Detection of Schistosoma mansoni Eggs in Feces through their Interaction with Paramagnetic Beads in a Magnetic Field
|
|
|
- Cecilia Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Detection of Schistosoma mansoni Eggs in Feces through their Interaction with Paramagnetic Beads in a Magnetic Field Candida Fagundes Teixeira, Erli Neuhauss, Renata Ben, Juliano Romanzini, Carlos Graeff-Teixeira* Laboratórios de Parasitologia Molecular e de Biologia Parasitária, Instituto de Pesquisas Biomédicas e Faculdade de Biociências, PUCRS, Porto Alegre, Brazil Abstract Background: Diagnosis of intestinal schistosomiasis in low endemic areas is a problem because often control measures have reduced egg burdens in feces to below the detection limits of classical coproparasitological methods. Evaluation of molecular methods is hindered by the absence of an established standard with maximum sensitivity and specificity. One strategy to optimize method performance, where eggs are rare events, is to examine large amounts of feces. A novel diagnostic method for isolation of Schistosoma mansoni eggs in feces, and an initial evaluation of its performance is reported here. Methodology/Principal Findings: Known amounts of S. mansoni eggs were seeded into 30 g of normal human feces and subjected to a sequence of spontaneous sedimentation, sieving, Ritchie method, incubation and isolation through interaction with paramagnetic beads. Preliminary tests demonstrated the efficacy of lectins as ligands, but they also indicated that the paramagnetic beads alone were sufficient to isolate the eggs under a magnetic field through an unknown mechanism. Eggs were identified by microscopic inspection, with a sensitivity of 100% at 1.3 eggs per gram of feces (epg). Sensitivity gradually decreased to 25% at a concentration of 0.1 epg. In a preliminary application of the new method to the investigation of a recently established focus in southern Brazil, approximately 3 times more eggs were detected than with the thick-smear Kato-Katz method. Conclusions/Significance: The novel S. mansoni detection method may significantly improve diagnosis of infections with low burdens in areas of recent introduction of the parasite, areas under successful control of transmission, or in infected travelers. It may also improve the evaluation of new treatments and vaccines. Citation: Teixeira CF, Neuhauss E, Ben R, Romanzini J, Graeff-Teixeira C (2007) Detection of Schistosoma mansoni Eggs in Feces through their Interaction with Paramagnetic Beads in a Magnetic Field. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 1(2): e73. doi: /journal.pntd Editor: Jeffrey Bethony, George Washington University, United States of America Received: February 6, 2007; Accepted: July 25, 2007; Published: November 14, 2007 Copyright: ß 2007 Teixeira et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Funding: Partial financial support was provided by PUCRS. C Graeff-Teixeira (307872/2004-1, PQ ID) and CF Teixeira (114325/03-0) are recipients of CNPq-Brazil fellowships and a CNPq-Brazil grant. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Competing Interests: C Graeff-Teixeira, CF Teixeira and E Neuhauss have a patent pending on Helmintex. * graeteix@gmail.com Introduction In areas with recent introduction of Schistosoma mansoni transmission or areas where control efforts have reduced parasitic burden, the classical parasitological methods for finding eggs in stools do not demonstrate sufficient sensitivity [1,2,3]. Travelers may have light S. mansoni infections of difficult definitive diagnosis [4]. Molecular diagnostic tools are an alternative detection method, but more extensive validation in areas of low endemicity is still lacking. Very sensitive egg detection systems are desirable as methods for definitive diagnosis and are the standard for evaluation of other indirect diagnostic methods, such as serological tests. Since S. mansoni eggs are large and have a peculiar shape and a lateral spine, they are easily recognized visually, using a microscope, leading to a definitive diagnosis with few possibilities of false-negative results. Increased amounts and/or numbers of fecal samples, the use of differential fecal concentration methods or even application of mathematical modeling have been tested in order to improve sensitivity of parasitological diagnosis, but none of these approaches have been convincing enough to warrant extensive field trials [5,6]. Paramagnetic beads coupled to a variety of ligands are available for different applications such as purification of whole cells, organelles, nucleic acids, proteins and other molecules [7,8], and may be used for S. mansoni antigen detection [9]. Magnetic separation has also been applied for parasitological diagnosis, for example, in detection of cryptosporidiosis and giardiasis [10]. Here we report the preliminary evaluation of a highly sensitive method for isolation and detection of S. mansoni eggs from large amounts of feces which is based on their interaction with paramagnetic beads in a magnetic field. Materials and Methods Laboratory samples of Schistosoma mansoni were maintained by passages through Swiss albino mice and Biomphalaria glabrata. Both parasite and molluscs came from a local Esteio strain (Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil). Eggs were recovered by artificial digestion of livers, from experimentally infected rodents, in 4% KOH for 2 h at 46uC. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases Volume 1 Issue 2 e73
2 Author Summary Schistosomiasis mansoni is a parasitic infection that affects approximately 200 million people, mainly in the tropics. The worms live inside the veins of intestines and liver and produce eggs that are eliminated within feces. If the eggs reach water, a ciliated larva is released and enters snails to develop into a larva infective to man and other vertebrates. Most infections evolve without overt disease, but severe intestinal, hepatic, pulmonary and cerebromedulary dysfunctions may occur after many years. Definitive diagnosis is made through the identification of eggs in stool. Classical diagnostic methods fail to detect infection when the number of eggs is low (e.g., in areas where control measures have decreased the intensity of infection or in the case of light infections in travelers who have had only brief exposure). A new and very sensitive method is reported here, in which eggs are isolated from large amounts of feces through their interaction with magnetic beads. After incubation with the fecal sediment, eggs co-migrate with the beads towards a magnet attached to the test tube. This improvement in diagnostic methodology will strengthen efforts to control schistosomiasis. Experiments with lectins as ligands Stock solutions (1 mg/ml) of five biotinilated lectins were prepared with a ph 7.6 lectin buffer (6.057 g TRIS, 8.7 g NaCl, g MgCl 2, g CaCl 2 and 0.02% sodium azide, per Litre) [11]. The five lectins (SIGMA, USA), reported in the literature as ligands to the surface of S. mansoni eggs [12,13,14], were: Triticum vulgaris (L5142), Concavalin A (C2272), Ulex europeaus (L8262), Arachis hypogea (L6135), and Lycopersicum esculentum (L0651). Microtubes containing 100 eggs in 100 ml PBS plus 50 ml of lectins at several concentrations (5 mg/ml, 10 mg/ml and 20 mg/ ml) were incubated at room temperature for 1 h. After a washing step with PBS, the volume was adjusted to 1.5 ml and paramagnetic beads covered with streptavidin (Bangs Labs, USA) were added to a final concentration of 1.4% (v/v). Incubation was performed in an orbital shaker, at room temperature, for 1 h. Eggs and beads, without lectins, were incubated as a negative control. The microtubes containing the preparations were connected to a magnet (Dynal, Oslo, Norway) for 3 min, supernatants were removed, and the sediments retained at the wall were collected and examined under a microscope for counting of S. mansoni eggs. Several combinations of lectins were also tested under the