Overview of the Parenteral Nutrition Process and use of PN in Long Term Care
|
|
|
- Abigail Hawkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Disclosures The speaker is an employee of Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC Overview of the Parenteral Process and use of PN in Long Term Alyce Newton, MS, RDN, LDN, CNSC Medical Science Liaison Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC Objectives A Valuable Support Intervention Objectives: Recognize indications and goals of PN therapy related to long term care PN serves as an important therapeutic modality that is used in adults, children and infants for a variety of indications. 1 Review the steps of the PN process, including assessment, ordering, preparation, and administration Discuss clinical recommendations and review tools available to help clinicians navigate the PN process PN has been shown to: be life saving in patients with intestinal failure 2 and subacute/chronic radiation enteropathy 3 significantly reduce morbidity in malnourished patients 4 reduce the risk of complications in patients receiving preoperative PN 4 Identify PN formulation options for long term care facilities 1. Ayers P, et al. JPEN. 2014;38(3): Raman M, et al. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2007;32(4): Bozzetti F, et al. Clinical. 2009;28(4): Jeejeebhoy KN. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;74(2): A.S.P.E.N.: American Society for Parenteral and Enteral
2 The PN process is complex and involves multiple disciplines Standardizing the PN Process: ensuring safety is in the process Standardization incorporates technical and practice standards into a process so the same level of safe care 1 is delivered Standardization opportunities exist at each step of PN process 1 A.S.P.E.N. and ISMP guidelines and recommendations encourage standardization of the PN process 1,2 Develop Policies Procedures Education Competency s Use PN order and label Templates Standardized commercially available PN A.S.P.E.N.=American Society for Parenteral and Enteral ; ISMP=Institute for Safe Medication Practices 5 1. Ayers P, et al. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014;38(3): Rich DS, Copyright et al. Hosp Fresenius Pharm. Kabi AG 2013;48(4): The PN Process: The PN Process: Team and/or Reviews patient data / / Giver Conducts nutrition assessment History and Physical Exam, Anthropometrics, Laboratory tests Estimates nutrient requirements Determines nutrition intervention and nutrition prescription based on therapy goals and clinical condition Communicates with prescriber as needed Boullata J. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2012;36:11S. 7 8
3 The PN Process: : Determining What is Needed When determining an appropriate prescription, a clinician must decide: Appropriate Use IV Access / / Giver Indications Peripheral Central PN Ingredients PN Instructions Macronutrients (protein, lipids, dextrose) Micronutrients (vitamins, trace elements, electrolytes) Fluid Total volume Infusion rate Start and stop times 9 Ayers PA, et al. A.S.P.E.N. Parenteral Handbook. 2014; : Indications 1-4 Selection of Vascular Access Device INDICATIONS Mechanical or physiological failure of GI tract Prolonged or paralytic ileus Intestinal obstruction Mesenteric ischemia High output fistula Dysmotility Malabsorption Short bowel syndrome Intractable vomiting Severe diarrhea Intolerance or inadequacy of enteral/ oral feeding Inability to gain access to the GI tract Central Central venous catheter placed into a large vein (jugular, subclavian) Single, double, or triple lumen catheter PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) Confirm tip location in superior vena cava Peripheral Peripheral venous catheter placed in small peripheral vein (typically in upper extremities) Internal Jugular Vein Tunneled Central Venous Catheter PICC (Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter) Trans-lumbar/ Trans-hepatic Venous Access Subclavian Vein Subcutaneous Port Cephalic Vein Cephalic Venous Access Basilic Vein Peripheral Catheter GI = gastrointestinal 1. Ayers PA, et al. A.S.P.E.N. PN Handbook 2014; Van Gossum A, et al. Clin Nutr. 2009;28(4): A.S.P.E.N. Board of Directors, JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2002;26(1 Suppl):1SA-138SA. 4. McClave Copyright SA, et Fresenius al. JPEN Kabi J Parenter AG Enteral Nutr. 2016;40(2): Femoral Venous Access (or Saphenous Vein may be used)
4 : determining IV Access (Peripheral vs Central) Ordering PN Peripheral Central Duration 1 to 2 weeks >1 week Protein Calorie Malnutrition None to Mild Moderate to Severe Fluid High volume May minimize volume Meet Nutrient Requirements Minimally Needs met Determine fluid needs Determine nutrient requirements - Amino acids, carbohydrates, lipids, total energy, electrolytes Calculate the composition of the PN solution - Impact of drug shortages - Disease state considerations Use a standardized order form Osmolarity <900 mosm/l No restriction 13 : Macronutrients Fluid Requirements A.S.P.E.N. Suggested Intake for Adult s 1-5 Stable 30 to 40 ml/kg/day Critically Ill Minimum needed to deliver adequate macronutrients Energy Needs 20 to 30 kcal/kg/d 25 to 30 kcal/kg/d PN : Micronutrients Vitamins and Trace Elements Vitamins and trace elements should always be considered when prescribing PN VITAMINS IV MVI 1 (10 ml) A, D, IU E, K, mcg B 1 B 2 B 3 B 5 B 6 B 12 C Biotin mcg Folate mcg " Protein Needs 0.8 to 1 g/kg/d 1.2 to 2 g/kg/d! DOSE! Zn (/ml)! Cu (/ml)! Mn (mcg/ml)! Cr (mcg/ml)! Se (mcg/ml)! Lipid Needs Carbohydrate Needs 1 g/kg/d OR Hold or limit to 100g 1 st week then 2, 20-30% energy needs 3,4 1 (4 to 5 /kg/min) 5 MTE-4! 3-5 ml! 1! 0.4! 100! 4! -! MTE-4 Concentrate! 1 ml! 5! 1! 500! 10! -! MTE-5 5 ml! 1! 0.4! 100! 4! 20!! MTE-5 Concentrate! 1 ml! 5! 1! 500! 10! 60! 1. Vanek V et al. Nutr Clin Pract 2012;27: RDA = Recommended Dietary Allowances & Adequate Intake 16
5 PN : Micronutrients Electrolytes : Calculation of PN Components Electrolyte a Standard Daily Requirement Factors that Increase Needs Sodium 1 to 2 meq/kg a Diarrhea, vomiting,ng suction, GI losses Potassium 1 to 2 meq/kg a Diarrhea, vomiting,ng suction, medications, refeeding, GI losses Phosphorus 20 to 40 mmol High dextrose intake, refeeding Acetate Chloride As needed to maintain acid-base balance As needed to maintain acid-base balance Renal insufficiency, metabolic acidosis, GI bicarbonate losses Metabolic alkalosis, volume depletion Available Salt Sodium Chloride Sodium Acetate Sodium Phosphate Potassium Chloride Potassium Acetate Potassium Phosphate Sodium phosphate Potassium phosphate Sodium Acetate, Potassium Acetate Sodium Chloride, Potassium Chloride Calcium 10 to 15 meq High protein intake Calcium gluconate Magnesium 8 to 20 meq GI losses, drugs, refeeding Ayers PA, et al. A.S.P.E.N. Parenteral Handbook. 2014; Magnesium Sulfate 17 PN Component Stable Adult 1 80 kg Adult Daily Requirements Fluid ml/kg/d a ml Total Energy kcal/kg/d b kcal Protein g/kg/d g protein Lipids 1 g/kg/d OR 20-30% total energy Carbohydrate /kg/min 2 3 /kg/min 3 a May vary if the patient has ongoing fluid losses b. Varies according to activity levels 80 g OR g/d dextrose g dextrose g dextrose 3 1. Ayers P, et al. A.S.P.E.N. Parenteral Handbook 2014; Clinical Practice 2. Mirtallo JM, et al. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2004;28(6):S39-S Lipids: A.S.P.E.N. Guidelines and Recommendations 1,2,3,4 ILE are an essential component to PN 20 30% daily kcal from fat Choice of Soybean Oil or 4-oil blend (Soy, MCT, Olive, Fish-Smoflipid ) EFA: 2 4% total calories from linoleic acid % total calories from alpha-linolenic acid Long term patients- provide up to 1 gm/kg/day (Soybean Oil) or 1-2 g/kg/day Smoflipid Hold ILE for TG > 400 /dl (All types of Lipid Emulsions) 1 Hise M and Brown JC. Chapter: Lipids. The ASPEN Adult Support Core Curriculum, 2 nd Ed. p Vanek VW, Seidner DL, Allen P, et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2012;27(2): McClave S et al. JPEN J Parent Enteral Nutr 2016; 40 (2): Staun M et al. Clin Nutr 2009; 28: : Calculation of PN Components 1-2 PN Component Stable Adult 1 80 kg Adult Daily Req. EXAMPLE Central PN Formula (Progression to Goal) EXAMPLE Fluid 30 to 40 ml/kg/day ml Start mL; advance to 2400 ml as tolerated Energy 20 to 30 kcal/kg/d kcal ~2000 kcal (25 kcal/kg) Protein 0.8 to 1 g/kg/d g protein 80 g amino acids (320 kcal) Lipid 1 g/kg/d OR 20-30% energy needs 3,4 Carbohydrate /kg/min 2 3 /kg/min 3 <2 /kg/min 80 g OR g/d dextrose g dextrose g dextrose 3 <300 g dextrose 3 50 g lipid Soybean (500 kcal) OR 80 g Smoflipid Remainder kcal: Start g dextrose 2 ; advance to g dextrose 3 ( kcal) 1. Ayers P, et al. A.S.P.E.N. Parenteral Handbook 2014; Clinical Practice 2. Mirtallo Copyright JM, et Fresenius al. JPEN Kabi J Parenter AG Enteral Nutr. 2004;28(6):S39-S70. 20
6 : Calculation Example of PN Components 1-2 PN Component Stable Adult 1 80 kg Adult Requirements Sodium! 1 to 2 meq/kg/d 80 to 160 meq/d Potassium! 1 to 2 meq/kg/d 80 to 160 meq/d Phosphorus! 20 to 40 mmol/d 20 to 40 mmol/d Calcium! 10 to 15 meq/d 10 to 15 meq/d Magnesium! 8 to 20 meq/d 8 to 20 meq/d Multivitamin Injection Multi trace element injection Central PN Formula 80 meq Sodium Chloride 80 meq Potassium Acetate 30 mmol Sodium Phosphate 12 meq Calcium Gluconate 10 meq Magnesium Sulfate Full Dose Full Dose Full Dose Full Dose Full Dose Full Dose 1. Ayers P, et al. A.S.P.E.N. PN Handbook. 2014; Calculating the PN Solution: An Example Compound PN Solution using available components: 10% Amino Acids, 50% dextrose, 20% ILE (soybean oil) RX: 80 gm amino acids, 350 gm dextrose, 50 gm lipid, 2.4 liters Amino acids 800 ml of 10% amino acids (80 g x 4 kcal/g = 320 kcal) Dextrose 700 ml of 50% dextrose (350 g x 3.4 kcal/g = 1190 kcal) Lipid 250 ml of 20% ILE (50 g x 10 kcal/g = 5 concentration for TNA stability (20g/L minimum) Fluid 800 ml ml ml = 1750 ml + electrolytes + sterile water to equal 2400 ml Energy (25 kcal/kg) = 2010 kcal PN Order Form Using Calculations for 80 kg Person (Example) The PN Process: Information Name Medical Record Record Number Number Birth Birth Date/Age Location Allergies Height and and Dosing Dosing Weight: Weight: Ht: Ht: cm cm 183 Dosing Dosing Wt: kg Wt: kg 80 Diagnosis(es)/Indication(s) for PN Diagnosis(es)/Indication(s) for PN Intestinal Obstruction Vascular Access Device/Location CVC type Location Vascular Access Device/Location CVC type PICC Location Superior Vena Cava Date Time Macronutrients Date/Time Amount/day Amino acids g Base Macronutrients Dextrose Formula g Amount/kg/day Amount/day IV Amino Fat emulsion acids 80 g g Electrolytes Dextrose 350 g Sodium IV fat emulsion phosphate 50 mmol of phosphate g (Sodium meq) Note: Electrolytes Electrolytes Sodium chloride meq Sodium acetate meq ordered as salts Sodium phosphate 30 mmol Potassium phosphate mmol of phosphate (Potassium meq) Potassium Sodium chloride chloride meq 80 meq Potassium Sodium acetate meq meq Magnesium Potassium sulfate/chloride phosphate meq mmol Calcium Potassium gluconate chloride meq meq Vitamins, Potassium Trace acetate Elements 80 meq Multi-component Magnesium sulfate vitamins 10 ml meq Multi-component trace elements ml Calcium gluconate 12 meq Other Additives (eg, individual vitamins or trace elements, regular insulin) Vitamins, Trace Elements, Additives PN Instructions: FOR CENTRAL (PERIPHERAL) VEIN ADMINISTRATION ONLY Total Multi-component volume ml vitamins 10 ml Overfill volume ml Infusion Multi-component rate ml/h trace elements Start 1-5 and Stop ml times Dose depends on product Cycle Other information additives (eg, individual vitamins or trace elements, cysteine, regular insulin) Do as clinically not use after appropriate date/time and compatible *******Discard any unused volume after 24 hours******* PN Prescriber Instructions and Contact Information Institution/ Total volume ml 2400 Name Infusion rate ml/h, 100 Start and Stop times Institution/ Cycle information Address Prescriber Telephone and contact Number information Ingredients dosed per day MUST evaluate prescription for compatibility Boullata J. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2012;36:11S. / / Giver 2
7 The PN Process: The PN Process: Review/Verification Prior to preparation/compounding, the PN order has to be reviewed and verified by a pharmacist The review process includes two steps: Clinical review: check if the dosing of each nutrient is appropriate for the individual patient Pharmaceutical review: check if the ordered components are compatible and if the preparation is expected to be stable / / Giver of PN order from handwritten or printed RX into the pharmacy system. Computerized physician order entry (CPOE) system eliminates this step Boullata J. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2012;36:11S. Customized [patient specific] Standardized [institution specific] 2 ASHP national survey of pharmacy practice in hospital settings: and administration 2014 Types of PN Preparations Compounded Boullata J. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2012;36:11S. Manufactured Multi-chamber [commercially available] Purpose: The survey evaluated practices and technologies related to dispensing and administration. Methods: A stratified random sample of pharmacy directors at 1435 general and children s medical-surgical hospitals in the US were surveyed by mail. Results: "#$%&'()*)+!,$+-&%!&.!/&'0&1)%()2!31+#(+(&)!4100&#+!"#$0*#*+(&)5!!! 6!7&50(+*85! 3! ;<()<=!/&''$#>(*88?! >&'0&1)%()2! %$A(>$!! E!FG! #$! %%&'! ()&*! (&+! (+&,! FG!H!II! $%! $,&-! (%&#! '&%! (*&'! =GG!!<=II! %#! *%&*! (%&*! (%&*! *&-! ;GG!H!=II! ')! +(&%! -)! -$&'! (+&,! JGG!H!JII! $'! (,&-! -#&*! -*&#! $&-! KGG!H!FII! *$! '&'! -)&#! *)! (&$! шϲϭϭ! %*! #&'! %(&-! $)! %+$! %-.! (#&*.! (*&#.! $$,! -*! (%&*! +)&%! ('&%!! 9!4+*..$%!:$%5! 3&!"3! 5&81+(&)5! 0#$0*#$%! -)&*! (&,! )! )! )! )! )! ((&+.! ((&*!! Pedersen CA, et al. AJHP 2015; 72:
