Human milk fortification
|
|
|
- Benjamin Mathews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INAC 2017 Human milk fortification Pr Jean-Charles Picaud Neonatology, Hôpital de la croix Rousse Claude Bernard university Lyon 1 Lyon, France
2 Human milk has specific beneficial effects in preterm infants Sufficient- and good quality- postnatal growth is beneficial for preterm infants Unfortified HM does not support sufficient nutrients intake and postnatal growth ESPGHAN 2010: advocates the use of human milk for preterm infants as standard practice, provided it is fortified with added nutrients where necessary to meet requirements. Fortifed HM is the reference nutrition for VLBW infants during hospitalization
3 Fortification of HM Objectives: To add precise amounts of fortifier without bacteriological contamination (hygiene) Standard fortification Multicomponent fortifier Individualized fortification Multicomponent fortifier ± Protein, Fat, Carbohydrates Milk preparation center Dedicated room in or close to the unit At bedside Proximity babies Hygiene Precision
4 Standardized fortification Composition of multicomponent fortifiers and protein fortifier (per g powder) Name Suppletine Fortipré Fortema FM85 Enfa mil Simi lac Nutriprem (Aptamil PS) Manufacturer Lactalis Nestle Danone Nestle MJ Ross Danone Energy (Kcal) 3,6 3,5 3, (L) 3.9 (L) 3.4 Protein (g) 0,2 0.2 PH 0,3 PH 0.2 EH PH Na (mg) 6, , K (mg) 3, , Ca (mg) Ph (mg) Iron (mg)
5 Standardized fortification May be inappropriate for some preterm infants fed HM: Slower growth than infants fed a preterm formula Significant proportion are growth retardated at discharge Henriksen 2009: 127 VLBW infants fed fortified (std) HM BW < P10: 33% at birth 58% at discharge Due to Variability of nutrients needs in various clinical situations (ELBW, severe intrauterine growth restriction, BPD, ) NB: ESPGHAN 2010 «No specific recommendations are provided for infants with a weight below 1000 g because data are lacking «The needs of infants with specific diseases (e.g., bronchopulmonary dysplasia, congenital heart disease, short bowel syndrome) are not specifically addressed in this commentary. Variability of nutrients content of human milk
6 Standardized fortification Multicomponent fortifiers increase osmolality of HM Human milk mosmol/kg No evidence was found for a causal relation between the osmolality of nutrients and the development of necrotizing enterocolitis. Delay in gastric emptying if osmolality > 450 mosmol/kg Warning about feeding oral high osmolar electrolyte supplements and medications (Pearson 2012, Kriessl 2013)
7 mosm/kg Prot. Int. (g/kg.d) Standard fortification of HM: 3 multicomponent fortifiers Protein intake (for 160 ml/kg/d) & osmolality (mosm/kg) * 500 Increased risk > 450 mosm/kg LM LM + 4% MCF1 LM + 5% MCF2 LM + 4% MCF3 LM + 8% MCF1 1 MCF, multicomponent fortifier 1 (Suppletine), 2 (Fortipre), 3 (Aptamil) * Mean osmolality (3 differents HM) at H24 Osmolality of new products!
8 Rosas Acta Pediatr 2016 Fresh HM Fortified with extensively hydrolyzed MCF (FM85) Protein supplement D C B A Osmomolality up to 550 mosm/kg
9 Osmolality (mosm/kg) What happens in the first 2 hours after fortification? 500 suppl4% /3 of the increase occurs immediatley at time of fortification Time (min) Fortification «at bedside» is not efficient to prevent the significant increase in osmolality Improve multicomponent fortifiers composition
10 Standardized fortification may help, but could be insufficient to cover the needs of preterm infants Improve standard fortification Individualized fortification Early beginning, Lipids as energy source, Protein content Standardize HM composition Targeted Fortification Evaluate individual protein utilization Adjustable Fortification Optimization of postnatal growth
11 Standardized fortification may help, but could be insufficient to cover the needs of preterm infants Improve standard fortification Individualized fortification Early beginning, Lipids as energy source, Protein content,. Standardize HM composition Targeted Fortification Evaluate individual protein utilization Adjustable Fortification Optimization of postnatal growth
12 Standardized fortification Early beginning of multicomponent fortification Early versus Delayed Human Milk Fortification in Very Low Birth Weight Infants A Randomized Controlled Trial (Shah 2016) 100 VLBW infants, multicomponent fortifier started at 20 or 100 ml/kg.d Early Delayed BW (g) GA (wks) SGA (<P10) (%) Start to feed (d) 3 3 Age full feed (d) Feeding intolerance (%) Cumulative protein intake M1 (g/kg) SGA at discharge (<P10) (%) No significant difference Higher protein intake (energy idem) but no significant effect on feeding tolerance or time to reach full feeding volume. NB: 2/3 infants presented EUGR!
