TITLE: NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIA. Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD
|
|
|
- Mervin Cox
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NO. OF PAGES: Page 1 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIA NAME/ Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE: NAME/ Catherine McDonnell, Clinical Nurse Manager, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE: NAME/ Dr Ahmad Monavari, Director of NCIMD (National Centre for Inherited Metabolic Disorders) SIGNATURE: DATE:
2 NO. OF PAGES: Page 2 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE: DEFINITIONS: PRESENTATION: DIAGNOSIS: MANAGEMENT: NURSING MANAGEMENT OF THE PATIENT WITH METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIA REVIEW: REFERENCES:... 17
3 NO. OF PAGES: Page 3 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A 1. PURPOSE: The objectives in preparation of Nursing Guidelines for Management of Inherited Metabolic Disorders (IMD) are to increase the knowledge base of nursing staff involved in the delivery of care to patients with an IMD, provide a resource material for reference and ultimately ensure the consistent delivery of high quality care to patients attending the National Centre for Metabolic Disorders (NCIMD). Readers of this document are reminded that prescription of dietary regimes and all medications (including insulin, minerals, vitamins and trace elements) is the responsibility of the Metabolic Consultant. These guidelines may only be used under the supervision and guidance of a Metabolic Consultant. The document authors wish to thank the various Doctors, Nurses, parents and patients who have worked in and attended the National Centre throughout the years, contributing greatly in the process to our knowledge and experience of Inherited Metabolic Disorders. 2. DEFINITIONS: (M.M.A) is a recessively inherited disorder which is caused by a deficiency of methylmalonyl-coa mutase (Ogier de Baulny et al, 2012). The enzyme is a vitamin B12 dependant enzyme. Patients with M.M.A are unable to metabolise the amino acids isoleucine, methionine, threonine, valine and some fats (Yannicelli, 1988) This condition is caused by: Decreased or absent enzyme (methylmalonyl CoA mutase) activity. Inadequate amounts of adenosylcobalamin (Vit. B12) due to dietary limitations, poor intake or inherited defects of Vit. B12 metabolism. With MMA the offending organic acid metabolites of Propionic acid and Methylmalonic acid accumulate in body fluids. These substances then spill into the urine. The excessive build-up of these substances causes a secondary deficiency of Co-enzyme A (CoA) causing the symptoms of. PREVALENCE 1: 50,000 (Ogier de Baulny et al, 2012)
4 NO. OF PAGES: Page 4 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A 3. PRESENTATION: Symptoms of M.M.A. may occur in the first days of life, intermittently later in infancy, or chronically, as the child grows. Acute infection or excessive protein intake may trigger symptoms such as Refusal to eat Poor sucking reflex Vomiting Dehydration is a frequent finding in patients with MMA (Ogier de Baulny et al, 2012). Acidosis Failure to thrive Lethargy Seizures Developmental delay Where left untreated, M.M.A. may result in developmental delay and/or death. 4. DIAGNOSIS: 4.1. Diagnosis is suspected on the clinical presenting signs & symptoms of the patient and on examination of laboratory investigation results i.e. Metabolic acidosis Hypoglycaemia Hyperlactataemia Hyperglycinaemia Hepatomegaly Hyperammonaemia Raised lactate, pyruvate Neutropenia (bone marrow depression is caused by Propionic acid metabolites). Thrombocytopenia Elevated urea and creatinine 4.2. Diagnosis is confirmed on the following; Clinical presentation Acylcarnitines (increased propionylcarnitine) Analysis of urine organic acids - (Highly suggestive diagnostic metabolites are methylmalonic acid & methyl citrate). The organic acids are nearly always abnormal during times of stress/illness and can be otherwise commonly normal between acute illnesses (Van Gosen, 2008) Serum amino acids. Glycine and Alaninine accumulates in plasma (Harris, 1988; Ogier de Baulny et al, 2012). Skin biopsy to detect decreased amounts of enzyme activity.
5 NO. OF PAGES: Page 5 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A Mutational analysis Further tests will determine if the problem is due to deficiency of the enzyme or deficiency of adenosylcobalamin vitamin B Newborn Screening / High Risk Screening is currently not screened for in the Irish Newborn Population. High Risk Screening will be performed in the Maternity Hospital on siblings born to families with a known positive history (in consultation with the Metabolic Consultant). Prenatal diagnosis is possible by chorionic villi sampling in the first trimester or direct measurement of metabolites in amniotic fluid in 2 nd trimester (Ogier de Baulny et el, 2012). 5. MANAGEMENT: Emergency Treatment 5.1. Protein Restriction; Stop natural protein intake (infant formula / breast feeding / food products which are sources of protein). Rehydration - MMA is very well cleared by urinary excretion, hydration is thus the mainstay of treatment. Ensure adequate calorie intake to prevent catabolism and promote anabolism. Administration of intravenous glucose, lipids and for more severe presentations, condition specific IV amino acid mixture - to minimize ammonia production from endogenous protein breakdown. Haemodialysis or Peritoneal dialysis may be recommended on initial presentation with markedly elevated propionic acid metabolites and elevated ammonia levels. Administration of Carnitine this is essential for the transport of fats across the mitochondria, but is lost in urine bound to organic acids when amino acidopathies occur After initial treatment for acidosis, long-term treatment consists of: Restrict intake of isoleucine, threonine, methionine and valine (natural protein) and odd-chain fatty acids. Supplement natural protein intake with a synthetic amino acid drink, which is free from the offending amino acids. Ensure adequate calorie intake to prevent catabolism Free foods (i.e. non-protein) e.g. fruit, vegetables, sugars, fats and specially manufactured low-protein foods. Administration of vitamin and mineral supplements.
