Creating Feeding Guidelines: Optimizing Growth is Complicated
|
|
|
- Cody Fox
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Creating Feeding Guidelines: Optimizing Growth is Complicated PQCNC Initiative: Increasing Use of Mother s Milk for the Very Low Birthweight Babies in the Critical Care Centers of North Carolina Webinar 4/11/2011 L Dunn
2 Goals of nutritional support for the preterm infant: most are met with use of MBM Optimize short-term outcomes Optimize short-term growth Prevent feeding-related morbidities NEC Central line complications, including sepsis Osteopenia of prematurity Optimize long-term outcomes
3 Postnatal growth failure is a major issue for the VLBW infants In an NIHCD cohort of VLBW infants, 97% were below 10 th % at 36 wks, but only 22% had been born SGA (Lemons, Peds 2001;107:e1-e8) the birth of an ELBW infant is a nutritional emergency (from R. Lawrence s textbook Breastfeeding, 7 th ed, 2011, chapter 15 Premature Infants and Breastfeeding )
4 Better postnatal growth appears to be associated with better neurological outcome Ehrenkranz et al (Peds 2006;117: ) found increased neurological impairment in ELBW infants with poor weight gain (55% if gained only 12 gm/kg/d but 29% if gained 21 gm/kg/d) Lucas et al (BMJ 1998;317:1481-7) found more CP and lower IQ s in group of <1850 gm infants who had received standard term formula vs group who had received enriched formula Latal-Hajnal et al (J Peds 2003;143: ) found improved neurological outcomes with better postnatal growth (of interest, was not correlated with growth status at birth)
5 MBM and DBM are considered insufficient for the VLBW infants (especially with respect to protein, calcium, phosphorus and some vitamins), but early use of IV protein and human milk fortification may help close the gaps
6 Topics to be addressed today Recommendations concerning early parenteral protein/tpn o when and how much to start Recommendations concerning multicomponent fortification of M/DBM o when should fortification begin? o how should fortification be achieved? What are other things that can be done to address poor weight gain? What are the unknowns concerning TPN and fortification?
7 Background re: provision of protein for the VLBW infants In utero, the fetus receives more protein than can be incorporated for growth, so the excess is used for energy; glucose is taken up as needed for other metabolic needs After delivery we usually give an excess of glucose but usually far insufficient protein Studies show that our premature infants quickly develop a protein deficit when standard use of protein is used, and that the deficit usually is not overcome through the hospitalization
8 Cumulative protein deficit which occurs when protein is started after the first day and then gradually increased *** g/kg/day needed over 8 week period to make up this deficit Embleton ND. Early Hum Dev 2007;83:
9 Recommended protein intake Week of gestation Parenteral protein intake wks gm/kg/d term Thureen. Presentation Oct 2,2008, Neonatal Nutrition, Development and Management Minneapolis MN and Ziegler. Aggressive nutrition of the VLBW infant, Clin Perinatology 2002;29:225. Weight Up to 1kg Range (reducing amount if growth sufficient) Protein intake gm/kg/d Agostini. Enteral Nutrient Supply for Preterm infants: Commentary from the European Society for Paed Gastronenterol, Hepatol, and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. JPGN 2010;50:85-91
10 Change in recommendations for dietary protein requirement Recent recommendations are to give more protein, and to start it earlier AAP (Pediatric Nutrition Handbook 4 th ed 2008) gm/kg/d Consensus recommendations (Tsang et al. Nutrition of the Preterm Infant: Scientific Basis and Practical Guidelines. 2005) <1000 gms gm/kg/d gms mg/kd/d
11 Current recommendations for IV protein Start with 2-3 gms/kg/d* within the first 24 hours of life Increase to gms/kg/d for the VLBW infants* (*use higher end for the ELBW infants) From ElHassan 2011 And CPQCC 2008
12 Early Aggressive Parenteral Nutrition Should include use of IV lipid, start at 2-3 g/kg/day and increase to doses as high as gm/kg/d over the first few days of life Outcomes of more aggressive TPN use: positive nitrogen balance within 48 hours improved albumin synthesis little azotemia (more info on BUN s later), no metabolic acidosis (normal HCO3), little hyperammonemia lower serum glucose lower incidence of weight <10 th percentile at 36 weeks corrected age suboptimal head circumference at 18 months Thureen et al. Pediatr Res. 2003;53: Ibrahim et al. J Perinatol 2004;24: Drechenpohl et al.pediatrics 2008;122: Poindexter et al. J Pediatr 2006;148:
13 Can an aggressive nutritional approach improve outcomes? At least 4 studies show that early TPN has ability to decrease postnatal weight loss, and to improve overall weight gain and length, and head circumference at hospital discharge (Dinerstein J Perinatol 2006;26:436-42, Wilson Arch Dis Child FNE 1997;77:F4-11, Christensen J Perinatol 2006;26:37-43, and Valentine J Perinatol 2009;29: )
14 Current recommendations for fortifying breastmilk Start when enteral feeds are at ml/kg/d Use multicomponent fortification Fortifiers contain vitamins, minerals, including calcium and phosphorus, and protein; variable amount of fat and carbohydrate Note: in the past, protein has often fallen below recommended levels (as has fat content) even when milk is fully fortified CPQCC 2008
15 Options for fortifiers Options in the USA are currently undergoing change, and include fortifiers that are the traditional powdered cow-milk derived (Abbott labs), new liquid cow-milk derived (Mead Johnson s is out now, and Abbott plans to roll out theirs in a few months) as well as a relatively new liquid human-milk derived (Prolacta) Another option is to use high calorie formula (such as Sim 30)
16 Cow-milk derived fortification improves growth and bony density From Cochrane Database, meta-analysis by Kuschel and Harding (2004) >600 babies, 13 RCT s (published from ) Results: Improved weight gain (2.3 gm/kg/d) Improved length and HC (both increase 0.12 cm/wk) Improved bone mineral content Higher BUN (but none> 20) No adverse effects (such as death, feeding intolerance or NEC) found to be significant However, of note, little long-term follow up
17 How to choose among fortifiers? As noted, in the USA, we are in the midst of changes, with the liquid cow-milk derived form just now being introduced by two companies Few head-to-head comparisons have been made A big unknown is whether displacing MBM by a fraction will decrease the protective impact of MBM Hopefully more research will be available soon One head to head trial was recently published
18 Sullivan et al. An exclusively human milk-based diet is associated with a lower rate of NEC than a diet of human milk and bovine milk-based products. J Peds 2010;156: Only article to date to compare the human-milk derived fortifier head to head with cow-milk derived fortifier; unfortunately they supplemented one group with formula, not donor milk Among 11 units, 207 babies were randomized. Avg wt ~900 gms, avg GA ~27 wks, were nearly equally divided among 3 groups: MBM+donor milk+ humanmilk derived HMF started at 100 ml/kg/d enteral feeds, MBM+donor milk+human-milk derived HMF started at 40 ml/kg/d enteral feeds, or MBM+formula+cow-milk derived HMF
19 Sullivan et al. An exclusively human milk-based diet is associated with a lower rate of NEC than a diet of human milk and bovine milk-based products. J Peds 2010;156: results: no difference in time on TPN/length of time with central lines in, weight gain, length of stay, or combined outcome of late-onset sepsis or NEC However, medical NEC itself was reduced from 16% (bovine group) vs 6% (human group) and surgical NEC was reduced from 10% to 2% But how to separate out the impact of the fortifier vs the formula??
