Up to now, gel electrophoresis remains the most powerful
|
|
|
- Warren Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 pubs.acs.org/ac Polyacrylamide Gel with Switchable Trypsin Activity for Analysis of Proteins Fangjie Liu,, Mingliang Ye,*, Chunli Wang,, Zhengyan Hu,, Yi Zhang,, Hongqiang Qin,, Kai Cheng,, and Hanfa Zou*, CAS Key Lab of Separation Sciences for Analytical Chemistry, National Chromatographic R&A Center, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian , China Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing , China *S Supporting Information ABSTRACT: Trypsin was immobilized on a variety of materials to improve digestion efficiency. However, because the immobilized trypsin will digest proteins during electrophoresis, direct immobilization of active trypsin in polyacrylamide gel will compromise the protein separation. To overcome this problem, here we report a novel polyacrylamide gel with switchable trypsin activity. It was prepared by copolymerization of the PEG trypsin aprotinin complex during the gel-casting step. Because the inhibitor aprotinin binds strongly with trypsin at alkaline ph, this novel gel does not display hydrolytic activity during electrophoresis. After electrophoresis, the activity of trypsin embedded in gel could be recovered by simply washing away the bound inhibitor at a low ph. It was demonstrated that this unique switchable activity design allowed high resolution of the complex protein mixture during electrophoresis and highly efficient digestion of the separated proteins in situ in the gel after electrophoresis. Up to now, gel electrophoresis remains the most powerful protein separation technology for proteomics. The twodimensional gel electrophoresis (2DE) enables effective resolution of more than 5000 proteins. 1 Combined with mass spectrometry, it is an indispensible complement of shot-gun proteomics for protein analysis. 2 To identify proteins in the gel, gel-separated proteins are first excised and digested by a sequence-specific protease such as trypsin into peptides, and then the proteolytically derived peptides were eluted for MS analysis. 3 To digest the proteins in the gel slices, the protease outside must come into contact with the separated proteins in the gel, which is often achieved by incubating the dehydrated gel slices with buffer-containing protease in the classical in-gel digestion protocol. 4 Most of the components in the buffer will diffuse into the gel network, provided that the components are tiny enough. Unfortunately, the protease is not always small enough. Some useful proteases such as the Glu-C protease (MW 29 kda) are not efficient for in-gel digestion because their sizes are above the limit (25 kda) of efficiently entering in the gel. 5 Trypsin (MW 24 kda) is relatively small and therefore generally used for the in-gel digestion procedure. However, the gels for separation of small proteins (<2 kda) are more dense and the trypsin cannot access these proteins either. To overcome the problem of limited accessibility of the protease to the substrate protein, some alternative ways have been developed. 6 On-membrane digestion is one of these methods. By definition, it means that the proteins entangled in the gel matrix can be transferred to blotting membranes and were then directly digested on the membranes. However, considering that the blotting membranes are originally produced to adsorb proteins, the proteases introduced to perform the digestion and the digested peptide will be adsorbed as well. 5 To overcome this limitation, high concentrations of acetonitrile were often used; however, this method cannot lead to high recovery of large and hydrophobic peptides. 7 Another approach to digest proteins adsorbed on the membrane is to dissolve the membranes using some organic solvents prior to digestion Though many efforts have been made to improve this method, its performance is still not good enough because of the partial solubility of proteins or peptides in this system for dissolving membranes. Another interesting approach used to overcome the protease accessibility problem is to use reversible polyacrylamide gels. 11 After electrophoresis, the filament frame of this type of gel could be conditionally cleaved to expose the proteins inside. Whereas this method directly counteracted the problem of low enzyme accessibility, it was not widely utilized as expected probably because of its difficulty in gel preparation and poor resolution. 5 Trypsin has been immobilized on a number of matrices for protein digestion in MS-based protein analysis This approach has many advantages, including highly efficient digestion rate, reduced autolysis products, etc. Can we immobilize trypsin on the polyacrylamide gel for electrophoresis of proteins? To prepare such a gel is not difficult. The key issues include the following: (1) there should be no Received: June 13, 2013 Accepted: July 16, 2013 Published: July 16, American Chemical Society 7024
2 Scheme 1. Schematic Illustration of the Workflow for Analysis of Proteins by the Trypsin Activity Switchable Gel. a a (A) The gel with embedded trypsin-inhibitor complex, (B) separation of proteins by the novel gel via electrophoresis, and (C) in-situ digestion of separated proteins by the trypsin embedded in the gel after washing away inhibitors. hydrolysis activity in the gel during electrophoresis. (2) The hydrolysis activity could be turned on after electrophoresis. To achieve this purpose, we proposed a promising in situ digestion scheme, as shown in Scheme 1. Trypsin was copolymerized in the polyacrylamide gel during the gel-casting stage. To prevent the possible digestion of proteins by the embedded trypsin during electrophoresis, the hydrolysis activity of trypsin was suppressed by a reversible enzyme inhibitor. After electrophoresis, the hydrolysis activity of trypsin was recovered by removing the inhibitor. This switchable activity design would allow for high resolution of the complex protein mixture during electrophoresis and highly efficient digestion of the separated proteins in situ in the gel after electrophoresis. EXPERIMENTAL SECTION For casting the gel embedded with trypsin, we simply mixed 100 μl of10μg/μl trypsin (in 1 mm HCl aqueous solution) with the other components, 2.4 ml Milli-Q H 2 O, 1.25 ml of 40% acrylamide/bis solution (29: 1, Bio-Rad), 1.3 ml of 1.5 M Tris-HCl buffer (ph 8.8), 50 μl of 10% SDS, 50 μl of 10% ammonium persulfate, and 3 μl of TEMED (Table S1 of the Supporting Information), and then we left it to polymerize at room temperature. As for other SDS PAGE gradient gels, including the conventional gels and the gels embedded with the trypsin aprotinin and PEG trypsin aprotinin complexes, they were prepared in the same way (see the Supporting Information). To monitor the trypsin activity of the prepared gels with trypsin, a gel slice ( cm 2, 2 μg trypsin) was excised and cut into pieces in 1 ml of 50 mm NH 4 HCO 3 buffer in an Eppendorf tube. The synthetic peptide (2 μg) was then added to the above tube for digestion at 37 C for about 1 h. Hydrolysis products were then detected by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight-mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS). For the analysis of HeLa proteins by the gel embedded with the PEG trypsin aprotinin complex, we loaded 16 μg of HeLa proteins onto each lane. After electrophoresis, the gel was stained by the Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 dye. It was destained by aqueous solution containing 50% ethanol and 10% acetic acid, and then the gel was cut into eight slices. The destaining solution also washed the inhibitor aprotinin away. The buffer with gel slices was then switched with the 50 mm NH 4 HCO 3 buffer for in situ digestion overnight at 37 C. The resulting digests were then analyzed by LC MS/MS (see the Supporting Information). 7025
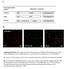
