CHEM 3391B TERM TEST - Winter March 8 Elborn Collge EC2155 (EC 2155) 10:30 12:15 SYLLABUS
|
|
|
- Mervyn Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHEM 3391B ERM ES - Winter March 8 Elborn Collge EC2155 (EC 2155) 10:30 12:15 SYLLABUS he erm est content will be weighted approximately 90% Lecture Material and 10% Presentation Executive Summaries (see below) All lectures - up to hursday 1 st March 2018 (all of the Bio unit from this week). Questions taken from the Executive Summaries of the Presentation #1 and #2 - need to know major points from 4 Executive Summaries of each presentation as outlined. (Yes, your two are part of the four each time). here will be no Periodic able provided. Bring a calculator. Pencils and coloured pens helpful - just not "red". You will need to know the Periodic able entries up to Kr. riads involving Cu and Zn needed. Also, Pb, Bi. Place in the table and electronic configurations and common (bio) oxidation states. Hard/soft examples. he goals of this instructor are that by attending the lectures and reading the notes you will have a very good grasp of the material. he essence of this first part is remembering that providing examples is important. And those examples need to have some detail - the Compare & Contrast ideas. So, reading from the beginning and checking you follow the arguments is a very good first step. I try not to ask questions about small points (but my big point might be your small point). (A) Introduction - lots of detail. Check the end of the unit for key points (B) Metals - part 1 Check: metals - essential; toxic; metallodrugs; etc (C) Periodic able basics part 2 All the inorganic material; binding constants; be able to calculate H/S/G/K given the other information. Amino acids that bind metals; heme b; (= Greek delta) () Bio - Note several sections not included - need to check your notes. Be able to discuss the role of specific metal-binding amino acids and draw the structures of the metal-binding amino acids protein structure etc In Kaim.. p 1-116; but you should thumb through the rest noting may be images and paragraphs we have covered - - I liked the cycles and heme protein examples that we saw last week.-- there's a very nice section on p 200 about Cyt oxidase - heme a. Zinc starting on p we have covered in part already. Really a read through would be useful. But - my questions and their answers come from the notes and what I have said in class. 3391B-2018-ermest-syllabus-2018march8-rev-18-a.docx Page 1 of 1
2 o be included for sure from 2018 MarkedUp pdfs INRO/INORG/BIO O2 binding to myoglobin heme Broadly defined, bioinorganic chemistry is the study of inorganic elements, with an emphasis on metals, in living systems. 1. Which elements are necessary for life? 2. How about their chemical speciation? 3. What are their physiological roles? 4. What are their mechanisms of action? 5. How did we evolve to use those elements? 6. Why are some metals toxic? 7. Can metals be used therapeutically? Name 4 metals with greater than about 1 g in the average 70 kg Man Give an example of two element that have critical physiological role but its abundance (is far less than 1 g in the typical 70kg man (Se/Co/ highlighted What is an essential element? What Is an Essential Element? In order for an element to be classified as essential, it must satisfy all of these criteria for essentiality: 1) When the element is removed from the diet, a physiological or structural abnormality appears. 2) he addition of the element to the diet restores or relieves the abnormality. 3) he element has a specific biochemical function even if the function of the element is not fully understood, as in the case of many ultratrace elements. 4) he element follows a dose-response curve. -- see later. 1
3 5) Essential elements can be classified according to either the amount present in the body or the dietary requirement (recommended daily intake/allowance): 6) Bulk elements 7) Major elements / macronutrients / macrominerals 8) Minor elements / micronutrients / microminerals race elements Ultratrace elements Name 4 essential metals (not Na/K/Ca) 4 toxic metals Cd, Hg, Pb, As, Cr6+** Mg, e, Co, Zn,Cu, Mn, Mo, Cr, Ni, 4 therapeutically important metals Li, Cu, Ag, Au, Pt, Bi What is the class and give an example --- Oxidoreductase: Oxidoreductases catalyze oxidation reduction reactions. At least one substrate becomes oxidized and at least one substrate becomes reduced. Also the transfer of H and O atoms. Alcohol dehydrogenase - Zn (x2); catalases (e-heme x4); xanthine oxidase (Mo & es) (xanthine to uric acid) 2) ransferase What is the difference between a Metalloenzyme and a metal-activated enzyme? Explain 4 differences and provide an example for each of the metal and the enzyme Metalloenzymes Metalloenzymes metal is firmly bound metal to protein ratio is constant metal to enzyme activity ratio is constant metal is unique no enzyme activity without metal Examples of metalloenzymes: 2
4 superoxide dismutase (Zn and Cu) carboxypeptidase A (Zn) CPA carbonic anhydrase (Zn) CA cytochrome oxidase (e and Cu) CcOx xanthine oxidase (Mo, Co and e) Metal-activated enzymes metal is reversibly bound metal to protein ratio is variable metal to enzyme activity ratio is variable metal is not necessarily unique enzyme activity may continue without metal Examples of metal-activated enzymes creatine kinase (Mg, Mn, Ca or Co) glycogen phosphorylase kinase (Ca) salivary and pancreatic alpha-amylases raw the hemec in myoglobin - being careful about the peripheral decoration. What is the explanation for the change between the hemes in oxy- and deoxyhemoglobin? he key amino acid in myoglobin that binds to the heme iron is which amino acid and which sequence number? (His 93) ioxygen can be reduced to water list the intermediate species. Which is the most deadly to the cell? (O2 - - superoxide) Please attempt the calculation, then choose the best answer from those given and finally select the submit button to see whether you were correct. Calculate the entropy changes at 25 C, for the following reactions: Zn2+ + 2NH3 <=> [Zn(NH3)2]2+ ΔH = kj mol-1 and log10 β2 = 5.01 Zn2+ + en <=> [Zn(en)]2+ ΔH = kj mol-1 and log10 β = 6.15 ( R=8.314 JK-1mol-1) 3
5 A) -190, -214 JK-1mol-1 B) 1.9, 25.2 JK-1mol-1 C) -5.3, -4.1 JK-1mol-1 ) 23, 300 JK-1mol-1 None of these, or I don't know. Which of the following amino acids binds preferentially to softer metals? Give a list Know the metal binding amino acids and their structures raw the R group for Cys, His and yr 4