20 Also note impact of powdered fortifier on antibacterial actions of human milk Cow-milk derived fortifier containing iron decreased the antibacterial action of human milk (against E coli, S aureus, GBS and E sakazakii) Chan. Effects of powdered milk fortifiers on the antibacterial actions of human milk. J Perinatol 2002;23: However, the same group tested the human-milk derived fortifier (with little iron) and found no decrease in antibacterial action Chan. Effects of a human milk-derived human milk fortifier on the antibacterial actions of human milk. Breastfeed Med 2007;2:
21 A bit more about Prolacta: use and costs Prolacta is a for-profit milk bank (the only one in the USA; about 14 non-profit milk banks are open in the North America) A donor milk product is available from Prolacta Several fortifiers available (+4, +6, +8) The +4 fortifier comes as 10 ml in a bottle ready to be mixed with 40 ml of human milk But cost is a big factor, and is something hospitals have to struggle with daily
22 Ethical dilemma: the human-milk derived fortifier appears preferable, but cost is huge Standardized Prolacta donor milk product, $30/oz, vs. HMBANA product (without nutritional analysis), $4/oz Estimated cost of different forms of 24 cal breastmilk, 100 ml: MBM+ 4 pkgs HMF/100ml: $6 HMBANA DBM+ 4 pkgs HMF/100 ml: $19 MBM + Prolacta +4/100 ml: $125 Prolacta DBM + Prolacta HMF +4/100 ml: $225 MBM + Prolacta +8/100ml: $250 Estimated cost (per Prolacta estimates) for the Prolacta fortifier per <750 gm baby in our unit was $10,000/baby; even adjusting for the cost of NEC in our unit (5 cases of medical NEC in 5 yrs, and 1 case of surgical NEC) using the product would result in an extra ~$7,000/baby
23 How to balance costs? And, for example, if we estimated the cost to be an extra $10,000 to use in all of our <1500 gms babies here at WakeMed, we would spend about $1.5 million/yr just for the use of the fortifier [to put that in perspective, we use about 300 oz/mo of donor milk, at ~$4/oz, which equals (300 oz x $4.00 x 12mo) about $14,400 total, for the milk alone, for all of these babies combined, for the year]
24 Beyond the multicomponent fortifier, adding additional enteral protein improves growth as well Reminder: requirement for growth estimated (Ziegler) to be 4.3 gm/kg/d for the <1000 gm baby, and 3.2 gm/kg/d for the gm baby Under our present system with the powdered fortifier, fortified breast milk provides ~ gm/kg/d when fed at 120 kcal/gm/d, EPF and SSC provide 3.6; the new high protein formula (Enfamil) provides`4.2, and the new liquid fortifier (MJ) provides >4 When we use added propass at ¼ tsp/100 ml, we add 0.3 gm/100ml of protein, at ½ tsp/100 ml, we add 0.6 gm/100 ml Can improve short-term weight gain, length and head circumference May increase BUN But plenty of caveats: Most information about protein is from babies fed formula Very little long-term follow up on these babies (no proof that increasing fortification of breast milk leads to better neurological outcome) Hopefully the future will bring us more badly-needed information
25 Adjustable fortification of human milk fed to preterm infants: Does it make a difference? (Arslanoglu S et al. J Perinatol. 2006;26:614 62) Compared protein fortification with human milk fortifier plus bovine whey protein to standard fortification Study group received incremental increases in protein Average intake of 3.2 g/kg/day compared to 2.9 g/kg/day Significant differences Weight gain +3 gm/kg/day Head circumference +0.4 mm/day Weight and head circumference gain were significantly (P<0.05) correlated with protein intake No significant differences between groups in BUN, creatinine, calcium, or phosphorus
26 Possible ways to prevent suboptimal weight gain To help prevent poor weight gain secondary to protein insufficiency, provide sufficient IV protein from first day/hour Address techniques that may enhance fat delivery (bolus feeds, short tubing, being sure syringe is empty at end of infusion, trying to avoid separation of fat fortifier components) Careful and frequent monitoring is critical (aim for ~15-20 gm/kg/d) and recheck every several days; modify your approach if these guidelines are not being met (Ehrenkranz Peds 2006 and Uhing Clinics in Perinatology 2011)
27 Preventing suboptimal infant weight gain: helping mother understand how her milk supply can be optimized Review mother s pumping routine Determine if she is Using a hospital grade breast pump Pumping until all milk is removed Hands on pumping Bringing in all of her milk not just the first morning collection which is lower in fat/calories (and make sure the nurses are not using only that milk) Inadvertently separating her milk into fore milk and hind milk, and bringing in more fore milk than hind Meier P, et al. Breastfeeding Medicine, Jun 2006; 1(2): Morton J, et al. J Perinatol. 2009;29:757,
28 Other ways of troubleshooting poor weight gain If weight gain insufficient after infant has been on 160 ml/kg/d of 24 cal milk for a week, insure oldest breast milk (higher in protein) available is being used. May also consider: Hindmilk (higher in fat) Increasing volume to ml/kg/d (if infant does not have CLD) Adding 5 th pack of HMF Adding more protein (?aim for BUN to be 9-14*) *Arslanoglu, J Perinat 2006
29 Troubleshooting poor weight gain, cont d?possible role of kangaroo care in enhancing weight gain (Cochrane review 2003, Conge- Agudelo 2003)?possible role of physical activity (Schultze, Cochrane review 2009 showed improved weight gain of 2.3 gm/kg/d); possible improvement of bone health, as well
30 Prevention of osteopenia of prematurity Provide recommended dietary intakes: Calcium mg/kg/day Phosphorus mg/kg/day Vitamin D IU Rigo J et al. Acta Paediatrics.2007; Moyer-Mileur LJ. Pediatrics 2008;28: Kislal F, Dilmen U. Pediatrics International 2008;50: Wagner C, Greer F. Section on Breastfeeding and Committee on Nutrition. AAP. Pediatrics 2008;122:1142. Optimize that provided by parenteral nutrition o Computer assisted ordering o Calcium/phosphorus solubility curves o Cysteine hydrochloride o Calcium:phosphorus ratio Porcelli P et al. J Am Coll Nutr. 1997;16:238.