8 Commercially Available Multi-Chamber PN: Pros and Cons The PN Process: Potential Advantages Ease and convenience for prescribers Minimizes misinterpretation of orders and calculation errors Decreases compounding errors Increases cost savings from decreased nurse/pharmacist time Minimizes impact of shortages Potential Disadvantages Education required for new bag technology 1L or 2L multi-chamber bags may not meet total nutrient requirements in 24 hrs Requires additives, such as vitamins and trace minerals 2-chamber bags may require addition of IV lipid emulsion or piggybacking May not meet all patients nutrient needs Labeling, storage and delivery of PN prior to administration Labels for PN formulations should be standardized and should include: Content Route of administration Date and time of administration Infusion duration and infusion rates Gervasio J. JPEN. 2012;36:40S-41S. Mirtallo JM, et al. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2004;28:S39-S70. PN Label for 80 kg Person (Example) The PN Process: Information Name Medical Record Number Birth Date/Age Location Height and Dosing Weight: Ht: _183 cm Dosing Wt: 80 kg Diagnosis(es)/Indication(s) for PN Intestinal Obstruction Vascular Access Device/Location CVC type PICC Location:_Right Superior Vena Cava Date Time Macronutrients Amount/day Amino acids 80 g Dextrose 350 g IV Fat emulsion 50 g Electrolytes Sodium phosphate 30 mmol of phosphate (Sodium meq) Sodium chloride 80 meq Sodium acetate meq Potassium phosphate mmol of phosphate (Potassium meq) Potassium chloride meq Potassium acetate 80 meq Magnesium sulfate 10 meq Calcium gluconate 12 meq Vitamins, Trace Elements Multi-component vitamins 10 ml Multi-component trace elements 5 ml Other Additives (eg, individual vitamins or trace elements, regular insulin) PN Instructions: FOR CENTRAL (PERIPHERAL) VEIN ADMINISTRATION ONLY Total volume 2400 ml Overfill volume ml Infusion rate 100 ml/h Start and Stop times Cycle information Do not use after date/time *******Discard any unused volume after 24 hours******* Prescriber and Contact Information Institution/ Name Institution/ Address Telephone Number Ingredients dosed in amount per day Label should have same sequence of ingredients and must match order / / Giver Ayers P, et al. JPEN. 2014;38(3): Boullata J. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2012;36:11S. 3
9 The PN Process: The First 24 Hours The first step is the verification of the PN order according to the five rights Right patient Right drug Right dose (and rate) This process includes: Safe and effective management of all medical devices and equipment used Initial volume may be lower than goal volume (start at goal amino acids and lipids; progress to goal volume and dextrose as tolerated) Check labs before and after initiation of PN, including electrolytes, glucose, and acid-base status Observe for changes in fluid status: monitor intake and output, presence of edema, vital signs, and weight Right route Right time Ayers P, et al. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014;38(3): Safe administration of medications in conjunction with PN therapy and optimal care of vascular access devices 4 The PN Process: Parameters and Frequency Parameter Initiation Critically Ill Stable Electrolytes Daily Daily* 1-2 x / wk Glucose Daily Daily 1-2 x / wk / / Giver Triglycerides Day 1 Weekly Weekly Liver Enzymes Day 1 Daily* Weekly CBC Day 1 Daily* Weekly Dyspnea/SOB /Edema Daily Daily Daily Weight, I/O Daily Daily Daily Temperature Daily Daily Daily CBC = complete blood count *Until stable and then 1-2x per week. SOB = shortness of breath Boullata J. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2012;36:11S. 4 Ayers P, et al. A.S.P.E.N. PN Handbook. 2014;185. I/O = intake and output
10 The PN Process: for complications PN Complications Metabolic Infectious Mechanical Refeeding Syndrome Fluid and electrolyte abnormalities Acid/base imbalance Hepatic complications LFT elevation Fatty liver Cholestasis Liver failure Metabolic imbalances Hyper/hypoglycemia Essential fatty acid deficiency Vitamin/trace element deficiencies Metabolic bone disease Catheter-related bacteremia or sepsis Related to: Access device Exit site Surrounding skin Septic thrombosis LFT=liver function test Occlusions, thrombosis, leakage, breakage, malposition of access device Equipment failure Ayers P, et al. A.S.P.E.N. Parenteral Handbook Can result in serious morbidity or mortality 1 A.S.P.E.N. survey 2 25% of reported adverse events related to PN caused temporary or permanent harm 4.8% resulted in a near-death event or death Severe complications may lead to increased LOS and additional costs 1,3,4 refeeding syndrome, hyperglycemia, catheter infections LOS = Length of Stay 1.McClave SA, et al. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2009; 33(3): Seres D, et al. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2006;30(3): Turpin RS, et al. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2011;9(5): Pontes-Arruda, et al. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2012;36: Transitioning Off PN Transitions of : Long Term to and from hospital and home 1. Gradual transition to avoid complications 2. Combine PN and enteral to provide all nutrient goals during transition Provide multivitamins and trace minerals orally as well as via IV during transition 3. Provide PN until 60% of energy needs can be met enterally 4. Communicate with primary team that PN is being stopped as: Other IV fluid may be needed Electrolyte supplementation may be needed Insulin in PN bag is being stopped Glucose source is being stopped Discharge from hospital or Healthcare Facility (HCF) Communication is KEY! Request Discharge PN order form for LTC facility infusion Copy of patient flowsheet with labs, notes etc. Contact information of inhouse PN prescriber Ensure that there is a an outpatient physician to sign PN orders LTC Facility to HCF or Home Communication is KEY! Send: RX to HCF or Home Infusion provider Copy of patient flowsheet with labs, notes, etc. Contact information of LTC facility prescriber Maintain contact during discharge from LTC to home or HCF
11 Risks in the PN Process Long term Errors: PN not indicated Inexperienced clinician Order inappropriate Dosing Errors: Doses outside normal ranges Incorrect PN volume Incorrect infusion rate of incompatible components Review/Verification/ errors Misinterpretation of abbreviations and dose designations Incomplete/missing evaluation for compatibility and stability Selection of the wrong ingredient Drug omission / Preparation/ Compounding/ Errors: Product mix-up Errors in sterile compounding technique Incompatible or missing additives Incorrect or incomplete labelling Incorrect storage not kept at recommended temperature / Giver PN Errors: Wrong patient, drug, dose, route, time Contamination of infusion system Errors: Inexperienced labs not ordered or reviewed PN not adjusted as needed Absence of essential PN components unnoticed LPN s may not be permitted to care for or use the PN catheters in many states RN may be the only person on LTC staff with central line catheter care responsibilities. RN experience with catheter care and PN administration varies. Infection is the most serious consequence of non-sterile catheter care and may result in sepsis/death RNs can be trained in catheter care by certified infusion nurses familiar with PN administration and catheter care Check with RN manager in facility to learn of interest/skill set Ask pharmacy if RN catheter care/pn administration teaching available Infusion s Society (INS) skilled in catheter care and administration Resources Available to Promote Safe of the PN Process Summary PN Safety Checklists PN Safety Preparation Checklist PN Prescribing Checklist PN Order Review and Verification Checklist PN Compounding Checklist PN Checklist Parenteral Safety Consensus Recommendations Related Publication Product Shortages Educational Opportunities Adverse Event and Error Reporting Program The PN process is complex, starting with patient assessment and progressing through order writing, compounding, and administration Standardization of the PN Process can help improve safe provision of PN. Multichamber PN bags may be part of the standardized process. Regulatory requirements may affect compounding decisions Published clinical guidelines, nutrient recommendations, and toolkits are available to help clinicians navigate each step of the PN process and provide appropriate, safe care for their patients