same conditions and at a final individual concentration of 40 mg/ml. Experiment with different beads Paramagnetic beads coupled with 1) anti-rabbit-igg (Dynal, Oslo, Norway); 2) a monoclonal antibody anti-cryptosporidium (Dynal, Oslo, Norway); 3) streptavidin (Bangs Lab, USA); 4) streptavidin followed by biotinylated lectin (SIGMA, USA), were incubated with eggs in distilled water, under the conditions described above. A preparation with eggs and without beads (negative control) and another with eggs and a latex (non-magnetic) bead coupled to Protein A (Dynal, Oslo, Norway) were also tested. Seeding experiment in feces with and without lectins Based on the results from the previous experiment, 10 S. mansoni eggs were seeded in 30 g of normal human feces. The fecal sample was suspended and stirred in 250 ml of water, filtered through 8 layers of surgical gauze into a conical cup, left for 1 h at RT, re-suspended in distilled water and the spontaneous sedimentation repeated until a clear supernatant was obtained. Sediment was sieved through 100 (S1), 200 (S2) and 325 (S3) meshes per square inch metal sieves. The fraction retained at S3 was submitted to the method of Ritchie [15] and the procedure was repeated usually twice or as necessary to get a clear supernatant without a ring of debris. The final sediment was incubated either with or without 20 mg/ml of biotinylated Triticum vulgaris as previously described in the lectin experiments. Paramagnetic beads were coupled with streptavidin (Bangs Lab, USA). Seeding experiment to evaluate sensitivity Eggs were added at different concentrations (60, 40, 30, 20, 10, 7 and 3) per 30 g of normal human feces, corresponding respectively to 2.0, 1.3, 1.0, 0.6, 0.3, 0.2, 0.1 eggs per gram of feces (epg). The fecal samples were processed as described above, except that lectins were not employed and uncoated paramagnetic beads (BioMag, BM547/7065, Bangs Lab, USA) were used to isolate the eggs. The novel method was employed for the first time in the investigation of two infected individuals from a potential new focus of transmission in Porto Alegre, the capital of Brazil s southernmost State. For each sample (whole evacuation) 2 thick fecal smears or Kato-Katz method [16] were prepared and 30 g of feces were processed with the new method. The method and kit, including the reagents, magnet and sieves, have been named Helmintex (patent pending). Ethical oversight The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Public Health Central Laboratory of Rio Grande do Sul (LACEN/RS). The normal feces used in the seeding experiments were donated by three of the authors (C G-T, CFT, and JR). Informed consent was obtained from the two infected individuals who donated feces for the study. Results Table 1 shows the percentage of eggs found in the supernatant (SN) and in the pellet (SD) formed at the wall of the microtube in contact with the magnet. Both the negative control and the several preparations with lectins contained most of the eggs in the pellet. The results indicated that both negative control and several combinations of lectins were effective at promoting isolation of the eggs (Table 2). The data in Table 3 were used to compare treatments with different beads, and confirmed that lectins were not essential and that paramagnetic beads were necessary for isolation of the eggs, since latex beads and eggs alone did not migrate to the magnet. The results of the seeding experiment in feces with and without lectins (data not shown), besides confirming that lectins were not essential, demonstrated that isolation of eggs occurred in the presence of fecal sediment. Based on these initial results we decided to use uncoupled beads for future testing. The recovery of seeded eggs in fecal samples is shown in Table 4. Sensitivity was 100% with egg burdens of 2 and 1.3 epg and gradually decreased to 20% as the egg burden was reduced to 0.1 epg. The investigation of the new focus in Porto Alegre revealed one infection (Patient A) out of 6 individuals of the family and the confirmation of infection in the index case (Patient B), with total numbers of eggs per sample as shown in Table 5. Discussion The Kato-Katz (KK) method is the cornerstone for parasitological diagnosis of S. mansoni infection. The KK method has the advantage of being a simple and inexpensive procedure, which has PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases Volume 1 Issue 2 e73
3 Table 1. Percentage of S. mansoni eggs recovered in supernatant (SN) and pellet (SD) after seeding experiments with different concentrations of biotinilated lectins and paramagnetic beads covered with streptavidin. Lectins SN or SD 0 mg/ml 5 mg/ml 10 mg/ml 20 mg/ml Triticum vulgaris SN (%) SD (%) Concavalim A SN (%) SD (%) Ulex europeaus SN (%) SD (%) Arachis hypogaea SN (%) SD (%) Lycopersicum SN (%) esculentum SD (%) doi: /journal.pntd t001 justified its widespread use in the classical endemic areas of intestinal schistosomiasis [17]. Several efforts have been made to develop more sensitive diagnostic tools, such as immunoassays for detection of S. mansoni antibodies [1] or antigens [18], PCR [19] methods, and examination of large amounts of feces with isolation of eggs in a Percoll gradient [5]. Molecular methods have not been properly evaluated for sensitivity since current parasitological methods themselves lack sensitivity and few of them have undergone extensive field evaluations [17]. Assays for detection of antigens may not have the expected high sensitivity and specificity when employed for diagnosis in low endemicity areas or in light infections of travelers [18,20]. In the southernmost transmission focus of schistosomiasis in Brazil, most of the infected individuals examined had less than 1 epg and were usually diagnosed only after examination of several samples with increasing amounts of feces [2]. Efforts to develop a much more sensitive detection method originated with the idea of collecting and examining the entire evacuation of individuals who are of high epidemiological risk but who have consistently tested negative by coproparasitological examinations. Table 2. Percentage of S. mansoni eggs recovered in supernatant (SN) and pellet (SD) after seeding experiments with different combinations of biotinilated lectins and interaction with paramagnetic beads covered with streptavidin. Lectins SN SD Ca+Ue 3 97 Ca+Ah 5 95 Ca+Tv Negative control 1 99 Eu+Ah 6 94 Ca+Le 6 94 Eu+Tv 7 93 Negative control 2 98 Eu+Lê 4 96 Ah+Tv 2 98 Ah+Lê 2 98 Tv+Lê 1 99 Negative control For every of three experiments, there was a negative control: eggs and beads without lectins. Triticum vulgaris (Tv); Concavalim A (Ca); Ulex europeaus (Ue); Arachis hypogaea (Ah); Lycopersicum esculentum (Le) doi: /journal.pntd t002 Attempts were made to isolate eggs from large final fecal sediments using sucrose density columns and paramagnetic beads covered with anti-s. mansoni-egg-surface antibodies raised in rabbits without success (data not shown). Using the Helmintex method described here, efficient isolation was achieved when lectins were used as ligands to the paramagnetic beads. Isolation of the eggs was also unexpectedly achieved when only beads and eggs were incubated (negative control), suggesting that ligands were unnecessary for isolation of the eggs. Although a detailed explanation of the mechanism of isolation is lacking, it clearly depends on the magnetic field and the presence of paramagnetic beads since eggs alone did not migrate to the magnet. It is possible Table 3. Percentage of S. mansoni eggs recovered in supernatant (SN) and pellet (SD) after three repetitions of seeding experiments: paramagnetic microspheres covered with different ligands, latex beads covered with Protein A and egg suspension as negative control. Repeat SN or SD Negative control Paramagnetic beads covered with Latex beads covered with Protein A Positive control Antibody antirabbit IgG Streptavidin Antibody anti- Cryptosporidium 1st SN SD nd SN SD rd SN SD A preparation resulting from the incubation of eggs with biotinilated lectins and interaction with magnetic beads covered with streptavidin was also included as a positive control. doi: /journal.pntd t003 PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases Volume 1 Issue 2 e73
