AMINO ACIDS Description of Amino acids and their functions in plants
|
|
|
- Derick Gallagher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AMINO ACIDS Description of Amino acids and their functions in plants
2 Technical Report 1. Introduction... 3 Proteic amino acids... 5 Amino acids in plants Amino acids functions Aliphatic... 6 Acids Basics Hydroxylic Sulfur-containing Amidic Conclusions ARTAL Solutions Aminotal Super Vegeamino... 22
3 1. Introduction Amino acids are organic molecules composed by Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen. Their components are grouped into 3 major groups: a carboxylic acid (-COOH), an amino group (-NH2) and a lateral chain (-R). We can find two classes of amino acids inside a living being: a) Proteic amino acids: These amino acids do their function by aggregating themselves to other amino acids, making the molecules known as proteins. Proteins play an essential role in every metabolic pathway and in every structural part of the body. They are the bricks of which the body of the organism is made (structural proteins), as well as the motor that make the metabolism work properly (enzymes).
4 b) Non-proteic amino acids: These amino acids are not part of any proteins. They do their function by themselves, not by creating complexes with other amino acids. All the proteic amino acids, when they realize a function by themselves, are examples of non-proteic amino acids but there are more kinds of non-proteic amino acids that are not included in the list of the proteic ones. Examples of these amino acids are hydroxyproline, ornithine, mimosine, canavanine Furthermore, we can find to types of amino acids depending on the orientation of the amine group (-NH2) in the molecule. The pair of identical molecules with only this difference between them both are called enantiomers. When we find the amino group on the right, we call it D-enantiomer and when it is on the left we call it L-enantiomer. L-enantiomer D-enantiomer
5 Proteic amino acids We can find up to 20 different types of proteic amino acids inside a living being, all in the L-form enantiomer. The difference between the 20 proteic amino acids is the composition of the lateral chain. Depending of the lateral chain we can find: Alanine (ala), arginine (arg), aspargine (asn), aspartic acid (asp), cysteine (cys), glutamine (gln), glutamic acid (glu), glycine (gly), histidine (his), isoleucine (ile), leucine (leu), lysine (lys), methionine (met), phenylalanine (phe), proline (pro), serine (ser), threonine (thr), tryptophan (trp), tyrosine (tyr), valine (val). These amino acids are grouped due to the chemical properties of their lateral chain. Aliphatic (no cyclic lateral chain) - alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, proline, valine. Aromatic (cyclic lateral chain) phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine. Acidic - aspartic acid glutamic acid. Basic arginine, histidine, lysine. Hydroxylic (with an OH group in the lateral chain) - serine, threonine. Sulphur-containing (-SH group in the lateral chain) - cysteine, methionine. Amidic (containing amide group -NH2 in the side chain) asparagine, glutamine.
6 Amino acids in plants Plants are able to synthetize their own amino acids through five pathways, named after the precursor of the pathway. We can find: a) Pyruvate family: Alanine, valine and leucine are synthetized through this pathway. b) Oxaloacetate family: Aspartic acid/asparagine, lysine, threonine, methionine and isoleucine. c) Alfa-cetoglutarate family: Glutamic acid/glutamine, proline, hidroxy proline and arginine. d) Shikimate family: Tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophan and histidine. e) Calvin cycle family: Glycine, serine and cysteine. Animals cannot synthetize phenylalanine, histidine, tryptophan, valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine and threonine. They are called essential amino acids and animals need to ingest them through a vegetal diet in order to dispose of them in the body. 2. Amino acids functions. Aliphatic Alanine Accumulated under anoxia, helps the production of ATP when the floor is waterlogged and no oxygen is available to create ATP, which is the main source of energy that the plant use to do its chemical reactions. Extra alanine helps the plant survive this kind of stress. Increases the Nitrogen uptake so less Nitrogen is required when fertilization has to be done.
7 Glycine This amino acid plays various serious roles when it forms part of proteins. There is a family composed by all the proteins who have high presence of this amino acid within them, known as Glycine Rich Proteins (GRP) which take part in many processes: a) They are implicated in the formation of the cell wall, leading to a better disposal of the structural tissue of the plant. b) Also GRP play a role in the defense against some diseases like the turnip vein-clearing tobamovirus. This is because Glycine plays a role in the deposition of callose, which impedes the movements of the viruses and diseases through the conductive system of the plant. c) This family plays a very important role in reproduction. It is a key element on the hydration of the pollen, process that allows the pollen to enter inside the ovaries. d) They are highly expressed in the stoma guard cells, where helps the regulation of the opening and closure if the stoma to prevent water loss when heat stress conditions occurs. e) They seem to play a role in cold shock adaptation of plants.