6 About how many amino acids are required for normal physiological mammalian chemistry? 20 How many have to be in the diet.? 9-11 List 4 stabilization energies that hold the 30 structure together - Note 4 types of bio-interaction plus 1 =5) i) hydrogen bonding, ii) hydrophobic interactions between hydrophobic side chains (always very organic, not ionic induced dipoles); (and van der Waals forces) iii) ionic bonds or electrostatic bonds; iv) disulfide bridges the strongest because these are the only true covalent bond that cross-links the protein - a major component of tertiary structures (and also quaternary structures) and (v) bonds to metals also covalent bonds but can be displaced by competition raw a diagram that explains briefly what a molecular chaperone isa molecular chaperone is 5
7 Student Number: with answers Name of Student: he University of Western Ontario Chemistry 3391B - example exam questions not everything was covered the same this year s answers and typos corrected as used HE WRIEN PAR O HIS ES includes material similar to this current year the format of the exam is NO necessarily the same. 1. (4 marks) Complete the following: i) Arrange K +, Na +, Mg 2+, Cl by size smaller on the LHS ii) Write out the triad of elements: with Cu as the lightest with Zn as the lightest iii) Write out the six BLOCK elements before Zn: Mg 2+ <Na + < K + < Cl Cu Ag Au Zn Cd Hg he set includes Cr, Mn, e, Zn Co, Ni, Cu, Zn (2 marks) Which statements are RUE concerning significant human exposure to mercury in any form from eating livers of cattle from eating shellfish from drinking contaminated water from the dust from old paint from preservatives used on wood from vaccines from dental amalgams from fungicides used on grain 2. Identify all of the following metal(s) that in some form is/are known to cause neurological disease at low exposure levels? (WRIE ALL CORREC LEERS ON HE ANSWER SHEE OR QU. 10) A) Na B) Ca C) Hg ) Mn E) Cd ) Zn Identify all of the following that are known to be essential elements for human life. (LIS ALL) A) Na B) Cr C) Hg ) Mn E) Cd ) Zn 5. Which single protein of the following transports e in the blood stream? A) erritin B) Myoglobin C) Carbonic Anhydrase ) ransferrin E) Cytochrome C 6. In a typical 70 kg human there is less than 1 gram (1000mg) for which metals? (Circle the letter of RUE answers and write all these letters on to the answer sheet provided) A) Ca B) Cr C) Pb ) Mn E) e ) Cu 7. How many amino acids are required by humans? A) 15 B) 20 C) 30 ) 45 B 8. How many must be part of our diet? A) None B) All C) 5 ) 10 E) he chlorophyll molecule has which metal bound to the ring? A) Mn B) e C) Zn ) Ca E) Mg ) Co E 10. Zinc is: i) only present in ultratrace amounts in a typical 70 kg person ii) available in many common foods in the diet, especially meat, eggs, and seafoods iii) necessary for development and functioning of the brain iv) deficiency is unusual unless there is liver disease present v) high zinc in the diet is dangerous because zinc can be toxic A) all B) ii, iii, iv, only C) i, ii, iii, iv, only ) i, v only E) i, iv, v only AB C,,,,,, Ans B C B
8 Chemistry 3391B sample exam questions SUEN NAME: Page 2 of Significant human lead exposure is from? i) water pipes ii) paint in old houses iii) cigarette smoke iv) smelting v) burning coal vi) preservatives on wood A) all B) i, ii, vi only C) iii, iv, v, vi only ) ii, iii, iv only E) i, ii, iv only 12. If the Ksp of HgS is 10-53, calculate the volume of water (in L) at ph7 containing one Hg 2+ ion (Avogadro s Number = 6.02 x ). A) Less than 1.0 ml B) 1.0 to 100 ml C) 100 ml to 2 L ) 2 L to 20 L E) 20 L to 1000 L Which of the following is a potential source of metal poisoning specifically discussed in class? E E A) Some vibrant pottery glazes/ colors contain high levels of toxic cobalt B) Many fertilizers are sourced from minerals laced with aluminum C) Some children s toys can contain dangerous amounts of mercury ) Some candies have been identified with high levels of toxic copper E) Some jewelry has recently been found to contain high levels of cadmium 15. he electronic configuration of e 3+ includes: A) 4s 2 3d 3 B) 4s 1 3d 4 C) 4s 0 3d 6 ) 4s 0 3d 5 E) 4s 0 3d How many of the following statements is/are rue concerning the role of Iron, e, in biology? i. When the atmosphere became oxygen rich the insoluble iron salts from the original rocks dissolved and the iron then entered into the evolutionary chain ii. Soluble iron salts are still plentiful in the environment so modern organism still use iron for many functions iii. Iron can usually be replaced by other metals because it is a transient metal in enzymes iv. Iron is only used in the heme protein myoglobin and hemoglobin v. In a healthy adult body, iron is the most abundant d block metal A) Only 1; B) only 2; C) only 3; ) only 4; E) all Which statement(s) is/are RUE concerning the ligand esferrioxamine B? (i) It binds using a combination of N and S donor atoms (ii) It binds only with O donor atoms (iii) It binds only with S donor atoms (iv) It binds using a total of 4 O and 2 N donor atoms (v) Is a very Hard ligand (vi) Predicted to bind very strongly to e 3+ A A) (i) and (v) only; B) (i), (iv), (v) and (vi) only; C) (ii) only; ) (ii), (v) and (vi) only; E) (iv), (v), and (vi) only 18. Which list contains below contains only HAR ligands? A) CYS, ME, and CO B) EA 4, CYS, and HIS C) EA 4, YR, and CN ) YR, EA 4, and GLUAMIC ACI E) 3 PO 4, Se 2 and 2 CO B-Sample-ermest-Questions & Answers.docx Page 2 of 3