12 Check your Knowledge! Check your Knowledge! 1. What is/are indications for parenteral nutrition? a. at the end of life who can no longer eat or drink b. refuses a gastrostomy tube c. has had a partial intestinal resection and GI fluid losses have caused dehydration, despite tube feedings, oral rehydration solutions and a modified diet d. has a complete intestinal obstruction and a feeding tube and surgery are not options. 2. What are the steps to ordering PN: Sort in order from beginning to end a. Use a standardized order form b. Determine nutrient and fluid requirements c. Calculate the composition of the PN solution d. Verify indication for and appropriateness of PN e. c and d Check your Knowledge! Check your Knowledge! 3. Severe complications of PN may be prevented by: a. Standardizing the PN process b. Using only Enteral c. Hiring more pharmacists d. Including insulin in PN bags e. Restricting prescribing privileges to physicians only 4. Risks for errors in the PN process exist at which step the process (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY) a. PN ordering b. PN compounding c. PN administration d. PN monitoring e. Transitions of care 56 57
13 Questions?
Risk Management in Parenteral Nutrition. J. Boullata
 Risk Management in Parenteral Nutrition J. Boullata Objectives Upon completion of this session, the participant will be able to: Describe safety issues with parenteral nutrition (PN) Present the PN-use
Risk Management in Parenteral Nutrition J. Boullata Objectives Upon completion of this session, the participant will be able to: Describe safety issues with parenteral nutrition (PN) Present the PN-use
Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406
 Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406 Malnutrition 30 50% of hospitalized patients 95% of nursing home patients Resulting in reduced quality of life & increased health care costs May be remedied by providing
Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406 Malnutrition 30 50% of hospitalized patients 95% of nursing home patients Resulting in reduced quality of life & increased health care costs May be remedied by providing
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition
 Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention?
 Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success
 Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success Mandy Corrigan, MPH, RD, CNSC Nutrition Support Clinician mandycorrigan1@gmail.com
Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success Mandy Corrigan, MPH, RD, CNSC Nutrition Support Clinician mandycorrigan1@gmail.com
Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition
 Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Audis Bethea, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor Therapeutics I December 5 & 9, 2003 Parenteral Nutrition Definition process of supplying nutrients via the intravenous route
Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Audis Bethea, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor Therapeutics I December 5 & 9, 2003 Parenteral Nutrition Definition process of supplying nutrients via the intravenous route
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology
 Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology Presenter: Pam Wagner, RD, CNSC Learning Objectives List indications for initiating PN in oncology patients Describe considerations when determining an appropriate candidate
Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology Presenter: Pam Wagner, RD, CNSC Learning Objectives List indications for initiating PN in oncology patients Describe considerations when determining an appropriate candidate
The Drug Shortage Crisis
 Objectives: The Drug Shortage Crisis Jay M. Mirtallo, MS, RPh, BCNSP, FASHP Director, MS in Health System Pharmacy Associate Professor of Clinical Pharmacy The Ohio State University, College of Pharmacy
Objectives: The Drug Shortage Crisis Jay M. Mirtallo, MS, RPh, BCNSP, FASHP Director, MS in Health System Pharmacy Associate Professor of Clinical Pharmacy The Ohio State University, College of Pharmacy
THE AUTHOR OF THIS WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE: PARENTERAL NUTRITION (PN)
 WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
Nutrition Services at a glance
 Nutrition Services at a glance Ragini Raghuveer, MS, RD, LD/N Systems Clinical Nutrition Manager Linette De Armas, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian Melissa Lorenzo, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian 1 Learning Objectives
Nutrition Services at a glance Ragini Raghuveer, MS, RD, LD/N Systems Clinical Nutrition Manager Linette De Armas, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian Melissa Lorenzo, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian 1 Learning Objectives
10/28/2015. Disclaimer. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer Omnicare, Inc., as a provider of Infusion Pharmacy Services, is committed to the establishment and maintenance of the highest quality of care in infusion therapy services. This Infusion Therapy
Disclaimer Omnicare, Inc., as a provider of Infusion Pharmacy Services, is committed to the establishment and maintenance of the highest quality of care in infusion therapy services. This Infusion Therapy
Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition. J. Eastwood (UK)
 ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 Pharmaceutical Session Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition J. Eastwood (UK) Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition
ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 Pharmaceutical Session Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition J. Eastwood (UK) Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT. Dr. Sarath Gopalan
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
Nutrition care plan for surgical patients. Objectives
 Slide 1 Nutrition care plan for surgical patients Surgical Nutrition Training Module Level 1 Philippine Society of General Surgeons Committee on Surgical Training In this session we will discuss the most
Slide 1 Nutrition care plan for surgical patients Surgical Nutrition Training Module Level 1 Philippine Society of General Surgeons Committee on Surgical Training In this session we will discuss the most
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 October 2011
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
Review and comments on the 2014 recommendations for parenteral nutrition usage by ASPEN
 105 Review and comments on the 2014 recommendations for parenteral nutrition usage by ASPEN Submitted: August 10, 2015 Posted: August 31, 2015 Author: Luisito Llido, MD Clinical Nutrition Service, St.