8 Isoleucine Together with valine, leucine and isoleucine they form the branched-chain amino acids, which play an important role in structural proteins. Also this amino acid plays a major role in the root development. Lack of this amino acids will shorten the roots drastically. Leucine Leucine is located in large quantities in a kind of proteins called Leucine- Rich Repeat Receptor Kinases, a family of protein placed in the cell wall with that trigger lots of important processes for the cell, like cell proliferation, stem cell maintenance, hormone perception, host-specific as well as non-hostspecific defense response, wounding response, and symbiosis with mycorhizes.
9 The functions of this amino acid are numerous, so a high disposal of this amino acid will help the plant grow fast and healthy. Proline It acts as a compatible solute. A compatible solute is a small solute, dissolved in the cellular matrix, who avoid osmotic imbalance. Osmosis works like this: When you have a liquid with a semipermeable membrane (this is, water can pass through it but not the solutes dissolved in the water) the water is compartmented in two zones. The osmotic pressure makes the water goes through the membrane to the zone where the solute concentration is higher to compensate the excess of solutes and to maintain an osmotic equilibrium. A compatible solute, proline in this case, helps the cell keeping water inside of it when hydric stress occur. When no water is available in the soil, and the concentration of solutes is high in it, water tends to leave the cell because the osmotic pressure. Proline increases the quantity of solutes inside the cell,
10 balancing the inner concentration and the outer concentration, balancing the osmotic pressure and keeping the water inside the cells. Also a compatible solute helps when low temperatures occur. The water freezes at lower temperatures when it has high concentration of solutes in it. The cell matrix is full of water and if it freezes, water crystals are formed damaging the cell structure like a knife. Solved Proline helps this freeze temperature to be lower, and it impedes the ice crystals not to be formed, and to avoid this damage produced by them. Proline also diminishes the oxidative effect of oxygen free radicals. It stabilizes the anti-oxidant proteins in the cell matrix making them live longer and increasing their activity. Proline play a key role in the plant response to all kinds of stress but also has been shown that the addition of proline helps the set of some fruits, like apples. Valine It has been found no specific functions of this amino acid beyond forming part of proteins.
11 Aromatics Phenylalanine L-Phenylalanine is the main precursor of the phenylpropanoid compounds that play key roles in the plant. This compounds are synthetized by the enzyme Phenylalanine ammonia lyase and they have several functions: a) They help the plant to deal with biotic stresses. These compounds accumulate in wounded or infected areas, damaged by herbivores or fungus, insects Some of these compounds are also toxics for herbivores. Also lignin is a derived compound of this phenylpropanoids, and is the compound that makes the wood, hardening the plant and reducing the damage that herbivores can cause to it. b) They help the plant to deal with abiotic stresses. Flavonoids and isoflavonoids, both derived from phenylpropanoid, reduce the harmful effect of the UV light to the plant. Also they absorb light when high insolation occurs, because photosynthesis reduces its efficiency with high light intensity.
12 This compounds can t be synthetized when there is a lack of phenylalanine, so a good supply of this amino acid is key for a good grow of the plant. Tryptophan This amino acid is the precursor of auxins (indol-3-acetic acid), process made by the plant naturally just with a 2-steps biochemical pathway. Auxins are a group of hormones involved in the plant s growth, especially in the formation of roots and cell elongation. They also delay foliar senescence. Because of this, tryptophan is needed for the plant to grow properly, especially when vegetative growth occurs. Tyrosine Tyrosine is the precursor of the catecholamines. These compounds are relative well known, adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine are part of this family of compounds. In plants they stimulate in some cases the growth of the
13 plant indirectly. Dopamine stimulate the production of ethylene in some plants, and this ethylene is the compound that stimulates the growth and the fruit ripening. Acids Aspartic acid The function of this amino acid is to be part of proteins and also it is the metabolic substrate from which lysine, threonine, methionine and isoleucine are produced. Also it acts as a substrate for the Krebs cycle, which is the one of the main producer of energetic metabolites. Glutamic acid In its ionized form, glutamate, it serves as the first organic form in which inorganic Nitrogen (ammonia) is fixed. Furthermore, this amino acid serves of Nitrogen donor for the biosynthesis of all the amino acids. This amino acid has roles for itself. It is important for the pollination: it increases the pollen germination and the length of the pollinic tube, key for the fertilization of the ovule.