9 Chemistry 3391B sample exam questions SUEN NAME: Page 3 of Which list below only contains metals that are considered HAR metals when they have one of their usual their oxidation state(s)? A) Cd and Hg B) Na, K, and Ca C) Cu, Co, and Zn ) Ca, Mg, and Au E) Na, K, and Pt 20. Using H for Hard, S for Soft & I for Intermediate, identify the requested pairs (HH, SS, SH, HS, IH, IS, HI, or SI as appropriate) answer this and the following question (the metals will have their usual oxidation state) Which of the following pairs are SS? (i) Ca & CYS (ii) HgCH3 + & CYS (iii) Ca & MEHIONINE (iv) e(2+) & HIS (v) Hg(2+) + & YROSINE A) (i), (ii), (iii) only; B) (ii), (v) only; C) (i), (iii), (iv), (v), only; ) (iii), (iv), (v) only; E) (ii) only 21. he electronic configuration for Mn(3+) is: (Note: the superscripted numbers are left on the line to aid clarity so read 3d4 3s0 as 3d 4 4s 0 ) A) [Ar] 3d4 4s0 B) [Ar] 3d3 4s2 C) [Ar] 3d5 4s0 ) [Ar] 3d2 4s2 E) [Ar] 3d2 4s0 22. Which statement(s) is/are correct concerning the molecule that is the basis for heme (PPIX)? (i) here is a hydrophobic side and a hydrophilic side (ii) When drawing, one needs to place four (4) methyl groups somewhere along the perimeter of the ring. (iii) When drawing, one needs to place two vinyl on the perimeter adjacent to each other (iv) When drawing, one needs to place 2 propionic acid groups on the perimeter adjacent to each other.. (v) here are eight (8) places that the ring can be modified on the pyrrole perimeter but two (2) are not substituted and remain protons. B HS SS HS II SH E A B A) All; B) (i), (ii) and (iv) only; C) (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv) only; ) (i), ii), and (iii) only; E)(i) and (ii) only 3391B-Sample-ermest-Questions & Answers.docx Page 3 of 3
Sheet #5 Dr. Mamoun Ahram 8/7/2014
 P a g e 1 Protein Structure Quick revision - Levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary. - Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids residues. It determines the other
P a g e 1 Protein Structure Quick revision - Levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary. - Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids residues. It determines the other
PHAR3316 Pharmacy biochemistry Exam #2 Fall 2010 KEY
 1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
BioInorganic Chemistry of Zinc Chemistry 2211a
 BioInorganic Chemistry of Zinc Chemistry 2211a ZINC R17-iJ ZINC R17-iJ The role of zinc (an essential group 12 metal) 1. Zinc is everywhere in our environment 2. Zinc is a constituent of over 300 enzymes
BioInorganic Chemistry of Zinc Chemistry 2211a ZINC R17-iJ ZINC R17-iJ The role of zinc (an essential group 12 metal) 1. Zinc is everywhere in our environment 2. Zinc is a constituent of over 300 enzymes
Porphyrins: Chemistry and Biology
 Porphyrins: Chemistry and Biology 20.109 Lecture 6 24 February, 2011 Goals Explore some essential roles of heme in biology Appreciate how ature has used the same cofactor to achieve diverse functions Gain
Porphyrins: Chemistry and Biology 20.109 Lecture 6 24 February, 2011 Goals Explore some essential roles of heme in biology Appreciate how ature has used the same cofactor to achieve diverse functions Gain
Elemental analysis in clinical practice
 Elemental analysis in clinical practice Nicholas J Miller FRCPath, Laboratory Director, Biolab Medical Unit, ThermoFisher summer symposium 7 th June 2011, QEII Conference Centre Nutritional Elements Macro
Elemental analysis in clinical practice Nicholas J Miller FRCPath, Laboratory Director, Biolab Medical Unit, ThermoFisher summer symposium 7 th June 2011, QEII Conference Centre Nutritional Elements Macro
Unit 3: Chemistry of Life Mr. Nagel Meade High School
 Unit 3: Chemistry of Life Mr. Nagel Meade High School IB Syllabus Statements 3.2.1 Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. 3.2.2 Identify amino acids, glucose, ribose and fatty acids from
Unit 3: Chemistry of Life Mr. Nagel Meade High School IB Syllabus Statements 3.2.1 Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. 3.2.2 Identify amino acids, glucose, ribose and fatty acids from
Globular proteins Proteins globular fibrous
 Globular proteins Globular proteins Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form in a biologically functional way. Globular
Globular proteins Globular proteins Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form in a biologically functional way. Globular
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2009 Examination #5 ANSWER KEY For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2009 Examination #5 ANSWER KEY For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Hemoglobin & Sickle Cell Anemia Exercise
 Name StarBiochem Hemoglobin & Sickle Cell Anemia Exercise Learning Objectives In this exercise, you will use StarBiochem, a protein 3D viewer, to explore the structure of the normal hemoglobin protein
Name StarBiochem Hemoglobin & Sickle Cell Anemia Exercise Learning Objectives In this exercise, you will use StarBiochem, a protein 3D viewer, to explore the structure of the normal hemoglobin protein
Proteins. (b) Protein Structure and Conformational Change
 Proteins (b) Protein Structure and Conformational Change Protein Structure and Conformational Change Proteins contain the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O2) and nitrogen (N2) Some may also
Proteins (b) Protein Structure and Conformational Change Protein Structure and Conformational Change Proteins contain the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O2) and nitrogen (N2) Some may also
Ch5: Macromolecules. Proteins
 Ch5: Macromolecules Proteins Essential Knowledge 4.A.1 The subcomponents of biological molecules and their sequence determine the properties of that molecule A. Structure and function of polymers are derived
Ch5: Macromolecules Proteins Essential Knowledge 4.A.1 The subcomponents of biological molecules and their sequence determine the properties of that molecule A. Structure and function of polymers are derived
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
By Andrew & Erin Oxford, Bethel
 Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
! Proteins are involved functionally in almost everything: " Receptor Proteins - Respond to external stimuli. " Storage Proteins - Storing amino acids
 Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group! Proteins are involved functionally in almost everything: Proteins Multi-purpose molecules 2007-2008 Enzymatic proteins - Speed up chemical reactions!
Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group! Proteins are involved functionally in almost everything: Proteins Multi-purpose molecules 2007-2008 Enzymatic proteins - Speed up chemical reactions!
Chapter 7. Heme proteins Cooperativity Bohr effect
 Chapter 7 Heme proteins Cooperativity Bohr effect Hemoglobin is a red blood cell protein that transports oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. Hemoglobin is an allosteric protein that displays cooperativity
Chapter 7 Heme proteins Cooperativity Bohr effect Hemoglobin is a red blood cell protein that transports oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. Hemoglobin is an allosteric protein that displays cooperativity
Bridging task for 2016 entry. AS/A Level Biology. Why do I need to complete a bridging task?