31 Using enteral nutrition to prevent osteopenia of prematurity Classically was thought to be problem with insufficient phosphorus Role of maternal Vit D status may be important for some babies Enteral nutrition Start enteral feeds early Start HMF, 4 Advance to 150ml/kg/day providing estimated calcium of 213mg/kg/day and phosphorus 120 mg/kg/d If fluid restricted, consider 6 pks/100ml Advance to ml/kg/day providing calcium 250mg/kg/day and phosphorus 140 mg/kg/d
32 This is what we hope to avoid Former 25 and 6/7 wk 760 gm Twin A, fed unfortified MBM until ~3/25
33 This is looking better Former 27 wk 865 gm infant, fed all 24 cal MBM plus PP
34 But. It s Complicated
35 Uncertain aspects: what is optimal growth? Generally optimal growth is felt to be that equal to the intrauterine growth curve However, both hypertension and insulin resistance has been reported in the LBW babies who had rapid catch-up growth after birth (Law, Circulation 2002 & Singhal, Lancet 2003) Eriksson et al (BMJ 1999;318: ) found death from coronary artery disease was increased in LBW infants, especially those who achieved catch-up growth to the 50% or higher by 7 years of age Information summary from Uhing and Das, Optimizing Growth in the Preterm infant, Clinics in Perinatology 2009;36:
36 If infant received fortified MBM and achieved better postnatal growth, is that associated with better neurological outcome? Ehrenkranz et al (Peds 2006;117: ) found increased neurological impairment in ELBW infants with poor weight gain (55% if gained only 12 gm/kg/d but 29% if gained 21 gm/kg/d) (no details of nutritional regimen) Lucas et al (BMJ 1998;317:1481-7) found more CP and lower IQ s in group of <1850 gm infants who had received standard term formula vs group who had received enriched formula (formula-fed) Latal-Hajnal et al (J Peds 2003;143: ) found improved neurological outcomes with better postnatal growth (no details of nutritional regimen) ***Lucas et al. Randomized outcome trial of human milk fortification and developmental outcome in preterm infants. Am J Clin Nutr 1996;64: Only RCT of fortified breast milk with longterm follow up. Note: overall, intake of MBM was <50% during hospital stay. MDI scores 106 (fortified) vs 104(unfortified) at 18 mo s not considered significant
37 And there may be another side of the coin with respect to IV protein Clark et al (Effects of two different doses of amino acid supplementation on growth and blood amino acid levels in premature neonates admitted to the intensive care unit: a RCT. Peds 2007;120: ) studied 122 VLBW infants: randomized to low AA (start at 0.5 gm/kg/d and advance to max of 2.5) or start at 1.5 and advance to 3.5 Results: significant differences in serum AA levels, raising fear of toxicity
38 And this month, another article about high amino acid levels Blanco (Plasma amino acid concentrations during aggressive nutritional therapy in ELBW infants. J Peds 2011;158: ) found similarly elevated amino acids in some babies. Half received a standard protocol (starting at 0.5, and advancing by that amount daily). The more-aggressive regimen was to start AA in first 24 hours at 2 gms/kg/d, and to advance by 1 gm/kg/d up to max of 4. Their protocol was to draw serum ammonia levels if BUN was >60, and they would hold amino acid infusions if ammonia was >91umol/L (day 1) or 79 (day 3). 9 babies out of 61 had the elevated BUN levels, 6 of those had the specified high ammonia levels. 8 of the 9 babies with high BUN s were in the aggressive protein group. ***There needs to be a balance. We should be cognizant of a possibly negative neurologic effect, with the higher protein levels. Possibly following the protocol re: BUN and ammonia levels above would be reasonable(?).
39 Other issues related to neonatal nutrition Note: the influence of fortifiers and other additives in milk has not been tested rigorously for effects on NEC or other gastrointestinal complications (Hay, 2010) Should the IUGR babies have a different feeding regimen? (They seem to be at higher risk for NEC, may not be able to metabolize protein as well) Is the current trend of accepting lower oxygen sats and hematocrits going to decrease ability to grow optimally?
40 Other issues related to neonatal nutrition What is the role of shielding TPN from phototherapy? [less oxidation of certain amino acids and vitamins,?less BPD (Chessex, J Peds 2007) and?less hypertriglyceridemia (Kashu, Arch Dis Child FNE 2009)] Can changing feeding practices around transfusions decrease the NEC related to blood transfusions?? What about transition home? Pre/postbiotics
41 And other uncertain aspects How do you differentiate impact of intrauterine programming, early neonatal nutrition and later childhood nutrition on CV health, and how do you differentiate nutritional impacts vs all the other possible impacts of early birth on brain development? (and the list could continue from here ) ***Continue to watch nutrition field for other developments, especially as we watch these VLBW infants grow up Information summary from Uhing and Das, Optimizing Growth in the Preterm infant, Clinics in Perinatology 2009;36:
42 Summary: Mother s milk is best for short and longterm outcomes for the VLBW infant. We are still learning the best way to otherwise support neonatal nutritional needs. Thanks. Questions/comments?
43 References CPQCC Quality Improvement Toolkit, Nutritional Support of the VLBW Infant, Adamkin. Nutritional management of the very low-birthweight infant. Parts I and II. NeoReviews 2006;7:e602-e614. ElHassan and Kaiser. Parenteral nutrition in the neonatal intensive care Unit. NeoReviews 2011; 12:e130-e140. Hay. Strategies of feeding the preterm infant. Neonatology 2008;94: Martin et al. Nutritional practices and growth velocity in the first month of life in extremely premature infants. Pediatrics 2009;124: Uhing and Das, Optimizing growth in the preterm infant. Clinics in Perinatology 2009;36: NICHD Cochrane Neonatal Collaborative Research Database Kuschel and Harding. Multicomponent fortified human milk for promoting growth in preterm infants (2004) Kuschel and Harding. Protein supplementation of human milk for promoting growth in preterm infants (2000)
44 Porcelli and Sisk. Increased parenteral amino acid administration to ELBW infants during early postnatal life. J Ped Gastroenterol Nutr 2002;34:174-9 Study from Wake Forest Univ VLBW infants received a modified regimen of higher aa intakes, up to 4 gm/kg/d. Specifically they received doses as high as 3.3 gm/kg/d of aa by end of wk 1, and 3.8 by end of wk 2 No increase in acidosis, minimal increase in BUN Better growth from wk 1
45 Cow-milk derived fortification improves growth and bony density Fortified vs Unfortified Human Milk > 600 infants; randomized* Growth Weighted Mean Difference Weight gain (g/kg/d) [2.7; 4.6] Length (cm/wk) [0.07; 0.18] Head circumference (cm/wk) [0.07; 0.16] Bone mineral content (mg/cm) [3.8; 12.8] Nitrogen balance (mg/kg/d) + 66 [35; 97] BUN (mg/dl) +16 [8; 24] Relative Risk Relative Risk Feeding intolerance 2.9 [0.6; 13] NS Necrotizing enterocolitis 1.3 [0.7; 2.5] NS Death 1.5 [0.7; 3.3] NS Kuschel CA & Harding JE 2004 The Cochrane Library *Some comparisons with partial supplements
46 Another researcher, using different methods, found variable impact of fortification on the antibacterial properties of breastmilk Quan et al. The effect of nutritional additives on antiinfective factors in human milk. Clin Peds 1988:33;235-8) Researchers measured lysozyme activity, IgA, specific IgA to certain E coli serotypes, and E coli growth in frozen human milk, comparing impact of various additives Results: all cow milk based formulas (Sim, Sim Sp Care, Enf, EPF) decreased lysozyme activity by 41-74%, though no differences in total IgA was seen. Fortifier decreased lysozyme by 19% However, only the cow-milk formulas actually enhanced bacterial growth
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD
 Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
Post Discharge Nutrition. Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP
 Post Discharge Nutrition Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest:
Post Discharge Nutrition Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest:
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants
 Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Preterm Dietary Supplements
 Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL?
 HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
4/15/2014. Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth. Improving early nutrition. Problem Identification
 Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants
 QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants Amy B. Hair, MD Assistant s Professor of Program Director of Neonatal Nutrition Program Director of NICU Intestinal Rehab Team Section of Neonatology Department
QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants Amy B. Hair, MD Assistant s Professor of Program Director of Neonatal Nutrition Program Director of NICU Intestinal Rehab Team Section of Neonatology Department
(1 280 ± 286) g; (1 436 ± 201) g
 259 ( 100730) : 34 1 800 g 24 (, 11 ) (, 13 ) 50%, 100 ml / (kg d) FM85, ; (30.6 ± 2.9), (1 280 ± 286) g; (31.6 ± 1.9), (1 436 ± 201) g, 81.6%, 34.1 24.6 d [18.9 vs 17.1 g / (kg d), P = 0.364] (1.16 vs
259 ( 100730) : 34 1 800 g 24 (, 11 ) (, 13 ) 50%, 100 ml / (kg d) FM85, ; (30.6 ± 2.9), (1 280 ± 286) g; (31.6 ± 1.9), (1 436 ± 201) g, 81.6%, 34.1 24.6 d [18.9 vs 17.1 g / (kg d), P = 0.364] (1.16 vs
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes
 Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of
 Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Breast Milk is for Babies, Cows Milk is for
Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Breast Milk is for Babies, Cows Milk is for
Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health
 Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Jane Alsweiler Frank Bloomfield Anna Tottman Barbara Cormack Tanith Alexander Jane Harding Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Why
Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Jane Alsweiler Frank Bloomfield Anna Tottman Barbara Cormack Tanith Alexander Jane Harding Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Why
Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD
 Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD PORTLAND, OREGON ANDI MARKELL NUTRITION CONSULTANT Conflict of Interest I had no conflict of interest until 2015 when I was asked to join the Nutrition Advisory
Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD PORTLAND, OREGON ANDI MARKELL NUTRITION CONSULTANT Conflict of Interest I had no conflict of interest until 2015 when I was asked to join the Nutrition Advisory
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi
 Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan
 Disclosure Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan Penni Davila Hicks, PhD, RD Medical Science Liaison Abbott Nutrition Columbus, Ohio I am currently an employee of Abbott Nutrition Images
Disclosure Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan Penni Davila Hicks, PhD, RD Medical Science Liaison Abbott Nutrition Columbus, Ohio I am currently an employee of Abbott Nutrition Images
Nutrition in the premie World
 SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS
 ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS A Capstone Seminar Paper for NTR 690: Seminar in Nutrition Presented to Dr. Rayane AbuSabha Department of Nutrition Sciences Sage Graduate School In Partial Fulfillment
ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS A Capstone Seminar Paper for NTR 690: Seminar in Nutrition Presented to Dr. Rayane AbuSabha Department of Nutrition Sciences Sage Graduate School In Partial Fulfillment
1 University of Kansas School of Medicine-Wichita, Department of Pediatrics 2 Wesley Medical Center, Department of Neonatology
 Impact of on Very Low Birth Weight Infants Siddharthan Sivamurthy, M.D. 1, Carolyn R. Ahlers-Schmidt, Ph.D. 1, Katherine S. Williams, M.Ed. 1, Jared Shaw 2, Paula Delmore, M.S.N. 2, Barry T. Bloom, M.D.
Impact of on Very Low Birth Weight Infants Siddharthan Sivamurthy, M.D. 1, Carolyn R. Ahlers-Schmidt, Ph.D. 1, Katherine S. Williams, M.Ed. 1, Jared Shaw 2, Paula Delmore, M.S.N. 2, Barry T. Bloom, M.D.
Postdischarge nutrition,
 Postdischarge nutrition, is there a role for human milk? Harrie N. Lafeber MD,Ph.D. Professor of Neonatology, VU university medical center, Amsterdam, NL Ehrencranz et al. Indirect calorimetry 120-130
Postdischarge nutrition, is there a role for human milk? Harrie N. Lafeber MD,Ph.D. Professor of Neonatology, VU university medical center, Amsterdam, NL Ehrencranz et al. Indirect calorimetry 120-130
Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines
 Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines Nutrition Committee March 2018 Overall Aim 2 Provision of appropriate nutrition to neonates in a timely and safe manner to facilitate adequate growth and development
Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines Nutrition Committee March 2018 Overall Aim 2 Provision of appropriate nutrition to neonates in a timely and safe manner to facilitate adequate growth and development
Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon
 Nutrition & Growth in Premature Infant Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon PART ONE : THE GROWTH OF THE PREMATURE INFANT ARE WE ON THE RIGHT
Nutrition & Growth in Premature Infant Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon PART ONE : THE GROWTH OF THE PREMATURE INFANT ARE WE ON THE RIGHT
Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant. Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant
 Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant What s the right strategy? Infants born small-for-gestational age (SGA) are at higher risk for adult diseases.
Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant What s the right strategy? Infants born small-for-gestational age (SGA) are at higher risk for adult diseases.
HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet
 HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet To ensure long-term health and development of preterm infants, an early nutritional support is utmost important. Breast milk is undoubtedly
HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet To ensure long-term health and development of preterm infants, an early nutritional support is utmost important. Breast milk is undoubtedly
Fortification of Maternal Expressed Breast Milk
 Fortification of Maternal Expressed Breast Milk Title: Version: 2 Ratification Date: April 2016 Review Date: April 2019 Approval: Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline Group 20 th April 2016 Author:
Fortification of Maternal Expressed Breast Milk Title: Version: 2 Ratification Date: April 2016 Review Date: April 2019 Approval: Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline Group 20 th April 2016 Author:
11/4/10 SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP SAM: PREVENT MALNUTRITION 200. Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure
 Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Optimal Distribution and Utilization of Donated Human Breast Milk: A Novel Approach
 653738JHLXXX10.1177/0890334416653738Journal of Human LactationSimpson et al research-article2016 Original Research: Brief Report Optimal Distribution and Utilization of Donated Human Breast Milk: A Novel
653738JHLXXX10.1177/0890334416653738Journal of Human LactationSimpson et al research-article2016 Original Research: Brief Report Optimal Distribution and Utilization of Donated Human Breast Milk: A Novel
Enteral nutrition for optimal growth in preterm infants
 Review article Kim Korean MJ J Pediatr Enteral 2016;59(12):466-470 nutrition pissn 1738-1061 eissn 2092-7258 Korean J Pediatr Enteral nutrition for optimal growth in preterm infants Myo-Jing Kim, MD Department
Review article Kim Korean MJ J Pediatr Enteral 2016;59(12):466-470 nutrition pissn 1738-1061 eissn 2092-7258 Korean J Pediatr Enteral nutrition for optimal growth in preterm infants Myo-Jing Kim, MD Department
Postnatal growth failure Causes, consequences and prevention
 Postnatal growth failure Causes, consequences and prevention Bielsko March 9, 2014 Ekhard E. Ziegler, M.D. Fomon Infant Nutrition Unit University of Iowa 1995; 26-29 weeks gestation NICHD Growth Observational
Postnatal growth failure Causes, consequences and prevention Bielsko March 9, 2014 Ekhard E. Ziegler, M.D. Fomon Infant Nutrition Unit University of Iowa 1995; 26-29 weeks gestation NICHD Growth Observational
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth. Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida
 Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
Short- and long-term effects of individualized enteral protein supplementation in preterm newborns
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2013; 55: 365-370 Original Short- and long-term effects of individualized enteral protein supplementation in preterm newborns Ebru Ergenekon¹, Şebnem Soysal ², İbrahim
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2013; 55: 365-370 Original Short- and long-term effects of individualized enteral protein supplementation in preterm newborns Ebru Ergenekon¹, Şebnem Soysal ², İbrahim
ENTERAL NUTRITION Identifying risk of patients for enteral feeding problems: Low risk: Moderate risk: High risk:
 ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
Disclosure Statement
 Disclosure Statement Employee Spouse: Johnson & Johnson Consultant Mead Johnson Nutrition- clinical area: Growth and growth assessment of preterm infants Speakers Bureau Mead Johnson Nutrition- clinical
Disclosure Statement Employee Spouse: Johnson & Johnson Consultant Mead Johnson Nutrition- clinical area: Growth and growth assessment of preterm infants Speakers Bureau Mead Johnson Nutrition- clinical
Role of human milk fortifier on weight gain in very low birth weight babies
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Verma GK et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):353-358 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Verma GK et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):353-358 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
Impact of Human Milk on the Neurodevelopment of the Preterm Infant
 Impact of Human Milk on the Neurodevelopment of the Preterm Infant Richard J. Schanler, MD, FAAP Cohen Children s Medical Center Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell New Hyde Park, New York November
Impact of Human Milk on the Neurodevelopment of the Preterm Infant Richard J. Schanler, MD, FAAP Cohen Children s Medical Center Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell New Hyde Park, New York November
Not found an answer to your question? Contact
 NUTRITION Supporting information This guideline and supporting information has been prepared with reference to the following: Ben XM. Nutritional management of newborn infants: practical guidelines. World
NUTRITION Supporting information This guideline and supporting information has been prepared with reference to the following: Ben XM. Nutritional management of newborn infants: practical guidelines. World
RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition
 RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition A Strong Beginning Mindy Morris, DNP, NNP-BC, CNS Extremely Low Birth Weight Program Coordinator Objectives Understand the challenges associated with the
RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition A Strong Beginning Mindy Morris, DNP, NNP-BC, CNS Extremely Low Birth Weight Program Coordinator Objectives Understand the challenges associated with the
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant. Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW infants
 Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
Objectives. Neonatal Nutrition, Growth and Neurodevelopment. Brain Development through Term Gestation
 Objectives Neonatal Nutrition, Growth and Neurodevelopment Sara Ramel MD Assistant Professor Division of Neonatology University of Minnesota Children s Hospital sramel@umn.edu Influence of growth and nutrition
Objectives Neonatal Nutrition, Growth and Neurodevelopment Sara Ramel MD Assistant Professor Division of Neonatology University of Minnesota Children s Hospital sramel@umn.edu Influence of growth and nutrition
Minimal Enteral Nutrition
 Abstract Minimal Enteral Nutrition Although parenteral nutrition has been used widely in the management of sick very low birth weight infants, a smooth transition to the enteral route is most desirable.
Abstract Minimal Enteral Nutrition Although parenteral nutrition has been used widely in the management of sick very low birth weight infants, a smooth transition to the enteral route is most desirable.
NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
 NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
Protein Intake and Growth in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review
 554698GPHXXX10.1177/2333794X14554698Global Pediatric HealthTonkin et al research-article2014 Review Article Protein Intake and Growth in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review Global Pediatric Health January-December
554698GPHXXX10.1177/2333794X14554698Global Pediatric HealthTonkin et al research-article2014 Review Article Protein Intake and Growth in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review Global Pediatric Health January-December
Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
WOMEN S AND INFANT HEALTH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 WOMEN S AND INFANT HEALTH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES SUBJECT/TITLE: Post Discharge Preterm Formula: Neonates Draft June 19, 2009 DATE ESTABLISHED: DATE REVISED: NUMBER: PAGE: 1 of 11 PURPOSE To enhance
WOMEN S AND INFANT HEALTH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES SUBJECT/TITLE: Post Discharge Preterm Formula: Neonates Draft June 19, 2009 DATE ESTABLISHED: DATE REVISED: NUMBER: PAGE: 1 of 11 PURPOSE To enhance
For$fying Human Milk May 2014
 For$fying Human Milk May Feeding Premature Infants: Why, When, & What To Add To Human Milk 1 RONALD S. COHEN, MD MEDICAL DIRECTOR - PICN LUCILE S. PACKARD CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRICS
For$fying Human Milk May Feeding Premature Infants: Why, When, & What To Add To Human Milk 1 RONALD S. COHEN, MD MEDICAL DIRECTOR - PICN LUCILE S. PACKARD CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRICS
Symposium 3. Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life
 Symposium 3 Fl id d N t iti S t f th Fluid and Nutrition Support of the Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life Guidelines for the Provision of Amino Acids in the Preterm Infant During the First Week
Symposium 3 Fl id d N t iti S t f th Fluid and Nutrition Support of the Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life Guidelines for the Provision of Amino Acids in the Preterm Infant During the First Week
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS. David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA
 HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants. Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital
 Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Melinda Elliott, MD FAAP Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group
 Melinda Elliott, MD FAAP Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Disclosures I have had no disclosures August
Melinda Elliott, MD FAAP Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Disclosures I have had no disclosures August
Human Milk for Preterm Infants and Fortification
 Protein in the Feeding of Preterm Infants Bhatia J, Shamir R, Vandenplas Y (eds): Protein in Neonatal and Infant Nutrition: Recent Updates. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 86, pp 109 119, (DOI: 10.1159/000442730)
Protein in the Feeding of Preterm Infants Bhatia J, Shamir R, Vandenplas Y (eds): Protein in Neonatal and Infant Nutrition: Recent Updates. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 86, pp 109 119, (DOI: 10.1159/000442730)
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction
 Case Presentation for the Course in Clinical Nutrition GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction Dr. med. Chantal Cripe-Mamie Division of Neonatology Department
Case Presentation for the Course in Clinical Nutrition GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction Dr. med. Chantal Cripe-Mamie Division of Neonatology Department
Comparison of a Powdered, Acidified Liquid, and Non-Acidified Liquid Human Milk Fortifier on Clinical Outcomes in Premature Infants
 nutrients Article Comparison of a Powdered, Acidified Liquid, and Non-Acidified Liquid Human Milk Fortifier on Clinical Outcomes in Premature Infants Melissa Thoene 1, *, Elizabeth Lyden 2, Kara Weishaar
nutrients Article Comparison of a Powdered, Acidified Liquid, and Non-Acidified Liquid Human Milk Fortifier on Clinical Outcomes in Premature Infants Melissa Thoene 1, *, Elizabeth Lyden 2, Kara Weishaar
Human Milk Analysis Measure protein, fat and carbohydrate. The first step in a healthy preterm baby s life is nutrition
 Human Milk Analysis Measure protein, fat and carbohydrate The first step in a healthy preterm baby s life is nutrition Preterm babies Premature babies are incredibly fragile and what we do during the first
Human Milk Analysis Measure protein, fat and carbohydrate The first step in a healthy preterm baby s life is nutrition Preterm babies Premature babies are incredibly fragile and what we do during the first
Is It Possible to Prevent Necrotizing Enterocolitis?