6 NO. OF PAGES: Page 6 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A If tests show adenosylcobalamin (Vit. B 12 ) aides M.C.M. activity, it may be given intramuscularly, either daily or on alternate days (as per doctor s prescription). Neonatal forms are rarely vitamin responsive (Ogier de Baulny et al, 2012) Large doses of carnitine are given orally or intravenously to assist the excretion of organic metabolites. It transports fatty acid into the mitochondria where they can be utilised for energy. Metronidazole (antibiotic) is used to clear the gut bacteria, which is responsible for 40% of propionic acid production (Ogier de Baulny et al, 2012).
7 NO. OF PAGES: Page 7 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A 6. NURSING MANAGEMENT OF THE PATIENT WITH METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIA Nursing observation and attention to detail is vital. The reporting of episodes of vomiting or diarrhoea or headache and instigation of treatment may be life-saving. 1. GENERAL OBSERVATIONS: SKIN Assess colour, peripheral perfusion Decreased peripheral perfusion and pallor may indicate shock/stress. Assess if intact / dry / broken (especially skin folds and nappy area). Red or broken areas may be early signs of protein deficiency. Ensure skin is kept clean and dry and nappy is changed frequently. HAIR Assess if coarse / brittle / alopecia present May indicate low serum protein / zinc levels. Natural protein may need to be increased. If not tolerating dietary protein enterally, consider need to administer intravenously.
8 NO. OF PAGES: Page 8 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A WEIGHT Measure weight To assist in assessment of hydration status. To ensure medications dosage and dietary prescriptions are correct. 2. NEUROLOGICAL STATUS: Assess neurological status using Glasgow Coma Scale to demonstrate altered levels of consciousness, muscle weakness or seizures. If ambulant observe for ataxia and report to medical team. Risk of encephalopathy secondary to hyperammonaemia. Seizures resulting from hypoglycaemia. 3. VITAL SIGNS: TEMPERATURE Monitor temperature 4 hourly or more frequently if indicated. Pyrexia of over 38.5 Celsius may indicate underlying infection. F.B.C., L.F.T S, blood cultures, serum amino acids, blood gas and urine for quantitative MMA. Levels should be obtained to evaluate condition.
9 NO. OF PAGES: Page 9 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A Report abnormalities in vital signs to the metabolic team. Hypothermia may suggest need for more calories or may indicate overwhelming infection. PULSE Tachycardia may indicate Infection Acidosis Fluid overload Dehydration RESPIRATION Tachypnoea may indicate Infection Fluid Acidosis - can have a metabolic acidosis with an increased anion gap (Ogier de Baulny et al, 2012) 4. URINE: If unwell, urine should be obtained for quantitative MMA levels and / or qualitative analysis for Propionic metabolites. Levels of MMA in the urine alter constantly and normal levels are particular to the individual. Elevated MMA may prompt reduction of natural protein intake (decided by Metabolic Consultant).
10 NO. OF PAGES: Page 10 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A (5-10 mls Universal container must be frozen until transfer to the laboratory ) If on I.V. Dextrose infusion, test urine regularly for glucose. Inform Metabolic team if glycosuria is present. Urinalysis carried out on admission & daily thereafter. 5. BLOOD GLUCOSE & LACTATE Measure 4-6 hourly when unwell and while on intravenous therapy. It may not be possible to reduce rate / concentration of glucose infusion due to calorie requirements. An insulin infusion may be prescribed (decided by Metabolic Consultant). - Ketonuria is a common finding and indicates catabolism prompt action is required. - Elevated urine ph and metabolic acidosis in blood may indicate renal tubular acidosis with increased bicarbonate losses (tubulopathy). - Specific gravity - Indication of level of hydration. Increased specific gravity occurs in case of dehydration. Decreased specific gravity occurs in patients with renal failure or after excessive fluid intake. Present if catabolic / ketoacidosis. Hypoglycaemia and hyperlactataemia are frequently found in patients with MMA (Ogier de Baulny et al, 2012). Hyperglycaemia may occur as a result of high dextrose concentration / volumes required to fulfil calorie requirements. Refer to Medical Guidelines handbook regarding prescription of insulin and consult Metabolic Consultant / Registrar on call. Insulin doses appropriate for use in patients with Insulin Dependent diabetes are not appropriate for use in Metabolic Patients.
11 NO. OF PAGES: Page 11 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A 6. DIET: NATURAL PROTEIN On initial presentation and during episodes of illness and crisis, protein intake will be discontinued or restricted (decision will be taken by consultant). Necessary for normal growth and development. Initially, infants will receive their protein requirements from infant formula. Consequently, protein content of solids introduced from weaning onwards must be included in total daily protein allowance. Protein allowance is counted in exchanges 1 gram of natural protein = 1 exchange SYNTHETIC PROTEIN (Amino Acid drink). Supplements natural protein. Contains all amino acids except those that cannot be metabolized. Wide range of low protein products available to provide variety in diet, curb hunger and provide energy.
12 NO. OF PAGES: Page 12 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A LOW PROTEIN / PROTEIN FREE PRODUCTS Provides calories required to prevent catabolism. Do not contain amino acids. Carbohydrate and Fat (maxijul and fat solution) or Energyvits (proprietary formula). EMERGENCY / UNWELL REGIME Different regimes may be prescribed according to patients status. Natural Protein: may be ¼, ½, ¾, or full (i.e. proportion of normal daily protein intake). The reduction of natural protein reduces the risk of encephalopathy. Synthetic Protein may be reduced only if patient is very unwell. Prescribed calorie intake may be increased by 10 % or 20% of normal daily calorie intake (referred to as 110% or 120% calories). Increasing calorie intake prevents catabolism, thus reducing the risk of encephalopathy.
