019 Madison Fitzgerald PA-C, Celia Flores PA-C OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the
YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS
 YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS INTRODUCTION: Your health care team may prescribe a program of home Enteral nutrition (or home tube feeding) designed to meet your nutritional
YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS INTRODUCTION: Your health care team may prescribe a program of home Enteral nutrition (or home tube feeding) designed to meet your nutritional
Gastrostomy Tube Management
 Gastrostomy Tube Management Information for School Nurse Services and School Health Services Disclaimer: The information in this pamphlet is for information purposes only. Please follow individual school
Gastrostomy Tube Management Information for School Nurse Services and School Health Services Disclaimer: The information in this pamphlet is for information purposes only. Please follow individual school
Enteral Nutrition. Introduction. Brooks Health Care, Inc. Patient Instruction 1
 Introduction Receiving Nutrition through a feeding tube will take some time to get used to, but it s important to remember that you can still enjoy many of the things you ve always enjoyed. With time and
Introduction Receiving Nutrition through a feeding tube will take some time to get used to, but it s important to remember that you can still enjoy many of the things you ve always enjoyed. With time and
Western General Hospital Tubefeeding Group Radiologically Inserted Gastrostomy Protocol, October 2008
 Lothian University Hospitals Division Western General Hospital Protocol for the Care of Radiologically Inserted Gastrostomy Tube 14 FG Medicina G Tube CARE OF PATIENT FOLLOWING TUBE INSERTION OBSERVATIONS
Lothian University Hospitals Division Western General Hospital Protocol for the Care of Radiologically Inserted Gastrostomy Tube 14 FG Medicina G Tube CARE OF PATIENT FOLLOWING TUBE INSERTION OBSERVATIONS
Suprapubic and Mitrofanoff Catheter Care
 Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Education for Self Administration of Intravenous Therapy HOME IV THERAPY PICC. Portacath
 HOME IV THERAPY PICC Portacath Who To contact Cardio-Respiratory Integrated Specialist Services (CRISS) Office hours 0800 1630 hours Ph: 364 0167 Weekends and after hours, phone Christchurch Hospital operator
HOME IV THERAPY PICC Portacath Who To contact Cardio-Respiratory Integrated Specialist Services (CRISS) Office hours 0800 1630 hours Ph: 364 0167 Weekends and after hours, phone Christchurch Hospital operator
TUBES R US. Enteral Access & Management
 TUBES R US SHEILA BELL, MS, RN, CPNP PC Christine Gangi, RN, CPN Center for Gastrointestinal Motility and Functional Disorders Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition Enteral Access & Management
TUBES R US SHEILA BELL, MS, RN, CPNP PC Christine Gangi, RN, CPN Center for Gastrointestinal Motility and Functional Disorders Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition Enteral Access & Management
My patient has a feeding tube
 My patient has a feeding tube What does that mean? Martha Kliebenstein, MSN, RN Clinical Educator Types of tubes Gastrostomy (G-tube) Gastrostomy jejunostomy (G-J tube) Naso gastric (NG tube) Naso jejunal
My patient has a feeding tube What does that mean? Martha Kliebenstein, MSN, RN Clinical Educator Types of tubes Gastrostomy (G-tube) Gastrostomy jejunostomy (G-J tube) Naso gastric (NG tube) Naso jejunal
MICAFUNGIN MIXING
 1 1-800-862-2731 MICAFUNGIN MIXING Drug Name: MICAFUNGIN Volume and Rate: over 1 hour Schedule: KEY POINTS: FLUSHING: Saline Micafungin Saline Heparin 1. Always wash your hands with an antibacterial soap
1 1-800-862-2731 MICAFUNGIN MIXING Drug Name: MICAFUNGIN Volume and Rate: over 1 hour Schedule: KEY POINTS: FLUSHING: Saline Micafungin Saline Heparin 1. Always wash your hands with an antibacterial soap
Date Issued Planned Review PGN No: Part of NTW(C)29 - Trust Standard for Assessment and Management of Physical Health Author/Designation
 Trust Standard for Assessment and Management of Physical Health Policy Practice Guidance Note Enteral Tube Care, Management and Feeding (Gastrostomy and Jejunostomy) V01 Date Issued Planned Review PGN