13 Standardized fortification Improvment of fortifiers composition Human milk based fortifier Not yet fully available in Europe (except in Austria) Cost-benefit ratio in all health care systems? HM consuming Efficacy reported only in NICUs with high prevalence of NEC (16%) (Sullivan et al. 2010)
14 Standardized fortification Improvment of fortifiers composition Lipids to replace partly carbohydrates as energy source Multicenter randomized controled trial: DIAMOND study Control HM fortifier (chmf=fm85) vs. New HM fortifier (nhmf): Main outcome: weight gain over a 21 days-period Secondary outcomes: digestive tolerance, LC-PUFA status
15 Composition of fortifiers
16 Nutrients intake and osmolality 3 g/100 kcal 3.5 g/100 kcal * Calculation based on the composition of preterm HM: 1.6 g & 67 kcl per 100mL Osmolality at H (mosm/kg)
17 EFFICACY : Weight gain
18 EFFICACY : LC-PUFAs Agostoni 2010 Recommendations > : :1 <30%DHA DHA at D21 chmf nhmf P Red blood cell 5.1 ± ± phosphatidylethanolamine
19 TOLERANCE Digestive tolerance No difference Metabolic tolerance: Serum urea
20 In summary, the new fortifier Increased protein content (en protein to energy ratio) helped to improved short-term weight gain Replacement of carbohydrates by lipids reduction of osmolality good digestive tolerance Improvment of LC-PUFAs status
21 Standardized fortification may help, but could be insufficient to cover the needs of preterm infants Improve standard fortification Individualized fortification Lipids as energy source, protein content, early beginning Standardize HM composition Targeted Fortification Evaluate individual protein utilization Adjustable Fortification Optimization of postnatal growth
22 Individualized fortification of HM Targeted Fortification Analysis of HM and then fortification to reach the targeted nutrient intake (NB: requires frequent milk analyse) by adding: - protein: Polberger lipids: De Halleux prot, fat, carbohydrates: Rochow 2013, McLeod 2016 RCT Marlocchi 2016 Makes an assumption about nutrient s needs (ESPGHAN 2010: HM! ELBW!) Adjustable fortification Protein fortification adjusted to the metabolic response evaluated through periodic determinations of serum urea - Arsanoglu 2010 RCT - Alan 2015 Takes into consideration actual protein status in each infant
23 Individualized targeted fortification of HM Rochow 2013: single center, prospective case-control study HM + HMF (Similac) Only ±Fat±Prot±Carbohydr. (n=10) (n=20) BW (g) 880± ±310 GA (wks) 27.1± ±1.6 P (g/kg/d) 19.7± ±2.7 Weight gain similar in both groups (< fetal growth rate!) McLeod N=20/group: VLBW (<30 weeks), AGA Fortification based on assumed composition to target g protein/kg.d & kcal/kg.d. Weight gain similar in both groups (< fetal growth rate!) No difference in anthropometry and fat mass % at discharge
24 Adjustable protein fortification in VLBW infants N=32 VLBW ( 31weeks, 1400g) [RCT] (Arsanoglu 2006) HM+ std fortification bovine HMF (FM85) until D18 Then adjustable protein fortification ProMix (whey protein) according to blood urea level <3 mmol/l (9 mg/dl): +1 level of fortification > 5 mmol/l (14 mg/dl): -1 level of fortification 3-5 mmol/l (9-14 mg/dl): no change Based on bovine HMF (FM85) ± ProMix (whey prot: 0.3g/0.4g per g powder) Main outcome criteria: Weight gain
25 In summary, (pragmatic) fortification of HM Start Early : well-tolerated enteral intake at 50 to 80 ml/kg.d Multicomponent fortification (well-tolerated & efficient) Increase of fortified HM intake up to well-tolerated full-enteral feeding ( ml/kg.d) Monitor Tolerance (digestive & metabolic) Weight gain Individualize fortification (monitor carefully postnatal growth) Targeted? If dedicated staff and infrared analyzer(s) Adjustable? Easier (no assessment of HM composition) and proven short-term efficacy on weight and HC growth
26 Evaluation of individualized nutritional care Population: Characteristics, growth Total (N=240) GA, weeks 29.2 ± 2.2 GA <28 wks, n (%) 80 (33) Birth weight, g 1230 ± 375 BW <-1DS, n (%) 49 (20) Antenatal steroids, n (%) 230 (96) Hospital stay, days 54 ± 23 GA at discharge, wks 37 ± 2 Body weight at discharge, g 2781 ± 478 Weight gain birth-discharge, g/kg.d 14.7 ± 2.3 EUGR*, n (%) 64 (27) EUGR= weight at discharge Z-score for age < -1 SD or change in Z-score between birth and discharge of more than 1 DS Croix Rousse hospital , Larcade J
27 Body weight, crown-heel length and head circumference Z-scores for age (mean±1sd) between birth and discharge in 240 VLBW infants. 1,5 1 0,5 0-0,5-1 -1,5-2 -2,5 Senterre 2011 (N=102), Birth: SD ; Discharge: SD NAISSANCE Birth J7 D7 J14 D14 J21 D21 J28 D28 J35 D35 J42 D42 SORTIE Discharge POIDS TAILLE PC Croix Rousse hospital , Larcade J
28 Fat mass (%) at discharge 30 N= weeks at 11 weeks of life 30 N= weeks at 6 weeks of life Filles Garçons Filles Garçons Girls Boys Girls Boys Preterm infants at birth at wks PCA (Hawkes 2011)* Term infants at 6-12 weeks of life (Carberry 2010)* 0 *assessed by Peapod Croix Rousse hospital , Larcade J
29 Nutrients intake during hospitalization 5 Protein intake (g/kg.d) wks, wks 4,5 4 3, J7 J14 J21 J28 J35 J42 Energy intake (Kcal/kg.d) 4,5 4 3,5 3 2,5 2 Protein/energy ratio (g/100 kcal) J7 J14 J21 J28 J35 J42 D7 D14 D21 D28 D35 D D7 D14 D21 D28 D35 D42 J7 J14 J21 J28 J35 J42 Croix Rousse hospital , Larcade J
30 CONCLUSION Available products allow individualized nutrition that could help to optimize the nutritional care of preterm infants fed human milk Strategy of HM fortification should be decided based on evidence and feasability (staff, organization) in each unit and based on a common policy unit
31 Thank you for your attention You are welcome! In Glasgow, UK October 5-6, 2017 European Milk Bank Association
32
33 mosm/kg Prot. Int. (g/kg.d) Adjustable fortification: protein supplement (PS) (0,5-1 g/dl) Protein intake (for 160 ml/kg/d) & osmolality at H24 (mosm/kg) 500 Increased risk > 450 mosm/kg LM + MCF1 4% + PS 0.5% LM + MCF1 4% + PS 1% LM + MCF2 4% + PS 0.5% LM + MCF2 4% + PS 1% LM + MCF3 3% + PS 0.5% LM + MCF3 3% + PS 1% LM + MCF3 4% + PS 0.5% LM + MCF3 4% + PS 1% MCF, multicomponent fortifier 1 (Suppletine), 2 (Fortipre), 3 (Aptamil)
34 Protein utilization in preterm and term infants N (mg) N Intake N retention N urinary Preterm Term Intake Retention Urinary PT-HM PTF1 PTF2 PTF3 PTF4 T-HM TF Adapted from: Putet , Rigo , Cooke 2006
35 After discharge: fortification of HM? N=39 BW 1300g, GA 29wks 50% of milk intake + fortifier 3 months after discharge No difference in breastfeeding duration LF+ WEIGHT LF At 12 months CA, weight, length, BMC LENGTH At 18 monts (n=27) Bayley II: no difference LF+ LF (O Connor 2008, Aimone 2009)
36 After discharge: fortification of HM? N=320, GA=24-32 wks, BW= g -HM Fortified (17.5 kcal & 1.4 g in ml HM in feeding bottle or cup, once/d) Vs. Unfortified HM - PF (68 kcal & 2g) During 4 months after discharge Same duration of BF At 12 months CA: no difference in growth (Zacchariessen 2011)
37 Individualized targeted fortification of HM Multicomponent HMF + complementary fat Observational study 1 - Assessment of milk composition 2 - Energy fortification with Lipids Liquigen (1ml =0.5 g MCT) Aim: 4 g/100 ml 3 Addition of HM fortifier (Enfamil) Aim: 4,3 g Protein/kg.d 4 Analysis of milk composition Better weight gain Linear growth, HC: no effect Body composition?! De Halleux 2007
38 Targeted fortification (Rochow et al. 2013) Multicomponent HMF ± complementary fat / Protein / Carbohydrates Every 12 hours a hard job! «Nurses, neonatal research laboratory staff, dieteticians, physicians, nurse practitioners and technicians from nutrition services were involved» «Additional workload of 5-10 min per milk batch»
39 Adjustable protein fortification in VLBW infants Observational study Control Intervention (n=16) (n=15) GA, weeks 27.7 ± ± BW, g 992 ± ± Energy intake (Kcal/kg.day) 122 ± ± Protein intake (g/kg/d) 2.7 ± ± 0.3 < Weight velocity (g/kg.day) 20.4 ± ± Length velocity (mm/d) 1.1 ± ± HC velocity (mm/d) 0.9 ± ± mean ± SD Alan et al. Early Hum Dev 2013
