Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant. J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014
|
|
|
- Kathleen Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014
2 DISCLOSURES Dr. Lorenz has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interests to resolve. Dr. Lorenz has disclosed that his presentation involves discussion of the off-label uses of insulin and albuterol.
3 OUTLINE Briefly review functional limitations of the immature kidney Discuss challenges of early fluid, electrolyte, and nutritional management of the extremely preterm infant
4 RENAL IMMATURITY Decreased GFR/body wt or surface area limited ability to excrete Na load: PT FT < adult limited ability to excrete water load: PT < FT < adult Decreased proximal and distal tubular capacity to conserve Na in PT increased urinary Na loss decreased ability to conserve Na: PT < FT adult late onset hyponatremia in the PT
5 RENAL IMMATURITY Decreased capacity of the distal tubule to secrete potassium limited ability to excrete K load Decreased capacity of the proximal tubule to reabsorb HCO3 and decreased distal tubular capacity to secrete H + : PT < FT < adult mild, anion gap nl metabolic acidosis in PT with usual intake
6 RENAL IMMATURITY Decreased urine concentrating capacity: 500 mosm/l in PT v 600 in FT v 1500 in adult limited ability to conserve free water Minimally decreased urine diluting capacity in PT: < 75 Osm/L in PT v 50 Osm/L in FT & adult little effect on ability of the PT to secrete a water load
7 Challenges of F&E Management of the Extremely Preterm infant Insensible water loss (IWL) Postnatal changes in body water and electrolytes Phases of postnatal F&E adaptation
8 Insensible Water Loss The major route of water loss in the early life in the extremely preterm infant Not under feed back control Largely a function of environmental humidity, gestational & postnatal age, antenatal steroid exposure (ANS) Highly variable Very little data < 26 weeks GA; none < 24 weeks
9 TEWL v Relative Humidity 19 healthy, AGA term infants within the first 30 h of life Environment: Incubator T amb were maintained within narrow limits to maintain T R C. Relative humidity varied TEWL measured from the intrascapular skin surface using the water vapor pressure gradient method Hammarlund K et al. Acta Paediatr Scand 1977
10 TEWL v Relative Humidity Hammarlund K et al. Acta Paediatr Scand 1977; 66:553
11 TEWL v Gestational & Postnatal Age 43 healthy, AGA infants wk GA (n = 1-11 at each wk of gestation) within the first 24 h of life None exposed to ANS Environment: Incubator w/ T amb were maintained within narrow limits to maintain T R C. Relative humidity 50% TEWL calculated from measurement of water vapor pressure gradient at three skin surface sites using an equation derived from the evaporation rate at 19 sites weighted for proportion of body surface area represented by each site Hammarlund K et al. Acta Paediatr Scand 1983
12 TEWL v Gestational Age ml/kg/day respiratory IWL depending on inspired humidity and RR n = 9. Data from Hammarlund et al. Acta Paediatr Scand 1983
13 TEWL at wk v Postnatal Age ml/kg/day respiratory IWL depending on inspired humidity and RR Data from Hammarlund et al. Acta Paediatr Scand 1983
14 Calculated IWL & Antenatal Steroids Retrospective review of 30 AGA neonates < 1000g 16 received prenatal steroids and 14 did not at the discretion of OB (before 1994 NIH Consensus Statement) Fluid intake managed to allow 4% wt loss/day with a maximum loss of 15-20% in the first week Groups similar except for prenatal steroid exposure IWL calculated = total fluid intake fluid output + change in wt (g) Omar SA et al. Pediatr 1999
15 Calculated IWL & Antenatal Steroids Omar SA et al. Pediatr 1999
16 TEWL at wk with ANS Exposure 13 AGA infants 24 (n=3) and 25 (n=10) wk GA on IMV 11 exposed to ANS Environment: Incubator T amb were maintained within narrow limits to maintain T R C. Relative humidity 50% TEWL calculated from measurement of water vapor pressure gradient at three skin surface sites Ågren J et al. Acta Paediatr 1998
17 TEWL at wk with ANS Exposure (ml/kg/day) age n mean ± SD 5-22 hr ± hr ± 59 3 days ± 59 7 days ± days 8 66 ± 22 Ågren J et al. Acta Paediatr 1998
18 Challenges in F&E Management of the Extremely Preterm infant Insensible water loss (IWL) Postnatal changes in body water and electrolytes Phases of postnatal F&E adaptation
19 Early Postnatal Changes in F & E Balance: WATER & SODIUM Decrease in Extracellular volume: Negative water balance: Loss of % of birth weight Sodium balance proportionate to water balance: Maintain serum [Na + ] mmol/l
20 Postnatal Weight Loss and Change 13 PT infants in ECW Volume median birth wt 1170 g; range g median GA 28 wk; range wk Fluid therapy managed to allow postnatal wt loss of as much as 10% of birth wt ECW volume (sucrose space) measured at < 12 hr of life & when > 5% of birth wt had been lost. Bauer K & Versmold H. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 1989: 360:37-42
21 Postnatal Weight Loss and Change in ECW Volume 1200 g/ml * * weight extracellular volume Bauer K & Versmold H. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 1989: 360: 37-42
22 Postnatal Decrease in ECW Volume is Physiologic It occurs in spite of large variation in water & sodium intake (Lorenz JM et al. J Pediatr 1982; Shaffer SG & Meade VM. J Pediatr 1989) It occurs even if caloric intake mitigates postnatal wt loss (Heimler R et al. J Pediatr 1993) When postnatal wt loss is regained, ECW volume per kg body wt remains stable at the new lower level (Singhi S et al. Indian J Med Res 1995) Attenuation of this decrease may be associated with increased morbidity (Bell & Acarregui. Cochrane Database of Sys Rev 2008; Costarino AT et al. J Pediatr 1992