4 Table 4. Eggs of S. mansoni recovered after seeding experiments where different numbers of eggs were mixed with 30g of normal human feces. Eggs per gram (Total eggs per 30 g) 3 (0.1) 7 (0.24) 10 (0.34) 20 (0.67) 30 (1.0) 40 (1.34) 60 (2) Repetitions nd (*) nd nd nd Total eggs Recovery (%) ,9 Sensitivity 20% 50% 50% 60% 80% 100% 100% (*) nd: not done doi: /journal.pntd t004 that the eggs were carried along with the beads as they aligned themselves with the force of the magnetic field and moved towards the magnet. It is not a highly specific interaction since a substantial amount of fecal debris also migrated towards the magnet. However, the reduction in the volume of final sediment and the concentration of eggs in this sediment appeared to be the basis for success of this very sensitive method. The amount of feces (30 g) used for this test was arbitrarily chosen. It is anticipated that ongoing field tests of the method will demonstrate whether amounts larger than 30 g should be examined. This novel method is far more sensitive then other existing coproparasitological tests. Nevertheless it is expected that additional modifications could be made that may further improve the performance of the Helmintex method. Although Helmintex is a relatively expensive (US$ 0.80 per sample) and laborious method, it is more sensitive than KK. This method was able to detect 1.3 epg with 100% sensitivity while studies of KK indicate that its sensitivity is reduced to 60% at egg burdens lower than 100 epg [3]. Data Table 5. Identification of S. mansoni eggs by the methods of Kato-Katz and Helmintex in samples from two infected individuals from a new focus of intestinal schistosomiasis in Porto Alegre, southern Brazil. Patients Kato-Katz Helmintex Patient B (index case) Sample 1 2 slides-negative 3 slides 1 egg Sample 2 2 slides 1 egg 8 slides 61 eggs Sample 3 2 slides 2 eggs 10 slides 29 eggs Totals 6 slides 3 eggs 21 slides 91 eggs Patient A Sample 1 2 slides negative 10 slides negative Sample 2 2 slides negative 10 slides 1 eggs Sample 3 2 slides negative 10 slides 24 eggs Totals 6 slides 0 eggs 30 slides 25 eggs doi: /journal.pntd t005 presented in Table 5 indicated that approximately 30 times more eggs were recovered using Helmintex, than using KK, resulting in recoveries of 91 and 25 for Helmintex compared to 3 and 0 for KK, in patients B and A, respectively. The best performance of the egg hatching method was reported in the literature to have a sensitivity of 100% with 12 epg and 80% with 1 epg [21]. This novel detection method is not meant to replace other classical methods (e.g., thick smear KK) for S. mansoni screening. However, in low endemicity areas it may be part of a series of screening steps including epidemiological surveys with quantification methods of risk behavior, KK and serology. For case-control studies Helmintex will be useful as criterion of uninfected groups and, in travelers, it will improve the ability to make a definitive diagnosis in an ever increasing amount of people returning home after brief contact with transmission foci abroad resulting in a very light infection [3]. It may also serve as an extremely valuable tool to be used as the standard for evaluation of other diagnostic tests and vaccines. Author Contributions Conceived and designed the experiments: CGT CFT RB. Performed the experiments: CFT RB EN JR. Analyzed the data: CGT CFT JR. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: CGT RB EN JR. Wrote the paper: CGT CFT. References 1. Alarcón-de-Noya B, Cesari IM, Losada S, Colmenares C, Balzán C, et al. (1997) Evaluation of alkaline phosphatase immunoassay and comparison with other diagnostic methods in areas of low transmission of schistosomiasis. Acta Trop 66: Graeff-Teixeira C, Valar C, Moraes CK, Salvany AM, Brum CO, et al. (2004) The initial epidemiological studies in the low endemicity schistosomiasis area in Esteio, Rio Grande do Sul, the southernmost Brazilian State, 1997 to Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 99: Noya O, Alarcón-de-Noya B, Losada S, Colmenares C, Guzmán C, et al. (2002) Laboratory diagnosis of schistosomiasis in áreas of low transmission. A review of a line of research. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 97(Suppl 1): Corachan M (2002) Schistosomiasis and international travel. Clin Infect Dis 35: Eberl M, al-sherbiny M, Hagan P, Ljubojevic S, Thomas AW, et al. (2002) A novel and sensitive method to monitor helminth infections by faecal sampling. Acta Trop 83: Polman K, De Vlas SJ, Gryseels B, Deelder AM (2000) Relating serum circulating anodic antigens to faecal egg counts in Schistosoma mansoni infections: a modeling approach. Parasitology 121: Kretzer JW, Lehmann R, Schmelcher M, Banz M, Kim KP, et al. (2007) Use of high-affinity cell wall-binding domains of bacteriophage endolysins for immobilization and separation of bacterial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 73: Zembutsu A, Waga S (2006) De novo assembly of genuine replication forks on an immobilized circular plasmid in Xenopus egg extracts. Nucleic Acids Res 34: e Gunderson SG, Haagensen I, Jonassen TO, Figenschau KJ, de Jonge N, et al. (1992) Magnetic bead antigen capture enzyme-linked immunoassay in microtitre trays for rapid detection of schistosomal circulating anodic antigen. J Immunol Methods 148: Moss DM, Arrowood MJ (2001) Quantification of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts in mouse fecal specimens using immunomagnetic particles and two-color flow cytometry. J Parasitol 87: Leathem AJ, Brooks SA (1988) Light microscopy: overview and basic methods. In: Rhodes JM, Milton JD, eds. Lectin Methods and Protocols Human Press: New Jersey, USA. 10 p. 12. Beisler KG, Nakao M, Matsuda H, Tanaka H (1984) Characterization of the carbohydrates of Schistosoma japonicum adult worm, egg and cercaria by analysis of lectin binding and antibody reaction. Jap J Exp Med 54: PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases Volume 1 Issue 2 e73
5 13. Colditz IG, Jambre LF, Hosse R (2002) Use of lectin binding characteristics to identify gastrointestinal parasite eggs in faeces. Vet Parasitol 105: Robjin MLM, Wuhrer M, Korneles D, Deelder AM, Geyer R, et al. (2005) Mapping fucosylated epitopes on glycoproteins and glycolipids of Schistosoma mansoni cercarie, adult worms and eggs. Parasitology 130: Ritchie L (1948) An ether sedimentation technique for routine stool examinations. Bull US Army Med Depart 8: Katz N, Chaves A, Pellegrino J (1972) A simple device for quantitative stool thick smear technique in schistosomiasis mansoni. Rev Inst Med trop S Paulo 14: Doenhoff MJ, Chiodini PL, Hamilton JV (2004) Specific and sensitive diagnosis of schistosome infection: can it be done with antibodies? Trends Parasitol 20: van Lieshout L, Polderman AM, Deelder AM (2000) Immunodiagnosis of schistosomiasis by determination of the circulating antigens CAA and CCA, in particular in individuals with recent or light infections. Acta Tropica 77: Pontes LA, Dias-Neto E, Rabello A (2003) Comparison of a polymerase chain reaction and the Kato-Katz technique for diagnosing infection with Schistosoma mansoni. Am J Trop Med Hyg 68: Van Lieshout L, Gangaram Panday U, De Jonge N, Krijger FW, Oostburg BFJ, et al. (1995) Immunodiagnosis of schistosomiasis mansoni in a low endemic area of Surinam by determination of the circulating antigens CAA and CCA. Acta Trop 59: Zicker F, Katz N, Wolf J (1977) Avaliação do teste de eclosão de miracídios na esquistossomose mansonica. Rev Inst Med Trop S Paulo 19: PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases Volume 1 Issue 2 e73
Diagnostiek van schistosomiasis door antigeen-detectie (CAA en CCA): op zoek naar die ene worm.