Trust Standard for Assessment and Management of Physical Health Policy Practice Guidance Note Enteral Tube Care, Management and Feeding (Gastrostomy and Jejunostomy) V01 Date Issued Planned Review PGN
Tube Feeding At Home. A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers
 A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers Tube Feeding at Home This guidebook is for Date RD 2 Table of Contents What is Tube Feeding?... 4 Your Feeding Tube... 4 Checking and Maintaining Your Feeding
A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers Tube Feeding at Home This guidebook is for Date RD 2 Table of Contents What is Tube Feeding?... 4 Your Feeding Tube... 4 Checking and Maintaining Your Feeding
Steps for Giving an Enema
 Patient and Family Education Steps for Giving an Enema 1 of 6 Step 1: Gather supplies Fun activities for your child Enema bag 26 fr. Silicone Catheter with 30ml balloon 30ml syringe (slip tip) to inflate
Patient and Family Education Steps for Giving an Enema 1 of 6 Step 1: Gather supplies Fun activities for your child Enema bag 26 fr. Silicone Catheter with 30ml balloon 30ml syringe (slip tip) to inflate
Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults. Clinical Nutrition Services
 Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults Clinical Nutrition Services CEAC 0078 April 2017 Table of Contents To Obtain Tube Feeding Formula...2 To Obtain Tube Feeding Supplies... 3 Tube Feeding....4 Types
Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults Clinical Nutrition Services CEAC 0078 April 2017 Table of Contents To Obtain Tube Feeding Formula...2 To Obtain Tube Feeding Supplies... 3 Tube Feeding....4 Types
Tube Feeding at Home. Your Nutrition Partner. Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit
 Your Nutrition Partner Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit www.abbottnutrition.com. Tube Feeding at Home 2013 Abbott Laboratories LITHO IN USA 60715-017/March
Your Nutrition Partner Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit www.abbottnutrition.com. Tube Feeding at Home 2013 Abbott Laboratories LITHO IN USA 60715-017/March
ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Central Venous Access Devices
 For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Central Venous Access Devices Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Central Venous Access Devices Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
Policies & Procedures. RNSP - RN Procedure. I.D. Number: 1097
 Policies & Procedures Title: ESOPHAGEAL TAMPONADE TUBE (MINNESOTA Tube) ASSISTING WITH INSERTION, CARE OF A PATIENT, ASSISTING WITH REMOVAL RNSP - RN Procedure I.D. Number: 1097 Authorization [x] Nursing
Policies & Procedures Title: ESOPHAGEAL TAMPONADE TUBE (MINNESOTA Tube) ASSISTING WITH INSERTION, CARE OF A PATIENT, ASSISTING WITH REMOVAL RNSP - RN Procedure I.D. Number: 1097 Authorization [x] Nursing
Optimal nutrition in critically ill children
 Optimal nutrition in critically ill children MODULE 4 Good safety practices required for nutritional therapy Developed by The Asia Pacific Middle East Consensus Working Group on Nutrition Therapy in the
Optimal nutrition in critically ill children MODULE 4 Good safety practices required for nutritional therapy Developed by The Asia Pacific Middle East Consensus Working Group on Nutrition Therapy in the
STANDARDIZED PROCEDURE REPROGRAMMING AND REFILLING INTRATHECAL BACLOFEN PUMPS and ACCESSING THE CATHETER ACCESS PORT (Adult,Peds)
 I. Definition The purpose of this procedure is to allow the Advanced Health Practitioner (AHP) to reprogram and refill intrathecal Baclofen pumps, as well as access the catheter access port for those AHPs
I. Definition The purpose of this procedure is to allow the Advanced Health Practitioner (AHP) to reprogram and refill intrathecal Baclofen pumps, as well as access the catheter access port for those AHPs
HOME TUBE FEEDING BASICS
 HOME TUBE FEEDING BASICS UBC DIETETICS PROGRAM Module 1 of 2 SCOPE OF THESE MODULES Modules 1 & 2 address the following Nutrition Care Process steps Intervention Monitoring and Evaluation Assessment and
HOME TUBE FEEDING BASICS UBC DIETETICS PROGRAM Module 1 of 2 SCOPE OF THESE MODULES Modules 1 & 2 address the following Nutrition Care Process steps Intervention Monitoring and Evaluation Assessment and
What is a catheter? What do I need to learn about catheter care?