40 Additional protein fortification in ELBW infants Picaud et al. JPGN 2016 Retrospective chart review N=152 ELBW infants (<1250 g) Croix Rousse hospital, Lyon 32% needed a protein suplement (entire protein) to reach a weight gain 20/kg.d Protein intake (g/kg.d) Prot./Cal. ratio (g/100 kcal) Wk 0 3,4 2,1 Wk 1 4,1 2,5 Wk 2 4,2 2,5 Median (min,max) Z-scores before and after additional protein supplementation ( ) Weight Length HC
41 Example of individual postnatal growth curves 27wks, 820g 27 wks 920 g 25 wks 780 g HOP. CROIX ROUSSE, LYON
42 Impact of breastfeeding / human milk Specific effect on health of preterm infants Short term (hospitalization) Adaptation to extrauterine life Hemodynamic (hypotension, persistent ductus arteriosus) Growth Digestive tolerance (necrotizing enterocolitis) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia Retinopathy Neurology (IVH, PVL, ROP, deafness) Infections (EOS, LOS) Parents-infant relationship Long term (infancy, adulthood) Respiratory (asthma) Neurological and cognitive (handicap, learning at school) Growth (final height, qualiy of growth) Metabolic et cardiovascular diseases Quality of life, parents-infant relationship
43 Postnatal growth & further development in preterm infants Weight gain during hospitalization Ehrenkranz 2006 cognitive development (2 years) Ehrenkranz et al renal function (8 years) Bacchetta et al FFM accretion during hospitalization associated with improved speed of processing in preterm infants. Pfister et al associated with Improved neurodevelopment at 1 year CA for VLBW Infants. Ramel J Pediatr 2016
Preterm Dietary Supplements
 Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL?
 HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
Postdischarge nutrition,
 Postdischarge nutrition, is there a role for human milk? Harrie N. Lafeber MD,Ph.D. Professor of Neonatology, VU university medical center, Amsterdam, NL Ehrencranz et al. Indirect calorimetry 120-130
Postdischarge nutrition, is there a role for human milk? Harrie N. Lafeber MD,Ph.D. Professor of Neonatology, VU university medical center, Amsterdam, NL Ehrencranz et al. Indirect calorimetry 120-130
Post Discharge Nutrition. Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP
 Post Discharge Nutrition Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest:
Post Discharge Nutrition Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest:
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD
 Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants
 QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants Amy B. Hair, MD Assistant s Professor of Program Director of Neonatal Nutrition Program Director of NICU Intestinal Rehab Team Section of Neonatology Department
QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants Amy B. Hair, MD Assistant s Professor of Program Director of Neonatal Nutrition Program Director of NICU Intestinal Rehab Team Section of Neonatology Department
Postnatal growth failure Causes, consequences and prevention
 Postnatal growth failure Causes, consequences and prevention Bielsko March 9, 2014 Ekhard E. Ziegler, M.D. Fomon Infant Nutrition Unit University of Iowa 1995; 26-29 weeks gestation NICHD Growth Observational
Postnatal growth failure Causes, consequences and prevention Bielsko March 9, 2014 Ekhard E. Ziegler, M.D. Fomon Infant Nutrition Unit University of Iowa 1995; 26-29 weeks gestation NICHD Growth Observational
Objectives. Neonatal Nutrition, Growth and Neurodevelopment. Brain Development through Term Gestation
 Objectives Neonatal Nutrition, Growth and Neurodevelopment Sara Ramel MD Assistant Professor Division of Neonatology University of Minnesota Children s Hospital sramel@umn.edu Influence of growth and nutrition
Objectives Neonatal Nutrition, Growth and Neurodevelopment Sara Ramel MD Assistant Professor Division of Neonatology University of Minnesota Children s Hospital sramel@umn.edu Influence of growth and nutrition
Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan
 Disclosure Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan Penni Davila Hicks, PhD, RD Medical Science Liaison Abbott Nutrition Columbus, Ohio I am currently an employee of Abbott Nutrition Images
Disclosure Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan Penni Davila Hicks, PhD, RD Medical Science Liaison Abbott Nutrition Columbus, Ohio I am currently an employee of Abbott Nutrition Images
4/15/2014. Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth. Improving early nutrition. Problem Identification
 Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
Optimal Distribution and Utilization of Donated Human Breast Milk: A Novel Approach
 653738JHLXXX10.1177/0890334416653738Journal of Human LactationSimpson et al research-article2016 Original Research: Brief Report Optimal Distribution and Utilization of Donated Human Breast Milk: A Novel
653738JHLXXX10.1177/0890334416653738Journal of Human LactationSimpson et al research-article2016 Original Research: Brief Report Optimal Distribution and Utilization of Donated Human Breast Milk: A Novel
Protein Intake and Growth in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review
 554698GPHXXX10.1177/2333794X14554698Global Pediatric HealthTonkin et al research-article2014 Review Article Protein Intake and Growth in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review Global Pediatric Health January-December
554698GPHXXX10.1177/2333794X14554698Global Pediatric HealthTonkin et al research-article2014 Review Article Protein Intake and Growth in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review Global Pediatric Health January-December
NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
 NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon
 Nutrition & Growth in Premature Infant Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon PART ONE : THE GROWTH OF THE PREMATURE INFANT ARE WE ON THE RIGHT
Nutrition & Growth in Premature Infant Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon PART ONE : THE GROWTH OF THE PREMATURE INFANT ARE WE ON THE RIGHT
Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD
 Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD PORTLAND, OREGON ANDI MARKELL NUTRITION CONSULTANT Conflict of Interest I had no conflict of interest until 2015 when I was asked to join the Nutrition Advisory
Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD PORTLAND, OREGON ANDI MARKELL NUTRITION CONSULTANT Conflict of Interest I had no conflict of interest until 2015 when I was asked to join the Nutrition Advisory
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes
 Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Short- and long-term effects of individualized enteral protein supplementation in preterm newborns
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2013; 55: 365-370 Original Short- and long-term effects of individualized enteral protein supplementation in preterm newborns Ebru Ergenekon¹, Şebnem Soysal ², İbrahim
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2013; 55: 365-370 Original Short- and long-term effects of individualized enteral protein supplementation in preterm newborns Ebru Ergenekon¹, Şebnem Soysal ², İbrahim
Impact of Human Milk on the Neurodevelopment of the Preterm Infant
 Impact of Human Milk on the Neurodevelopment of the Preterm Infant Richard J. Schanler, MD, FAAP Cohen Children s Medical Center Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell New Hyde Park, New York November
Impact of Human Milk on the Neurodevelopment of the Preterm Infant Richard J. Schanler, MD, FAAP Cohen Children s Medical Center Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell New Hyde Park, New York November
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi
 Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS
 ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS A Capstone Seminar Paper for NTR 690: Seminar in Nutrition Presented to Dr. Rayane AbuSabha Department of Nutrition Sciences Sage Graduate School In Partial Fulfillment
ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS A Capstone Seminar Paper for NTR 690: Seminar in Nutrition Presented to Dr. Rayane AbuSabha Department of Nutrition Sciences Sage Graduate School In Partial Fulfillment
Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health
 Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Jane Alsweiler Frank Bloomfield Anna Tottman Barbara Cormack Tanith Alexander Jane Harding Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Why
Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Jane Alsweiler Frank Bloomfield Anna Tottman Barbara Cormack Tanith Alexander Jane Harding Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Why
Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of
 Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Breast Milk is for Babies, Cows Milk is for
Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Breast Milk is for Babies, Cows Milk is for
Disclosure Statement
 Disclosure Statement Employee Spouse: Johnson & Johnson Consultant Mead Johnson Nutrition- clinical area: Growth and growth assessment of preterm infants Speakers Bureau Mead Johnson Nutrition- clinical
Disclosure Statement Employee Spouse: Johnson & Johnson Consultant Mead Johnson Nutrition- clinical area: Growth and growth assessment of preterm infants Speakers Bureau Mead Johnson Nutrition- clinical
Nutrition in the premie World
 SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
Fortification of Maternal Expressed Breast Milk
 Fortification of Maternal Expressed Breast Milk Title: Version: 2 Ratification Date: April 2016 Review Date: April 2019 Approval: Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline Group 20 th April 2016 Author:
Fortification of Maternal Expressed Breast Milk Title: Version: 2 Ratification Date: April 2016 Review Date: April 2019 Approval: Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline Group 20 th April 2016 Author:
Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant. Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant
 Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant What s the right strategy? Infants born small-for-gestational age (SGA) are at higher risk for adult diseases.
Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant Feeding the Small for Gestational Age Infant What s the right strategy? Infants born small-for-gestational age (SGA) are at higher risk for adult diseases.
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
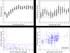 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet
 HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet To ensure long-term health and development of preterm infants, an early nutritional support is utmost important. Breast milk is undoubtedly
HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet To ensure long-term health and development of preterm infants, an early nutritional support is utmost important. Breast milk is undoubtedly
Enteral nutrition for optimal growth in preterm infants
 Review article Kim Korean MJ J Pediatr Enteral 2016;59(12):466-470 nutrition pissn 1738-1061 eissn 2092-7258 Korean J Pediatr Enteral nutrition for optimal growth in preterm infants Myo-Jing Kim, MD Department
Review article Kim Korean MJ J Pediatr Enteral 2016;59(12):466-470 nutrition pissn 1738-1061 eissn 2092-7258 Korean J Pediatr Enteral nutrition for optimal growth in preterm infants Myo-Jing Kim, MD Department
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants
 Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
For$fying Human Milk May 2014
 For$fying Human Milk May Feeding Premature Infants: Why, When, & What To Add To Human Milk 1 RONALD S. COHEN, MD MEDICAL DIRECTOR - PICN LUCILE S. PACKARD CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRICS
For$fying Human Milk May Feeding Premature Infants: Why, When, & What To Add To Human Milk 1 RONALD S. COHEN, MD MEDICAL DIRECTOR - PICN LUCILE S. PACKARD CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRICS
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS. David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA
 HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
Human Milk Analysis Measure protein, fat and carbohydrate. The first step in a healthy preterm baby s life is nutrition
 Human Milk Analysis Measure protein, fat and carbohydrate The first step in a healthy preterm baby s life is nutrition Preterm babies Premature babies are incredibly fragile and what we do during the first
Human Milk Analysis Measure protein, fat and carbohydrate The first step in a healthy preterm baby s life is nutrition Preterm babies Premature babies are incredibly fragile and what we do during the first
(1 280 ± 286) g; (1 436 ± 201) g
 259 ( 100730) : 34 1 800 g 24 (, 11 ) (, 13 ) 50%, 100 ml / (kg d) FM85, ; (30.6 ± 2.9), (1 280 ± 286) g; (31.6 ± 1.9), (1 436 ± 201) g, 81.6%, 34.1 24.6 d [18.9 vs 17.1 g / (kg d), P = 0.364] (1.16 vs
259 ( 100730) : 34 1 800 g 24 (, 11 ) (, 13 ) 50%, 100 ml / (kg d) FM85, ; (30.6 ± 2.9), (1 280 ± 286) g; (31.6 ± 1.9), (1 436 ± 201) g, 81.6%, 34.1 24.6 d [18.9 vs 17.1 g / (kg d), P = 0.364] (1.16 vs
Role of human milk fortifier on weight gain in very low birth weight babies
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Verma GK et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):353-358 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Verma GK et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):353-358 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
Nutrition of preterm infants in relation to bronchopulmonary dysplasia
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Nutrition of preterm infants in relation to bronchopulmonary dysplasia Andreas Wemhöner 1,2*, Daniel Ortner 1, Edda Tschirch 1,2, Alexander Strasak 3, Mario Rüdiger 1,2 Open Access Background:
RESEARCH ARTICLE Nutrition of preterm infants in relation to bronchopulmonary dysplasia Andreas Wemhöner 1,2*, Daniel Ortner 1, Edda Tschirch 1,2, Alexander Strasak 3, Mario Rüdiger 1,2 Open Access Background:
Comparison of a Powdered, Acidified Liquid, and Non-Acidified Liquid Human Milk Fortifier on Clinical Outcomes in Premature Infants
 nutrients Article Comparison of a Powdered, Acidified Liquid, and Non-Acidified Liquid Human Milk Fortifier on Clinical Outcomes in Premature Infants Melissa Thoene 1, *, Elizabeth Lyden 2, Kara Weishaar
nutrients Article Comparison of a Powdered, Acidified Liquid, and Non-Acidified Liquid Human Milk Fortifier on Clinical Outcomes in Premature Infants Melissa Thoene 1, *, Elizabeth Lyden 2, Kara Weishaar
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth. Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida
 Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
Not found an answer to your question? Contact
 NUTRITION Supporting information This guideline and supporting information has been prepared with reference to the following: Ben XM. Nutritional management of newborn infants: practical guidelines. World
NUTRITION Supporting information This guideline and supporting information has been prepared with reference to the following: Ben XM. Nutritional management of newborn infants: practical guidelines. World
Title: Authors: Corresponding Author: Abbreviations:
 Title: Comparing different methods of human breast milk fortification using measured versus assumed macronutrient composition to target reference growth: a RCT Authors: Gemma McLeod 1 ; Jill Sherriff 2
Title: Comparing different methods of human breast milk fortification using measured versus assumed macronutrient composition to target reference growth: a RCT Authors: Gemma McLeod 1 ; Jill Sherriff 2
Creating Feeding Guidelines: Optimizing Growth is Complicated
 Creating Feeding Guidelines: Optimizing Growth is Complicated PQCNC Initiative: Increasing Use of Mother s Milk for the Very Low Birthweight Babies in the Critical Care Centers of North Carolina Webinar
Creating Feeding Guidelines: Optimizing Growth is Complicated PQCNC Initiative: Increasing Use of Mother s Milk for the Very Low Birthweight Babies in the Critical Care Centers of North Carolina Webinar
Patent Ductus Arteriosus: Philosophy or Pathology?
