TPN. Prof John Sinn. MBBS (Syd), D Paed, DCH, M Med(Clin Epi), FRACP. Consultant Neonatologist and Allergist
|
|
|
- Melvin Chapman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TPN Prof John Sinn MBBS (Syd), D Paed, DCH, M Med(Clin Epi), FRACP Consultant Neonatologist and Allergist The University of Sydney The Children s Hospital, Westmead Royal North Shore Hospital
2 Nutrition Calculator: Nutricia Preterm
3 NSW Neonatal TPN Consensus Group 9 NICU in NSW 10 NICU in other states
4 Background There are 61 different neonatal formulations Objectives: (a) deliver the recommended PN intakes to majority of the neonatal population (b) are safe, stable and compatible solutions with a long shelf life, (c) the regimen is easy and safe to implement and avoids error by rotating frontline staff (d) are cost-effective
5 Methods Consensus through: (a) reviewing the current nutrition practices, strengths and drawbacks (b) evaluating the latest evidence (e) develop standardized parenteral TPN formulations
6
7 Starter TPN
8 Starter 3g/kg/d of Protein 10% dextrose 1mmol/kg/d Na 1mmol/kg/d Acetate 0 Potassium
9 Starter TPN
10 Standard Term
11 Standard Term 12.5% dextrose 1.4g/kg/d Protein 1mmol/kg/d of Ca and P04 0.8mmol/kg/d Acetate 1.3mmol/kg/d Potassium
12 TERM TPN
13 Standard Preterm
14 Standard 3.6g/kg/d Protein 1.9mmol/kg/d Ca 1.5mmol/kg/d P04
15 7.5% Glucose Preterm
16 High Sodium = 8mmol/kg/d Na
17 Background Sinn JK 1,2, Reddy VS 1, Paradisis M 1,2, Bowers S 1, Berry R 1 1 Newborn Care Centre, Royal North Shore Hospital, Sydney, Australia], 2 University of Sydney John Sinn: jsinn@med.usyd.edu.au Changing TPN bags every 24 hrs is common practice in NICU. A few units are using 48 hour bags. To date there has been no published studies comparing these practices. Methods This retrospective study compares the infection rates and costs associated with 24 vs 48 hr TPN bag changes over two consecutive period 11/07 to 5/08 & 10/08-9/09 TPN: 24 hour Period: Pharmacy added to every standard bag prepared by Baxter. Thereby every bag was a custom bag TPN: 48 hour Period 48 vs 24 hour Neonatal TPN bags: Cost Benefit Analysis Baxter prepares all bags as standard bags and 15% bags were custom 24 hr bags Period Number of patients Babies on TPN hr bags Period Mean birth weight (g) Mean gestation Mean duration of TPN Results 11.8 days days Septic Rate 24 hr bag period N = hr bag period N = 386 Culture proven 11 9 Sepsis episodes Organisms isolated Staph epi 9 Ecoli 2 Staph epi 6 Ecoli 1 Strep 1 Nursing Time per 48hr period 24 hr bag period 48hr bag period Checking TPN 10 min 2 nurses 2 min 2 nurses Change TPN 20 min 2 nurses 20 min 2 nurses Per 48hr 120 mins 44 mins The 48hr bag save nurses time by 76 min every 48hrs per patient Cost difference per year 100 patients per year av 14 days on TPN Consumables 24 hr bag Period TPN $ hr bag Period IV lines $30 $15 Gloves Swabs Dressing pack filter Biochem $ testing of before use total $ $ hr bag 48 hrs bag Differenc period period e 1400 bags 700 bags 700 bags Cost of bags $ Consumables per $ $15253 $ bag change Nursing staff time 2800 hr 513hrs 2286 hrs Pharmacy staff time 422 days 26 days min /bag Conclusions Changing from 24 hr to 48 hr TPN bags did not increase the risk of infections and there were significant cost savings in using 48 hr bags. Our unit saved $ per annum by changing from 24 to 48 hour bags. Pharmacy time was equivalent to 2 FTE to prepare the individual bags compared to 5 weeks work per year for 48hour bags
18 Changing Bags 48hrs amino acid-dextrose solutions hypertonic (1200 to 2000 mosm/l) acidic (ph ) does not support the growth of most micro organisms these extreme conditions have proven to be bactericidal (Didier, Fischer et al. ; Sacks GS 2002). AA/Dextrose Hang time to 48 hours reduced the incidence of Central Line Associated Blood Stream Infections (Bolessity 2011) Changing both AA/Dextrose and lipid bag/syringes and tubing set at the same time avoids re-spiking of TPN bags with the already used infusion set, thereby preventing contamination.
19
20 Hang time Lipids 2 RCTs the lipid administration set changes in NICU 72-hour vs 24 hours vs 48hrs. Results: 166 infants Microbial contamination more at 72 hour change. higher fungal contamination if change 24 hrs compared to 48 hours. negligible impact on peroxide concentrations and vitamin degradation.
21 TPN Manufacturing Plant
22 TPN plant
23 Key Points Formulations to be commenced soon after birth. The maximum TFR is generally limited to 150 ml/kg/day. ie lipid emulsion 3 g/kg/day and 135 ml/kg/day of AA/Dextrose solutions. The contents of the AA/Dextrose formulations are calculated to provide the RDIs at 135 ml/kg/day. Hanging time for AA/Dextrose and lipids is 48 hours. Recommended Ca/Ph molar ratio of 1.3:1 is maintained in the solutions. Zinc, selenium and iodine are added to AA/Dextrose formulations Other trace elements not required unless TPN for > 1/12 of TPN
24 Calorie requirements (ESPGHAN 2005) kcal/kg/day VLBW infants maximal intakes glucose at 12 g/kg/day, protein at 4 gm/kg/day lipids at 3 gm/k/day,
25 Calorie requirements Caloric Value per gram Protein 4 kcal Glucose 4kcal Lipid 9-10 kcal Liberal fluid intake: increased trends of PDA, NEC, CLD, and iivh (Bell 2008). Liberal glucose infusion with insulin support offered no clinical benefit (Beardsall 2008).