 Bridging task for 2016 entry AS/A Level Biology Why do I need to complete a bridging task? The task serves two purposes. Firstly, it allows you to carry out a little bit of preparation before starting
Bridging task for 2016 entry AS/A Level Biology Why do I need to complete a bridging task? The task serves two purposes. Firstly, it allows you to carry out a little bit of preparation before starting
BIOCHEMISTRY 460 FIRST HOUR EXAMINATION FORM A (yellow) ANSWER KEY February 11, 2008
 WRITE YOUR AND I.D. NUMBER LEGIBLY ON EVERY PAGE PAGES WILL BE SEPARATED FOR GRADING! CHECK TO BE SURE YOU HAVE 6 PAGES, (print): ANSWERS INCLUDING COVER PAGE. I swear/affirm that I have neither given
WRITE YOUR AND I.D. NUMBER LEGIBLY ON EVERY PAGE PAGES WILL BE SEPARATED FOR GRADING! CHECK TO BE SURE YOU HAVE 6 PAGES, (print): ANSWERS INCLUDING COVER PAGE. I swear/affirm that I have neither given
Biochemistry 15 Doctor /7/2012
 Heme The Heme is a chemical structure that diffracts by light to give a red color. This chemical structure is introduced to more than one protein. So, a protein containing this heme will appear red in
Heme The Heme is a chemical structure that diffracts by light to give a red color. This chemical structure is introduced to more than one protein. So, a protein containing this heme will appear red in
Proteins and their structure
 Proteins and their structure Proteins are the most abundant biological macromolecules, occurring in all cells and all parts of cells. Proteins also occur in great variety; thousands of different kinds,
Proteins and their structure Proteins are the most abundant biological macromolecules, occurring in all cells and all parts of cells. Proteins also occur in great variety; thousands of different kinds,
G = Energy of activation
 Biochemistry I, CHEM 4400 Exam 2 10:00 Fall 2015 Dr. Stone Name rate forward = k forward [reactants] rate reverse = k reverse [products] K eq = [products]/[reactants] ΔG = ΔH - TΔS ΔG = ΔG + RT ln Q Q
Biochemistry I, CHEM 4400 Exam 2 10:00 Fall 2015 Dr. Stone Name rate forward = k forward [reactants] rate reverse = k reverse [products] K eq = [products]/[reactants] ΔG = ΔH - TΔS ΔG = ΔG + RT ln Q Q
Micro-review. Element reducing oxidizing Fe Fe 2+ (high) Fe 3+ (low) Cu Cu sulfides Cu 2+ (moderate) S HS - (high) SO4 2- (high) Mo
 Micro-review Element reducing oxidizing environment environment Fe Fe 2+ (high) Fe 3+ (low) Cu Cu sulfides Cu 2+ (moderate) (low) S HS - (high) S4 2- (high) Mo [MonS4-n] 2- MoS2 (low) V V 3+, V 4+ sulfides
Micro-review Element reducing oxidizing environment environment Fe Fe 2+ (high) Fe 3+ (low) Cu Cu sulfides Cu 2+ (moderate) (low) S HS - (high) S4 2- (high) Mo [MonS4-n] 2- MoS2 (low) V V 3+, V 4+ sulfides
Hemoglobin & Sickle Cell Anemia Exercise
 Name StarBiochem Hemoglobin & Sickle Cell Anemia Exercise Background Hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and for returning
Name StarBiochem Hemoglobin & Sickle Cell Anemia Exercise Background Hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and for returning
Bioinformatics for molecular biology
 Bioinformatics for molecular biology Structural bioinformatics tools, predictors, and 3D modeling Structural Biology Review Dr Research Scientist Department of Microbiology, Oslo University Hospital -
Bioinformatics for molecular biology Structural bioinformatics tools, predictors, and 3D modeling Structural Biology Review Dr Research Scientist Department of Microbiology, Oslo University Hospital -
Matrix Reference Materials - SCP SCIENCE
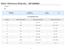 EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
Chapter 20. Proteins & Enzymes. Proteins & Enzymes - page 1
 Chapter 20 Proteins & Enzymes Proteins & Enzymes - page 1 Proteins & Enzymes Part 1: Amino Acids The building blocks of proteins are -amino acids, small molecules that contain a carboxylic acid and an
Chapter 20 Proteins & Enzymes Proteins & Enzymes - page 1 Proteins & Enzymes Part 1: Amino Acids The building blocks of proteins are -amino acids, small molecules that contain a carboxylic acid and an
Understand how protein is formed by amino acids
 Identify between fibrous and globular proteins Understand how protein is formed by amino acids Describe the structure of proteins using specific examples Functions of proteins Fibrous proteins Globular
Identify between fibrous and globular proteins Understand how protein is formed by amino acids Describe the structure of proteins using specific examples Functions of proteins Fibrous proteins Globular
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs. Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison
 Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
Biology 2E- Zimmer Protein structure- amino acid kit
 Biology 2E- Zimmer Protein structure- amino acid kit Name: This activity will use a physical model to investigate protein shape and develop key concepts that govern how proteins fold into their final three-dimensional
Biology 2E- Zimmer Protein structure- amino acid kit Name: This activity will use a physical model to investigate protein shape and develop key concepts that govern how proteins fold into their final three-dimensional
Assignment #1: Biological Molecules & the Chemistry of Life
 Assignment #1: Biological Molecules & the Chemistry of Life A. Important Inorganic Molecules Water 1. Explain why water is considered a polar molecule. The partial negative charge of the oxygen and the
Assignment #1: Biological Molecules & the Chemistry of Life A. Important Inorganic Molecules Water 1. Explain why water is considered a polar molecule. The partial negative charge of the oxygen and the
THE INFLUENCE OF MINERALS ON THE STABILITY OF PREMIX AND FEED COMPONENTS
 THE INFLUENCE OF MINERALS ON THE STABILITY OF PREMIX AND FEED COMPONENTS Richard Murphy Ph.D. Alltech European Bioscience Centre Ireland THE INFLUENCE OF MINERALS ON THE STABILITY OF PREMIX AND FEED COMPONENTS
THE INFLUENCE OF MINERALS ON THE STABILITY OF PREMIX AND FEED COMPONENTS Richard Murphy Ph.D. Alltech European Bioscience Centre Ireland THE INFLUENCE OF MINERALS ON THE STABILITY OF PREMIX AND FEED COMPONENTS
Qualitative test of protein-lab2
 1- Qualitative chemical reactions of amino acid protein functional groups: Certain functional groups in proteins can react to produce characteristically colored products. The color intensity of the product
1- Qualitative chemical reactions of amino acid protein functional groups: Certain functional groups in proteins can react to produce characteristically colored products. The color intensity of the product