 Patent Ductus Arteriosus: Philosophy or Pathology? Disclosure Ray Sato, MD is a speaker for Prolacta Biosciences, Inc. This presentation will discuss off-label uses of acetaminophen and ibuprofen. RAY
Patent Ductus Arteriosus: Philosophy or Pathology? Disclosure Ray Sato, MD is a speaker for Prolacta Biosciences, Inc. This presentation will discuss off-label uses of acetaminophen and ibuprofen. RAY
A Preemie is out of the NICU Now What!? Care of the Ex Preterm Neonate
 A Preemie is out of the NICU Now What!? Care of the Ex Preterm Neonate Shawn Hollinger, MD FAAP FRCPC Assistant Professor Neonatology Department of Pediatrics Adjunct Professor Obstetrics and Gynecology
A Preemie is out of the NICU Now What!? Care of the Ex Preterm Neonate Shawn Hollinger, MD FAAP FRCPC Assistant Professor Neonatology Department of Pediatrics Adjunct Professor Obstetrics and Gynecology
Protein Requirements in Preterm Infants: Effect of Different Levels of Protein Intake on Growth and Body Composition
 0031-3998/05/5805-0855 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Vol. 58, No. 5, 2005 Copyright 2005 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Protein Requirements in Preterm Infants: Effect of Different
0031-3998/05/5805-0855 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Vol. 58, No. 5, 2005 Copyright 2005 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Protein Requirements in Preterm Infants: Effect of Different
ENTERAL NUTRITION Identifying risk of patients for enteral feeding problems: Low risk: Moderate risk: High risk:
 ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
Individualized Fortification of Breast Milk for Preterm Infants Miami Neonatology nd Annual International Conference
 Miami Neonatology 2018 42nd Annual International Conference Overview Mother s breast milk is notably considered the gold standard for infants nutrition. However, Christoph Fusch, MD, PhD, discusses evidence
Miami Neonatology 2018 42nd Annual International Conference Overview Mother s breast milk is notably considered the gold standard for infants nutrition. However, Christoph Fusch, MD, PhD, discusses evidence
GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction
 Case Presentation for the Course in Clinical Nutrition GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction Dr. med. Chantal Cripe-Mamie Division of Neonatology Department
Case Presentation for the Course in Clinical Nutrition GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction Dr. med. Chantal Cripe-Mamie Division of Neonatology Department
Body Composition in Very Preterm Infants During Their Hospital Stay
 Body Composition in Very Preterm Infants During Their Hospital Stay Nada Al-Theyab Bachelor degree of Applied Medical Science (Nutrition and Dietetics) Master of Science (Nutrition) A thesis submitted
Body Composition in Very Preterm Infants During Their Hospital Stay Nada Al-Theyab Bachelor degree of Applied Medical Science (Nutrition and Dietetics) Master of Science (Nutrition) A thesis submitted
Hazards and Benefits of Postnatal Steroids. David J. Burchfield, MD Professor and Chief, Neonatology University of Florida
 Hazards and Benefits of Postnatal Steroids David J. Burchfield, MD Professor and Chief, Neonatology University of Florida Disclosures I have no financial affiliations or relationships to disclose. I will
Hazards and Benefits of Postnatal Steroids David J. Burchfield, MD Professor and Chief, Neonatology University of Florida Disclosures I have no financial affiliations or relationships to disclose. I will
Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines
 Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines Nutrition Committee March 2018 Overall Aim 2 Provision of appropriate nutrition to neonates in a timely and safe manner to facilitate adequate growth and development
Neonatal Nutrition Management Guidelines Nutrition Committee March 2018 Overall Aim 2 Provision of appropriate nutrition to neonates in a timely and safe manner to facilitate adequate growth and development
Working group reports: evaluation of the evidence to support practice guidelines for nutritional care of preterm infants the Pre-B Project 1 4
 AJCN. First published ahead of print January 20, 2016 as doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.117309. Working group reports: evaluation of the evidence to support practice guidelines for nutritional care of preterm infants
AJCN. First published ahead of print January 20, 2016 as doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.117309. Working group reports: evaluation of the evidence to support practice guidelines for nutritional care of preterm infants
Satellite Symposium. Sponsored by
 Satellite Symposium Sponsored by Management of fluids and electrolytes in the preterm infant in the first week of life Pam Cairns St Michaels Hospital Bristol Healthy, term, breast fed babies Limited intake
Satellite Symposium Sponsored by Management of fluids and electrolytes in the preterm infant in the first week of life Pam Cairns St Michaels Hospital Bristol Healthy, term, breast fed babies Limited intake
Update on mangement of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Dr. Trinh Thi Thu Ha
 Update on mangement of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants Dr. Trinh Thi Thu Ha Outline 1. Overview of PDA 2. Timing of screening PDA? 3. When to treat PDA? Timing of ductal closure Prenatal
Update on mangement of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants Dr. Trinh Thi Thu Ha Outline 1. Overview of PDA 2. Timing of screening PDA? 3. When to treat PDA? Timing of ductal closure Prenatal
Is It Possible to Prevent Necrotizing Enterocolitis?