23 Take home messages Contraction of the extracellular water space is physiologic Liberal v restricted fluid administration liberal fluid administration may allow higher caloric intake restricted fluid administration may decrease prevalence of co-morbidities requires vigilance for hypernatremia
24 Early Postnatal Changes in F&E Balance: POTASSIUM Internal balance: intracellular extracellular potassium shift in extremely preterm infants in the first hr of life External balance: negative during diuresis/natriuresis with contraction of the ECW space
25 External K Balance in the 1 st 72 hr of life 24 AGA male infants < 37 weeks GA w/urine output > 1ml/kg/hr x 24 hr: group wk (n = 9) group wk (n = 9) group wk (n = 6) Serum [K] via radial arterial catheter on DOL 1-3 Sato K et al. J Pediatr 1995;126:109
26 Magnitude of ICW ECW K SHIFT v GA during the first 24 hours of life ICF ECF shift = [(ECV birth - wt lost 24h ) x serum [K] 24h ] + (ECV birth x Serum [K] birth ) - (urine output/24 hr x urine [K]) Sato K et al. J Pediatr 1995;126:109
27 Serum [K] v Age in Very Preterm AGA Neonates 31 AGA ELBW infants 539 to 1000g (GAs weeks) No antenatal steroid exposure No exogenous potassium administered until serum [K] was normal & not rising and urine output was > 1 ml/kg/hr Lorenz et al J Pediatr 1997
28 Serum [K] v Age in wk GA Neonates Mean +/- SEM Mean =/- SEM Lorenz et al J Pediatr 1997
29 Effect of Antenatal Steroids on ICW ECW K shift in extremely preterm infants Retrospective review of 30 AGA neonates < 1000g 16 received prenatal steroids and 14 did not at the discretion of OB (before 1994 NIH Consensus Statement) Fluid intake managed to allow 4% wt loss/day with a maximum loss of 15-20% in the first week Groups similar except for prenatal steroid exposure K intake withheld until serum [K] normal and urine output > 1 ml/kg/hr Omar SA et al. Pediatr 2002; 106:561
30 Effect of Antenatal Steroids Potassium Balance Omar SA et al. Pediatr 2002; 106:561
31 Effect of Antenatal Steroids on ICW ECW potassium shift in extremely preterm infants Omar SA et al. Pediatr 2002; 106:561
32 Take home messages Although the pathophysiology of ICW ECW potassium shift in extremely preterm infants in the first hr of life is poorly understood, it is very likely maladaptive ANS decreases the risk of non-oliguric hyperkalemia Exogenous potassium should be withheld until serum [K] is normal and not rising and urine output is > 1 ml/kg/hr A decrease in serum [K] can be anticipated with the onset of postnatal diuresis/natriuresis
33 Challenges in F&E Management of the Extremely Preterm infant Insensible water loss (IWL) Postnatal changes in body water and electrolytes Phases of postnatal F&E adaptation
34 Postnatal Renal, F & E Adaptation Phase Antediuretic Diuretic/ Natriuretic Homeostatic Age Birth - 2 days 1-5 days After 2-5 days Urine Output Na + Excretion K + Excretion Low Minimal Minimal Abrupt Abrupt Abrupt then intake then intake then intake H 2 O balance Na + balance K + balance <Intake - IWL Neg Neg Markedly Neg Markedly Neg Markedly Neg Na + balance 0,then+ w/ growth 0,then+ w/ growth ECV (ml) Stable or Abrupt 1. Na + balance 2. w/ growth
35 Postnatal Renal, F & E Adaptation Phase Antediuretic Diuretic/ Natriuretic Homeostatic Water intake IWL to allow 2-5 % wt loss per day up to total of 8-15 % Volume to optimize caloric intake without fluid retention Sodium intake None Begin when serum [Na + ] is stable with weight loss or ing; as necessary to maintain serum [Na + ] wnl Approximate Na + loss growth allowance. Na + requirement will be inversely proportional to gestational age Potassium intake None 1-3 mmol/kg/d if serum [K + ] < 5-6 mmol/l & not ing 2 3 mmol/kg/d to maintain serum [K + ] wnl
36 Postnatal Renal, F & E Adaptation: Common Problems Antediuretic Diuretic/Natriuretic Homeostatic Water intoxication with unexpectedly low IWL Hypernatremia with unexpectedly high IWL Hyperkalemia Hypernatremia with an excessive rate of weight loss Hyperglycemia Water and sodium retention with PDA or CLD Water and sodium depletion with or without hyponatremia Hypokalemia
37 A System for Managing F&E Rx Estimate what changes in balances are appropriate Monitor parameters q 8-12 hr to estimate actual balances which result Estimate the intakes to the necessary to achieve these balances based on the range of outputs anticipated Administer these intakes
38 Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm infant Glucose Amino acids Intralipids Enteral feeding
39 Why Early Nutrition for Extremely Preterm Infant? Poor postnatal growth is common among extreme preterm infants. Poor postnatal growth may have long-term consequences, e.g. short stature, impaired neurodevelopment. Poor postnatal growth has been attributed to protein & energy deficits that accrue in the 1 st weeks of life. It was hypothesized that early protein intake may improve growth
40 Glucose Requirement/Tolerance Target glucose administration rate minimum necessary to prevent hypoglycemia maximum tolerated w/o hyperglycemia to conserve limited energy stores and minimize catabolism Glucose Utilization Rate Minimal Metabolic Rate During the First Week of Life 60 ml D10W/kg/24 hr provides 120 ml D10W/kg/24 hr provides 4-7 mg/kg/min kcal/kg/24 hr 3.5 mg glucose/kg/min 20 kcal/kg/day 7.1 glucose/kg/min 41 kcal/kg/24 hr
