Sacral Unilateral Spinal Anaesthesia With 0.25% Hypobaric Bupivacaine
|
|
|
- Dale Merritt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: , p-issn: Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. I (Sep. 2015), PP Sacral Unilateral Spinal Anaesthesia With 0.25% Hypobaric Bupivacaine Radhashyam Paria 1, Smarajit Surroy 1, Mousumi Majumder 1, Anshuman Paria 2 Baishakhi Paria 3, Soma Sengupta 4, GoutamDas, 5 1 (dept of Anesthesiology, Howrah Orthopedic Hospital, Eastern Railways, WB) 2 dept of Neonatology, SSKM hospital, WB) 3 (Department of Community Medicine, National Medical College) 4 (dept of Anesthesiology, SSKM hospital, WB) 5 (Department of Pediatric Medicine, BC Roy PGIPS, West Bengal) Abstracts: Background And Objectives: The geriatric patients with limited reserved organs are very prone to develop cardiovascular instability during surgical procedures. Various anaesthetic techniques are advocated for the above purpose. Spinal anaesthesia is one of them and very useful in lower limb surgeries although it is frequently complicated with hemodynamic instability. Unilateral spinal anaesthesia on the surgical side through the dorsal foramen of the sacrum with local hypobaric anaesthetic contributes the hemodynamic stability. METHODS: 100 patients with physical status ASA II and III were submitted to sacral spinal anesthesia in the lateral position with the surgical side uppermost. They were administered 3ml of 0.25% of injection bupivacaine through the 2nd dorsal sacral foramen and maintained the same position for another 15 minutes. RESULTS: All patients developed the sensory and motor block in the uppermost lower limb without hemodynamic instability throughout the operative period including postoperative one. Blood pressure and pulse showed almost static within the normal range of short variation. CONCLUSION: Hypobaric bupivacaine (7.5 mg) produced both motor and the sensory block of the uppermost leg without hemodynamic disturbance when administered through the 2nd dorsal foramen of the sacrum in the lateral position of patients. Key Words: Local anaesthetic, hypobaric, bupivacaine, Hemodynamic, nerve injury I. Introduction Caudal continuation of the brainstem forms the spinal cord protected by the vertebral column of the spines. Spinal nerves formed by the combination of dorsal roots carrying sensory axons and ventral roots carrying motor axons exit from the vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramen between two adjacent vertebrae. The distance of mm between right and left spinal nerve roots is very important for the involvement of unilateral nerve roots block or posterior roots block. The beneficial effects of the unilateral block during the lower limbs surgical procedures in geriatric patients are highly notable. Its appreciation by other medical associates acquires a vital place in the practicing field of anaesthesia although the unilateral anaesthetic procedure is performed through the lumbar route (lumbar spinal anaesthesia) with hyperbaric local anaesthetic. But, till now, no literature in support of the unilateral sacral spinal anaesthesia with local hypobaric anesthetic is available. So it was assumed that sacral spinal anaesthesia{1} with hypobaric local anaesthetic might produce limited block height with the provision of hemodynamic stability and unilateral block on nondependent side of the body. The supplementary peripheral nerve block acting in the same surgical field was added to prolong the perioperative analgesia for major surgeries of the lower limb. On the basis of such hypothesis, this study was undertaken to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of sacral unilateral spinal anaesthesia with the hypobaric local anaesthetic solution in the lateral position and keeping the surgical side on the top. II. Method With acceptance of approval from medical ethical review broad and advanced informed consent from a group of 100 unselected patients belonging to ASA class II and III, were admitted for lower limb surgeries. They were operated for fracture repair, knee replacement, hip replacement and knee arthroscopy in the period of June 2014 to May They were scheduled for surgery under the sacral spinal anaesthesia with local anesthetic 0.25% injection bupivacaine through its dorsal foramen. Their consents were signed after the full explanation about the expected benefits and results, side effects and complications of the sacral spinal DOI: / Page
2 anaesthesia through its dorsal foramen. Every participant was subjected to preoperative visit to exclude the contraindication of the proposed procedure. Patients with the history of Psychological disorders, coronary artery disease, uncontrolled hypertension, intracranial mass, head injury, local cellulitis at the site, coagulation disorders, allergy to local anesthetic were excluded from the study. Patients were scheduled for the lower limb orthopedic operations like the hip replacement, repairing of fracture on the femur, tibia, knee joint and ankle joint, hemi-arthroplasty, knee replacement and foot. Patients for skin grafting were also included in this study. In the O.T, peripheral infusion and non invasive monitoring were started. Anatomical landmarks [2-10] were identified. We identified the spinous process of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4) and the tip of the coccyx. Next, we located the mid-point of above two landmarks as the third sacral vertebra (S3). The first sacral vertebra (S1) was located as mid-point of L4 and S3. The second sacral vertebra (S2) is found at the mid-point between S1 and S3 and at the level of the posterior superior iliac spine which is externally detected by dimple of skin. The spinous processes of S1 and S2 are found approximately 2.5 cm apart, and their respective foramina lie 1.5 cm caudal and lateral to them. Similarly, S3 foramina lie 1.5 cm caudal and lateral to S3 vertebra. Simultaneously, as premedication, each and every participant was administered peripheral nerve block like the femoral nerve block [2, 3, 10] for the surgeries on the hip, femur and knee joint. The popliteal fossa block [4] was advocated for the surgeries on tibia, fibula, ankle joint and foot with deposition of 30 ml of 0.5% injection ropivacaine through the nerve stimulator needle by lateral approach. [11-13] After identification of S2 dorsal sacral foramen, local infiltration with 6 ml of 1% injection xylocaine over sacrum Quincke types spinal needle (Spinocan Spinal Anesthesia Needles 27G 3.5 inches, B Braun) was introduced obliquely towards midline through the identified point keeping surgical side up. The spinal needle in the most of the cases touched the bone and then the needle was withdrawn slightly and redirected either cephalad or caudal to enter the expected foramen and to penetrate the dural sac. After the flow of clear CSF, 3 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine was injected through the needle. After intrathecal deposition of local anesthetic in lateral position, the patient remained in the same position for another fifteen minutes to develop motor and sensory block on the nondependent lower limb. Heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and oxygen concentration were recorded every three minutes for first 10 minutes after which they were recorded at every ten minutes interval. In cases of lower limb surgeries, the upper level of sensory block was assessed by pinprick and motor block by modified Bromage scale. The modified Bromage scale was estimated as follows: 0 = lifting up the extended leg, 1 = flexed knee with full ankle movement, two =no knee movement, partial ankle movement, 3 = complete paralysis. We also recorded the onset time of sensory and motor block as the time gap between the spinal injection and unilateral loss of sensation and loss of motor activity of the nondependent lower limb respectively. Similarly, we calculated the duration of the sensory and motor block and sent all collected data for statistical analysis using Graphpad Prism 5. The supplementary oxygen supply was administered to each patient at the rate of 3l/min through nasal route. III. Results 100 (one hundred) aged patient of male-female ratio 60:40 were successfully anesthetized for lower limbs surgical procedures with help of the combination of sacral spinal anesthesia, depositing hypobaric local anesthetic (0.25% bupivacaine) at the bottom of dural sac through the 1st or 2nd sacral dorsal foramen and specific peripheral nerve block acting on the same surgical field. The demographic profile is cited in the table no 1. The sensory and motor block of the nondependent lower limb showed delay onset time. The duration of the motor and sensory block prolonged. The nerve block profile is cited in Table no 1. The nondependent leg developed both motor and sensory block. The dependent side remained free from both motor and sensory block before and after operation. The most striking feature of this study was the hemodynamic profile cited on the table no 1. All patients showed stable blood pressure and heart rate above the normal level throughout the operative period. All patients needed less intravenous fluid therapy. IV. Discussion The fracture cases are usually associated with excruciating pain with exaggeration on movement during transport and intrathecal procedure increasing stress, strain and agony of the patients. They need profound analgesia to control surgical stress response during and after surgery. The systemic analgesics are usually undesirable for elderly patients to avoid central depression and associated hypoxia. The use of fascia iliac compartment block (FICB) is appropriate to relieve pain from the area supplied by femoral and obturator nerve between hip to the knee joint. Similarly, the preoperative popliteal fossa block is suitable to relieve pain from DOI: / Page
