South West Midlands Neonatal Network Parenteral Nutrition Guideline. May 2017
|
|
|
- Lydia Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 South West Milans Neonatal Network Parenteral Nutrition Guieline May 2017 Prouce for SWMNN by Dr Gemma Holer, Consultant Neonatologist, CH, Dr Gill Preston, Clinical Fellow, CH, Louise Whitticase, Lea Pharmacist, CH, Sara Clarke, Senior Specialist Neonatal Dietitian, SWMNN with contributions from SWMNN Nutrition Group.
2 1. Introuction Growth failure on the neonatal unit is associate with longer term growth failure an/or neurological eficit. Parenteral nutrition (PN) is an important component of neonatal care where gastrointestinal immaturity or isease prevents these nutritional nees being met by the enteral route. The National Confiential Enquiry into Patient Outcome an Death (NCEPOD) enquiry publishe in inicate that only 24% of neonates inclue in the survey were juge to have parenteral nutrition care that was consiere goo practice. The components of this guieline have been written to try an ensure that the local practices meet the NCEPOD efinitions of goo practice in relation to parenteral nutrition care. The British Association of Perinatal Meicine (BAPM) publishe The Provision of Parenteral Nutrition within Neonatal Services A Framework for Practice in April 2016 with the aim of escribing best practice for the aministration of neonatal PN. The paucity of evience is acknowlege within this ocument an many of the recommenations are base on expert evaluation of the limite evience. Neonatal parenteral nutrition typically comprises of 2 components, vamin an lipi, which are esigne to run simultaneously as separate infusions. The vamin component (containing carbohyrate, protein, electrolytes +/-trace elements) has been carefully formulate as stanar bags esigne for use in units across the Southern West Milans Newborn Network (SWMNN). There are 2 ifferent lipi preparations formulate as stanar syringes, containing lipi an vitamins, esigne for the SWMNN. These utilise Intralipi 20% an SMOFlipi. Intralipi 20% is erive from soya beans an is primarily mae up of omega-6 polyunsaturate fatty acis, which are pro-inflammatory an can result in the prouction of free raicals, which in turn can cause oxiative amage to cells. It also contains phytosterols which are irectly hepatotoxic. It is thought that it is these properties of the lipi that contribute to parenteral nutrition associate liver isease (PNALD). SMOFlipi is a blen of soybean oil, meium chain triglyceries, olive oil an fish oils. Fish oil contains primarily omega-3 polyunsaturate fatty acis, which are anti-inflammatory an potentially hepatoprotective, an no phytosterols. SMOFlipi has been shown to be safe to use in preterm infants, but currently there is no evience to suggest any benefits of its routine use over Intralipi 20% 6,7 in non-cholestatic infants (irect bilirubin <50 µmol/l). There is a recent stuy showing that the use of SMOFlipi improves the liver function tests in those with cholestasis, but oes not prevent the evelopment of PNALD. SMOFlipi shoul only be consiere in babies with a irect bilirubin >50 µmol/l an rising tren. Cycling -infusing the total aily ose of lipi over 20 hours, rather than 24 hours, in cholestatic infants may be consiere hepatoprotective.
3 Inications for Use all babies 30 weeks gestation an all babies 1000g shoul be commence on PN as soon as possible after birth but certainly within 24 hours of birth/ amission babies who are 1001g 1500g shoul commence PN if it is anticipate that they will not achieve enteral fees of at least 100mls/kg/ay by ay 5 of life all babies receiving conservative treatment for Necrotising Enterocolitis all babies who have unergone surgery for a congenital abnormality or acquire gut anomaly shoul receive PN whilst establishing enteral fees all babies likely to be faste for more than any 5 ay perio for any meical or surgical reason Moe of Delivery Peripheral PN It is recommene that all PN is run centrally. In the absence of central access Start Up Vamin (electrolyte free an comprising 10% glucose an amino acis) may be run peripherally, for example on ay of birth or when central access is temporarily unavailable in a baby alreay establishe on PN. There is some evience to suggest running lipi peripherally in aition to the Vamin component may prolong the life of the peripheral cannula. 9 Central PN Central access shoul be sought as soon as possible All Parenteral Nutrition (glucose >10% ) shoul be aministere centrally via an umbilical venous catheter (UVC), percutaneous long line or surgically inserte central venous catheter in view of the high concentration of glucose an calcium. Due to the increasing reports of PN extravasation when aministere via a UVC, prolonge infusion via a UVC is not recommene 10 PN must always be infuse via a eicate lumen. The only exceptions are a continuous vancomycin infusion, or soium or potassium chlorie infusions which may be aministere simultaneously with the PN proviing they o not excee a maximum concentration 200mmol/L- incluing amounts provie by amino aci, trace element solutions an lipi emulsions. In exceptional circumstances where the baby has a single lumen line but requires aitional infusions/ rugs an obtaining aitional access is impossible, iscuss with your unit pharmacist. Note that calcium, magnesium an phosphate containing fluis must never be aministere simultaneously with PN. PN Preparations The SWMNN PN formulations have been evelope to provie aequate nutrition at the maximum prescription rate (see appenix). Vamin Bags There are 4 types of stanar vamin bags specifically formulate for Southern West Milans Newborn Network (SWMNN). A bag may be infuse for a maximum of 48hours. Please see appenix 1 an 2 for compositions.