26 Blood Urea Nitrogen Reflection of a higher AA oxidation rate. BUN reference values for human umbilical cord blood are 7.5 to 14.3 mmol/l (te Braake, van den Akker et al. 2005). BUNs (up 20mmol/L) without other metabolic compromise such as metabolic acidosis. (Clark, Chace et al. 2007; Blanco CL 2008)
27 Amino Acids Protein requirements: to stop catabolism (a) Protein accretion goal of 2 gm/kg/day (b) Rate of protein loss of 1.1 to 1.5 gm/kg/day (c) Efficiency of protein retention of 70%. Therefore: AA intake of 1.1 to 2.5 g/kg/day caloric intake of kcal/kg/day is required to positive nitrogen balance.
28 Clarke,2007 Blanco,2007 Kasyap,2007 Thureen,2003 Safety and efficacy No infants Study centre Study population Intervention multicentre Begin 1.5g within 48 H <30 wks ELBW <1250gm <1300gm 2gm at birth 18% of energy/protein 3g/kg/d Advancement Increase by 1gm Increase by 1 gm Max 3.5gm 4gm 4gm 3gm Control group Begin 1gm within 48 h Advancement 0.5gm/kg/day Increase by 0.5gm 0.5gm at birth Max 2.5g/kg/d 3g/kg/d 3g/kg/d 1g/kg/d 12.5% energy as protein. Result No diff in growth. Plasma AA higher. No diff in growth. Higher BUN.TPN ceased in 20% Improved growth increased protein accretion. Well tolerated
29 Amino acid administration to premature infants directly after birth te Braake, F.W.J et al, J Pediatr vol. 147, , RCT BW <1500 g n =135 10% Dextrose to start stepwise increase in AA intake to 2.4 g AA/(kg.d) by day 3 (n=69). vs 2.4 g AA/(kg.d) from birth onward Results. No adverse side effects in the group with high protein start AA concentrations were within reference ranges
30 Aggressive early TPN in LBW infants, Ibrahim et al, J.Perinatology 24; : gm, 24-32/40 n=16: AA 3.5g/k/d and Lipids 3g/k/d within 2 h of life n =16: AA 2g/k/d and Lipids 0.5 g/k/d on day 2 of life Results: strongly improved nitrogen balance and energy intake without any negative effect BUN Cholesterol triglycerides metabolic acidosis.
31 First-Week Protein and Energy Intakes Are Associated 18-Month Developmental Outcomes in ELBW Stephens et al, Pediatrics 2009;123; Retrospective study. 148 ELBW Results During week 1, each 1 g/ kg/day in protein intake had a 8.2-point increase in the MDI; higher protein intake was also associated with lower likelihood of length 10 th percentile
32 Early provision of parenteral amino acids in ELBW neurodevelopmental outcome, Poindexter BB et al, J Pediatr Mar;148(3): infants, RCT Early n = 182 Late n = 836 Infants were stratified by 5 days of life > 3 g/kg/day < 3g/kg/d
33 RESULTS: Poindexter: Results At 36 weeks CA, improvement Weight Length Head circumference in favour of the infants who received early AA; the odds of having wt < 10 th % for age was 4x higher for infants in the late group.
34 Carbohydrates The optimal glucose/lipid ratio: 60:40 to 75:25 of non-protein calories. Maximal glucose oxidation in Preterm: 8.3 mg/kg/min (12 g/kg/day) Term: 13 mg/kg/min (18 g/kg/day) (ESPGHAN 2005)
35 Carbohydrates NIRTURE Trial (Beardsall 2008): Multicentre European trial Early insulin vs no insulin use Aimed to recruit 500 infants. Recruitment was suspended after 389 infants. Data and safety monitoring committee, on an interim analysis, suggested abnormal ultrasound images with an excess of IVH and PVL with insulin group
36 Preterm: NSW Group Consensus On balance not to routinely exceed 10% Dex 10% Dex provide 13.5 gm/kg/day at 135 ml/kg/day Term: (ESPHAGN 12 g/kg/day). dextrose is 12.5% - provides 17 g/kg/day (ESPHAGN 18 g/kg/day)
37 Na: K: Electrolytes Both hyponatremia and hypernatremia are a problem and so some Na supplementation in the starter PN solution. Starter PN solution is K free RDI at 135ml/kg/d of Standard PN solution
38 ACETATE RCT of acetate in preterm neonates receiving TPN Peters et al, Archives of Disease in Childhood 1997;77:F12 F15 58 neonates of < 32 weeks GA, TPN from D 3 -D 10 standard parenteral nutrition vs replacement of any chloride dose > 3 mmol/kg/day as acetate
39 Results Acetate (0 to 14.2 mmol/kg/day) reduced the incidence of hyperchloraemia from 77% to 25%, a increase in BE from day 5 onwards an increased ph (day 8, 7.34 vs 7.26) The acetate group received less bicarbonate (median 0 mmol vs 4.8 mmol) and less colloid (41 ml/kg vs 204 ml/kg). Conclusion Acetate in neonatal TPN reduces metabolic acidosis and hyperchloraemia.
40 Change in practice The results of this study are now being put into practice on a systematic basis on their neonatal unit. The only change has been the definition of a maximum dose of acetate of 6 mmol/kg/day, because of concerns over hypercarbia. A daily dose at this level represents a mean blood pco2 of 8 kpa. The anion regimen is therefore the first 3 mmol provided as chloride, the next 6 mmol as acetate, and thereafter as chloride again.
41 ESPGHAN 2005 Calcium and Phosphate mmol Ca/kg/day and P04 mmol/kg/day Ca:P ratio in the range of AAP 2009 Recommendations: Ca:Ph ratio of 1.7:1 by weight (1.3:1 by molar ratio, similar to the fetal mineral accretion ratio) allows for the highest absolute retention of both minerals. This ratio equates to 1.9 mmol/k/day of calcium 1.45 mmol/k/day of phosphorus. ie1 Kg baby receiving 150 ml per day of AA/Dextrose formulation, we need to add 12.6 mmol Ca and 9.6 mmol P in 1 litre PN bag.
42 Ca P04 in TPN NSW Organic calcium (calcium gluconate) organic phosphate in a molar ratio of 1.3:1. The current Ca gluconate and inorganic phosphate contents at a ratio of 1.3:1 (12 and 9 mmol/l) provide RDIs. Baxter Stability Manual doesn t support Ca and inorganic Ph in excess of 12 and 10 mmol per litre respectively. Outcome: Final formulations will contain no more than 12 mmol Ca and 9/10 mmol Ph per litre.