3 the area below knee supplied by the sciatic nerve as analgesia without central depression and hampering hemodynamic status [3, 4, 10]. FICB provides analgesia of high quality [14-16] superior to systemic opioid [17,18] but inferior to epidural analgesia with fewer complications.[19] Postoperative analgesia with femoral nerve block after surgery on knee joint improves satisfactory. [20] The potential dangers of intravascular injection, systemic toxicity, mechanical nerve damage and infection are extremely rare. The large volume of local anaesthetic needed for peripheral nerve block causes infrequently drug toxicity. So, close observation with monitoring at least for the first 15 minutes is essential and mandatory. The hemodynamic stability along with profound and prolonged analgesia is contributed by combined sacral spinal anesthesia [8,9,10] with preoperative popliteal fossa block for below knee surgery or FICB for the hip to knee surgeries. The peripheral nerve block acting on the same surgical field acts as the adjuvant to the spinal anesthesia like intrathecal administration of fentanyl or clonidine. The combination of spinal anaesthesia and preoperative specific peripheral nerve block acting at the same surgical field offers the advantages of both components by minimizing their respective disadvantages. This combination also contributes hemodynamic stability, rapid onset of block and profound prolonged analgesia during and after surgery with the complete abolition of the neural transmission in the block area. The unilateral spinal anaesthesia is the occurrence of an asymmetric distribution of the spinal anaesthesia between the operative side and the non-operative side. The slow deposition of local anaesthetic to the neural tissue of one limb causes the motor and sensory block on the same limb. Spinal anaesthesia is an excellent regional intrathecal anaesthetic procedure with the provision of profound and reversible nerve block in the lower portion of the body by relatively simple injection of the small amount of local anesthetic. However, such a good anesthetic procedure is frequently undignified as the most unpredictable and unreliable anesthetic technique with variable duration and extension of the block. Overall, most frequently, conventional spinal anesthesia with local hyperbaric anesthetic is alleged to produce hypotension during the intrathecal procedure. This hemodynamic related allegation makes spinal anesthesia controversial to be the best and most acceptable technique of anesthesia for more than lower half of the body. The sacral portion of the dural sac is the lowest access to communicate with the intrathecal space and to deposit the local anesthetic for motor and the sensory block of the lumbosacral segments of the spinal cord. The dural space between 2nd sacral (S2) vertebra and 2nd lumbar (L2) vertebra is devoid of the spinal cord along with the segments for the autonomic outflow. On the other hand, it is packed with lumbosacral spinal nerve roots to exit through the specific intervertebral foramen to form nerves and plexus outside the vertebral canal. Deposition of local hyperbaric anesthetic in the lowermost part of dural sac through the 2nd or 1st dorsal sacral foramen causes involvement of nerves from below upward. The sacral component gets the first chance to get contact with the concentrated solution of local anesthetic. Next to the sacral component, the lumbar component gets the chance to be affected by the comparatively less concentrated solution of local anesthetic. Usually, fifth sacral (S5) to first lumber (L1) spinal nerve roots undergo both motor and sensory block with less extension of sympathetic involvement and get the recovery in the reverse way. Preferential involvement of nerves in favour of nondependent side by intrathecal deposition of local anesthetic (hypobaric) in the lateral decubitus handles the frequent development of unilateral block in the nondependent side. The asymmetrical distribution of the block at the dependent and nondependent sides is due to the slight difference in densities between local hypobaric anesthetic (1.003 g/ml) and CSF (1.006 g/ml). This disparity of density of two different solutions offers an appropriate and justifiable explanation to have a limited block on the non-dependent side with local hypobaric anaesthetic in lateral decubitus. In this lateral position, the local hypobaric anaesthetic travels transversely from dependent side to nondependent side to block both motor and sensory nerves of the nondependent side. In the course of time, utilization of local anesthetic by cephalad spread decreases the drug concentration to equalize the disparity of densities of local anesthetic and CSF automatically. A complete distribution of drug to neural tissue restricts the upper limit of the block. The thoracic segments for sympathetic outflow usually escape from the involvement of local anesthetic administered intrathecally at the bottom of dural sac through the 2nd dorsal sacral foramen. The sacral spinal anesthesia with local hypobaric anesthetic contributes more hemodynamic stability to patients. This beneficial effect of spinal anesthesia with local hypobaric anesthetic is useful for lower limbs surgeries particularly for aged patients with minimal organ reserve. The local anaesthetic deposited at the bottom of dural sac forms a uniform mixture with lumbosacral CSF and acquires an unidirectional cephalad extension of diluted and ineffective admixture of local anesthetic to produce hemodynamic instability. The distribution of local anaesthetic to adjacent neural tissue during the cephalad spread also decreases the concentration of the drug. The long intrathecal distance through CSF to the spinal segments of sympathetic outflow (thoracic) also acts as a guard against cardiovascular disturbance. The angulated position of the lumbosacral joint is also a contributory factor for the rapid spread of concentrated local anesthetic to the spinal segments of sympathetic outflow. DOI: / Page
4 The lateral decubitus of the patient with the surgical side uppermost for about 15 minutes helps to deposit the hypobaric local anesthetic to the nerve roots on the surgical side. The nondependent part undergoes motor and sensory block. The dependent side remains free from the neural block in the lateral position although partial sensory and motor block is seen when the patient is turned to supine. Most probably it is due to the presence of excess amount of local anesthetic in the intrathecal space. The influences of different factors regulating the onset of the unilateral block in the lower limb surgery are giving below. The gauge of the spinal needle, baricity of the local anesthetic solution, the position of the patient and the rate of injection are the most important factors to regulate the unilateral block. Needle: Fast injection of local anesthetic producing turbulent flow provides a homogenous mixture with CSF with quick reduction of baric gradient avoiding migration of the local anesthetic to produce the unilateral block. The slow injection of local anesthetic producing laminar flow helps to maintain baric gradient for migration of local anesthetic providing the unilateral block. The spinal needles of 20G, 22G [22] and 29G [23] are reported to produce the unilateral block. Baricity of local anesthetic: The hyperbaric anesthetic solution has a tendency to produce unilateral block on the dependent side in lateral decubitus of the patient whereas local hypobaric anesthetic produces unilateral block on the nondependent side on the same position of the patient. Position: The sitting position of the patient during the intrathecal procedure is not capable to produce the unilateral block. The lateral decubitus with the operative side on the table is the main criterion of the unilateral block with hyperbaric local anaesthetic. But, the lateral decubitus with the operative side at the top is essential for the development of unilateral block with the local hypobaric anaesthetic. Maintenance of the lateral decubitus for a determined length of time is essential to fix the anesthetic drug at neural tissue on the operative side. However, it is difficult to define the ideal length of time to maintain the position of the patient. The use of the slow administration of low-dose of either hyperbaric or hypobaric local anaesthetic solution causes the unilateral block on the surgical side.