105 Review and comments on the 2014 recommendations for parenteral nutrition usage by ASPEN Submitted: August 10, 2015 Posted: August 31, 2015 Author: Luisito Llido, MD Clinical Nutrition Service, St.
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition. in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT. Dzulfikar DLH. Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
 The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: PARENTERAL NUTRITION AND INTRAVENOUS FAT EMULSION (ADULT AND PEDIATRICS) Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN II 12/80
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: PARENTERAL NUTRITION AND INTRAVENOUS FAT EMULSION (ADULT AND PEDIATRICS) Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN II 12/80
Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick Neonatal Pharmacist
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
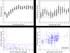 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Parenteral Nutrition. What is Parenteral Nutrition? Goals of Parenteral Nutrition
 Parenteral Nutrition Diamond Pharmacy Services What is Parenteral Nutrition? Intravenous feeding that provides a patient with fluids and essential nutrients during a time of gastrointestinal function disruption
Parenteral Nutrition Diamond Pharmacy Services What is Parenteral Nutrition? Intravenous feeding that provides a patient with fluids and essential nutrients during a time of gastrointestinal function disruption
Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 March Date of the Marketing Authorisation (national procedure): 18 December 1997
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 March 2008 INTRALIPIDE 20 PER CENT, emulsion for infusion 100 ml in Excel container (PE/PP) (CIP: 355 096-5) 250
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 March 2008 INTRALIPIDE 20 PER CENT, emulsion for infusion 100 ml in Excel container (PE/PP) (CIP: 355 096-5) 250
Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ
 Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ Outline Refeeding Syndrome What is refeeding syndrome? What Electrolytes and minerals are involved? Who is at risk? How to manage
Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ Outline Refeeding Syndrome What is refeeding syndrome? What Electrolytes and minerals are involved? Who is at risk? How to manage
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc
 Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
NOTE: The first appearance of terms in bold in the body of this document (except titles) are defined terms please refer to the Definitions section.
 TITLE PARENTERAL NUTRITION ADMINISTRATION AND MONITORING SCOPE Provincial: Acute Care APPROVAL AUTHORITY Clinical Operations Executive Committee SPONSOR Pharmacy Services, Nutrition Services, and Health
TITLE PARENTERAL NUTRITION ADMINISTRATION AND MONITORING SCOPE Provincial: Acute Care APPROVAL AUTHORITY Clinical Operations Executive Committee SPONSOR Pharmacy Services, Nutrition Services, and Health
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients. Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
Current concepts in Critical Care Nutrition
 Current concepts in Critical Care Nutrition Dr.N.Ramakrishnan AB (Int Med), AB (Crit Care), MMM, FACP, FCCP, FCCM Director, Critical Care Services Apollo Hospitals, Chennai Objectives Why? Enteral or Parenteral
Current concepts in Critical Care Nutrition Dr.N.Ramakrishnan AB (Int Med), AB (Crit Care), MMM, FACP, FCCP, FCCM Director, Critical Care Services Apollo Hospitals, Chennai Objectives Why? Enteral or Parenteral
Vanessa Kumpf, PharmD, BCNSP Clinical Pharmacist Center for Human Nutri;on
 Vanessa Kumpf, PharmD, BCNSP Clinical Pharmacist Center for Human Nutri;on Learn what you can do to: Maximize TPN benefits Minimize TPN-related problems Learn how to monitor your therapy Learn how to read
Vanessa Kumpf, PharmD, BCNSP Clinical Pharmacist Center for Human Nutri;on Learn what you can do to: Maximize TPN benefits Minimize TPN-related problems Learn how to monitor your therapy Learn how to read
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter
 Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Issues in Enteral Feeding: Malnutrition
 Issues in Enteral Feeding: Malnutrition A webinar for HealthTrust Members February 22, 2019 Co-sponsored by HealthTrust and V NOS Continuing Education Provider Presented by: Kathleen Stoessel, RN, BSN,
Issues in Enteral Feeding: Malnutrition A webinar for HealthTrust Members February 22, 2019 Co-sponsored by HealthTrust and V NOS Continuing Education Provider Presented by: Kathleen Stoessel, RN, BSN,
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION. Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
WHEN To Initiate Parenteral Nutrition A Frequent Question With New Answers
 WHEN To Initiate Parenteral Nutrition A Frequent Question With New Answers Ainsley Malone, MS, RD, LD, CNSC, FAND, FASPEN Dubai International Nutrition Conference 2018 Disclosures No commercial relationship
WHEN To Initiate Parenteral Nutrition A Frequent Question With New Answers Ainsley Malone, MS, RD, LD, CNSC, FAND, FASPEN Dubai International Nutrition Conference 2018 Disclosures No commercial relationship
Nutritional intervention in hospitalised paediatric patients. Dr Y.K.Amdekar
 Nutritional intervention in hospitalised paediatric patients Dr Y.K.Amdekar Back to basics Suboptimal nutrient intake is always dangerous in health and more so in disease to feed or not to feed is it a
Nutritional intervention in hospitalised paediatric patients Dr Y.K.Amdekar Back to basics Suboptimal nutrient intake is always dangerous in health and more so in disease to feed or not to feed is it a
Introduction to Clinical Nutrition
 M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients
 Fluid Dextrose Amino acid Lipid Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients (Calculated for normal organ function and normal caloric requirements) PN orders are due by 11 AM daily Newborn
Fluid Dextrose Amino acid Lipid Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients (Calculated for normal organ function and normal caloric requirements) PN orders are due by 11 AM daily Newborn
Scott A. Lynch, MD, MPH,FAAFP Assistant Professor
 Scott A. Lynch, MD, MPH,FAAFP Assistant Professor Lynch.Scott@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Nutrition in the Hospital Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development 2nd Annual Inpatient Medicine for