3. Hydrogen bonds form between which atoms? Between an electropositive hydrogen and an electronegative N, O or F.
 Chemistry of Life Answers 1. Differentiate between an ionic and covalent bond. Provide an example for each. Ionic: occurs between metals and non-metals, e.g., NaCl Covalent: occurs between two non-metals;
Chemistry of Life Answers 1. Differentiate between an ionic and covalent bond. Provide an example for each. Ionic: occurs between metals and non-metals, e.g., NaCl Covalent: occurs between two non-metals;
Student number. University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Structure and Function In Biochemistry
 University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 19356 Structure and Function In Biochemistry Midterm Test, March 3, 1998. Time allowed, 90 min. Answer questions 120 on the computer scoring
University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 19356 Structure and Function In Biochemistry Midterm Test, March 3, 1998. Time allowed, 90 min. Answer questions 120 on the computer scoring
Sheet #8 Dr. Nafeth Abu-Tarboush 13/07/2014
 Done by 1 Ali Khresat Structure-function relationship of proteins we have talked about proteins, the structure of proteins and features of proteins now we will talk about how this structure is related
Done by 1 Ali Khresat Structure-function relationship of proteins we have talked about proteins, the structure of proteins and features of proteins now we will talk about how this structure is related
2. Which of the following amino acids is most likely to be found on the outer surface of a properly folded protein?
 Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 2 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 2 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Answer three from questions 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9.
 BCH 4053 May 1, 2003 FINAL EXAM NAME There are 9 pages and 9 questions on the exam. nly five are to be answered, each worth 20 points. Answer two from questions 1, 2, 3, and 4 Answer three from questions
BCH 4053 May 1, 2003 FINAL EXAM NAME There are 9 pages and 9 questions on the exam. nly five are to be answered, each worth 20 points. Answer two from questions 1, 2, 3, and 4 Answer three from questions
Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review
 Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review 1.Know the difference between ionic and covalent bonds In order to complete outer shells in electrons bonds can be Ionic; one atom donates or receives electrons Covalent; atoms
Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review 1.Know the difference between ionic and covalent bonds In order to complete outer shells in electrons bonds can be Ionic; one atom donates or receives electrons Covalent; atoms
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Types of proteins Proteins can be divided into two groups according to structure: Fibrous (fiber-like with a uniform secondary-structure
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Types of proteins Proteins can be divided into two groups according to structure: Fibrous (fiber-like with a uniform secondary-structure
Chapter Three (Biochemistry)
 Chapter Three (Biochemistry) 1 SECTION ONE: CARBON COMPOUNDS CARBON BONDING All compounds can be classified in two broad categories: organic compounds and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are made
Chapter Three (Biochemistry) 1 SECTION ONE: CARBON COMPOUNDS CARBON BONDING All compounds can be classified in two broad categories: organic compounds and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are made
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2.
 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
Molecules of Life. Chapter 22. Great Idea: A cell s major parts are constructed from a few simple molecular building blocks 1
 Molecules of Life Chapter 22 Great Idea: A cell s major parts are constructed from a few simple molecular building blocks 1 Chapter Outline Organic Molecules Organic Chemistry Proteins: The Workhorses
Molecules of Life Chapter 22 Great Idea: A cell s major parts are constructed from a few simple molecular building blocks 1 Chapter Outline Organic Molecules Organic Chemistry Proteins: The Workhorses
Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209. Petr Tůma Eva Samcová
 Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209 Petr Tůma Eva Samcová History and nomenclature of enzymes 1810, Gay-Lussac made an experiment with yeats alter saccharide to ethanol and CO 2 Fermentation From
Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209 Petr Tůma Eva Samcová History and nomenclature of enzymes 1810, Gay-Lussac made an experiment with yeats alter saccharide to ethanol and CO 2 Fermentation From
Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22
 Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22 Importance of Proteins Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in
Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22 Importance of Proteins Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in
OVERVIEW OF RESPIRATION AND LOOSE ENDS. What agents? What war?
 5.19.06 OVERVIEW OF RESPIRATION AND LOOSE ENDS What agents? What war? 1 Ubiquinone or Coenzyme Q: small hydrophobic molecule that can pick up or donate electrons The respiratory chain contains 3 large
5.19.06 OVERVIEW OF RESPIRATION AND LOOSE ENDS What agents? What war? 1 Ubiquinone or Coenzyme Q: small hydrophobic molecule that can pick up or donate electrons The respiratory chain contains 3 large
PBL SEMINAR. HEMOGLOBIN, O 2 -TRANSPORT and CYANOSIS An Overview
 1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR HEMOGLOBIN, O 2 -TRANSPORT and CYANOSIS
1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR HEMOGLOBIN, O 2 -TRANSPORT and CYANOSIS
KEY NAME (printed very legibly) UT-EID
 BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2007 KEY NAME (printed very legibly) UT-EID EXAMINATION II Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 7 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2007 KEY NAME (printed very legibly) UT-EID EXAMINATION II Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 7 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
Review of Energetics Intro
 Review of Energetics Intro Learning Check The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy can be Created Destroyed Converted All of the above Learning Check The second law of thermodynamics essentially
Review of Energetics Intro Learning Check The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy can be Created Destroyed Converted All of the above Learning Check The second law of thermodynamics essentially
