Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Methylmalonic acidemia (or aciduria)
|
|
|
- Mervyn Hunt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 orphananesthesia Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Methylmalonic acidemia (or aciduria) Disease name: Methylmalonic acidemia ICD 10: E71.1 Synonyms: Methylmalonic aciduria, MMA, isolated methylmalonic acidemia Methylmalonic acidemia (MMA) is a group of rare (approx. 1:50,000) autosomal recessive disorders of amino acid metabolism, involving defects in the conversion of methylmalonyl- CoA to succinyl-coa (which would normally enter the Krebs cycle). The defect is genetically heterogeneous, and can be due to the lack of the enzyme methylmalonyl-coa mutase (mut 0 ), partial reduction in its activity (mut - ), or to defects in cobalamin metabolism (vit B 12 is a cofactor required in the conversion of methylmalonyl-coa to succinyl-coa). These defects result in the accumulation of methylmalonic acid. Clinical presentation varies and depends on the genetic diagnosis. The most severe form is mut 0, which usually presents in the neonatal period, while other forms may present later in infancy and childhood, when triggers of increased protein catabolism (infection, dehydration, trauma, surgery, stress) cause metabolic decompensation. The presentation may be nonspecific, such as vomiting, lethargy and tachypnoea. Neurological manifestations include encephalopathy, seizures, hypotonia and stroke. Gastrointestinal complaints include recurrent vomiting, failure to thrive, and pancreatitis. If the acute crisis is untreated it may progress to coma and death. Medicine in progress Perhaps new knowledge Every patient is unique Perhaps the diagnostic is wrong Find more information on the disease, its centres of reference and patient organisations on Orphanet: 1
2 Disease summary Biochemical hallmarks of an acute metabolic decompensation are metabolic acidosis, an increased anion gap (caused by lactate, ketones and organic acids), elevated lactate and ketones ± hyperammonaemia. Long-term complications include failure to thrive, chronic kidney disease or renal failure, pancreatitis, pancytopaenia, osteopaenia and intellectual disability. Cardiac involvement is rare, but includes dilated cardiomyopathy and prolonged QTc interval. Several patients have been reported with metabolic stroke and optic atrophy. Long-term management is aimed at preventing metabolic decompensation. Patients are placed on a protein-restricted diet, given carnitine supplements (to promote the increased excretion of toxic metabolites) and hydroxycobalamin if cobalamin responsive. Administration of metronidazole is aimed at reducing the burden of acid-producing bacteria in the gut. Ammonia scavenging drugs including carglumic acid, a synthetic analogue of N-acetyl glutamate, can be used to manage hyperammonaemia. Kidney, liver, or combined kidney-liver transplantation is increasingly being performed in patients with MMA. While transplanting either or both organs does not cure the disease, the aim is to supply a certain amount of the missing enzyme. Methylmalonyl CoA mutase is mainly expressed in the liver, but renal transplantation will partially replace some mutase activity. Transplanting kidneys in MMA patients with renal failure both restores the impaired renal function and improves the metabolic enzyme defect, and thus reduces the number of episodes of metabolic decompensation and hospitalisation, and allows liberalisation of the diet. It does not prevent neurological complications. Liver transplantation is considered as a treatment option particularly in patients with frequent decompensations. Combined liver kidney transplantation is a potential treatment option but is associated with more postoperative complications than single organ transplantation. Typical surgery Insertion of long term intravenous access lines or ports (for treatment, fluids, blood sampling or TPN) Gastrostomy or GJ tube insertion Imaging studies, including CT and MRI Skin biopsy (usually done under local anaesthesia) Examination under anaesthesia (e.g. eyes) or brainstem auditory evoked responses (for hearing loss) Placement of haemodialysis catheters Transplantation (kidney, liver or both) Type of anaesthesia General or loco-regional anaesthetic techniques may be used where appropriate. 2
3 Blood tests include: Necessary additional diagnostic procedures (preoperative) Blood gas, lactate and ammonia (metabolic acidosis / hyperammonaemia is a sign of decompensated disease, and should prompt a review and discussion about the timing of elective surgery). Glucose and ketones reviewing anabolic state Full blood count - looking for chronic anaemia, neutropaenia, thrombocytopaenia. Urea and electrolytes chronic renal failure occurs in up to 50% and is most reliably assessed by the glomerular filtration rate. Hyperkalaemia has been associated with ventricular tachycardia and cardiac arrest after induction of anaesthesia in a child with MMA. Amylase and lipase (particularly in patients with history of previous acute or acute on chronic pancreatitis) Cardiac evaluation: while cardiac involvement is considered to be rare, prolonged QTc and cardiomyopathy have been described. A baseline ECG and echocardiogram would be recommended (children may be asymptomatic if they perform very limited exercise). Careful assessment and consultation with the patient s specialist is advised to determine metabolic stability and timing of surgery. Patient s metabolic status should be optimised prior to elective surgery. Particular preparation for airway management There are no specific airway complications described with MMA per se. Particular preparation for transfusion or administration of blood products Patients with MMA may have a chronic anaemia or be pancytopaenic as a result of acute or chronic bone marrow suppression. This may or may not require transfusion, depending on the surgery being performed. There are no specific requirements described for transfusion of blood products. Particular preparation for anticoagulation No particular concerns around anticoagulation are described. The disease is not typically associated with thrombosis or the need for anticoagulation. 3
4 Particular precautions for positioning, transport or mobilisation Patients may be osteopaenic and at risk of fractures, and are also at risk of poor wound healing. Careful positioning is required. Probable interaction between anaesthetic agents and patient s long term medication Patients may be on anticonvulsants that may alter the metabolism of some anaesthetic drugs. Patients with movement disorders may be on L-dopa, clonazepam, or baclofen. Anaesthesiologic procedure Preoperatively, the aim is to avoid prolonged fasting as it may cause protein catabolism and a metabolic crisis. Patients should be fasted as per standard guidelines, but prolonged fasting and dehydration should be avoided. The individual day-to-day fasting tolerance of the patient can be used as a baseline. Encourage the intake of clear, glucose polymer-containing fluids until two hours preoperatively, or provide intravenous 10% glucose in 0.45% or 0.9% saline, as follows: 8-10 mg/kg/min for neonates and infants 6-7 mg/kg/min for children 5-6 mg/kg/min for adolescents 4-5 mg/kg/min for adults It is recommended that this infusion is continued throughout the surgical procedure and postoperatively until feeds are re-established. TPN should be continued if the patient is TPNdependent. All chronic medication should be continued in the perioperative period. If the child is unwell or in the setting of metabolic decompensation (metabolic acidosis, elevated lactate and hyperammonaemia revealed on preoperative blood tests), elective surgery should not be performed. In the setting of emergency surgery, preoperative and perioperative haemodialysis should be considered. Intraoperatively: Induction can be inhalational or intravenous. Some children may be overweight, making intravenous access difficult. There is no contraindication to the use of the volatile agents. While it is unlikely to be a problem if used for the induction of anaesthesia, avoid nitrous oxide for maintenance, especially in patients with cobalamin metabolism defects, as it inhibits vitamin B 12 dependent enzymes. 4