 Diagnostiek van schistosomiasis door antigeen-detectie (CAA en CCA): op zoek naar die ene worm. Govert van Dam, Claudia de Dood, Djoeke Kornelis, Elisa Tjon Kon Fat, Rebecca van Grootveld, Lisette van
Diagnostiek van schistosomiasis door antigeen-detectie (CAA en CCA): op zoek naar die ene worm. Govert van Dam, Claudia de Dood, Djoeke Kornelis, Elisa Tjon Kon Fat, Rebecca van Grootveld, Lisette van
SCHISTOSOMIASIS MANSONI: IMMUNOBLOT ANALYSIS TO DIAGNOSE AND DIFFERENTIATE RECENT AND CHRONIC INFECTION
 Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 61(2), 1999, pp. 302307 Copyright 1999 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene SCHISTOSOMIASIS MANSONI: IMMUNOBLOT ANALYSIS TO DIAGNOSE AND DIFFERENTIATE RECENT
Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 61(2), 1999, pp. 302307 Copyright 1999 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene SCHISTOSOMIASIS MANSONI: IMMUNOBLOT ANALYSIS TO DIAGNOSE AND DIFFERENTIATE RECENT
PARATEST STABILITY STUDY, SYSTEM USED FOR DIAGNOSIS OF INTESTINAL PARASITES
 PARATEST STABILITY STUDY, SYSTEM USED FOR DIAGNOSIS OF INTESTINAL PARASITES Rev.00 January 10, 2011 1. Introduction Intestinal parasitic diseases represent a serious public health issue in underdeveloped
PARATEST STABILITY STUDY, SYSTEM USED FOR DIAGNOSIS OF INTESTINAL PARASITES Rev.00 January 10, 2011 1. Introduction Intestinal parasitic diseases represent a serious public health issue in underdeveloped
District NTD Training module 9 Learners Guide
 District NTD Training module 9 Learners Guide Session 3: Diagnostic and laboratory tools for filarial worms, Soil- Transmitted Helminths and Schistosomiasis Key message addressed to communities: Community
District NTD Training module 9 Learners Guide Session 3: Diagnostic and laboratory tools for filarial worms, Soil- Transmitted Helminths and Schistosomiasis Key message addressed to communities: Community
Bilharzia (Schistosomiasis)
 For qualitative detection of: Bilharzia (Schistosomiasis) (25 Diagnostic tests) URINE CCA TEST FOR SCHISTOSOMIASIS (BILHARZIA) INDICATIONS FOR USE: The urine-cca (Circulating Cathodic Antigen) cassette
For qualitative detection of: Bilharzia (Schistosomiasis) (25 Diagnostic tests) URINE CCA TEST FOR SCHISTOSOMIASIS (BILHARZIA) INDICATIONS FOR USE: The urine-cca (Circulating Cathodic Antigen) cassette
News and Notes. Parasitology Comprehensive 5 February Sample Preparation and Quality Control. 13 A Helminthes Only
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Recent reports in the literature have indicated a high rate of Cryptosporidium sp. false positive associated with Rapid Cartridge
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Recent reports in the literature have indicated a high rate of Cryptosporidium sp. false positive associated with Rapid Cartridge
Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica.
 TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
Modelling Macroparasitic Diseases
 Modelling Macroparasitic Diseases Ben Collyer January 23, 2018 Ben Collyer Modelling Macroparasitic Diseases January 23, 2018 1 / 25 Parasitic worms Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are able to
Modelling Macroparasitic Diseases Ben Collyer January 23, 2018 Ben Collyer Modelling Macroparasitic Diseases January 23, 2018 1 / 25 Parasitic worms Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are able to
Effect of praziquantel administration on hepatic stereology of mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni and fed a low-protein diet
 Volume 42 (9) 776-869 September 2009 Braz J Med Biol Res, September 2009, Volume 42(9) 812-815 Effect of praziquantel administration on hepatic stereology of mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni and
Volume 42 (9) 776-869 September 2009 Braz J Med Biol Res, September 2009, Volume 42(9) 812-815 Effect of praziquantel administration on hepatic stereology of mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni and
Copyright 2012 The Authors. Deposited on: 9 January 2013
 Smith, H., Doenhoff, M., Aitken, C., Bailey, W., Ji, M., Dawson, E., Gilis, H., Spence, G., Alexander, C., and van Gool, T. (2012) Comparison of schistosoma mansoni soluble cercarial antigens and soluble
Smith, H., Doenhoff, M., Aitken, C., Bailey, W., Ji, M., Dawson, E., Gilis, H., Spence, G., Alexander, C., and van Gool, T. (2012) Comparison of schistosoma mansoni soluble cercarial antigens and soluble
Stitaya Sirisinha, Runglawan Chawengkirttikul.and. Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand.
 Stitaya Sirisinha, Runglawan Chawengkirttikul.and Rasana Sennswan Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand. Abstract. Monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked
Stitaya Sirisinha, Runglawan Chawengkirttikul.and Rasana Sennswan Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand. Abstract. Monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked
Humoral Immune Responses in Patients with Acute Schistosoma mansoni Infection Who Were Followed Up for Two Years After Treatment
 304 CLINICAL ARTICLES Humoral Immune Responses in Patients with Acute Schistosoma mansoni Infection Who Were Followed Up for Two Years After Treatment Ana L. T. Rabello, Maria Monica A. Garcia, From the
304 CLINICAL ARTICLES Humoral Immune Responses in Patients with Acute Schistosoma mansoni Infection Who Were Followed Up for Two Years After Treatment Ana L. T. Rabello, Maria Monica A. Garcia, From the
Origination Date: 25 Mar 2004 Total Pages: Effective Date: 18 Sep 2012 SOP Number LTC-SOP-17 v2.0. Network Name, Title Signature Date
 Title: Stool Processing and Cryptosporidium/Giardia Origination Date: 25 Mar 2004 Total Pages: Effective Date: 18 Sep 2012 SOP Number LTC-SOP-17 v2.0 Prepared By: Bill Kabat and Nancy Isham of the Supersedes
Title: Stool Processing and Cryptosporidium/Giardia Origination Date: 25 Mar 2004 Total Pages: Effective Date: 18 Sep 2012 SOP Number LTC-SOP-17 v2.0 Prepared By: Bill Kabat and Nancy Isham of the Supersedes
infection in mice ic disease in the tropics. Emergence of praziquantel- resistence strains urged the need for new
 Efficacy of Randia nilotica methanol extractt Saada M. Nour et al Efficacy of Randia nilotica methanol extract against Schistosoma mansoni infection in mice Abstract: Introduction: Schistosomiasis is an
Efficacy of Randia nilotica methanol extractt Saada M. Nour et al Efficacy of Randia nilotica methanol extract against Schistosoma mansoni infection in mice Abstract: Introduction: Schistosomiasis is an
Schistosomiasis. Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University
 Schistosomiasis Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University Topics Definition The Pathogen Epidemiology Etiology and Life Cycle Pathobiology Clinical manifestations Diagnosis
Schistosomiasis Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University Topics Definition The Pathogen Epidemiology Etiology and Life Cycle Pathobiology Clinical manifestations Diagnosis
Parasitology. Helminthology (Helminths)
 Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
Author. Published. Journal Title. Copyright Statement. Downloaded from. Link to published version. Griffith Research Online
 A drug-based intervention study on the importance of buffaloes for human Schistosoma japonicum infection around Poyang Lake, Peoples Republic of China. Author Guo, Jiagang, Li, Yuesheng, Gray, Darren,
A drug-based intervention study on the importance of buffaloes for human Schistosoma japonicum infection around Poyang Lake, Peoples Republic of China. Author Guo, Jiagang, Li, Yuesheng, Gray, Darren,
Up-Converting Phosphor Technology-Based Lateral Flow Assay for Detection of Schistosoma Circulating Anodic Antigen in Serum
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 2008, p. 171 176 Vol. 46, No. 1 0095-1137/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.00877-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Up-Converting
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 2008, p. 171 176 Vol. 46, No. 1 0095-1137/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.00877-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Up-Converting
Target Product Profile Soil-Transmitted Helminth Surveillance Diagnostic
 Target Product Profile Soil-Transmitted Helminth Surveillance Diagnostic Use case: Preventive chemotherapy (PC) reduction/stopping decision General to all platforms and biomarkers Table of Contents Executive
Target Product Profile Soil-Transmitted Helminth Surveillance Diagnostic Use case: Preventive chemotherapy (PC) reduction/stopping decision General to all platforms and biomarkers Table of Contents Executive
José Carlos Sousa-Figueiredo 1,2, Martha Betson 1, Narcis B. Kabatereine 3, J. Russell Stothard 1 * Abstract. Introduction
 The Urine Circulating Cathodic Antigen (CCA) Dipstick: A Valid Substitute for Microscopy for Mapping and Point-Of-Care Diagnosis of Intestinal Schistosomiasis José Carlos Sousa-Figueiredo 1,2, Martha Betson
The Urine Circulating Cathodic Antigen (CCA) Dipstick: A Valid Substitute for Microscopy for Mapping and Point-Of-Care Diagnosis of Intestinal Schistosomiasis José Carlos Sousa-Figueiredo 1,2, Martha Betson
Application of μmacs Streptavidin MicroBeads for the analysis of HIV-1 directly from patient plasma
 Excerpt from MACS&more Vol 8 1/2004 Application of μmacs Streptavidin MicroBeads for the analysis of HIV-1 directly from patient plasma L. Davis Lupo and Salvatore T. Butera HIV and Retrovirology Branch,
Excerpt from MACS&more Vol 8 1/2004 Application of μmacs Streptavidin MicroBeads for the analysis of HIV-1 directly from patient plasma L. Davis Lupo and Salvatore T. Butera HIV and Retrovirology Branch,
Prof. Mahmoud Rushdi. Assiut University Egypt.