14 Also it is the substrate for the formation of proline, hidroxy proline and arginine. Arginine Basics Arginine is the main source of nitrogen reservoir and also recycles the nitrogen. One of its functions is to distribute Nitrogen all over the plant. This amino acid is the substrate for the production of Nitric Oxide. Nitric oxide is a compound that plays several roles in the plant: a) Acts as part of the infection-resistance systems. b) Helps the mycorrhization process to be stablished in the plant. This process is a symbiosis (win-win relationship) between the plant and a beneficial fungus that is set in the plant s roots. c) Serves as initiator for the root development and the development of lateral roots. Auxins are also implicated in this process. d) Regulates aperture/closure of the stomata, epidermic holes in the leaves who open and closes depending on the outer temperature. If the temperature is high the stomata close to avoid losing water through these holes, but if the temperature is not high the stomata are open to allow gaseous exchange from the inside of the plant to the atmosphere. Also polyamides are synthetized from Arginine as well. The plant s representatives of these element are putrescine, spermidine and spermine. Polyamides are hormone-like compounds that modulate several processes:
15 a) Cell division. b) Dormancy breaking of tubers and germination of seeds, c) Stimulation, support and development of flower buds d) Embryogenesis, fruit set fruit ripening and growth. e) Plant morphogenesis. f) Response to biotic and abiotic stresses such as high/low temperatures, salinity, pollution In conclusion, arginine plays multi-faceted roles in lots of plants process. It is a key amino acid for the plant correct development and for it to face the biotical and abiotical stresses that the plant may suffer. Histidine Acts as Nickel and Zinc chelating at cell ph, both minerals needed for a correct enzyme function. It plays an essential role for embryo survival, without which high rate embryo abortions occur in plants. Lysine
16 It has been found no specific functions of this amino acid beyond forming part of proteins. Hydroxylic Serine Serine has an important role in the plant function. Its derivate, phosphatidylserine, is part of the structure of the cell membrane and its lack leads to deformity of this layer, which leads to some serious problems like: a) Lower on the tolerance of the plants to stress. b) Increase of the embryo abortion rate on some species. c) Total male gametophyte lethality in some species. d) Altered mineral balance. e) Decrease of the folate production, which is key for the formation of embryos and post-embryonic root development. f) Inefficiency on the control of the photorespiration, leading to energy availability problems for the plant. A good supply of this amino acids will help the plant not to have these conditions.
17 Threonine It has been linked the role of this amino acid to plant defense mechanism and the signaling of different metabolic pathways but very little is known about the function of this amino acid, despite the fact that it is present in the structure of many different proteins. Sulfur-containing Cysteine This amino acid is the precursor and pathway activator of many of other key compounds, such as vitamins, antioxidants and many defense compounds, so a good supply of this amino acid will lead the plant to improve the resistance to stress, diseases and infections. One special product that is synthetized from this amino acid (together with glycine and glutamic acid) is the glutathione. This compound is a powerful antioxidant which helps the organism to deal with free radicals formed in the metabolism, helping retarding senescence and plant damage.
18 Methionine It transports sulfured groups through the plant in the form of S- adenosylmethionine, the major donor for transmethylation reactions. This reactions are present, for example, during the production of some vitamins like B12 or the production of phosphatidilcoline, an essential cell membrane compound. This amino acid is also the precursor for the biosynthesis of ethylene, compound that allows the fruit ripening. So the role of this amino acid is key for the plant growth since it is needed for the production of ethylene, but it is also important for the general metabolism of the plant since transmethylation is a very common and important reaction in the plant. Amidic Asparagine Asparagine plays a central role in Nitrogen transport and storage in plants, and it is implicated in Nitrogen metabolism in different phases:
19 a) Nitrogen mobilization in germinating seeds. Asparagine is the main distributor of Nitrogen all over the plant. Germinating seeds need Nitrogen supplies before they can be autonomous in the production of nitrogenous compounds, so Arginine carries the nitrogenous compounds from the plant leaves to the seeds. b) Nitrogen recycling and flow in vegetative cells in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Asparagine responds to stresses like darkness, salinity or damage where the plant starts to starve. Recycling of Nitrogen is key for the plant having enough nitrogenous substances not to starve at the first stages of these stresses. c) Nitrogen remobilization from source to sink organs. Nitrogen is absorbed mainly by the roots and it has to be transported all over the plant. The source organs in this case are the roots, and the sink organs are the part of the plant that needs this Nitrogen. But this transport also occurs when some organs, like the leaves, start the senescence process. Senescence is the wilt of any organ. In deciduous trees for example this process is massive, and the leaves that fall are full of nutrients and elements like Nitrogen. This Nitrogen has to be recycled to other parts of the plant to avoid losing it in form of Asparagine. Glutamine
20 This amino acid shares the Nitrogen recycling function with Asparagine. It recycles the Nitrogen that respiration produces and also a small portion of the exportations of the senescent organs are transported by this amino acid. 3. Conclusions The general effects of the amino acids in the plant could be summarized into six: a) Forming the structural proteins and the enzymes that will allow the plant to grow and to develop its metabolic processes. b) Acting directly as amino acids, or as part of proteins, in the anti-stress mechanisms that will protect the plant from infections or another kinds of stress. c) Helping the plant to absorb, transport and recycle the nutrients. d) Being the substrates from which many compounds, like hormones or other amino acids, are synthetized. e) Regulating the osmotic pressure of the cells and tissues. f) Chelating some Micronutrients like Zinc, Copper or Iron.