5 While propofol was traditionally thought to be contraindicated for patients with MMA, it has recently been shown to be safe for both the induction and maintenance of anaesthesia or sedation in the setting of metabolically stable patients. For major surgery (such as transplantation) or in unwell children, it would seem prudent to avoid propofol for the maintenance of anaesthesia due to its mitochondrial effects. Dehydration and hypotension can trigger a metabolic crisis. Patients should be well hydrated with dextrose in saline as above. Despite a theoretical concern over the use of lactate-containing fluids, a recent study has not shown an association between the use of Ringer s Lactate and metabolic decompensation. The use of catecholamines may cause catabolism leading to metabolic decompensation. Catecholamine use should be avoided where possible and all parameters closely monitored if catecholamines are required. Sufficient depth of anaesthesia and analgesia must be maintained to avoid surgical stress. Consider using drugs to decrease ammonia with continuous infusion intraoperatively Monitor blood gases, lactate, electrolytes, glucose and ammonia during longer procedures. Manage hyperglycaemic patients with an insulin infusion. Be aware that they may be very sensitive to insulin as their pancreases function normally, and hypoglycaemia is a risk. Consider starting insulin at a low dose, eg 0.02 IU/kg/hr and titrate to effect. Avoid blood in the gastrointestinal tract that could act as a protein load and trigger decompensation. Consider placing a throat pack or gastric tube where appropriate, e.g. dental work, tonsillectomy. Avoid the use of steroids due to their catabolic effects and risk of triggering acute decompensation (there is no evidence as to whether a single dose used to prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting is safe or not, so it would seem prudent to avoid). Avoid nephrotoxic drugs due to their potential to precipitate or aggravate renal disease. Patients may be neutropaenic increasing the risk of sepsis and line sepsis. Observe local infection control practices and antibiotic guidelines. Prolonged QTc interval is a rare complication. Caution with using drugs that prolong the QT interval. Anti-emetics: it is recommended that metoclopramide is avoided. Use ondansetron. Paracetamol, opiates and loco-regional anaesthetic techniques can be used for analgesia. Avoid non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The use of muscle relaxants is not contraindicated. Monitoring of their effects and of their reversal would seem prudent in hypotonic children. 5
6 Particular or additional monitoring Regular measurement of glucose, arterial blood gases, lactate, ammonia and potassium is recommended. Possible complications Dehydration, hypotension, hypoxia, the stress of surgery and anaesthesia, and the presence of intercurrent illness and infection can all trigger a metabolic crisis, leading to metabolic acidosis, hyperlactataemia and / or hyperammonaemia. Hyperkalaemia secondary to metabolic acidosis has been described as causing intraoperative ventricular tachycardia and cardiac arrest. Postoperative care Patients should be closely monitored after anaesthesia for signs of clinical deterioration, and should be managed in high-dependency settings where appropriate. Intravenous fluids should be continued until the child tolerates enteral feeding. Feeding can be commenced as is appropriate for the surgical procedure. Patients should not be without protein > 48hours; if enteral intake is not possible early postoperatively, TPN should be considered. The child should only be discharged after full recovery, once tolerating their usual diet and medication, and with normal metabolic results. The patient s metabolic team should guide dietary management and discharge. Information about emergency-like situations / Differential diagnostics Differential diagnoses for the acute metabolic crisis in MMA include sepsis, respiratory distress and diabetic ketoacidosis. MMA can also present with seizures or a reduced level of consciousness. Any delay in recovery from anaesthesia should prompt checking of blood gases, glucose, electrolytes and ammonia. Management of the acute crisis includes rehydration, providing glucose as a metabolic substrate (as above) while avoiding hyperglycaemia, and correcting any electrolyte abnormalities and acid-base disturbances. Consider dialysis for persistent acidosis or hyperammonaemia. Ambulatory anaesthesia Patients with MMA would not typically be considered for day-case anaesthesia. They should not be discharged home until they are fully recovered and have normal metabolic results. Discussion should be held with the metabolic team before considering ambulatory anaesthesia. 6
7 Obstetrical anaesthesia The safe use of epidural anaesthesia for labour has been described. No anaesthetic complications are described during anaesthesia for Caesarean sections. 7
8 Literature and internet links 1. Baumgartner M, et al. Proposed guidelines for the diagnosis and management of methylmalonic and propionic academia. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2014, 9: Baum VC, O Flaherty JE. Anesthesia for Genetic, Metabolic and Dysmorphic Syndromes of Childhood. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Stuart G, Ahmad N. Perioperative care of children with inherited metabolic disorders. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia, Critical Care and Pain 2011, 11(2): Bodamer O, et al. Organic acidemias Ktena YP et al. Propofol administration in patients with methylmalonic academia and intracellular cobalamin metabolism disorders: a review of theoretical concern and clinical experiences in 28 patients. Journal of inherited metabolic disease 2015, May 19 (Epub ahead of print) 7. Ruzkova K et al. Anesthesia and organic aciduria: is the use of lactated Ringer s solution absolutely contraindicated? Paediatric Anaesthesia 2015, May 5 (Epub ahead of print) 8. Raval DB et al. Methylmalonic acidemia (MMA) in pregnancy: a case series and literature review. Journal of inherited and metabolic disease 2015, Jan 8 (Epub ahead of print) 9. Chao PW et al. Acute life-threatening arrhythmias caused by severe hyperkalemia after induction of anesthesia in an infant with methylmalonic acidemia. J Chin Med Assoc 2012, 75(5): Ho D et al. Anaesthesia for liver transplantation in a patient with methylmalonic acidaemia. Paediatr Anaesth 2000, 10(2): Kasahara M et al. Current role of liver transplantation for methylmalonic acidemia: a review of the literature. Pediatr Transplant 2006, 10(8): Manzoni D et al. Anaesthesia for liver transplantation in two infants with an organic acidaemia. Pediatr Transplant 2006, 10(5): Prada C et al. Cardiac disease in Methylmalonic Acidemia. Journal of Pediatrics 2011; 159: McGuire PJ et al. Combined liver-kidney transplant for the management of methylmalonic aciduria: A case report and review of the literature. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism 2008; 93: Stevenson T et al. Long-term outcome following pediatric liver transplantation for metabolic disorders. Pediatric Transplant 2010 Mar; 14(2): Babe C et al. Perioperative management of living-donor liver transplantation for methylmalonic academia. Pediatric Anesthesia 2016; 26:
9 Last date of modification: January 2017 This guideline has been prepared by: Author Clover-Ann Lee, Anaesthesiologist, Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children, London, United Kingdom Peer revision 1 Chiaki Baba, Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive care, National Center for Child Health and Development, Okura, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo, Japan karaki-c@ncchd.go.jp Peer revision 2 Anupam Chakrapani, Department of Metabolic Medicine, Great Ormond Street Hospital, Great Ormond Street, London, United Kingdom anupam.chakrapani@gosh.nhs.uk 9
TITLE: NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIA. Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD
 NO. OF PAGES: Page 1 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIA NAME/ Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE: NAME/
NO. OF PAGES: Page 1 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIA NAME/ Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE: NAME/
Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from. Glutaric acidemia type 1
 orphananesthesia Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Disease name: Glutaric acidemia type 1 Glutaric acidemia type 1 ICD 10: E72.3 - Disorders of lysine and hydroxylysine metabolism
orphananesthesia Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Disease name: Glutaric acidemia type 1 Glutaric acidemia type 1 ICD 10: E72.3 - Disorders of lysine and hydroxylysine metabolism
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis)
 Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from. Maple syrup urine disease
 orphananesthesia Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Disease name: Maple syrup urine disease ICD 10: E71.0 Maple syrup urine disease Synonyms: MSUD, branched-chain ketoaciduria, branched-chain-alpha-ketoacid
orphananesthesia Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Disease name: Maple syrup urine disease ICD 10: E71.0 Maple syrup urine disease Synonyms: MSUD, branched-chain ketoaciduria, branched-chain-alpha-ketoacid
Introduction to Organic Acidemias. Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.
 Introduction to Organic Acidemias Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.2014 A Brief Historical Overview Garrod, Archibald E. 1902. The Incidence of
Introduction to Organic Acidemias Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.2014 A Brief Historical Overview Garrod, Archibald E. 1902. The Incidence of
Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review -
 Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review - Guideline development group International interdisciplinary guideline
Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review - Guideline development group International interdisciplinary guideline
For healthcare professionals Methylmalonic Acidurias
 www.e-imd.org For healthcare professionals Methylmalonic Acidurias Methylmalonic acidurias (MMAurias) comprise a group of inborn errors of metabolism characterized by an isolated accumulation of methylmalonic
www.e-imd.org For healthcare professionals Methylmalonic Acidurias Methylmalonic acidurias (MMAurias) comprise a group of inborn errors of metabolism characterized by an isolated accumulation of methylmalonic
Metabolic Precautions & ER Recommendations
 Metabolic Precautions & ER Recommendations * To whom correspondence Sumit Parikh, should MD be addressed Center for Pediatric Neurology Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, OH UMDF 2010 The catabolic state Entering
Metabolic Precautions & ER Recommendations * To whom correspondence Sumit Parikh, should MD be addressed Center for Pediatric Neurology Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, OH UMDF 2010 The catabolic state Entering
3 HYDROXY 3 METHYLGLUTARYL CoA (3 HMG CoA) LYASE DEFICIENCY RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES
 3 HYDROXY 3 METHYLGLUTARYL CoA (3 HMG CoA) LYASE DEFICIENCY RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES Patient s name: Date of birth: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
3 HYDROXY 3 METHYLGLUTARYL CoA (3 HMG CoA) LYASE DEFICIENCY RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES Patient s name: Date of birth: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
ISOVALERIC ACIDAEMIA -ACUTE DECOMPENSATION (standard version)
 Contact Details Name: Hospital Telephone: This protocol has 5 pages ISOVALERIC ACIDAEMIA -ACUTE DECOMPENSATION (standard version) Please read carefully. Meticulous treatment is very important as there
Contact Details Name: Hospital Telephone: This protocol has 5 pages ISOVALERIC ACIDAEMIA -ACUTE DECOMPENSATION (standard version) Please read carefully. Meticulous treatment is very important as there
Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Mucolipidosis II and III
 orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Mucolipidosis II and III Disease name: Mucolipidosis Type 2 and 3 ICD 10: E77.0 Synonyms: Mucolipidosis type 2 - I-cell disease N-acetyl-glucosamine
orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Mucolipidosis II and III Disease name: Mucolipidosis Type 2 and 3 ICD 10: E77.0 Synonyms: Mucolipidosis type 2 - I-cell disease N-acetyl-glucosamine
Organic acidaemias (OAs) & Urea cycle disorders (UCDs) PRESENTATION & MANAGEMENT
 Great Ormond Street Hospital London 20/04/2018 Organic acidaemias (OAs) & Urea cycle disorders (UCDs) PRESENTATION & MANAGEMENT Spyros P. Batzios, MD, MSc, PhD OAs & UCDs How do they present? neonatal
Great Ormond Street Hospital London 20/04/2018 Organic acidaemias (OAs) & Urea cycle disorders (UCDs) PRESENTATION & MANAGEMENT Spyros P. Batzios, MD, MSc, PhD OAs & UCDs How do they present? neonatal
Methylmalonic aciduria
 Methylmalonic aciduria Introductory information Written by: F. Hörster, S. Kölker & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Methylmalonic aciduria MMA 2 Methylmalonic aciduria
Methylmalonic aciduria Introductory information Written by: F. Hörster, S. Kölker & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Methylmalonic aciduria MMA 2 Methylmalonic aciduria
Isovaleric Acidemia: Quick reference guide
 Isovaleric Acidemia: Quick reference guide Introduction Isovaleric acidemia (IVA) is an inborn error of the leucine pathway caused by defects of the isovaleryl-oadehydrogenase (IV). The clinical presentation
Isovaleric Acidemia: Quick reference guide Introduction Isovaleric acidemia (IVA) is an inborn error of the leucine pathway caused by defects of the isovaleryl-oadehydrogenase (IV). The clinical presentation
Cardiac Disease in Organic Acidemias
 Cardiac Disease in Organic Acidemias Kathryn Chatfield, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Division of Cardiology University of Colorado School of Medicine Children s Hospital Colorado Introduction