 By Prof. Mahmoud Rushdi Faculty of Veterinary Mdii Medicine Assiut University Egypt Precautions to be taken during collection and preservation of fecal sample 2 1 Precautions during collection of fecal
By Prof. Mahmoud Rushdi Faculty of Veterinary Mdii Medicine Assiut University Egypt Precautions to be taken during collection and preservation of fecal sample 2 1 Precautions during collection of fecal
E. Histolytica IgG ELISA Kit
 E. Histolytica IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3193 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
E. Histolytica IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3193 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 5 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
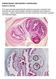 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 5 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 47 year-old male presented with symptoms that were consistent with possible late adult-onset epilepsy (frequent headaches and occasional seizures).
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 5 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 47 year-old male presented with symptoms that were consistent with possible late adult-onset epilepsy (frequent headaches and occasional seizures).
Received 21 July 2017; revised 26 December 2017; editorial decision 23 January 2018; accepted 24 January 2018
 Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2017; 111: 572 578 doi:10.1093/trstmh/try010 Advance Access publication 2 March 2018 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic performance of Mini Parasep solvent-free faecal parasite concentrator
Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2017; 111: 572 578 doi:10.1093/trstmh/try010 Advance Access publication 2 March 2018 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic performance of Mini Parasep solvent-free faecal parasite concentrator
Citation for published version (APA): Ochodo, E. A. (2014). Strengthening methods of diagnostic accuracy studies s-hertogenbosch: Boxpress
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Strengthening methods of diagnostic accuracy studies Ochodo, Eleanor Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Ochodo, E. A. (2014). Strengthening
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Strengthening methods of diagnostic accuracy studies Ochodo, Eleanor Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Ochodo, E. A. (2014). Strengthening
Detection Rate of Urinary Schistosomiasis in El khiar Villages White Nile State, Sudan
 Pyrex Journal of Biomedical Research Vol 3 (5) pp. 34-38 June, 2017 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.pyrexjournals.org/pjbr ISSN: 2579-1222 Copyright 2017 Pyrex Journals Full Length
Pyrex Journal of Biomedical Research Vol 3 (5) pp. 34-38 June, 2017 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.pyrexjournals.org/pjbr ISSN: 2579-1222 Copyright 2017 Pyrex Journals Full Length
PARASITOLOGICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RHESUS MONKEYS INFECTED WITH CHINESE MAINLAND STRAIN OF SCHISTOSOMA JAPONICUM
 PARASITOLOGICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RHESUS MONKEYS INFECTED WITH CHINESE MAINLAND STRAIN OF SCHISTOSOMA JAPONICUM He Yi-Xun, Yu Qi-Fang and Hu Ya-Qing Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese
PARASITOLOGICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RHESUS MONKEYS INFECTED WITH CHINESE MAINLAND STRAIN OF SCHISTOSOMA JAPONICUM He Yi-Xun, Yu Qi-Fang and Hu Ya-Qing Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese
Status of Vaccine Research and Development of Vaccines for Schistosomiasis Prepared for WHO PD-VAC
 Status of Vaccine Research and Development of Vaccines for Schistosomiasis Prepared for WHO PD-VAC I. About the Disease and Pathogen Basic information on pathogen, including transmission, estimated global
Status of Vaccine Research and Development of Vaccines for Schistosomiasis Prepared for WHO PD-VAC I. About the Disease and Pathogen Basic information on pathogen, including transmission, estimated global
Cryptosporidium Veterinary
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
The Awareness of Health Professionals in Diagnostic Techniques for Intestinal Parasites in Gaza Strip, Palestine
 Original Article The Awareness of Health Professionals in Diagnostic Techniques for Intestinal Parasites in Gaza Strip, Palestine Hindi AI Department of Medical Technology Sciences, Islamic University
Original Article The Awareness of Health Professionals in Diagnostic Techniques for Intestinal Parasites in Gaza Strip, Palestine Hindi AI Department of Medical Technology Sciences, Islamic University
The role of migration for the schistosomiasis occurrence in the south /southwestern of Minas Gerais state, Brazil
 The role of migration for the schistosomiasis occurrence in the south /southwestern of Minas Gerais state, Brazil Raquel Lopes Martins Souza 1, Maurílio Pacheco-Neto 1, Cybele Gargioni 2, Marcos José Marques
The role of migration for the schistosomiasis occurrence in the south /southwestern of Minas Gerais state, Brazil Raquel Lopes Martins Souza 1, Maurílio Pacheco-Neto 1, Cybele Gargioni 2, Marcos José Marques
The Effect of Treatment on the Age-antibody Relationship in Children Infected with Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma haematobium
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 97(Suppl. I): 173-180, 2002 173 The Effect of Treatment on the -antibody Relationship in Children Infected with Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma haematobium
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 97(Suppl. I): 173-180, 2002 173 The Effect of Treatment on the -antibody Relationship in Children Infected with Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma haematobium
Accuracy of circulating cathodic antigen tests for rapid mapping of Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium infections in Southern Sudan
 Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:10.1111/j.1365-3156.2011.02815.x volume 16 no 9 pp 1099 1103 september 2011 Accuracy of circulating cathodic antigen tests for rapid mapping of Schistosoma
Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:10.1111/j.1365-3156.2011.02815.x volume 16 no 9 pp 1099 1103 september 2011 Accuracy of circulating cathodic antigen tests for rapid mapping of Schistosoma
Human Immune Responses to Schistosoma mansoni Vaccine Candidate Antigens
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, May 2000, p. 2797 2803 Vol. 68, No. 5 0019-9567/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Human Immune Responses to Schistosoma mansoni
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, May 2000, p. 2797 2803 Vol. 68, No. 5 0019-9567/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Human Immune Responses to Schistosoma mansoni
Oxamniquine, praziquantel and lovastatin association in the experimental Schistosomiasis mansoni
 450 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 103(5): 450-454, August 2008 Oxamniquine, praziquantel and lovastatin association in the experimental Schistosomiasis mansoni Neusa Araújo/ +, Ana Carolina
450 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 103(5): 450-454, August 2008 Oxamniquine, praziquantel and lovastatin association in the experimental Schistosomiasis mansoni Neusa Araújo/ +, Ana Carolina
Helminths in tropical regions
 Helminths in tropical regions Schistosoma spp. Blood flukes Schistosomiasis is one of the most widespread parasitic infections in humans Humans are the principal hosts for: Schistosoma mansoni, Schistosoma
Helminths in tropical regions Schistosoma spp. Blood flukes Schistosomiasis is one of the most widespread parasitic infections in humans Humans are the principal hosts for: Schistosoma mansoni, Schistosoma
Downloaded from:
 O Hara, GA; Elliott, AM (2016) HIV and Helminths - Not All Worms Created Equal? Trends in parasitology. ISSN 1471-4922 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2016 Downloaded from: http://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/3327115/
O Hara, GA; Elliott, AM (2016) HIV and Helminths - Not All Worms Created Equal? Trends in parasitology. ISSN 1471-4922 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2016 Downloaded from: http://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/3327115/
Toxocara. Cat # Toxocara ELISA. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay. ELISA-Indirect; Antigen Coated Plate
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
362 JID 2013:207 (15 January) BRIEF REPORT
 BRIEF REPORT Schistosoma mansoni Infection in Preschool-Aged Children: Development of Immunoglobulin E and Immunoglobulin G 4 Responses to Parasite Allergen-Like Proteins Angela Pinot de Moira, 1 Jose
BRIEF REPORT Schistosoma mansoni Infection in Preschool-Aged Children: Development of Immunoglobulin E and Immunoglobulin G 4 Responses to Parasite Allergen-Like Proteins Angela Pinot de Moira, 1 Jose
A new rapid diagnostic test for detection of anti-schistosoma mansoni and anti-schistosoma haematobium antibodies
 Coulibaly et al. Parasites & Vectors 2013, 6:29 RESEARCH Open Access A new rapid diagnostic test for detection of anti-schistosoma mansoni and anti-schistosoma haematobium antibodies Jean T Coulibaly 1,2,3,4*,
Coulibaly et al. Parasites & Vectors 2013, 6:29 RESEARCH Open Access A new rapid diagnostic test for detection of anti-schistosoma mansoni and anti-schistosoma haematobium antibodies Jean T Coulibaly 1,2,3,4*,
MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A
 MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A Specifications and performance P.1 Comparison of the conventional method P.2 Operation methods and composition P.4 Amount of starting sample P.5 Analysis after exosomes
MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A Specifications and performance P.1 Comparison of the conventional method P.2 Operation methods and composition P.4 Amount of starting sample P.5 Analysis after exosomes
CONTENTS. STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1
 CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze.