[24-26] Rate of injection: The rate of injection through the spinal needle depends on the internal diameter of the needle. Larger internal diameter causes the free flow of the drug into subarachnoid space resulting turbulence within CSF with the preference of bilateral block. On the other hand, half reduction of the internal diameter of the spinal needle causes four times reduction of flow with a greater preference of unilateral block on the surgical side. Small amount of hypobaric local anaesthetic is needed to provide unilateral spinal anaesthesia through the sacral route in the lateral position of patient keeping the surgical side at the top. This technique is capable to provide the maximal hemodynamic stability. This hemodynamic stability and profound analgesia makes the technique suitable for lower limb operations in geriatric group of patients with limited organs reserve. V. Conclusion The usefulness of the sacral unilateral spinal anaesthesia with hypobaric (0.25%) injection bupivacaine and specific peripheral nerve block acting on the same surgical field in geriatric group of patients is associated with unlimited benefits of maximal hemodynamic stability and profound analgesia without central depression. References [1]. Paria R, Surroy S, Majumder M, Paria A, Paria B, Das G. Sacral spinal anesthesia. Indian J Anesth. 2014; 58(1) : 80-2 [2]. Volka, J,D,. Hadzic,A,. Drobnik, l,.ernest,a,.reiss,w,. Thys,D,M. Anatomical landmarks for femoral nerve block: A comparison of four needle insertion sites. Anesth. Analg. 89;1467:1999. [3]. Paria R, Surroy S, Majumder M, Paria B, Sengupta S, Das G, Paria A. Combination of Fascia iliaca Compartment Block on the surgical side with sacral spinal anesthesia for Hip to Knee surgery IOSR- JDMS 2014; 13(12) [4]. Paria R, Surroy S, Majumder M, Paria B, Sengupta S, Das G, Paria A. Combination of Sacral Spinal Anesthesia and Popliteal Fossa Block on Surgical Side for Below Knee Surgery IOSR- JDMS 2014; 13(10) [5]. Paria R, Surroy S, Majumder M, Paria B, Sengupta S, Paria A. Sacral Saddle Block IOSR-JDMS 2014; 13(4) [6]. Paria R, Surroy S, Majumder M, Paria B, Sengupta S, Paria A. Sacral Epidural Anesthesia IOSR-JD MS 2014; 13(5) [7]. Paria R, Combined Sacral Spinal Epidural Anesthesia. IOSR- JDMS 2014; 13(11): [8]. Paria R, Surroy S, Majumder M, Paria B, Sengupta S, Paria A. Das G. Saddle block for Day Care and Ambulatory Surgery in Anorectal Procedure.IOSR- JDMS 2014; 13 (9) [9]. Paria R Surroy S, Majumder M, Paria B, Sengupta S, Das G, Paria A. Intentional unilateral sacral epidural IOSR- JDMS 2014; 13(12) [10]. Paria R, Surroy S, Majumder M, Paria B, Sengupta S, Das G, Paria A. Role of preoperative Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block on the side of femur surgery IOSR- JDMS 2014; 13(6) [11]. Mcleod, D, H., Wong, D.H., Vaghadia, H., Claridge, R.J., Merrick,P.M., Lateral popliteal sciatic nerve block comparedwith ankle block for analgesia following foot surgery. Can. J. Anesth. 42: [12]. Hansen,E, Eshelman,M.R, Cracchiolo, A.3rd. Popliteal fossa neural blockade as the sole anesthetic technique for outpatient foot and ankle surgery. Foot Ankle Int.21:38, DOI: / Page
5 [13]. Singelyn, F. J, Gouverneur, J. M., Gribomont, B. F. Popliteal sciatic nerve block aided by nerve stimulator: A reliable technique for foot and ankle surgery. Reg. Anesth. 16: 278, [14]. Dahl JB, Christiansen CL, Daugaard JJ, et al. Continuous blockade of the lumbar plexus after knee surgery: Postoperative analgesia and bupivacaine plasma concentrations. Anaesthesia 1988;43: [15]. Edwards E, Wright M. Continuous low dose 3-in-1 nerve blockade for postoperative pain relief after total knee replacement. Anesth Analg 1992;75: [16]. Matheny JM, Hanks GA, Rung GW, et al. Comparison of patient-controlled analgesia and continuous lumbar plexus block after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy 1993;9: [17]. Serpell MG, Millar FA, Thomson MF. Comparison of lumbar plexus block versus conventional opioid analgesia after total knee replacement. Anaesthesia 1991;46:275- [18]. Schultz P, Anker-Moller E, Dahl JB, et al. Postoperative pain treatment after open knee surgery: continuous lumbar plexus block with bupivacaine versus epidural morphine. Reg Anesth [19]. Schultz P, Christensen E, Anker-Moller E, Spangsberg N, Dahl J, Fauno P. Postoperative pain treatment after open knee surgery: continuous lumbar plexus block with bupivacaine versus epidural morphine. Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. 1991;16(1): [20]. Mulroy, M.F, Larkin, K.L., Batra, M.S., Hodgson, P.S., Owens, B.D., Femoral nerve block with 0.25% or 0.5% bupivacaine improves postoperative analgesia following outpatient arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament repair. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 26; 24:2001. [21]. Lui, A.C.P., T.Z. Polis and N.J. Cicutti, Densities of cerebrospinal fluid and spinal anaesthetic solutions in surgical patients at body temperature. Can. J. Anaesth.1998: 45; [22]. Tanasichuk MA, Schultz EA, Matthews JH, Van bergen FH. Spinal hemianalgesia: An evaluation of a method its applicability, and influence on the incidence of hypotension. Anesthesiology. 1961;22:74 85 [23]. Meyer J, Enk D, Penner M. Unilateral spinal anesthesia using low-flow injection through a 29-gauge Quincke needle. Anesth Analg. 1996;82: [24]. Povey HM, Jacobsen J, Westergaard-Nielsen J. Subarachnoid analgesia with hyperbaric 0.5% bupivacaine: Effect of a 60-min period of sitting. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1989;33: [25]. Kuusniemi KS, Pihlajamäki KK, Pitkänen MT, Korkeila JE. A low-dose hypobaric bupivacaine spinal anesthesia for knee arthroscopies. Reg Anesth. 1997;22: [26]. Kuusniemi KS, Pihlajamäki KK, Irjala JK, Jaakkola PW, Pitkänen MT, Korkeila JE. Restricted spinal anaesthesia for ambulatory surgery: A pilot study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1999;16:2 6. Age (years) 72.37±5.08 Height (Cm) ± ±3.02 Weight (Kg) Sex (M:F) 60:40 NERVE BLOCK PROFILE Onset of sensory block at T12 (min) 15.56±4.56 Onset of motor block (min) 13.36±5.46 Duration of motor block (min) ±12.56 Duration of sensory block (min) ±9.69 HEMODYNAMIC PROFILE Systolic blood pressure (mmhg) ±5.65 Heart beats (beats/min) 85.54±1.76 Oxygen saturation (%) 98.53±0.89 ANALGESIC PROFILE Postoperative analgesic(hours) 16.52±2.65 Table 1 : Showing demographic profile, hemodynamic profile and analgesic profile of patients. DOI: / Page
Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent Option For Day Care Surgeries
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. III. (Feb. 2014), PP 09-13 Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. III. (Feb. 2014), PP 09-13 Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent
Reliable Routes For 100% Caudal Anesthesia in Adults.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 11 Ver. IV (Nov. 2014), PP 35-39 Reliable Routes For 100% Caudal Anesthesia in Adults. Radhashyam
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 11 Ver. IV (Nov. 2014), PP 35-39 Reliable Routes For 100% Caudal Anesthesia in Adults. Radhashyam
Induction position for spinal anaesthesia: Sitting versus lateral position
 11 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Induction position for spinal anaesthesia: Sitting versus lateral position Khurrum Shahzad, Gauhar Afshan Abstract Objective: To compare the effect of induction position on block characteristics
11 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Induction position for spinal anaesthesia: Sitting versus lateral position Khurrum Shahzad, Gauhar Afshan Abstract Objective: To compare the effect of induction position on block characteristics
Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia
 Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia Jean Daniel Eloy, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director Rutgers-New Jersey Medical School Rutgers The State University of New Jersey Peripheral Nerve Block
Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia Jean Daniel Eloy, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director Rutgers-New Jersey Medical School Rutgers The State University of New Jersey Peripheral Nerve Block
Spread of subarachnoid hyperbaric amethocaine in adolescents
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 1995; 74: 41-45 Spread of subarachnoid hyperbaric amethocaine in adolescents Y. HIRABAYASHI, R. SHIMIZU, K. SAITOH, H. FUKUDA Summary We have compared the spread of subarachnoid
British Journal of Anaesthesia 1995; 74: 41-45 Spread of subarachnoid hyperbaric amethocaine in adolescents Y. HIRABAYASHI, R. SHIMIZU, K. SAITOH, H. FUKUDA Summary We have compared the spread of subarachnoid
Ropivacaine for Unilateral Spinal Anesthesia; Hyperbaric or Hypobaric?