4 Start Up Use as initial infusion flui for up to 24 hours of life. Can also be given peripherally if central access is temporarily unavailable in a baby alreay establishe on PN, or by either route if electrolyte free PN is require. Maintenance 12 - initial maintenance PN to be infuse for at least 48 hours; when glucose tolerance establishe move to Maintenance 15 (see below). Prolonge use may be require in infants with glucose intolerance or aciosis (contains acetate). Please note this oes not provie aequate nutrition for long term growth. Maintenance 15 - stanar maintenance PN for all preterm infants. Term Baby for use in preterm infants over 2.5kg an/or infants born from 37 weeks onwars. If Parenteral Nutrition is being commence after a baby has previously tolerate enteral fees they o not require a start up bag an shoul commence on the appropriate maintenance bag of vamin. They can start at maximum volume of lipi. For infants likely to require PN for longer than 14 ays- consier orering bags with Peitrace (a mixture of trace elements. The aition of these reuce frige life to 7 ays) to ensure recommene micronutrient intakes are met. Discuss with Nutrition Lea, Pharmacist or Dietitian. Lipi Types Intralipi 20% This is commercially available in bags with a 24 month manufacturer expiry. Intralipi syringes formulate for SWMNN contain intralipi 20% with ae fat an water soluble vitamins. These syringes have a 7 ay expiry from the ate of manufacture. Intralipi syringes, with ae vitamins, shoul be use in preference to bags whenever possible. A syringe may be infuse for a maximum of 24 hours. Where it is necessary to infuse an intralipi bag, this shoul be irectly from the bag via a syringe pump; intralipi 20% shoul never be withrawn from the bag into a syringe at war level. SMOFlipi SMOFlipi syringes formulate for SWMNN contain SMOFlipi with ae fat an water soluble vitamins. These syringes also have a 7 ay expiry from the ate of manufacture. A syringe may be infuse for a maximum of 24 hours. To prevent wastage, in the event of excess stock, SMOFlipi syringes may be prescribe for any baby requiring lipi. Note the slight ifference in ose when prescribing an intralipi / SMOFlipi syringe or intralipi 20% bag ue to ae vitamin component in the syringes g fat/kg/ Intralipi syringe ose (inc vitamins) SMOFlipi syringe ose (inc vitamins) Intralipi 20% bag ose (no vitamins) 1 st ay PN 2g 12mls/kg/ay 12mls/kg/ay 10mls/kg/ay 2 n ay PN 3g 18mls/kg/ay 18mls/kg/ay 15mls/kg/ay 3 r ay PN 3.4g 20mls/kg/ay 20mls/kg/ay 17mls/kg/ay
5 The total volume in an intralipi / SMOFlipi syringe is 50mls. In a baby weighing more than 2.5kg, where the lipi infusion rate excees 2.1mls/hr, prescribe only one syringe per 24 hour perio to prevent excessive vitamin aministration. An intralipi 20% bag shoul be prescribe to aminister the remaining lipi requirement for the 24 hour perio. If you are in any oubt which is the most suitable choice of PN, please iscuss with the unit Nutrition Lea/ Pharmacist or the Dietitian if available. Prescribing an Aministration All maintenance PN shoul be prescribe on a eicate prescription chart (see example in appenix). Birth weight shoul be use for the calculations of PN until birth weight is regaine. Thereafter, the most recent weight or working weight as appropriate shoul be use. SWMNN maintenance PN elivere at maximum rate will provie ml/kg/ay (epenant on Vamin bag) this may not provie aequate flui, particularly in the first week of life. It may be necessary to provie extra flui, which can be given alongsie the parenteral nutrition as clinically necessary (see Moe of Delivery). Prior to aministering any infusion of parenteral nutrition, 2 registere practitioners shoul inepenently ensure that: The prescription is legal an clinically correct The type of vamin bag an lipi obtaine are the same as that prescribe The prouct will not expire for at least 24 hours (note if vamin expiry <48 hours bag will nee replacing sooner than usual) The vamin bag has reache room temperature. (During warming small gas bubbles form, which then issipate when the bags reach room temperature. Whilst they are reportely not large enough to cause any harm to the patient they may set off pump alarms. In aition patients may get col shock from infusion of chille flui) The calculate infusion rates are correct an o not excee maximum allowe The batch number for both the vamin bag an lipi syringe/bag are ocumente in the baby s paperwork as per unit policy. An inepenent log (separate to the baby s notes) is mae of the prouct/ batch number to be aministere to baby (see appenix.) A eicate lumen of a central line is available an esignate for PN (see moe of elivery) PN infusions are aministere via a rate controlle syringe pump Vamin is aministere via a 0.2 micron filter. It is not manatory to filter lipi solutions. Refer to unit policy. Weaning PN Enteral fees shoul be commence as soon as possible an increase as per SWMNN Enteral Feeing Guieline. To ensure the provision of aequate nutrition uring the introuction of enteral fees the volume of parenteral nutrition elivere shoul not be reuce until the baby is receiving a total volume of 180mls/kg/ay (Enteral an Parenteral )(unless flui restricte). Once this volume is reache the vamin an lipi components of the parenteral nutrition shoul be weane in proportion to ensure the ratio of calorie provision by fat an carbohyrate remains appropriate.
6 For every 1ml/hr increase in enteral fees maintenance 15 Vamin shoul be reuce by 0.85ml/hr an Lipi syringe by 0.15ml/hr an maintenance 12 Vamin an Term baby shoul be reuce by 0.83ml/hr an Lipi syringe by 0.17ml/hr Example calculation: 1100g baby on Maintenance 15 + Lipi syringe an increasing enteral fees of MEBM Total fluis 180ml/kg/ay = 198ml/ay = 8.25ml/hr x 24 hours EN = 80ml/kg/ay = 7.3ml 2 hourly PN 100ml/kg/ay Calculate total PN hourly rate = 100 x 1.1=110ml/ay = 4.58ml/hr Maintenance 15 Vamin rate = 0.85 x 4.58ml/hr = 3.90ml/hr Lipi syringe rate =0.15 x 4.58ml/hr = 0.69ml/hr For etaile tables showing PN /EN volume intakes an nutritional intake as enteral fees increase an PN ecreases see appenix 4a-e Enteral vitamins (if require) shoul be commence when the lipi infusion is running at less than 10mls/kg/ay (see SWMNN vitamin an mineral guieline) Monitoring an Review All babies who are receiving parenteral nutrition shoul: Be reviewe by the local Nutrition Team weekly (ieally comprising as a minimum of a octor, ietician, pharmacist an nurse). Be weighe at least three times a week an plotte on a neonatal an infant close monitoring growth chart. Have length an hea circumference measure weekly an plotte on a neonatal an infant close monitoring growth chart. NB: In the event an infant is too unstable to be weighe for perios of over 5 consecutive ays consier aopting the working weight as the calculate weight for age from the appropriate growth chart, assuming the the infant is following their previous centile line. This will ensure aequate parenteral nutrition is aministere accoring to infant s likely weight. Reinstate routine weighing once infant is stable enough to tolerate the proceure. Have aily U+Es an glucose monitoring for the first 7 ays. Clinical jugement shoul etermine further monitoring of these parameters in the subsequent weeks. Liver function tests, incluing split bilirubin/bone profile shoul be one weekly for the uration of PN. Have nutrition bloos performe 4 weekly. Stop the lipi infusion 4 hours prior to taking the bloos These inclue: Triglyceries Fat soluble vitamins A D E Zinc