41 Importance of AA Administration protein balance = g /kg/day 26 weeks: protein balance = g /kg/day Denne SC & Poindexter BB Semin Pernatol 2007
42 Early Amino Acid Administration Observational studies suggest preserving protein stores and promoting protein accretion are critical to improved growth outcomes in extremely preterm infants Providing amino acids, even with a low energy intake, increases endogenous protein by increasing protein synthesis, thus increasing protein balance. Even 1.0 to 1.5 g/kg/day of parenteral amino acids and 30 to 45 kcal/kg/day can change protein balance from negative to zero or somewhat positive. (Van Doudoever JB et al. J Pediatr 1995; Rivera A et al. Pediatr Res 1993) Greater calorie intake reduces proteolysis and a larger intake of both protein and calories leads to anabolism. (Thureen PJ. Pediatr Res 2003)
43 Protein Balance with Early AA Administration in ELBW infants Van Douover 1993 Rivera 1995 Thureen 2003 From Deene SC & Boindexter BB Semin Perinatol 2007
44 Early Amino Acid Administration Prompt provision of parenteral amino acids is recommended for ELBW infants (AAP Nutrition Handbook, 2009): Initiate g/kg/d within hours of birth Advance to 4.0 g/kg/d by g/kg/d steps [approx. 4.0 g/kg/day is required to match fetal protein accretion] However, randomized controlled trials have been too small to confirm long-term safety of early protein intake at this level, especially for extremely preterm infants. Over an more extended period, adequate provision of energy (1 g N:100 Kcal) is probably necessary to avoid toxicity. Provision of energy and protein intakes that promote anabolism require increased phosphate and protein intake to prevent hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, and hypercalcemia (Molto SJ. Clin Nutr 2013).? Optimal amino acid fluid composition
45 Take home messages A minimum glucose administration rate of 6 mg/kg/min is recommended Initiation of parenteral AA shortly after birth is recommended - data are insufficient to specify an optimal, safe rate of administration 1.0 to 1.5 g/kg/day of parenteral amino acids and 30 kcal/kg/day can change protein balance from negative to zero or somewhat positive approximately 4.0 g/kg/day is required to match fetal protein accretion
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES
 INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants. Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital
 Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Satellite Symposium. Sponsored by
 Satellite Symposium Sponsored by Management of fluids and electrolytes in the preterm infant in the first week of life Pam Cairns St Michaels Hospital Bristol Healthy, term, breast fed babies Limited intake
Satellite Symposium Sponsored by Management of fluids and electrolytes in the preterm infant in the first week of life Pam Cairns St Michaels Hospital Bristol Healthy, term, breast fed babies Limited intake
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY
 INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD
 Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 27 Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance 1 Body Fluids Intracellular fluid compartment All fluids inside cells of body About 40% of total body weight Extracellular fluid compartment All fluids
Chapter 27 Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance 1 Body Fluids Intracellular fluid compartment All fluids inside cells of body About 40% of total body weight Extracellular fluid compartment All fluids
H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance
 H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance Body Fluids Intracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid inside the cells 40% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid outside of cells 20% of body
H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance Body Fluids Intracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid inside the cells 40% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid outside of cells 20% of body
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants
 Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM
 WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant. Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW infants
 Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview
 RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PBL MBBS IV VJ. Temple 1 What is Renal Tubular
RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PBL MBBS IV VJ. Temple 1 What is Renal Tubular
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE
 Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Diuretic Use in Neonates
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Diuretic Use in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/ Diuretics
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Diuretic Use in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/ Diuretics
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS. David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA
 HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi
 Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
 NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance
 25 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully
25 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + )
 Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
Acid-Base Tutorial 2/10/2014. Overview. Physiology (2) Physiology (1)
 Overview Acid-Base Tutorial Nicola Barlow Physiology Buffering systems Control mechanisms Laboratory assessment of acid-base Disorders of H + ion homeostasis Respiratory acidosis Metabolic acidosis Respiratory
Overview Acid-Base Tutorial Nicola Barlow Physiology Buffering systems Control mechanisms Laboratory assessment of acid-base Disorders of H + ion homeostasis Respiratory acidosis Metabolic acidosis Respiratory
Management of Acute Kidney Injury in the Neonate. Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami Miller School of Medicine / Holtz Children s Hospital
 Management of Acute Kidney Injury in the Neonate Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami Miller School of Medicine / Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Summarize the dilemmas in diagnosing & recognizing
Management of Acute Kidney Injury in the Neonate Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami Miller School of Medicine / Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Summarize the dilemmas in diagnosing & recognizing
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION. Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140
 هللامسب Na regulation: Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140 meq\l. Na is important because: -It determines the volume of extracellular fluid : the more Na intake will expand extracellular
هللامسب Na regulation: Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140 meq\l. Na is important because: -It determines the volume of extracellular fluid : the more Na intake will expand extracellular
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance
 Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Author: Contact Name and Job Title.
 Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Author: Contact Name and Job Title of Fluid and Electrolytes in Neonates D2 (prev.d14) Version 3 : Dr. Ai May Lee,
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Author: Contact Name and Job Title of Fluid and Electrolytes in Neonates D2 (prev.d14) Version 3 : Dr. Ai May Lee,
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth. Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida
 Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
Chapter 21. Diuretic Agents. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Acid Base Balance. Chapter 26 Balance. ph Imbalances. Acid Base Balance. CO 2 and ph. Carbonic Acid. Part 2. Acid/Base Balance
 Acid Base Balance Chapter 26 Balance Part 2. Acid/Base Balance Precisely balances production and loss of hydrogen ions (ph) The body generates acids during normal metabolism, tends to reduce ph Kidneys:
Acid Base Balance Chapter 26 Balance Part 2. Acid/Base Balance Precisely balances production and loss of hydrogen ions (ph) The body generates acids during normal metabolism, tends to reduce ph Kidneys:
Fluids, Electrolytes and Nutrition
 B9 Fluids, Electrolytes and Nutrition Jacqui Hoffman, DNP, ARNP, NNP-BC NNP Track Coordinator; Clinical Assistant Professor College of Nursing, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL Neonatal Nurse Practitioner
B9 Fluids, Electrolytes and Nutrition Jacqui Hoffman, DNP, ARNP, NNP-BC NNP Track Coordinator; Clinical Assistant Professor College of Nursing, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL Neonatal Nurse Practitioner
Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ
 Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ Outline Refeeding Syndrome What is refeeding syndrome? What Electrolytes and minerals are involved? Who is at risk? How to manage
Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ Outline Refeeding Syndrome What is refeeding syndrome? What Electrolytes and minerals are involved? Who is at risk? How to manage
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Resuscitation of the Critically ill Foal
 Resuscitation of the Critically ill Foal Sick Cell Syndrome Foal: Wishful Warm Blood filly DOB: March 25 1 AM Admission Date: March 25 11:25 AM 10 hours old Wishful History Born at 1 AM on March 25 Foal
Resuscitation of the Critically ill Foal Sick Cell Syndrome Foal: Wishful Warm Blood filly DOB: March 25 1 AM Admission Date: March 25 11:25 AM 10 hours old Wishful History Born at 1 AM on March 25 Foal
Chapter 24 Water, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 24 Water, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Total body water for 150 lb. male = 40L 65% ICF 35% ECF 25% tissue fluid 8% blood plasma, lymph 2% transcellular fluid (CSF, synovial fluid) Water Movement
Chapter 24 Water, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Total body water for 150 lb. male = 40L 65% ICF 35% ECF 25% tissue fluid 8% blood plasma, lymph 2% transcellular fluid (CSF, synovial fluid) Water Movement
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari
![Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari](/thumbs/90/104323364.jpg) Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
TPN. Prof John Sinn. MBBS (Syd), D Paed, DCH, M Med(Clin Epi), FRACP. Consultant Neonatologist and Allergist
 TPN Prof John Sinn MBBS (Syd), D Paed, DCH, M Med(Clin Epi), FRACP Consultant Neonatologist and Allergist The University of Sydney The Children s Hospital, Westmead Royal North Shore Hospital Nutrition