 Rev Bras Anestesiol 212; 62: 3: 298-311 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Ropivacaine for Unilateral Spinal Anesthesia; Hyperbaric or Hypobaric? Mehmet Cantürk 1, Oya Kılcı 1, Dilşen Ornek 1, Levent
Rev Bras Anestesiol 212; 62: 3: 298-311 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Ropivacaine for Unilateral Spinal Anesthesia; Hyperbaric or Hypobaric? Mehmet Cantürk 1, Oya Kılcı 1, Dilşen Ornek 1, Levent
Intrathecal 0.75% Isobaric Ropivacaine Versus 0.5% Heavy Bupivacaine for Elective Cesarean Delivery: A Randomized Controlled Trial
 Intrathecal 0.75% Isobaric Ropivacaine Versus 0.5% Heavy Bupivacaine for Elective Cesarean Delivery: A Randomized Controlled Trial Surjeet Singh, 1 V.P. Singh, 2 Manish Jain, 3 Kumkum Gupta, 3 Bhavna Rastogi,
Intrathecal 0.75% Isobaric Ropivacaine Versus 0.5% Heavy Bupivacaine for Elective Cesarean Delivery: A Randomized Controlled Trial Surjeet Singh, 1 V.P. Singh, 2 Manish Jain, 3 Kumkum Gupta, 3 Bhavna Rastogi,
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly -
 SPINAL ANAESTHETIC SPREAD ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 37 28 th NOVEMBER 2006 Dr Graham Hocking Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Medicine, John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, UK Email: ghocking@btinternet.com
SPINAL ANAESTHETIC SPREAD ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 37 28 th NOVEMBER 2006 Dr Graham Hocking Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Medicine, John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, UK Email: ghocking@btinternet.com
WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML)
 , 49, 2013, 3 63 (5 MG/ML) (5 MG/ML).,.,.,..,..,, SPINAL ANESTHESIA: COMPARISON OF ISOBARIC ROPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) D. Tzoneva, Vl. Miladinov, Al. Todorov, M. P. Atanasova,
, 49, 2013, 3 63 (5 MG/ML) (5 MG/ML).,.,.,..,..,, SPINAL ANESTHESIA: COMPARISON OF ISOBARIC ROPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) D. Tzoneva, Vl. Miladinov, Al. Todorov, M. P. Atanasova,
EFFECTS OF POSTURE AND BARICITY ON SPINAL ANAESTHESIA WITH 0.5 % BUPIVACAINE 5 ML
 Br.J. Anaesth. (1988), 61, 139-143 EFFECTS OF POSTURE AND BARICITY ON SPINAL ANAESTHESIA WITH 0.5 % BUPIVACAINE 5 ML A Double-Blind Study R. W. D. MITCHELL, G. M. R. BOWLER, D. B. SCOTT AND H. H. EDSTROM
Br.J. Anaesth. (1988), 61, 139-143 EFFECTS OF POSTURE AND BARICITY ON SPINAL ANAESTHESIA WITH 0.5 % BUPIVACAINE 5 ML A Double-Blind Study R. W. D. MITCHELL, G. M. R. BOWLER, D. B. SCOTT AND H. H. EDSTROM
Comparative Study of Intrathecal Ropivacaine and Levobupivacaine With Fentanyl And Magnesium As Adjuvants For Lower Abdominal Surgeries
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861. Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. II. (May. 214), PP 39-43 Comparative Study of Intrathecal Ropivacaine and Levobupivacaine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861. Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. II. (May. 214), PP 39-43 Comparative Study of Intrathecal Ropivacaine and Levobupivacaine
Section: Anaesthesia. Original Article INTRODUCTION
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.5.AN4 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Randomized Clinical Comparison of Three Different Doses of Bupivacaine with Fentanyl for TURP-Search for Optimal
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.5.AN4 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Randomized Clinical Comparison of Three Different Doses of Bupivacaine with Fentanyl for TURP-Search for Optimal
Lower Extremity Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia. Stephanie Duffy, CRNA Regional Anesthesia Faculty Acute Pain Service NMCSD
 Lower Extremity Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia Stephanie Duffy, CRNA Regional Anesthesia Faculty Acute Pain Service NMCSD Objectives Review anatomy of lumbosacral plexus Lumbar plexus blocks Psoas
Lower Extremity Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia Stephanie Duffy, CRNA Regional Anesthesia Faculty Acute Pain Service NMCSD Objectives Review anatomy of lumbosacral plexus Lumbar plexus blocks Psoas
MD (Anaesthesiology) Title (Plan of Thesis) (Session )
 S.No. 1. Comparative Assessment of Sequential organ failure Assessment (SOFA) score and Multiple Organ Dysfunction Score (Mode) in Outcome Prediction among ICU Patients. 2. Comparison of Backpain after
S.No. 1. Comparative Assessment of Sequential organ failure Assessment (SOFA) score and Multiple Organ Dysfunction Score (Mode) in Outcome Prediction among ICU Patients. 2. Comparison of Backpain after
Epidural anaesthesia and analgesia
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Epidural anaesthesia and analgesia Author : Matthew Gurney Categories : Vets Date : June 1, 2009 Matthew Gurney discusses
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Epidural anaesthesia and analgesia Author : Matthew Gurney Categories : Vets Date : June 1, 2009 Matthew Gurney discusses
Dr. K.Raja Sekhar, Dr. B. Venu Gopalan, Asst. Professor.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 12 Ver. IV (Dec. 2015), PP 52-57 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of Bupivacaine with
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 12 Ver. IV (Dec. 2015), PP 52-57 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of Bupivacaine with
Spinal At T 10 (10 th Thoracic)
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 8 Ver. II (Aug. 2014), PP 28-32 Spinal At T 10 (10 th Thoracic) Radhashyam Paria 1, Smarajit
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 8 Ver. II (Aug. 2014), PP 28-32 Spinal At T 10 (10 th Thoracic) Radhashyam Paria 1, Smarajit
Epidural Analgesia in Labor - Whats s New
 Epidural Analgesia in Labor - Whats s New Wichelewski Josef 821 Selective neural blockade has many clinical applications in medicine but nowhere has its use been so well accepted than in the field of Obstetrics.
Epidural Analgesia in Labor - Whats s New Wichelewski Josef 821 Selective neural blockade has many clinical applications in medicine but nowhere has its use been so well accepted than in the field of Obstetrics.
How and why to do an epidural in dogs and cats? Which Indications and which drugs?