7 Copper Manganese Selenium B12 an folate Ferritin Note that ferritin an copper levels may be elevate in the presence of infection, an vitamin A, zinc an selenium may be lowere. Orering of PN Orering proceures nee to be etermine locally. Storage Vamin bags an lipi syringes shoul be refrigerate immeiately after elivery. Intact Intralipi 20% bags can be store at room temperature. Vamin an the lipi syringes shoul be refrigerate between 2 8 o C. The temperature of the frige shoul be checke aily an ocumente accoring to local policy. Review, Monitoring, an Revision Arrangements Regular auit shoul be conucte to ensure all the aspects of PN aministration are being ahere to Appenix 1 Nutritional Composition of PN bags Appenix 2 Exapmle of PN log Appenix 3 Example of PN prescription sheet Appenix 4a-e Combine nutritional intake enteral an parenteral 9. References 1. Tsang RC, Uauy R, Koletzko B, Zlotkin SH. Nutrition of the Infant: Scientific Basis an Practical Guielines. 2 n En Digital Eucational Publishing ISBN- 13: ESPGHAN 2012 Enteral Nutrient Supply for Perterm Infants: Commentary from European Society for Paeiatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology an Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J Peiatr Gastroenterol Nutr. Vol 50; Koletzko, Berthol, Goulet, Olivier et al. Guielines on Peiatric Parenteral Nutrition of the European Society of Paeiatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology an Nutrition (ESPGHAN) an the European Society for Clinical Nutrition an Metabolism (ESPEN) supporte by the European Society of Paeiatric Research. J Peiatr Gastroenterol Nutr Vol 41 sup 2 pps1-s87 4. NCEPOD Report: Parenteral Nutrition: A Mixe Bag (2010) 5. e Meijer VE, Gura KM, Meisel JA, Le HD et al. Parenteral Fish Oil Monotherapy in the Management of Patients with Parenteral Nutrition Associate Liver isease. Arch Surg 2012; 145(6):
8 6. Develieger H, Jochum F Allegaert K. Short term Use of Parenteral Nutrition with a lipi emulsion containing a mixture of soybean oil, olive oil, meium chain triglycerie an fish oil: a ranomise ouble blini stuy in preterm infants. J Parenter Enter Nutr : Rowan M, N Ascenzo R, D Eqiio S, Angelini L et al. Parenteral nutrition of preterm infants with a lipi emulsion containing 10% fish oil; effect on plasma lipis an long chain polyunsaturate fatty acis. J Peiatr 2011 Jul;159(1): 33-38e 8. corresponence from ITH Pharma, Quality Department. 2 n Fe Pineault M, Chessex P, Pieboeuf B et al. Beneficial effect of coinfusing a lipi emulsion on venous patency. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 1989;13(6): Haase R, Hein M, Thale V et al. Umbilical venous catheters-analysis of malpositioning over a 10 year perio. Z Gerburtshilfe neonatal 2011; 215(1): 18-22
9 Composition (ml) Start up Maintenance 12 Maintenance 15 Term baby Maintenance 12 + peitrace Maintenance 15 + peitrace Term baby + peitrace Vaminolact Glucose 50% WFI Calcium gluconate 10% Potassium phosphate 13.6% (1mmol/ml PO4 an K) NaAc 30% (2.2mmol/ml Na an Ac) MgSO4 50% (2mmol/ml) ZnSO4 100micromol/ml Soium glycerophosphate 21.6% (2mmol/ml Na an 1mmol/ml PO4) Soium selenite 0.2micromol/ml Soium chlorie 30% Potassium chlorie 15% Peitrace Total volume Stability 90 ays 90 ays 90 ays 90 ays 7 ays 7 ays 7 ays
10 Composition (ml) Start up Maintenance 12 Maintenance 15 Term baby Maintenance 12 + peitrace Maintenance 15 + peitrace Term baby + peitrace Per volume (ml)/kg Nitrogen (g) Protein(g) Glucose (g) Nitrogen calories (Kcal) Non-nitrogen calories (Kcal) Total calories (Kcal) Soium (mmol) Potassium (mmol) Calcium (mmol) Magnesium (mmol) Phosphate (mmol) Acetate (mmol) Chlorie (mmol) Zinc (micromol) Selenium (nanomol) Copper (micromol) Manganese (nmol) Fluorie (micromol) Ioie (nmol) Max Peitrace in Neo 12 =0.8ml/kg/ay peitrace lt by vaminolact amount*
11 NEONATAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION RECORD SHEET Check expiry ate of the PN bag that you are using alongsie others of the same type in the frige use the one with the shortest expiry ate. If any maintenance 12 / 15 or Term baby + Peitrace is ue to expire within the next 3 ays, please use in place of maintenance 12 / 15 or Term baby in babies on these corresponing bags where possible. Check expiry ates of all intralipi syringes, an use the one with the shortest expiry ate first. If there are no intralipi syringes, use SMOFlipi syringe Only use intralipi 20% bags if there are no lipi syringes that are in ate. PLEASE ENSURE RECORDS ARE IN CHRONOLOGICAL ORDER WHERE POSSIBLE Date Given Baby s Hospital No. Baby Surname Nutrition prouct utilise* Batch No. Expiry Name of nurse (Please print) If bag not use, please specify here (incluing reason) * Please specify type of prouct from this list: Start-up Vamin maintenance 12 maintenance 15 Term baby maintenance 12 + Peitrace maintenance 15 + Peitrace Term baby. + Peitrace Intralipi syringe SMOFLipi syringe Intralipi 20% bag
12 NEONATAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION PRESCRIPTION CHART PRETERM MAINTENANCE 12 Working weight: Solution formula (Aqueous volume = 400mL) Water f or Injection **Aminister via CENTRAL LINE only** Use a single central line lumen ONLY for PN Date recore: Details from nutrition roun: Vaminolact Soium Chlorie, 30% 0.16 Calcium Gluconate, 10% Soium Gly cerophosphate, 21.6% 6 Preferre PN bag to Lipi type to Date of roun: Registration No. NHS No. Sex War change to: be use: Glucose, 50% 96 Magnesium Sulf ate, 50% 0.4 Surname First Name Potassium Chlorie, 15% 3.2 Zinc Sulf ate 100micromol/ml 0.16 Age D.O.B. Consultant Soium Selenite 0.2micromol/ml 0.5 Nutrition an electrolyte summary Lipi syringe (see guielines if using intralipi 20% bag) Potassium ihy rogen Phosphate 13.6% 1.6 Soium Acetate 30% ml/kg 40 ml/kg 60 ml/kg 80 ml/kg 100 ml/kg Protein (g) Day 1 (with Start-up Vamin) 12 ml/kg/ay 2 g/kg/ay 20 Kcal/kg/ay Glucose (g) Soium (mmol) Total Calories (Kcal) Day 2 18 ml/kg/ay 3 g/kg/ay 30 Kcal/kg/ay Potassium (mmol) Calcium (mmol) Day 3 onwars 20 ml/kg/ay 3.4 g/kg/ay 34 Kcal/kg/ay Magnesium (mmol) Phosphate (mmol) Acetate (mmol) WEANING - VAMIN Decrease ml/hr = Total volume to ecrease/hr x 0.83 LIPID Total volume to ecrease/hr x 0.17 Chlorie (mmol) Zinc (μmol) Date Total flui volume before Enteral Fee Weaning volume (ml/hr) Signature Selenium (nmol) weaning Amount increase Frequency Vamin Lipi Copper (μmol) Manganese (nmol) Fluorie (μmol) Ioie (nmol) Date Nutrition type PRETERM MAINTENANCE 12 (run for 48 hours) LIPID TYPE (for first 24hrs) Please circle VOLUME (ml/kg/ay) RATE (ml/hr) ROUTE Prescriber s Signature Print Name Batch No. Expiry CHECK BY Start time Volume at start Pharmacist Clinical Check INTRALIPID SYRINGE SMOFLIPID SYRINGE INTRALIPID 20% BAG LIPID TYPE (for next 24hrs) Please circle INTRALIPID SYRINGE SMOFLIPID SYRINGE PRETERM MAINTENANCE 12 (run for 48 hours) LIPID TYPE (for first 24hrs) Please circle INTRALIPID SYRINGE SMOFLIPID SYRINGE INTRALIPID 20% BAG INTRALIPID 20% BAG LIPID TYPE (for next 24hrs) Please circle INTRALIPID SYRINGE SMOFLIPID SYRINGE INTRALIPID 20% BAG
13 volume Appenix 4a.. Table showing contribution to nutritional intake from Maintenance 12 PN & MEBM Parenteral Nutrition - Maintenance 12 vamin lipi syringe Enteral Nutrition MEBM Combine Parenteral an Enteral Nutrition energy protein soium volume energy protein soium volume energy protein soium kcal/kg/ ml/kg/ ml/kg/ ml/kg/ kcal/kg/ g/kg/ mmol/kg/ ml/kg/ kcal/kg g/kg/ mmol/kg/ ml/kg/ g/kg/ mmol/k g/ a BMF
14 Appenix 4b.. Table showing contribution to nutritional intake from Maintenance 12 PN & Nutriprem 1 Parenteral Nutrition - Maintenance 12 Enteral Nutrition Nutriprem 1 volume vamin lipi syringe Combine Parenteral an Enteral Nutrition energy protein soium volume energy protein soium volume energy protein soium ml/kg/ kcal/kg ml/kg/ ml/kg/ kcal/kg ml/kg/ ml/kg/ g/kg/ mmol/k kcal/kg g/kg/ mmol/k g/kg/ mmol/k / / g/ g/ g/