 Is It Possible to Prevent Necrotizing Enterocolitis? Ravi Mangal Patel, MD MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA @institutopgg @ravimpatelmd Disclosures
Is It Possible to Prevent Necrotizing Enterocolitis? Ravi Mangal Patel, MD MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA @institutopgg @ravimpatelmd Disclosures
1 University of Kansas School of Medicine-Wichita, Department of Pediatrics 2 Wesley Medical Center, Department of Neonatology
 Impact of on Very Low Birth Weight Infants Siddharthan Sivamurthy, M.D. 1, Carolyn R. Ahlers-Schmidt, Ph.D. 1, Katherine S. Williams, M.Ed. 1, Jared Shaw 2, Paula Delmore, M.S.N. 2, Barry T. Bloom, M.D.
Impact of on Very Low Birth Weight Infants Siddharthan Sivamurthy, M.D. 1, Carolyn R. Ahlers-Schmidt, Ph.D. 1, Katherine S. Williams, M.Ed. 1, Jared Shaw 2, Paula Delmore, M.S.N. 2, Barry T. Bloom, M.D.
Welsh Neonatal Network
 Welsh Neonatal Network Clinical Guideline: All Wales Enteral Feeding Guideline for Preterm Infants Authors: Isabel Fraser, Paediatric Dietitian, CAVUHB Jo Males, Paediatric Dietitian, ABUHB Kate Harrod-Wild,
Welsh Neonatal Network Clinical Guideline: All Wales Enteral Feeding Guideline for Preterm Infants Authors: Isabel Fraser, Paediatric Dietitian, CAVUHB Jo Males, Paediatric Dietitian, ABUHB Kate Harrod-Wild,
Protein Needs of Preterm Infants: Why Are They So Difficult to Meet?
 Protein in the Feeding of Preterm Infants Bhatia J, Shamir R, Vandenplas Y (eds): Protein in Neonatal and Infant Nutrition: Recent Updates. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 86, pp 121 128, (DOI: 10.1159/000442732
Protein in the Feeding of Preterm Infants Bhatia J, Shamir R, Vandenplas Y (eds): Protein in Neonatal and Infant Nutrition: Recent Updates. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 86, pp 121 128, (DOI: 10.1159/000442732
11/4/10 SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP SAM: PREVENT MALNUTRITION 200. Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure
 Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Human Milk for Preterm Infants and Fortification
 Protein in the Feeding of Preterm Infants Bhatia J, Shamir R, Vandenplas Y (eds): Protein in Neonatal and Infant Nutrition: Recent Updates. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 86, pp 109 119, (DOI: 10.1159/000442730)
Protein in the Feeding of Preterm Infants Bhatia J, Shamir R, Vandenplas Y (eds): Protein in Neonatal and Infant Nutrition: Recent Updates. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 86, pp 109 119, (DOI: 10.1159/000442730)
NICU Sodium Administration to Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants: Relationships with Recommendations and Growth
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Open Access Master's Theses 2013 NICU Sodium Administration to Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants: Relationships with Recommendations and Growth Donna Kelly
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Open Access Master's Theses 2013 NICU Sodium Administration to Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants: Relationships with Recommendations and Growth Donna Kelly
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS IN THE PRETERM INFANT EVIDENCE FOR & AGAINST TREATMENT
 PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS IN THE PRETERM INFANT EVIDENCE FOR & AGAINST TREATMENT Dr. Youssef Abou Zanouna, FRCPI, FACC Consultant Pediatric Cardiologist King Fahd Military Medical Complex Dhahran Introduction
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS IN THE PRETERM INFANT EVIDENCE FOR & AGAINST TREATMENT Dr. Youssef Abou Zanouna, FRCPI, FACC Consultant Pediatric Cardiologist King Fahd Military Medical Complex Dhahran Introduction
New Ideas in the Nutrition of the ELBW Infant. Reese H Clark, MD
 New Ideas in the Nutrition of the ELBW Infant Reese H Clark, MD 1 DISCLOSURES I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflicts of interest to resolve. I will not discuss any unapproved
New Ideas in the Nutrition of the ELBW Infant Reese H Clark, MD 1 DISCLOSURES I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflicts of interest to resolve. I will not discuss any unapproved
Early and aggressive nutritional strategy (parenteral and enteral) decreases postnatal growth failure in very low birth weight infants
 (2006) 26, 436 442 r 2006 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 0743-8346/06 $30 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early and aggressive nutritional strategy (parenteral and enteral) decreases postnatal
(2006) 26, 436 442 r 2006 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 0743-8346/06 $30 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early and aggressive nutritional strategy (parenteral and enteral) decreases postnatal
Macronutrients and Development. Dr Julian Eason Chair NICU Corniche Hospital, Abu Dhabi
 Macronutrients and Development Dr Julian Eason Chair NICU Corniche Hospital, Abu Dhabi Corniche Hospital 64 Bed NICU 8000 deliveries Tertiary referral for Fetal medicine and High Risk Maternity 1000 NICU
Macronutrients and Development Dr Julian Eason Chair NICU Corniche Hospital, Abu Dhabi Corniche Hospital 64 Bed NICU 8000 deliveries Tertiary referral for Fetal medicine and High Risk Maternity 1000 NICU
A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial of Olive Oil Added to Human Breast Milk for Weight Gaining in Very Low Birth Weight Infants
 A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial of Olive Oil Added to Human Breast Milk for Weight Gaining in Very Low Birth Weight Infants Elaheh Amini; M.D.,2, Mamak Shariat; M.D.,2, Fatemeh Nayeri; M.D.,2, Firuzeh
A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial of Olive Oil Added to Human Breast Milk for Weight Gaining in Very Low Birth Weight Infants Elaheh Amini; M.D.,2, Mamak Shariat; M.D.,2, Fatemeh Nayeri; M.D.,2, Firuzeh
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Jeong et al. BMC Pediatrics (2016) 16:113 DOI /s
 Jeong et al. BMC Pediatrics (2016) 16:113 DOI 10.1186/s12887-016-0648-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The successful accomplishment of nutritional and clinical outcomes via the implementation of a multidisciplinary
Jeong et al. BMC Pediatrics (2016) 16:113 DOI 10.1186/s12887-016-0648-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The successful accomplishment of nutritional and clinical outcomes via the implementation of a multidisciplinary
NUTRITION and. Child Growth & Development. Washington, DC May 2-3, Kay Dewey. UC-Davis and Alive & Thrive
 Clean, Fed & Nurtured: Joining forces to promote child growth and development NUTRITION and Child Growth & Development Washington, DC May 2-3, 2013 Kay Dewey UC-Davis and Alive & Thrive Nutrition Basics
Clean, Fed & Nurtured: Joining forces to promote child growth and development NUTRITION and Child Growth & Development Washington, DC May 2-3, 2013 Kay Dewey UC-Davis and Alive & Thrive Nutrition Basics
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES
 INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY
 INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
Short-Term Outcome Of Different Treatment Modalities Of Patent Ductus Arteriosus In Preterm Infants. Five Years Experiences In Qatar
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 7 Number 2 Short-Term Outcome Of Different Treatment Modalities Of Patent Ductus Arteriosus In Preterm Infants. Five Years Experiences In
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 7 Number 2 Short-Term Outcome Of Different Treatment Modalities Of Patent Ductus Arteriosus In Preterm Infants. Five Years Experiences In
Are Enteral Intakes of Protein, Lipid, Carbohydrate, Energy, Calcium, and Phosphorus in VLBW Preterm Infants Meeting Current Expert Recommendations?