3 Analytical Chemistry Figure 1. Monitor the trypsin activity by MALDI-TOF-MS. (A) Direct analysis of the synthetic peptide (VIFIEHAKRKG, MW Da), incubation of the synthetic peptide with (B) the blank gel without trypsin, (C) the gel with embedded trypsin, (D) the gel with the embedded trypsin aprotinin complex; (E) the same gel with (D) except with the removal of aprotinin with vigorous washing at low ph. Figure 2. Separation of protein standards by the (A) gel with embedded trypsin in the presence of 0.3% SDS, (B) gel with the embedded trypsin ABA complex, (C, D) gel with the embedded trypsin aprotinin complex, (G) gel with the embedded PEG trypsin aprotinin complex, (E, F, H) parallel control gels without trypsin. (A, B, C, E) were stained by Coomassie; (D, F, G, H) were stained by silver. Markers 1 and 2 had a prestained protein ladder of 10 recombinant proteins and a prestained protein molecular weight marker of 6 natural proteins, respectively. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION For separation by SDS PAGE, a high concentration of SDS (0.3% SDS) could be added in the running buffer for separation of proteins. The trypsin may lose its activity under this condition. After separation, the trypsin may gain its activity when the SDS is removed from the gel by repeated washing. If the above assumption were true, then a simple solution could be developed to control the activity of trypsin embedded in the gel without any additional inhibitors. Thus, we first tested if the trypsin still had activity when they were entrapped in the gel with the presence of 0.3% SDS. The gel slice was incubated with the synthetic peptide to detect the trypsin activity. A control experiment was performed as identical to above, except that a gel slice from a SDS PAGE gel without trypsin was used. Figure 1 gives the MALDI-TOF-MS spectra for analysis of the products. Two main hydrolysis product peaks of and were observed for the gel slice with copolymerized trypsin (Figure 1C), while only one peak at (Figure 1B) corresponding to the intact peptide (Figure 1A) was observed for the gel without trypsin. This indicated that trypsin encapsulated in the hydrogel network still has hydrolysis activity. Thus the SDS presented in the gel cannot diminish its activity. We also applied the prepared gel containing trypsin for electrophoresis of protein mixture, however clear protein bands were barely observed after electrophoresis (Figure 2A). This was not surprising since the trypsin entrapped in the gel still 7026
4 Scheme 2. Schematic Illustration for the Coupling of Trypsin to PEG Macromolecule Figure 3. Separation of protein standards by the (A) gel with the embedded PEG trypsin aprotinin complex and the (B) control gel without trypsin. Fractionation of total HeLa cell lysate by the gel with the PEG trypsin aprotinin complex. (C) SDS PAGE image stained by Coomassie, and (D) the number of peptides identified from each fraction. preserved hydrolysis activity, which would inevitably cut the proteins during electrophoresis. Therefore, without the addition of an additional inhibitor, the gel with switchable trypsin activity cannot be prepared. P-aminobenzamidine (ABA) is a popular inhibitor of trypsinlike serine proteases. We tried to use ABA to prepare such a gel. However, when the ABA hydrochloride was added with trypsin to the polymerization solution, precipitation was observed. This was because a neutral complex was formed when ABA, a cation, mixed with the anionic surfactant SDS. We attempted to use the prepared gel for separation of proteins. Clear protein bands were not obtained either (Figure 2B). We then turned to test another trypsin inhibitor, aprotinin. It is a small polypeptide with a MW of 6512 that can reversibly couple to trypsin with a 1: 1 stiochiometry to form a complex. 15 This complex was very stable over a narrow ph range centered around ph 8.3 and would be dissociated only when the ph was lower than 3. This unique ph dependent association/ dissociation characteristic between trypsin and aprotinin makes aprotinin a perfect inhibitor for preparation of the activity switchable gel. To test the inhibition and recovery of the trypsin activity, two gel slices with the same size were excised from the prepared gel containing the complex. One gel slice was directly incubated with the synthetic peptides in the NH 4 HCO 3 buffer. No hydrolysis products were observed, indicating that no trypsin activity was presented in the gel (Figure 1D). Another gel slice was washed by 1% acetic acid solution (ph < 3) to remove aprotinin. It was found that the 7027 substrate peptide was digested, which indicated that trypsin recovered its hydrolysis activity without a hitch (Figure 1E). The washing at low ph led to the dissociation of the complex, and because aprotinin was relatively small (MW 6512 Da), it could easily get out of the gel, leaving trypsin alone in the gel network. Once the ph was changed back to around ph 8.0, the gel slice displayed a predominant hydrolysis activity. In this way, the activity of trypsin entrapped in the gel can be switched off and then on as required. The prepared trypsin aprotinin gel was applied for separation of protein standards (i.e., the prestained protein ladder). Compared with that in Figure 2 (panels A and B), clear protein bands were observed for this gel, as shown in Figure 2 (panels C and D). More importantly, the separation of these proteins were as good as that of the control experiment using the gel without trypsin (Figure 2, panels E and F). The above data indicated that the presence of the complex in the gel did not deteriorate the separation. However, it could be seen that the background for the trypsin aprotinin gels were not homogeneous. For both silver and Coomassie staining gels, the bottom sections were much darker than the top sections (Figure 2, panels C and D). This indicated that the trypsin aprotinin embedded in the gel probably moved down in the electric field during the electrophoresis. To prepare a gel with homogeneous trypsin activity, the movement of the complex in the gel during electrophoresis must be prevented. To prevent the mobility of the complex, we attempted to increase its size by coupling the trypsin to the PEG
5 macromolecule, as shown in Scheme 2. The hydrophilic PEG macromolecule has 4-arms, and on every arm there was a reactive group N-hydroxy succinimide (NHS) ester, which could readily react with the primary amines. The obtained gel was applied to separation of protein standards followed by staining with silver. It was found that the background of the gel was homogeneous in color, indicating that trypsin movement during SDS PAGE was prevented (Figure 2, panels G and H). Compared with the control gel, the gel embedded with the PEG trypsin aprotinin complex unexpectedly preserved favorable separation performance, or even better, because each band of protein mixture was far apart from the others (Figure 3A). Due to its robust separation performance, SDS PAGE was often used for fractionation of proteins in proteomics analysis. 4 We then applied the casted SDS PAGE system for analysis of the complex HeLa cell protein. The high performance of this gel was confirmed by the good separation of protein markers. The digests from each fraction (Figure 3C) were subjected to LC MS analysis performed on a LTQ linear mass spectrometer. On average, about eight hundreds peptides were identified from each fraction (Figure 3D). With consideration that only about 2 μg of proteins were present in a gel slice and only half were loaded for LC MS/MS analysis, the above numbers were excellent. To make sure the peptides identified from each fraction were due to in situ digestion, a control experiment was performed as above, except that a gel without any trypsin was used. It was found that almost no peptide was identified, which indicated that the proteins in the gel were successfully digested in situ by the trypsin immobilized in the gel. Similar numbers of peptides identified from the early fractions and later fractions indicated that the hydrolysis activity was present throughout the gel, which confirmed that the trypsin complex did not move down the gel during electrophoresis. The above results clearly indicated that the prepared gel with switchable trypsin activity was readily applied to the analysis of complex protein samples. CONCLUSIONS A novel gel with immobilized trypsin was prepared by embedment of a PEG trypsin aprotinin complex in the gel network during the gel-casting step. The big size of the complex prevented the movement of trypsin in the electric field during electrophoresis. The complex of trypsin with an inhibitor allowed the separation of proteins by electrophoresis without any risk of digestion. After removing the inhibitor at low ph, in situ digestion of proteins in the gel was successfully achieved without additional trypsin. This switchable activity design allowed high resolution of complex protein mixture during electrophoresis and highly efficient digestion of the separated proteins in situ in the gel after electrophoresis. As a prototype gel system with switchable protease activity, its performance is expected to be improved by further optimization. ASSOCIATED CONTENT *S Supporting Information Detailed experimental procedures, lists of components, and amounts acquired for gel preparation. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at AUTHOR INFORMATION Corresponding Author *H.F.Z.: , hanfazou@dicp.ac.cn; tel, ; fax, M.L.Y.: , mingliang@dicp.ac.cn; tel, ; fax, Notes The authors declare no competing financial interest. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Financial support from the Creative Research Group Project of NSFC (Grant ), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants and ), the China State Key Basic Research Program Grant (Grants 2012CB910101, 2013CB911202, and 2012CB910604), National Key Special Program on Infection Diseases (Grant 2012ZX ), and the Analytical Method Innovation Program of MOST (Grant 2012IM030900) are grateful acknowledged. REFERENCES (1) Gorg, A.; Weiss, W.; Dunn, M. J. Proteomics 2004, 4, (2) Aebersold, R.; Mann, M. Nature 2003, 422, (3) Wilm, M.; Shevchenko, A.; Houthaeve, T.; Breit, S.; Schweigerer, L.; Fotsis, T.; Mann, M. Nature 1996, 379, (4) Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havlis, J.; Olsen, J. V.; Mann, M. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, (5) Rabilloud, T.; Vaezzadeh, A. R.; Potier, N.; Lelong, C.; Leize- Wagner, E.; Chevallet, M. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2009, 28, (6) Lahm, H. W.; Langen, H. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, (7) Bunai, K.; Nozaki, M.; Hamano, M.; Ogane, S.; Inoue, T.; Nemoto, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Yamane, K. Proteomics 2003, 3, (8) Luque-Garcia, J. L.; Zhou, G.; Sun, T. T.; Neubert, T. A. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, (9) Luque-Garcia, J. L.; Zhou, G.; Spellman, D. S.; Sun, T. T.; Neubert, T. A. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2008, 7, (10) Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, W. J.; He, Q. Z.; Li, J. L.; Chen, P.; Wang, X. C.; Liang, S. P. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, (11) Bornemann, S.; Rietschel, B.; Baltruschat, S.; Karas, M.; Meyer, B. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, (12) Luckarift, H. R.; Spain, J. C.; Naik, R. R.; Stone, M. O. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, (13) Samanta, B.; Yang, X. C.; Ofir, Y.; Park, M. H.; Patra, D.; Agasti, S. S.; Miranda, O. R.; Mo, Z. H.; Rotello, V. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, (14) Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Youn, J. K.; Bin Na, H.; Yu, T.; Kim, H.; Lee, S. M.; Koo, Y. M.; Kwak, J. H.; Park, H. G.; Chang, H. N.; Hwang, M.; Park, J. G.; Kim, J.; Hyeon, T. Small 2008, 4, (15) Raspi, G.; Lo Moro, A.; Spinetti, M.; Molinari, M. The Analyst 1989, 114,
Improve Protein Analysis with the New, Mass Spectrometry- Compatible ProteasMAX Surfactant
 Improve Protein Analysis with the New, Mass Spectrometry- Compatible Surfactant ABSTRACT Incomplete solubilization and digestion and poor peptide recovery are frequent limitations in protein sample preparation
Improve Protein Analysis with the New, Mass Spectrometry- Compatible Surfactant ABSTRACT Incomplete solubilization and digestion and poor peptide recovery are frequent limitations in protein sample preparation
Agilent Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit
 Agilent 5188-2749 Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit Agilent Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit Instructions Kit Contents The Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit includes sufficient reagents for approximately
Agilent 5188-2749 Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit Agilent Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit Instructions Kit Contents The Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit includes sufficient reagents for approximately
In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit
 INSTRUCTIONS In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit 3747 N. Meridian Road P.O. Box 117 Rockford, IL 61105 89871 1468.2 Number Description 89871 In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit, sufficient reagents for approximately
INSTRUCTIONS In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit 3747 N. Meridian Road P.O. Box 117 Rockford, IL 61105 89871 1468.2 Number Description 89871 In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit, sufficient reagents for approximately
PosterREPRINT A NOVEL APPROACH TO MALDI-TOF-MS SAMPLE PREPARATION. Presented at ABRF 2002, Austin, Texas, USA, 9th - 12th March 2002.
 Introduction A NOVEL APPROACH TO MALDI-TOF-MS SAMPLE PREPARATION Ed Bouvier 2, Jeff Brown 1, Emmanuelle Claude 1, John L. Gebler 2, Weibin Chen 2, *Dominic Gostick 1, Kevin Howes 1, James Langridge 1,
Introduction A NOVEL APPROACH TO MALDI-TOF-MS SAMPLE PREPARATION Ed Bouvier 2, Jeff Brown 1, Emmanuelle Claude 1, John L. Gebler 2, Weibin Chen 2, *Dominic Gostick 1, Kevin Howes 1, James Langridge 1,
Supplementary material: Materials and suppliers
 Supplementary material: Materials and suppliers Electrophoresis consumables including tris-glycine, acrylamide, SDS buffer and Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-2 dye (CBB) were purchased from Ameresco (Solon,
Supplementary material: Materials and suppliers Electrophoresis consumables including tris-glycine, acrylamide, SDS buffer and Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-2 dye (CBB) were purchased from Ameresco (Solon,
Use of Nitrocellulose Membranes for Protein Characterization by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry
 Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5102-5108 Use of Nitrocellulose Membranes for Protein Characterization by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Jose L. Luque-Garcia, Ge Zhou, Tung-Tien Sun,*,
Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5102-5108 Use of Nitrocellulose Membranes for Protein Characterization by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Jose L. Luque-Garcia, Ge Zhou, Tung-Tien Sun,*,
(III) MALDI instrumentation
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava (I) Basics of MALDI-TF (II) Sample preparation In-gel digestion Zip-tip sample clean-up Matrix and sample plating (III) MALDI instrumentation 2 1 (I) Basics of MALDI-TF Analyte
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava (I) Basics of MALDI-TF (II) Sample preparation In-gel digestion Zip-tip sample clean-up Matrix and sample plating (III) MALDI instrumentation 2 1 (I) Basics of MALDI-TF Analyte
Trypsin Mass Spectrometry Grade
 058PR-03 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Trypsin Mass Spectrometry Grade A Chemically Modified, TPCK treated, Affinity Purified
058PR-03 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Trypsin Mass Spectrometry Grade A Chemically Modified, TPCK treated, Affinity Purified
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical properties of SDS-stable low molecular weight alkaline serine protease from Citrullus Colocynthis Muhammad Bashir Khan, 1,3 Hidayatullah khan, 2 Muhammad
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical properties of SDS-stable low molecular weight alkaline serine protease from Citrullus Colocynthis Muhammad Bashir Khan, 1,3 Hidayatullah khan, 2 Muhammad
Multiplex Protein Quantitation using itraq Reagents in a Gel-Based Workflow
 Multiplex Protein Quantitation using itraq Reagents in a Gel-Based Workflow Purpose Described herein is a workflow that combines the isobaric tagging reagents, itraq Reagents, with the separation power
Multiplex Protein Quantitation using itraq Reagents in a Gel-Based Workflow Purpose Described herein is a workflow that combines the isobaric tagging reagents, itraq Reagents, with the separation power
Proteomics Grade. Protocol. Catalog # Agilent Technologies. Research Use Only. Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures. Version A, January 2010
 Proteomics Grade Trypsin Catalog #204310 Protocol Version A, January 2010 Research Use Only. Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures. Agilent Technologies Notices Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2010 No part of