 AMVAC/RoSAVA 2014 How and why to do an epidural in dogs and cats? Which Indications and which drugs? Prof. Yves Moens Dipl ECVAA Why do epidurals? A part of a balanced anesthesia A means to provide analgesia
AMVAC/RoSAVA 2014 How and why to do an epidural in dogs and cats? Which Indications and which drugs? Prof. Yves Moens Dipl ECVAA Why do epidurals? A part of a balanced anesthesia A means to provide analgesia
Anatomy and principles of the fascia iliaca block
 Anatomy and principles of the fascia iliaca block Dr Ganesh Kumar 23 rd November 2016 Courtesy Dr Fred Sage Objectives Why do peripheral nerves blocks work? Why choose FIB over FNB? How does it work? How
Anatomy and principles of the fascia iliaca block Dr Ganesh Kumar 23 rd November 2016 Courtesy Dr Fred Sage Objectives Why do peripheral nerves blocks work? Why choose FIB over FNB? How does it work? How
Perioperative Pain Management
 Perioperative Pain Management Overview and Update As defined by the Anesthesiologist's Task Force on Acute Pain Management are from the practice guidelines from the American Society of Anesthesiologists
Perioperative Pain Management Overview and Update As defined by the Anesthesiologist's Task Force on Acute Pain Management are from the practice guidelines from the American Society of Anesthesiologists
Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty
 Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Typical approach Describe anesthesia technique Rather Describe issues with THA and TKA How anesthesia can modify Issues Total Hip Total Knee Blood Loss ++
Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Typical approach Describe anesthesia technique Rather Describe issues with THA and TKA How anesthesia can modify Issues Total Hip Total Knee Blood Loss ++
A study of the anatomy of the caudal space using magnetic resonance imaging
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 1997; 78: 391 395 A study of the anatomy of the caudal space using magnetic resonance imaging I. M. CRIGHTON, B. P. BARRY AND G. J. HOBBS Summary We have studied, in 37 adult
British Journal of Anaesthesia 1997; 78: 391 395 A study of the anatomy of the caudal space using magnetic resonance imaging I. M. CRIGHTON, B. P. BARRY AND G. J. HOBBS Summary We have studied, in 37 adult
FASCIAL PLANE BLOCKS TOM BARIBEAULT MSN, CRNA
 FASCIAL PLANE BLOCKS TOM BARIBEAULT MSN, CRNA TECHNIQUES Abdominal Wall TAP Rectus Sheath Quadratus Lumborum Erector Spinae Chest PECS I & II Erector Spinae TECHNIQUES Knee Ipack/LIA Hip Fascia Iliaca
FASCIAL PLANE BLOCKS TOM BARIBEAULT MSN, CRNA TECHNIQUES Abdominal Wall TAP Rectus Sheath Quadratus Lumborum Erector Spinae Chest PECS I & II Erector Spinae TECHNIQUES Knee Ipack/LIA Hip Fascia Iliaca
Comparison of Bolus Bupivacaine, Fentanyl, and Mixture of Bupivacaine with Fentanyl in Thoracic Epidural Analgesia for Upper Abdominal Surgery
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/156 Comparison of Bolus Bupivacaine, Fentanyl, and Mixture of Bupivacaine with Fentanyl in Thoracic Epidural Analgesia for Upper Abdominal Surgery Sachin Gajbhiye
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/156 Comparison of Bolus Bupivacaine, Fentanyl, and Mixture of Bupivacaine with Fentanyl in Thoracic Epidural Analgesia for Upper Abdominal Surgery Sachin Gajbhiye
Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan, BA a James Capon, BS, MS a Hayden Smith, BA a Alexandra Napoli, BS a Patrick Gaspar, MD b
 Pre-operative Lumbar Plexus Block Provides Superior Post-operative Analgesia when compared with Fascia Iliaca Block or General Anesthesia alone in Hip Arthroscopy Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan,
Pre-operative Lumbar Plexus Block Provides Superior Post-operative Analgesia when compared with Fascia Iliaca Block or General Anesthesia alone in Hip Arthroscopy Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan,
Continuous Spinal Anaesthesia
 Continuous Spinal Anaesthesia Ph. Biboulet Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine, Lapeyronie University Hospital, Montpellier France CSA story : 1906 Dean 1944 Tuohy 1991 CSA revisited
Continuous Spinal Anaesthesia Ph. Biboulet Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine, Lapeyronie University Hospital, Montpellier France CSA story : 1906 Dean 1944 Tuohy 1991 CSA revisited
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
Neural Blocks in Pain Medicine D R M A R G A R E T E B O N E M B C H B F R C A F F P M R C A C O N S U LTA N T I N PA I N M E D I C I N E
 Neural Blocks in Pain Medicine D R M A R G A R E T E B O N E M B C H B F R C A F F P M R C A C O N S U LTA N T I N PA I N M E D I C I N E Stellate Ganglion Block Lumbar Sympathetic Block Requirements Diagnosis
Neural Blocks in Pain Medicine D R M A R G A R E T E B O N E M B C H B F R C A F F P M R C A C O N S U LTA N T I N PA I N M E D I C I N E Stellate Ganglion Block Lumbar Sympathetic Block Requirements Diagnosis
DOI: / Page. 1 Dr. Seetharamaiah.S., 2 Dr. G.R.Santhilatha, 3 Dr. T.Venugopala rao, 4 Dr. Venugopalan.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VII (Sep. 2015), PP 44-48 www.iosrjournals.org To evaluate the efficacy of Inj. Dexmedetomidine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VII (Sep. 2015), PP 44-48 www.iosrjournals.org To evaluate the efficacy of Inj. Dexmedetomidine
Dr Kelly Jones Anesthesiologist at Northwest Orthopedics
 Dr Kelly Jones Anesthesiologist at Northwest Orthopedics Decrease narcotic use in the immediate post operative period. Better Pain Control Less side effects then General Anesthesia Sedation Post operative
Dr Kelly Jones Anesthesiologist at Northwest Orthopedics Decrease narcotic use in the immediate post operative period. Better Pain Control Less side effects then General Anesthesia Sedation Post operative
IN the ordinary type of spinal analgesia, whether induced by
 95 SPINAL ANALGESIA, WITH SACRAL ESCAPE* By DR. K. E. MADAN, M.D., D.A., D.O.M.S., F.I.C.A., Lecturer, King Edward Medical College, and Chief Anastketist, Mayo Hospital, Lahore IN the ordinary type of
95 SPINAL ANALGESIA, WITH SACRAL ESCAPE* By DR. K. E. MADAN, M.D., D.A., D.O.M.S., F.I.C.A., Lecturer, King Edward Medical College, and Chief Anastketist, Mayo Hospital, Lahore IN the ordinary type of
Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5% Bupivacaine Plus Buprenorphine in Brachial Plexus Block
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. 2016), PP 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5%
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. 2016), PP 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5%
Paraspinal Blocks a new paradigm in truncal analgesia
 Paraspinal Blocks a new paradigm in truncal analgesia Ki Jinn Chin, MBBS (Hons), MMed, FRCPC Associate Professor Toronto Western Hospital University of Toronto Online Resources https://youtu.be/lockhd
Paraspinal Blocks a new paradigm in truncal analgesia Ki Jinn Chin, MBBS (Hons), MMed, FRCPC Associate Professor Toronto Western Hospital University of Toronto Online Resources https://youtu.be/lockhd
The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia
 The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia This study has been published: The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated
The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia This study has been published: The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION METHODS
 Comparative Study of Intrathecal 0.5% Isobaric Versus 0.5% Hyperbaric Bupivacaine in Same Volume and Dose to Assess the Quality of Spinal Anaesthesia and Haemodynamic Changes Occurring During Cesarean
Comparative Study of Intrathecal 0.5% Isobaric Versus 0.5% Hyperbaric Bupivacaine in Same Volume and Dose to Assess the Quality of Spinal Anaesthesia and Haemodynamic Changes Occurring During Cesarean
Combination of Ultra-low Dose Bupivacaine and Fentanyl for Spinal Anaesthesia in Out-patient Anorectal Surgery
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2008; 36: 964 970 Combination of Ultra-low Dose Bupivacaine and Fentanyl for Spinal Anaesthesia in Out-patient Anorectal Surgery A GURBET, G TURKER, NK GIRGIN,
The Journal of International Medical Research 2008; 36: 964 970 Combination of Ultra-low Dose Bupivacaine and Fentanyl for Spinal Anaesthesia in Out-patient Anorectal Surgery A GURBET, G TURKER, NK GIRGIN,