Scott A. Lynch, MD, MPH,FAAFP Assistant Professor Lynch.Scott@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Nutrition in the Hospital Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development 2nd Annual Inpatient Medicine for
Unit 11. Objectives. Indications for IV Therapy. Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids. 3 categories. Maintenance Replacement Restoration
 Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
ESPEN Congress Florence 2008
 ESPEN Congress Florence 2008 PN Guidelines presentation PN Guidelines in home parenteal nutrition M. Staun (Denmark) ESPEN-guidelines for home parenteral nutrition (HPN) Michael Staun, Andre Van Gossum,
ESPEN Congress Florence 2008 PN Guidelines presentation PN Guidelines in home parenteal nutrition M. Staun (Denmark) ESPEN-guidelines for home parenteral nutrition (HPN) Michael Staun, Andre Van Gossum,
CE Prn. Pharmacy Continuing Education from WF Professional Associates ABOUT WFPA LESSONS TOPICS ORDER CONTACT PHARMACY EXAM REVIEWS
 CE Prn Pharmacy Continuing Education from WF Professional Associates ABOUT WFPA LESSONS TOPICS ORDER CONTACT PHARMACY EXAM REVIEWS Parenteral Nutrition: Feeding Our Patients In this lesson we focus on
CE Prn Pharmacy Continuing Education from WF Professional Associates ABOUT WFPA LESSONS TOPICS ORDER CONTACT PHARMACY EXAM REVIEWS Parenteral Nutrition: Feeding Our Patients In this lesson we focus on
Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
Appropriate Use of Enteral Nutrition: Part 1 A Team-Based Approach to. Presented at A.S.P.E.N. s Clinical Nutrition Week January 24, 2012 Orlando, FL
 Appropriate Use of Enteral Nutrition: Part 1 A Team-Based Approach to Overcoming Clinical Barriers Presented at A.S.P.E.N. s Clinical Nutrition Week January 24, 2012 Orlando, FL According to the Commission
Appropriate Use of Enteral Nutrition: Part 1 A Team-Based Approach to Overcoming Clinical Barriers Presented at A.S.P.E.N. s Clinical Nutrition Week January 24, 2012 Orlando, FL According to the Commission
Long term monitoring. Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital
 Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
Clinical Policy: Total Parenteral Nutrition and Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition Reference Number: CP.PHAR.205
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.PHAR.205 Effective Date: 05.16 Last Review Date: 02.18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.PHAR.205 Effective Date: 05.16 Last Review Date: 02.18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. Dextrose Injection USP. (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Dextrose Injection USP (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher Pfizer Canada Inc. 17300 Trans-Canada Highway Kirkland,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Dextrose Injection USP (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher Pfizer Canada Inc. 17300 Trans-Canada Highway Kirkland,
Intensive Care Nutrition. Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA
 Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Parenteral Nutrition in IBD: Any indication?
 Parenteral Nutrition in IBD: Any indication? Name: Institution: Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, Brussels, Belgium Clinical case 42 year old male Crohn s disease since he was 16 years old
Parenteral Nutrition in IBD: Any indication? Name: Institution: Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, Brussels, Belgium Clinical case 42 year old male Crohn s disease since he was 16 years old
Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition. Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health
 Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health Child is not a miniature adult Specific for child growth and
Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health Child is not a miniature adult Specific for child growth and
Nutrition Intervention After Gastric Bypass Revision
 Nutrition Intervention After Gastric Bypass Revision With an Anastomotic Leak Ali Fox- Montana Dietetic Intern Objectives 1. Describe the etiology of anastomotic leak post Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (G.B.)
Nutrition Intervention After Gastric Bypass Revision With an Anastomotic Leak Ali Fox- Montana Dietetic Intern Objectives 1. Describe the etiology of anastomotic leak post Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (G.B.)
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION L-Leucine Ph. Eur 0.620% w/v L-Isoleucine
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION L-Leucine Ph. Eur 0.620% w/v L-Isoleucine
Clinical Policy: Total Parenteral Nutrition and Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.163 Last Review Date: 04/18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications Revision Log Parenteral
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.163 Last Review Date: 04/18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications Revision Log Parenteral
Central Line Care and Management
 Central Line Care and Management What is a Central Line/ CVAD? (central venous access device) A vascular infusion device that terminates at or close to the heart or in one of the great vessels (aorta,
Central Line Care and Management What is a Central Line/ CVAD? (central venous access device) A vascular infusion device that terminates at or close to the heart or in one of the great vessels (aorta,
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion , version 1.1
 EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
IDPN. A Piece of the Puzzle for Dialysis Patients Nutrition. Toll Free: Toll Free:
 IDPN A Piece of the Puzzle for Dialysis Patients Nutrition Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Executive Infusion is pleased to announce our nutritional services which include Intradialytic
IDPN A Piece of the Puzzle for Dialysis Patients Nutrition Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Executive Infusion is pleased to announce our nutritional services which include Intradialytic
What s New in Parenteral Nutrition?
 1 What s New in Parenteral Nutrition? พ นโทหญ ง ส รกานต เตชะวณ ช MD, MSc, ABPNS ห วหน าหน วยโภชนศาสตร คล น ก กองอาย รกรรม โรงพยาบาลพระมงก ฎเกล า 7 กรกฎาคม พ.ศ. 2559 What s New in Parenteral Nutrition?
1 What s New in Parenteral Nutrition? พ นโทหญ ง ส รกานต เตชะวณ ช MD, MSc, ABPNS ห วหน าหน วยโภชนศาสตร คล น ก กองอาย รกรรม โรงพยาบาลพระมงก ฎเกล า 7 กรกฎาคม พ.ศ. 2559 What s New in Parenteral Nutrition?
Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Due 2/13/15 60 points. Ht: 5 11 Current wt: 156 # UBW: 167 # Serum albumin: 3.