Proteomics Grade Trypsin Catalog #204310 Protocol Version A, January 2010 Research Use Only. Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures. Agilent Technologies Notices Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2010 No part of
Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range
 Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry
 Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Basic principles An attractive feature of the time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometer is its
Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Basic principles An attractive feature of the time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometer is its
In-Solution Digestion for proteomics
 In-Solution Digestion for proteomics Guidelines for sample preparation (How to protect your samples from contamination with keratin) 1. Try to avoid any contact of samples and solutions with dust, skin
In-Solution Digestion for proteomics Guidelines for sample preparation (How to protect your samples from contamination with keratin) 1. Try to avoid any contact of samples and solutions with dust, skin
Mass Spectrometry. Mass spectrometer MALDI-TOF ESI/MS/MS. Basic components. Ionization source Mass analyzer Detector
 Mass Spectrometry MALDI-TOF ESI/MS/MS Mass spectrometer Basic components Ionization source Mass analyzer Detector 1 Principles of Mass Spectrometry Proteins are separated by mass to charge ratio (limit
Mass Spectrometry MALDI-TOF ESI/MS/MS Mass spectrometer Basic components Ionization source Mass analyzer Detector 1 Principles of Mass Spectrometry Proteins are separated by mass to charge ratio (limit
Trypsin Digestion Mix
 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name 239PR Trypsin Digestion Mix Provides optimal buffered conditions for in gel trypsin digestion
G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name 239PR Trypsin Digestion Mix Provides optimal buffered conditions for in gel trypsin digestion
Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada *For correspondence:
 Zymogram Assay for the Detection of Peptidoglycan Hydrolases in Streptococcus mutans Delphine Dufour and Céline M. Lévesque * Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Zymogram Assay for the Detection of Peptidoglycan Hydrolases in Streptococcus mutans Delphine Dufour and Céline M. Lévesque * Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto,
HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit
 HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI009 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5/20 Duration of Experiment: ~ 2 days Day 1: 6-8 hours (SDS- PAGE and Electroblotting) Day 2: 3 hours
HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI009 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5/20 Duration of Experiment: ~ 2 days Day 1: 6-8 hours (SDS- PAGE and Electroblotting) Day 2: 3 hours
Supplementary Information. Top-down/bottom-up mass spectrometry workflow using dissolvable polyacrylamide gels
 Supplementary Information Top-down/bottom-up mass spectrometry workflow using dissolvable polyacrylamide gels Nobuaki Takemori,,* Ayako Takemori,, Piriya Wongkongkathep, Michael Nshanian, Rachel R. Ogorzalek
Supplementary Information Top-down/bottom-up mass spectrometry workflow using dissolvable polyacrylamide gels Nobuaki Takemori,,* Ayako Takemori,, Piriya Wongkongkathep, Michael Nshanian, Rachel R. Ogorzalek
PTM Discovery Method for Automated Identification and Sequencing of Phosphopeptides Using the Q TRAP LC/MS/MS System
 Application Note LC/MS PTM Discovery Method for Automated Identification and Sequencing of Phosphopeptides Using the Q TRAP LC/MS/MS System Purpose This application note describes an automated workflow
Application Note LC/MS PTM Discovery Method for Automated Identification and Sequencing of Phosphopeptides Using the Q TRAP LC/MS/MS System Purpose This application note describes an automated workflow
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
The distribution of log 2 ratio (H/L) for quantified peptides. cleavage sites in each bin of log 2 ratio of quantified. peptides
 Journal: Nature Methods Article Title: Corresponding Author: Protein digestion priority is independent of their abundances Mingliang Ye and Hanfa Zou Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 The distribution
Journal: Nature Methods Article Title: Corresponding Author: Protein digestion priority is independent of their abundances Mingliang Ye and Hanfa Zou Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 The distribution
4th Multidimensional Chromatography Workshop Toronto (January, 2013) Herman C. Lam, Ph.D. Calibration & Validation Group
 4th Multidimensional Chromatography Workshop Toronto (January, 2013) Herman C. Lam, Ph.D. Calibration & Validation Group MDLC for Shotgun Proteomics Introduction General concepts Advantages Challenges
4th Multidimensional Chromatography Workshop Toronto (January, 2013) Herman C. Lam, Ph.D. Calibration & Validation Group MDLC for Shotgun Proteomics Introduction General concepts Advantages Challenges
ProteaseMAX Surfactant, Trypsin Enhancer
 Technical Bulletin ProteaseMAX Surfactant, Trypsin Enhancer INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS V2071 AND V2072. PRINTED IN USA. Revised 1/10 ProteaseMAX Surfactant, Trypsin Enhancer All technical literature
Technical Bulletin ProteaseMAX Surfactant, Trypsin Enhancer INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS V2071 AND V2072. PRINTED IN USA. Revised 1/10 ProteaseMAX Surfactant, Trypsin Enhancer All technical literature
NOTES & TIPS. Evaluation of the Efficiency of In-Gel Digestion of Proteins by Peptide Isotopic Labeling and MALDI Mass Spectrometry
 All articles available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on NOTES & TIPS Evaluation of the Efficiency of In-Gel Digestion of Proteins by Peptide Isotopic Labeling and MALDI Mass Spectrometry Anna Shevchenko
All articles available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on NOTES & TIPS Evaluation of the Efficiency of In-Gel Digestion of Proteins by Peptide Isotopic Labeling and MALDI Mass Spectrometry Anna Shevchenko
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. R 2 GlcNAcβ1 4GlcNAcβ1 Asn
 GlycoProfile II Enzymatic In-Solution N-Deglycosylation Kit Product Code PP0201 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Glycosylation is one of the most common posttranslational
GlycoProfile II Enzymatic In-Solution N-Deglycosylation Kit Product Code PP0201 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Glycosylation is one of the most common posttranslational
MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry
 MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry Nan Kleinholz Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Facility The Ohio State University Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Workshop What is MALDI Imaging? MALDI: Matrix Assisted
MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry Nan Kleinholz Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Facility The Ohio State University Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Workshop What is MALDI Imaging? MALDI: Matrix Assisted
Double charge of 33kD peak A1 A2 B1 B2 M2+ M/z. ABRF Proteomics Research Group - Qualitative Proteomics Study Identifier Number 14146
 Abstract The 2008 ABRF Proteomics Research Group Study offers participants the chance to participate in an anonymous study to identify qualitative differences between two protein preparations. We used
Abstract The 2008 ABRF Proteomics Research Group Study offers participants the chance to participate in an anonymous study to identify qualitative differences between two protein preparations. We used
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Microwave-assisted Kochetkov amination followed by permanent charge derivatization: A facile strategy for glycomics Xin Liu a,b, Guisen Zhang* a, Kenneth Chan b and
Electronic Supplementary Information Microwave-assisted Kochetkov amination followed by permanent charge derivatization: A facile strategy for glycomics Xin Liu a,b, Guisen Zhang* a, Kenneth Chan b and
DetergentOUT Tween. DetergentOUT GBS10. OrgoSol DetergentOUT
 252PR 01 G-Biosciences, St Louis, MO. USA 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name DetergentOUT Detergent Removal Systems For the Removal of Detergents