21 4. ARTAL Solutions Aminotal Super AMINOTAL SUPER is a bioactivator with a high concentration of free amino acids obtained by acid hydrolysis. Due to its elevated content of amino acids the application of this product: Will activate the crop metabolism. Will provide enough Nitrogen to its development. Will improve the microelements assimilation (thanks to the complexing effect of the amino acids). Will enhance the pesticides effect. AMINOTAL SUPER application is recommended during the active growth stages of the crop and during the freezing periods since it invigorates the crop and improves its development under stress conditions. The aminogram of the product is the following: ASP-VAL-GLU(9%)-PHE-SER-ILE-GLY-LEU-THR-LYS-ARG-HIS-ALA- PRO-TYR-HYP-MET AMINOTAL SUPER presents a fully assimilable formula, so it can be applied through foliar or radicular way. AMINOTAL SUPER is recommended for all kinds of crops: Fruit (pip and pit), citrus, horticulturals, cereals and ornamentals. ELEMENT GUARANTEED COMPOUNDS Free Amino acids 30,00% w/w = 37,0% w/v Total Nitrogen 9,00% w/w = 11,16% w/v Soluble Liquid ---
22 Vegeamino VEGEAMINO is a bioactivator with a high concentration of vegetal origin obtained by hydrolysis. The application of this product in the crop: Will activate the crop metabolism. Will provide enough Nitrogen to its development. Will improve the microelements assimilation (thanks to the complexing effect of the amino acids). Will enhance the pesticides effect. AMINOTAL SUPER application is recommended during the active growth stages of the crop and during the freezing periods since it invigorates the crop and improves its development under stress conditions. The aminogram of the product is the following: ASP-VAL-GLU(14%)-PHE-SER-ILE-GLY(5%)-LEU-THR-LYS-ARG-HIS- ALA-PRO-TYR-HYP-MET AMINOTAL SUPER presents a fully assimilable formula, so it can be applied through foliar or radicular way. AMINOTAL SUPER is recommended for all kinds of crops: Fruit (pip and pit), citrus, horticulturals, cereals and ornamentals. ELEMENT GUARANTEED COMPOUNDS Free Amino acids 20,00% w/w = 24,00% w/v Total Nitrogen 3,90% w/w = 4,83% w/v Soluble Liquid ---
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
CHM333 LECTURE 6: 1/25/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID:
 AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr.Diala
 number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5
 Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]
![Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]](/thumbs/84/90818314.jpg) Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
AP Bio. Protiens Chapter 5 1
 Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids. Amino acid metabolism
 Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Methionine (Met or M)
 Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes
 1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Amino acid metabolism
 Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Cells N5 Homework book
 1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Maha AbuAjamieh. Tamara Wahbeh. Mamoon Ahram
 12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Nitrogen Metabolism. Overview
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides
 Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
1. (38 pts.) 2. (25 pts.) 3. (15 pts.) 4. (12 pts.) 5. (10 pts.) Bonus (12 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D.
 What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Primary source of nitrogen
What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Primary source of nitrogen
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Amino acids. You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures.
 Amino acids You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures. If you wanna make any classification in the world, you have to find what
Amino acids You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures. If you wanna make any classification in the world, you have to find what
Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions. Proteins
 Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions Proteins Proteins Naturally occurring bioorganic polyamide polymers containing a sequence of various combinations of 20 amino acids. Amino acids contain the elements carbon,
Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions Proteins Proteins Naturally occurring bioorganic polyamide polymers containing a sequence of various combinations of 20 amino acids. Amino acids contain the elements carbon,
Introduction to proteins and protein structure
 Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Amino Acids. Lecture 4: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where?
 Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS
 AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
Aminocore Complex Liquid
 Aminocore Complex Liquid Product description Datasheet What is it? Aminocore complex is a short chain peptides and L-α-amino acid-based product from enzymatic hydrolysis for foliar application. The product
Aminocore Complex Liquid Product description Datasheet What is it? Aminocore complex is a short chain peptides and L-α-amino acid-based product from enzymatic hydrolysis for foliar application. The product
Amino Acid Metabolism
 Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Protein and Amino Acid Analysis. Chemistry M3LC
 Protein and Amino Acid Analysis Chemistry M3LC Proteins Proteins are made up of amino acids: H2N-CHR-COOH + H3N-CHR-COO - neutral form zwitterionic form There are twenty standard amino acids: A ala alanine
Protein and Amino Acid Analysis Chemistry M3LC Proteins Proteins are made up of amino acids: H2N-CHR-COOH + H3N-CHR-COO - neutral form zwitterionic form There are twenty standard amino acids: A ala alanine
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection
 Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
PROTEINS. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Acid L-form * * Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 O = N -C -C-O.
 Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
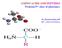 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
Product Name : Fish s Amino Nutrients
 Product Name : Fish s Amino Nutrients Bio Organic Fertilizer Provides Quality Nitrogen, Among with Other Nutrients to Plants Fish Hydrolysate Fertilizer is an excellent source of many nutrients. As natural,
Product Name : Fish s Amino Nutrients Bio Organic Fertilizer Provides Quality Nitrogen, Among with Other Nutrients to Plants Fish Hydrolysate Fertilizer is an excellent source of many nutrients. As natural,
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
Nitrogen Metabolism. Overview
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Microbial Enhanced Fish Fertilizer Supplement with Vitamins and Nutrients for Plant Health
 Microbial Enhanced Fish Fertilizer Supplement with Vitamins and Nutrients for Plant Health INTRODUCTION: MicrobeBio Hydro Activator naturally occurring beneficial organisms, 100% organic proteins, and
Microbial Enhanced Fish Fertilizer Supplement with Vitamins and Nutrients for Plant Health INTRODUCTION: MicrobeBio Hydro Activator naturally occurring beneficial organisms, 100% organic proteins, and
Amino acids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester,
 Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Introduction to Peptide Sequencing
 Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Nitrogen Metabolism. Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Amino acids. (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi
 Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
Amino Acids. Review I: Protein Structure. Amino Acids: Structures. Amino Acids (contd.) Rajan Munshi
 Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
BIONOBEL S FERTIGRENA S (2 MgO) FERTIGRENA S (2 Mg0) FERTIGRENA S (2 Mg0)
 PRODUCT RANGE BIONOBEL 3.0.20 S FERTIGRENA 3.7.10 S (2 MgO) FERTIGRENA 3.10.5 S (2 Mg0) FERTIGRENA 4.6.10 S (2 Mg0) ORGANO-MINERAL FERTILIZERS ALLOWED IN ORGANIC FARMING BIONOBEL 3.0.20 S (15 SO3) Organic-mineral
PRODUCT RANGE BIONOBEL 3.0.20 S FERTIGRENA 3.7.10 S (2 MgO) FERTIGRENA 3.10.5 S (2 Mg0) FERTIGRENA 4.6.10 S (2 Mg0) ORGANO-MINERAL FERTILIZERS ALLOWED IN ORGANIC FARMING BIONOBEL 3.0.20 S (15 SO3) Organic-mineral
Amino acid composition of fibroin and sericin. Fibroin (%)
 Silk Fibroin and Sericin Fibroin and sericin have a chemical composition that is quite similar, but they differ substantially in terms of chemical behaviour and physical and structural characteristics:
Silk Fibroin and Sericin Fibroin and sericin have a chemical composition that is quite similar, but they differ substantially in terms of chemical behaviour and physical and structural characteristics:
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell
 A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels. Supplementary Information
 Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
9/16/15. Properties of Water. Benefits of Water. More properties of water
 Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals
 Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals Preben Bach Holm University of Aarhus Faculty of Agricultural Sciences Department of Genetics and Biotechnology
Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals Preben Bach Holm University of Aarhus Faculty of Agricultural Sciences Department of Genetics and Biotechnology
Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS
 Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS The word "Protein" was coined by J.J. Berzelius in 1838 and was derived from the Greek word "Proteios" meaning the first rank. Proteins are macromolecular polymers composed
Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS The word "Protein" was coined by J.J. Berzelius in 1838 and was derived from the Greek word "Proteios" meaning the first rank. Proteins are macromolecular polymers composed
PROTEIN. By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM
 PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaves
 Environ. Chem. 216, 13, 877 887 doi:1.171/en165_ac CSIRO 216 Supplementary material Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis
Environ. Chem. 216, 13, 877 887 doi:1.171/en165_ac CSIRO 216 Supplementary material Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis
Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids.
 Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
Amino Acids االحماض األمينية
 Amino Acids االحماض األمينية Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cell Structure Amino Acids The study of
Amino Acids االحماض األمينية Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cell Structure Amino Acids The study of
Human Biochemistry Option B
 Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Gentilucci, Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds CH 3
 Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acid Profile of MicroOrgano Liquid, Amino Powder, Spurt & AminoStart
 Amino Acid Profile of MicroOrgano Liquid, Amino Powder, Spurt & AminoStart 1/7 30.00 25.00 25.39 20.00 15.00 13.00 10.00 10.08 5.98 5.00 4.39 4.39 3.52 3.68 3.47 4.77 3.89 4.85 3.31 1.67 1.47 1.72 0.87
Amino Acid Profile of MicroOrgano Liquid, Amino Powder, Spurt & AminoStart 1/7 30.00 25.00 25.39 20.00 15.00 13.00 10.00 10.08 5.98 5.00 4.39 4.39 3.52 3.68 3.47 4.77 3.89 4.85 3.31 1.67 1.47 1.72 0.87
Midterm 1 Last, First
 Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Protein Investigator. Protein Investigator - 3
 Protein Investigator Objectives To learn more about the interactions that govern protein structure. To test hypotheses regarding protein structure and function. To design proteins with specific shapes.
Protein Investigator Objectives To learn more about the interactions that govern protein structure. To test hypotheses regarding protein structure and function. To design proteins with specific shapes.
AMINO ACIDS NON-ESSENTIAL ESSENTIAL
 Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
Metabolism of amino acids I. Josef Fontana
 Metabolism of amino acids I Josef Fontana EC Overview of the lecture Introduction to protein and amino acids metabolism Metabolic pathways of amino acids Transamination Conversion glutamate - glutamine
Metabolism of amino acids I Josef Fontana EC Overview of the lecture Introduction to protein and amino acids metabolism Metabolic pathways of amino acids Transamination Conversion glutamate - glutamine
Outline. Ø Standard Recommendations. Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins
 Protein 101 Outline Ø Standard Recommendations Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) Dietary Guidelines
Protein 101 Outline Ø Standard Recommendations Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) Dietary Guidelines
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
 Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Sheet #1 Dr. Mamoun Ahram 01/07/2014. Amino Acids
 Amino Acids Dr s office in physiology department in floor #1 Office hours: every day after 1 *How to study biochemistry for Dr. Mamoun s material: Slides will be sent before the lecture, try to read it
Amino Acids Dr s office in physiology department in floor #1 Office hours: every day after 1 *How to study biochemistry for Dr. Mamoun s material: Slides will be sent before the lecture, try to read it
Amino acid metabolism II
 Amino acid metabolism II Fates of amino acid carbon skeleton degradation to common intermediates pyruvate, intermediates of citric acid cycle, acetyl-coa Glucogenic AA precursors of glucose - degradation
Amino acid metabolism II Fates of amino acid carbon skeleton degradation to common intermediates pyruvate, intermediates of citric acid cycle, acetyl-coa Glucogenic AA precursors of glucose - degradation
PROTEINS. Building blocks, structure and function. Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties
 PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
Authors. Abstract. Introduction. Food
 Improved and Simplified Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry Method for the Analysis of Underivatized Free Ao Acids in Various Foods Application Food Authors
Improved and Simplified Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry Method for the Analysis of Underivatized Free Ao Acids in Various Foods Application Food Authors
Macromolecules Structure and Function
 Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications - Acids. Data No. Column Data Title Solutes Eluent Detection Data No.
 GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications: Acids For complete Product Description, Chromatograms Price & Delivery in Australia & New Zealand contact info@winlab.com.au or call 61 (0)7 3205 1209
GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications: Acids For complete Product Description, Chromatograms Price & Delivery in Australia & New Zealand contact info@winlab.com.au or call 61 (0)7 3205 1209
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES
 3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination #5: Section Five December 7, Name: (print) Section:
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