43 Trace elements ESPGHAN Recommendations 2005 PN solutions may be contaminated with aluminium and chromium. Patients with cholestatic jaundice should be monitored for copper toxicity. Renal impairment can t excrete Se, Mn, Mo, Zn & chromium. Trace elements are recommended with long term PN. Manganese (Mn) Dose not well documented for neonates. High Mn: cholestasis, and deposition in basal ganglia, thalamus, BS & cerebellum. Molybdenum (Mo) No reports of deficiency in infants. 1 ug/kg/day is adequate for the LBW infant on longterm PN. Selenium (Se) 2-3 ug/kg/day is recommended for LBWI on PN. Zinc (Zn) ug/kg/day for preterm & 250 ug/kg/day for term on PN.
44 AAP Recommendations If TPN is limited < than 4 weeks, only zinc need be added. Thereafter, addition of the remaining elements is advisable. Omit Manganese and copper in patients with obstructive jaundice. Omit in patients with renal dysfunction.
45 Trace Elements: AUSPEN vs Peditrace Neither Baxter s AUSPEN Trace element nor Peditrace contains the right combination for neonates. Peditrace 1 ml contains lot more fluorine than recommended Baxter s AUSPEN 1 ml contains lot less zinc and lot more copper, manganese and iodine Main concern:?any toxicity from these trace element mixtures e.g. copper, manganese, chromium etc.
46 Element AAP 2009 ESPGHAN 2005 Baxter AUSPEN 1 ml Peditrace 1 ml < gm 1500 gm Zinc, µg/kg/day Copper, µg/kg/day Selenium, µg/kg/day Chromium, µg/kg/day Manganese, µg/kg/day Molybdenum, µg/kg/day Iodine, µg/kg/day Fluorine, µg/kg/day µg µg /day 6.4 1??? 0 57
47 Selenium (Darlow 2003) Cochrane Meta-analysis: significant reduction in sepsis associated with selenium supplementation [summary RR 0.73 (0.57, 0.93); RD (-0.17, -0.02); NNT 10 (5.9, 50)].
48 Selenium and sepsis
49 NSW Group Consensus Group has agreed to add the following individual trace elements to all the bags: zinc, selenium and iodine. For other trace elements such as copper, manganese and chromium, the group will liaise with Baxter to develop a trace element preparation containing these and can be given separately. In summary, all the AA/Dextrose formulations should aim to supply the following trace element dosages at 135 ml/kg/day: Zinc ug/k/day Selenium 2-3 ug/k/day Iodine 1 ug/kg/day
50 Aluminium toxicity Excess AL: reduced developmental attainment.(bishop, Morley et al.). Ca gluconate and Na P04: glass ampoules have high AL Bulk non-glass have low AL
51 RCT heparin in TPN to prevent sepsis Heparin in Long Line Total Parenteral Nutrition (HILLTOP) trial. Birch et al, Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2010;95:F252 F257. RCT heparin 0.5 IU/ml with no heparin in TPN infused through a neonatal long line, Results: 210 infants were enrolled (TPN with heparin n=102, TPN without heparin n=108). There was a statistically significant reduction in all episodes of culture-positive CRS in those infants with heparin added to the TPN compared with those without heparin.
52 Iodine Infants are in negative iodine balance on current standard regimens of total parenteral nutrition. (ESPGHAN 2005) recommendation: A daily dosage of 1 ug/day was recommended in parenterally fed infants (AAP 2009) Recommendation: 1 ug/kg/day
53 Lipids Dosage: Dosage of lipid emulsions should not exceed the capacity for lipid clearance. (ESPGHAN 2005) Recommendations To prevent EFA deficiency: 0.25 g/kg/day to preterm and 0.1 g/kg/day to term The upper limit: In preterm infants, 3 g/kg/day In term infants, fat oxidation reaches a maximum at 4 g/kg/day. Lipids in the total fluid volume: 20% lipid emulsions contain 80% water. Eg 50 ml of clinoleic 20% or Intralipid 20% contain 41 ml(82%) water. 6 ml/kg/day 1 gm/kg/day, of which 5 ml (80%) is water 12 ml/kg/day 2 gm/kg/day, of which 10 ml (80%) is water 18 ml/kg/day 3 gm/kg/day, of which 15 ml (80%) is water When the lipids are gm/kg/day - count 15 ml/kg/day in TFR.
54 Lipids Many NSW units do not like to exceed parenteral fluid intake over 150 ml/kg/day. This means amino acid/dextrose solution should meet the amino acid, dextrose, electrolyte and other mineral intakes at 135 ml/kg/day Clinoleic 20% is the agreed lipid emulsion.
55 Parenteral fat emulsions based on olive and soybean oils: RCT Gobel,Koletzko et al,pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr Aug;37(2): Clinoleic: based on olive and soybean oils (ratio 4:1), less polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) Premature infants (gestational age, 28- <37 weeks) were randomized to receive one of the two emulsions within the first 72 hours of life.
56 Results 33 patients (15 soybean oil, 18 olive oil emulsion). lower PUFA supply with the olive/soybean oil emulsion enhance linoleic acid conversion. The olive oil-based emulsion is a valuable alternative for parenteral feeding of preterm infants who are often exposed to oxidative stress, while their antioxidative defense is weak.
57 Lipids The current IV lipid preparation in our unit is Clinoleic 20%. olive oil(80%) and soya oil(20%). Mono-unsaturated FA(65%), saturated FA(15%) essential polyunsaturated FA (20%).
58 NSW Group Consensus Following lipid emulsions in 50 ml amber coloured syringes and 150 ml bags Each 50 ml contains: Clinoleic 20% - 36 ml Vitalipid 10% ml Soluvit reconstituted in WFI 2.8 ml Total Volume: 50 ml
59 UV protection generates organic peroxides and hydrogen peroxide that represent an oxidative load. Light-exposed had higher levels of plasma triglycerides and hypertriglyceridaemia indicating decreased plasma clearance.