 Name: Wan yi Wang Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Due 2/13/15 60 points Mr. R, a 35 yo drug user, is hospitalized after a motor vehicle accident (MVA). He is currently suffering from
Name: Wan yi Wang Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Due 2/13/15 60 points Mr. R, a 35 yo drug user, is hospitalized after a motor vehicle accident (MVA). He is currently suffering from
Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition
 Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Mr. R, a 35 yo drug user, is hospitalized after a motor vehicle accident (MVA). He is currently suffering from a severe concussion and lapses of consciousness,
Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Mr. R, a 35 yo drug user, is hospitalized after a motor vehicle accident (MVA). He is currently suffering from a severe concussion and lapses of consciousness,
PARENTAL NUTRITION SUPPORT. Dr Rezzan Khan Consultant Nutritionist Shifa International Hospital
 PARENTAL NUTRITION SUPPORT Dr Rezzan Khan Consultant Nutritionist Shifa International Hospital Objectives Explain the indications and contraindications of PN Describe the types of PN How to set PN Explain
PARENTAL NUTRITION SUPPORT Dr Rezzan Khan Consultant Nutritionist Shifa International Hospital Objectives Explain the indications and contraindications of PN Describe the types of PN How to set PN Explain
10/3/2012. Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition A Comprehensive Review
 Critical Care Nutrition Foundation for Moving Forward Justine Turner MD PhD Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition University of Alberta I have the following financial relationships to
Critical Care Nutrition Foundation for Moving Forward Justine Turner MD PhD Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition University of Alberta I have the following financial relationships to
What s In The Bag? 3-in-1 versus 2-in-1 PN
 What s In The Bag? 3-in-1 versus 2-in-1 PN Amber Verdell, PharmD, BCPS, BCNSP Assistant Professor, Pharmacy Practice West Coast University, Los Angeles, CA Disclosures I have no commercial relationships
What s In The Bag? 3-in-1 versus 2-in-1 PN Amber Verdell, PharmD, BCPS, BCNSP Assistant Professor, Pharmacy Practice West Coast University, Los Angeles, CA Disclosures I have no commercial relationships
IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Serum Osmolality 275 to 295 Isotonic
 1 IV Fluids Nursing B23 2 Objectives 3 Serum Osmolality Serum osmolality solute concentration of a solution Higher osmolality means greater pulling power for water Normal serum osmolality is 275 to 295
1 IV Fluids Nursing B23 2 Objectives 3 Serum Osmolality Serum osmolality solute concentration of a solution Higher osmolality means greater pulling power for water Normal serum osmolality is 275 to 295
Intravenous Lipids: Clinical & Practical Updates. Nora AlBanyan, R.Ph., SSC-PhP, SSCPN, BCNSP
 Intravenous Lipids: Clinical & Practical Updates Nora AlBanyan, R.Ph., SSCPhP, SSCPN, BCNSP Disclosure Information I have no financial relationship to disclose. AND I will not discuss off label use and/or
Intravenous Lipids: Clinical & Practical Updates Nora AlBanyan, R.Ph., SSCPhP, SSCPN, BCNSP Disclosure Information I have no financial relationship to disclose. AND I will not discuss off label use and/or
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University
 ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
Targeted Employees/ Departments: Clinical Nutrition Department, Food Services Department, Catering Services, Nursing Department and Physicians
 1. Purpose: 1.1 To define the policy and establish applicable on procedure that will serve as guidelines for all staff involved in ordering meals (regular, therapeutic diets & nutritional supplements)
1. Purpose: 1.1 To define the policy and establish applicable on procedure that will serve as guidelines for all staff involved in ordering meals (regular, therapeutic diets & nutritional supplements)
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Pharmaceutical Services Offered in Hospitals
 Pharmaceutical Services Offered in Hospitals Product Services Research Services Teaching Services Support Services Clinical Services In-patients (hospitalized) Out-patients (ambulatory) In-patients (hospitalized)
Pharmaceutical Services Offered in Hospitals Product Services Research Services Teaching Services Support Services Clinical Services In-patients (hospitalized) Out-patients (ambulatory) In-patients (hospitalized)
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management
 Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach
 Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
The nutrient formulas used for parenteral nutrition are
 CASE REPORT Possible Incompatibility between Amino Acids and Copper in Solutions for Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition Maxime Thibault INTRODUCTION The nutrient formulas used for parenteral nutrition are
CASE REPORT Possible Incompatibility between Amino Acids and Copper in Solutions for Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition Maxime Thibault INTRODUCTION The nutrient formulas used for parenteral nutrition are
IV Fluids. Nursing B23. Objectives. Serum Osmolality
 IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Discuss the purpose of IV Discuss nursing interventions in IV therapy Identify complications of IV therapy Differentiate between peripheral line, central line, and PICC
IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Discuss the purpose of IV Discuss nursing interventions in IV therapy Identify complications of IV therapy Differentiate between peripheral line, central line, and PICC
Nutrition Therapy. Medical Coverage Policy Enteral/Parenteral EFFECTIVE DATE: POLICY LAST UPDATED: 11/20/2018 OVERVIEW
 Medical Coverage Policy Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition Therapy EFFECTIVE DATE: 01 20 2007 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 11/20/2018 OVERVIEW This policy describes the reimbursement for enteral and parenteral nutrition
Medical Coverage Policy Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition Therapy EFFECTIVE DATE: 01 20 2007 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 11/20/2018 OVERVIEW This policy describes the reimbursement for enteral and parenteral nutrition
Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN *
 For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer. Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy
 Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy Overview The pancreas and nutrition Nutrition screening - can we do this well?
Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy Overview The pancreas and nutrition Nutrition screening - can we do this well?
Sustain Follow-up Data Collection Form (Revised 2/4/2014) (both pediatric and adult elements) (Please select) (Please select)
 Patient Information Sustain Follow-up Data Collection Form (Revised 2/4/2014) (both pediatric and adult elements) Visit Date Patient Birth Date -- Gender (please select) What is the nature of this follow-up?
Patient Information Sustain Follow-up Data Collection Form (Revised 2/4/2014) (both pediatric and adult elements) Visit Date Patient Birth Date -- Gender (please select) What is the nature of this follow-up?
Jo Kuehn, RN, MSN, CPHQ Jenell Westhoven, RN, BSN
 Jo Kuehn, RN, MSN, CPHQ Jenell Westhoven, RN, BSN Disclosure Information Intravenous Therapy and Parenteral Nutrition Administration: Nursing In- Focus Jo Kuehn, RN, MSN, CPHQ and Jenell Westhoven, RN,
Jo Kuehn, RN, MSN, CPHQ Jenell Westhoven, RN, BSN Disclosure Information Intravenous Therapy and Parenteral Nutrition Administration: Nursing In- Focus Jo Kuehn, RN, MSN, CPHQ and Jenell Westhoven, RN,
Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline. Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine
 Document Control Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline Author Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine Department Medicine Version Date
Document Control Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline Author Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine Department Medicine Version Date
DISCLOSURE. Learning Objectives. Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition
 Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Nutrition Management in GI Diseases
 Nutrition Management in GI Diseases Aryono Hendarto MD Nutrition & Metabolic Diseases Division Department of Child Health Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital University of Indonesia 1 Patient s Care 1. Drugs 2.
Nutrition Management in GI Diseases Aryono Hendarto MD Nutrition & Metabolic Diseases Division Department of Child Health Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital University of Indonesia 1 Patient s Care 1. Drugs 2.
Nutrition. Chapter 45. Reada Almashagba
 Nutrition Chapter 45 1 Nutrition: - Nutrient are organic substances found in food and are required for body function - No one food provide all essential nutrient Major function of nutrition: providing
Nutrition Chapter 45 1 Nutrition: - Nutrient are organic substances found in food and are required for body function - No one food provide all essential nutrient Major function of nutrition: providing
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital
 By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
Parenteral Nutrition
 Parenteral Nutrition Standard Operating Procedures Stony Brook University Hospital Pharmacy Department Authors and Contributors: Amanda Waldeck, PharmD, BCPS Nutrition Support Pharmacist Alfredo Viera
Parenteral Nutrition Standard Operating Procedures Stony Brook University Hospital Pharmacy Department Authors and Contributors: Amanda Waldeck, PharmD, BCPS Nutrition Support Pharmacist Alfredo Viera
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Nutriflex plus Solution for Infusion Amino acids / Glucose / Electrolytes
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Nutriflex plus Solution for Infusion Amino acids / Glucose / Electrolytes Read all of this leaflet carefully. It provides a summary of information about your medicine.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Nutriflex plus Solution for Infusion Amino acids / Glucose / Electrolytes Read all of this leaflet carefully. It provides a summary of information about your medicine.