 Are Enteral Intakes of Protein, Lipid, Carbohydrate, Energy, Calcium, and Phosphorus in VLBW Preterm Infants Meeting Current Expert Recommendations? by Dawn Ving Yan Ng A thesis submitted in conformity
Are Enteral Intakes of Protein, Lipid, Carbohydrate, Energy, Calcium, and Phosphorus in VLBW Preterm Infants Meeting Current Expert Recommendations? by Dawn Ving Yan Ng A thesis submitted in conformity
Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant. J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014
 Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014 DISCLOSURES Dr. Lorenz has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict
Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014 DISCLOSURES Dr. Lorenz has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict
The gam. me of goose. Postma 2015 Lancet 385:
 3 Congreso Argentin node Neonatologia Buenos Aeres 1_3 July 2016 Nutrition and Bronchopulmonary dysplasia J Rigo MD PhD AN ND V Rigo MD PHD University of Liège, CHU de Liège, Belgium The gam me of goose
3 Congreso Argentin node Neonatologia Buenos Aeres 1_3 July 2016 Nutrition and Bronchopulmonary dysplasia J Rigo MD PhD AN ND V Rigo MD PHD University of Liège, CHU de Liège, Belgium The gam me of goose
Timing and tempo of first year growth in relation to cardiovascular and metabolic risk profile in early adulthood
 Note: for non-commercial purposes only Timing and tempo of first year growth in relation to cardiovascular and metabolic risk profile in early adulthood Anita Hokken-Koelega Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology
Note: for non-commercial purposes only Timing and tempo of first year growth in relation to cardiovascular and metabolic risk profile in early adulthood Anita Hokken-Koelega Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology
Dr Faeza Soobadar Paediatrician/Neonatologist SSRNH NICU
 An early start to life The Preterm Baby.. Dr Faeza Soobadar Paediatrician/Neonatologist SSRNH NICU 1 Definitions (1) Term 37-41 +6 wks Post-Term 42 wks Preterm
An early start to life The Preterm Baby.. Dr Faeza Soobadar Paediatrician/Neonatologist SSRNH NICU 1 Definitions (1) Term 37-41 +6 wks Post-Term 42 wks Preterm
By: Armend Lokku Supervisor: Dr. Lucia Mirea. Maternal-Infant Care Research Center, Mount Sinai Hospital
 By: Armend Lokku Supervisor: Dr. Lucia Mirea Maternal-Infant Care Research Center, Mount Sinai Hospital Background My practicum placement was at the Maternal-Infant Care Research Center (MiCare) at Mount
By: Armend Lokku Supervisor: Dr. Lucia Mirea Maternal-Infant Care Research Center, Mount Sinai Hospital Background My practicum placement was at the Maternal-Infant Care Research Center (MiCare) at Mount
Programming of NCDs in Preterm Infants Focus on Growth
 Note: for non-commercial purposes only Power of Programming 13 th Oct 2016 Programming of NCDs in Preterm Infants Focus on Growth Ken Ong Programme Leader MRC Epidemiology Unit, IMS, University of Cambridge,
Note: for non-commercial purposes only Power of Programming 13 th Oct 2016 Programming of NCDs in Preterm Infants Focus on Growth Ken Ong Programme Leader MRC Epidemiology Unit, IMS, University of Cambridge,
RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition
 RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition A Strong Beginning Mindy Morris, DNP, NNP-BC, CNS Extremely Low Birth Weight Program Coordinator Objectives Understand the challenges associated with the
RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition A Strong Beginning Mindy Morris, DNP, NNP-BC, CNS Extremely Low Birth Weight Program Coordinator Objectives Understand the challenges associated with the
Is NEC requiring surgery precipitated by a change in feeds? Observations from 50 consecutive cases. David Burge SIGNEC September 2015
 Is NEC requiring surgery precipitated by a change in feeds? Observations from 50 consecutive cases. David Burge SIGNEC September 2015 Clinical series Specific cases Other scenarios Published experience
Is NEC requiring surgery precipitated by a change in feeds? Observations from 50 consecutive cases. David Burge SIGNEC September 2015 Clinical series Specific cases Other scenarios Published experience
WOMEN S AND INFANT HEALTH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 WOMEN S AND INFANT HEALTH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES SUBJECT/TITLE: Post Discharge Preterm Formula: Neonates Draft June 19, 2009 DATE ESTABLISHED: DATE REVISED: NUMBER: PAGE: 1 of 11 PURPOSE To enhance
WOMEN S AND INFANT HEALTH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES SUBJECT/TITLE: Post Discharge Preterm Formula: Neonates Draft June 19, 2009 DATE ESTABLISHED: DATE REVISED: NUMBER: PAGE: 1 of 11 PURPOSE To enhance
What can we learn from the clinical studies in infants (on thickeners)?
 What can we learn from the clinical studies in infants (on thickeners)? Dominique Turck Member of the FAF WG Re-evaluation of FA in foods for infants below 16 weeks of age FA Stakeholders Workshop 30 November
What can we learn from the clinical studies in infants (on thickeners)? Dominique Turck Member of the FAF WG Re-evaluation of FA in foods for infants below 16 weeks of age FA Stakeholders Workshop 30 November
The health benefits of human milk for all infants, including those born extremely premature, have been increasingly
 An Exclusively Human Milk-Based Diet Is Associated with a Lower Rate of Necrotizing Enterocolitis than a Diet of Human Milk and Bovine Milk-Based Products Sandra Sullivan, MD, Richard J. Schanler, MD,
An Exclusively Human Milk-Based Diet Is Associated with a Lower Rate of Necrotizing Enterocolitis than a Diet of Human Milk and Bovine Milk-Based Products Sandra Sullivan, MD, Richard J. Schanler, MD,
11/4/10. Making Sense of Infant Formulas, Milk Fortifiers and Additives. Components of infant formula. Goals of Growth.