60
61 Energy Ratio 150ml/kg/d kcal 1g protein = 4kcal 1g COH = 3.4kcal 1g fat = 10kcal Glucose: Fat: Protein 53: 31: 16
62 Calculating Calories Carbohydrate: ml/24h TPN x % Dextrose x 3.4 kcal/g = kcal/kg 100 x wt (kg) Fat: ml/24h 20% intralipid x 2 kcal/ml = kcal/kg wt (kg) Protein: g/kg protein x 4 kcal/g = kcal/kg
63
64 Vitalipid N
65 Soluvit N
66 Lipid Syringes 1g/kg/d of lipid translates to 5-6 ml/k/d Lipids has (Vitalipid and soluvit) It has 50 ml syringe for small infants and 150 ml for infants over 3.5 Kg. Each syringe costs about $40, for 48hours
67 Element AAP <1000 gm AAP g ESPGHAN Vit A, IU/k/day Vit D, IU/k/day Vit E, IU/K/day mg 2.8 Vit K, µg/k/day Ascorbate, mg/k/day Thiamine, µg/k/day Up to Riboflavine, µg/k/day Pyridoxine, µg/k/day Nicotinamide, mg/k/day Lipid emulsion@ 3gm/kg/d Pantothenate, mg/k/day Biotin, µg/k/day Folate, µg/k/day Vit B12, µg/k/day
68 TPN guidelines
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients
 Fluid Dextrose Amino acid Lipid Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients (Calculated for normal organ function and normal caloric requirements) PN orders are due by 11 AM daily Newborn
Fluid Dextrose Amino acid Lipid Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients (Calculated for normal organ function and normal caloric requirements) PN orders are due by 11 AM daily Newborn
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
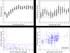 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition
 Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION. Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants. Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital
 Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick Neonatal Pharmacist
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant. J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014
 Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014 DISCLOSURES Dr. Lorenz has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict
Fluid & Electrolyte Management and Early Nutritional Care of the Extremely Preterm Infant J.M. Lorenz, M.D. April 2014 DISCLOSURES Dr. Lorenz has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict
Preterm Dietary Supplements
 Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD
 Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
Infant Nutrition & Growth to Optimize Outcome Fauzia Shakeel, MD Neonatologist All Children s Hospital / Johns Hopkins Medicine Affiliate Assistant Professor, University of South Florida September 2014
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT. Dr. Sarath Gopalan
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline
 Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline D6 Title of Guideline: Author: Contact name and job title Directorate & Speciality: Date of submission July 2017 Explicit definition of patient group to which
Nottingham Neonatal Service Clinical Guideline D6 Title of Guideline: Author: Contact name and job title Directorate & Speciality: Date of submission July 2017 Explicit definition of patient group to which
NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
 NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants
 Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Clinical Guideline: Parenteral Feeding of Infants on the Neonatal Unit.
 Clinical Guideline: Parenteral Feeding of Infants on the Neonatal Unit. Authors: Lynne Radbone, Lead Dietitian, East of England Perinatal Network/ Principal Paediatric Dietitian Dr Jennifer Birch, Consultant
Clinical Guideline: Parenteral Feeding of Infants on the Neonatal Unit. Authors: Lynne Radbone, Lead Dietitian, East of England Perinatal Network/ Principal Paediatric Dietitian Dr Jennifer Birch, Consultant
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi
 Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies
 Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies Introduction Nutrients Components of food required for the body s functioning Roles: Provide energy Building material Maintenance
Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies Introduction Nutrients Components of food required for the body s functioning Roles: Provide energy Building material Maintenance
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth. Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida
 Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
Nutrition Support for the ELBW Infant: Implications for More than Just Growth Josef Neu, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Florida AGA 27 week : How do we Nourish this Baby? Parenteral Nutrition:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 October 2011
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
NICU Nutrition Pathway
 NICU Nutrition Pathway Safely Infusing NICU TPN Starter and Custom TPN April17 th 2018 Pharmacists: Paul Kasprzak RPH BCPS Kelly Kopec PharmD Major Practice Changes in the Preparation and Administration
NICU Nutrition Pathway Safely Infusing NICU TPN Starter and Custom TPN April17 th 2018 Pharmacists: Paul Kasprzak RPH BCPS Kelly Kopec PharmD Major Practice Changes in the Preparation and Administration
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES
 INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant. Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW infants
 Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
Principles of nutrition in the preterm infant Dr. S. Navarro-Psihas Pädiatrie IV, Klinik für Neonatologie Medizinische Universität Innsbruck Importance of nutrition: Undernutrition is very common in VLBW
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition. in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT. Dzulfikar DLH. Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
 The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
Nutrition in the premie World
 SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
4/15/2014. Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth. Improving early nutrition. Problem Identification
 Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY
 INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention?
 Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Objectives. Background 4/23/2015. What s in a bag? A Clinical Review of Parenteral Nutrition. Ibrahim Sammour, MD FAAP.
 What s in a bag? A Clinical Review of Parenteral Nutrition Ibrahim Sammour, MD FAAP Objectives Background Indications in the NICU Risks and Complications What is in the bag? Protein Carbohydrate Fats Others
What s in a bag? A Clinical Review of Parenteral Nutrition Ibrahim Sammour, MD FAAP Objectives Background Indications in the NICU Risks and Complications What is in the bag? Protein Carbohydrate Fats Others
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes
 Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA1) Dietetic Management Pathway
 Glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA1) Dietetic Management Pathway Presumptive positive screen for GA1 See Clinical Management Guidelines and Clinical Referral Guidelines and Standards (www.bimdg.org) Unwell baby:
Glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA1) Dietetic Management Pathway Presumptive positive screen for GA1 See Clinical Management Guidelines and Clinical Referral Guidelines and Standards (www.bimdg.org) Unwell baby:
Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain
 Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain 1 of 5 PediaSure Grow & Gain is clinically proven * nutrition to help kids grow, and is a nutritious supplement for kids falling behind on growth. 1,2,3,4,5 May
Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain 1 of 5 PediaSure Grow & Gain is clinically proven * nutrition to help kids grow, and is a nutritious supplement for kids falling behind on growth. 1,2,3,4,5 May
PROJECT WOMEN S ANAEMIA. by My HealthWorks. Associate Member. 125A, 2nd Floor, Shahpur Jat, New Delhi ,
 PROJECT WOMEN S ANAEMIA by My HealthWorks Associate Member 125A, 2nd Floor, Shahpur Jat, New Delhi-110049, Whatsapp: 8076964582, Phone No: 011-26496673-(74) info@myhealthworks.in INTRODUCTION Anaemia is
PROJECT WOMEN S ANAEMIA by My HealthWorks Associate Member 125A, 2nd Floor, Shahpur Jat, New Delhi-110049, Whatsapp: 8076964582, Phone No: 011-26496673-(74) info@myhealthworks.in INTRODUCTION Anaemia is
11/4/10 SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP SAM: PREVENT MALNUTRITION 200. Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure
 Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
1 University of Kansas School of Medicine-Wichita, Department of Pediatrics 2 Wesley Medical Center, Department of Neonatology
 Impact of on Very Low Birth Weight Infants Siddharthan Sivamurthy, M.D. 1, Carolyn R. Ahlers-Schmidt, Ph.D. 1, Katherine S. Williams, M.Ed. 1, Jared Shaw 2, Paula Delmore, M.S.N. 2, Barry T. Bloom, M.D.