252PR 01 G-Biosciences, St Louis, MO. USA 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name DetergentOUT Detergent Removal Systems For the Removal of Detergents
Analysis of Electroblotted Proteins by Mass Spectrometry: Protein
 MCP Papers in Press. Published on October 15, 2007 as Manuscript M700415-MCP200 Analysis of Electroblotted Proteins by Mass Spectrometry: Protein Identification after Western Blotting Jose L. Luque-Garcia,
MCP Papers in Press. Published on October 15, 2007 as Manuscript M700415-MCP200 Analysis of Electroblotted Proteins by Mass Spectrometry: Protein Identification after Western Blotting Jose L. Luque-Garcia,
Lecture 3. Tandem MS & Protein Sequencing
 Lecture 3 Tandem MS & Protein Sequencing Nancy Allbritton, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology & Biophysics 824-9137 (office) nlallbri@uci.edu Office- Rm D349 Medical Science D Bldg. Tandem MS Steps:
Lecture 3 Tandem MS & Protein Sequencing Nancy Allbritton, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology & Biophysics 824-9137 (office) nlallbri@uci.edu Office- Rm D349 Medical Science D Bldg. Tandem MS Steps:
MALDI-TOF. Introduction. Schematic and Theory of MALDI
 MALDI-TOF Proteins and peptides have been characterized by high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) or SDS PAGE by generating peptide maps. These peptide maps have been used as fingerprints of protein
MALDI-TOF Proteins and peptides have been characterized by high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) or SDS PAGE by generating peptide maps. These peptide maps have been used as fingerprints of protein
The Detection of Allergens in Food Products with LC-MS
 The Detection of Allergens in Food Products with LC-MS Something for the future? Jacqueline van der Wielen Scope of Organisation Dutch Food and Consumer Product Safety Authority: Law enforcement Control
The Detection of Allergens in Food Products with LC-MS Something for the future? Jacqueline van der Wielen Scope of Organisation Dutch Food and Consumer Product Safety Authority: Law enforcement Control
Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples:
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples: Sample preparation for serum proteome analysis Sample
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples: Sample preparation for serum proteome analysis Sample
Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム
 Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム Add the following next to Description: Identification Dissolve 1 mg each of Heparin Sodium and Heparin Sodium Reference Standard for physicochemical test in 1 ml of water, and
Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム Add the following next to Description: Identification Dissolve 1 mg each of Heparin Sodium and Heparin Sodium Reference Standard for physicochemical test in 1 ml of water, and
Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Orthogonal Quadrupole TOF MS(MS) for Metabolite Identification
 22 SEPARATION SCIENCE REDEFINED MAY 2005 Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Orthogonal Quadrupole TOF MS(MS) for Metabolite Identification In the drug discovery process the detection and
22 SEPARATION SCIENCE REDEFINED MAY 2005 Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Orthogonal Quadrupole TOF MS(MS) for Metabolite Identification In the drug discovery process the detection and
Facile Cu(II) mediated conjugation of thioesters and thioacids to peptides and proteins under mild conditions
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Facile Cu(II) mediated conjugation of thioesters and thioacids to peptides
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Facile Cu(II) mediated conjugation of thioesters and thioacids to peptides
Supporting information
 S1 Supporting information Biodegradable Injectable Polymer Systems Exhibiting Temperature-Responsive Irreversible Sol-to-Gel Transition by Covalent Bond Formation Yasuyuki YOSHIDA 1,2, Keisuke KAWAHARA
S1 Supporting information Biodegradable Injectable Polymer Systems Exhibiting Temperature-Responsive Irreversible Sol-to-Gel Transition by Covalent Bond Formation Yasuyuki YOSHIDA 1,2, Keisuke KAWAHARA
2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
Tunable Hydrophobicity in DNA Micelles Anaya, Milena; Kwak, Minseok; Musser, Andrew J.; Muellen, Klaus; Herrmann, Andreas; Müllen, Klaus
 University of Groningen Tunable Hydrophobicity in DNA Micelles Anaya, Milena; Kwak, Minseok; Musser, Andrew J.; Muellen, Klaus; Herrmann, Andreas; Müllen, Klaus Published in: Chemistry DOI: 10.1002/chem.201001816
University of Groningen Tunable Hydrophobicity in DNA Micelles Anaya, Milena; Kwak, Minseok; Musser, Andrew J.; Muellen, Klaus; Herrmann, Andreas; Müllen, Klaus Published in: Chemistry DOI: 10.1002/chem.201001816
Integration of Cell Lysis, Protein Extraction, and Digestion into One Step for Ultrafast Sample Preparation for Phosphoproteome Analysis
 pubs.acs.org/ac Integration of Cell Lysis, Protein Extraction, and Digestion into One Step for Ultrafast Sample Preparation for Phosphoproteome Analysis Fangjie Liu,, Mingliang Ye,*, Yanbo Pan,, Yi Zhang,,
pubs.acs.org/ac Integration of Cell Lysis, Protein Extraction, and Digestion into One Step for Ultrafast Sample Preparation for Phosphoproteome Analysis Fangjie Liu,, Mingliang Ye,*, Yanbo Pan,, Yi Zhang,,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Development of a High Coverage Pseudotargeted Lipidomics Method Based on Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Qiuhui Xuan 1,2#, Chunxiu Hu 1#, Di Yu 1,2,
Supporting Information Development of a High Coverage Pseudotargeted Lipidomics Method Based on Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Qiuhui Xuan 1,2#, Chunxiu Hu 1#, Di Yu 1,2,
PHOSPHOPEPTIDE ANALYSIS USING IMAC SAMPLE PREPARATION FOLLOWED BY MALDI-MS and MALDI PSD MX
 PHOSPHOPEPTIDE ANALYSIS USING IMAC SAMPLE PREPARATION FOLLOWED BY MALDI-MS and MALDI PSD MX E. Claude 1, E. Emekwue 2, M. Snel 1, T. McKenna 1 and J. Langridge 1 1: Waters Corporation, Manchester, UK 2:
PHOSPHOPEPTIDE ANALYSIS USING IMAC SAMPLE PREPARATION FOLLOWED BY MALDI-MS and MALDI PSD MX E. Claude 1, E. Emekwue 2, M. Snel 1, T. McKenna 1 and J. Langridge 1 1: Waters Corporation, Manchester, UK 2:
Chapter PURIFICATION OF ALKALINE PROTEASES
 Chapter PURIFICATION OF ALKALINE PROTEASES E /xtracellular alkaline proteases produced by Bacillus sp. K 25 and bacillus pumilus K 242, were purified and the homogeneity was examined by electrophoresis.
Chapter PURIFICATION OF ALKALINE PROTEASES E /xtracellular alkaline proteases produced by Bacillus sp. K 25 and bacillus pumilus K 242, were purified and the homogeneity was examined by electrophoresis.
Chemical Biology, Option II Mechanism Based Proteomic Tagging Case History CH1
 Proteome Wide Screening of Serine Protease Activity Proc Natl Acad Sci 1999, 97, 14694; Proteomics 2001, 1, 1067; Proc Natl Acad Sci 2002, 99, 10335; Biochemistry 2001, 40, 4005; J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005,
Proteome Wide Screening of Serine Protease Activity Proc Natl Acad Sci 1999, 97, 14694; Proteomics 2001, 1, 1067; Proc Natl Acad Sci 2002, 99, 10335; Biochemistry 2001, 40, 4005; J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005,
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011
 Supporting Information Experimental details 1. Materials Ferric chloride (FeCl 3 6H 2 O), Ethylene glycol (EG) and Ammonium hydroxide (NH 3 H 2 O) were obtained from Beijing Chemical Regent Co. Ltd. (Beijing,
Supporting Information Experimental details 1. Materials Ferric chloride (FeCl 3 6H 2 O), Ethylene glycol (EG) and Ammonium hydroxide (NH 3 H 2 O) were obtained from Beijing Chemical Regent Co. Ltd. (Beijing,
Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics. Professor Xudong Yao Bioanalytical Chemistry Spring 2007
 Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Professor Xudong Yao Bioanalytical Chemistry Spring 2007 Proteomics and -omics Roles of mass spectrometry Comparative proteomics Chemical proteomics Protein, Proteome and
Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Professor Xudong Yao Bioanalytical Chemistry Spring 2007 Proteomics and -omics Roles of mass spectrometry Comparative proteomics Chemical proteomics Protein, Proteome and