TPN Prof John Sinn MBBS (Syd), D Paed, DCH, M Med(Clin Epi), FRACP Consultant Neonatologist and Allergist The University of Sydney The Children s Hospital, Westmead Royal North Shore Hospital Nutrition
4/15/2014. Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth. Improving early nutrition. Problem Identification
 Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
NATURAL HISTORY AND SURVIVAL OF PATIENTS WITH ASCITES. PATIENTS WHO DO NOT DEVELOP COMPLICATIONS HAVE MARKEDLY BETTER SURVIVAL THAN THOSE WHO DEVELOP
 PROGNOSIS Mortality rates as high as 18-30% are reported for hyponatremic patients. High mortality rates reflect the severity of underlying conditions and are not influenced by treatment of hyponatremia
PROGNOSIS Mortality rates as high as 18-30% are reported for hyponatremic patients. High mortality rates reflect the severity of underlying conditions and are not influenced by treatment of hyponatremia
BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD
 BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD 1. Extracellular space minutes 2. Intracellular space minutes to hours 3. Respiratory compensation 6 to 12 hours 4. Renal compensation hours, up to 2-3 days RENAL HYDROGEN SECRETION
BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD 1. Extracellular space minutes 2. Intracellular space minutes to hours 3. Respiratory compensation 6 to 12 hours 4. Renal compensation hours, up to 2-3 days RENAL HYDROGEN SECRETION
Nutritional Management of the Extremely Low Birth Weight Infant: An Evidence Based Clinical Practice Guideline
 UNLV Theses, Dissertations, Professional Papers, and Capstones 5-1-2012 Nutritional Management of the Extremely Low Birth Weight Infant: An Evidence Based Clinical Practice Guideline Dana J. Lunde University
UNLV Theses, Dissertations, Professional Papers, and Capstones 5-1-2012 Nutritional Management of the Extremely Low Birth Weight Infant: An Evidence Based Clinical Practice Guideline Dana J. Lunde University
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed
 DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
Overview. Fluid & Electrolyte Disorders. Water distribution. Introduction 5/10/2014
 Overview Fluid & Electrolyte Disorders Dr Nicola Barlow Clinical Biochemistry Department, City Hospital Introduction Fluid and electrolyte homeostasis Electrolyte disturbances Analytical parameters Methods
Overview Fluid & Electrolyte Disorders Dr Nicola Barlow Clinical Biochemistry Department, City Hospital Introduction Fluid and electrolyte homeostasis Electrolyte disturbances Analytical parameters Methods
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Technical University of Mombasa Faculty of Applied and Health Sciences
 Technical University of Mombasa Faculty of Applied and Health Sciences DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL SCIENCES UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES BMLS 12S -Regular
Technical University of Mombasa Faculty of Applied and Health Sciences DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL SCIENCES UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES BMLS 12S -Regular
Metabolic Alkalosis: Vomiting
 RENAL ANL) ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 213 Case 37 Metabolic Alkalosis: Vomiting Maria Cuervo is a 20-year-old philosophy major at a state university. When the "24-hour" stomach flu went around campus during
RENAL ANL) ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 213 Case 37 Metabolic Alkalosis: Vomiting Maria Cuervo is a 20-year-old philosophy major at a state university. When the "24-hour" stomach flu went around campus during
Symposium 3. Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life
 Symposium 3 Fl id d N t iti S t f th Fluid and Nutrition Support of the Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life Guidelines for the Provision of Amino Acids in the Preterm Infant During the First Week
Symposium 3 Fl id d N t iti S t f th Fluid and Nutrition Support of the Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life Guidelines for the Provision of Amino Acids in the Preterm Infant During the First Week
IV Fluids. I.V. Fluid Osmolarity Composition 0.9% NaCL (Normal Saline Solution, NSS) Uses/Clinical Considerations
 IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach
 Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
Preterm Dietary Supplements
 Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
MS1 Physiology Review of Na+, K+, H + /HCO 3. /Acid-base, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology
 MS1 Physiology Review of,, / /Acidbase, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology University of Florida College of Medicine Basic principles Proximal tubule Majority
MS1 Physiology Review of,, / /Acidbase, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology University of Florida College of Medicine Basic principles Proximal tubule Majority
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1
 Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Acid Base Balance. Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih. Clinical Chemistry Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih
 Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
1 University of Kansas School of Medicine-Wichita, Department of Pediatrics 2 Wesley Medical Center, Department of Neonatology
 Impact of on Very Low Birth Weight Infants Siddharthan Sivamurthy, M.D. 1, Carolyn R. Ahlers-Schmidt, Ph.D. 1, Katherine S. Williams, M.Ed. 1, Jared Shaw 2, Paula Delmore, M.S.N. 2, Barry T. Bloom, M.D.