Impact of on Very Low Birth Weight Infants Siddharthan Sivamurthy, M.D. 1, Carolyn R. Ahlers-Schmidt, Ph.D. 1, Katherine S. Williams, M.Ed. 1, Jared Shaw 2, Paula Delmore, M.S.N. 2, Barry T. Bloom, M.D.
Food for special medical purposes. phenylketonuria (PKU) Important notice: Suitable only for individuals with proven phenylketonuria.
 PKU Nutri 1 Energy Food for special medical purposes. For the dietary management of proven phenylketonuria (PKU) in infants from birth to 12 months and as a supplementary feed up to 3 years. An amino acid
PKU Nutri 1 Energy Food for special medical purposes. For the dietary management of proven phenylketonuria (PKU) in infants from birth to 12 months and as a supplementary feed up to 3 years. An amino acid
Fortisip Powder A high energy, high protein, nutritionally complete, powder supplement that can be mixed to desired energy concentration
 A high energy, high protein, nutritionally complete, powder supplement that can be mixed to desired energy concentration Features Flexibility to prepare to various energy concentrations: 1kcal/ml, 1.5kcal/ml
A high energy, high protein, nutritionally complete, powder supplement that can be mixed to desired energy concentration Features Flexibility to prepare to various energy concentrations: 1kcal/ml, 1.5kcal/ml
AuSPEN Micronutrient Guidelines Review Where we up to?
 AuSPEN Micronutrient Guidelines Review Where we up to? Emma Osland AdvAPD On behalf of the AuSPEN Guidelines Working Group Emma.Osland@health.qld.gov.au Azmat Ali Dietitian, Brisbane Lyn Gillanders Dietitian,
AuSPEN Micronutrient Guidelines Review Where we up to? Emma Osland AdvAPD On behalf of the AuSPEN Guidelines Working Group Emma.Osland@health.qld.gov.au Azmat Ali Dietitian, Brisbane Lyn Gillanders Dietitian,
Symposium 3. Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life
 Symposium 3 Fl id d N t iti S t f th Fluid and Nutrition Support of the Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life Guidelines for the Provision of Amino Acids in the Preterm Infant During the First Week
Symposium 3 Fl id d N t iti S t f th Fluid and Nutrition Support of the Pre-term Infant in the First Week of Life Guidelines for the Provision of Amino Acids in the Preterm Infant During the First Week
Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health
 Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Jane Alsweiler Frank Bloomfield Anna Tottman Barbara Cormack Tanith Alexander Jane Harding Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Why
Early Life Nutrition: Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Jane Alsweiler Frank Bloomfield Anna Tottman Barbara Cormack Tanith Alexander Jane Harding Feeding Preterm Babies for Lifelong Health Why
Product Information: PediaSure (Institutional)
 Product Information: PediaSure (Institutional) 1 of 5 PediaSure is a source of complete, balanced nutrition especially designed for children 1 to 13 years of age. May be used as the sole source of nutrition
Product Information: PediaSure (Institutional) 1 of 5 PediaSure is a source of complete, balanced nutrition especially designed for children 1 to 13 years of age. May be used as the sole source of nutrition
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL?
 HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
Parenteral Nutrition
 Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
Product Information: PediaSure 1.5 Cal with Fiber
 Product Information: PediaSure 1.5 Cal with Fiber 1 of 5 PEDIASURE 1.5 CAL WITH FIBER is a higher * caloric density product designed to meet the higher energy requirements of pediatric patients who are
Product Information: PediaSure 1.5 Cal with Fiber 1 of 5 PEDIASURE 1.5 CAL WITH FIBER is a higher * caloric density product designed to meet the higher energy requirements of pediatric patients who are
Olive oil, Soybean oil
 CLINOLEIC 20% Olive oil, Soybean oil Composition Refined olive oil and refined soys bean oil*... Corresponding to a content of essential fatty acids... 20.00 g 4.00 g Per 100 ml *Mixture of refined olive
CLINOLEIC 20% Olive oil, Soybean oil Composition Refined olive oil and refined soys bean oil*... Corresponding to a content of essential fatty acids... 20.00 g 4.00 g Per 100 ml *Mixture of refined olive
Introduce the basics of the newborn resuscitation period Practice calculations for TPN orders Learn how to manage basic ventilator settings
 Introduce the basics of the newborn resuscitation period Practice calculations for TPN orders Learn how to manage basic ventilator settings Complex concepts you may be expected to know Not taught this
Introduce the basics of the newborn resuscitation period Practice calculations for TPN orders Learn how to manage basic ventilator settings Complex concepts you may be expected to know Not taught this
Product Information:
 Product Information: Pro-Phree 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers who require extra calories, minerals, and vitamins and/or protein restriction. Use under medical supervision. Protein-free
Product Information: Pro-Phree 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers who require extra calories, minerals, and vitamins and/or protein restriction. Use under medical supervision. Protein-free
Not found an answer to your question? Contact
 NUTRITION Supporting information This guideline and supporting information has been prepared with reference to the following: Ben XM. Nutritional management of newborn infants: practical guidelines. World
NUTRITION Supporting information This guideline and supporting information has been prepared with reference to the following: Ben XM. Nutritional management of newborn infants: practical guidelines. World
Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain Therapeutic Nutrition
 Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain Therapeutic Nutrition Shake 1 of 5 PEDIASURE GROW & GAIN is clinically proven * nutrition to help kids grow and is a nutritious supplement for kids falling behind
Product Information: PediaSure Grow & Gain Therapeutic Nutrition Shake 1 of 5 PEDIASURE GROW & GAIN is clinically proven * nutrition to help kids grow and is a nutritious supplement for kids falling behind
Product Category: Pulmocare
