GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications - Acids. Data No. Column Data Title Solutes Eluent Detection Data No.
|
|
|
- Charla O’Connor’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications: Acids For complete Product Description, Chromatograms Price & Delivery in Australia & New Zealand contact or call 61 (0) Column Data Title Solutes Eluent Detection A01 ODS A02 ODS A03 ODS A0 ODS-2-00 InertsilODS-2 5µm 5µm 250.6mmI.D. 5µm 10.0 mm I.D. (Guard) mm I.D mm I.D. Free amino in Soft drink PTH-Amino in Green tea in Cheese 1. Aspartic acid (Asp) 2. Threonine (Thr) 3. Valine (Val). Methionine (Met) 5. Isoleucine (Ile) 6. Leucine (Leu) 7. Tryptophan (Trp) 1. Histidine (His) 2. Asparagine (Asn) 3. Arginine (Arg). Asparatic acid (Asp) 5. Glutamic acid (Glu) 6. Serine (Ser) 7. Glutamine (Gln) 8. Glycine (Gly) 9. Tyrosine (Tyr) 10. Alanine (Ala) 11. Threonine (Thr) 12. Methionine (Met) 13. Proline (Pro) 1. Tryptophan (Trp) 15. Phenylalanine (Phe) 16. Lysine (Lys) 17. Leucine (Leu) CH3OH CH3COONa (CH3COO)2 Cu C7H15- SO3Na 1. PTC-1-Theanine 1. PTC-1-Aspartic acid 2. PTC-1-Glutamic acid 3. PTC-1-Serine. PTC-1-Glycine 5. PTC-1-Histidine 6. PTC-1-Arginine 7. PTC-1-Threonine 8. PTC-1-Alanine 9. PTC-1-Proline 10. PTC-1-Tyrosine 11. PTC-1-Valine 12. PTC-1-Methionine 13. PTC-1-Isoleucine 1. PTC-1-Leucine 15. PTC-1-Phenylalanine 16. PTC-1-Lysine UV 230nm UV 25nm UV 25nm 1
2 Column Data Title Solutes Eluent Detection A05 C8-001 A06 ODS A07 ODS-001 A A Inertsil C mm I.D. (Guard) mm I.D mm I.D. Inertsil ODS mm I.D mm I.D. in Soysauce PTH-Amino and 1. Asparatic acid (Asp) 2. Glutamic acid (Glu) 3. Serine (Ser). Threonine (Thr) 5. Alanine (Ala) 6. Proline (Pro) 7. Valine (Val) 8. Isoleucine (Ile) 9. Leucine (Leu) 10. Phenylalanine (Phe) 11. Lysine (Lys) 1. Asparatic acid (Asp) 2. Glutamic acid (Glu) 3. Serine (Ser). Glycine (Gly) 5. Histidine (His) 6. Arginine (Arg) 7. Threonine (Thr) 8. Alanine (Ala) 9. Proline (Pro) 10. Tyrosine (Tyr) 11. Valine (Val) 12. Methionine (Met) 13. Cysteine (Cys) 1. Isoleucine (Ile) 15. Leucine (Leu) 16. Phenylalanine (Phe) 17. Lysine (Lys) 1. Lysine (0.5 mg/ml) 2. Threonine (0.3 mg/ml) 3. Proline (0.6 mg/ml). Valine (0.8 mg/ml) 5. Methionine (3 μg/ml) 1. Histidine (His 100 μg/ml) 2. Asparagine (Asn 100 μg/ml) 3. Arginine (Arg 100 μg/ml). Asparatic acid (Asp 100 μg/ml) 5. Glutamic acid (Glu 100 μg/ml) 6. Serine (Ser 100 μg/ml) 7. Glutamine (Gln 100 μg/ml) 8. Glycine (Gly 100 μg/ml) 9. Alanine (Ala 100 μg/ml) 10. Tyrosine (Tyr 100 μg/ml) 11. Threonine (Thr 100 μg/ml) 12. Methionine (Met 100 μg/ml) 13. Proline (Pro 100 μg/ml) 1. Tryptophan (Trp 100 μg/ml) 15. Phenylalanine (Phe 100 μg/ml) 16. Lysine (Lys 100 μg/ml) 17. Leucine (Leu 100 μg/ml) 1. Maleic acid (0.01 mg/ml) 2. Fumaric acid (0.01 mg/ml) 3. Asparagine (0.75 mg/ml). Aspartic acid (0.75 mg/ml) KH2PO NHH2PO C8H17- SO3Na 2