RIA ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 Sweta Salgaonkar et al Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10049-0040 Low-dose Bupivacaine with Fentanyl for Spinal Anesthesia during Ambulatory Inguinal Hernia Repair Surgery: A Comparison between 7.5
Sweta Salgaonkar et al Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10049-0040 Low-dose Bupivacaine with Fentanyl for Spinal Anesthesia during Ambulatory Inguinal Hernia Repair Surgery: A Comparison between 7.5
Comparison of clonidine adjuvants to ropivacaine in subclavian perivascular approach of supra clavicular brachial plexus block
 Original Research Article Comparison of clonidine adjuvants to ropivacaine in subclavian perivascular approach of supra clavicular brachial plexus block S. Arul Rajan 1, N. Sathyan 2*, T. Murugan 3 1 Assistant
Original Research Article Comparison of clonidine adjuvants to ropivacaine in subclavian perivascular approach of supra clavicular brachial plexus block S. Arul Rajan 1, N. Sathyan 2*, T. Murugan 3 1 Assistant
Brachial plexus blockade within the interscalene groove involves local anesthetic
 Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block- How I do it. Part 1 of a 2 part discussion on technique. Stuart Grant Professor of Anesthesiology Duke University Medical Center Durham NC Brachial plexus blockade within
Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block- How I do it. Part 1 of a 2 part discussion on technique. Stuart Grant Professor of Anesthesiology Duke University Medical Center Durham NC Brachial plexus blockade within
Original Article. MA Qadeer Khan 1, B Syamasundara Rao 2, SA Aasim 3 INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS
 Original Article A Comparative Evaluation of 0.5% Hyperbaric Ropivacaine with 0.5% Hyperbaric Bupivacaine for Sub-Arachnoid Block for Elective below Umbilical Surgeries MA Qadeer Khan 1, B Syamasundara
Original Article A Comparative Evaluation of 0.5% Hyperbaric Ropivacaine with 0.5% Hyperbaric Bupivacaine for Sub-Arachnoid Block for Elective below Umbilical Surgeries MA Qadeer Khan 1, B Syamasundara
Comparative Study of Equal Doses of Intrathecal Isobaric Bupivacaine and Isobaric Ropivacaine for Lower Limb Surgeries and Perineal Surgeries
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/229 Comparative Study of Equal Doses of Intrathecal Isobaric Bupivacaine and Isobaric Ropivacaine for Lower Limb Surgeries
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/229 Comparative Study of Equal Doses of Intrathecal Isobaric Bupivacaine and Isobaric Ropivacaine for Lower Limb Surgeries
Abdominal girth and vertebral column length can adjust spinal anesthesia for lower limb surgery, a prospective, observational study
 Zhou et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:22 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0184-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Abdominal girth and vertebral column length can adjust spinal anesthesia for lower limb surgery, a
Zhou et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:22 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0184-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Abdominal girth and vertebral column length can adjust spinal anesthesia for lower limb surgery, a
COMPARISON OF THE EFFECT OF TWO DIFFERENT DOSES OF 0.75% GLUCOSE-FREE ROPIVACAINE FOR SPINAL ANESTHESIA FOR LOWER LIMB AND LOWER ABDOMINAL SURGERY
 Two doses of ropivacaine for spinal anesthesia COMPARISON OF THE EFFECT OF TWO DIFFERENT DOSES OF.75% GLUCOSE-FREE ROPIVACAINE FOR SPINAL ANESTHESIA FOR LOWER LIMB AND LOWER ABDOMINAL SURGERY John On-Nin
Two doses of ropivacaine for spinal anesthesia COMPARISON OF THE EFFECT OF TWO DIFFERENT DOSES OF.75% GLUCOSE-FREE ROPIVACAINE FOR SPINAL ANESTHESIA FOR LOWER LIMB AND LOWER ABDOMINAL SURGERY John On-Nin
Original Article The spread of spinal anesthesia in term parturient: effect of hip/shoulder width ratio and vertebral column length
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):21562-21567 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0028307 Original Article The spread of spinal anesthesia in term parturient: effect of hip/shoulder width ratio and vertebral
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):21562-21567 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0028307 Original Article The spread of spinal anesthesia in term parturient: effect of hip/shoulder width ratio and vertebral
The Influence Of Temperature On Spread Of Intrathecal Levobupıvacaıne
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 29 Number 2 The Influence Of Temperature On Spread Of Intrathecal Levobupıvacaıne G Aydin, A Süslü, O Özlü, M Aksoy, R Polat Citation G Aydin, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 29 Number 2 The Influence Of Temperature On Spread Of Intrathecal Levobupıvacaıne G Aydin, A Süslü, O Özlü, M Aksoy, R Polat Citation G Aydin, A
Hyperbaric unilateral spinal anesthesia is frequently used in lower
 PERIODICUM BIOLOGORUM UDC 57:61 VOL. 115, No 2, 197 202, 2013 CODEN PDBIAD ISSN 0031-5362 Original scientific paper Unilateral spinal anesthesia with low dose bupivacaine and ropivacaine: hypobaric or
PERIODICUM BIOLOGORUM UDC 57:61 VOL. 115, No 2, 197 202, 2013 CODEN PDBIAD ISSN 0031-5362 Original scientific paper Unilateral spinal anesthesia with low dose bupivacaine and ropivacaine: hypobaric or
Comparison of Straight Versus Flexed Back in Combined Spinal Epidural Anesthesia for Gynecological Procedure
 Comparison of Versus Flexed Back in Combined Spinal Epidural Anesthesia for Gynecological Procedure Vaishali Waindeskar, Sheetal Songir, Mahima Batra, MR Gaikwad, Munir Ahmad Khan, Anuj Dubey Department
Comparison of Versus Flexed Back in Combined Spinal Epidural Anesthesia for Gynecological Procedure Vaishali Waindeskar, Sheetal Songir, Mahima Batra, MR Gaikwad, Munir Ahmad Khan, Anuj Dubey Department
Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks
 Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks CONTENTS: 1. Femoral Nerve Block 2. Popliteal Nerve Block Updated December 2017 1 1. Femoral Nerve Block Indications Surgery involving the knee, anterior thigh,
Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks CONTENTS: 1. Femoral Nerve Block 2. Popliteal Nerve Block Updated December 2017 1 1. Femoral Nerve Block Indications Surgery involving the knee, anterior thigh,
Assistant Professor, Anaesthesia Department, Govt. General Hospital / Guntur Medical College, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. 2016), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of 0.25% Ropivacaine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. 2016), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of 0.25% Ropivacaine
Efficacy of intrathecal fentanyl along with bupivacaine and bupivacaine alone in lower segment caesarean section
 Original Research Article Efficacy of intrathecal fentanyl along with bupivacaine and bupivacaine alone in lower segment caesarean section Kamalakar Karampudi 1*, J Ashwin 2 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant
Original Research Article Efficacy of intrathecal fentanyl along with bupivacaine and bupivacaine alone in lower segment caesarean section Kamalakar Karampudi 1*, J Ashwin 2 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant
Regional Anesthesia. procedure if required. However, many patients prefer to receive sedation either during the
 1 Regional Anesthesia Regional anaesthesia (or regional anesthesia) is anesthesia affecting only a large part of the body, such as a limb or the lower half of the body. Regional anaesthetic techniques
1 Regional Anesthesia Regional anaesthesia (or regional anesthesia) is anesthesia affecting only a large part of the body, such as a limb or the lower half of the body. Regional anaesthetic techniques
DORIS DUKE MEDICAL STUDENTS JOURNAL Volume V,
 Continuous Femoral Perineural Infusion (CFPI) Using Ropivacaine after Total Knee Arthroplasty and its Effect on Postoperative Pain and Early Functional Outcomes Eric Lloyd Scientific abstract Total Knee
Continuous Femoral Perineural Infusion (CFPI) Using Ropivacaine after Total Knee Arthroplasty and its Effect on Postoperative Pain and Early Functional Outcomes Eric Lloyd Scientific abstract Total Knee