13 NO. OF PAGES: Page 13 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A Calorie intake should be recorded for the child who is unwell. Calorie count ensures patient is receiving adequate calories to promote health and prevent catabolism. Nasogastric feeding may be necessary if not taking oral diet. If enteral feeding is not tolerated, intravenous nutrition will be required, i.e. - I.V. Dextrose (carbohydrate) - I.V lipids (fat) - I.V. Vaminolact (natural protein) To ensure adequate amounts of protein, fat and calories are achieved to meet daily requirements. 7. INTAKE AND OUTPUT Calculate mls / kg / 24hrs i.e. Total mls in 24hr period body weight in kgs. To ensure adequate fluid intake and early detection of fluid overload. Record losses - Vomit & stools & Urine output Losses may need to be replaced. Dehydration in MMA is very common as the renal clearance of Methylmalonic acid is very high and induces diuresis (Saudubray et al, 1991).
14 NO. OF PAGES: Page 14 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A 8. MEDICATIONS Adenosylcobalamin (Vit B 12 ) Administered by IM injection. Dose and frequency are titrated according to urinary MMA results. Carnitine Usually administered orally, but may be given intravenously. Necessary for the enzyme Methylmalonyl Co-A Mutase to function effectively. Transports toxic acyl-coa compounds from the cell for excretion. 100mg / kg per day is recommended to replenish free carnitine used in the excretion of toxic compounds (Yannicelli, 1988). Usually supplemented orally. Increased oral doses can cause frequent passage of loose stools, IV carnitine can be given as an alternative. Vitamins and minerals Supplementation may be necessary due to synthetic nature of the prescribed diet. 9. EDUCATION Teaching is an on-going process. Involves several members of the multidisciplinary team. Diet includes preparation of feeds.
15 NO. OF PAGES: Page 15 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A Well and Unwell Regimes Medications (side effects, IM administration etc.). Nasogastric tube insertion and use (if required). Volumes and calorific / protein content need to be adjusted according to condition. Signs & Symptoms of illness implications of delayed treatment or untreated illness. Ensures patient safety 10. MULTIDISCIPLINARY / FOLLOW UP CARE. Metabolic Clinic for dietetic, medical and nursing support. Blood testing at each OPD visit e.g. amino acids
16 NO. OF PAGES: Page 16 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A Urine samples may be requested at intervals between OPD visits. (Quantitative MMA) Psychology Social Work Chronic illness may have adverse effects on the family unit and relationships within the family. Psychologist and Social Worker input are necessary to assess coping mechanisms and difficulties with diet etc. To ensure that appropriate entitlements and services are accessed. Speech & Language Therapy Genetic counselling Implications for future pregnancies 25% risk of occurrence in other pregnancies to same partners.
17 NO. OF PAGES: Page 17 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A 7. REVIEW: This procedure shall be reviewed and updated at least every two years by the Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD in order to determine its effectiveness and appropriateness. It shall be assessed and amended as necessary during this period to reflect any changes in best practice, law, substantial organisational change and professional or academic change. 8. REFERENCES: Methylmalonic Acidaemia Higgins, C. (1996) Measurement of aspirin and paracetamol metabolites. Nursing Times. 92 (8): Leonard, J.V. (1995) The management and outcome of propionic and methylmalonic acidemia. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease. 18 (4), Ogier de Baulny H., Dionisi-Visi C. & Wendel U. (2012) Branched-chain Organic Acidurias/Acidaemias. In Inborn Metabolic Diseases: Diagnosis and Treatment (Saudubray J.M., van den Berge G. & Walter J.H. eds). 5th edition, Springer, Germany, pp Van Gosen, L. (2006) Organic acidemias: A methylmalonic and propionic focus. Journal of Pediatric Nursing 23(3), Yannicelli, S. (1988) Nutritional Support of Methylmalonic Acidemia. Metabolic Currents. 1(2), This document is designed for online viewing. Printed copies, although permitted, are deemed Uncontrolled from 24:00 hours on 05/04/2017
TITLE: NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH MAPLE SYRUP URINE DISEASE. Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD
 NO. OF PAGES: Page 1 of 18 SUPERCEDES: N/A NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH MAPLE SYRUP URINE DISEASE NAME/ Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE:
NO. OF PAGES: Page 1 of 18 SUPERCEDES: N/A NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH MAPLE SYRUP URINE DISEASE NAME/ Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE:
Methylmalonic aciduria
 Methylmalonic aciduria Introductory information Written by: F. Hörster, S. Kölker & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Methylmalonic aciduria MMA 2 Methylmalonic aciduria
Methylmalonic aciduria Introductory information Written by: F. Hörster, S. Kölker & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Methylmalonic aciduria MMA 2 Methylmalonic aciduria
TITLE: NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH UREA CYCLE DEFECTS. Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD
 NO. OF PAGES: Page 1 of 16 SUPERCEDES: N/A NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH UREA CYCLE DEFECTS NAME/ Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE: NAME/
NO. OF PAGES: Page 1 of 16 SUPERCEDES: N/A NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH UREA CYCLE DEFECTS NAME/ Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE: NAME/
ISOVALERIC ACIDAEMIA -ACUTE DECOMPENSATION (standard version)
 Contact Details Name: Hospital Telephone: This protocol has 5 pages ISOVALERIC ACIDAEMIA -ACUTE DECOMPENSATION (standard version) Please read carefully. Meticulous treatment is very important as there
Contact Details Name: Hospital Telephone: This protocol has 5 pages ISOVALERIC ACIDAEMIA -ACUTE DECOMPENSATION (standard version) Please read carefully. Meticulous treatment is very important as there
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis)
 Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
For healthcare professionals Methylmalonic Acidurias
 www.e-imd.org For healthcare professionals Methylmalonic Acidurias Methylmalonic acidurias (MMAurias) comprise a group of inborn errors of metabolism characterized by an isolated accumulation of methylmalonic
www.e-imd.org For healthcare professionals Methylmalonic Acidurias Methylmalonic acidurias (MMAurias) comprise a group of inborn errors of metabolism characterized by an isolated accumulation of methylmalonic
3 HYDROXY 3 METHYLGLUTARYL CoA (3 HMG CoA) LYASE DEFICIENCY RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES
 3 HYDROXY 3 METHYLGLUTARYL CoA (3 HMG CoA) LYASE DEFICIENCY RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES Patient s name: Date of birth: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
3 HYDROXY 3 METHYLGLUTARYL CoA (3 HMG CoA) LYASE DEFICIENCY RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES Patient s name: Date of birth: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
Introduction to Organic Acidemias. Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.