Parenteral Nutrition
 Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
Nutrition care plan. Components and development
 Nutrition care plan Components and development Objectives To define the nutrition care plan To present the components of the nutrition care plan To discuss the different approaches in determining the contents
Nutrition care plan Components and development Objectives To define the nutrition care plan To present the components of the nutrition care plan To discuss the different approaches in determining the contents
3/26/18. Total Parenteral Nutrition Roundtable Discussion. Disclosure Information. Objectives. Monitoring Parameters & Complications
 Total Parenteral Nutrition Roundtable Discussion Monitoring Parameters & Complications Jessica Pech MSN, APN, CPNP-PC Division of Pediatric Surgery Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago
Total Parenteral Nutrition Roundtable Discussion Monitoring Parameters & Complications Jessica Pech MSN, APN, CPNP-PC Division of Pediatric Surgery Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago
Małgorzata Łyszkowska
 Małgorzata Łyszkowska Department of Paediatric Surgery and Organ Transplantation The Children s Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw Poland Baltic Club 13-14.09.2013 Distinction Between Parenteral Nutrition
Małgorzata Łyszkowska Department of Paediatric Surgery and Organ Transplantation The Children s Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw Poland Baltic Club 13-14.09.2013 Distinction Between Parenteral Nutrition
PRODUCT INFORMATION. NAME OF MEDICINE VAMIN 14, VAMIN 14 Electrolyte Free and VAMIN 18 Electrolyte Free
 PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF MEDICINE VAMIN 14, VAMIN 14 Electrolyte Free and VAMIN 18 Electrolyte Free DESCRIPTION Table 1 Vamin 14 Vamin 14 Vamin 18 Electrolyte free Electrolyte free g/l % of total amino
PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF MEDICINE VAMIN 14, VAMIN 14 Electrolyte Free and VAMIN 18 Electrolyte Free DESCRIPTION Table 1 Vamin 14 Vamin 14 Vamin 18 Electrolyte free Electrolyte free g/l % of total amino
Product Information: EleCare (for Infants)
 1 of 5 Product Information: 2 of 5 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who cannot tolerate intact or hydrolyzed protein. EleCare is indicated for the dietary management
1 of 5 Product Information: 2 of 5 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who cannot tolerate intact or hydrolyzed protein. EleCare is indicated for the dietary management
Dietetic Outcomes in Home Parenteral Nutrition
 Dietetic Outcomes in Home Parenteral Nutrition Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian Intestinal Failure & Home Parenteral Nutrition St Mark s Hospital PENG Meeting November 2011 The Dietetic Outcomes Model
Dietetic Outcomes in Home Parenteral Nutrition Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian Intestinal Failure & Home Parenteral Nutrition St Mark s Hospital PENG Meeting November 2011 The Dietetic Outcomes Model
Product Category: EleCare
 EleCare Product Category: EleCare EleCare (for Infants) Updated 4/28/2016 Product Information: EleCare (for Infants) 1 of 4 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who
EleCare Product Category: EleCare EleCare (for Infants) Updated 4/28/2016 Product Information: EleCare (for Infants) 1 of 4 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who
Acute management of severe malnutrition. Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London
 Acute management of severe malnutrition Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London Malnutrition definition A state resulting from lack of uptake or intake of nutrition leading to altered body composition
Acute management of severe malnutrition Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London Malnutrition definition A state resulting from lack of uptake or intake of nutrition leading to altered body composition
Package leaflet: Information for the user. Aminoven 5% Solution for infusion Aminoven 10% Solution for infusion Aminoven 15% Solution for infusion
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Aminoven 5% Solution for infusion Aminoven 10% Solution for infusion Aminoven 15% Solution for infusion Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using
Package leaflet: Information for the user Aminoven 5% Solution for infusion Aminoven 10% Solution for infusion Aminoven 15% Solution for infusion Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using
PICUs have a larger operating budget than many other departments within the hospital
 به نام خدا Nutrition In PICU 2 A pediatric intensive care unit (also paediatric), usually abbreviated to PICU is an area within a hospital specializing in the care of critically ill infants, children,
به نام خدا Nutrition In PICU 2 A pediatric intensive care unit (also paediatric), usually abbreviated to PICU is an area within a hospital specializing in the care of critically ill infants, children,
Product Information: PediaSure Peptide 1.5 Cal
 Product Information: PediaSure Peptide 1.5 Cal 1 of 5 PEDIASURE PEPTIDE 1.5 is a nutritionally complete, peptide-based formula for the nutritional needs of children 1-13 years with malabsorption, maldigestion,
Product Information: PediaSure Peptide 1.5 Cal 1 of 5 PEDIASURE PEPTIDE 1.5 is a nutritionally complete, peptide-based formula for the nutritional needs of children 1-13 years with malabsorption, maldigestion,
NICU Nutrition Pathway
 NICU Nutrition Pathway Safely Infusing NICU TPN Starter and Custom TPN April17 th 2018 Pharmacists: Paul Kasprzak RPH BCPS Kelly Kopec PharmD Major Practice Changes in the Preparation and Administration
NICU Nutrition Pathway Safely Infusing NICU TPN Starter and Custom TPN April17 th 2018 Pharmacists: Paul Kasprzak RPH BCPS Kelly Kopec PharmD Major Practice Changes in the Preparation and Administration
Enteral Nutrition: Whom, Why, When, What and Where to Feed?
 Meier RF, Reddy BR, Soeters PB (eds): The Importance of Nutrition as an Integral Part of Disease Management. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 82, pp 53 59, (DOI: 10.1159/000382002) Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S.
Meier RF, Reddy BR, Soeters PB (eds): The Importance of Nutrition as an Integral Part of Disease Management. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 82, pp 53 59, (DOI: 10.1159/000382002) Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S.
Today s Objectives. What About Others? Progress in Other Countries. Utilization of the Nutrition Care Process in International Settings
 Utilization of the Nutrition Care Process in International Settings Sylvia Escott-Stump, MA, RD, LDN escottstumps@ecu.eduedu Today s Objectives Participants will be able to discuss the importance of using
Utilization of the Nutrition Care Process in International Settings Sylvia Escott-Stump, MA, RD, LDN escottstumps@ecu.eduedu Today s Objectives Participants will be able to discuss the importance of using
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants. Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital
 Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