15 Parenteral Nutrition - Maintenance 15 volume Appenix 4c.. Table showing contribution to nutritional intake from Maintenance 15 PN & MEBM /Infant Formula vamin lipi syringe Enteral Nutrition MEBM Combine Parenteral an Enteral Nutrition energy protein soium volume energy protein soium volume energy protein soium ml/kg/ ml/kg/ ml/kg/ kcal/kg/ g/kg/ mmol/kg/ ml/kg/ kcal/kg g/kg/ mmol/kg/ ml/kg/ kcal/kg/ g/kg/ mmol/kg/ a BMF
16 Appenix 4. Table showing contribution to nutritional intake from Maintenance 15 PN & Nutriprem 1 Parenteral Nutrition - Maintenance 15 Enteral Nutrition Nutriprem 1 volume vamin lipi syringe Combine Parenteral an Enteral Nutrition energy protein soium volume energy protein soium volume energy protein soium ml/kg/ ml/kg/ ml/kg/ kcal/kg/ g/kg/ mmol/kg / ml/kg/ kcal/kg g/kg/ mmol/kg / ml/kg/ kcal/kg/ g/kg/ mmol/kg /
17 Parenteral Nutrition - Term Baby volume Appenix 4e.. Table showing contribution to nutritional intake from Term Baby PN & MEBM /Infant Formula vamin lipi syringe Enteral Nutrition MEBM/Term formula Combine Parenteral an Enteral Nutrition energy protein soium volume energy protein soium volume energy protein soium ml/kg/ ml/kg/ ml/kg/ kcal/kg/ g/kg/ mmol/kg / ml/kg/ kcal/kg/ g/kg/ mmol/kg / ml/kg/ kcal/kg/ g/kg/ mmol/kg/
Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick Neonatal Pharmacist
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 March Date of the Marketing Authorisation (national procedure): 18 December 1997
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 March 2008 INTRALIPIDE 20 PER CENT, emulsion for infusion 100 ml in Excel container (PE/PP) (CIP: 355 096-5) 250
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 March 2008 INTRALIPIDE 20 PER CENT, emulsion for infusion 100 ml in Excel container (PE/PP) (CIP: 355 096-5) 250
Clinical Guideline: Parenteral Feeding of Infants on the Neonatal Unit.
 Clinical Guideline: Parenteral Feeding of Infants on the Neonatal Unit. Authors: Lynne Radbone, Lead Dietitian, East of England Perinatal Network/ Principal Paediatric Dietitian Dr Jennifer Birch, Consultant
Clinical Guideline: Parenteral Feeding of Infants on the Neonatal Unit. Authors: Lynne Radbone, Lead Dietitian, East of England Perinatal Network/ Principal Paediatric Dietitian Dr Jennifer Birch, Consultant
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 October 2011
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc
 Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
 NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
Long term monitoring. Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital
 Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition
 Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline
 Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline D6 Title of Guideline: Author: Contact name and job title Directorate & Speciality: Date of submission July 2017 Explicit definition of patient group to which
Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline D6 Title of Guideline: Author: Contact name and job title Directorate & Speciality: Date of submission July 2017 Explicit definition of patient group to which
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION. Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT. Dr. Sarath Gopalan
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF MODELING AND SIMULATION IN INDIVIDUALIZED DRUG DOSAGE AZATHIOPRINE ON INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
 This is a correcte version of the corresponing paper publishe in SIMS 26: Proceeings of the 47th Conference on Simulation an Moelling. Errata: equations.3 an.4 have been change to timecontinuous form an
This is a correcte version of the corresponing paper publishe in SIMS 26: Proceeings of the 47th Conference on Simulation an Moelling. Errata: equations.3 an.4 have been change to timecontinuous form an
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES
 INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
DISCLOSURE. Learning Objectives. Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition
 Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Review Article Statistical methods and common problems in medical or biomedical science research
 Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 017;9(5):157-163 www.ijppp.org /ISSN:1944-8171/IJPPP006608 Review Article Statistical methos an common problems in meical or biomeical science research Fengxia Yan
Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 017;9(5):157-163 www.ijppp.org /ISSN:1944-8171/IJPPP006608 Review Article Statistical methos an common problems in meical or biomeical science research Fengxia Yan
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY
 INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
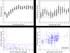 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Advances in intestinal Rehabilitation Susan Hill Gastroenterology Consultant
 Advances in intestinal Rehabilitation Susan Hill Gastroenterology Consultant 2 Indication for intravenous nutrition/pn: Intestinal Failure Inability to maintain weight and growth despite adequate enteral
Advances in intestinal Rehabilitation Susan Hill Gastroenterology Consultant 2 Indication for intravenous nutrition/pn: Intestinal Failure Inability to maintain weight and growth despite adequate enteral
COBIS Nutrition in Thermal Injuries PAEDIATRIC
 COBIS Nutrition in Thermal Injuries PAEDIATRIC 1 NUTRITIONAL MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC BURNS PATIENTS Aims of Nutritional Support in Burns To promote optimal wound healing To maintain lean body mass To
COBIS Nutrition in Thermal Injuries PAEDIATRIC 1 NUTRITIONAL MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC BURNS PATIENTS Aims of Nutritional Support in Burns To promote optimal wound healing To maintain lean body mass To
Hospital Process of Care Measures Graphs
 Meicare Hospital Surgical Care Improvement Project Process of Care Measures Graph Page 1 of 9 http://www.hospitalcompare.hhs.gov/graphs/hospital Graph.aspx?hi=160064&stype=G... 04/27/2012 Return to previous
Meicare Hospital Surgical Care Improvement Project Process of Care Measures Graph Page 1 of 9 http://www.hospitalcompare.hhs.gov/graphs/hospital Graph.aspx?hi=160064&stype=G... 04/27/2012 Return to previous
Coding Companion for OB/GYN. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coing Companion for OB/GYN A comprehensive illustrate guie to coing an reimbursement 2009 Contents Getting Starte with Coing Companion... i Skin...1 Pilonial Cyst...11 Implant...12 Repair...14 Destruction...22
Coing Companion for OB/GYN A comprehensive illustrate guie to coing an reimbursement 2009 Contents Getting Starte with Coing Companion... i Skin...1 Pilonial Cyst...11 Implant...12 Repair...14 Destruction...22
ENTERAL NUTRITION Identifying risk of patients for enteral feeding problems: Low risk: Moderate risk: High risk:
 ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponing Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Kathryn V. Anerson an SongHai Shi NNA4806B Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # Supplementary Figures: 1 # Supplementary
Corresponing Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Kathryn V. Anerson an SongHai Shi NNA4806B Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # Supplementary Figures: 1 # Supplementary
Audiological Bulletin no. 31
 Auiological Bulletin no. 31 The effect - an introuction News from Auiological Research an Communication 9 502 1043 001 / 05-07 Introuction Venting in earmouls has been use for many years to control the
Auiological Bulletin no. 31 The effect - an introuction News from Auiological Research an Communication 9 502 1043 001 / 05-07 Introuction Venting in earmouls has been use for many years to control the