3 Column Data Title Solutes Eluent Detection A10 CN A11 Diol-013 A12 ODS A13 # D01 C8-003 D02 Ph-003 Inertsil CN mm I.D. Inertsil Diol 5 μm 150 x.6 mm I.D. 5 μm 250 x.6 mm I.D. #2619 (150 x.0 mm I.D.) Inertsil C mmi.d. Inertsil Ph and Acids Compounds Amino GABA (detected by Post-Column method) Free fatty 1. Asparagine (0.75 mg/ml) 2. Aspartic acid (0.75 mg/ml) 3. Fumaric acid (0.01 mg/ml). Maleic acid (0.01 mg/ml) 1. Phenylalanine 2. Methionine 3. Valine. DOPA (3- dihydroxyphenylalanine) 5. Alanine 6. Serine 7. Citrulline 1. Asparagine (0.75 mg/ml) 2. Aspartic acid (0.75 mg/ml) 3. Fumaric acid (0.01 mg/ml). Maleic acid (0.01 mg/ml) 1. Aspartic acid [Asp] (0 nmol/ml) 2. Threonine [Thr] (0 nmol/ml) 3. Serine [Ser] (0 nmol/ml). Glutamic acid [Glu] (0 nmol/ml) 5. Proline [Pro] (108 nmol/ml) 6. Glycine [Gly] (0 nmol/ml) 7. Alanine [Ala] (0 nmol/ml) 8. Cysteine [Cys] (0 nmol/ml) 9. Valine [Val] (0 nmol/ml) 10. Methionine [Met] (0 nmol/ml) 11. Isoleucine [Ile] (0 nmol/ml) 12. Leucine [Leu] (0 nmol/ml) 13. Tyrosine [Tyr] (0 nmol/ml) 1. Phenylalanine [Phe] (0 nmol/ml) 15. GABA (0 nmol/ml) 16. Lysine [Lys] (0 nmol/ml) 17. Histidine [His] (0 nmol/ml) 18. Arginine [Arg] (0 nmol/ml) 1. 3-Dihydroxy phenyl acetic acid 2. Caffeic acid 3. p-hydroxy phenyl acetic acid. Vanillic acid 5. Gentisic acid 6. p-coumaric acid 7. Ferulic acid 8. m-coumaric acid 9. o-coumaric acid 10. Salicylic acid 1. Propionic acid 2. Butyric acid 3. Valeric acid. Caproic acid 5. Heptylic acid 6. Caprylic acid 7. Capric acid 8. Lauric acid 9. Myristic acid 10. Palmitic acid A) B) A/B = 85/15 w/w 20 mm (ph.0; ) FL Ex 360 nm Em 50nm 3
4 Column Data Title Solutes Eluent Detection D03 Ph-00 D0 C8-00 D05 ODS D06 ODS D07 ODS-80A- 00 D08 ODS-80A- 005 D09 AV D10 AV D Inertsil ph mmI.D. Inertsil C8 Inertsil ODS-80A Inertsil ODS-80A Bioptic AV-1 Bioptic AV-1 PBPB- Carboxylic Dicarboxylic Anion surfactants Organic acid Formic acid and Acetic acid 2-Phenylbutylic acid 3-Phenylbutylic acid Organic acid 1. Lauric acid(pbpb Deriv.) 2. Myristic acid(pbpb Deriv.) 3. Palmitic acid(pbpb Deriv.). Stearic acid(pbpb Deriv.) 1. Oxalic acid 2. Tartaric acid 3. Glycolic acid. Malonic acid 5. α-ketoglutaric acid 6. Lactic acid 7. Citric acid 8. Maleic acid 9. Fumaric acid 10. Succinic acid 11. Acrylic acid 1. Malonic acid 2. Succinic acid 3. Glutaric acid. Adipic acid 5. Pimelic acid 6. Azelaic acid 7. Sebacic acid 1. Sodium n-undecylsulfonate 2. n-dodecane sulfonate Na 3. Sodium n-tridecylsulfonate. Sodium n-tetradecylsulfonate 5. n-hexadecane sulfonate Na 1. Gallic acid 2. 3-Dihydroxy phenyl acetic acid 3. p-hydroxy benzoic acid. Caffeic acid 5. Vanillic acid 6. Gentisic acid 7. p-coumaric acid 8. Ferulic acid 9. m-coumaric acid 10. o-coumaric acid 11. Salicylic acid(each 5ppm) 1. Formic acid 0.1% 2. Acetic acid 0.1% NHH2PO NaClO 1. 2-Phenylbutylic acid KOH 1. H3C-CH-CH2-COOH CH3OH KOH 1. Fumaric acid(0.18mg/ml) 2. Acrylic acid(0.90mg/ml) 3. Itaconic acid(0.62mg/ml). Methacrylic acid(0.29mg/ml)