 Catheter care What is a catheter? A catheter is a tube that drains urine from your child s body. The catheter is connected to tubing and a bag to collect the urine. Catheters come in different sizes and
Catheter care What is a catheter? A catheter is a tube that drains urine from your child s body. The catheter is connected to tubing and a bag to collect the urine. Catheters come in different sizes and
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
Gastrostomy ( PEG ) tubes and the ED
 Gastrostomy ( PEG ) tubes and the ED Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) and radiology-inserted gastrostomy (RIG) have become the modality of choice for providing enteral access to patients who require
Gastrostomy ( PEG ) tubes and the ED Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) and radiology-inserted gastrostomy (RIG) have become the modality of choice for providing enteral access to patients who require
Home enteral feeding
 Home enteral feeding Item Type Article Authors Corrigan, Grainne Publisher Nursing in General Practice Journal Nursing in General Practice Download date 01/09/2018 00:39:10 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/10147/578880
Home enteral feeding Item Type Article Authors Corrigan, Grainne Publisher Nursing in General Practice Journal Nursing in General Practice Download date 01/09/2018 00:39:10 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/10147/578880
How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method
 How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method SETTING UP FOR AN INJECTION Select a clean, well-lit, flat working surface, such as a table. Take the ENBREL dose tray out of the refrigerator and place it on your
How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method SETTING UP FOR AN INJECTION Select a clean, well-lit, flat working surface, such as a table. Take the ENBREL dose tray out of the refrigerator and place it on your
Information about Feeding Tubes
 Information about Feeding Tubes By Theresa Imperato, RN and Lorraine Danowski, RD What is a feeding tube? It is a small, flexible tube, about ¼ in diameter that is an alternative route for nourishment
Information about Feeding Tubes By Theresa Imperato, RN and Lorraine Danowski, RD What is a feeding tube? It is a small, flexible tube, about ¼ in diameter that is an alternative route for nourishment
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female)
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
The Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy. Geoffrey Axiak Clinical Nutrition Nurse St. Luke s Hospital
 The Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Geoffrey Axiak Clinical Nutrition Nurse St. Luke s Hospital What is a P.E.G.? Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Indications for P.E.G. Insertion In cases of long-term
The Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Geoffrey Axiak Clinical Nutrition Nurse St. Luke s Hospital What is a P.E.G.? Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Indications for P.E.G. Insertion In cases of long-term
Initial placement 20FR Guidewire PEG kit REORDER NO:
 Initial placement 20FR Guidewire PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710802 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 20FR Guidewire
Initial placement 20FR Guidewire PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710802 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 20FR Guidewire
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 11/78 4/18 1 of 10 RESPONSIBILITY: RN (for chemo), LPN (nonchemo) PURPOSE: OBJECTIVE: To introduce medication
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 11/78 4/18 1 of 10 RESPONSIBILITY: RN (for chemo), LPN (nonchemo) PURPOSE: OBJECTIVE: To introduce medication
CCTC Minnesota Procedure: Minnesota Tube, Assisting with Insertion and Care of Patient
 CCTC Minnesota Procedure: Minnesota Tube, Assisting with Insertion and Care of Patient Purpose: To control bleeding from esophageal or gastric varices that have not responded to medical therapy (ie. Sclerotherapy,
CCTC Minnesota Procedure: Minnesota Tube, Assisting with Insertion and Care of Patient Purpose: To control bleeding from esophageal or gastric varices that have not responded to medical therapy (ie. Sclerotherapy,
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to to view current policies.
 If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5555 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5555 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to to view current policies.