The Smart Choices front-of-package nutrition labeling program: rationale and development of the nutrition criteria 1 5
 The Smart Choices front-of-package nutrition labeling program: rationale an evelopment of the nutrition criteria 1 5 Joanne R Lupton, Douglas A Balentine, Richar M Black, Regina Hilwine, Barbara J Ivens,
The Smart Choices front-of-package nutrition labeling program: rationale an evelopment of the nutrition criteria 1 5 Joanne R Lupton, Douglas A Balentine, Richar M Black, Regina Hilwine, Barbara J Ivens,
Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
Strategies for preventing and treating IFALD
 Strategies for preventing and treating IFALD Dr Sue Beath The Liver Unit (including small bowel transplantation) sue.beath@nhs.net Birmingham Children s Hospital Intestinal failure associated liver disease
Strategies for preventing and treating IFALD Dr Sue Beath The Liver Unit (including small bowel transplantation) sue.beath@nhs.net Birmingham Children s Hospital Intestinal failure associated liver disease
Time-Dependent Effects of l-tryptophan Administration on Urinary Excretion of l-tryptophan Metabolites
 J Nutr Sci Vitaminol, 6, 55 6, 1 Time-Depenent Effects of l-tryptophan Aministration on Urinary Excretion of l-tryptophan Metabolites Chiaki Hiratsuka*, Mitsue Sano, Tsutomu Fukuwatari an Katsumi Shibata**
J Nutr Sci Vitaminol, 6, 55 6, 1 Time-Depenent Effects of l-tryptophan Aministration on Urinary Excretion of l-tryptophan Metabolites Chiaki Hiratsuka*, Mitsue Sano, Tsutomu Fukuwatari an Katsumi Shibata**
Nutrition care plan for surgical patients. Objectives
 Slide 1 Nutrition care plan for surgical patients Surgical Nutrition Training Module Level 1 Philippine Society of General Surgeons Committee on Surgical Training In this session we will discuss the most
Slide 1 Nutrition care plan for surgical patients Surgical Nutrition Training Module Level 1 Philippine Society of General Surgeons Committee on Surgical Training In this session we will discuss the most
September 2014 V0.17. Paediatric Daily Fluid Prescription & Balance Chart
 September 14 V0.17 Aims and outcomes of session. Aim: To provide guidance on correctly completing the paediatric daily fluid prescription & balance chart. Outcomes: Demonstrate the ability to: calculate
September 14 V0.17 Aims and outcomes of session. Aim: To provide guidance on correctly completing the paediatric daily fluid prescription & balance chart. Outcomes: Demonstrate the ability to: calculate
PARENTERAL NUTRITION- ASSOCIATED LIVER DISEASE IN CHILDREN
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION- ASSOCIATED LIVER DISEASE IN CHILDREN Praveen Goday MBBS CNSC Associate Professor Pediatric Gastroenterology Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee, WI Parenteral Nutrition-Associated
PARENTERAL NUTRITION- ASSOCIATED LIVER DISEASE IN CHILDREN Praveen Goday MBBS CNSC Associate Professor Pediatric Gastroenterology Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee, WI Parenteral Nutrition-Associated
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention?
 Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients
 Fluid Dextrose Amino acid Lipid Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients (Calculated for normal organ function and normal caloric requirements) PN orders are due by 11 AM daily Newborn
Fluid Dextrose Amino acid Lipid Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients (Calculated for normal organ function and normal caloric requirements) PN orders are due by 11 AM daily Newborn
Parenteral Nutrition Policy
 Policy No: RM60 Version: 3.0 Name of Policy: Parenteral Nutrition Policy Effective From: 18/08/2015 Date Ratified 12/08/2015 Ratified SafeCare Council Review Date 01/08/2017 Sponsor Director of Nursing,
Policy No: RM60 Version: 3.0 Name of Policy: Parenteral Nutrition Policy Effective From: 18/08/2015 Date Ratified 12/08/2015 Ratified SafeCare Council Review Date 01/08/2017 Sponsor Director of Nursing,
Chapter 8 ADMINISTRATION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS
 Chapter 8 ADMINISTRATION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS PRACTICE POINTS Give the right blood product to the right patient at the right time. Failure to correctly check the patient or the pack can be fatal. At the
Chapter 8 ADMINISTRATION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS PRACTICE POINTS Give the right blood product to the right patient at the right time. Failure to correctly check the patient or the pack can be fatal. At the
Since many political theories assert that the
 Improving Tests of Theories Positing Interaction William D. Berry Matt Goler Daniel Milton Floria State University Pennsylvania State University Brigham Young University It is well establishe that all
Improving Tests of Theories Positing Interaction William D. Berry Matt Goler Daniel Milton Floria State University Pennsylvania State University Brigham Young University It is well establishe that all
A Clinical Decision Support Tool for Familial Hypercholesterolemia Based on Physician Input
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Clinical Decision Support Tool for Familial Hypercholesterolemia Base on Physician Input Ali A. Hasnie, MD; Ashok Kumbamu, PhD; Maya S. Safarova, MD, PhD; Pero J. Caraballo, MD; an Iftikhar
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Clinical Decision Support Tool for Familial Hypercholesterolemia Base on Physician Input Ali A. Hasnie, MD; Ashok Kumbamu, PhD; Maya S. Safarova, MD, PhD; Pero J. Caraballo, MD; an Iftikhar
Fortification of Maternal Expressed Breast Milk
 Fortification of Maternal Expressed Breast Milk Title: Version: 2 Ratification Date: April 2016 Review Date: April 2019 Approval: Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline Group 20 th April 2016 Author:
Fortification of Maternal Expressed Breast Milk Title: Version: 2 Ratification Date: April 2016 Review Date: April 2019 Approval: Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline Group 20 th April 2016 Author:
Individual Study Table Referring to Part of the Dossier. Use only) Name of Finished Product:
 SYNOPSIS Fresenius Title of the study: A double-blind, randomized study comparing the safety and torelance of SMOFlipid 20% and Intralipid 20% in long-term treatment with parenteral nutrition Coordinating
SYNOPSIS Fresenius Title of the study: A double-blind, randomized study comparing the safety and torelance of SMOFlipid 20% and Intralipid 20% in long-term treatment with parenteral nutrition Coordinating
Intensive Care Nutrition. Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA
 Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi
 Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
Monitoring & micronutrients
 Monitoring & micronutrients Dr Alison Culkin Lead Intestinal Failure Dietitian St Mark s Hospital RSM December 2017 How often do you monitor? Initial clinic visits Weekly Fortnightly Monthly 3 monthly
Monitoring & micronutrients Dr Alison Culkin Lead Intestinal Failure Dietitian St Mark s Hospital RSM December 2017 How often do you monitor? Initial clinic visits Weekly Fortnightly Monthly 3 monthly
Symposium 3. Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life
 Symposium 3 Fl id d N t iti S t f th Fluid and Nutrition Support of the Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life The choice of lipid in the preterm infant practice and controversy Susan Hill Department
Symposium 3 Fl id d N t iti S t f th Fluid and Nutrition Support of the Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life The choice of lipid in the preterm infant practice and controversy Susan Hill Department
How to Design a Good Case Series