General and Facile Surface Functionalization of Hydrophobic Nanocrystals with Poly(amino acid) for Cell Luminescence Imaging
 General and Facile Surface Functionalization of Hydrophobic Nanocrystals with Poly(amino acid) for Cell Luminescence Imaging Sheng Huang, Min Bai, Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering,
General and Facile Surface Functionalization of Hydrophobic Nanocrystals with Poly(amino acid) for Cell Luminescence Imaging Sheng Huang, Min Bai, Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering,
LECTURE-15. itraq Clinical Applications HANDOUT. Isobaric Tagging for Relative and Absolute quantitation (itraq) is a quantitative MS
 LECTURE-15 itraq Clinical Applications HANDOUT PREAMBLE Isobaric Tagging for Relative and Absolute quantitation (itraq) is a quantitative MS based method for quantifying proteins subject to various different
LECTURE-15 itraq Clinical Applications HANDOUT PREAMBLE Isobaric Tagging for Relative and Absolute quantitation (itraq) is a quantitative MS based method for quantifying proteins subject to various different
PosterREPRINT INTRODUCTION. 2-D PAGE of Mouse Liver Samples. 2-D PAGE of E.coli Samples. Digestion / Cleanup. EXPERIMENTAL 1-D PAGE of BSA Samples
 INTRODUCTION Identification and characterization of low abundance proteins separated by 2D gel electrophoresis is complicated by two important factors; the use of suitable staining techniques for the visualization
INTRODUCTION Identification and characterization of low abundance proteins separated by 2D gel electrophoresis is complicated by two important factors; the use of suitable staining techniques for the visualization
Comparison of mass spectrometers performances
 Comparison of mass spectrometers performances Instrument Mass Mass Sensitivity resolution accuracy Quadrupole 1 x 10 3 0.1 Da* 0.5-1.0 pmol DE-MALDI 2 x 10 4 20 ppm 1-10 fmol peptide 1-5 pmol protein Ion
Comparison of mass spectrometers performances Instrument Mass Mass Sensitivity resolution accuracy Quadrupole 1 x 10 3 0.1 Da* 0.5-1.0 pmol DE-MALDI 2 x 10 4 20 ppm 1-10 fmol peptide 1-5 pmol protein Ion
Systematic analysis of protein-detergent complexes applying dynamic light scattering to optimize solutions for crystallization trials
 Supporting information 1 2 3 Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: 4 5 6 7 8 Systematic analysis of protein-detergent complexes applying dynamic light scattering to optimize solutions for
Supporting information 1 2 3 Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: 4 5 6 7 8 Systematic analysis of protein-detergent complexes applying dynamic light scattering to optimize solutions for
The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device
 Supporting Information: The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device combined with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry Weiyi Xie,, Dan Gao,
Supporting Information: The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device combined with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry Weiyi Xie,, Dan Gao,
Step 4. Step 4. Choose MW markers. Choose MW markers. Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins
 Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins Choose MW markers 16 Step 4 Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins A Practical Approach, Third Edition An overview of basic techniques to benefit any life scientist using electrophoretic
Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins Choose MW markers 16 Step 4 Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins A Practical Approach, Third Edition An overview of basic techniques to benefit any life scientist using electrophoretic
Babu Antharavally, Ryan Bomgarden, and John Rogers Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL
 A Versatile High-Recovery Method for Removing Detergents from Low-Concentration Protein or Peptide Samples for Mass Spectrometry Sample Preparation and Analysis Babu Antharavally, Ryan Bomgarden, and John
A Versatile High-Recovery Method for Removing Detergents from Low-Concentration Protein or Peptide Samples for Mass Spectrometry Sample Preparation and Analysis Babu Antharavally, Ryan Bomgarden, and John
HPLC '88. Poster Presentation. Isolation of Thymosin B4 from Thymosin Fraction 5 by Reverse Phase HPLC
 Essentials in HPLC '88 Poster Presentation Isolation of Thymosin B4 from Thymosin Fraction 5 by Reverse Phase HPLC M. Badamchian, M.P. Strickler, M.J. Stone, A.L. Goldstein for Waters.bioresearchThe absolute,
Essentials in HPLC '88 Poster Presentation Isolation of Thymosin B4 from Thymosin Fraction 5 by Reverse Phase HPLC M. Badamchian, M.P. Strickler, M.J. Stone, A.L. Goldstein for Waters.bioresearchThe absolute,
Phosphorylation of proteins Steve Barnes Feb 19th, 2002 in some cases, proteins are found in a stable, hyperphosphorylated state, e.g.
 Phosphorylation of proteins Steve Barnes Feb 19th, 2002 in some cases, proteins are found in a stable, hyperphosphorylated state, e.g., casein more interestingly, in most other cases, it is a transient
Phosphorylation of proteins Steve Barnes Feb 19th, 2002 in some cases, proteins are found in a stable, hyperphosphorylated state, e.g., casein more interestingly, in most other cases, it is a transient
Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis
 nature methods Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis Jacek R Wi niewski, Alexandre Zougman, Nagarjuna Nagaraj & Matthias Mann Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1
nature methods Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis Jacek R Wi niewski, Alexandre Zougman, Nagarjuna Nagaraj & Matthias Mann Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1
Protein Identification and Phosphorylation Site Determination by de novo sequencing using PepFrag TM MALDI-Sequencing kit
 Application Note Tel: +82-54-223-2463 Fax : +82-54-223-2460 http://www.genomine.com venture ldg 306 Pohang techno park Pohang, kyungbuk, Korea(ROK) Protein Identification and Phosphorylation Site Determination
Application Note Tel: +82-54-223-2463 Fax : +82-54-223-2460 http://www.genomine.com venture ldg 306 Pohang techno park Pohang, kyungbuk, Korea(ROK) Protein Identification and Phosphorylation Site Determination
SMART Digest Kit Facilitating perfect digestion
 Questions Answers SMART Digest Kit Facilitating perfect digestion The modern biopharmaceutical and protein research laboratory is tasked with providing high quality analytical results, often in high-throughput,
Questions Answers SMART Digest Kit Facilitating perfect digestion The modern biopharmaceutical and protein research laboratory is tasked with providing high quality analytical results, often in high-throughput,
Expression constructs
 Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
The total protein test is a rough measure of all of the proteins in the plasma. Total protein measurements can reflect:
 Proteins Part 2 Introduction The total protein test is a rough measure of all of the proteins in the plasma. Total protein measurements can reflect: nutritional status, kidney disease, liver disease, and
Proteins Part 2 Introduction The total protein test is a rough measure of all of the proteins in the plasma. Total protein measurements can reflect: nutritional status, kidney disease, liver disease, and
Isomeric Separation of Permethylated Glycans by Porous Graphitic Carbon (PGC)-LC-MS/MS at High- Temperatures
 Supplementary Information Isomeric Separation of Permethylated Glycans by Porous Graphitic Carbon (PGC)-LC-MS/MS at High- Temperatures Shiyue Zhou 1, Yifan Huang 1, Xue Dong 1, Wenjing Peng 1, Lucas Veillon
Supplementary Information Isomeric Separation of Permethylated Glycans by Porous Graphitic Carbon (PGC)-LC-MS/MS at High- Temperatures Shiyue Zhou 1, Yifan Huang 1, Xue Dong 1, Wenjing Peng 1, Lucas Veillon
ISOELECTRIC TRAPPING AND MASS SPECTROMETRY: TOOLS FOR PROTEOMICS. A Dissertation STEPHANIE MARIE COLOGNA
 ISOELECTRIC TRAPPING AND MASS SPECTROMETRY: TOOLS FOR PROTEOMICS A Dissertation by STEPHANIE MARIE COLOGNA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
ISOELECTRIC TRAPPING AND MASS SPECTROMETRY: TOOLS FOR PROTEOMICS A Dissertation by STEPHANIE MARIE COLOGNA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
Proteins: Proteomics & Protein-Protein Interactions Part I
 Proteins: Proteomics & Protein-Protein Interactions Part I Jesse Rinehart, PhD Department of Cellular & Molecular Physiology Systems Biology Institute DNA RNA PROTEIN DNA RNA PROTEIN Proteins: Proteomics