Cardiac Disease in Organic Acidemias Kathryn Chatfield, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Division of Cardiology University of Colorado School of Medicine Children s Hospital Colorado Introduction
Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2
 Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2 Department of Paediatrics and Child Health University of Pretoria Tutor : Prof DF Wittenberg : dwittenb@medic.up.ac.za Aim of this
Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2 Department of Paediatrics and Child Health University of Pretoria Tutor : Prof DF Wittenberg : dwittenb@medic.up.ac.za Aim of this
Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy
 orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy Disease name: Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD) ICD 10: G71.0 Synonyms: Benign Scapuloperoneal
orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy Disease name: Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD) ICD 10: G71.0 Synonyms: Benign Scapuloperoneal
Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Welander distal myopathy
 orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Welander distal myopathy Disease name: Welander distal myopathy ICD 10: G71.0 Synonyms: late adult onset type 1 distal myopathy;
orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Welander distal myopathy Disease name: Welander distal myopathy ICD 10: G71.0 Synonyms: late adult onset type 1 distal myopathy;
Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department. Will Davies June 2014
 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Will Davies June 2014 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Overview Although individually rare, altogether they are 1:1000-2500
Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Will Davies June 2014 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Overview Although individually rare, altogether they are 1:1000-2500
Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Sanfilippo disease
 orphananesthesia Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Sanfilippo disease Disease name: Mucopolysaccharidosis type III ICD 10: E76.2 Synonyms: MPS III, Sanfilippo syndrome, Mucopolisaccaridosi
orphananesthesia Anaesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Sanfilippo disease Disease name: Mucopolysaccharidosis type III ICD 10: E76.2 Synonyms: MPS III, Sanfilippo syndrome, Mucopolisaccaridosi
UK NATIONAL METABOLIC BIOCHEMISTRY NETWORK GUIDELINES FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF HYPERAMMONAEMIA
 UK NATIONAL METABOLIC BIOCHEMISTRY NETWORK GUIDELINES FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF HYPERAMMONAEMIA Hyperammonaemia results from defective catabolism of amino acids to urea. Recognition and treatment of hyperammonaemia,
UK NATIONAL METABOLIC BIOCHEMISTRY NETWORK GUIDELINES FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF HYPERAMMONAEMIA Hyperammonaemia results from defective catabolism of amino acids to urea. Recognition and treatment of hyperammonaemia,
CEDIAMATE Metformin Tablets USP 500 mg
 CEDIAMATE Metformin Tablets USP 500 mg COMPOSITION: Cediamate Each un-coated tablet contains: Metformin Hydrochloride USP Excipients 500 mg Q.S PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacotherapeutic group: Blood Glucose lowering
CEDIAMATE Metformin Tablets USP 500 mg COMPOSITION: Cediamate Each un-coated tablet contains: Metformin Hydrochloride USP Excipients 500 mg Q.S PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacotherapeutic group: Blood Glucose lowering
Training Syllabus CLINICAL SYLLABUS
 Training Syllabus CLINICAL SYLLABUS SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated July 2006 This syllabus is intended as a guide. Whilst the training should be comprehensive,
Training Syllabus CLINICAL SYLLABUS SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated July 2006 This syllabus is intended as a guide. Whilst the training should be comprehensive,
Contribution of Nutrients in Complex Inborn Errors of Metabolism: The Case of Methylmalonic Aciduria (MMA)
 Contribution of Nutrients in Complex Inborn Errors of Metabolism: The Case of Methylmalonic Aciduria (MMA) Charles P. Venditti, MD, PhD Head, Organic Acid Research Section No conflicts of interest to declare
Contribution of Nutrients in Complex Inborn Errors of Metabolism: The Case of Methylmalonic Aciduria (MMA) Charles P. Venditti, MD, PhD Head, Organic Acid Research Section No conflicts of interest to declare
Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes
 Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control 1-800-876-4766 Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes these agents, found in virtually every household, common
Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control 1-800-876-4766 Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes these agents, found in virtually every household, common
National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children
 National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children Aim To provide guidance on the biochemical investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and
National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children Aim To provide guidance on the biochemical investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion , version 1.1
 EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
Secondary Energy Deficiencies in Organic Acidemias. Kimberly A Chapman MD PhD Children s National July 26, 2014
 Secondary Energy Deficiencies in Organic Acidemias Kimberly A Chapman MD PhD Children s National July 26, 2014 2 Goals of this talk Describe the secondary energy deficiencies seen in organic acidemias
Secondary Energy Deficiencies in Organic Acidemias Kimberly A Chapman MD PhD Children s National July 26, 2014 2 Goals of this talk Describe the secondary energy deficiencies seen in organic acidemias
The spectrum and outcome of the. neonates with inborn errors of. metabolism at a tertiary care hospital
 The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
THE ED APPROACH OF THE CHILD WITH SUSPECTED METABOLIC DISEASE
 THE ED APPROACH OF THE CHILD WITH SUSPECTED METABOLIC DISEASE Dr. Nadeem Qureshi M.D, FAAP, FCCM Associate Professor Pediatrics School of Medicine. St Louis University Attending Physician Pediatric Emergency
THE ED APPROACH OF THE CHILD WITH SUSPECTED METABOLIC DISEASE Dr. Nadeem Qureshi M.D, FAAP, FCCM Associate Professor Pediatrics School of Medicine. St Louis University Attending Physician Pediatric Emergency
Work-Up and Initial Management of Common Metabolic Emergencies in the Inpatient Setting
 Work-Up and Initial Management of Common Metabolic Emergencies in the Inpatient Setting Kristin Lindstrom, MD Division of Genetics and Metabolism Phoenix Children s Hospital AzAAP Pediatrics in the Red
Work-Up and Initial Management of Common Metabolic Emergencies in the Inpatient Setting Kristin Lindstrom, MD Division of Genetics and Metabolism Phoenix Children s Hospital AzAAP Pediatrics in the Red
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter
 Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Clinical Management of Organic Acidemias and OAA Natural History Registry. Kim Chapman MD PhD Children s National Rare Disease Institute
 Clinical Management of Organic Acidemias and OAA Natural History Registry Kim Chapman MD PhD Children s National Rare Disease Institute Disclosure Nothing to disclose concerning this lecture Organic acid?