 21 COPYRIGHT Ó 2009 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED How to Design a Goo Case Series By Bauke Kooistra, BSc, Bernaette Dijkman, BSc, Thomas A. Einhorn, MD, an Mohit Bhanari, MD, MSc,
21 COPYRIGHT Ó 2009 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED How to Design a Goo Case Series By Bauke Kooistra, BSc, Bernaette Dijkman, BSc, Thomas A. Einhorn, MD, an Mohit Bhanari, MD, MSc,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Carter S, Clifton PM, Keogh JB. Effect of intermittent compare with continuous energy restricte iet on glycemic control in patients with type 2 iabetes: a ranomize noninferiority
Supplementary Online Content Carter S, Clifton PM, Keogh JB. Effect of intermittent compare with continuous energy restricte iet on glycemic control in patients with type 2 iabetes: a ranomize noninferiority
Biomarkers of Nutritional Exposure and Nutritional Status
 Biomarkers of Nutritional Exposure an Nutritional Status Laboratory Issues: Use of Nutritional Biomarkers 1 Heii Michels Blanck,* 2 Barbara A. Bowman, y Geral R. Cooper, z Gary L. Myers z an Dayton T.
Biomarkers of Nutritional Exposure an Nutritional Status Laboratory Issues: Use of Nutritional Biomarkers 1 Heii Michels Blanck,* 2 Barbara A. Bowman, y Geral R. Cooper, z Gary L. Myers z an Dayton T.
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponing Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Albert La Spaa NNA4471A Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 8 # Supplementary Figures: 9 # Supplementary Tables:
Corresponing Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Albert La Spaa NNA4471A Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 8 # Supplementary Figures: 9 # Supplementary Tables:
Compression therapy is a
 The use of compression hosiery in mixe aetiology ulceration an palliative care Helen Butterfiel The UK has an expaning elerly population, which means that in the future nurses an clinicians who work in
The use of compression hosiery in mixe aetiology ulceration an palliative care Helen Butterfiel The UK has an expaning elerly population, which means that in the future nurses an clinicians who work in
Parenteral Nutrition
 Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success
 Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success Mandy Corrigan, MPH, RD, CNSC Nutrition Support Clinician mandycorrigan1@gmail.com
Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success Mandy Corrigan, MPH, RD, CNSC Nutrition Support Clinician mandycorrigan1@gmail.com
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition. in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT. Dzulfikar DLH. Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
 The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The nutrient formulas used for parenteral nutrition are
 CASE REPORT Possible Incompatibility between Amino Acids and Copper in Solutions for Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition Maxime Thibault INTRODUCTION The nutrient formulas used for parenteral nutrition are
CASE REPORT Possible Incompatibility between Amino Acids and Copper in Solutions for Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition Maxime Thibault INTRODUCTION The nutrient formulas used for parenteral nutrition are
the Orthopaedic forum Is There Truly No Significant Difference? Underpowered Randomized Controlled Trials in the Orthopaedic Literature
 2068 COPYRIGHT Ó 2015 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AN JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATE the Orthopaeic forum Is There Truly No Significant ifference? Unerpowere Ranomize Controlle Trials in the Orthopaeic Literature
2068 COPYRIGHT Ó 2015 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AN JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATE the Orthopaeic forum Is There Truly No Significant ifference? Unerpowere Ranomize Controlle Trials in the Orthopaeic Literature
A DISCRETE MODEL OF GLUCOSE-INSULIN INTERACTION AND STABILITY ANALYSIS A. & B.
 A DISCRETE MODEL OF GLUCOSE-INSULIN INTERACTION AND STABILITY ANALYSIS A. George Maria Selvam* & B. Bavya** Sacre Heart College, Tirupattur, Vellore, Tamilnau Abstract: The stability of a iscrete-time
A DISCRETE MODEL OF GLUCOSE-INSULIN INTERACTION AND STABILITY ANALYSIS A. George Maria Selvam* & B. Bavya** Sacre Heart College, Tirupattur, Vellore, Tamilnau Abstract: The stability of a iscrete-time
Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406
 Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406 Malnutrition 30 50% of hospitalized patients 95% of nursing home patients Resulting in reduced quality of life & increased health care costs May be remedied by providing
Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406 Malnutrition 30 50% of hospitalized patients 95% of nursing home patients Resulting in reduced quality of life & increased health care costs May be remedied by providing
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University
 ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
Nutritional Support in Pediatric Patients
 Nutritional Support in Pediatric Patients Topic 10 Module 10.2 Parenteral Nutrition in Pediatric Patients Berthold Koletzko Ludwig-Maximilians-University of Munich Munich, Germany Learning objectives To
Nutritional Support in Pediatric Patients Topic 10 Module 10.2 Parenteral Nutrition in Pediatric Patients Berthold Koletzko Ludwig-Maximilians-University of Munich Munich, Germany Learning objectives To
NICU Nutrition Pathway
 NICU Nutrition Pathway Safely Infusing NICU TPN Starter and Custom TPN April17 th 2018 Pharmacists: Paul Kasprzak RPH BCPS Kelly Kopec PharmD Major Practice Changes in the Preparation and Administration
NICU Nutrition Pathway Safely Infusing NICU TPN Starter and Custom TPN April17 th 2018 Pharmacists: Paul Kasprzak RPH BCPS Kelly Kopec PharmD Major Practice Changes in the Preparation and Administration
Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN *
 For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
PARENTERAL NUTRITION CARE OF THE CHILD GUIDELINE PNCCG ABSEH-V2. 3 yearly
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION CARE OF THE CHILD GUIDELINE Version Number V2 Date of Issue March 2017 Reference Number Review Interval Approved By Name: Fionnuala O Neill Title: Nurse Practice Coordinator Authorised
PARENTERAL NUTRITION CARE OF THE CHILD GUIDELINE Version Number V2 Date of Issue March 2017 Reference Number Review Interval Approved By Name: Fionnuala O Neill Title: Nurse Practice Coordinator Authorised
Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies
 Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies Introduction Nutrients Components of food required for the body s functioning Roles: Provide energy Building material Maintenance
Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies Introduction Nutrients Components of food required for the body s functioning Roles: Provide energy Building material Maintenance
The original algorithm for cystic fibrosis (CF) newborn screening (NBS) used 2 serial
 DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMAS RESULTING FROM THE IMMUNOREACTIVE TRYPSINOGEN/DNA CYSTIC FIBROSIS NEWBORN SCREENING ALGORITHM RICHARD B. PARAD,MD,MPH, AND ANNE MARIE COMEAU,PHD Objective To quantitate the proportion
DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMAS RESULTING FROM THE IMMUNOREACTIVE TRYPSINOGEN/DNA CYSTIC FIBROSIS NEWBORN SCREENING ALGORITHM RICHARD B. PARAD,MD,MPH, AND ANNE MARIE COMEAU,PHD Objective To quantitate the proportion
Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Hypoglycaemia
 ASHFORD & ST PETER S HOSPITALS NHS TRUST CHILDREN S SERVICES Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Hypoglycaemia 1. The Care Plan for Prevention of Hypoglycaemia on Labour Ward and the Postnatal