5 Column Data Title Solutes Eluent Detection D D13 ODS D1 C D15 C D16 C D D D mmi.d mmI.D mmI.D mmI.D. Organic acid Fatty acid Organic Acids Anion Surfactants 1. Oxalic acid (0.19mg/mL) 2. Tartaric acid (1.20mg/mL) 3. Glycolic acid(3.12mg/ml). Malonic acid(1.mg/ml) 5. Lactic acid(3.0mg/ml) 6. Acetic acid(3.0mg/ml) 7. Fumalic acid(0.015mg/ml) 8. Succinic acid(3.37mg/ml) 9. Acrylic acid(0.10mg/ml) 1. Linolenic acid(0.67mg/ml) 2. Linoleic acid(0.67mg/ml) 3. Oleic acid(0.67mg/ml) 1. Fumaric acid(0.18mg/ml) 2. Acrylic acid(0.90mg/ml) 3. Itaconic acid(0.62mg/ml). Methacrylic acid(0.29mg/ml) 1. Formic acid(0.5mg/ml) 2. α-ketoglutaric acid(0.05mg/ml) 3. Citric acid(0.5mg/ml). Maleic acid(0.005mg/ml) 5. Fumaric acid(0.005mg/ml) 1. Oxalic acid (0.19mg/mL) 2. Tartaric acid (1.20mg/mL) 3. Glycolic acid(3.12mg/ml). Malonic acid(1.mg/ml) 5. Lactic acid(3.0mg/ml) 6. Acetic acid(3.0mg/ml) 7. Fumalic acid(0.015mg/ml) 8. Succinic acid(3.37mg/ml) 9. Acrylic acid(0.10mg/ml) 1. Gallic acid 2. Dihydroxy benzoic acid 3. p-hydroxy benzoic acid. Caffeic acid 5. Vanillic acid 6. Gentisic acid 7. p-coumaric acid 8. Ferulic acid 9. m-coumaric acid 10. o-coumaric acid 11. Salicylic acid 1. Nonyl sulfonate Na C10 sulfonate Na C11 sulfonate Na C13 sulfonate Na C12 sulfate Na(SDS) C1 sulfonate Na C16 sulfonate Na Tartaric acid 1. meso-tartaric acid DL-Tartaric acid NHH2PO CH3OH NHH2PO NHH2PO NaClO Phosphate buffer UV 250 nm 5
6 Column Data Title Solutes Eluent Detection D D21 C D D23 ODS D2 ODS D25 CX mmI.D mmI.D mmI.D mmI.D mmI.D. Inertsil CX (5 µm mm I.D.) 2 Phthalic acid 1. Uracil Phthalic acid Formic acid (0.1 %) 2. Lactic acid (0.1 %) 3. Acetic acid (0.1 %). Propionic acid (0.1 %) 1. Formic acid (0.1 %) 2. Lactic acid (0.1 %) 3. Acetic acid (0.1 %). Propionic acid (0.1 %) alkylbenzene sulfonate Linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (n- LAS) (detected by Post-Column method) 1. Sodium Decylbenzenesulfonate C10H21C6HSO2Na(2.0mg/) 2. Sodium Undecylbenzenesulfonate C11H23C6HSO2Na(2.0mg/L) 3. Sodium Dodecylbenzenesulfonate C12H25C6HSO2Na(2.0mg/L). Sodium Tridecylbenzenesulfonate C13H27C6HSO2Na(2.0mg/L) 5. Sodium Tetradecylbenzenesulfonate C1H29C6HSO2Na(2.0mg/L) 1. Sodium n-decylbenzenesulfonate C10H21C6HSO2Na(2.0mg/L) 2. Sodium n- Undecylbenzenesulfonate C11H23C6HSO2Na(2.0mg/L) 3. Sodium n- Dodecylbenzenesulfonate C12H25C6HSO2Na(2.0mg/L). Sodium n- Tridecylbenzenesulfonate C13H27C6HSO2Na(2.0mg/L) 5. Sodium n- Tetradecylbenzenesulfonate C1H29C6HSO2Na(2.0mg/L) 1. Phosphoric acid (1.0 mg/ml) 2. Citric acid (1.0 mg/ml) 3. Malic acid (1.0 mg/ml). Succinic acid (1.0 mg/ml) 5. Lactic acid (1.0 mg/ml) 6. Acetic acid (1.0 mg/ml) 7. Pyroglutamic acid (1.0 mg/ml) NaClO NaClO TFA FL Ex 221 nm Em 28 nm FL Ex 221 nm Em 28 nm VIS 0 nm For complete Product Description, Chromatograms Price & Delivery in Australia & New Zealand contact info@winlab.com.au or call 61 (0)
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]
![Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]](/thumbs/84/90818314.jpg) Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Methionine (Met or M)
 Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
CHM333 LECTURE 6: 1/25/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID:
 AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a Novel Mixed-Mode HPLC Column
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Amino Acid Analyzer AAA400
 Amino Acid Analyzer AAA400 Determination of amino acid of hydrolyzates (food and feed) Column: LG ANB OSTION 3.6x340 12μm Eluents: sodium-citrate buffers, 0.2 M NaOH Aspartic Acid, Threonine, Serine, Glutamic
Amino Acid Analyzer AAA400 Determination of amino acid of hydrolyzates (food and feed) Column: LG ANB OSTION 3.6x340 12μm Eluents: sodium-citrate buffers, 0.2 M NaOH Aspartic Acid, Threonine, Serine, Glutamic
Introduction to Peptide Sequencing
 Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
AP Bio. Protiens Chapter 5 1
 Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Amino Acids. Review I: Protein Structure. Amino Acids: Structures. Amino Acids (contd.) Rajan Munshi
 Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Midterm 1 Last, First
 Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
1. (38 pts.) 2. (25 pts.) 3. (15 pts.) 4. (12 pts.) 5. (10 pts.) Bonus (12 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Investigating GCxGC separations using selective column chemistry and compound derivatization pairings for common metabolomics chemical compounds
 Investigating GCxGC separations using selective column chemistry and compound derivatization pairings for common metabolomics chemical compounds Julie Kowalski, Michelle Misselwitz and Jack Cochran Restek
Investigating GCxGC separations using selective column chemistry and compound derivatization pairings for common metabolomics chemical compounds Julie Kowalski, Michelle Misselwitz and Jack Cochran Restek
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides
 Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5
 Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
Cells N5 Homework book
 1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
Protein and Amino Acid Analysis. Chemistry M3LC
 Protein and Amino Acid Analysis Chemistry M3LC Proteins Proteins are made up of amino acids: H2N-CHR-COOH + H3N-CHR-COO - neutral form zwitterionic form There are twenty standard amino acids: A ala alanine
Protein and Amino Acid Analysis Chemistry M3LC Proteins Proteins are made up of amino acids: H2N-CHR-COOH + H3N-CHR-COO - neutral form zwitterionic form There are twenty standard amino acids: A ala alanine
Biology. Lectures winter term st year of Pharmacy study
 Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
PROTEINS. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Acid L-form * * Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 O = N -C -C-O.
 Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Amino Acids. Lecture 4: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where?
 Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
Analysis of free amino acids in tobacco with a new LC/MS/MS. procedure. S. C. Moldoveanu R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Co.
 Analysis of free amino acids in tobacco with a new LC/MS/MS procedure S. C. Moldoveanu R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Co. Jeff Zhu Eurofins Background A considerable number of analytical methods are reported in
Analysis of free amino acids in tobacco with a new LC/MS/MS procedure S. C. Moldoveanu R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Co. Jeff Zhu Eurofins Background A considerable number of analytical methods are reported in
Macromolecules Structure and Function
 Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr.Diala
 number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
Study of Amino Acids in DDGS
 Study of Amino Acids in DDGS Y. Zhang, J. V. Simpson and B. A. Wrenn National Corn-to-Ethanol Research Center Edwardsville, IL 62025 Hans Stein University of Illinois Urbana Champaign Gerald C. Shurson
Study of Amino Acids in DDGS Y. Zhang, J. V. Simpson and B. A. Wrenn National Corn-to-Ethanol Research Center Edwardsville, IL 62025 Hans Stein University of Illinois Urbana Champaign Gerald C. Shurson
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection
 Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Amino acid metabolism II
 Amino acid metabolism II Fates of amino acid carbon skeleton degradation to common intermediates pyruvate, intermediates of citric acid cycle, acetyl-coa Glucogenic AA precursors of glucose - degradation
Amino acid metabolism II Fates of amino acid carbon skeleton degradation to common intermediates pyruvate, intermediates of citric acid cycle, acetyl-coa Glucogenic AA precursors of glucose - degradation
Lecture 4. Grouping Amino Acid 7/1/10. Proteins. Amino Acids. Where Are Proteins Located. Nonpolar Amino Acids
 Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes
 1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination #5: Section Five December 7, Name: (print) Section:
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011
 Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
AMINO ACID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
Amino acid metabolism
 Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Cultivation of Yeast Cells and Induction of Autophagy Hayashi Yamamoto, Hitoshi Nakatogawa
 Cultivation of Yeast Cells and Induction of Autophagy Hayashi Yamamoto, Hitoshi Nakatogawa METHOD Preculture 1. Inoculate yeast cells (from a single colony) into 2 ml of liquid medium (YPD, SD/CA, or SD/DO
Cultivation of Yeast Cells and Induction of Autophagy Hayashi Yamamoto, Hitoshi Nakatogawa METHOD Preculture 1. Inoculate yeast cells (from a single colony) into 2 ml of liquid medium (YPD, SD/CA, or SD/DO
Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaves
 Environ. Chem. 216, 13, 877 887 doi:1.171/en165_ac CSIRO 216 Supplementary material Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis
Environ. Chem. 216, 13, 877 887 doi:1.171/en165_ac CSIRO 216 Supplementary material Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis
Metabolism of amino acids I. Josef Fontana
 Metabolism of amino acids I Josef Fontana EC Overview of the lecture Introduction to protein and amino acids metabolism Metabolic pathways of amino acids Transamination Conversion glutamate - glutamine
Metabolism of amino acids I Josef Fontana EC Overview of the lecture Introduction to protein and amino acids metabolism Metabolic pathways of amino acids Transamination Conversion glutamate - glutamine
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids. Amino acid metabolism
 Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Authors. Abstract. Introduction. Food
 Improved and Simplified Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry Method for the Analysis of Underivatized Free Ao Acids in Various Foods Application Food Authors
Improved and Simplified Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry Method for the Analysis of Underivatized Free Ao Acids in Various Foods Application Food Authors
Proteins. RWF Chemistry H2A
 Proteins RWF Chemistry H2A Proteins Proteins are made up of amino acids: H2N-CHR-COOH + H3N-CHR-COO - neutral form zwitterionic form There are twenty standard amino acids: A ala alanine R arg arginine
Proteins RWF Chemistry H2A Proteins Proteins are made up of amino acids: H2N-CHR-COOH + H3N-CHR-COO - neutral form zwitterionic form There are twenty standard amino acids: A ala alanine R arg arginine
Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2*
 Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2* 1 Department of Biotechnology, Akita Prefectural University, Akita City, Japan; 2 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2* 1 Department of Biotechnology, Akita Prefectural University, Akita City, Japan; 2 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Protein Investigator. Protein Investigator - 3
 Protein Investigator Objectives To learn more about the interactions that govern protein structure. To test hypotheses regarding protein structure and function. To design proteins with specific shapes.