Clinical Management of Organic Acidemias and OAA Natural History Registry Kim Chapman MD PhD Children s National Rare Disease Institute Disclosure Nothing to disclose concerning this lecture Organic acid?
Urea Cycle Defects. Dr Mick Henderson. Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust. MetBioNet IEM Introductory Training
 Urea Cycle Defects Dr Mick Henderson Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust The Urea Cycle The urea cycle enables toxic ammonia molecules to be converted to the readily excreted and non toxic
Urea Cycle Defects Dr Mick Henderson Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust The Urea Cycle The urea cycle enables toxic ammonia molecules to be converted to the readily excreted and non toxic
Summary question. How can pain relief during childbirth be improved? How can anaesthesia for Caesarean sections be improved?
 APPENDICES Appendix 1.The shortlist of 92 summary questions used for the prioritisation survey (i.e. those from which respondents were asked to choose their ten most important research priorities) Theme
APPENDICES Appendix 1.The shortlist of 92 summary questions used for the prioritisation survey (i.e. those from which respondents were asked to choose their ten most important research priorities) Theme
Metabolic diseases of the liver
 Metabolic diseases of the liver Central role in metabolism Causes and mechanisms of dysfunction Clinical patterns of metabolic disease Clinical approach to problem-solving Specific disorders Liver s central
Metabolic diseases of the liver Central role in metabolism Causes and mechanisms of dysfunction Clinical patterns of metabolic disease Clinical approach to problem-solving Specific disorders Liver s central
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION
 DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTCD) Recommendations on Emergency Management of Metabolic Disease
 Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTCD) Recommendations on Emergency Management of Metabolic Disease Patient s Name: Date of Birth: MRN in KFSH&RC: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTCD) Recommendations on Emergency Management of Metabolic Disease Patient s Name: Date of Birth: MRN in KFSH&RC: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
MITO 101 Illness. Neurometabolic Clinic Children s Medical Center and UT Southwestern Medical Center Hospitals and Clinics
 1 MITO 101 Illness Juan M. Pascual, MD, PhD Division of Pediatric Neurology Departments of Neurology, Physiology and Pediatrics The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Neurometabolic Clinic
1 MITO 101 Illness Juan M. Pascual, MD, PhD Division of Pediatric Neurology Departments of Neurology, Physiology and Pediatrics The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Neurometabolic Clinic
TITLE: NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH UREA CYCLE DEFECTS. Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD
 NO. OF PAGES: Page 1 of 16 SUPERCEDES: N/A NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH UREA CYCLE DEFECTS NAME/ Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE: NAME/
NO. OF PAGES: Page 1 of 16 SUPERCEDES: N/A NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH UREA CYCLE DEFECTS NAME/ Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE: NAME/
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate. Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics
 Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM)
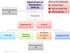 Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
PRODUCT INFORMATION. (RS)-N,N-Dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)phenylmethoxy]ethanamine dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
![PRODUCT INFORMATION. (RS)-N,N-Dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)phenylmethoxy]ethanamine dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate PRODUCT INFORMATION. (RS)-N,N-Dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)phenylmethoxy]ethanamine dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate](/thumbs/81/82665370.jpg) NORGESIC Orphenadrine citrate and paracetamol PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE MEDICINE Active ingredient: Chemical name: CAS number: 4682-36-4 Chemical structure: Orphenadrine citrate (RS)-N,N-Dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)phenylmethoxy]ethanamine
NORGESIC Orphenadrine citrate and paracetamol PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE MEDICINE Active ingredient: Chemical name: CAS number: 4682-36-4 Chemical structure: Orphenadrine citrate (RS)-N,N-Dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)phenylmethoxy]ethanamine
ARGININOSUCCINIC ACIDEMIA (or ARGININOSUCCINATE LYASE DEFICIENCY) RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES
 ARGININOSUCCINIC ACIDEMIA (or ARGININOSUCCINATE LYASE DEFICIENCY) RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES Patient s name: Date of birth: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt
ARGININOSUCCINIC ACIDEMIA (or ARGININOSUCCINATE LYASE DEFICIENCY) RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES Patient s name: Date of birth: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt
Hypoglycemia, Electrolyte disturbances and acid-base imbalances
 Hypoglycemia, Electrolyte disturbances and acid-base imbalances Pediatric emergency PICU division Pediatric department Medical faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, Electrolyte disturbances and acid-base imbalances Pediatric emergency PICU division Pediatric department Medical faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Hypoglycemia
Printed copies of this document may not be up to date, obtain the most recent version from
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Septic Shock Document Control Information Author Claire Fraser P.Ramnarayan Author Position tanp CATS Consultant Document Owner E. Polke Document
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Septic Shock Document Control Information Author Claire Fraser P.Ramnarayan Author Position tanp CATS Consultant Document Owner E. Polke Document
ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style. Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA
 ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Anabolic Eating well Calories eaten > body s needs BRAIN uses GLUCOSE MUSCLE uses GLUCOSE
ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Anabolic Eating well Calories eaten > body s needs BRAIN uses GLUCOSE MUSCLE uses GLUCOSE
UPDATE ON UREA CYCLE DISORDERS TREATMENT
 UPDATE ON UREA CYCLE DISORDERS TREATMENT George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Disclosure
UPDATE ON UREA CYCLE DISORDERS TREATMENT George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Disclosure
DIABETES MELLITUS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 DIABETES MELLITUS 1 DIABETES MELLITUS IN CHILDREN Introduction, Definition Classification, pathogenesis Clinical features Investigations and diagnosis Therapy and follow up Complications Carry home message
DIABETES MELLITUS 1 DIABETES MELLITUS IN CHILDREN Introduction, Definition Classification, pathogenesis Clinical features Investigations and diagnosis Therapy and follow up Complications Carry home message
Nutritional Demands of Disease and Trauma
 al Demands of Disease and Trauma Lecture 89 Medical School al Requirements Based on needs to support optimal physiological function Are changed by disease or injury metabolism is altered to prevent further
al Demands of Disease and Trauma Lecture 89 Medical School al Requirements Based on needs to support optimal physiological function Are changed by disease or injury metabolism is altered to prevent further
1.2 Synonyms There are several synonyms e.g. diaminomethanal, but in a medical context, this substance is always referred to as urea.