 If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5575 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5575 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care
 Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care Chapter 7 Intravenous Access and Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Topics Aseptic Technique Medication
Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care Chapter 7 Intravenous Access and Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Topics Aseptic Technique Medication
Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit REORDER NO:
 Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710805 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit is
Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710805 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit is
Freka Balloon Gastrostomy Feeding. CARE GUIDELINES For Patients & Carers
 Freka Balloon Gastrostomy Feeding CARE GUIDELINES For Patients & Carers Useful Contacts GP Hospital Dietitian Community Dietitian Nutrition Nurse District Nurse Nutrition Feed Company/Nurse Advisor Hospital
Freka Balloon Gastrostomy Feeding CARE GUIDELINES For Patients & Carers Useful Contacts GP Hospital Dietitian Community Dietitian Nutrition Nurse District Nurse Nutrition Feed Company/Nurse Advisor Hospital
A step-by-step preparation guide
 A step-by-step preparation guide This guide provides detailed instruction on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of Veletri (epoprostenol) for Injection. It is intended to be used after your healthcare
A step-by-step preparation guide This guide provides detailed instruction on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of Veletri (epoprostenol) for Injection. It is intended to be used after your healthcare
NHS GREATER GLASGOW & CLYDE CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (SOP) INSERTION & MAINTENANCE OF INDWELLING
 Page Page 1 of 6 AIM STATEMENT REQUIREMENTS LOCATION TIMING PROCEDURE To minimise the risk of secondary infection as a result of urinary catheterisation. A urinary catheter bypasses the body s normal defence
Page Page 1 of 6 AIM STATEMENT REQUIREMENTS LOCATION TIMING PROCEDURE To minimise the risk of secondary infection as a result of urinary catheterisation. A urinary catheter bypasses the body s normal defence
A step-by-step preparation guide
 A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Urinary System Diseases/Disorders. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats
 SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
Home Tube Feeding Guide for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Open Tube Feeding System
 HOME TUBE FEEDING Home Tube Feeding Guide for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Open Tube Feeding System Name: Dietitian: Telephone: Nurse: Telephone: Doctor: Telephone: Date: Prepared and Revised
HOME TUBE FEEDING Home Tube Feeding Guide for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Open Tube Feeding System Name: Dietitian: Telephone: Nurse: Telephone: Doctor: Telephone: Date: Prepared and Revised
CATHETER ACCESS KIT. For use with Prometra Programmable Infusion Systems
 CATHETER ACCESS KIT Caution: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Table of Contents Contents... 3 Description... 3 Indications... 3 Contraindications... 3
CATHETER ACCESS KIT Caution: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Table of Contents Contents... 3 Description... 3 Indications... 3 Contraindications... 3
Adult Trauma Feeding Access Guideline
 Adult Trauma Feeding Access Guideline Background: Enteral feeding access mode (NGT, NDT, PEG, PEG-J, Jejunostomy tube) dependent upon patient characteristics. Enteral feeding management guidelines aim
Adult Trauma Feeding Access Guideline Background: Enteral feeding access mode (NGT, NDT, PEG, PEG-J, Jejunostomy tube) dependent upon patient characteristics. Enteral feeding management guidelines aim
Chapter 29 Gastrointestinal Intubation
 Chapter 29 Gastrointestinal Intubation Intubation Intubation: placement of a tube into a body structure Types of intubation Orogastric: mouth to stomach Nasogastric: nose to stomach Nasointestinal: nose
Chapter 29 Gastrointestinal Intubation Intubation Intubation: placement of a tube into a body structure Types of intubation Orogastric: mouth to stomach Nasogastric: nose to stomach Nasointestinal: nose
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ
 PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION ALPROLIX [pronounced all prō liks] Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when ALPROLIX