1. Denaturation changes which of the following protein structure(s)?
 Chem 11 Fall 2008 Examination #5 ASWER KEY MULTIPLE CICE (20 pts. total; 2 pts. each) 1. Denaturation changes which of the following protein structure(s)? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. both b
Chem 11 Fall 2008 Examination #5 ASWER KEY MULTIPLE CICE (20 pts. total; 2 pts. each) 1. Denaturation changes which of the following protein structure(s)? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. both b
Gas Exchange in the Tissues
 Gas Exchange in the Tissues As the systemic arterial blood enters capillaries throughout the body, it is separated from the interstitial fluid by only the thin capillary wall, which is highly permeable
Gas Exchange in the Tissues As the systemic arterial blood enters capillaries throughout the body, it is separated from the interstitial fluid by only the thin capillary wall, which is highly permeable
Human Biochemistry. Enzymes
 Human Biochemistry Enzymes Characteristics of Enzymes Enzymes are proteins which catalyze biological chemical reactions In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process are called
Human Biochemistry Enzymes Characteristics of Enzymes Enzymes are proteins which catalyze biological chemical reactions In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process are called
Enzyme Mimics. Principles Cyclodextrins as Mimics Corands as Mimics Metallobiosites
 Enzyme Mimics Principles Cyclodextrins as Mimics Corands as Mimics Metallobiosites 1 Enzyme Mimics Biochemical systems: Binding is a trigger to events: Binding induces a conformational change in the receptor
Enzyme Mimics Principles Cyclodextrins as Mimics Corands as Mimics Metallobiosites 1 Enzyme Mimics Biochemical systems: Binding is a trigger to events: Binding induces a conformational change in the receptor
Student Guide. Concluding module. Visualizing proteins
 Student Guide Concluding module Visualizing proteins Developed by bioinformaticsatschool.eu (part of NBIC) Text Hienke Sminia Illustrations Bioinformaticsatschool.eu Yasara.org All the included material
Student Guide Concluding module Visualizing proteins Developed by bioinformaticsatschool.eu (part of NBIC) Text Hienke Sminia Illustrations Bioinformaticsatschool.eu Yasara.org All the included material
Biological Sciences 4087 Exam I 9/20/11
 Name: Biological Sciences 4087 Exam I 9/20/11 Total: 100 points Be sure to include units where appropriate. Show all calculations. There are 5 pages and 11 questions. 1.(20pts)A. If ph = 4.6, [H + ] =
Name: Biological Sciences 4087 Exam I 9/20/11 Total: 100 points Be sure to include units where appropriate. Show all calculations. There are 5 pages and 11 questions. 1.(20pts)A. If ph = 4.6, [H + ] =
Proteins. Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff. /3 rd class of pharmacy. PhD. Clinical Biochemistry
 Proteins /3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry a Greek word that means of first importance. It is a very important class of food molecules that provide organisms not
Proteins /3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry a Greek word that means of first importance. It is a very important class of food molecules that provide organisms not
Chemistry 20 Chapter 14 Proteins
 Chapter 14 Proteins Proteins: all proteins in humans are polymers made up from 20 different amino acids. Proteins provide structure in membranes, build cartilage, muscles, hair, nails, and connective tissue
Chapter 14 Proteins Proteins: all proteins in humans are polymers made up from 20 different amino acids. Proteins provide structure in membranes, build cartilage, muscles, hair, nails, and connective tissue
Oxidative phosphorylation & Photophosphorylation
 Oxidative phosphorylation & Photophosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation is the last step in the formation of energy-yielding metabolism in aerobic organisms. All oxidative steps in the degradation of
Oxidative phosphorylation & Photophosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation is the last step in the formation of energy-yielding metabolism in aerobic organisms. All oxidative steps in the degradation of
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Diala
 number 36 Done by Baraa Ayed Corrected by Moath Darweesh Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Porphyrin structure Biosynthesis of Heme Regulation of heme synthesis A clinical
number 36 Done by Baraa Ayed Corrected by Moath Darweesh Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Porphyrin structure Biosynthesis of Heme Regulation of heme synthesis A clinical
I) Choose the best answer: 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine.
 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
Chapter 3. Structure of Enzymes. Enzyme Engineering
 Chapter 3. Structure of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 3.1 Introduction With purified protein, Determining M r of the protein Determining composition of amino acids and the primary structure Determining the
Chapter 3. Structure of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 3.1 Introduction With purified protein, Determining M r of the protein Determining composition of amino acids and the primary structure Determining the
THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. DATE: Oct. 22, 2002 Midterm EXAMINATION. PAPER NO.: PAGE NO.: 1of 6 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO.: 2.277/60.
 PAPER NO.: PAGE NO.: 1of 6 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS You must mark the answer sheet with pencil (not pen). Put your name and enter your student number on the answer sheet. The examination consists of multiple
PAPER NO.: PAGE NO.: 1of 6 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS You must mark the answer sheet with pencil (not pen). Put your name and enter your student number on the answer sheet. The examination consists of multiple
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Biochemical Concepts. Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water. Pre-View 4.6. A Covalent Polar Molecule
 Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Soil Composition. Air
 Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
OPTION GROUP: BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 3 PROTEINS WORKBOOK. Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 3 PROTEINS WORKBOOK Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 1 Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 2 Instructions REVISION CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Regular
NAME: OPTION GROUP: BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 3 PROTEINS WORKBOOK Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 1 Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 2 Instructions REVISION CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Regular
Human Biochemistry Option B
 Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Question Expected Answers Mark Additional Guidance 1 (a) (i) peptide (bond / link) ; 1 DO NOT CREDIT dipeptide (a) (ii) hydrolysis ;
 Question Expected Answers Mark Additional Guidance 1 (a) (i) peptide (bond / link) ; 1 DO NOT CREDIT dipeptide (a) (ii) hydrolysis ; IGNORE name of bond (b) 1 water / H O, is, added / used / needed ; substrate
Question Expected Answers Mark Additional Guidance 1 (a) (i) peptide (bond / link) ; 1 DO NOT CREDIT dipeptide (a) (ii) hydrolysis ; IGNORE name of bond (b) 1 water / H O, is, added / used / needed ; substrate
االمتحان النهائي لعام 1122
 االمتحان النهائي لعام 1122 Amino Acids : 1- which of the following amino acid is unlikely to be found in an alpha-helix due to its cyclic structure : -phenylalanine -tryptophan -proline -lysine 2- : assuming
االمتحان النهائي لعام 1122 Amino Acids : 1- which of the following amino acid is unlikely to be found in an alpha-helix due to its cyclic structure : -phenylalanine -tryptophan -proline -lysine 2- : assuming
Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks)
 Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks) 1. Which one of the following incorrectly pairs an amino acid with a valid chemical characteristic a. Glycine, is chiral b. Tyrosine and tryptophan; at neutral
Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks) 1. Which one of the following incorrectly pairs an amino acid with a valid chemical characteristic a. Glycine, is chiral b. Tyrosine and tryptophan; at neutral
Details of Organic Chem! Date. Carbon & The Molecular Diversity of Life & The Structure & Function of Macromolecules
 Details of Organic Chem! Date Carbon & The Molecular Diversity of Life & The Structure & Function of Macromolecules Functional Groups, I Attachments that replace one or more of the hydrogens bonded to
Details of Organic Chem! Date Carbon & The Molecular Diversity of Life & The Structure & Function of Macromolecules Functional Groups, I Attachments that replace one or more of the hydrogens bonded to
Biologic Oxidation BIOMEDICAL IMPORTAN
 Biologic Oxidation BIOMEDICAL IMPORTAN Chemically, oxidation is defined as the removal of electrons and reduction as the gain of electrons. Thus, oxidation is always accompanied by reduction of an electron
Biologic Oxidation BIOMEDICAL IMPORTAN Chemically, oxidation is defined as the removal of electrons and reduction as the gain of electrons. Thus, oxidation is always accompanied by reduction of an electron
Chemistry of Carbon. All living things rely on one particular type of molecule: carbon
 Ach Chemistry of Carbon All living things rely on one particular type of molecule: carbon Carbon atom with an outer shell of four electrons can form covalent bonds with four atoms. In organic molecules,
Ach Chemistry of Carbon All living things rely on one particular type of molecule: carbon Carbon atom with an outer shell of four electrons can form covalent bonds with four atoms. In organic molecules,
paper and beads don t fall off. Then, place the beads in the following order on the pipe cleaner:
 Beady Pipe Cleaner Proteins Background: Proteins are the molecules that carry out most of the cell s dayto-day functions. While the DNA in the nucleus is "the boss" and controls the activities of the cell,
Beady Pipe Cleaner Proteins Background: Proteins are the molecules that carry out most of the cell s dayto-day functions. While the DNA in the nucleus is "the boss" and controls the activities of the cell,
Proteins. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Proteins Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Proteins are one of the most abundant organic molecules in living systems and have the most diverse range of functions of all macromolecules. Proteins may be structural, regulatory,
Proteins Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Proteins are one of the most abundant organic molecules in living systems and have the most diverse range of functions of all macromolecules. Proteins may be structural, regulatory,
Amino acids & Protein Structure Chemwiki: Chapter , with most emphasis on 16.3, 16.4 and 16.6
 Amino acids & Protein Structure Chemwiki: Chapter 16. 16.1, 16.3-16.9 with most emphasis on 16.3, 16.4 and 16.6 1 1. Most jobs (except information storage) in cells are performed by proteins. 2. Proteins
Amino acids & Protein Structure Chemwiki: Chapter 16. 16.1, 16.3-16.9 with most emphasis on 16.3, 16.4 and 16.6 1 1. Most jobs (except information storage) in cells are performed by proteins. 2. Proteins
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Q1: the overall folding of a single protein subunit is called : -tertiary structure -primary structure -secondary structure -quaternary structure -all of the above Q2 : disulfide
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Q1: the overall folding of a single protein subunit is called : -tertiary structure -primary structure -secondary structure -quaternary structure -all of the above Q2 : disulfide
H 2 O. Liquid, solid, and vapor coexist in the same environment
 Water H 2 O Liquid, solid, and vapor coexist in the same environment WATER MOLECULES FORM HYDROGEN BONDS Water is a fundamental requirement for life, so it is important to understand the structural and
Water H 2 O Liquid, solid, and vapor coexist in the same environment WATER MOLECULES FORM HYDROGEN BONDS Water is a fundamental requirement for life, so it is important to understand the structural and
Biomolecules. Unit 3
 Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
130327SCH4U_biochem April 09, 2013
 Option B: B1.1 ENERGY Human Biochemistry If more energy is taken in from food than is used up, weight gain will follow. Similarly if more energy is used than we supply our body with, weight loss will occur.
Option B: B1.1 ENERGY Human Biochemistry If more energy is taken in from food than is used up, weight gain will follow. Similarly if more energy is used than we supply our body with, weight loss will occur.
Biology Chapter 2 Review
 Biology Chapter 2 Review Vocabulary: Define the following words on a separate piece of paper. Element Compound Ion Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Molecule Hydrogen Bon Cohesion Adhesion Solution Solute Solvent
Biology Chapter 2 Review Vocabulary: Define the following words on a separate piece of paper. Element Compound Ion Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Molecule Hydrogen Bon Cohesion Adhesion Solution Solute Solvent
Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
H C. C α. Proteins perform a vast array of biological function including: Side chain
 Topics The topics: basic concepts of molecular biology elements on Python overview of the field biological databases and database searching sequence alignments phylogenetic trees microarray data analysis
Topics The topics: basic concepts of molecular biology elements on Python overview of the field biological databases and database searching sequence alignments phylogenetic trees microarray data analysis
UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH CHEM 4540 ENZYMOLOGY Winter 2005 Quiz #2: March 24, 2005, 11:30 12:50 Instructor: Prof R. Merrill ANSWERS
 UNIVERSITY F GUELPH CHEM 4540 ENZYMLGY Winter 2005 Quiz #2: March 24, 2005, 11:30 12:50 Instructor: Prof R. Merrill ANSWERS Instructions: Time allowed = 80 minutes. Total marks = 30. This quiz represents
UNIVERSITY F GUELPH CHEM 4540 ENZYMLGY Winter 2005 Quiz #2: March 24, 2005, 11:30 12:50 Instructor: Prof R. Merrill ANSWERS Instructions: Time allowed = 80 minutes. Total marks = 30. This quiz represents
QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS
 QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side chain that varies between different amino acids. Amino acids of
QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side chain that varies between different amino acids. Amino acids of
Scantron Instructions
 BIOLOGY 1A MIDTERM # 1 February 17 th, 2012 NAME SECTION # DISCUSSION GSI 1. Sit every other seat and sit by section number. Place all books and paper on the floor. Turn off all phones, pagers, etc. and
BIOLOGY 1A MIDTERM # 1 February 17 th, 2012 NAME SECTION # DISCUSSION GSI 1. Sit every other seat and sit by section number. Place all books and paper on the floor. Turn off all phones, pagers, etc. and
Protein Structure and Function
 Protein Structure and Function Protein Structure Classification of Proteins Based on Components Simple proteins - Proteins containing only polypeptides Conjugated proteins - Proteins containing nonpolypeptide
Protein Structure and Function Protein Structure Classification of Proteins Based on Components Simple proteins - Proteins containing only polypeptides Conjugated proteins - Proteins containing nonpolypeptide
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION. MACRONUTRIENTS Found in air and water carbon C oxygen hydrogen
 BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
Become A Health Coach Certification. Pillar 1: Nutrition, Health & Wellness Week 1. Copyright All Rights Reserved. Pillar 1 Week 1 Video 2 1
 Become A Health Coach Certification Pillar 1: Nutrition, Health & Wellness Week 1 1 Essential Nutrition : The Distilled Top 20% Of Nutrition, Health & Wellness Knowledge That Matters For Health Coaches
Become A Health Coach Certification Pillar 1: Nutrition, Health & Wellness Week 1 1 Essential Nutrition : The Distilled Top 20% Of Nutrition, Health & Wellness Knowledge That Matters For Health Coaches
Biology 12. Biochemistry. Water - a polar molecule Water (H 2 O) is held together by covalent bonds.