 Urea (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Urea 1.2 Synonyms There are several synonyms e.g. diaminomethanal, but in a medical context, this substance is always referred
Urea (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Urea 1.2 Synonyms There are several synonyms e.g. diaminomethanal, but in a medical context, this substance is always referred
Case TWO. Vital Signs: Temperature 36.6degC BP 137/89 HR 110 SpO2 97% on Room Air
 Mr N is a 64year old Chinese gentleman who is a heavy drinker, still actively drinking, and chronic smoker of >40pack year history. He has a past medical history significant for Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia,
Mr N is a 64year old Chinese gentleman who is a heavy drinker, still actively drinking, and chronic smoker of >40pack year history. He has a past medical history significant for Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia,
Unit 11. Objectives. Indications for IV Therapy. Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids. 3 categories. Maintenance Replacement Restoration
 Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN *
 For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition
 Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition Introduction Review clinical findings that may be suspicious of a metabolic
Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition Introduction Review clinical findings that may be suspicious of a metabolic
The following content was supplied by the author as supporting material and has not been copy-edited or verified by JBJS.
 Page 1 The following content was supplied by the author as supporting material and has not been copy-edited or verified by JBJS. Appendix TABLE E-1 Care-Module Trigger Events That May Indicate an Adverse
Page 1 The following content was supplied by the author as supporting material and has not been copy-edited or verified by JBJS. Appendix TABLE E-1 Care-Module Trigger Events That May Indicate an Adverse
Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease This guideline has been agreed by both NTS & CATS Document Control Information Author CATS/NTS Author Position
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease This guideline has been agreed by both NTS & CATS Document Control Information Author CATS/NTS Author Position
Anesthesia and Mitochondrial Cytopathies Bruce H. Cohen, MD, John Shoffner, MD, Glenn DeBoer, MD United Mitochondrial Disease Foundation, 1998
 Introduction Anesthesia and Mitochondrial Cytopathies Bruce H. Cohen, MD, John Shoffner, MD, Glenn DeBoer, MD United Mitochondrial Disease Foundation, 1998 This article will outline some basic aspects
Introduction Anesthesia and Mitochondrial Cytopathies Bruce H. Cohen, MD, John Shoffner, MD, Glenn DeBoer, MD United Mitochondrial Disease Foundation, 1998 This article will outline some basic aspects
2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY 3. COMPOSITION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 Title Page Product Information May 2000 1 (6) Product Nephrotect 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Nephrotect 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only 3.
Title Page Product Information May 2000 1 (6) Product Nephrotect 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Nephrotect 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only 3.
CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017
 CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017 DKA at organ level 3 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Characteristics Ketones positive Anion Gap > 12 (High) Blood Sugar > 14 (High) Bicarbonate
CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017 DKA at organ level 3 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Characteristics Ketones positive Anion Gap > 12 (High) Blood Sugar > 14 (High) Bicarbonate
50% Concentrated Injection
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE. The molecular weight of the compound is 246.5 and the CAS registry number is 10034-99-8. The molecular formula is MgSO4, 7H2O. DESCRIPTION MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE 50% CONCENTRATED
NAME OF THE MEDICINE. The molecular weight of the compound is 246.5 and the CAS registry number is 10034-99-8. The molecular formula is MgSO4, 7H2O. DESCRIPTION MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE 50% CONCENTRATED
General anesthesia. No single drug capable of achieving these effects both safely and effectively.
 General anesthesia General anesthesia is essential to surgical practice, because it renders patients analgesic, amnesia, and unconscious reflexes, while causing muscle relaxation and suppression of undesirable
General anesthesia General anesthesia is essential to surgical practice, because it renders patients analgesic, amnesia, and unconscious reflexes, while causing muscle relaxation and suppression of undesirable
Intro Who should read this document 2 Key practice points 2 What is new in this version 3 Background 3 Guideline Subsection headings
 Enhanced Recovery for Major Urology and Gynaecological Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Dr Dominic O Connor Additional author(s): Jane Kingham Authors Division: Anaesthesia Unique ID: DDCAna3(12)
Enhanced Recovery for Major Urology and Gynaecological Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Dr Dominic O Connor Additional author(s): Jane Kingham Authors Division: Anaesthesia Unique ID: DDCAna3(12)
Hyperglycaemic Emergencies GRI EDUCATION
 Hyperglycaemic Emergencies GRI EDUCATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Develop and describe your system of blood gas interpretation and recognise common patterns of acid-base abnormality. Describe the pathophysiology
Hyperglycaemic Emergencies GRI EDUCATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Develop and describe your system of blood gas interpretation and recognise common patterns of acid-base abnormality. Describe the pathophysiology
Final FRCA Written PAEDIATRICS Past Paper Questions November March 2014
 Final FRCA Written PAEDIATRICS Past Paper Questions November 1996- March 2014 March 2014 A 5-year-old patient presents for a myringotomy and grommet insertion as a day case. During your pre-operative assessment
Final FRCA Written PAEDIATRICS Past Paper Questions November 1996- March 2014 March 2014 A 5-year-old patient presents for a myringotomy and grommet insertion as a day case. During your pre-operative assessment
Medical APMLE. Podiatry and Medical.