Impact of on Very Low Birth Weight Infants Siddharthan Sivamurthy, M.D. 1, Carolyn R. Ahlers-Schmidt, Ph.D. 1, Katherine S. Williams, M.Ed. 1, Jared Shaw 2, Paula Delmore, M.S.N. 2, Barry T. Bloom, M.D.
IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA)
 IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION: PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING No clear definition in literature Permissive underfeeding definition prior to
IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION: PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING No clear definition in literature Permissive underfeeding definition prior to
BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation
 Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition
 RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition A Strong Beginning Mindy Morris, DNP, NNP-BC, CNS Extremely Low Birth Weight Program Coordinator Objectives Understand the challenges associated with the
RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition A Strong Beginning Mindy Morris, DNP, NNP-BC, CNS Extremely Low Birth Weight Program Coordinator Objectives Understand the challenges associated with the
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE
 NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
Disclaimer. Chapter 3 Disorder of Water, Electrolyte and Acid-base Professor A. S. Alhomida. Disorder of Water and Electrolyte
 Disclaimer King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry The texts, tables, figures and images contained in this course presentation (BCH 376) are not my own, they can be found on:
Disclaimer King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry The texts, tables, figures and images contained in this course presentation (BCH 376) are not my own, they can be found on:
Pathogenesis of Metabolic Acidosis in Preterm Infants
 Original Article Pathogenesis of Metabolic Acidosis in Preterm Infants DOI: IJNMR/2013/5233.1976 Acid Base Balance Section Christopher Geoffrey Alexander Aiken ABSTRACT Objective: To determine how the
Original Article Pathogenesis of Metabolic Acidosis in Preterm Infants DOI: IJNMR/2013/5233.1976 Acid Base Balance Section Christopher Geoffrey Alexander Aiken ABSTRACT Objective: To determine how the
Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick Neonatal Pharmacist
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition. in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT. Dzulfikar DLH. Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
 The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013 Cells form 4 basic tissue groups: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013 Cells form 4 basic tissue groups: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective
Salty Solutions or Salty Problems? Outline. Outline 29/04/2013
 Salty Solutions or Salty Problems? 18 th October 2012 Richard Seigne Anaesthetist 1 - Non fluid 40% T o t a l b o d y f l u i d 60% NaCl NaCl Intra-cellular fluid 2/3 KCl Interstitial fluid 3/4 of ECF
Salty Solutions or Salty Problems? 18 th October 2012 Richard Seigne Anaesthetist 1 - Non fluid 40% T o t a l b o d y f l u i d 60% NaCl NaCl Intra-cellular fluid 2/3 KCl Interstitial fluid 3/4 of ECF
CCRN Review - Renal. CCRN Review - Renal 10/16/2014. CCRN Review Renal. Sodium Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l
 CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
MSUD Dietetic Management Pathway
 MSUD Dietetic Management Pathway Presumptive positive screen for MSUD (symptomatic infant) Refer to Clinical Management Guidelines and Initial Clinical Referral Guidelines and Standards (www.bimdg.org)
MSUD Dietetic Management Pathway Presumptive positive screen for MSUD (symptomatic infant) Refer to Clinical Management Guidelines and Initial Clinical Referral Guidelines and Standards (www.bimdg.org)
** TMP mean page 340 in 12 th edition. Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2:
 QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
Physiology questions review
 Physiology questions review 1- The consumption of O2 by the kidney: a- decrease as blood flow increases b- regulated by erythropoiten c- remains constant as blood flow increase d- direct reflects the level
Physiology questions review 1- The consumption of O2 by the kidney: a- decrease as blood flow increases b- regulated by erythropoiten c- remains constant as blood flow increase d- direct reflects the level
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes
 Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only
 Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn 10% (ph 6), Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution
Aminosyn 10% (ph 6) Sulfite-Free AN AMINO ACID INJECTION Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Aminosyn 10% (ph 6), Sulfite-Free, (an amino acid injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution
Chapter 20 8/23/2016. Fluids and Electrolytes. Fluid (Water) Fluid (Water) (Cont.) Functions