Evaluation of the Effect of Magnesium Sulphate as Adjunct to Epidural Bupivacaine: An Institutional Based Study
 Original article: Evaluation of the Effect of Magnesium Sulphate as Adjunct to Epidural Bupivacaine: An Institutional Based Study RajulSubhash Karmakar 1, ShishirRamachandra Sonkusale 1* 1Associate Professor,
Original article: Evaluation of the Effect of Magnesium Sulphate as Adjunct to Epidural Bupivacaine: An Institutional Based Study RajulSubhash Karmakar 1, ShishirRamachandra Sonkusale 1* 1Associate Professor,
A Randomised Controlled Study Comparing Intrathecal Hyperbaric Bupivacaine And Isobaric Bupivacaine In Common Urological Procedures
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 8 Ver. II (Aug. 2014), PP 04-08 A Randomised Controlled Study Comparing Intrathecal Hyperbaric
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 8 Ver. II (Aug. 2014), PP 04-08 A Randomised Controlled Study Comparing Intrathecal Hyperbaric
I. Chien, I.C. Lu, F.Y. Wang, et al airway management [9]. An examination of a patient s back for spinal landmarks was reported to be a better predict
![I. Chien, I.C. Lu, F.Y. Wang, et al airway management [9]. An examination of a patient s back for spinal landmarks was reported to be a better predict I. Chien, I.C. Lu, F.Y. Wang, et al airway management [9]. An examination of a patient s back for spinal landmarks was reported to be a better predict](/thumbs/92/108339438.jpg) SPINAL PROCESS LANDMARK AS A PREDICTING FACTOR FOR DIFFICULT EPIDURAL BLOCK: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY IN TAIWANESE PATIENTS I Chien, I-Chen Lu, Fu-Yuan Wang, Lee-Ying Soo, Kwong-Leung Yu, and Chao-Shun Tang
SPINAL PROCESS LANDMARK AS A PREDICTING FACTOR FOR DIFFICULT EPIDURAL BLOCK: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY IN TAIWANESE PATIENTS I Chien, I-Chen Lu, Fu-Yuan Wang, Lee-Ying Soo, Kwong-Leung Yu, and Chao-Shun Tang
Controlled Trial of Wound Infiltration with Bupivacaine for Post Operative Pain Relief after Caesarean Section
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.23, No.2, June 2001 Controlled Trial of Wound Infiltration with Bupivacaine for Post Operative Pain Relief after Caesarean Section Omar Momani, MD, MBBS, JBA* Objective: The
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.23, No.2, June 2001 Controlled Trial of Wound Infiltration with Bupivacaine for Post Operative Pain Relief after Caesarean Section Omar Momani, MD, MBBS, JBA* Objective: The
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
 Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
A Staged Approach to Analgesia After Hip Arthroscopy Using Multimodal Analgesia & Elective Ultrasound Guided Fascia Iliaca Block
 A Staged Approach to Analgesia After Hip Arthroscopy Using Multimodal Analgesia & Elective Ultrasound Guided Fascia Iliaca Block James T. Beckmann MD Stephen K. Aoki MD Stephen Guyette MD Jeffrey Swenson
A Staged Approach to Analgesia After Hip Arthroscopy Using Multimodal Analgesia & Elective Ultrasound Guided Fascia Iliaca Block James T. Beckmann MD Stephen K. Aoki MD Stephen Guyette MD Jeffrey Swenson
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Labor Epidural: Local Anesthetics and Beyond
 Goals: Labor Epidural: Local Anesthetics and Beyond Pedram Aleshi MD The Changing Practice of Anesthesia September 2012 Review Concept of MLAC Local anesthetic efficacy Local anesthetic sparing effects:
Goals: Labor Epidural: Local Anesthetics and Beyond Pedram Aleshi MD The Changing Practice of Anesthesia September 2012 Review Concept of MLAC Local anesthetic efficacy Local anesthetic sparing effects:
British Journal of Anaesthesia 103 (5): (2009) doi: /bja/aep263 Advance Access publication September 28, 2009
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 103 (5): 750 4 (2009) doi:10.1093/bja/aep263 Advance Access publication September 28, 2009 REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA Comparison of intrathecal fentanyl and sufentanil in low-dose
British Journal of Anaesthesia 103 (5): 750 4 (2009) doi:10.1093/bja/aep263 Advance Access publication September 28, 2009 REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA Comparison of intrathecal fentanyl and sufentanil in low-dose
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord
 Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
Original Article INTRODUCTION. Abstract
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/600 Randomized Clinical Comparison of Epidural Bupivacaine with Fentanyl and Epidural Levobupivacaine with Fentanyl
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/600 Randomized Clinical Comparison of Epidural Bupivacaine with Fentanyl and Epidural Levobupivacaine with Fentanyl
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Peripheral Nerve Blocks
 Peripheral Nerve Blocks N U R S I N G E D U C A T I O N JPS Acute Pain Service Peripheral nerve blocks are used as part of a multimodal analgesic program which provides the patient with safe and effective
Peripheral Nerve Blocks N U R S I N G E D U C A T I O N JPS Acute Pain Service Peripheral nerve blocks are used as part of a multimodal analgesic program which provides the patient with safe and effective
Tarek M Sarhan, Assistant professor of Anesthesiology, Faculty of Medicine, Alexandria University
 7 ANALGESIA FOR TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL FISTULA REPAIR IN NEONATES : A COMPARISON OF SINGLE SHOT THORACIC PARAVERTEBRAL BLOCK AND EPIDURAL BLOCK WITH ROPIVACAINE Tarek M Sarhan, Assistant professor of Anesthesiology,
7 ANALGESIA FOR TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL FISTULA REPAIR IN NEONATES : A COMPARISON OF SINGLE SHOT THORACIC PARAVERTEBRAL BLOCK AND EPIDURAL BLOCK WITH ROPIVACAINE Tarek M Sarhan, Assistant professor of Anesthesiology,
Comparative evaluation of ropivacaine versus dexmedetomidine and ropivacaine in epidural anesthesia in lower limb orthopaedic surgeries
 Original Research Article Comparative evaluation of ropivacaine versus dexmedetomidine and ropivacaine in epidural anesthesia in lower limb orthopaedic surgeries Vivek Maratha 1*, Manu Kapil 2, Sandeep
Original Research Article Comparative evaluation of ropivacaine versus dexmedetomidine and ropivacaine in epidural anesthesia in lower limb orthopaedic surgeries Vivek Maratha 1*, Manu Kapil 2, Sandeep
Plantar Flexion Seems More Reliable than Dorsiflexion with Labat s Sciatic Nerve Block: A Prospective, Randomized Comparison
 Plantar Flexion Seems More Reliable than Dorsiflexion with Labat s Sciatic Nerve Block: A Prospective, Randomized Comparison Manuel Taboada, MD*, Peter G. Atanassoff, MD, Jaime Rodríguez, MD, PhD*, Joaquín
Plantar Flexion Seems More Reliable than Dorsiflexion with Labat s Sciatic Nerve Block: A Prospective, Randomized Comparison Manuel Taboada, MD*, Peter G. Atanassoff, MD, Jaime Rodríguez, MD, PhD*, Joaquín
Lower Limb Nerves. Clinical Anatomy
 Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries
 Original Research Article Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries P V Praveen Kumar 1*, Sreemanth 2 1 Associate Professor,
Original Research Article Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries P V Praveen Kumar 1*, Sreemanth 2 1 Associate Professor,
Original Article INTRODUCTION. Abstract
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/147 Comparing Two Different Doses of Clonidine as an Adjuvant to Bupivacaine in Blind Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/147 Comparing Two Different Doses of Clonidine as an Adjuvant to Bupivacaine in Blind Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block
Objectives. Conflict of Interest Disclosure. Neuraxial and Regional Anesthesia in the Pediatric Population
 Neuraxial and Regional Anesthesia in the Pediatric Population Lauren Renner, MS, RN-BC, PNP Sharon Wrona, DNP, RN-BC, PNP, PMHS, AP- PMN.... Conflict of Interest Disclosure Conflicts of Interest for ALL
Neuraxial and Regional Anesthesia in the Pediatric Population Lauren Renner, MS, RN-BC, PNP Sharon Wrona, DNP, RN-BC, PNP, PMHS, AP- PMN.... Conflict of Interest Disclosure Conflicts of Interest for ALL
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Investigation performed at the University of Rochester, Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation, Rochester, NY USA