 Medical APMLE Podiatry and Medical http://killexams.com/exam-detail/apmle Question: 290 Signs and symptoms of hemolytic transfusion reactions include: A. Hypothermia B. Hypertension C. Polyuria D. Abnormal
Medical APMLE Podiatry and Medical http://killexams.com/exam-detail/apmle Question: 290 Signs and symptoms of hemolytic transfusion reactions include: A. Hypothermia B. Hypertension C. Polyuria D. Abnormal
Nutritional Interventions in Primary Mitochondrial Disorders
 Nutritional Interventions in Primary Mitochondrial Disorders Carolyn J Ellaway MBBS PhD FRACP CGHGSA Genetic Metabolic Disorders Service Sydney Children s Hospital Network Disciplines of Child and Adolescent
Nutritional Interventions in Primary Mitochondrial Disorders Carolyn J Ellaway MBBS PhD FRACP CGHGSA Genetic Metabolic Disorders Service Sydney Children s Hospital Network Disciplines of Child and Adolescent
Salicylates commonly cause tinnitus, deafness, nausea and vomiting (salicylism). Hyperventilation results from stimulation of respiratory centre.
 Aspirin poisoning CLINICAL FEATURES Salicylates commonly cause tinnitus, deafness, nausea and vomiting (salicylism). Hyperventilation results from stimulation of respiratory centre. Severe poisoning causes
Aspirin poisoning CLINICAL FEATURES Salicylates commonly cause tinnitus, deafness, nausea and vomiting (salicylism). Hyperventilation results from stimulation of respiratory centre. Severe poisoning causes
Seizures Emergency Treatment
 Seizures Emergency Treatment Emergency Seizures SEIZURE CLASSIFICATION Cluster seizures - 2 or more generalized convulsive seizures in 24 hours Simon R. Platt BVM&S MRCVS Dipl. ACVIM (Neurology) Dipl.ECVN
Seizures Emergency Treatment Emergency Seizures SEIZURE CLASSIFICATION Cluster seizures - 2 or more generalized convulsive seizures in 24 hours Simon R. Platt BVM&S MRCVS Dipl. ACVIM (Neurology) Dipl.ECVN
M0BCore Safety Profile
 M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Aciclovir Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Dispersible tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Oral suspensions 200 mg or 400 mg per 5 ml. Freeze
M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Aciclovir Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Dispersible tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Oral suspensions 200 mg or 400 mg per 5 ml. Freeze
Acute Management of Sick Infants with Suspected Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Indian J Pediatr (July 2011) 78(7):854 859 DOI 10.1007/s12098-011-0422-0 SYMPOSIUM ON PICU PROTOCOLS OF AIIMS Acute Management of Sick Infants with Suspected Inborn Errors of Metabolism Neerja Gupta Madhulika
Indian J Pediatr (July 2011) 78(7):854 859 DOI 10.1007/s12098-011-0422-0 SYMPOSIUM ON PICU PROTOCOLS OF AIIMS Acute Management of Sick Infants with Suspected Inborn Errors of Metabolism Neerja Gupta Madhulika
MD (Anaesthesiology) Title (Plan of Thesis) (Session )
 S.No. 1. To study the occurrence of postoperative hyponatremia in paediatric patients under 2 years of age 2. Influence of timing of intravenous fluid therapy on maternal hemodynamics in patients undergoing
S.No. 1. To study the occurrence of postoperative hyponatremia in paediatric patients under 2 years of age 2. Influence of timing of intravenous fluid therapy on maternal hemodynamics in patients undergoing
Final Core Safety Profile for propofol 10 mg/ml (1%) and 20 mg/ml (2%) emulsion for injection or infusion
 CSP Drug Substance Propofol Date September 04 2014 Final Core Safety Profile for propofol 10 mg/ml (1%) and 20 mg/ml (2%) emulsion for injection or infusion CORE SAFETY PROFILE 4.3 Contraindications Propofol
CSP Drug Substance Propofol Date September 04 2014 Final Core Safety Profile for propofol 10 mg/ml (1%) and 20 mg/ml (2%) emulsion for injection or infusion CORE SAFETY PROFILE 4.3 Contraindications Propofol
IV Fluids. I.V. Fluid Osmolarity Composition 0.9% NaCL (Normal Saline Solution, NSS) Uses/Clinical Considerations
 IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
Zorbtive. Zorbtive (somatropin) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.24 Subject: Zorbtive Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 20, 2018 Zorbtive Description Zorbtive
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.24 Subject: Zorbtive Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 20, 2018 Zorbtive Description Zorbtive
HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up
 HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up Dr. Josephine Chong Clinical Professional Consultant Centre of Inborn Errors
HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up Dr. Josephine Chong Clinical Professional Consultant Centre of Inborn Errors
Effect of carglumic acid with or without ammonia scavengers on hyperammonaemia in acute decompensation episodes of organic acidurias
 Chakrapani et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2018) 13:97 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-018-0840-4 RESEARCH Open Access Effect of carglumic acid with or without ammonia scavengers on hyperammonaemia
Chakrapani et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2018) 13:97 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-018-0840-4 RESEARCH Open Access Effect of carglumic acid with or without ammonia scavengers on hyperammonaemia
Dr Ben Edwards Consultant Anaesthetist Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
 Dr Ben Edwards Consultant Anaesthetist Sheffield Teaching Hospitals 70-75,000 #NOF per annum (costs 2 billion) 10% die within 1 month 33% die within 1 year Operative delays >48hs more than doubles risk
Dr Ben Edwards Consultant Anaesthetist Sheffield Teaching Hospitals 70-75,000 #NOF per annum (costs 2 billion) 10% die within 1 month 33% die within 1 year Operative delays >48hs more than doubles risk
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders- an update. Fiona Carragher Biochemical Sciences, GSTS Pathology St Thomas Hospital, London
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders- an update Fiona Carragher Biochemical Sciences, GSTS Pathology St Thomas Hospital, London An update. Overview of metabolism Clinical presentation and outcome Diagnostic
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders- an update Fiona Carragher Biochemical Sciences, GSTS Pathology St Thomas Hospital, London An update. Overview of metabolism Clinical presentation and outcome Diagnostic
PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker
 PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE PROLONGED RELEASE TABLETS IP
 For 0 the use only of a Registered Medical Practitioner or hospital or a laboratory This package insert is continually updated: Please read carefully before using a new pack METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE PROLONGED
For 0 the use only of a Registered Medical Practitioner or hospital or a laboratory This package insert is continually updated: Please read carefully before using a new pack METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE PROLONGED
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
PFIZER INC. Study Center(s): A total of 6 centers took part in the study, including 2 in France and 4 in the United States.
 PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When
 UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Department of Pediatrics Icahn School of
UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Department of Pediatrics Icahn School of
SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE
 SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated December 2014: Vassili Valayannopoulos and Andrew Morris Paediatrics is an independent medical specialty based on the knowledge and
SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated December 2014: Vassili Valayannopoulos and Andrew Morris Paediatrics is an independent medical specialty based on the knowledge and
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Definition: Diabetic Ketoacidosis is one of the most serious acute complications of diabetes. It s more common in young patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. It s usually characterized
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Definition: Diabetic Ketoacidosis is one of the most serious acute complications of diabetes. It s more common in young patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. It s usually characterized
Metabolic Disorders. Chapter Thomson - Wadsworth
 Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease Document Control Information Author CATS/NTS Author Position CC Transport Services Document Owner E. Polke
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease Document Control Information Author CATS/NTS Author Position CC Transport Services Document Owner E. Polke
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) IAP UG Teaching slides
 INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
Package Insert. Elkar
 Package Insert Elkar Product Summary 1. Name of the medicinal product Elkar 500 mg tablets 2. Qualitative and quantitative composition Each tablet contains levocarnitine 500 mg. 3. Pharmaceutical form
Package Insert Elkar Product Summary 1. Name of the medicinal product Elkar 500 mg tablets 2. Qualitative and quantitative composition Each tablet contains levocarnitine 500 mg. 3. Pharmaceutical form
Dr. Gavin Parker PINCHER CREEK AB 140
 Society of Rural Physicians of Canada 26TH ANNUAL RURAL AND REMOTE MEDICINE COURSE ST. JOHN'S NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR APRIL 12-14, 2018 Dr. Gavin Parker PINCHER CREEK AB 140 MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA Malignant
Society of Rural Physicians of Canada 26TH ANNUAL RURAL AND REMOTE MEDICINE COURSE ST. JOHN'S NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR APRIL 12-14, 2018 Dr. Gavin Parker PINCHER CREEK AB 140 MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA Malignant
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia
 Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Glucophage XR is contra-indicated during breast-feeding.
 Name GLUCOPHAGE XR 1000 mg Prolonged release tablets Active ingredient Metformin hydrochloride Composition Each Glucophage XR 1000 mg prolonged release tablet contains as active ingredient 1000 mg metformin
Name GLUCOPHAGE XR 1000 mg Prolonged release tablets Active ingredient Metformin hydrochloride Composition Each Glucophage XR 1000 mg prolonged release tablet contains as active ingredient 1000 mg metformin
Metformin Hydrochloride
 Metformin Hydrochloride 500 mg, 850 mg, 500 mg LA and 750 mg LA Tablet Description Informet is a preparation of metformin hydrochloride that belongs to a biguanide class of oral antidiabetic drugs. Metformin
Metformin Hydrochloride 500 mg, 850 mg, 500 mg LA and 750 mg LA Tablet Description Informet is a preparation of metformin hydrochloride that belongs to a biguanide class of oral antidiabetic drugs. Metformin
Hormone Therapy + Metformin (STAMPEDE Trial Arm K)
 Hormone Therapy + Metformin (STAMPEDE Trial Arm K) Systemic Therapy in Advancing or Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Evaluation of Drug Efficacy - A multi-arm randomised controlled trial *** See Protocol For
Hormone Therapy + Metformin (STAMPEDE Trial Arm K) Systemic Therapy in Advancing or Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Evaluation of Drug Efficacy - A multi-arm randomised controlled trial *** See Protocol For
Paediatric Clinical Chemistry
 Paediatric Clinical Chemistry Dr N Oosthuizen Dept Chemical Pathology UP 2011 Paediatric biochemistry The child is not a miniature adult Physiological development Immature organ systems Growing individual
Paediatric Clinical Chemistry Dr N Oosthuizen Dept Chemical Pathology UP 2011 Paediatric biochemistry The child is not a miniature adult Physiological development Immature organ systems Growing individual
PRODUCT INFORMATION RESONIUM A. Na m
 PRODUCT INFORMATION RESONIUM A NAME OF THE MEDICINE Non-proprietary Name Sodium polystyrene sulfonate Chemical Structure CH - 2 CH SO 3 Na + n CAS Number 28210-41-5 [9003-59-2] CH 2 CH SO - 3 m DESCRIPTION
PRODUCT INFORMATION RESONIUM A NAME OF THE MEDICINE Non-proprietary Name Sodium polystyrene sulfonate Chemical Structure CH - 2 CH SO 3 Na + n CAS Number 28210-41-5 [9003-59-2] CH 2 CH SO - 3 m DESCRIPTION
9/11/2012. Chapter 11. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Endocrine Emergencies. Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes
 Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
PHARMACOLOGY AND PHARMACOKINETICS
 DRUG GUIDELINE Insulin, human neutral (Actrapid ) Intravenous Infusion for SCOPE (Area): FOR USE IN: Critical Care Unit, Emergency Department and Operating Suite EXCLUSIONS: Paediatrics (seek Paediatrician
DRUG GUIDELINE Insulin, human neutral (Actrapid ) Intravenous Infusion for SCOPE (Area): FOR USE IN: Critical Care Unit, Emergency Department and Operating Suite EXCLUSIONS: Paediatrics (seek Paediatrician