Protein Investigator Objectives To learn more about the interactions that govern protein structure. To test hypotheses regarding protein structure and function. To design proteins with specific shapes.
Gentilucci, Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds CH 3
 Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino acids. (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi
 Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
ASMS 2014, (Jun 16, 2014, Baltimore, USA) Development of a novel amino acids analysis column for LC-MS without derivatization
 ASMS 2014, (Jun 16, 2014, Baltimore, USA) Development of a novel amino acids analysis column for LC-MS without derivatization VERVIEW We have developed a novel amino acid separation column for LC-MS without
ASMS 2014, (Jun 16, 2014, Baltimore, USA) Development of a novel amino acids analysis column for LC-MS without derivatization VERVIEW We have developed a novel amino acid separation column for LC-MS without
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Level and activity of D-amino acids in mouse brain tissue and blood
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Level and activity of D-amino acids in mouse brain tissue and blood Choyce A. Weatherly 1, Siqi Du 1, Curran Parpia 1, Polan T. Santos 2, Adam
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Level and activity of D-amino acids in mouse brain tissue and blood Choyce A. Weatherly 1, Siqi Du 1, Curran Parpia 1, Polan T. Santos 2, Adam
9/16/15. Properties of Water. Benefits of Water. More properties of water
 Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
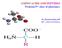 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
Table 1. Gas chromatographic and mass spectrometric data of the identified hydrophilic
 Table 1. Gas chromatographic and mass spectrometric data of the identified hydrophilic compounds. Compound RT a RRT b RI c Quantification ion d Other characteristic ions Amino acids Alanine 9.109 0.499
Table 1. Gas chromatographic and mass spectrometric data of the identified hydrophilic compounds. Compound RT a RRT b RI c Quantification ion d Other characteristic ions Amino acids Alanine 9.109 0.499
Proximate composition, amino acid and fatty acid composition of fish maws. Department of Biology, Lingnan Normal University, Zhanjiang, , China
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Proximate composition, amino acid and fatty acid composition of fish maws Jing Wen a, Ling Zeng b *, Youhou Xu c, Yulin Sun a, Ziming Chen b and Sigang Fan d a Department of Biology,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Proximate composition, amino acid and fatty acid composition of fish maws Jing Wen a, Ling Zeng b *, Youhou Xu c, Yulin Sun a, Ziming Chen b and Sigang Fan d a Department of Biology,
Chapter 4: Information and Knowledge in the Protein Insulin
 Chapter 4: Information and Knowledge in the Protein Insulin This chapter will calculate the information and molecular knowledge in a real protein. The techniques discussed in this chapter to calculate
Chapter 4: Information and Knowledge in the Protein Insulin This chapter will calculate the information and molecular knowledge in a real protein. The techniques discussed in this chapter to calculate
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes
 Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell
 A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
18 Amino Acid Oxidation and Production of Urea W. H. Freeman and Company
 18 Amino Acid Oxidation and Production of Urea 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Last Class of Biomolecules For Energy 1. Production of acetyl-coa. Glucose. To pyruvate via glycolysis. To acetyl-coa by
18 Amino Acid Oxidation and Production of Urea 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Last Class of Biomolecules For Energy 1. Production of acetyl-coa. Glucose. To pyruvate via glycolysis. To acetyl-coa by
AA s are the building blocks of proteins
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
NABIL KILLINY ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PLANT PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA. Citrus responses to huanglongbing
 NABIL KILLINY ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PLANT PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA Citrus responses to huanglongbing HLB is Vector-borne Disease! Vector psyllids Pathogen Ca. Liberibacter asiaticus. Host Citrus spp.