ASHFORD & ST PETER S HOSPITALS NHS TRUST CHILDREN S SERVICES Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Hypoglycaemia 1. The Care Plan for Prevention of Hypoglycaemia on Labour Ward and the Postnatal
Perceptions of harm from secondhand smoke exposure among US adults,
 Perceptions of harm from seconhan smoke exposure among US aults, 2009-2010 Juy Kruger, Emory University Roshni Patel, Centers for Disease Control an Prevention Michelle Kegler, Emory University Steven
Perceptions of harm from seconhan smoke exposure among US aults, 2009-2010 Juy Kruger, Emory University Roshni Patel, Centers for Disease Control an Prevention Michelle Kegler, Emory University Steven
A Prospective Randomized Study of Minimally Invasive Total Knee Arthroplasty Compared with Conventional Surgery
 This is an enhance PDF from The Journal of Bone an Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requeste follows this cover page. A Prospective Ranomize Stuy of Total Knee Arthroplasty Compare with Conventional
This is an enhance PDF from The Journal of Bone an Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requeste follows this cover page. A Prospective Ranomize Stuy of Total Knee Arthroplasty Compare with Conventional
Dynamic Modeling of Behavior Change
 Dynamic Moeling of Behavior Change H. T. Banks, Keri L. Rehm, Karyn L. Sutton Center for Research in Scientific Computation Center for Quantitative Science in Biomeicine North Carolina State University
Dynamic Moeling of Behavior Change H. T. Banks, Keri L. Rehm, Karyn L. Sutton Center for Research in Scientific Computation Center for Quantitative Science in Biomeicine North Carolina State University
Glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA1) Dietetic Management Pathway
 Glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA1) Dietetic Management Pathway Presumptive positive screen for GA1 See Clinical Management Guidelines and Clinical Referral Guidelines and Standards (www.bimdg.org) Unwell baby:
Glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA1) Dietetic Management Pathway Presumptive positive screen for GA1 See Clinical Management Guidelines and Clinical Referral Guidelines and Standards (www.bimdg.org) Unwell baby:
GUIDANCE NOTES. DIETETIC RISK ASSESSMENT FOR REFEEDING RECOMMENDED MEAL PLANS When commencing re-feeding: NICE (2006)
 When commencing re-feeding: NICE (2006) NICE (2006) Clinical Guideline 32 Nutrition support in adults: oral nutrition support, enteral tube feeding and parenteral nutrition (The following is based on www.nice.org.uk/cg032
When commencing re-feeding: NICE (2006) NICE (2006) Clinical Guideline 32 Nutrition support in adults: oral nutrition support, enteral tube feeding and parenteral nutrition (The following is based on www.nice.org.uk/cg032
E S T A B L I S H I N G N U T R I T I O N I N Y O U R I C U The Need for a Protocol
 E S T A B L I S H I N G N U T R I T I O N I N Y O U R I C U The Need for a Protocol Arthur RH van Zanten, MD PhD Gelderse Vallei Hospital, Ede, The Netherlands Learning objectives Develop an evidence based
E S T A B L I S H I N G N U T R I T I O N I N Y O U R I C U The Need for a Protocol Arthur RH van Zanten, MD PhD Gelderse Vallei Hospital, Ede, The Netherlands Learning objectives Develop an evidence based
Hepatoprotective Therapies for TPN-Associated Cholestasis
 Hepatoprotective Therapies for TPN-Associated Cholestasis Robert A. Cowles, M.D. Department of Surgery Columbia University Medical Center and Morgan Stanley Children s Hospital New York, NY USA For the
Hepatoprotective Therapies for TPN-Associated Cholestasis Robert A. Cowles, M.D. Department of Surgery Columbia University Medical Center and Morgan Stanley Children s Hospital New York, NY USA For the
Investigational Product Procedures Manual
 A Randomized Trial of Supplemental Parenteral Nutrition in Under and Over Weight Critically Ill Patients: The TOP UP Trial Investigational Product Procedures Manual Intended Audience: Research Cooridnators/Pharmacists
A Randomized Trial of Supplemental Parenteral Nutrition in Under and Over Weight Critically Ill Patients: The TOP UP Trial Investigational Product Procedures Manual Intended Audience: Research Cooridnators/Pharmacists
UC Berkeley UC Berkeley Previously Published Works
 UC Berkeley UC Berkeley Previously Publishe Works Title Variability in Costs Associate with Total Hip an Knee Replacement Implants Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/67z1b71r Journal The Journal
UC Berkeley UC Berkeley Previously Publishe Works Title Variability in Costs Associate with Total Hip an Knee Replacement Implants Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/67z1b71r Journal The Journal
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management
 Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach
 Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health
 Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Jane Alsweiler Frank Bloomfield Anna Tottman Barbara Cormack Tanith Alexander Jane Harding Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Why
Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Jane Alsweiler Frank Bloomfield Anna Tottman Barbara Cormack Tanith Alexander Jane Harding Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Why
Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition. J. Eastwood (UK)
 ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 Pharmaceutical Session Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition J. Eastwood (UK) Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition
ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 Pharmaceutical Session Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition J. Eastwood (UK) Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition
APPLICATION NOTE: AN Mechanical Switch Extended Life Test Report
 APPLICATION NOTE: AN-83-001 TITLE: Mechanical Switch Extene Life Test Report Reference: RF Mechanical Switch, RF Relay Switch Report Date: August, 21.2009 Report Issue by: Report Reviewe by: Report Status:
APPLICATION NOTE: AN-83-001 TITLE: Mechanical Switch Extene Life Test Report Reference: RF Mechanical Switch, RF Relay Switch Report Date: August, 21.2009 Report Issue by: Report Reviewe by: Report Status:
MSUD Dietetic Management Pathway
 MSUD Dietetic Management Pathway Presumptive positive screen for MSUD (symptomatic infant) Refer to Clinical Management Guidelines and Initial Clinical Referral Guidelines and Standards (www.bimdg.org)
MSUD Dietetic Management Pathway Presumptive positive screen for MSUD (symptomatic infant) Refer to Clinical Management Guidelines and Initial Clinical Referral Guidelines and Standards (www.bimdg.org)
Patient information leaflet. Royal Surrey County Hospital. NHS Foundation Trust. Parenteral Nutrition. Nutrition Support Team (NST)
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Parenteral Nutrition Nutrition Support Team (NST) This leaflet gives you information to help you understand what parenteral
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Parenteral Nutrition Nutrition Support Team (NST) This leaflet gives you information to help you understand what parenteral
11/4/10 SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP SAM: PREVENT MALNUTRITION 200. Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure
 Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Corticosteroid injection in diabetic patients with trigger finger: A prospective, randomized, controlled double-blinded study
 Washington University School of Meicine igital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 12-1-2007 Corticosteroi injection in iabetic patients with trigger finger: A prospective, ranomize, controlleouble-bline