 Introduction to Organic Acidemias Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.2014 A Brief Historical Overview Garrod, Archibald E. 1902. The Incidence of
Introduction to Organic Acidemias Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.2014 A Brief Historical Overview Garrod, Archibald E. 1902. The Incidence of
Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review -
 Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review - Guideline development group International interdisciplinary guideline
Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review - Guideline development group International interdisciplinary guideline
Organic acidaemias (OAs) & Urea cycle disorders (UCDs) PRESENTATION & MANAGEMENT
 Great Ormond Street Hospital London 20/04/2018 Organic acidaemias (OAs) & Urea cycle disorders (UCDs) PRESENTATION & MANAGEMENT Spyros P. Batzios, MD, MSc, PhD OAs & UCDs How do they present? neonatal
Great Ormond Street Hospital London 20/04/2018 Organic acidaemias (OAs) & Urea cycle disorders (UCDs) PRESENTATION & MANAGEMENT Spyros P. Batzios, MD, MSc, PhD OAs & UCDs How do they present? neonatal
Isovaleric Acidemia: Quick reference guide
 Isovaleric Acidemia: Quick reference guide Introduction Isovaleric acidemia (IVA) is an inborn error of the leucine pathway caused by defects of the isovaleryl-oadehydrogenase (IV). The clinical presentation
Isovaleric Acidemia: Quick reference guide Introduction Isovaleric acidemia (IVA) is an inborn error of the leucine pathway caused by defects of the isovaleryl-oadehydrogenase (IV). The clinical presentation
Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Methylmalonic acidemia (or aciduria)
 orphananesthesia Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Methylmalonic acidemia (or aciduria) Disease name: Methylmalonic acidemia ICD 10: E71.1 Synonyms: Methylmalonic aciduria, MMA, isolated
orphananesthesia Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Methylmalonic acidemia (or aciduria) Disease name: Methylmalonic acidemia ICD 10: E71.1 Synonyms: Methylmalonic aciduria, MMA, isolated
Medical Foods for Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Medical Foods for Inborn Errors of Metabolism Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.014 02/18/2000 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 08/23/2013 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Medical Foods for Inborn Errors of Metabolism Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.014 02/18/2000 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 08/23/2013 Section: Medicine Place(s)
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) IAP UG Teaching slides
 INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2
 Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2 Department of Paediatrics and Child Health University of Pretoria Tutor : Prof DF Wittenberg : dwittenb@medic.up.ac.za Aim of this
Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2 Department of Paediatrics and Child Health University of Pretoria Tutor : Prof DF Wittenberg : dwittenb@medic.up.ac.za Aim of this
Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency
 Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase
Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase
THE ED APPROACH OF THE CHILD WITH SUSPECTED METABOLIC DISEASE
 THE ED APPROACH OF THE CHILD WITH SUSPECTED METABOLIC DISEASE Dr. Nadeem Qureshi M.D, FAAP, FCCM Associate Professor Pediatrics School of Medicine. St Louis University Attending Physician Pediatric Emergency
THE ED APPROACH OF THE CHILD WITH SUSPECTED METABOLIC DISEASE Dr. Nadeem Qureshi M.D, FAAP, FCCM Associate Professor Pediatrics School of Medicine. St Louis University Attending Physician Pediatric Emergency
Urea Cycle Defects. Dr Mick Henderson. Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust. MetBioNet IEM Introductory Training
 Urea Cycle Defects Dr Mick Henderson Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust The Urea Cycle The urea cycle enables toxic ammonia molecules to be converted to the readily excreted and non toxic
Urea Cycle Defects Dr Mick Henderson Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust The Urea Cycle The urea cycle enables toxic ammonia molecules to be converted to the readily excreted and non toxic
MSUD. Maple Syrup Urine Disease. TEMPLE Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning. Information for families after a positive newborn screening
 Maple Syrup Urine Disease MSUD Information for families after a positive newborn screening ADAPTED Adapted by BY the THE Dietitians DIETITIANS Group GROUP BIMDG British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group
Maple Syrup Urine Disease MSUD Information for families after a positive newborn screening ADAPTED Adapted by BY the THE Dietitians DIETITIANS Group GROUP BIMDG British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group
GA-1. Glutaric Aciduria Type 1. TEMPLE Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning. Information for families after a positive newborn screening
 Glutaric Aciduria Type 1 GA-1 Information for families after a positive newborn screening Adapted by the Dietitians Group BIMDG British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group BASED ON THE ORIGINAL TEMPLE WRITTEN
Glutaric Aciduria Type 1 GA-1 Information for families after a positive newborn screening Adapted by the Dietitians Group BIMDG British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group BASED ON THE ORIGINAL TEMPLE WRITTEN
Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department. Will Davies June 2014
 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Will Davies June 2014 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Overview Although individually rare, altogether they are 1:1000-2500
Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Will Davies June 2014 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Overview Although individually rare, altogether they are 1:1000-2500
Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency
 Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase MCAD
Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase MCAD
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Training Syllabus CLINICAL SYLLABUS
 Training Syllabus CLINICAL SYLLABUS SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated July 2006 This syllabus is intended as a guide. Whilst the training should be comprehensive,
Training Syllabus CLINICAL SYLLABUS SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated July 2006 This syllabus is intended as a guide. Whilst the training should be comprehensive,
Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when
 CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
UNDERSTANDING METHYLMALONIC ACIDEMIA
 UNDERSTANDING METHYLMALONIC ACIDEMIA What is methylmalonic acidemia? Methylmalonic acidemia ( METH-EL-MAL-ON-IC ACID-UREEA) is genetic disorder that affects how protein is broken down in the body. It is
UNDERSTANDING METHYLMALONIC ACIDEMIA What is methylmalonic acidemia? Methylmalonic acidemia ( METH-EL-MAL-ON-IC ACID-UREEA) is genetic disorder that affects how protein is broken down in the body. It is
Information for health professionals
 Introduction of a new screening test for newborn babies in Wales Newborn bloodspot screening for Medium chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (MCADD) Newborn bloodspot screening for MCADD is being introduced
Introduction of a new screening test for newborn babies in Wales Newborn bloodspot screening for Medium chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (MCADD) Newborn bloodspot screening for MCADD is being introduced
National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children
 National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children Aim To provide guidance on the biochemical investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and
National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children Aim To provide guidance on the biochemical investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and
TEMPLE MCADD. Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP. British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group
 TEMPLE Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group MADD BASED ON THE ORIGINAL TEMPLE WRITTEN BY BURGARD AND WENDEL VERSION 2, FEBRUARY
TEMPLE Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group MADD BASED ON THE ORIGINAL TEMPLE WRITTEN BY BURGARD AND WENDEL VERSION 2, FEBRUARY
Metabolic Disorders. Chapter Thomson - Wadsworth
 Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY
 INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES
 INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
Package Insert. Elkar
 Package Insert Elkar Product Summary 1. Name of the medicinal product Elkar 500 mg tablets 2. Qualitative and quantitative composition Each tablet contains levocarnitine 500 mg. 3. Pharmaceutical form
Package Insert Elkar Product Summary 1. Name of the medicinal product Elkar 500 mg tablets 2. Qualitative and quantitative composition Each tablet contains levocarnitine 500 mg. 3. Pharmaceutical form
Newborn Screening & Methods for Diagnosing Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Newborn Screening & Methods for Diagnosing Inborn Errors of Metabolism Patricia Jones, PhD DABCC FACB UT Southwestern Medical Center Children s Medical Center Dallas, Texas Learning Objectives Justify
Newborn Screening & Methods for Diagnosing Inborn Errors of Metabolism Patricia Jones, PhD DABCC FACB UT Southwestern Medical Center Children s Medical Center Dallas, Texas Learning Objectives Justify
The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments
 CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
BIOTIN (BIOTINIDASE) DEFICIENCY Marc E. Tischler, PhD; University of Arizona
 BIOTIN (BIOTINIDASE) DEFICIENCY Marc E. Tischler, PhD; University of Arizona BIOTIN (BIOTINIDASE) DEFICIENCY biotin in the body is recycled by its removal from carboxylase enzymes to which it is attached
BIOTIN (BIOTINIDASE) DEFICIENCY Marc E. Tischler, PhD; University of Arizona BIOTIN (BIOTINIDASE) DEFICIENCY biotin in the body is recycled by its removal from carboxylase enzymes to which it is attached
Medium Chain Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency
 Medium Chain Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency WHAT is MCADD? MCADD occurs due to a deficiency of the enzyme medium chain acyl-coa dehydrognease (MCADD). This enzyme breaks down certain fats in the food
Medium Chain Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency WHAT is MCADD? MCADD occurs due to a deficiency of the enzyme medium chain acyl-coa dehydrognease (MCADD). This enzyme breaks down certain fats in the food
Metabolic Precautions & ER Recommendations
 Metabolic Precautions & ER Recommendations * To whom correspondence Sumit Parikh, should MD be addressed Center for Pediatric Neurology Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, OH UMDF 2010 The catabolic state Entering
Metabolic Precautions & ER Recommendations * To whom correspondence Sumit Parikh, should MD be addressed Center for Pediatric Neurology Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, OH UMDF 2010 The catabolic state Entering
HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up
 HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up Dr. Josephine Chong Clinical Professional Consultant Centre of Inborn Errors
HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up Dr. Josephine Chong Clinical Professional Consultant Centre of Inborn Errors
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Work-Up and Initial Management of Common Metabolic Emergencies in the Inpatient Setting
 Work-Up and Initial Management of Common Metabolic Emergencies in the Inpatient Setting Kristin Lindstrom, MD Division of Genetics and Metabolism Phoenix Children s Hospital AzAAP Pediatrics in the Red
Work-Up and Initial Management of Common Metabolic Emergencies in the Inpatient Setting Kristin Lindstrom, MD Division of Genetics and Metabolism Phoenix Children s Hospital AzAAP Pediatrics in the Red
Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTCD) Recommendations on Emergency Management of Metabolic Disease
 Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTCD) Recommendations on Emergency Management of Metabolic Disease Patient s Name: Date of Birth: MRN in KFSH&RC: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTCD) Recommendations on Emergency Management of Metabolic Disease Patient s Name: Date of Birth: MRN in KFSH&RC: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION L-Leucine Ph. Eur 0.620% w/v L-Isoleucine
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION L-Leucine Ph. Eur 0.620% w/v L-Isoleucine
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial,
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial,
Table of Contents. Contents Page
 Table of Contents Contents Page What is PA?... 1-6 Treatment for PA... 6-13 Inheritance of PA... 14-15 Testing for PA... 15-18 Occurrence of PA... 18 Resources... 19-20 Glossary...21-24* The information