 Intra-articular cocktail offers clinical advantages over femoral nerve block for postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing arthroscopic hip surgery Sean Childs, MD; Sonia Pyne, MD; Kiritpaul Nandra,
Intra-articular cocktail offers clinical advantages over femoral nerve block for postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing arthroscopic hip surgery Sean Childs, MD; Sonia Pyne, MD; Kiritpaul Nandra,
COMPARATIVE ANAESTHETIC PROPERTIES OF VARIOUS LOCAL ANAESTHETIC AGENTS IN EXTRADURAL BLOCK FOR LABOUR
 Br.J. Anaesth. (1977), 49, 75 COMPARATIVE ANAESTHETIC PROPERTIES OF VARIOUS LOCAL ANAESTHETIC AGENTS IN EXTRADURAL BLOCK FOR LABOUR D. G. LITTLEWOOD, D. B. SCOTT, J. WILSON AND B. G. COVINO SUMMARY Various
Br.J. Anaesth. (1977), 49, 75 COMPARATIVE ANAESTHETIC PROPERTIES OF VARIOUS LOCAL ANAESTHETIC AGENTS IN EXTRADURAL BLOCK FOR LABOUR D. G. LITTLEWOOD, D. B. SCOTT, J. WILSON AND B. G. COVINO SUMMARY Various
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
Intraspinal (Neuraxial) Analgesia Community Nurses Competency Test
 Intraspinal (Neuraxial) Analgesia Community Nurses Competency Test 1 Intraspinal (Neuraxial) Analgesia for Community Nurses Competency Test 1) Name the two major classifications of pain. i. ii. 2) Neuropathic
Intraspinal (Neuraxial) Analgesia Community Nurses Competency Test 1 Intraspinal (Neuraxial) Analgesia for Community Nurses Competency Test 1) Name the two major classifications of pain. i. ii. 2) Neuropathic
USRA OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY
 USRA OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY Christian R. Falyar, CRNA, DNAP Department of Nurse Anesthesia Virginia Commonwealth University Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Christian Falyar, DO NOT have a
USRA OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY Christian R. Falyar, CRNA, DNAP Department of Nurse Anesthesia Virginia Commonwealth University Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Christian Falyar, DO NOT have a
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
MD (Anaesthesiology) Title (Plan of Thesis) (Session )
 S.No. 1. COMPARATIVE STUDY OF CENTRAL VENOUS CANNULATION USING ULTRASOUND GUIDANCE VERSUS LANDMARK TECHNIQUE IN PAEDIATRIC CARDIAC PATIENT. 2. TO EVALUATE THE ABILITY OF SVV OBTAINED BY VIGILEO-FLO TRAC
S.No. 1. COMPARATIVE STUDY OF CENTRAL VENOUS CANNULATION USING ULTRASOUND GUIDANCE VERSUS LANDMARK TECHNIQUE IN PAEDIATRIC CARDIAC PATIENT. 2. TO EVALUATE THE ABILITY OF SVV OBTAINED BY VIGILEO-FLO TRAC
A Comparative Study of Epidural, Bupivacaine with Buprenorphine and Bupivacaine with Fentanyl in Lower Limb Surgeries
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 12 Ver. III (Dec. 2014), PP 23-28 A Comparative Study of Epidural, Bupivacaine with Buprenorphine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 12 Ver. III (Dec. 2014), PP 23-28 A Comparative Study of Epidural, Bupivacaine with Buprenorphine
Lumbar spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 08
 What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
Where should you palpate the pulse of different arteries in the lower limb?
 Where should you palpate the pulse of different arteries in the lower limb? The femoral artery In the femoral triangle, its pulse is easily felt just inferior to the inguinal ligament midway between the
Where should you palpate the pulse of different arteries in the lower limb? The femoral artery In the femoral triangle, its pulse is easily felt just inferior to the inguinal ligament midway between the
LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2. Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
Regional Anesthesia. Fatiş Altındaş Dept. of Anesthesiology
 Regional Anesthesia Fatiş Altındaş Dept. of Anesthesiology Regional anesthesia - Definition Renders a specific area of the body, e.g. foot, arm, lower extremities insensating to stimulus of surgery or
Regional Anesthesia Fatiş Altındaş Dept. of Anesthesiology Regional anesthesia - Definition Renders a specific area of the body, e.g. foot, arm, lower extremities insensating to stimulus of surgery or
CASE REPORT. REGIONAL NERVE BLOCK FOR FEMORO-POPLITEAL AND TIBIAL ARTERIAL RECONSTRUCTIONS Aarti Balakrishnan 1, Sahajanand H 2
 REGIONAL NERVE BLOCK FOR FEMORO-POPLITEAL AND TIBIAL ARTERIAL RECONSTRUCTIONS Aarti Balakrishnan 1, Sahajanand H 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Aarti Balakrishnan, Sahajanand H. Regional nerve block for femoro-popliteal
REGIONAL NERVE BLOCK FOR FEMORO-POPLITEAL AND TIBIAL ARTERIAL RECONSTRUCTIONS Aarti Balakrishnan 1, Sahajanand H 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Aarti Balakrishnan, Sahajanand H. Regional nerve block for femoro-popliteal
East and Central African Journal of Surgery Volume 15 Number 2. July/August 2010.
 Levels of Bifurcation of the Sciatic Nerve among Ugandans at School of Biomedical Sciences Makerere and Mulago Hospital Uganda J. Kukiriza, H. Kiryowa, J. Turyabahika, J. Ochieng C.B.R. Ibingira Makerere
Levels of Bifurcation of the Sciatic Nerve among Ugandans at School of Biomedical Sciences Makerere and Mulago Hospital Uganda J. Kukiriza, H. Kiryowa, J. Turyabahika, J. Ochieng C.B.R. Ibingira Makerere
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Comparison of Intrathecal Hyperbaric 0.5% Bupivacaine, Isobaric 0.5% Levobupivacaine and Isobaric
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Comparison of Intrathecal Hyperbaric 0.5% Bupivacaine, Isobaric 0.5% Levobupivacaine and Isobaric
Single Dose Preemptive Thoracic Paravertebral Block For Postoperative Pain Relief After Cholecystectomy
 10 Single Dose Preemptive Thoracic Paravertebral Block For Postoperative Pain Relief After Cholecystectomy Tarek Atef Tawfic *, MD; Mohamed Medhat Khalil *, MD *Lecturer of anaesthesia, faculty of medicine,
10 Single Dose Preemptive Thoracic Paravertebral Block For Postoperative Pain Relief After Cholecystectomy Tarek Atef Tawfic *, MD; Mohamed Medhat Khalil *, MD *Lecturer of anaesthesia, faculty of medicine,
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB. Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
Anatomy of the Nervous System. Brain Components
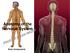 Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government
 Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government Introduction Brief update Two main topics Use of Gabapentin Local Infiltration Analgesia
Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government Introduction Brief update Two main topics Use of Gabapentin Local Infiltration Analgesia
Time duration to safety sitting in parturient receiving spinal anesthesia for cesarean section with 0.5% Bupivacaine and morphine
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 3 June 2010; 485-489 Brief Communication (Original) Time duration to safety sitting in parturient receiving spinal anesthesia for cesarean section with 0.5% Bupivacaine and
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 3 June 2010; 485-489 Brief Communication (Original) Time duration to safety sitting in parturient receiving spinal anesthesia for cesarean section with 0.5% Bupivacaine and
Effect of transdermal nitroglycerin patch on intrathecal neostigmine with bupivacaine for post operative analgesia
 Original Research Article Effect of transdermal nitroglycerin patch on intrathecal neostigmine with bupivacaine for post operative analgesia Viralben P. Patel 1*, Prakash Patel 2, Shweta S. Mehta 3, Gunvanti
Original Research Article Effect of transdermal nitroglycerin patch on intrathecal neostigmine with bupivacaine for post operative analgesia Viralben P. Patel 1*, Prakash Patel 2, Shweta S. Mehta 3, Gunvanti
International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN Volume 3, Issue 6, Nov-Dec 2015.
 Anesthesiology Original Article International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 3, Issue 6, Nov-Dec 2015. Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF INTRATHECAL
Anesthesiology Original Article International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 3, Issue 6, Nov-Dec 2015. Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF INTRATHECAL