NABIL KILLINY ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PLANT PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA Citrus responses to huanglongbing HLB is Vector-borne Disease! Vector psyllids Pathogen Ca. Liberibacter asiaticus. Host Citrus spp.
A Brief Summary of Important Online Bioinformatics Databases and Genomic Application Algorithms
 A Brief Summary of Important Online Bioinformatics Databases and Genomic Application Algorithms Compiled 2005, James F. Lynn Abstract: This is, by no means, a complete compendium of all the databases and
A Brief Summary of Important Online Bioinformatics Databases and Genomic Application Algorithms Compiled 2005, James F. Lynn Abstract: This is, by no means, a complete compendium of all the databases and
USER GUIDE. Can You Complete An Amino Acid Analysis In 15:00 Minutes?...now you can! USERGUIDE
 USER GUIDE USERGUIDE Can You Complete An Amino Acid Analysis In 15:00 Minutes?...now you can! Amino acid analysis kits for: Sample Prep Derivatization GC or LC Analysis 1 USERGUIDE Table of Contents Obstacles
USER GUIDE USERGUIDE Can You Complete An Amino Acid Analysis In 15:00 Minutes?...now you can! Amino acid analysis kits for: Sample Prep Derivatization GC or LC Analysis 1 USERGUIDE Table of Contents Obstacles
Head. Tail. Carboxyl group. group. group. air water. Hydrocarbon chain. lecture 5-sa Seth Copen Goldstein 2.
 Lipids Some lipid structures Organic compounds Amphipathic Polar head group (hydrophilic) Non-polar tails (hydrophobic) Lots of uses Energy storage Membranes Hormones Vitamins HO O C H 2 C CH 2 H 2 C CH
Lipids Some lipid structures Organic compounds Amphipathic Polar head group (hydrophilic) Non-polar tails (hydrophobic) Lots of uses Energy storage Membranes Hormones Vitamins HO O C H 2 C CH 2 H 2 C CH
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam )ومن أحياها(
 Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
Outline. Ø Standard Recommendations. Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins
 Protein 101 Outline Ø Standard Recommendations Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) Dietary Guidelines
Protein 101 Outline Ø Standard Recommendations Ø Minimum / Optimal / Maximum CONFUSION? Ø Quality Ø Impact of Shifting from Animal to Plant-Based Proteins Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) Dietary Guidelines
STUDY AND COMPARISON OF AMINO ACIDS IN RED AND GREEN APPLES
 IJPSR (2017), Volume 8, Issue 10 (Research Article) Received on 23 March, 2017; received in revised form, 24 April, 2017; accepted, 27 May, 2017; published 01 October, 2017 STUDY AND COMPARISON OF AMINO
IJPSR (2017), Volume 8, Issue 10 (Research Article) Received on 23 March, 2017; received in revised form, 24 April, 2017; accepted, 27 May, 2017; published 01 October, 2017 STUDY AND COMPARISON OF AMINO
SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM
 SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM When we eat food such as a tuna fish sandwich, the polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are digested to smaller molecules that are absorbed into the cells of our body. As these
SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM When we eat food such as a tuna fish sandwich, the polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are digested to smaller molecules that are absorbed into the cells of our body. As these
0010 Amino Acids 40 Profile - Plasma
 Accession #: Order #: G1234567 Date Collected: Date Received: 01/22/2013 Reference #: Patient: Date of Birth: 02/05/1962 Date of Report: Telephone: 7704464583 Ordering Physician: 1234 Main St. Anywhere,
Accession #: Order #: G1234567 Date Collected: Date Received: 01/22/2013 Reference #: Patient: Date of Birth: 02/05/1962 Date of Report: Telephone: 7704464583 Ordering Physician: 1234 Main St. Anywhere,
Review II: The Molecules of Life
 Review II: The Molecules of Life Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2007 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2007 Outline Introduction Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids
Review II: The Molecules of Life Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2007 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2007 Outline Introduction Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids
Introduction to proteins and protein structure
 Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Introduction. Basic Structural Principles PDB
 BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