 Is It Possible to Prevent Necrotizing Enterocolitis? Ravi Mangal Patel, MD MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA @institutopgg @ravimpatelmd Disclosures
Is It Possible to Prevent Necrotizing Enterocolitis? Ravi Mangal Patel, MD MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA @institutopgg @ravimpatelmd Disclosures
Human milk fortification
 INAC 2017 Human milk fortification Pr Jean-Charles Picaud Neonatology, Hôpital de la croix Rousse Claude Bernard university Lyon 1 Lyon, France Human milk has specific beneficial effects in preterm infants
INAC 2017 Human milk fortification Pr Jean-Charles Picaud Neonatology, Hôpital de la croix Rousse Claude Bernard university Lyon 1 Lyon, France Human milk has specific beneficial effects in preterm infants
Learning Objectives. At the conclusion of this module, participants should be better able to:
 Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this module, participants should be better able to: Treat asymptomatic neonatal hypoglycemia with buccal dextrose gel Develop patient-specific approaches to intravenous
Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this module, participants should be better able to: Treat asymptomatic neonatal hypoglycemia with buccal dextrose gel Develop patient-specific approaches to intravenous
A Preemie is out of the NICU Now What!? Care of the Ex Preterm Neonate
 A Preemie is out of the NICU Now What!? Care of the Ex Preterm Neonate Shawn Hollinger, MD FAAP FRCPC Assistant Professor Neonatology Department of Pediatrics Adjunct Professor Obstetrics and Gynecology
A Preemie is out of the NICU Now What!? Care of the Ex Preterm Neonate Shawn Hollinger, MD FAAP FRCPC Assistant Professor Neonatology Department of Pediatrics Adjunct Professor Obstetrics and Gynecology
The Nutritional Emergency of the Preterm Infant
 11/4/10 Disclosures Addressing the Nutritional Emergency of the Preterm Infant Jae Kim, MD, PhD Neonatologist and Pediatric Gastroenterologist University of California, San Diego The Nutritional Emergency
11/4/10 Disclosures Addressing the Nutritional Emergency of the Preterm Infant Jae Kim, MD, PhD Neonatologist and Pediatric Gastroenterologist University of California, San Diego The Nutritional Emergency
Protein Needs of Preterm Infants: Why Are They So Difficult to Meet?
 Protein in the Feeding of Preterm Infants Bhatia J, Shamir R, Vandenplas Y (eds): Protein in Neonatal and Infant Nutrition: Recent Updates. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 86, pp 121 128, (DOI: 10.1159/000442732
Protein in the Feeding of Preterm Infants Bhatia J, Shamir R, Vandenplas Y (eds): Protein in Neonatal and Infant Nutrition: Recent Updates. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 86, pp 121 128, (DOI: 10.1159/000442732
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY
 INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
Vitamin D during pregnancy and breastfeeding
 Vitamin D during pregnancy and breastfeeding Getting the right nutrients and eating well when you re pregnant or breastfeeding is important for your baby s growth and development. Vitamin D helps you to
Vitamin D during pregnancy and breastfeeding Getting the right nutrients and eating well when you re pregnant or breastfeeding is important for your baby s growth and development. Vitamin D helps you to
Significant benefits to infant host defense, gastrointestinal
 Outcomes of Human Milk-Fed Premature Infants Richard J. Schanler, MD, FAAP, FABM*, Significant benefits to infant host defense, sensory-neural development, gastrointestinal maturation, and some aspects
Outcomes of Human Milk-Fed Premature Infants Richard J. Schanler, MD, FAAP, FABM*, Significant benefits to infant host defense, sensory-neural development, gastrointestinal maturation, and some aspects
Hazards and Benefits of Postnatal Steroids. David J. Burchfield, MD Professor and Chief, Neonatology University of Florida
 Hazards and Benefits of Postnatal Steroids David J. Burchfield, MD Professor and Chief, Neonatology University of Florida Disclosures I have no financial affiliations or relationships to disclose. I will
Hazards and Benefits of Postnatal Steroids David J. Burchfield, MD Professor and Chief, Neonatology University of Florida Disclosures I have no financial affiliations or relationships to disclose. I will
PRACTICE GUIDELINES WOMEN S HEALTH PROGRAM
 C Title: NEWBORN: HYPOGLYCEMIA IN NEONATES BORN AT 35+0 WEEKS GESTATION AND GREATER: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT IN THE FIRST 72 HOURS Authorization Section Head, Neonatology, Program Director, Women s Health
C Title: NEWBORN: HYPOGLYCEMIA IN NEONATES BORN AT 35+0 WEEKS GESTATION AND GREATER: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT IN THE FIRST 72 HOURS Authorization Section Head, Neonatology, Program Director, Women s Health
Nutrition in preterm infants before and after hospital discharge
 2009 SNL All rights reserved Nutrition in preterm infants before and after hospital discharge There is accumulating evidence that nutrition has important effects on both short- and longterm outcomes. Good
2009 SNL All rights reserved Nutrition in preterm infants before and after hospital discharge There is accumulating evidence that nutrition has important effects on both short- and longterm outcomes. Good
CIRCULAR OF INFORMATION PASTEURIZED HUMAN MILK
 CIRCULAR OF INFORMATION PASTEURIZED HUMAN MILK PLEASE READ CAREFULLY 1. General Information This circular supplements the information contained on the labels of bottles of pasteurized human milk. The Public
CIRCULAR OF INFORMATION PASTEURIZED HUMAN MILK PLEASE READ CAREFULLY 1. General Information This circular supplements the information contained on the labels of bottles of pasteurized human milk. The Public
Introduce the basics of the newborn resuscitation period Practice calculations for TPN orders Learn how to manage basic ventilator settings
 Introduce the basics of the newborn resuscitation period Practice calculations for TPN orders Learn how to manage basic ventilator settings Complex concepts you may be expected to know Not taught this
Introduce the basics of the newborn resuscitation period Practice calculations for TPN orders Learn how to manage basic ventilator settings Complex concepts you may be expected to know Not taught this
Strategy For Reaching Optimal Growth and Development of Preterm Infants. Dr. dr. Rinawati Rohsiswatmo, Sp.A(K)
 Strategy For Reaching Optimal Growth and Development of Preterm Infants Dr. dr. Rinawati Rohsiswatmo, Sp.A(K) Premature Birth before reaching 37 weeks ' gestation. Incidence in Indonesia was 15.5% 2/3
Strategy For Reaching Optimal Growth and Development of Preterm Infants Dr. dr. Rinawati Rohsiswatmo, Sp.A(K) Premature Birth before reaching 37 weeks ' gestation. Incidence in Indonesia was 15.5% 2/3
Timing and tempo of first year growth in relation to cardiovascular and metabolic risk profile in early adulthood
 Note: for non-commercial purposes only Timing and tempo of first year growth in relation to cardiovascular and metabolic risk profile in early adulthood Anita Hokken-Koelega Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology
Note: for non-commercial purposes only Timing and tempo of first year growth in relation to cardiovascular and metabolic risk profile in early adulthood Anita Hokken-Koelega Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES
 INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
11/21/2016. Panel. Compelling Evidence for Nursing Advocates for an Exclusive Human Milk Diet (EHMD) in the NICU. NANN Annual Education Conference
 Compelling Evidence for Nursing Advocates for an Exclusive Human Milk Diet (EHMD) in the NICU NANN Annual Education Conference Terry S. Johnson, APN, NNP-BC, CLEC, ASPPS, MN, CE 2 Panel TERRY JOHNSON,
Compelling Evidence for Nursing Advocates for an Exclusive Human Milk Diet (EHMD) in the NICU NANN Annual Education Conference Terry S. Johnson, APN, NNP-BC, CLEC, ASPPS, MN, CE 2 Panel TERRY JOHNSON,
Maternal and Infant Nutrition Briefs
 Maternal and Infant Nutrition Briefs A research-based newsletter prepared by the University of California for professionals interested in maternal and infant nutrition March/April 2003 New Guidelines on
Maternal and Infant Nutrition Briefs A research-based newsletter prepared by the University of California for professionals interested in maternal and infant nutrition March/April 2003 New Guidelines on
Our Journey Toward Elimination of. Necrotizing Enterocolitis 4/16/2018. Disclosure. Presentation Outline. Clinical Presentation of NEC
 Our Journey Toward Elimination of Necrotizing Enterocolitis RAY SATO, M.D. TACOMA GENERAL HOSPITAL NICU APRIL 2018 Disclosure Ray Sato, MD has no financial relationship to disclose or conflicts of interest
Our Journey Toward Elimination of Necrotizing Enterocolitis RAY SATO, M.D. TACOMA GENERAL HOSPITAL NICU APRIL 2018 Disclosure Ray Sato, MD has no financial relationship to disclose or conflicts of interest
Early and aggressive nutritional strategy (parenteral and enteral) decreases postnatal growth failure in very low birth weight infants
 (2006) 26, 436 442 r 2006 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 0743-8346/06 $30 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early and aggressive nutritional strategy (parenteral and enteral) decreases postnatal
(2006) 26, 436 442 r 2006 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 0743-8346/06 $30 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early and aggressive nutritional strategy (parenteral and enteral) decreases postnatal
Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick Neonatal Pharmacist
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
Clinical Guideline: Enteral Feeding Vitamin supplementation
 East of England Perinatal Network Clinical Guideline: Enteral Feeding Vitamin supplementation Authors: Lynne Radbone, Principal Paediatric Dietitian For use in: EoE Neonatal Units Guidance specific to
East of England Perinatal Network Clinical Guideline: Enteral Feeding Vitamin supplementation Authors: Lynne Radbone, Principal Paediatric Dietitian For use in: EoE Neonatal Units Guidance specific to
2015 Prolacta Bioscience
 Housekeeping Items 1 Presentation will be available on-demand http://www.prolacta.com/webinars/feeding-protocols 2 Turn up your speaker volume 3 Use the Ask a Question feature 4 Use the full screen feature
Housekeeping Items 1 Presentation will be available on-demand http://www.prolacta.com/webinars/feeding-protocols 2 Turn up your speaker volume 3 Use the Ask a Question feature 4 Use the full screen feature
11/8/12. KERNICTERUS: The reason we have to care about bilirubin. MANAGING JAUNDICE IN THE BREASTFEEDING INFANT AKA: Lack of Breastfeeding Jaundice
 MANAGING JAUNDICE IN THE BREASTFEEDING INFANT AKA: Lack of Breastfeeding Jaundice November 16, 2012 Orange County Lawrence M. Gartner, M.D. University of Chicago and Valley Center, California KERNICTERUS:
MANAGING JAUNDICE IN THE BREASTFEEDING INFANT AKA: Lack of Breastfeeding Jaundice November 16, 2012 Orange County Lawrence M. Gartner, M.D. University of Chicago and Valley Center, California KERNICTERUS:
Guidelines for the prescribing of specialist infant formula in primary care: Luton and Bedfordshire
 Guidelines for the prescribing of specialist infant formula in primary care: Luton and Bedfordshire September 2017 This document is a revised edition written and agreed by paediatricians, paediatric dietitians,
Guidelines for the prescribing of specialist infant formula in primary care: Luton and Bedfordshire September 2017 This document is a revised edition written and agreed by paediatricians, paediatric dietitians,
Welsh Neonatal Network
 Welsh Neonatal Network Clinical Guideline: All Wales Enteral Feeding Guideline for Preterm Infants Authors: Isabel Fraser, Paediatric Dietitian, CAVUHB Jo Males, Paediatric Dietitian, ABUHB Kate Harrod-Wild,
Welsh Neonatal Network Clinical Guideline: All Wales Enteral Feeding Guideline for Preterm Infants Authors: Isabel Fraser, Paediatric Dietitian, CAVUHB Jo Males, Paediatric Dietitian, ABUHB Kate Harrod-Wild,
Babies 1500g. Caffeine citrate. Sodium Acid Phosphate (1mmol/ml) Ferrous Fumarate (Galfer 140mg/5ml) Infloran. Abidec BMF
 Babies 1500g Infloran Caffeine citrate BMF Sodium Acid Phosphate (1mmol/ml) Abidec Ferrous Fumarate (Galfer 140mg/5ml) Dose Half capsule BD 10mg/kg once daily (write as caffeine citrate) 2% BMF each feed
Babies 1500g Infloran Caffeine citrate BMF Sodium Acid Phosphate (1mmol/ml) Abidec Ferrous Fumarate (Galfer 140mg/5ml) Dose Half capsule BD 10mg/kg once daily (write as caffeine citrate) 2% BMF each feed
Nutrient Requirements For Preterm Infant Formulas 1,2,3
 Nutrient Requirements For Preterm Infant Formulas 1,2,3 Catherine J. Klein, 4 Editor Life Sciences Research Office, 9650 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20814 ABSTRACT Achieving appropriate growth and
Nutrient Requirements For Preterm Infant Formulas 1,2,3 Catherine J. Klein, 4 Editor Life Sciences Research Office, 9650 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20814 ABSTRACT Achieving appropriate growth and
OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General
![OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General](/thumbs/85/91909911.jpg) OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [3040000234] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: 3040000424 Neonatal Circumcision Order Set 3040000522 Neonatal Herpes Viral Order Set 3040000524
OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [3040000234] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: 3040000424 Neonatal Circumcision Order Set 3040000522 Neonatal Herpes Viral Order Set 3040000524
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 High Protein
 Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 High Protein 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants who may need extra protein to help support
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 High Protein 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants who may need extra protein to help support
11/4/10. Making Sense of Infant Formulas, Milk Fortifiers and Additives. Components of infant formula. Goals of Growth.