Table of Contents Contents Page What is PA?... 1-6 Treatment for PA... 6-13 Inheritance of PA... 14-15 Testing for PA... 15-18 Occurrence of PA... 18 Resources... 19-20 Glossary...21-24* The information
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018
 ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Inborn Errors Of Metabolism Urea Cycle Disorders Diagnosis And Care F. Feillet (FR) Urea cycle disorders, diagnosis and care F Feillet National reference centre for Inborn errors
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Inborn Errors Of Metabolism Urea Cycle Disorders Diagnosis And Care F. Feillet (FR) Urea cycle disorders, diagnosis and care F Feillet National reference centre for Inborn errors
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style. Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA
 ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Anabolic Eating well Calories eaten > body s needs BRAIN uses GLUCOSE MUSCLE uses GLUCOSE
ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Anabolic Eating well Calories eaten > body s needs BRAIN uses GLUCOSE MUSCLE uses GLUCOSE
ARGININOSUCCINIC ACIDEMIA (or ARGININOSUCCINATE LYASE DEFICIENCY) RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES
 ARGININOSUCCINIC ACIDEMIA (or ARGININOSUCCINATE LYASE DEFICIENCY) RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES Patient s name: Date of birth: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt
ARGININOSUCCINIC ACIDEMIA (or ARGININOSUCCINATE LYASE DEFICIENCY) RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES Patient s name: Date of birth: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt
SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE
 SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated December 2014: Vassili Valayannopoulos and Andrew Morris Paediatrics is an independent medical specialty based on the knowledge and
SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated December 2014: Vassili Valayannopoulos and Andrew Morris Paediatrics is an independent medical specialty based on the knowledge and
ENDURANCE SPORTS NUTRITION
 ENDURANCE SPORTS NUTRITION Complex carbohydrates with low glycemic index Simple carbohydrates with high glycemic index + complex carbs + proteins + electrolytes Simple carbs + complex carbs + proteins
ENDURANCE SPORTS NUTRITION Complex carbohydrates with low glycemic index Simple carbohydrates with high glycemic index + complex carbs + proteins + electrolytes Simple carbs + complex carbs + proteins
Contribution of Nutrients in Complex Inborn Errors of Metabolism: The Case of Methylmalonic Aciduria (MMA)
 Contribution of Nutrients in Complex Inborn Errors of Metabolism: The Case of Methylmalonic Aciduria (MMA) Charles P. Venditti, MD, PhD Head, Organic Acid Research Section No conflicts of interest to declare
Contribution of Nutrients in Complex Inborn Errors of Metabolism: The Case of Methylmalonic Aciduria (MMA) Charles P. Venditti, MD, PhD Head, Organic Acid Research Section No conflicts of interest to declare
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Amino Acid Disorders. What is ASAL deficiency? Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Neonatal Hypoglycaemia Guidelines
 N.B. Staff should be discouraged from printing this document. This is to avoid the risk of out of date printed versions of the document. The Intranet should be referred to for the current version of the
N.B. Staff should be discouraged from printing this document. This is to avoid the risk of out of date printed versions of the document. The Intranet should be referred to for the current version of the
2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY 3. COMPOSITION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 Title Page Product Information May 2000 1 (6) Product Nephrotect 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Nephrotect 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only 3.
Title Page Product Information May 2000 1 (6) Product Nephrotect 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Nephrotect 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only 3.
The laboratory investigation of lactic acidaemia. J Bonham/T Laing
 The laboratory investigation of lactic acidaemia J Bonham/T Laing Reference range Typical ranges for blood lactate are: Newborn 0.3-2.2 mmol/l Nielsen J et al1 1994 1-12mo 0.9-1.8 mmol/l Bonnefont et al
The laboratory investigation of lactic acidaemia J Bonham/T Laing Reference range Typical ranges for blood lactate are: Newborn 0.3-2.2 mmol/l Nielsen J et al1 1994 1-12mo 0.9-1.8 mmol/l Bonnefont et al
TEMPLE. Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP. British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group
 TEMPLE Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group BASED ON THE ORIGINAL TEMPLE WRITTEN BY KOLKER AND BURGARD GA1 Information for
TEMPLE Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group BASED ON THE ORIGINAL TEMPLE WRITTEN BY KOLKER AND BURGARD GA1 Information for
Metabolic Changes in ASD. Norma J. Arciniegas, MD Simón E. Carlo, MD Instituto Filius
 Metabolic Changes in ASD Norma J. Arciniegas, MD Simón E. Carlo, MD Instituto Filius 12 patients 3 Autism: Ages 3/3/3.7 3 PDD: Ages 3/3/6 3 Asperger: Ages 6/7/15.1 3 Speech delay and Sensory Problems (SHL):
Metabolic Changes in ASD Norma J. Arciniegas, MD Simón E. Carlo, MD Instituto Filius 12 patients 3 Autism: Ages 3/3/3.7 3 PDD: Ages 3/3/6 3 Asperger: Ages 6/7/15.1 3 Speech delay and Sensory Problems (SHL):
PKU PKU. Phenylketonuria TEMPLE. Information for families following Information for families after a positive newborn screening
 PKU Phenylketonuria PKU Information for families following newborn a positive screening newborn screening Information for families after a positive newborn screening Information for families after a positive
PKU Phenylketonuria PKU Information for families following newborn a positive screening newborn screening Information for families after a positive newborn screening Information for families after a positive
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter
 Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Clinical Management of Organic Acidemias and OAA Natural History Registry. Kim Chapman MD PhD Children s National Rare Disease Institute
 Clinical Management of Organic Acidemias and OAA Natural History Registry Kim Chapman MD PhD Children s National Rare Disease Institute Disclosure Nothing to disclose concerning this lecture Organic acid?
Clinical Management of Organic Acidemias and OAA Natural History Registry Kim Chapman MD PhD Children s National Rare Disease Institute Disclosure Nothing to disclose concerning this lecture Organic acid?