Proteins: Proteomics & Protein-Protein Interactions Part I Jesse Rinehart, PhD Department of Cellular & Molecular Physiology Systems Biology Institute DNA RNA PROTEIN DNA RNA PROTEIN Proteins: Proteomics
Minimalistic encapsulated proteomic sample processing applied to copy number
 Nature Methods Minimalistic encapsulated proteomic sample processing applied to copy number estimation in eukaryotic cells Nils A. Kulak, Garwin Pichler, Igor Paron, Nagarjuna Nagaraj and Matthias Mann
Nature Methods Minimalistic encapsulated proteomic sample processing applied to copy number estimation in eukaryotic cells Nils A. Kulak, Garwin Pichler, Igor Paron, Nagarjuna Nagaraj and Matthias Mann
Peptide sequencing using chemically assisted fragmentation (CAF) and Ettan MALDI-ToF Pro mass spectrometry
 application note Ett MALDI-ToF Pro Peptide sequencing using chemically assisted fragmentation (CAF) d Ett MALDI-ToF Pro mass spectrometry Key words: MALDI-ToF, PSD, peptide sequencing, chemically assisted
application note Ett MALDI-ToF Pro Peptide sequencing using chemically assisted fragmentation (CAF) d Ett MALDI-ToF Pro mass spectrometry Key words: MALDI-ToF, PSD, peptide sequencing, chemically assisted
Collagenase Assay Kit
 Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen types
Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen types
Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) for the Retention of Highly Polar Analytes
 Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) for the Retention of Highly Polar Analytes Eric S. Grumbach,, Diane M. Diehl and Jeffrey R. Mazzeo 2003 Waters Corp. Outline Introduction HILIC Definition
Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) for the Retention of Highly Polar Analytes Eric S. Grumbach,, Diane M. Diehl and Jeffrey R. Mazzeo 2003 Waters Corp. Outline Introduction HILIC Definition
Technical Note # TN-31 Redefining MALDI-TOF/TOF Performance
 Bruker Daltonics Technical Note # TN-31 Redefining MALDI-TOF/TOF Performance The new ultraflextreme exceeds all current expectations of MALDI-TOF/TOF technology: A proprietary khz smartbeam-ii TM MALDI
Bruker Daltonics Technical Note # TN-31 Redefining MALDI-TOF/TOF Performance The new ultraflextreme exceeds all current expectations of MALDI-TOF/TOF technology: A proprietary khz smartbeam-ii TM MALDI
Sequence Identification And Spatial Distribution of Rat Brain Tryptic Peptides Using MALDI Mass Spectrometric Imaging
 Sequence Identification And Spatial Distribution of Rat Brain Tryptic Peptides Using MALDI Mass Spectrometric Imaging AB SCIEX MALDI TOF/TOF* Systems Patrick Pribil AB SCIEX, Canada MALDI mass spectrometric
Sequence Identification And Spatial Distribution of Rat Brain Tryptic Peptides Using MALDI Mass Spectrometric Imaging AB SCIEX MALDI TOF/TOF* Systems Patrick Pribil AB SCIEX, Canada MALDI mass spectrometric
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Degradation of Paraoxon and the Chemical Warfare Agents VX, Tabun and Soman by the Metal-Organic Frameworks UiO-66- NH 2, MOF-808, NU-1000 and PCN-777. Martijn C. de Koning,* Marco
Supporting Information Degradation of Paraoxon and the Chemical Warfare Agents VX, Tabun and Soman by the Metal-Organic Frameworks UiO-66- NH 2, MOF-808, NU-1000 and PCN-777. Martijn C. de Koning,* Marco
Supporting Information for:
 Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
VaTx1 VaTx2 VaTx3. VaTx min Retention Time (min) Retention Time (min)
 a Absorbance (mau) 5 2 5 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6 2 3 4 5 6 VaTx2 High Ca 2+ Low Ca 2+ b 38.2 min Absorbance (mau) 3 2 3 4 5 3 2 VaTx2 39.3 min 3 4 5 3 2 4. min 3 4 5 Supplementary Figure. Toxin Purification For
a Absorbance (mau) 5 2 5 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6 2 3 4 5 6 VaTx2 High Ca 2+ Low Ca 2+ b 38.2 min Absorbance (mau) 3 2 3 4 5 3 2 VaTx2 39.3 min 3 4 5 3 2 4. min 3 4 5 Supplementary Figure. Toxin Purification For
SCS MOLECULAR WEIGHT MARKERS 2,500-17,000 Caltons
 LECTROPHORES/S Revised November 1992 SCS MOLECULAR WEIGHT MARKERS 2,500-17,000 Caltons I NTRODUCTION Electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), an anionic detergent,
LECTROPHORES/S Revised November 1992 SCS MOLECULAR WEIGHT MARKERS 2,500-17,000 Caltons I NTRODUCTION Electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), an anionic detergent,
Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry. Supporting Information
 Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry M. Montana Quick, Christopher M. Crittenden, Jake A. Rosenberg, and Jennifer S. Brodbelt
Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry M. Montana Quick, Christopher M. Crittenden, Jake A. Rosenberg, and Jennifer S. Brodbelt
ab Glycated Protein Detection Kit
 Version 1 Last updated 27 July 2017 ab219802 Glycated Protein Detection Kit For the detection of glycated proteins (AGEs) using a simple polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis-based method. This product is
Version 1 Last updated 27 July 2017 ab219802 Glycated Protein Detection Kit For the detection of glycated proteins (AGEs) using a simple polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis-based method. This product is
ph Switchable and Fluorescent Ratiometric Squarylium Indocyanine Dyes as Extremely Alkaline Sensors
 ph Switchable and Fluorescent Ratiometric Squarylium Indocyanine Dyes as Extremely Alkaline Sensors Jie Li, Chendong Ji, Wantai Yang, Meizhen Yin* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering,
ph Switchable and Fluorescent Ratiometric Squarylium Indocyanine Dyes as Extremely Alkaline Sensors Jie Li, Chendong Ji, Wantai Yang, Meizhen Yin* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering,
STUDIES ON MUSTARD-STIMULATED PROTEASES AND INHIBITORS IN HUMAN EPIDERMAL KERATINOCYTES (HEK): DEVELOPMENT OF ANTIVESICANT DRUGS
 STUDIES ON MUSTARD-STIMULATED PROTEASES AND INHIBITORS IN HUMAN EPIDERMAL KERATINOCYTES (HEK): DEVELOPMENT OF ANTIVESICANT DRUGS Xiannu Jin 1, Radharaman Ray 2, Guang Xu 1 and Prabhati Ray 1 1 Department
STUDIES ON MUSTARD-STIMULATED PROTEASES AND INHIBITORS IN HUMAN EPIDERMAL KERATINOCYTES (HEK): DEVELOPMENT OF ANTIVESICANT DRUGS Xiannu Jin 1, Radharaman Ray 2, Guang Xu 1 and Prabhati Ray 1 1 Department
Chapter 3. Protein Structure and Function
 Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Development of a Human Cell-Free Expression System to Generate Stable-Isotope-Labeled Protein Standards for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry
 Development of a Human Cell-Free Expression System to Generate Stable-Isotope-Labeled Protein Standards for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Ryan D. omgarden 1, Derek aerenwald 2, Eric Hommema 1, Scott Peterman
Development of a Human Cell-Free Expression System to Generate Stable-Isotope-Labeled Protein Standards for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Ryan D. omgarden 1, Derek aerenwald 2, Eric Hommema 1, Scott Peterman
DetergentOUT Detergent Removal Systems
 252PR-04 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name DetergentOUT Detergent Removal Systems For the Removal of Detergents from Peptide
252PR-04 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name DetergentOUT Detergent Removal Systems For the Removal of Detergents from Peptide
Mass spectrometry Technologies in Lipid chemistry
 Mass spectrometry Technologies in Lipid chemistry Rabah Soliymani University Of Helsinki Protein Chemistry Unit Biomedicum Helsinki Rabah.soliymani@helsinki.fi Complex_&_dynamic_mixtures (few copies to
Mass spectrometry Technologies in Lipid chemistry Rabah Soliymani University Of Helsinki Protein Chemistry Unit Biomedicum Helsinki Rabah.soliymani@helsinki.fi Complex_&_dynamic_mixtures (few copies to
Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Local Goat Milk Casein for Nutraceutical Value
 Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Local Goat Milk Casein for Nutraceutical Value Mohd Akmal Azhar 1,*, and Norshafiqa Salim 2 1 Faculty of Engineering Technology, UMP Gambang, Lebuhraya Tun Razak,
Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Local Goat Milk Casein for Nutraceutical Value Mohd Akmal Azhar 1,*, and Norshafiqa Salim 2 1 Faculty of Engineering Technology, UMP Gambang, Lebuhraya Tun Razak,
Fig.S1 ESI-MS spectrum of reaction of ApA and THPTb after 16 h.