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION ALPROLIX [pronounced all prō liks] Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when ALPROLIX
Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube This information will help you care for your drainag e g astrostomy tube (g-tube). About Your Drainage G-Tube A drainage g-tube is
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube This information will help you care for your drainag e g astrostomy tube (g-tube). About Your Drainage G-Tube A drainage g-tube is
How to Set Up and Infuse Your TPN
 Page 1 of 10 How to Set Up and Infuse Your TPN Important: Do not change any of the supplies listed here. Keep supplies away from children. Only your home care nurse or persons trained by Fairview Home
Page 1 of 10 How to Set Up and Infuse Your TPN Important: Do not change any of the supplies listed here. Keep supplies away from children. Only your home care nurse or persons trained by Fairview Home
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION
 IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION NiaStase RT (eptacog alfa, activated) Activated Recombinant Human Blood Coagulation Factor VII Room Temperature Stable This leaflet is Part III of
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION NiaStase RT (eptacog alfa, activated) Activated Recombinant Human Blood Coagulation Factor VII Room Temperature Stable This leaflet is Part III of
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AND GIVING AN INJECTION OF ENBREL POWDER
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AND GIVING AN INJECTION OF ENBREL POWDER Introduction The following instructions explain how to prepare and inject Enbrel powder for injection. Please read the instructions carefully
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AND GIVING AN INJECTION OF ENBREL POWDER Introduction The following instructions explain how to prepare and inject Enbrel powder for injection. Please read the instructions carefully
ALPROLIX Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Do not Do not YOUR KIT CONTAINS:
 ALPROLIX Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Read the Instructions for Use before you start using ALPROLIX and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
ALPROLIX Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Read the Instructions for Use before you start using ALPROLIX and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
Pfizer, BeneFIX R2 Recombinant Factor IX
 Pfizer, BeneFIX R2 Recombinant Factor IX BeneFIX, Recombinant Factor IX, is indicated for the prevention and control of bleeding episodes in people with hemophilia B (Christmas Disease). BeneFIX is also
Pfizer, BeneFIX R2 Recombinant Factor IX BeneFIX, Recombinant Factor IX, is indicated for the prevention and control of bleeding episodes in people with hemophilia B (Christmas Disease). BeneFIX is also
Patient Solutions CARE AND MAINTENANCE OF FEEDING TUBES AND COMPLICATIONS MIEKE HABECK
 Patient Solutions CARE AND MAINTENANCE OF FEEDING TUBES AND COMPLICATIONS MIEKE HABECK CARE OF FEEDING TUBES - AGENDA Types of Tubes Tube Maintenance Stoma Care Complications - management and prevention
Patient Solutions CARE AND MAINTENANCE OF FEEDING TUBES AND COMPLICATIONS MIEKE HABECK CARE OF FEEDING TUBES - AGENDA Types of Tubes Tube Maintenance Stoma Care Complications - management and prevention
Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems
 If you require this leaflet in any other format, e.g., large print, please telephone 01935 384256 Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems Useful organisations Ms Society Helpline Tel: 0808 800
If you require this leaflet in any other format, e.g., large print, please telephone 01935 384256 Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems Useful organisations Ms Society Helpline Tel: 0808 800
NURSES GUIDE TO TUBE FEEDING
 NURSES GUIDE TO TUBE FEEDING PRESENTED BY: J E F F S O U Z A, F N P CAPITAL NURSING EDUCATION OBJECTIVES Identify types of feeding tubes and accessories Recognize enteral devices with ENFit connectors
NURSES GUIDE TO TUBE FEEDING PRESENTED BY: J E F F S O U Z A, F N P CAPITAL NURSING EDUCATION OBJECTIVES Identify types of feeding tubes and accessories Recognize enteral devices with ENFit connectors
How to Change a. Foley catheter. Patient Education Rehabilitation Nursing. Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver
 Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