Glycogen Storage Disease
 Glycogen Storage Disease 1 Introduction The food we eat is usually used for growth, tissue repair and energy. The body stores what it does not use. Excess sugar, or glucose, is stored as glycogen in the
Glycogen Storage Disease 1 Introduction The food we eat is usually used for growth, tissue repair and energy. The body stores what it does not use. Excess sugar, or glucose, is stored as glycogen in the
The spectrum and outcome of the. neonates with inborn errors of. metabolism at a tertiary care hospital
 The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick Neonatal Pharmacist
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
CARE OF THE NEWBORN HYPOGLYCAEMIA
 CARE OF THE NEWBORN HYPOGLYCAEMIA Background Definition A true blood glucose of less than 2.6 mmol/l venous sample. Neonatal hypoglycaemia is commonly defined as a true blood glucose of less than 2.6 mmol/l
CARE OF THE NEWBORN HYPOGLYCAEMIA Background Definition A true blood glucose of less than 2.6 mmol/l venous sample. Neonatal hypoglycaemia is commonly defined as a true blood glucose of less than 2.6 mmol/l
M0BCore Safety Profile
 M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Aciclovir Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Dispersible tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Oral suspensions 200 mg or 400 mg per 5 ml. Freeze
M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Aciclovir Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Dispersible tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Oral suspensions 200 mg or 400 mg per 5 ml. Freeze
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
MCADD. Synonyms: MCADD, Medium chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency, medium chain fat oxidation defect and ACADM defect.
 MCADD Synonyms: MCADD, Medium chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency, medium chain fat oxidation defect and ACADM defect. Biochemical background: MCADD is an inherited disease caused by a change on chromosome
MCADD Synonyms: MCADD, Medium chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency, medium chain fat oxidation defect and ACADM defect. Biochemical background: MCADD is an inherited disease caused by a change on chromosome
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Glucose Intravenous Infusion BP 10% w/v solution for infusion Glucose (as glucose monohydrate)
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Glucose Intravenous Infusion BP 10% w/v solution for infusion Glucose (as glucose monohydrate) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Glucose Intravenous Infusion BP 10% w/v solution for infusion Glucose (as glucose monohydrate) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine
DIABETES AND ENTERAL FEEDING
 DIABETES AND ENTERAL FEEDING kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? This leaflet is for people with diabetes established on an enteral feeding regimen, and for the people who support them at home, in residential
DIABETES AND ENTERAL FEEDING kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? This leaflet is for people with diabetes established on an enteral feeding regimen, and for the people who support them at home, in residential
Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM)
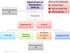 Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
Paediatric Directorate
 Paediatric Directorate Dehydration Guidelines Primary cause of dehydration diarrhoea +/- vomiting. Approximately 10%Children < 5yrs present with gastroenteritis each year Diagnosis History - sudden change
Paediatric Directorate Dehydration Guidelines Primary cause of dehydration diarrhoea +/- vomiting. Approximately 10%Children < 5yrs present with gastroenteritis each year Diagnosis History - sudden change
Hypoglycemia in congenital hyperinsulinism
 How a normal body works: Our body is constantly at work. Our cells need a source of energy, and this source of energy is called glucose. The process is quite simple; think of it like an assembly line.
How a normal body works: Our body is constantly at work. Our cells need a source of energy, and this source of energy is called glucose. The process is quite simple; think of it like an assembly line.
Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration. May 16/17
 Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration May 16/17 Volume Depletion (hypovolemia): refers to any condition in which the effective circulating volume is reduced. It can be produced by salt and water loss
Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration May 16/17 Volume Depletion (hypovolemia): refers to any condition in which the effective circulating volume is reduced. It can be produced by salt and water loss
Metabolic diseases of the liver
 Metabolic diseases of the liver Central role in metabolism Causes and mechanisms of dysfunction Clinical patterns of metabolic disease Clinical approach to problem-solving Specific disorders Liver s central
Metabolic diseases of the liver Central role in metabolism Causes and mechanisms of dysfunction Clinical patterns of metabolic disease Clinical approach to problem-solving Specific disorders Liver s central
Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University
 Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University objectives Overview Definition of dehydration Causes of dehydration Types of dehydration Diagnosis, signs and symptoms Management of dehydration Complications
Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University objectives Overview Definition of dehydration Causes of dehydration Types of dehydration Diagnosis, signs and symptoms Management of dehydration Complications
Urea Cycle Disorders Prior Authorization Program Summary
 Urea Cycle Disorders Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Agent(s) Indication(s) Dosing -Adjunctive therapy in the chronic management of patients with urea cycle disorders
Urea Cycle Disorders Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Agent(s) Indication(s) Dosing -Adjunctive therapy in the chronic management of patients with urea cycle disorders
MITO 101 Illness. Neurometabolic Clinic Children s Medical Center and UT Southwestern Medical Center Hospitals and Clinics
 1 MITO 101 Illness Juan M. Pascual, MD, PhD Division of Pediatric Neurology Departments of Neurology, Physiology and Pediatrics The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Neurometabolic Clinic
1 MITO 101 Illness Juan M. Pascual, MD, PhD Division of Pediatric Neurology Departments of Neurology, Physiology and Pediatrics The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Neurometabolic Clinic
Glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA1) Dietetic Management Pathway
 Glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA1) Dietetic Management Pathway Presumptive positive screen for GA1 See Clinical Management Guidelines and Clinical Referral Guidelines and Standards (www.bimdg.org) Unwell baby:
Glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA1) Dietetic Management Pathway Presumptive positive screen for GA1 See Clinical Management Guidelines and Clinical Referral Guidelines and Standards (www.bimdg.org) Unwell baby:
UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When
 UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Department of Pediatrics Icahn School of
UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Department of Pediatrics Icahn School of
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients. Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
Acute Management of Sick Infants with Suspected Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Indian J Pediatr (July 2011) 78(7):854 859 DOI 10.1007/s12098-011-0422-0 SYMPOSIUM ON PICU PROTOCOLS OF AIIMS Acute Management of Sick Infants with Suspected Inborn Errors of Metabolism Neerja Gupta Madhulika
Indian J Pediatr (July 2011) 78(7):854 859 DOI 10.1007/s12098-011-0422-0 SYMPOSIUM ON PICU PROTOCOLS OF AIIMS Acute Management of Sick Infants with Suspected Inborn Errors of Metabolism Neerja Gupta Madhulika
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion , version 1.1
 EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year Three Developed Summer 2017 Objectives Understand Acute Kidney Injury and its relevance to patient care. Brief revision of the Anatomy and physiology
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year Three Developed Summer 2017 Objectives Understand Acute Kidney Injury and its relevance to patient care. Brief revision of the Anatomy and physiology
Please inform the Diabetes Nurse Specialist that this patient has been admitted within 24hrs of admission.
 Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis Care Bundle (V1. Issued October 2014 Review October 2015) Improving patient care This pack includes: DKA Management Guideline Name: (Patient Addressograph) DOB: Hospital No:
Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis Care Bundle (V1. Issued October 2014 Review October 2015) Improving patient care This pack includes: DKA Management Guideline Name: (Patient Addressograph) DOB: Hospital No:
Providing the Right Fuels for FOD s. Elaina Jurecki, MS, RD Regional Metabolic Nutritionist Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Oakland, CA
 Providing the Right Fuels for FOD s Elaina Jurecki, MS, RD Regional Metabolic Nutritionist Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Oakland, CA Providing the Right Fuels for FOD s The Body s Use of Energy Fat
Providing the Right Fuels for FOD s Elaina Jurecki, MS, RD Regional Metabolic Nutritionist Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Oakland, CA Providing the Right Fuels for FOD s The Body s Use of Energy Fat
Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition
 Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition Introduction Review clinical findings that may be suspicious of a metabolic
Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition Introduction Review clinical findings that may be suspicious of a metabolic
Executive Summary Management of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus during illness in children and young people under 18 years (Sick Day Rules)
 Executive Summary Management of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus during illness in children and young people under 18 years (Sick Day Rules) SETTING FOR STAFF PATIENTS Medical and nursing staff Children and young
Executive Summary Management of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus during illness in children and young people under 18 years (Sick Day Rules) SETTING FOR STAFF PATIENTS Medical and nursing staff Children and young
Suboptimal hydration harms patients.
 Suboptimal hydration harms patients. NHS Fife is committed to improving hydration management. To achieve this we need your help! In 2014 new fluid balance charts were implemented in the Victoria Hospital,
Suboptimal hydration harms patients. NHS Fife is committed to improving hydration management. To achieve this we need your help! In 2014 new fluid balance charts were implemented in the Victoria Hospital,
PKU TEMPLE. Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED AND ENDORSED BY ASIEM FOR USE IN ANZ DESIGNED AND ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP
 TEMPLE Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED AND ENDORSED BY ASIEM FOR USE IN ANZ Australasian Society for Inborn Errors of Metabolism DESIGNED AND ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP PKU British
TEMPLE Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED AND ENDORSED BY ASIEM FOR USE IN ANZ Australasian Society for Inborn Errors of Metabolism DESIGNED AND ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP PKU British
Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 Title Page Information Aminosteril N-Hepa 8% November 2001 1 (7) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml solution
Title Page Information Aminosteril N-Hepa 8% November 2001 1 (7) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml solution
Monitor patient s ability to self-administer insulin. (To evaluate safe administration of drug.)
 Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Regular Insulin (Humulin, Novolin) Assessment Prior to administration: Assess any patient allergies. Older forms of insulin are made from beef and pork and may
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Regular Insulin (Humulin, Novolin) Assessment Prior to administration: Assess any patient allergies. Older forms of insulin are made from beef and pork and may
Good hydration checklist
 Good hydration checklist Staying hydrated is very important because our bodies need the right balance of water and electrolytes to help them function properly. Drink the right amount and types of fluid
Good hydration checklist Staying hydrated is very important because our bodies need the right balance of water and electrolytes to help them function properly. Drink the right amount and types of fluid
PHARMACOLOGY AND PHARMACOKINETICS
 DRUG GUIDELINE Insulin, human neutral (Actrapid ) Intravenous Infusion for SCOPE (Area): FOR USE IN: Critical Care Unit, Emergency Department and Operating Suite EXCLUSIONS: Paediatrics (seek Paediatrician
DRUG GUIDELINE Insulin, human neutral (Actrapid ) Intravenous Infusion for SCOPE (Area): FOR USE IN: Critical Care Unit, Emergency Department and Operating Suite EXCLUSIONS: Paediatrics (seek Paediatrician
Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from. Maple syrup urine disease
 orphananesthesia Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Disease name: Maple syrup urine disease ICD 10: E71.0 Maple syrup urine disease Synonyms: MSUD, branched-chain ketoaciduria, branched-chain-alpha-ketoacid
orphananesthesia Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Disease name: Maple syrup urine disease ICD 10: E71.0 Maple syrup urine disease Synonyms: MSUD, branched-chain ketoaciduria, branched-chain-alpha-ketoacid
TEMPLE HCU. Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED AND ENDORSED BY ASIEM FOR USE IN ANZ DESIGNED AND ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP
 TEMPLE Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED AND ENDORSED BY ASIEM FOR USE IN ANZ Australasian Society for Inborn Errors of Metabolism DESIGNED AND ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP HCU British
TEMPLE Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning ADAPTED AND ENDORSED BY ASIEM FOR USE IN ANZ Australasian Society for Inborn Errors of Metabolism DESIGNED AND ADAPTED BY THE DIETITIANS GROUP HCU British