 Components of infant formula Making Sense of Infant Formulas, Milk Fortifiers and Additives Jae Kim, MD, PhD UCSD Medical Center Division of Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology,
Components of infant formula Making Sense of Infant Formulas, Milk Fortifiers and Additives Jae Kim, MD, PhD UCSD Medical Center Division of Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology,
Melinda Elliott, MD FAAP Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group
 Melinda Elliott, MD FAAP Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Disclosures I have had no disclosures August
Melinda Elliott, MD FAAP Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Disclosures I have had no disclosures August
2015 Prolacta Bioscience
 Housekeeping Items 1 Presentation will be available on-demand http://www.prolacta.com/webinars/feeding-protocols 2 Turn up your speaker volume 3 Use the Ask a Question feature 4 Use the full screen feature
Housekeeping Items 1 Presentation will be available on-demand http://www.prolacta.com/webinars/feeding-protocols 2 Turn up your speaker volume 3 Use the Ask a Question feature 4 Use the full screen feature
11/21/2016. Panel. Compelling Evidence for Nursing Advocates for an Exclusive Human Milk Diet (EHMD) in the NICU. NANN Annual Education Conference
 Compelling Evidence for Nursing Advocates for an Exclusive Human Milk Diet (EHMD) in the NICU NANN Annual Education Conference Terry S. Johnson, APN, NNP-BC, CLEC, ASPPS, MN, CE 2 Panel TERRY JOHNSON,
Compelling Evidence for Nursing Advocates for an Exclusive Human Milk Diet (EHMD) in the NICU NANN Annual Education Conference Terry S. Johnson, APN, NNP-BC, CLEC, ASPPS, MN, CE 2 Panel TERRY JOHNSON,
Minimal Enteral Nutrition
 Abstract Minimal Enteral Nutrition Although parenteral nutrition has been used widely in the management of sick very low birth weight infants, a smooth transition to the enteral route is most desirable.
Abstract Minimal Enteral Nutrition Although parenteral nutrition has been used widely in the management of sick very low birth weight infants, a smooth transition to the enteral route is most desirable.
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING. Quak Seng Hock
 SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
Babies 1500g. Caffeine citrate. Sodium Acid Phosphate (1mmol/ml) Ferrous Fumarate (Galfer 140mg/5ml) Infloran. Abidec BMF
 Babies 1500g Infloran Caffeine citrate BMF Sodium Acid Phosphate (1mmol/ml) Abidec Ferrous Fumarate (Galfer 140mg/5ml) Dose Half capsule BD 10mg/kg once daily (write as caffeine citrate) 2% BMF each feed
Babies 1500g Infloran Caffeine citrate BMF Sodium Acid Phosphate (1mmol/ml) Abidec Ferrous Fumarate (Galfer 140mg/5ml) Dose Half capsule BD 10mg/kg once daily (write as caffeine citrate) 2% BMF each feed
CHILDREN: NUTRITIONALS Prescription Required Provided by the Wisconsin WIC Program to Children (1 through 4 Years of Age)
 P-40077C (03/2016) CHILDREN: NUTRITIONALS Prescription Required Provided by the Wisconsin WIC Program to Children (1 through 4 Years of Age) A Prescription, for treatment of a diagnosed medical condition,
P-40077C (03/2016) CHILDREN: NUTRITIONALS Prescription Required Provided by the Wisconsin WIC Program to Children (1 through 4 Years of Age) A Prescription, for treatment of a diagnosed medical condition,
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant. Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW infants
 Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
SAMPLE. V.12.1 Special Report: Very Low Birthweight Neonates. I. Introduction
 I. Introduction V.12.1 Special Report: Very Low Birthweight Neonates The delivery of a very low birth weight infant continues to present many challenges to families and health care providers in spite of
I. Introduction V.12.1 Special Report: Very Low Birthweight Neonates The delivery of a very low birth weight infant continues to present many challenges to families and health care providers in spite of
Supporting improved nutrition for appropriate growth and improved long-term health outcomes
 Supporting improved nutrition for appropriate growth and improved long-term health outcomes ZTC831/07/2015 The first 1000 days are a critical period for growth and development Achieving optimal nutrition
Supporting improved nutrition for appropriate growth and improved long-term health outcomes ZTC831/07/2015 The first 1000 days are a critical period for growth and development Achieving optimal nutrition
Nutrition Management in GI Diseases
 Nutrition Management in GI Diseases Aryono Hendarto MD Nutrition & Metabolic Diseases Division Department of Child Health Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital University of Indonesia 1 Patient s Care 1. Drugs 2.
Nutrition Management in GI Diseases Aryono Hendarto MD Nutrition & Metabolic Diseases Division Department of Child Health Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital University of Indonesia 1 Patient s Care 1. Drugs 2.
Carlo Agostoni Fondazione IRCCS Department of Maternal and Pediatric Sciences University of Milan, Italy
 Carlo Agostoni Fondazione IRCCS Department of Maternal and Pediatric Sciences University of Milan, Italy Energy Protein Fat quality docosahexaenoic acid Micronutrients Vitamin D Dieting during lactation?
Carlo Agostoni Fondazione IRCCS Department of Maternal and Pediatric Sciences University of Milan, Italy Energy Protein Fat quality docosahexaenoic acid Micronutrients Vitamin D Dieting during lactation?
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University
 ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
Strategy For Reaching Optimal Growth and Development of Preterm Infants. Dr. dr. Rinawati Rohsiswatmo, Sp.A(K)
 Strategy For Reaching Optimal Growth and Development of Preterm Infants Dr. dr. Rinawati Rohsiswatmo, Sp.A(K) Premature Birth before reaching 37 weeks ' gestation. Incidence in Indonesia was 15.5% 2/3
Strategy For Reaching Optimal Growth and Development of Preterm Infants Dr. dr. Rinawati Rohsiswatmo, Sp.A(K) Premature Birth before reaching 37 weeks ' gestation. Incidence in Indonesia was 15.5% 2/3
Parenteral nutrition on growth of low birth weight infants.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (7): 3040-3047 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Parenteral nutrition on growth of low birth weight infants. Qiaoling Wu #, Xin Yuan #, Shaofeng Wang, Xia Li, Bingjuan Han,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (7): 3040-3047 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Parenteral nutrition on growth of low birth weight infants. Qiaoling Wu #, Xin Yuan #, Shaofeng Wang, Xia Li, Bingjuan Han,