Home Care Services HomeMed MedEQUIP Michigan Visiting Care Michigan Visiting Nurses Wheelchair Seating Service PROCEDURE
 UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITALS AND HEALTH CENTERS UMHHC-HCS: 253.054 First Approved Date: 3/2010 Home Care Services HomeMed MedEQUIP Michigan Visiting Care Michigan Visiting Nurses Wheelchair Seating
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITALS AND HEALTH CENTERS UMHHC-HCS: 253.054 First Approved Date: 3/2010 Home Care Services HomeMed MedEQUIP Michigan Visiting Care Michigan Visiting Nurses Wheelchair Seating
HOMES AND SENIORS SERVICES. APPROVAL DATE: February 2011 REVISION DATE: January 2015; July 2018
 POLICY: Page 1 of 6 A resident requiring enteral (tube) feeding as a sole source or adjunctive nutrition support have access to a comprehensive enteral feeding program and receive appropriate support from
POLICY: Page 1 of 6 A resident requiring enteral (tube) feeding as a sole source or adjunctive nutrition support have access to a comprehensive enteral feeding program and receive appropriate support from
Home Enteral Nutrition: What happens after discharge? Niamh Maher Senior Dietitian HSE Dublin North East
 Home Enteral Nutrition: What happens after discharge? Niamh Maher Senior Dietitian HSE Dublin North East Nutrition Support Study Day April 25 th 2012 Home enteral nutrition (HEN) Enteral tube feeding is
Home Enteral Nutrition: What happens after discharge? Niamh Maher Senior Dietitian HSE Dublin North East Nutrition Support Study Day April 25 th 2012 Home enteral nutrition (HEN) Enteral tube feeding is
Nephrostomy Tube Care
 Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 416 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: ENEMAS 1. PURPOSE: A. To relieve distention and gas by absorption,
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 416 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: ENEMAS 1. PURPOSE: A. To relieve distention and gas by absorption,
Administering Intravenous Medication By Syringe Pump
 Administering Intravenous Medication By Syringe Pump CEAC 0820 February 2015 Administering Intravenous Medication By Syringe Pump You must change the tubing every day around the same time each day. Always
Administering Intravenous Medication By Syringe Pump CEAC 0820 February 2015 Administering Intravenous Medication By Syringe Pump You must change the tubing every day around the same time each day. Always
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ
 PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION ALPROLIX [pronounced all prō liks] Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when ALPROLIX
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION ALPROLIX [pronounced all prō liks] Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when ALPROLIX
Ponsky * PEG Safety System - "Pull" Bard * PEG Safety System - "Guidewire" Information for Use
 Ponsky * PEG Safety System - "Pull" Bard * PEG Safety System - "Guidewire" Information for Use Rx only Single patient use DEHP-Free This product and package do not contain natural rubber latex STERILE
Ponsky * PEG Safety System - "Pull" Bard * PEG Safety System - "Guidewire" Information for Use Rx only Single patient use DEHP-Free This product and package do not contain natural rubber latex STERILE
NOTE: The first appearance of terms in bold in the body of this document (except titles) are defined terms please refer to the Definitions section.
 TITLE PARENTERAL NUTRITION ADMINISTRATION AND MONITORING SCOPE Provincial: Acute Care APPROVAL AUTHORITY Clinical Operations Executive Committee SPONSOR Pharmacy Services, Nutrition Services, and Health
TITLE PARENTERAL NUTRITION ADMINISTRATION AND MONITORING SCOPE Provincial: Acute Care APPROVAL AUTHORITY Clinical Operations Executive Committee SPONSOR Pharmacy Services, Nutrition Services, and Health
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial
 Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel multiple-dose vial? A multiple-dose vial contains
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel multiple-dose vial? A multiple-dose vial contains
Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal tube
 Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal This factsheet tells you how to care for your feeding and how to take your feed and medications via your. Your dietitian needs to fill in parts of this factsheet.
Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal This factsheet tells you how to care for your feeding and how to take your feed and medications via your. Your dietitian needs to fill in parts of this factsheet.
Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use
 Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use Be sure that you read, understand, and follow the Instructions for Use before injecting HEMLIBRA. Your healthcare
Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use Be sure that you read, understand, and follow the Instructions for Use before injecting HEMLIBRA. Your healthcare
Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter
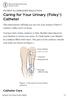 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections. No Action Rationale
 Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections Preparation Overview No Action Rationale 1 Collect and check all equipment 2 Check that the packaging of all
Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections Preparation Overview No Action Rationale 1 Collect and check all equipment 2 Check that the packaging of all
Why You Switched to the Tiger 2 Self-Advancing Nasal Jejunal Feeding Tube
 Why You Switched to the Tiger 2 Self-Advancing Nasal Jejunal Feeding Tube Ease of Use Self-advancing technology minimises hands-on time for clinicians. Requires no additional devices or costly capital
Why You Switched to the Tiger 2 Self-Advancing Nasal Jejunal Feeding Tube Ease of Use Self-advancing technology minimises hands-on time for clinicians. Requires no additional devices or costly capital
Feeding Protocols Enteral or Parenteral. AM Poleÿ 2012
 Practical aspects on Feeding Protocols Enteral or Parenteral AM Poleÿ 2012 Enteral Feeding Facts A reduction in mortality Prophylaxis for stress ulcers Full-strength Time to start enteral nutrition If
Practical aspects on Feeding Protocols Enteral or Parenteral AM Poleÿ 2012 Enteral Feeding Facts A reduction in mortality Prophylaxis for stress ulcers Full-strength Time to start enteral nutrition If
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag
 Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide)
 Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide) A Guide for Patients in the Home Phone Number: Nurse/Contact: Central Venous Catheters This manual is a guide for
Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide) A Guide for Patients in the Home Phone Number: Nurse/Contact: Central Venous Catheters This manual is a guide for
Geoffrey Axiak M.Sc. Nursing (Manch.), B.Sc. Nursing, P.G. Dip. Nutrition & Dietetics Clinical Nutrition Practice Nurse
 The Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Geoffrey Axiak M.Sc. Nursing (Manch.), B.Sc. Nursing, P.G. Dip. Nutrition & Dietetics Clinical Nutrition Practice Nurse What is a P.E.G.? Percutaneous Endoscopic
The Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Geoffrey Axiak M.Sc. Nursing (Manch.), B.Sc. Nursing, P.G. Dip. Nutrition & Dietetics Clinical Nutrition Practice Nurse What is a P.E.G.? Percutaneous Endoscopic
Education for self administration of intravenous therapy HOME IV THERAPY. 30 minute - Baxter Pump Tobramycin
 HOME IV THERAPY Tobramycin Tobramycin Check the order on the drug chart This can change when the results from your blood test come through. Your doctor will change the order, if required. A copy of the
HOME IV THERAPY Tobramycin Tobramycin Check the order on the drug chart This can change when the results from your blood test come through. Your doctor will change the order, if required. A copy of the
Policy x.xxx. Issued: Artificial Airways and Airway Care. ABC Home Medical Company Policy & Procedure Manual. A. Tracheostomy Tubes ( trach tubes)
 A. Tracheostomy Tubes ( trach tubes) A tracheotomy is a surgical procedure whereby an opening is cut into the trachea of the patient for the purpose of inserting a tube (trach tube). The trach tube allows
A. Tracheostomy Tubes ( trach tubes) A tracheotomy is a surgical procedure whereby an opening is cut into the trachea of the patient for the purpose of inserting a tube (trach tube). The trach tube allows
Emergency clamp should always be readily available in case of accidental catheter fracture
 Note: Please see individual policies for further information. Flushing best practice: Always use a 10 diameter syringe or larger when first accessing and when flushing vascular access device (VAD) Use
Note: Please see individual policies for further information. Flushing best practice: Always use a 10 diameter syringe or larger when first accessing and when flushing vascular access device (VAD) Use
EVOGAM. Information for patients Evogam 2014 NZ Patient Brochure Update v11
 EVOGAM Information for patients 11881 Evogam 2014 NZ Patient Brochure Update v11 Information for patients and caregivers about EVOGAM This booklet is designed to help you follow the training you will have
EVOGAM Information for patients 11881 Evogam 2014 NZ Patient Brochure Update v11 Information for patients and caregivers about EVOGAM This booklet is designed to help you follow the training you will have
Patient Information Publications Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health
 Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health What is a subcutaneous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous
Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health What is a subcutaneous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous
Having a PEG tube inserted
 Having a PEG tube inserted This information leaflet is for patients who are having a PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) tube inserted. It explains what is involved, what to expect and what significant
Having a PEG tube inserted This information leaflet is for patients who are having a PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) tube inserted. It explains what is involved, what to expect and what significant
Home Total Parenteral Nutrition
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Home Total Parenteral Nutrition This information will help teach you and your caregiver how to give total parenteral nutrition (TPN) at home. You will also receive a copy
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Home Total Parenteral Nutrition This information will help teach you and your caregiver how to give total parenteral nutrition (TPN) at home. You will also receive a copy
Managing your suprapubic catheter
 Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter
 Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY
 Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Administering Intravenous Medication By Slow IV Push
 Administering Intravenous Medication By Slow IV Push CEAC 0818 February 2015 Administering Intravenous Medication By Slow Intravenous Push Always record the time you administer your flushes and medication
Administering Intravenous Medication By Slow IV Push CEAC 0818 February 2015 Administering Intravenous Medication By Slow Intravenous Push Always record the time you administer your flushes and medication
MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM
 MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM SUBJECT Use of Closed Needleless Access Device with Hemodialysis Central Venous Catheters (CVC) SECTION CODE 30.20.04 30.20 Vascular Access AUTHORIZATION Professional Advisory Committee,
MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM SUBJECT Use of Closed Needleless Access Device with Hemodialysis Central Venous Catheters (CVC) SECTION CODE 30.20.04 30.20 Vascular Access AUTHORIZATION Professional Advisory Committee,
Baxter, ADVATE Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant)
 Baxter, ADVATE Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant) ADVATE, Recombinant Antihemophilic Factor, is indicated for the prevention and control of bleeding episodes in people with hemophilia A (classical hemophilia).