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
TUBEX: High-definition Rapid Diagnostics for Typhoid and Other Diseases. LIM Pak Leong Chairman, IgGENE Hong Kong
 TUBEX: High-definition Rapid Diagnostics for Typhoid and Other Diseases LIM Pak Leong Chairman, IgGENE Hong Kong pllim@iggene.com Slide latex agglutination test rock 2 min NEGATIVE POSITIVE antibody-coated
TUBEX: High-definition Rapid Diagnostics for Typhoid and Other Diseases LIM Pak Leong Chairman, IgGENE Hong Kong pllim@iggene.com Slide latex agglutination test rock 2 min NEGATIVE POSITIVE antibody-coated
Chagas disease: Challenges in Diagnostics
 Chagas disease: Challenges in Diagnostics Emily Adams Royal Tropical Institute (KIT), KIT Biomedical Research The Netherlands e-mail: e.adams@kit.nl Aims of KIT Biomedical Research To contribute to the
Chagas disease: Challenges in Diagnostics Emily Adams Royal Tropical Institute (KIT), KIT Biomedical Research The Netherlands e-mail: e.adams@kit.nl Aims of KIT Biomedical Research To contribute to the
ISOTHERMAL AMPLIFICATION IN MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEPING SICKNESS
 Molecular Diagnostics Symposium 2014 Zurich, 27 February 2014 ISOTHERMAL AMPLIFICATION IN MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEPING SICKNESS Stijn Deborggraeve Parasite Diagnostics Unit, Institute of Tropical Medicine
Molecular Diagnostics Symposium 2014 Zurich, 27 February 2014 ISOTHERMAL AMPLIFICATION IN MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEPING SICKNESS Stijn Deborggraeve Parasite Diagnostics Unit, Institute of Tropical Medicine
Intestinal parasitism among students in three localities in South Wello, Ethiopia
 Original article Intestinal parasitism among students in three localities in South Wello, Ethiopia Tsehai Assefa, Tilahun Woldemichael, Amare Dejene Abstract: A cross-sectional study to estimate the prevalence
Original article Intestinal parasitism among students in three localities in South Wello, Ethiopia Tsehai Assefa, Tilahun Woldemichael, Amare Dejene Abstract: A cross-sectional study to estimate the prevalence
Department of Helminthology, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok; 4
 COMPARATIVE STUDIES ON THE PATHOLOGICAL FINDINGS AND MORTALITY IN SCHISTOSOMA MANSONI INFECTED MICE AFTER TREATMENT WITH ARTESUNATE AND THE CURRENT ANTISCHISTOSOMAL DRUGS Ruangyuth Chaiworaporn 1, Yaowapa
COMPARATIVE STUDIES ON THE PATHOLOGICAL FINDINGS AND MORTALITY IN SCHISTOSOMA MANSONI INFECTED MICE AFTER TREATMENT WITH ARTESUNATE AND THE CURRENT ANTISCHISTOSOMAL DRUGS Ruangyuth Chaiworaporn 1, Yaowapa
Genetic Epidemiology of Fecal Egg Excretion During Schistosoma mansoni Infection in an Endemic Area in Minas Gerais, Brazil
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 96, Suppl: 49-55, 2001 Genetic Epidemiology of Fecal Egg Excretion During Schistosoma mansoni Infection in an Endemic Area in Minas Gerais, Brazil J Bethony/*,
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 96, Suppl: 49-55, 2001 Genetic Epidemiology of Fecal Egg Excretion During Schistosoma mansoni Infection in an Endemic Area in Minas Gerais, Brazil J Bethony/*,
Crypto / Giardia Ag Combo (Fecal) ELISA
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
MagniSort Mouse CD4 Naive T cell Enrichment Kit Catalog Number: RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
 Page 1 of 2 MagniSort Mouse CD4 Naive T cell Enrichment Kit RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Mouse splenocytes were unsorted (left) or sorted with the MagniSort Mouse CD4
Page 1 of 2 MagniSort Mouse CD4 Naive T cell Enrichment Kit RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Mouse splenocytes were unsorted (left) or sorted with the MagniSort Mouse CD4
Comparison of Formol-Ether, Direct Smear and Nigrosine Methylene Blue for the Diagnosis of Human Intestinal Parasites
 Journal of Microbiology Research and Reviews Vol. (): -, August, www.resjournals.org/jmr Comparison of Formol-Ether, Direct Smear and Nigrosine Methylene Blue for the Diagnosis of Human Intestinal Parasites
Journal of Microbiology Research and Reviews Vol. (): -, August, www.resjournals.org/jmr Comparison of Formol-Ether, Direct Smear and Nigrosine Methylene Blue for the Diagnosis of Human Intestinal Parasites
TRACP & ALP Assay Kit
 Cat. # MK301 For Research Use TRACP & ALP Assay Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Introduction...3 Components...4 Materials Required but not Provided...4 V. Storage...4
Cat. # MK301 For Research Use TRACP & ALP Assay Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Introduction...3 Components...4 Materials Required but not Provided...4 V. Storage...4
Chromatin IP (Isw2) Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles.
 Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Received 11 May 2004/Returned for modification 3 August 2004/Accepted 8 September 2004
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Nov. 2004, p. 1165 1170 Vol. 11, No. 6 1071-412X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.11.6.1165 1170.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Nov. 2004, p. 1165 1170 Vol. 11, No. 6 1071-412X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.11.6.1165 1170.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
Veterinary Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases Department of Pathology and Animal Health Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Naples
 Veterinary Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases Department of Pathology and Animal Health Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Naples Federico II Via della Veterinaria, 1-80137 Naples, Italy www.flotac.unina.it
Veterinary Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases Department of Pathology and Animal Health Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Naples Federico II Via della Veterinaria, 1-80137 Naples, Italy www.flotac.unina.it
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program. Parasitology (General) 01 February Sample Preparation and Quality Control
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Parasitology (General) 01 February 2011 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology (General) is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Parasitology (General) 01 February 2011 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology (General) is
Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 2.417, ISSN: , Volume 4, Issue 2, March 2016
 THE EFFECT OF ENTERIC PARASITIC INFECTION ON SERUM ELEMENTS (COPPER) AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS ON EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS (RABBITS) ABSTRACT AHMED JASIM ALBAYATI* ALI S. HASAN** *Dept. of Pathology College of
THE EFFECT OF ENTERIC PARASITIC INFECTION ON SERUM ELEMENTS (COPPER) AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS ON EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS (RABBITS) ABSTRACT AHMED JASIM ALBAYATI* ALI S. HASAN** *Dept. of Pathology College of
Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit
 PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
Catalog # OKDA00123 SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION
 Aviva Systems Biology 5754 Pacific Center Blvd., Suite 201, San Diego, CA 92121, USA Tel: 858-552-6979 Fax: 858-552-6975 www.avivasysbio.com Email: info@avivasysbio.com Giardia lamblia ELISA Kit Catalog
Aviva Systems Biology 5754 Pacific Center Blvd., Suite 201, San Diego, CA 92121, USA Tel: 858-552-6979 Fax: 858-552-6975 www.avivasysbio.com Email: info@avivasysbio.com Giardia lamblia ELISA Kit Catalog
IVD. DRG Toxocara canis ELISA (EIA-3518) Revised 12 Feb rm (Vers. 6.1)
 Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. Intended Use For the qualitative screening of serum IgG antibodies to Toxocara using an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. Intended Use For the qualitative screening of serum IgG antibodies to Toxocara using an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12
 Diagnostic Microbiology Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12 Electron Microscopy 106 virus particles per ml required for visualization, 50,000-60,000 magnification normally used. Viruses may be detected
Diagnostic Microbiology Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12 Electron Microscopy 106 virus particles per ml required for visualization, 50,000-60,000 magnification normally used. Viruses may be detected
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze.
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
See external label 2 C-8 C = C-REACTIVE PROTEIN (CRP) LATEX SLIDE TEST
 CORTEZ DIAGNOSTICS, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
CORTEZ DIAGNOSTICS, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia.
 Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
Major Article. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 50(3): , May-June, 2017 doi: /
 doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0423-2016 Major Article Sensitivity and specificity of the circulating cathodic antigen rapid urine test in the diagnosis of Schistosomiasis mansoni infection and evaluation of morbidity
doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0423-2016 Major Article Sensitivity and specificity of the circulating cathodic antigen rapid urine test in the diagnosis of Schistosomiasis mansoni infection and evaluation of morbidity
Module 3: Overview of HIV Testing Technologies
 Module 3: Overview of HIV Testing Technologies Purpose Pre-requisite Modules Module Time Learning Objectives To provide the participants with a basic knowledge of HIV testing and how HIV rapid test results
Module 3: Overview of HIV Testing Technologies Purpose Pre-requisite Modules Module Time Learning Objectives To provide the participants with a basic knowledge of HIV testing and how HIV rapid test results
Mapping cancer, cardiovascular and malaria research in Brazil
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 853-867 Mapping cancer, cardiovascular and malaria research ISSN 1-879X Overview 853 Mapping cancer, cardiovascular and malaria research in
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 853-867 Mapping cancer, cardiovascular and malaria research ISSN 1-879X Overview 853 Mapping cancer, cardiovascular and malaria research in
Item Catalog Number Manufacturer 1,4-Dithioerythritol (1 g) D9680 Sigma-Aldrich
 SOP: Nuclei isolation from fresh mouse tissues and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 01/12/2011 Modified by: E. Giste/ T. Canfield (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei and subsequent
SOP: Nuclei isolation from fresh mouse tissues and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 01/12/2011 Modified by: E. Giste/ T. Canfield (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei and subsequent
Recent Diagnostic Methods for Intestinal Parasitic Infections
 Recent Diagnostic Methods for Intestinal Parasitic Infections By Dr. Doaa Abdel Badie Salem Lecturer of Medical Parasitology, Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Agenda Intestinal parasites. Traditional Diagnostic
Recent Diagnostic Methods for Intestinal Parasitic Infections By Dr. Doaa Abdel Badie Salem Lecturer of Medical Parasitology, Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Agenda Intestinal parasites. Traditional Diagnostic
Schistosomiasis mansoni and soil-transmitted helminthiasis in Bushulo village, southern Ethiopia
 Original article Schistosomiasis mansoni and soil-transmitted helminthiasis in Bushulo village, southern Ethiopia Ashenafi Terefe 1, Techalew Shimelis 2, Mulugeta Mengistu 2, Asrat Hailu 3, Berhanu Erko
Original article Schistosomiasis mansoni and soil-transmitted helminthiasis in Bushulo village, southern Ethiopia Ashenafi Terefe 1, Techalew Shimelis 2, Mulugeta Mengistu 2, Asrat Hailu 3, Berhanu Erko
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detection of Antibody to Gnathostoma Antigen in Patients with Intermittent Cutaneous Migratory Swelling
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 1986, p. 847-851 95-1137/86/5847-5$2./ Copyright D 1986, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 23, No. 5 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detection of Antibody
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 1986, p. 847-851 95-1137/86/5847-5$2./ Copyright D 1986, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 23, No. 5 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detection of Antibody
INFLUENCE OF SACCHAROSE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF CERCARIAE FROM Schistosoma mansoni STRAINS BH AND SJ
 SACCHAROSE AND S. mansoni CERCARIAE 43 INFLUENCE OF SACCHAROSE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF CERCARIAE FROM Schistosoma mansoni STRAINS BH AND SJ BRUNO, T. I. B., ZANOTTI-MAGALHÃES, E. M., MAGALHÃES, L. A. and
SACCHAROSE AND S. mansoni CERCARIAE 43 INFLUENCE OF SACCHAROSE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF CERCARIAE FROM Schistosoma mansoni STRAINS BH AND SJ BRUNO, T. I. B., ZANOTTI-MAGALHÃES, E. M., MAGALHÃES, L. A. and
EFFICACY OF SODIUM METAPERIODATE (SMP)-ELISA FOR THE SERODIAGNOSIS OF SCHISTOSOMIASIS MEKONGI
 EFFICACY OF SODIUM METAPERIODATE (SMP)-ELISA FOR THE SERODIAGNOSIS OF SCHISTOSOMIASIS MEKONGI Masashi Kirinoki 1, Yuichi Chigusa 1, Hiroshi Ohmae 2, Muth Sinuon 3, Duong Socheat 3, Jun Matsumoto 4, Viroj
EFFICACY OF SODIUM METAPERIODATE (SMP)-ELISA FOR THE SERODIAGNOSIS OF SCHISTOSOMIASIS MEKONGI Masashi Kirinoki 1, Yuichi Chigusa 1, Hiroshi Ohmae 2, Muth Sinuon 3, Duong Socheat 3, Jun Matsumoto 4, Viroj
The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei from tissue. Item. Catalog No Manufacturer
 SOP: Nuclei isolation from tissue and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 090923 Modified by: P. Sabo. (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei from tissue. Ordering Information Item.
SOP: Nuclei isolation from tissue and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 090923 Modified by: P. Sabo. (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei from tissue. Ordering Information Item.
HAV IgG/IgM Rapid Test
 HAV IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cat. No.:DTS649 Pkg.Size: Intended use CD HAV IgG/IgM Rapid Test is a solid phase immunochromatographic assay for the rapid, qualitative and differential detection of IgG and IgM
HAV IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cat. No.:DTS649 Pkg.Size: Intended use CD HAV IgG/IgM Rapid Test is a solid phase immunochromatographic assay for the rapid, qualitative and differential detection of IgG and IgM
Schistosome life cycle.
 Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Downloaded from:
 Zhou, XN; Xu, J; Chen, HG; Wang, TP; Huang, XB; Lin, DD; Wang, QZ; Tang, L; Guo, JG; Wu, XH; Feng, T; Chen, JX; Guo, J; Chen, SH; Li, H; Wu, ZD; Peeling, RW (2011) Tools to support policy decisions related
Zhou, XN; Xu, J; Chen, HG; Wang, TP; Huang, XB; Lin, DD; Wang, QZ; Tang, L; Guo, JG; Wu, XH; Feng, T; Chen, JX; Guo, J; Chen, SH; Li, H; Wu, ZD; Peeling, RW (2011) Tools to support policy decisions related
Giardia lamblia (flagellates)
 Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
Schistosomiasis (or bilharziosis) is a tropical parasitic
 367 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Acute Schistosomiasis in a Cluster of Travelers From Rwanda: Diagnostic Contribution of Schistosome DNA Detection in Serum Compared to Parasitology and Serology Jan Clerinx, MD, Emmanuel
367 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Acute Schistosomiasis in a Cluster of Travelers From Rwanda: Diagnostic Contribution of Schistosome DNA Detection in Serum Compared to Parasitology and Serology Jan Clerinx, MD, Emmanuel
MALARIA P. FALCIPARUM / P. VIVAX
 MALARIA P. FALCIPARUM / P. VIVAX 1. EXPLANATION OF THE TEST: Malaria is a serious, sometimes fatal, parasitic disease characterized by fever, chills, and anemia and is caused by a parasite that is transmitted
MALARIA P. FALCIPARUM / P. VIVAX 1. EXPLANATION OF THE TEST: Malaria is a serious, sometimes fatal, parasitic disease characterized by fever, chills, and anemia and is caused by a parasite that is transmitted
SP.718 Special Topics at Edgerton Center: D-Lab Health: Medical Technologies for the Developing World
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu SP.718 Special Topics at Edgerton Center: D-Lab Health: Medical Technologies for the Developing World Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu SP.718 Special Topics at Edgerton Center: D-Lab Health: Medical Technologies for the Developing World Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our
Exosomes Immunocapture and Isolation Tools: Immunobeads
 Product Insert Exosomes Immunocapture and Isolation Tools: Immunobeads HBM-BOLF-##/##-# HBM-BOLC-##/##-# HBM-BTLF-##/##-# Overall Exosome capture from Human Biological fluids Overall Exosome capture from
Product Insert Exosomes Immunocapture and Isolation Tools: Immunobeads HBM-BOLF-##/##-# HBM-BOLC-##/##-# HBM-BTLF-##/##-# Overall Exosome capture from Human Biological fluids Overall Exosome capture from
available at journal homepage:
 Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (2008) 102, 179 185 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/trst Multiplex real-time PCR
Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (2008) 102, 179 185 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/trst Multiplex real-time PCR
PARASITOLOGICAL EXAMINATIONS CATALOGUE OF SERVICES AND PRICE LIST
 INSTITUTE OF PARASITOLOGY Biomedical Research Center Seltersberg Justus Liebig University Giessen Schubertstrasse 81 35392 Giessen Germany Office: +49 (0) 641 99 38461 Fax: +49 (0) 641 99 38469 Coprological
INSTITUTE OF PARASITOLOGY Biomedical Research Center Seltersberg Justus Liebig University Giessen Schubertstrasse 81 35392 Giessen Germany Office: +49 (0) 641 99 38461 Fax: +49 (0) 641 99 38469 Coprological
The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry. Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013
 The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013 What is it? Hey! Look at that! Something is reacting in here! I just wish I knew what it
The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013 What is it? Hey! Look at that! Something is reacting in here! I just wish I knew what it
MagniSort Mouse CD4 T cell Enrichment Kit Catalog Number: RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
 Page 1 of 2 MagniSort Mouse CD4 T cell Enrichment Kit RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Mouse splenocytes were unsorted (left) or sorted with the MagniSort Mouse CD4 T cell
Page 1 of 2 MagniSort Mouse CD4 T cell Enrichment Kit RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Mouse splenocytes were unsorted (left) or sorted with the MagniSort Mouse CD4 T cell
Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area. Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3)
 Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3) and Yasuhiko AND01),3) 1) Central Clinical Laboratoly, Tokai University
Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3) and Yasuhiko AND01),3) 1) Central Clinical Laboratoly, Tokai University
Comercial Rafer in Zaragoza
 Comercial Rafer in Zaragoza 06.04.2017 ~A novel affinity method to isolate and identify intact Exosomes~ Taku Funakoshi (Mr.) Wako Chemicals GmbH Laboratory Chemicals Division Manager Research fields of
Comercial Rafer in Zaragoza 06.04.2017 ~A novel affinity method to isolate and identify intact Exosomes~ Taku Funakoshi (Mr.) Wako Chemicals GmbH Laboratory Chemicals Division Manager Research fields of
Comparison of indirect hemagglutination assay (IHA) and coprological diagnosis of schistosomosis in cows and buffaloes
 Indian J. Anim. Res., 49 (4) 2015 : 503-507 Print ISSN:0367-6722 / Online ISSN:0976-0555 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com/www.ijaronline.in Comparison of indirect hemagglutination
Indian J. Anim. Res., 49 (4) 2015 : 503-507 Print ISSN:0367-6722 / Online ISSN:0976-0555 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com/www.ijaronline.in Comparison of indirect hemagglutination
Antibody responses to Ascarisderived. glycolipids: the role of phosphorylcholine
 2 Antibody responses to Ascarisderived proteins and glycolipids: the role of phosphorylcholine by E. van Riet, M. Wuhrer, S. Wahyuni, K. Retra, A. M. Deelder, A. G. M. Tielens, D. van der Kleij & M. Yazdanbakhsh
2 Antibody responses to Ascarisderived proteins and glycolipids: the role of phosphorylcholine by E. van Riet, M. Wuhrer, S. Wahyuni, K. Retra, A. M. Deelder, A. G. M. Tielens, D. van der Kleij & M. Yazdanbakhsh
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
Accuracy of Urine Circulating Cathodic Antigen Test for the Diagnosis of Schistosoma mansoni in Preschool- Aged Children before and after Treatment
 Accuracy of Urine Circulating Cathodic Antigen Test for the Diagnosis of Schistosoma mansoni in Preschool- Aged Children before and after Treatment Jean T. Coulibaly 1,2,3,4, Yves K. N Gbesso 5, Stefanie
Accuracy of Urine Circulating Cathodic Antigen Test for the Diagnosis of Schistosoma mansoni in Preschool- Aged Children before and after Treatment Jean T. Coulibaly 1,2,3,4, Yves K. N Gbesso 5, Stefanie
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HUMAN GEOHELMINTH INFECTIONS (ASCARIASIS, TRICHURIASIS AND NECATORIASIS) IN LUSHUI AND PUER COUNTIES, YUNNAN PROVINCE, CHINA
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HUMAN GEOHELMINTH INFECTIONS (ASCARIASIS, TRICHURIASIS AND NECATORIASIS) IN LUSHUI AND PUER COUNTIES, YUNNAN PROVINCE, CHINA Zhang Lili 1, Zhang
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HUMAN GEOHELMINTH INFECTIONS (ASCARIASIS, TRICHURIASIS AND NECATORIASIS) IN LUSHUI AND PUER COUNTIES, YUNNAN PROVINCE, CHINA Zhang Lili 1, Zhang
A Microfluidic ExoSearch Chip for Multiplexed Exosome Detection Towards Bloodbased Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information A Microfluidic ExoSearch Chip for Multiplexed Exosome Detection
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information A Microfluidic ExoSearch Chip for Multiplexed Exosome Detection