 Components of infant formula Making Sense of Infant Formulas, Milk Fortifiers and Additives Jae Kim, MD, PhD UCSD Medical Center Division of Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology,
Components of infant formula Making Sense of Infant Formulas, Milk Fortifiers and Additives Jae Kim, MD, PhD UCSD Medical Center Division of Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology,
Copyright Rush Mothers' Milk Club, All rights reserved. 1. Mothers Own Milk Feedings and VLBW Infants
 Paula P. Meier, RN, PhD, FAAN Director for Clinical Research and Lactation Neonatal Intensive Care And Professor of Women, Children and Family Nursing And Professor of Pediatrics Rush University Medical
Paula P. Meier, RN, PhD, FAAN Director for Clinical Research and Lactation Neonatal Intensive Care And Professor of Women, Children and Family Nursing And Professor of Pediatrics Rush University Medical
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING. Quak Seng Hock
 SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
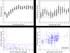 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Cysteine Supplementation in Parenteral-fed Critically ill Neonates:
 Cysteine Supplementation in Parenteral-fed Critically ill Neonates: A Randomized Trial Investigating Glutathione Synthesis Stephen B. Shew, M.D. UCLA Division of Pediatric Surgery Nov 29, 2006 Background
Cysteine Supplementation in Parenteral-fed Critically ill Neonates: A Randomized Trial Investigating Glutathione Synthesis Stephen B. Shew, M.D. UCLA Division of Pediatric Surgery Nov 29, 2006 Background
Product Information: Similac Special Care 30
 Product Information: Similac Special Care 30 1 of 5 A 30 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. First 30-Cal/fl oz ready-to-feed liquid preterm infant
Product Information: Similac Special Care 30 1 of 5 A 30 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. First 30-Cal/fl oz ready-to-feed liquid preterm infant
Case Study. The 4-year journey of feeding intolerance of an enterally-fed child from 9 months of age. Synopsis. Introduction/Overview
 Case Study The 4-year journey of feeding intolerance of an enterally-fed child from 9 months of age Library image Emma Liesl Silbernagl, Clinical lead HEN Dietitian, Home Enteral Nutrition Team, Lewisham
Case Study The 4-year journey of feeding intolerance of an enterally-fed child from 9 months of age Library image Emma Liesl Silbernagl, Clinical lead HEN Dietitian, Home Enteral Nutrition Team, Lewisham
Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/
The health benefits of human milk for all infants, including those born extremely premature, have been increasingly
 An Exclusively Human Milk-Based Diet Is Associated with a Lower Rate of Necrotizing Enterocolitis than a Diet of Human Milk and Bovine Milk-Based Products Sandra Sullivan, MD, Richard J. Schanler, MD,
An Exclusively Human Milk-Based Diet Is Associated with a Lower Rate of Necrotizing Enterocolitis than a Diet of Human Milk and Bovine Milk-Based Products Sandra Sullivan, MD, Richard J. Schanler, MD,
FIAP, FICN, FAMS, FNNF
 Passport Size Photo Name:- Dr BD Bhatia Qualification:-MD, DCH, FIAP, FICN, FAMS, FNNF Current Designation:- Professor and Head Pediatrics,Heritage Institute of Medical Sciences,Varanasi President elect
Passport Size Photo Name:- Dr BD Bhatia Qualification:-MD, DCH, FIAP, FICN, FAMS, FNNF Current Designation:- Professor and Head Pediatrics,Heritage Institute of Medical Sciences,Varanasi President elect
METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0
 METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 Page 1 of 10 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline To provide guidance on the prevention of metabolic bone disease in the neonate. All
METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 Page 1 of 10 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline To provide guidance on the prevention of metabolic bone disease in the neonate. All
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management
 Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Product Information: Similac Special Care 30 With Iron
 Product Information: Similac Special Care 30 With Iron 1 of 5 A 30 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. Use under medical supervision. First 30-Cal/fl
Product Information: Similac Special Care 30 With Iron 1 of 5 A 30 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. Use under medical supervision. First 30-Cal/fl
Is NEC requiring surgery precipitated by a change in feeds? Observations from 50 consecutive cases. David Burge SIGNEC September 2015
 Is NEC requiring surgery precipitated by a change in feeds? Observations from 50 consecutive cases. David Burge SIGNEC September 2015 Clinical series Specific cases Other scenarios Published experience
Is NEC requiring surgery precipitated by a change in feeds? Observations from 50 consecutive cases. David Burge SIGNEC September 2015 Clinical series Specific cases Other scenarios Published experience
New Ideas in the Nutrition of the ELBW Infant. Reese H Clark, MD
 New Ideas in the Nutrition of the ELBW Infant Reese H Clark, MD 1 DISCLOSURES I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflicts of interest to resolve. I will not discuss any unapproved
New Ideas in the Nutrition of the ELBW Infant Reese H Clark, MD 1 DISCLOSURES I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflicts of interest to resolve. I will not discuss any unapproved