 Product Category: Pulmocare Pulmocare Updated 4/8/2014 Product Information: Pulmocare 1 of 5 PULMOCARE is designed for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, or respiratory
Product Category: Pulmocare Pulmocare Updated 4/8/2014 Product Information: Pulmocare 1 of 5 PULMOCARE is designed for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, or respiratory
Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 March Date of the Marketing Authorisation (national procedure): 18 December 1997
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 March 2008 INTRALIPIDE 20 PER CENT, emulsion for infusion 100 ml in Excel container (PE/PP) (CIP: 355 096-5) 250
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 March 2008 INTRALIPIDE 20 PER CENT, emulsion for infusion 100 ml in Excel container (PE/PP) (CIP: 355 096-5) 250
Intensive Care Nutrition. Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA
 Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS. David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA
 HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
HOW TO DO EARLY NUTRITION in VLBW INFANTS David H Adamkin M.D. University of Louisville USA NUTRITIONAL CHALLENGES in EARLY NUTRITION Strategies to Prevent Postnatal Growth Failure Early Total Parenteral
Product Information: Propimex -1
 Product Information: Propimex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with propionic or methylmalonic acidemia. Methionine- and valine-free; low in isoleucine and threonine. Use under medical
Product Information: Propimex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with propionic or methylmalonic acidemia. Methionine- and valine-free; low in isoleucine and threonine. Use under medical
ESPGHAN ESPEN Guidelines on Paediatric Parenteral Nutrition
 ESPEN Congress Cannes 2003 Organised by the Israel Society for Clinical Nutrition Education and Clinical Practice Programme Session: Nutritional Guidelines: ESPEN and other Societies : TPN in Children:
ESPEN Congress Cannes 2003 Organised by the Israel Society for Clinical Nutrition Education and Clinical Practice Programme Session: Nutritional Guidelines: ESPEN and other Societies : TPN in Children:
ENTERAL NUTRITION Identifying risk of patients for enteral feeding problems: Low risk: Moderate risk: High risk:
 ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
Product Category: Promote
 Promote Product Category: Promote Promote Promote with Fiber Updated 5/23/2018 Promote Complete, balanced high protein nutrition Product Information: Promote 1 of 4 Promote Complete, balanced high protein
Promote Product Category: Promote Promote Promote with Fiber Updated 5/23/2018 Promote Complete, balanced high protein nutrition Product Information: Promote 1 of 4 Promote Complete, balanced high protein
Product Information: Phenex -1
 Product Information: Phenex -1 1 of 5 For nutrition support of infants and toddlers with phenylketonuria (PKU). Phenylalanine-free Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine-free to allow greater intake
Product Information: Phenex -1 1 of 5 For nutrition support of infants and toddlers with phenylketonuria (PKU). Phenylalanine-free Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine-free to allow greater intake
Product Information: Ketonex -1
 Product Information: 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Isoleucine-, leucine- and valine-free. Use under medical supervision. Branched-chain amino acid-free
Product Information: 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Isoleucine-, leucine- and valine-free. Use under medical supervision. Branched-chain amino acid-free
Product Information: Jevity 1 Cal
 Product Information: Jevity 1 Cal 1 of 5 JEVITY 1 CAL is a fiber-fortified tube-feeding formula. For tube feeding. For supplemental or sole-source nutrition. May be used for oral feeding of patients with
Product Information: Jevity 1 Cal 1 of 5 JEVITY 1 CAL is a fiber-fortified tube-feeding formula. For tube feeding. For supplemental or sole-source nutrition. May be used for oral feeding of patients with
PRODUCT INFORMATION. DESCRIPTION Addaven is a concentrated trace element solution for infusion which is clear and colourless to slightly yellow.
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Addaven NAME OF MEDICINE Addaven is a concentrated trace element solution containing the following simple salts: chromic chloride hexahydrate (CAS No.:10060-12-5), cupric chloride dihydrate
PRODUCT INFORMATION Addaven NAME OF MEDICINE Addaven is a concentrated trace element solution containing the following simple salts: chromic chloride hexahydrate (CAS No.:10060-12-5), cupric chloride dihydrate
NUTRITION GUIDELINES DRAFT - work in progress January 18 th 2016
 GAIN NORDIC PARTNERSHIP NUTRITION GUIDELINES DRAFT - work in progress January 18 th 2016 A MULTI-SECTOR PARTNERSHIP FOR IMPROVED NUTRITION The GAIN Nordic Partnership aims to deliver nutritious foods to
GAIN NORDIC PARTNERSHIP NUTRITION GUIDELINES DRAFT - work in progress January 18 th 2016 A MULTI-SECTOR PARTNERSHIP FOR IMPROVED NUTRITION The GAIN Nordic Partnership aims to deliver nutritious foods to
Product Information: Tyrex -1
 Product Information: Tyrex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with tyrosinemia types I, II or III. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free. Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free
Product Information: Tyrex -1 1 of 5 Nutrition support of infants and toddlers with tyrosinemia types I, II or III. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free. Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine- and tyrosine-free
Parenteral Nutrition. What is Parenteral Nutrition? Goals of Parenteral Nutrition
 Parenteral Nutrition Diamond Pharmacy Services What is Parenteral Nutrition? Intravenous feeding that provides a patient with fluids and essential nutrients during a time of gastrointestinal function disruption
Parenteral Nutrition Diamond Pharmacy Services What is Parenteral Nutrition? Intravenous feeding that provides a patient with fluids and essential nutrients during a time of gastrointestinal function disruption
Product Information: Glucerna 1.2 Cal
 Product Information: Glucerna 1.2 Cal 1 of 5 GLUCERNA 1.2 CAL is a calorically dense formula that has CarbSteady, including low glycemic carbohydrates clinically shown to help minimize blood glucose response.