 Biology 12 Biochemistry Water - a polar molecule Water (H 2 O) is held together by covalent bonds. Electrons in these bonds spend more time circulating around the larger Oxygen atom than the smaller Hydrogen
Biology 12 Biochemistry Water - a polar molecule Water (H 2 O) is held together by covalent bonds. Electrons in these bonds spend more time circulating around the larger Oxygen atom than the smaller Hydrogen
Synthesis of ATP, the energy currency in metabolism
 Synthesis of ATP, the energy currency in metabolism Note that these are simplified summaries to support lecture material Either Substrate-level phosphorylation (SLP) Or Electron transport phosphorylation
Synthesis of ATP, the energy currency in metabolism Note that these are simplified summaries to support lecture material Either Substrate-level phosphorylation (SLP) Or Electron transport phosphorylation
FIRST BIOCHEMISTRY EXAM Tuesday 25/10/ MCQs. Location : 102, 105, 106, 301, 302
 FIRST BIOCHEMISTRY EXAM Tuesday 25/10/2016 10-11 40 MCQs. Location : 102, 105, 106, 301, 302 The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes, Mechanisms, and Control General theory of enzyme action, by Leonor Michaelis
FIRST BIOCHEMISTRY EXAM Tuesday 25/10/2016 10-11 40 MCQs. Location : 102, 105, 106, 301, 302 The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes, Mechanisms, and Control General theory of enzyme action, by Leonor Michaelis
Biology 5A Fall 2010 Macromolecules Chapter 5
 Learning Outcomes: Macromolecules List and describe the four major classes of molecules Describe the formation of a glycosidic linkage and distinguish between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides
Learning Outcomes: Macromolecules List and describe the four major classes of molecules Describe the formation of a glycosidic linkage and distinguish between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides
ESSENTIAL TRACE ELEMENTS PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY
 ESSENTIAL TRACE ELEMENTS PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY Back to Basics: Elements Remember that all matter is made of elements An element is a substance in its simplest
ESSENTIAL TRACE ELEMENTS PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY Back to Basics: Elements Remember that all matter is made of elements An element is a substance in its simplest
Lecture 10 More about proteins
 Lecture 10 More about proteins Today we're going to extend our discussion of protein structure. This may seem far-removed from gene cloning, but it is the path to understanding the genes that we are cloning.
Lecture 10 More about proteins Today we're going to extend our discussion of protein structure. This may seem far-removed from gene cloning, but it is the path to understanding the genes that we are cloning.
ENZYMES: CLASSIFICATION, STRUCTURE
 ENZYMES: CLASSIFICATION, STRUCTURE Enzymes - catalysts of biological reactions Accelerate reactions by a millions fold Common features for enzymes and inorganic catalysts: 1. Catalyze only thermodynamically
ENZYMES: CLASSIFICATION, STRUCTURE Enzymes - catalysts of biological reactions Accelerate reactions by a millions fold Common features for enzymes and inorganic catalysts: 1. Catalyze only thermodynamically
Chemistry and Biochemistry 153A Spring Exam 2
 hemistry and Biochemistry 153A Spring 2011 Exam 2 Instructions: You will have 1 hour 45 minutes to complete the exam. You may use a pencil (recommended) or blue or black ink pen to write your answers.
hemistry and Biochemistry 153A Spring 2011 Exam 2 Instructions: You will have 1 hour 45 minutes to complete the exam. You may use a pencil (recommended) or blue or black ink pen to write your answers.
Ch 07. Microbial Metabolism
 Ch 07 Microbial Metabolism SLOs Differentiate between metabolism, catabolism, and anabolism. Fully describe the structure and function of enzymes. Differentiate between constitutive and regulated enzymes.
Ch 07 Microbial Metabolism SLOs Differentiate between metabolism, catabolism, and anabolism. Fully describe the structure and function of enzymes. Differentiate between constitutive and regulated enzymes.
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2010
 BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2010 NAME (printed very legibly) KEY UT-EID EXAMINATION III Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 8 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2010 NAME (printed very legibly) KEY UT-EID EXAMINATION III Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 8 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
Protein Structure Danilo V. Rogayan Jr.
 Protein Structure Danilo V. Rogayan Jr. RMTU San Marcelino Outline I Categories of Proteins Fibrous proteins Globular proteins II Protein Denaturation & Renaturation III Functions of Proteins IV Journal
Protein Structure Danilo V. Rogayan Jr. RMTU San Marcelino Outline I Categories of Proteins Fibrous proteins Globular proteins II Protein Denaturation & Renaturation III Functions of Proteins IV Journal
Bio 100 Serine Proteases 9/26/11
 Assigned Reading: 4th ed. 6.4.1 The Chymotrypsin Mechanism Involves Acylation And Deacylation Of A Ser Residue p. 213 BOX 20-1 Penicillin and β-lactamase p. 779 6.5.7 Some Enzymes Are Regulated By Proteolytic
Assigned Reading: 4th ed. 6.4.1 The Chymotrypsin Mechanism Involves Acylation And Deacylation Of A Ser Residue p. 213 BOX 20-1 Penicillin and β-lactamase p. 779 6.5.7 Some Enzymes Are Regulated By Proteolytic