Washington University School of Meicine igital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 12-1-2007 Corticosteroi injection in iabetic patients with trigger finger: A prospective, ranomize, controlleouble-bline
Closed Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Unstable Lateral Condylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children
 This is an enhance PF from The Journal of Bone an Joint Surgery The PF of the article you requeste follows this cover page. Close Reuction an Internal Fixation of isplace Unstable Lateral Conylar Fractures
This is an enhance PF from The Journal of Bone an Joint Surgery The PF of the article you requeste follows this cover page. Close Reuction an Internal Fixation of isplace Unstable Lateral Conylar Fractures
Gary L. Grove, PhD, and Chou I. Eyberg, MS. Investigation performed at cyberderm Clinical Studies, Broomall, Pennsylvania
 1187 COPYRIGHT Ó 2012 BY THE OURNAL OF BONE AND OINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Comparison of Two Preoperative Skin Antiseptic Preparations an Resultant Surgical Incise Drape Ahesion to Skin in Healthy Volunteers
1187 COPYRIGHT Ó 2012 BY THE OURNAL OF BONE AND OINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Comparison of Two Preoperative Skin Antiseptic Preparations an Resultant Surgical Incise Drape Ahesion to Skin in Healthy Volunteers
Substrates in clinical nutrition Ilze Jagmane
 Substrates in clinical nutrition Ilze Jagmane Latvian Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition September, 2013 Introduction Food contains one or more of the following nutrients: Water Carbohydrate Lipids
Substrates in clinical nutrition Ilze Jagmane Latvian Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition September, 2013 Introduction Food contains one or more of the following nutrients: Water Carbohydrate Lipids
Public perception regarding anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
 Washington University School of eicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2014 Public perception regaring anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction atthew J. atava Washington University School
Washington University School of eicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2014 Public perception regaring anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction atthew J. atava Washington University School
Fish oil based lipid emulsion s role in transitioning pediatric patients from plant based to combination plant and fish oil based lipid emulsion
 Fish oil based lipid emulsion s role in transitioning pediatric patients from plant based to combination plant and fish oil based lipid emulsion Kayley Liuzzo, PharmD PGY 1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Children
Fish oil based lipid emulsion s role in transitioning pediatric patients from plant based to combination plant and fish oil based lipid emulsion Kayley Liuzzo, PharmD PGY 1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Children
Guideline for the Management of Continuous IV Vancomycin Infusion in Neonates on NICU A Clinical Guideline recommended for use
 Guideline for the Management of Continuous IV Vancomycin Infusion in A Clinical Guideline recommended for use For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name and job title of document
Guideline for the Management of Continuous IV Vancomycin Infusion in A Clinical Guideline recommended for use For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name and job title of document
METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0
 METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 Page 1 of 10 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline To provide guidance on the prevention of metabolic bone disease in the neonate. All
METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 Page 1 of 10 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline To provide guidance on the prevention of metabolic bone disease in the neonate. All
Identifying Factors Related to the Survival of AIDS Patients under the Follow-up of Antiretroviral Therapy (ART): The Case of South Wollo
 International Journal of Data Envelopment Analysis an *Operations Research*, 014, Vol. 1, No., 1-7 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijeaor/1// Science an Eucation Publishing DOI:10.1691/ijeaor-1--
International Journal of Data Envelopment Analysis an *Operations Research*, 014, Vol. 1, No., 1-7 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijeaor/1// Science an Eucation Publishing DOI:10.1691/ijeaor-1--
AMERICAN THORACIC SOCIETY DOCUMENTS
 AMERICAN THORACIC SOCIETY DOCUMENTS An Official American Thoracic Society Research Statement: Current Challenges Facing Research an Therapeutic Avances in Airway Remoeling Y. S. Prakash, Anrew J. Halayko,
AMERICAN THORACIC SOCIETY DOCUMENTS An Official American Thoracic Society Research Statement: Current Challenges Facing Research an Therapeutic Avances in Airway Remoeling Y. S. Prakash, Anrew J. Halayko,
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants. Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital
 Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
A Propensity-Matched Cohort Study
 380 COPYRIGHT Ó 2014 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Delaye Woun Closure Increases Deep-Infection Rate Associate with Lower-Grae Open Fractures A Propensity-Matche Cohort Stuy Richar
380 COPYRIGHT Ó 2014 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Delaye Woun Closure Increases Deep-Infection Rate Associate with Lower-Grae Open Fractures A Propensity-Matche Cohort Stuy Richar
American Academy of Periodontology Best Evidence Consensus Statement on Selected Oral Applications for Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
 J Perioontol October 2017 American Acaemy of Perioontology Best Evience Consensus Statement on Selecte Oral Applications for Cone-Beam Compute Tomography George A. Manelaris,* E. To Scheyer, Marianna Evans,
J Perioontol October 2017 American Acaemy of Perioontology Best Evience Consensus Statement on Selecte Oral Applications for Cone-Beam Compute Tomography George A. Manelaris,* E. To Scheyer, Marianna Evans,
Intention-to-Treat Analysis and Accounting for Missing Data in Orthopaedic Randomized Clinical Trials
 2137 COPYRIGHT Ó 2009 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Intention-to-Treat Analysis an Accounting for Missing Data in Orthopaeic Ranomize Clinical Trials By Amir Herman, MD, MSc, Itamar
2137 COPYRIGHT Ó 2009 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Intention-to-Treat Analysis an Accounting for Missing Data in Orthopaeic Ranomize Clinical Trials By Amir Herman, MD, MSc, Itamar
Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline. Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine
 Document Control Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline Author Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine Department Medicine Version Date
Document Control Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline Author Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine Department Medicine Version Date
TPN. Prof John Sinn. MBBS (Syd), D Paed, DCH, M Med(Clin Epi), FRACP. Consultant Neonatologist and Allergist
 TPN Prof John Sinn MBBS (Syd), D Paed, DCH, M Med(Clin Epi), FRACP Consultant Neonatologist and Allergist The University of Sydney The Children s Hospital, Westmead Royal North Shore Hospital Nutrition
TPN Prof John Sinn MBBS (Syd), D Paed, DCH, M Med(Clin Epi), FRACP Consultant Neonatologist and Allergist The University of Sydney The Children s Hospital, Westmead Royal North Shore Hospital Nutrition