Product Information: Glucerna 1.2 Cal 1 of 5 GLUCERNA 1.2 CAL is a calorically dense formula that has CarbSteady, including low glycemic carbohydrates clinically shown to help minimize blood glucose response.
Product Information: Vital AF 1.2 Cal
 Product Information: Vital AF 1.2 Cal 1 of 5 VITAL AF 1.2 CAL is Advanced Formula therapeutic nutrition with ingredients to help manage inflammation and symptoms of GI intolerance. For tube or oral feeding.
Product Information: Vital AF 1.2 Cal 1 of 5 VITAL AF 1.2 CAL is Advanced Formula therapeutic nutrition with ingredients to help manage inflammation and symptoms of GI intolerance. For tube or oral feeding.
Human Nutrition. How our diet determines Health & Wellness
 Human Nutrition How our diet determines Health & Wellness Nutrition The study of food How it nourishes our body How it influences health A mix of Biological and Social Science Relatively new Pragmatic
Human Nutrition How our diet determines Health & Wellness Nutrition The study of food How it nourishes our body How it influences health A mix of Biological and Social Science Relatively new Pragmatic
Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
Product Category: EleCare
 EleCare Product Category: EleCare EleCare (for Infants) Updated 4/28/2016 Product Information: EleCare (for Infants) 1 of 4 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who
EleCare Product Category: EleCare EleCare (for Infants) Updated 4/28/2016 Product Information: EleCare (for Infants) 1 of 4 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who
Product Information: Nepro with Carb Steady
 Product Information: Nepro with Carb Steady 1 of 5 NEPRO WITH CARBSTEADY is therapeutic nutrition specifically designed to help meet the nutritional needs of patients on dialysis (Stage 5 chronic kidney
Product Information: Nepro with Carb Steady 1 of 5 NEPRO WITH CARBSTEADY is therapeutic nutrition specifically designed to help meet the nutritional needs of patients on dialysis (Stage 5 chronic kidney
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Medical conditions that require parenteral nutrition for supply of energy and essential fatty acids.
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Alphalipid 200 mg/ml emulsion for infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml of the emulsion contain: Soya-bean oil,
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Alphalipid 200 mg/ml emulsion for infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml of the emulsion contain: Soya-bean oil,
Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
Product Category: Perative
 Product Category: Perative Perative Updated 4/8/2014 Product Information: Perative 1 of 5 PERATIVE is designed for metabolically stressed patients who can benefit from an enteral formula supplemented with
Product Category: Perative Perative Updated 4/8/2014 Product Information: Perative 1 of 5 PERATIVE is designed for metabolically stressed patients who can benefit from an enteral formula supplemented with
Product Information: PediaSure Peptide 1.5 Cal
 Product Information: PediaSure Peptide 1.5 Cal 1 of 5 PEDIASURE PEPTIDE 1.5 is a nutritionally complete, peptide-based formula for the nutritional needs of children 1-13 years with malabsorption, maldigestion,
Product Information: PediaSure Peptide 1.5 Cal 1 of 5 PEDIASURE PEPTIDE 1.5 is a nutritionally complete, peptide-based formula for the nutritional needs of children 1-13 years with malabsorption, maldigestion,
APPENDIX 1 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SmPC Country: Lebanon Date of approval : 17/08/2011 Procedure : National APPENDIX 1 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1- NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DECAN, concentrate for solution for infusion 2- QUALITATIVE
SmPC Country: Lebanon Date of approval : 17/08/2011 Procedure : National APPENDIX 1 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1- NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DECAN, concentrate for solution for infusion 2- QUALITATIVE
Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan
 Disclosure Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan Penni Davila Hicks, PhD, RD Medical Science Liaison Abbott Nutrition Columbus, Ohio I am currently an employee of Abbott Nutrition Images
Disclosure Nutrition for the Preterm Infant: Developing a Plan Penni Davila Hicks, PhD, RD Medical Science Liaison Abbott Nutrition Columbus, Ohio I am currently an employee of Abbott Nutrition Images
DISCLOSURE. Learning Objectives. Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition
 Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet
 HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet To ensure long-term health and development of preterm infants, an early nutritional support is utmost important. Breast milk is undoubtedly
HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet To ensure long-term health and development of preterm infants, an early nutritional support is utmost important. Breast milk is undoubtedly
BROILER. Nutrition Specifications. An Aviagen Brand
 BROILER 708 Nutrition Specifications 2014 An Aviagen Brand Introduction Nutrition specifications for Ross 708 broilers are given in the following tables for a range of production and market situations
BROILER 708 Nutrition Specifications 2014 An Aviagen Brand Introduction Nutrition specifications for Ross 708 broilers are given in the following tables for a range of production and market situations
Protein Deposition in Growing and Finishing Pigs
 1 Protein Deposition in Growing and Finishing Pigs DETERMINING WHOLE BODY PROTEIN DEPOSITION RATES IN PIGS. Mark L. Lorschy, Doug A. Gillis, John F. Patience and Kees de Lange. Summary There is controversy
1 Protein Deposition in Growing and Finishing Pigs DETERMINING WHOLE BODY PROTEIN DEPOSITION RATES IN PIGS. Mark L. Lorschy, Doug A. Gillis, John F. Patience and Kees de Lange. Summary There is controversy
RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition
 RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition A Strong Beginning Mindy Morris, DNP, NNP-BC, CNS Extremely Low Birth Weight Program Coordinator Objectives Understand the challenges associated with the
RD s In Practice: Advancing Pediatric Nutrition A Strong Beginning Mindy Morris, DNP, NNP-BC, CNS Extremely Low Birth Weight Program Coordinator Objectives Understand the challenges associated with the
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 1. PRODUCT NAME ADDAVEN (infusion, solution concentrate) NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each 10 ml ampoule of Addaven contains: Chromic chloride hexahydrate 53.33 µg
1. PRODUCT NAME ADDAVEN (infusion, solution concentrate) NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each 10 ml ampoule of Addaven contains: Chromic chloride hexahydrate 53.33 µg
STANDARD FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS
 STANDARD 2.9.4 FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS Purpose This Standard defines and regulates the composition and labelling of foods specially formulated to assist sports people in achieving specific
STANDARD 2.9.4 FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS Purpose This Standard defines and regulates the composition and labelling of foods specially formulated to assist sports people in achieving specific
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc
 Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
Product Information: Glucerna Therapeutic Nutrition Shake
 Product Information: Glucerna Therapeutic Nutrition Shake 1 of 5 GLUCERNA THERAPEUTIC NUTRITION SHAKE has CARBSTEADY, including low glycemic carbohydrates clinically shown to help minimize blood glucose
Product Information: Glucerna Therapeutic Nutrition Shake 1 of 5 GLUCERNA THERAPEUTIC NUTRITION SHAKE has CARBSTEADY, including low glycemic carbohydrates clinically shown to help minimize blood glucose
Re: Important changes to Fortisip Powder
 18 June 2014 Dear valued customer Nutricia Ltd 37 Banks Road, Mount Wellington Auckland, New Zealand PO Box 62 523 Greenlane, Auckland 1546 Tel: 0800 688 747 Re: Important changes to Fortisip Powder Nutricia
18 June 2014 Dear valued customer Nutricia Ltd 37 Banks Road, Mount Wellington Auckland, New Zealand PO Box 62 523 Greenlane, Auckland 1546 Tel: 0800 688 747 Re: Important changes to Fortisip Powder Nutricia
STANDARD FOR FOLLOW-UP FORMULA CODEX STAN Adopted in Amended in 1989, 2011, 2017.