 Chapter 20 Fluids and Electrolytes All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Fluid (Water) Functions Provides an extracellular transportation
Chapter 20 Fluids and Electrolytes All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Fluid (Water) Functions Provides an extracellular transportation
Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES
 Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES Body Water Content Water Balance: Normal 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 Metab Food Fluids Stool Breath Sweat Urine
Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES Body Water Content Water Balance: Normal 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 Metab Food Fluids Stool Breath Sweat Urine
Answers and Explanations
 Answers and Explanations 1. The answer is D [V B 4 b]. Distal K + secretion is decreased by factors that decrease the driving force for passive diffusion of K + across the luminal membrane. Because spironolactone
Answers and Explanations 1. The answer is D [V B 4 b]. Distal K + secretion is decreased by factors that decrease the driving force for passive diffusion of K + across the luminal membrane. Because spironolactone
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Electrolyte Disorders in ICU. Debashis Dhar
 Electrolyte Disorders in ICU Debashis Dhar INTRODUCTION Monovalent ions most important Na,K main cations and Cl &HCO - 3 main anions Mg,Ca & Phosphate are major divalent ions Normal Physiology Body tries
Electrolyte Disorders in ICU Debashis Dhar INTRODUCTION Monovalent ions most important Na,K main cations and Cl &HCO - 3 main anions Mg,Ca & Phosphate are major divalent ions Normal Physiology Body tries
Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).
![Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside). Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).](/thumbs/80/80478709.jpg) 1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
HYPOGLYCEMIA IN SICK PRETERM INFANTS AND THE THERAPEUTIC EFFECT OF 12.5% DEXTROSE IN WATER COMPARED WITH 10% DEXTROSE IN WATER
 HYPOGLYCEMIA IN SICK PRETERM INFANTS AND THE THERAPEUTIC EFFECT OF 12.5% DEXTROSE IN WATER COMPARED WITH 10% DEXTROSE IN WATER F. Nili * and M. Ghafuri Department of Pediatrics, Division of Neonatology,
HYPOGLYCEMIA IN SICK PRETERM INFANTS AND THE THERAPEUTIC EFFECT OF 12.5% DEXTROSE IN WATER COMPARED WITH 10% DEXTROSE IN WATER F. Nili * and M. Ghafuri Department of Pediatrics, Division of Neonatology,
Professor and Director. Children s Hospital of Richmond
 Evaluation of AKI in term and premature infants Timothy E. Bunchman Professor and Director Pediatric Nephrology & Transplantation Children s Hospital of Richmond Virginia Commonwealth Univ. School of Medicine
Evaluation of AKI in term and premature infants Timothy E. Bunchman Professor and Director Pediatric Nephrology & Transplantation Children s Hospital of Richmond Virginia Commonwealth Univ. School of Medicine
Bicarbonate in the NICU
 OMG Bicarbonate in the NICU A Useless Therapy? At first I thought I was going to have to refute the paper Then I got into it and thought: I m so confused Then I learned a lot HOPEFULLY I CAN LEARN YOU
OMG Bicarbonate in the NICU A Useless Therapy? At first I thought I was going to have to refute the paper Then I got into it and thought: I m so confused Then I learned a lot HOPEFULLY I CAN LEARN YOU
Volume and Electrolytes. Fluid and Electrolyte Management. Why 125ml? Question. Normal fluid requirement. Normal losses
 Volume and Electrolytes Fluid and Electrolyte Management Pre-existing deficits of excesses Ongoing losses or gains Ajai K. Malhotra, MD VCU School of Medicine 1 2 Question Why 125ml? Intern said so Chief
Volume and Electrolytes Fluid and Electrolyte Management Pre-existing deficits of excesses Ongoing losses or gains Ajai K. Malhotra, MD VCU School of Medicine 1 2 Question Why 125ml? Intern said so Chief
Neonatal Fluid Therapy Not my mother s physiology!!
 Neonatal Fluid Therapy Not my mother s physiology!! Physiologic Approach to Neonatal Fluid Therapy General principles of fluid balance Fetal physiology of fluid balance Neonatal physiology of fluid balance
Neonatal Fluid Therapy Not my mother s physiology!! Physiologic Approach to Neonatal Fluid Therapy General principles of fluid balance Fetal physiology of fluid balance Neonatal physiology of fluid balance
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
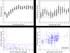 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Fluid and Electrolytes: Parenteral
 Article fluid & electrolytes Fluid and Electrolytes: Parenteral Fluid Therapy Kenneth B. Roberts, MD* Objectives After completing this article, readers should be able to: 1. Relate maintenance fluid and
Article fluid & electrolytes Fluid and Electrolytes: Parenteral Fluid Therapy Kenneth B. Roberts, MD* Objectives After completing this article, readers should be able to: 1. Relate maintenance fluid and
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL?
 HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital
 By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 November 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2013 May ; 83(5): 779 782. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.468. Need to quickly excrete K +? Turn off NCC Alicia A. McDonough 1 and
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2013 May ; 83(5): 779 782. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.468. Need to quickly excrete K +? Turn off NCC Alicia A. McDonough 1 and
Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function. GI Tract and Kidneys
 Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function GI Tract and Kidneys Australian and New Zealand Resuscitation Council Joint Guidelines Outline Emphasis on the infant - PICU Kidney Gastrointestinal
Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function GI Tract and Kidneys Australian and New Zealand Resuscitation Council Joint Guidelines Outline Emphasis on the infant - PICU Kidney Gastrointestinal
Fluids, Electrolytes, and Nutrition
 B9 Fluids, Electrolytes, and Nutrition Jacqui Hoffman, DNP, ARNP, NNP-BC NNP Track Coordinator, College of Nursing University of Florida, Gainesville, FL Neonatal Nurse Practitioner Pediatrix Medical Group,
B9 Fluids, Electrolytes, and Nutrition Jacqui Hoffman, DNP, ARNP, NNP-BC NNP Track Coordinator, College of Nursing University of Florida, Gainesville, FL Neonatal Nurse Practitioner Pediatrix Medical Group,
1. 09/07/16 Ch 1: Intro to Human A & P 1
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 09/07/16 Ch 1: Intro to Human A & P 1 2. 09/19/16 Ch 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance 5 i 1 09/19/16 Chapter 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 09/07/16 Ch 1: Intro to Human A & P 1 2. 09/19/16 Ch 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance 5 i 1 09/19/16 Chapter 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base
Hyponatremia in Heart Failure: why it is important and what should we do about it?
 Objectives Hyponatremia in Heart Failure: why it is important and what should we do about it? Pathophysiology of sodium and water retention in heart failure Hyponatremia in heart failure (mechanism and
Objectives Hyponatremia in Heart Failure: why it is important and what should we do about it? Pathophysiology of sodium and water retention in heart failure Hyponatremia in heart failure (mechanism and
Randomised controlled trial of postnatal sodium supplementation on body composition in 25 to 30 week gestational age infants
 F24 Section of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine, Imperial College School of Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, London W12 0NN G Hartnoll N Modi P Bétrémieux Correspondence to: Dr Neena Modi Email: nmodi@ic.ac.uk
F24 Section of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine, Imperial College School of Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, London W12 0NN G Hartnoll N Modi P Bétrémieux Correspondence to: Dr Neena Modi Email: nmodi@ic.ac.uk
Mannitol-induced Metabolic Alkalosis
 Electrolyte & Blood Pressure :, 00 ) Mannitolinduced Metabolic Alkalosis Kyung Pyo Kang, M.D., Sik Lee, M.D., Kyung Hoon Lee, M.D., and Sung Kyew Kang, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute
Electrolyte & Blood Pressure :, 00 ) Mannitolinduced Metabolic Alkalosis Kyung Pyo Kang, M.D., Sik Lee, M.D., Kyung Hoon Lee, M.D., and Sung Kyew Kang, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute
5/18/2017. Specific Electrolytes. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium
 Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
SOCM Fluids Electrolytes and Replacement Products PFN: SOMRXL09. Terminal Learning Objective. References. Hours: 2.0 Last updated: November 2015
 SOCM Fluids Electrolytes and Replacement Products PFN: SOMRXL09 Hours: 2.0 Last updated: November 2015 Slide 1 Terminal Learning Objective Action: Communicate knowledge of Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid
SOCM Fluids Electrolytes and Replacement Products PFN: SOMRXL09 Hours: 2.0 Last updated: November 2015 Slide 1 Terminal Learning Objective Action: Communicate knowledge of Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid
Inter Inter Pretation of Acid Base Disturbance in Critically ill Patients. By :-: Dr. Vinay Bhomia M.D.
 Inter Inter Pretation of Acid Base Disturbance in Critically ill Patients. By :-: Dr. Vinay Bhomia M.D. Normal Blood PH 7.35 to 7.45 Crucial importance to maintain homeostatic function of Body. Any Significant
Inter Inter Pretation of Acid Base Disturbance in Critically ill Patients. By :-: Dr. Vinay Bhomia M.D. Normal Blood PH 7.35 to 7.45 Crucial importance to maintain homeostatic function of Body. Any Significant