Baxter, ADVATE Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant) ADVATE, Recombinant Antihemophilic Factor, is indicated for the prevention and control of bleeding episodes in people with hemophilia A (classical hemophilia).
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates May 2016 By Katee Miller, PharmD Candidate, Mohamed Jalloh, PharmD, & Zara Risoldi Cochrane, PharmD, MS, FASCP Introduction Enteral nutrition (EN) through a tube is the preferred
Long-Term Care Updates May 2016 By Katee Miller, PharmD Candidate, Mohamed Jalloh, PharmD, & Zara Risoldi Cochrane, PharmD, MS, FASCP Introduction Enteral nutrition (EN) through a tube is the preferred
GASTRO-INTESTINAL (ENTERAL)
 GASTRO-INTESTINAL (ENTERAL) GASTRO-INTESTINAL (ENTERAL) 127 B A C D Gastrostomy Feeding Tubes & Accessories Tri-Funnel Replacement Gastrostomy Tube Green inflator cuff, sterile. Bard 12 French, 5 cc balloon,
GASTRO-INTESTINAL (ENTERAL) GASTRO-INTESTINAL (ENTERAL) 127 B A C D Gastrostomy Feeding Tubes & Accessories Tri-Funnel Replacement Gastrostomy Tube Green inflator cuff, sterile. Bard 12 French, 5 cc balloon,
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: PARENTERAL NUTRITION AND INTRAVENOUS FAT EMULSION (ADULT AND PEDIATRICS) Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN II 12/80
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: PARENTERAL NUTRITION AND INTRAVENOUS FAT EMULSION (ADULT AND PEDIATRICS) Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN II 12/80
Urinary Catheters. Prevalence of Infections
 Urinary Catheterisation Urinary catheterisation is defined as an intervention to enable the emptying of the bladder by insertion of a catheter. Catheters can be short term less than 28 days or long term
Urinary Catheterisation Urinary catheterisation is defined as an intervention to enable the emptying of the bladder by insertion of a catheter. Catheters can be short term less than 28 days or long term
BAYER: KOGENATE FS WITH BIOSET (Recombinant FVIII)
 BAYER: KOGENATE FS WITH BIOSET (Recombinant FVIII) KOGENATE FS, Recombinant Antihemophilic Factor, is indicated for the prevention and control of bleeding episodes in people with hemophilia A (classical
BAYER: KOGENATE FS WITH BIOSET (Recombinant FVIII) KOGENATE FS, Recombinant Antihemophilic Factor, is indicated for the prevention and control of bleeding episodes in people with hemophilia A (classical
ASPEN Safe Practices for Enteral Nutrition Therapy
 ASPEN Safe Practices for Enteral Nutrition Therapy Ainsley Malone, MS, RDN, CNSC, FAND, FASPEN Nutrition Support Dietitian Mt. Carmel West Hospital ASPEN Clinical Practice Specialist Disclosure I have
ASPEN Safe Practices for Enteral Nutrition Therapy Ainsley Malone, MS, RDN, CNSC, FAND, FASPEN Nutrition Support Dietitian Mt. Carmel West Hospital ASPEN Clinical Practice Specialist Disclosure I have
Instruction Guide to Sterile Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