 STANDARD FOR FOLLOW-UP FORMULA CODEX STAN 156-1987 Adopted in 1987. Amended in 1989, 2011, 2017. CODEX STAN 156-1987 2 1. SCOPE This standard applies to the composition and labelling of follow-up formula.
STANDARD FOR FOLLOW-UP FORMULA CODEX STAN 156-1987 Adopted in 1987. Amended in 1989, 2011, 2017. CODEX STAN 156-1987 2 1. SCOPE This standard applies to the composition and labelling of follow-up formula.
Product Information: Ensure Plus Therapeutic Nutrition
 Product Information: Ensure Plus Therapeutic Nutrition 1 of 5 ENSURE PLUS provides concentrated calories and protein to help patients gain or maintain healthy weight. ENSURE PLUS can benefit patients who
Product Information: Ensure Plus Therapeutic Nutrition 1 of 5 ENSURE PLUS provides concentrated calories and protein to help patients gain or maintain healthy weight. ENSURE PLUS can benefit patients who
D.K.M COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS) VELLORE-1 DEPARTMENT OF FOODS AND NUTRITION ESSENTIAL OF MICRO NUTRIENTS
 D.K.M COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS) VELLORE-1 DEPARTMENT OF FOODS AND NUTRITION ESSENTIAL OF MICRO NUTRIENTS Class: II M.Sc Subject Code: 15CPFN3A Unit - I (6 Marks Questions) 1. Write a note on performed
D.K.M COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS) VELLORE-1 DEPARTMENT OF FOODS AND NUTRITION ESSENTIAL OF MICRO NUTRIENTS Class: II M.Sc Subject Code: 15CPFN3A Unit - I (6 Marks Questions) 1. Write a note on performed
Product Information: Perative
 Product Information: Perative 1 of 5 PERATIVE is designed for metabolically stressed patients who can benefit from an enteral formula supplemented with arginine. For tube feeding. For supplemental or sole-source
Product Information: Perative 1 of 5 PERATIVE is designed for metabolically stressed patients who can benefit from an enteral formula supplemented with arginine. For tube feeding. For supplemental or sole-source
Broiler Nutrition Specifications
 Broiler Nutrition Specifications 2 Introduction 3 Table 1: Nutrition Specifications for As-Hatched Broilers - Target Live Weight
Broiler Nutrition Specifications 2 Introduction 3 Table 1: Nutrition Specifications for As-Hatched Broilers - Target Live Weight
Product Category: Promote
 Product Category: Promote Promote Promote with Fiber Updated 4/28/2016 Very-High-Protein Nutrition Product Information: Promote 1 of 5 Very-High-Protein Nutrition PROMOTE is a complete, balanced, very-high-protein
Product Category: Promote Promote Promote with Fiber Updated 4/28/2016 Very-High-Protein Nutrition Product Information: Promote 1 of 5 Very-High-Protein Nutrition PROMOTE is a complete, balanced, very-high-protein
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018
 ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Lipid Emulsions In Parenteral Nutrition The Abc Of Parenteral Lipid Emulsions P. Austin (UK) ESPEN Congress, Madrid, September 2018 The ABC of parenteral lipid emulsions Dr Peter
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Lipid Emulsions In Parenteral Nutrition The Abc Of Parenteral Lipid Emulsions P. Austin (UK) ESPEN Congress, Madrid, September 2018 The ABC of parenteral lipid emulsions Dr Peter
Product Information: Ensure Plus Therapeutic Nutrition
 Product Information: Ensure Plus Therapeutic Nutrition 1 of 5 ENSURE PLUS provides concentrated calories and protein to help patients gain or maintain healthy weight. ENSURE PLUS can benefit patients who
Product Information: Ensure Plus Therapeutic Nutrition 1 of 5 ENSURE PLUS provides concentrated calories and protein to help patients gain or maintain healthy weight. ENSURE PLUS can benefit patients who
IMPACT OF PRE-SLAUGHTER WITHDRAWAL OF VITAMIN SUPPLEMENTS ON PIG PERFORMANCE AND MEAT QUALITY. conditions was not addressed in the present study.
 IMPACT OF PRE-SLAUGHTER WITHDRAWAL OF VITAMIN SUPPLEMENTS ON PIG PERFORMANCE AND MEAT QUALITY John F. Patience and Doug Gillis SUMMARY Research reported in last year s Annual Report indicated that withdrawal
IMPACT OF PRE-SLAUGHTER WITHDRAWAL OF VITAMIN SUPPLEMENTS ON PIG PERFORMANCE AND MEAT QUALITY John F. Patience and Doug Gillis SUMMARY Research reported in last year s Annual Report indicated that withdrawal