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Experiment Cleavage of dinucleotides Dinucleotides (ApA, CpC, GpG, UpU) were purchased from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Experiment Cleavage of dinucleotides Dinucleotides (ApA, CpC, GpG, UpU) were purchased from
SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES
 1 SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES Proteins are important in food processing and food product development, as they are
1 SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES Proteins are important in food processing and food product development, as they are
PNGase F Instruction Manual
 PNGase F Instruction Manual Catalog Number 170-6883 Bio-Rad Laboratories, 2000 Alfred Nobel Dr., Hercules, CA 94547 4006094 Rev A Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction...1 Section 2 Kit Components and
PNGase F Instruction Manual Catalog Number 170-6883 Bio-Rad Laboratories, 2000 Alfred Nobel Dr., Hercules, CA 94547 4006094 Rev A Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction...1 Section 2 Kit Components and
Proteins. Amino acids, structure and function. The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2012 Robert J. Lefkowitz Brian K. Kobilka
 Proteins Amino acids, structure and function The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2012 Robert J. Lefkowitz Brian K. Kobilka O O HO N N HN OH Ser65-Tyr66-Gly67 The Nobel prize in chemistry 2008 Osamu Shimomura,
Proteins Amino acids, structure and function The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2012 Robert J. Lefkowitz Brian K. Kobilka O O HO N N HN OH Ser65-Tyr66-Gly67 The Nobel prize in chemistry 2008 Osamu Shimomura,
TGX and TGX Stain-Free FastCast Acrylamide Kits
 Electrophoresis TGX and TGX Stain-Free FastCast Acrylamide Kits The newest frontier for handcast gels It s Time to Expect More from Handcast Gels! FastCast kits provide unparalleled convenience and performance.
Electrophoresis TGX and TGX Stain-Free FastCast Acrylamide Kits The newest frontier for handcast gels It s Time to Expect More from Handcast Gels! FastCast kits provide unparalleled convenience and performance.
Oligosaccharide Profiling of O-linked Oligosaccharides Labeled with 2 Aminobenzoic Acid (2-AA)
 Oligosaccharide Profiling of O-linked Oligosaccharides Labeled with 2 Aminobenzoic Acid (2-AA) Elisabeth A. Kast and Elizabeth A. Higgins GlycoSolutions Corporation, Worcester, MA Data originally presented
Oligosaccharide Profiling of O-linked Oligosaccharides Labeled with 2 Aminobenzoic Acid (2-AA) Elisabeth A. Kast and Elizabeth A. Higgins GlycoSolutions Corporation, Worcester, MA Data originally presented
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. PhosDecor Fluorescent Phosphoprotein In-Gel Detection Kit. Catalog Number PDECOR Storage Temperature 2 8 C
 PhosDecor Fluorescent Phosphoprotein In-Gel Detection Kit Catalog Number PDECOR Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Phosphorylation is an important covalent posttranslational
PhosDecor Fluorescent Phosphoprotein In-Gel Detection Kit Catalog Number PDECOR Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Phosphorylation is an important covalent posttranslational
Combination of 2-D Gel and Liquid-Phase Electrophoretic Separations as Proteomic Tools in Neuroscience. Analytical 2-D. Electrophoresis.
 electrophoresis tech note 2859 Combination of 2-D Gel and Liquid-Phase Electrophoretic Separations as Proteomic Tools in Neuroscience Pia Davidsson, Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Experimental Neuroscience
electrophoresis tech note 2859 Combination of 2-D Gel and Liquid-Phase Electrophoretic Separations as Proteomic Tools in Neuroscience Pia Davidsson, Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Experimental Neuroscience
BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, Tissue-Specific Isoenzymes
 BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, 2007 Background Information Tissue-Specific Isoenzymes A. BIOCHEMISTRY The basic pattern of glucose oxidation is outlined in Figure 3-1. Glucose is split
BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, 2007 Background Information Tissue-Specific Isoenzymes A. BIOCHEMISTRY The basic pattern of glucose oxidation is outlined in Figure 3-1. Glucose is split
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Glycan Reductive Isotope-coded Amino Acid Labeling (GRIAL) for Mass Spectrometry-based
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Glycan Reductive Isotope-coded Amino Acid Labeling (GRIAL) for Mass Spectrometry-based
Catalytic decarboxylative alkylation of β-keto acids with sulfonamides via the cleavage of carbon nitrogen and carbon carbon bonds
 Catalytic decarboxylative alkylation of β-keto acids with sulfonamides via the cleavage of carbon nitrogen and carbon carbon bonds Cui-Feng Yang, Jian-Yong Wang and Shi-Kai Tian* Joint Laboratory of Green
Catalytic decarboxylative alkylation of β-keto acids with sulfonamides via the cleavage of carbon nitrogen and carbon carbon bonds Cui-Feng Yang, Jian-Yong Wang and Shi-Kai Tian* Joint Laboratory of Green
Automated Sample Preparation/Concentration of Biological Samples Prior to Analysis via MALDI-TOF Mass Spectroscopy Application Note 222
 Automated Sample Preparation/Concentration of Biological Samples Prior to Analysis via MALDI-TOF Mass Spectroscopy Application Note 222 Joan Stevens, Ph.D.; Luke Roenneburg; Tim Hegeman; Kevin Fawcett
Automated Sample Preparation/Concentration of Biological Samples Prior to Analysis via MALDI-TOF Mass Spectroscopy Application Note 222 Joan Stevens, Ph.D.; Luke Roenneburg; Tim Hegeman; Kevin Fawcett
A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* Previous studies (1, 2) have shown that after the ingestion of caffeine
 A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* BY HERBERT H. CORNISH AND A. A. CHRISTMAN (From the Department of Biological Chemistry, Medical School, University of Michigan,
A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* BY HERBERT H. CORNISH AND A. A. CHRISTMAN (From the Department of Biological Chemistry, Medical School, University of Michigan,
Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics - Lecture 4 - Matthias Trost Newcastle University
 Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics - Lecture 4 - Matthias Trost Newcastle University matthias.trost@ncl.ac.uk previously Peptide fragmentation Hybrid instruments 117 The Building Blocks of Life DNA RNA Proteins
Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics - Lecture 4 - Matthias Trost Newcastle University matthias.trost@ncl.ac.uk previously Peptide fragmentation Hybrid instruments 117 The Building Blocks of Life DNA RNA Proteins
Research Article Study on Optimal Conditions of Alcalase Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Soybean Protein Isolate
 Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology 9(2): 154-158, 2015 DOI: 10.19026/ajfst.9.1952 ISSN: 2042-4868; e-issn: 2042-4876 2015 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Submitted: February 13, 2015 Accepted:
Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology 9(2): 154-158, 2015 DOI: 10.19026/ajfst.9.1952 ISSN: 2042-4868; e-issn: 2042-4876 2015 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Submitted: February 13, 2015 Accepted:
